Submitted:
01 October 2024
Posted:
01 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
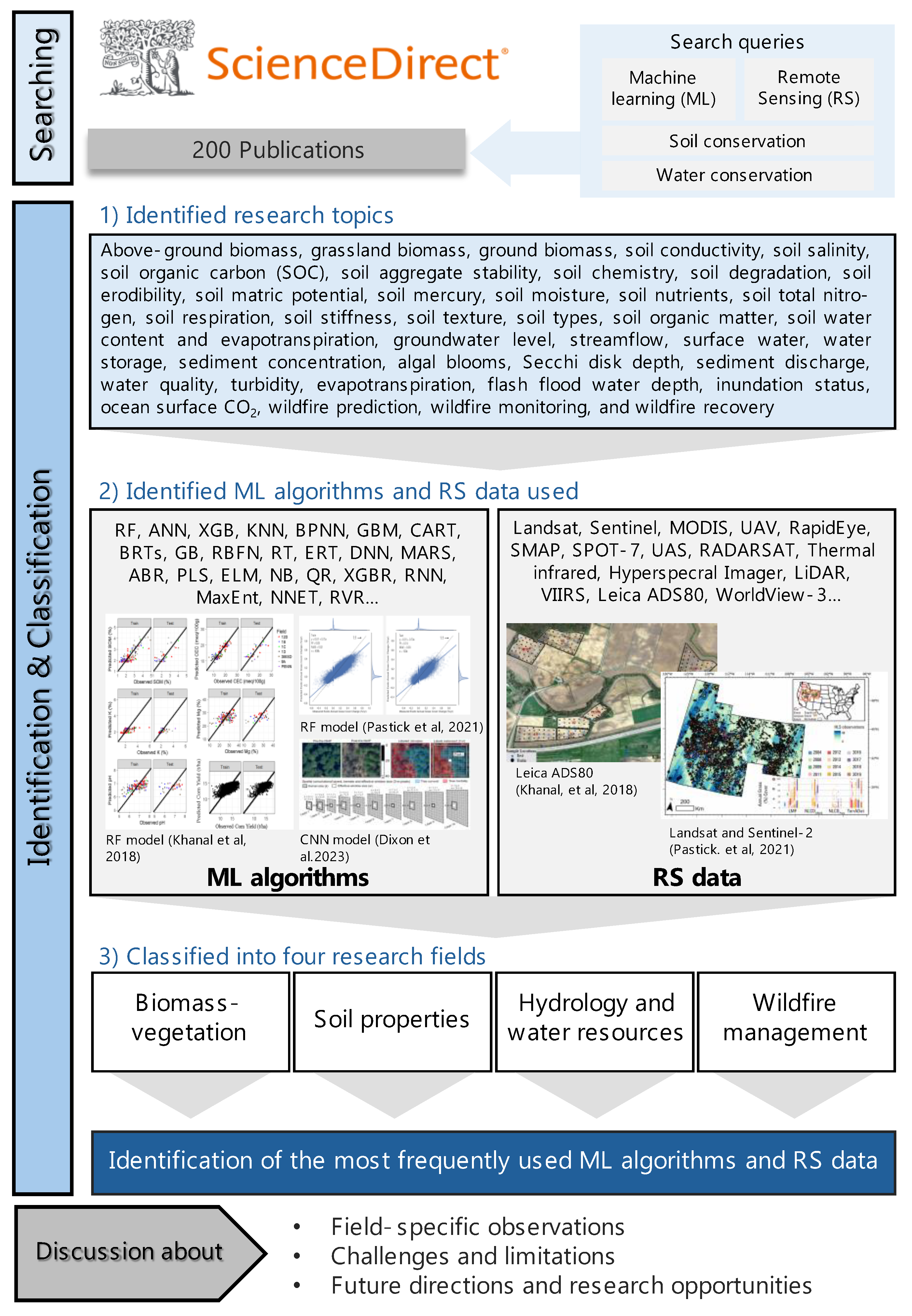
2. Materials and Methods
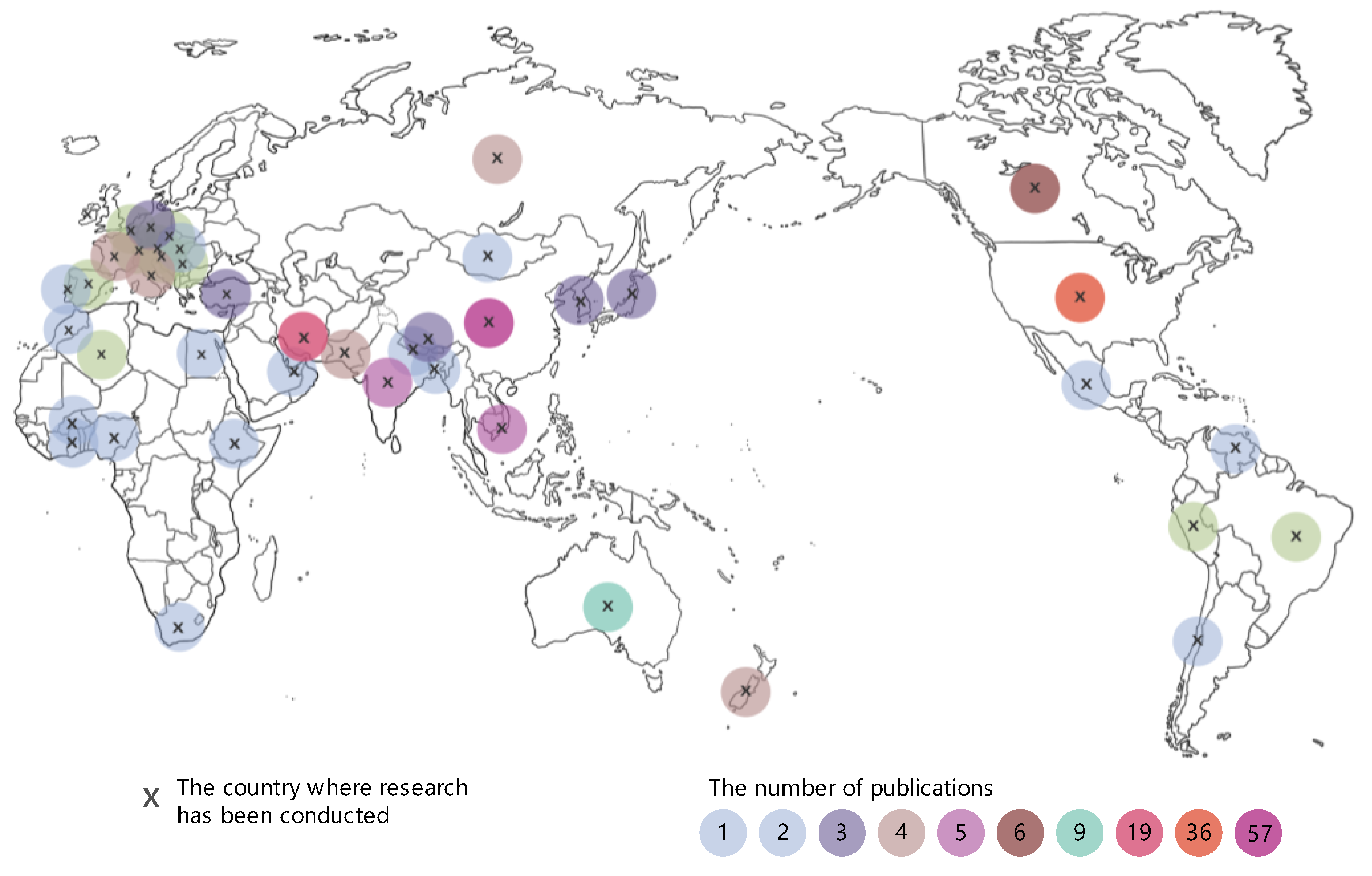
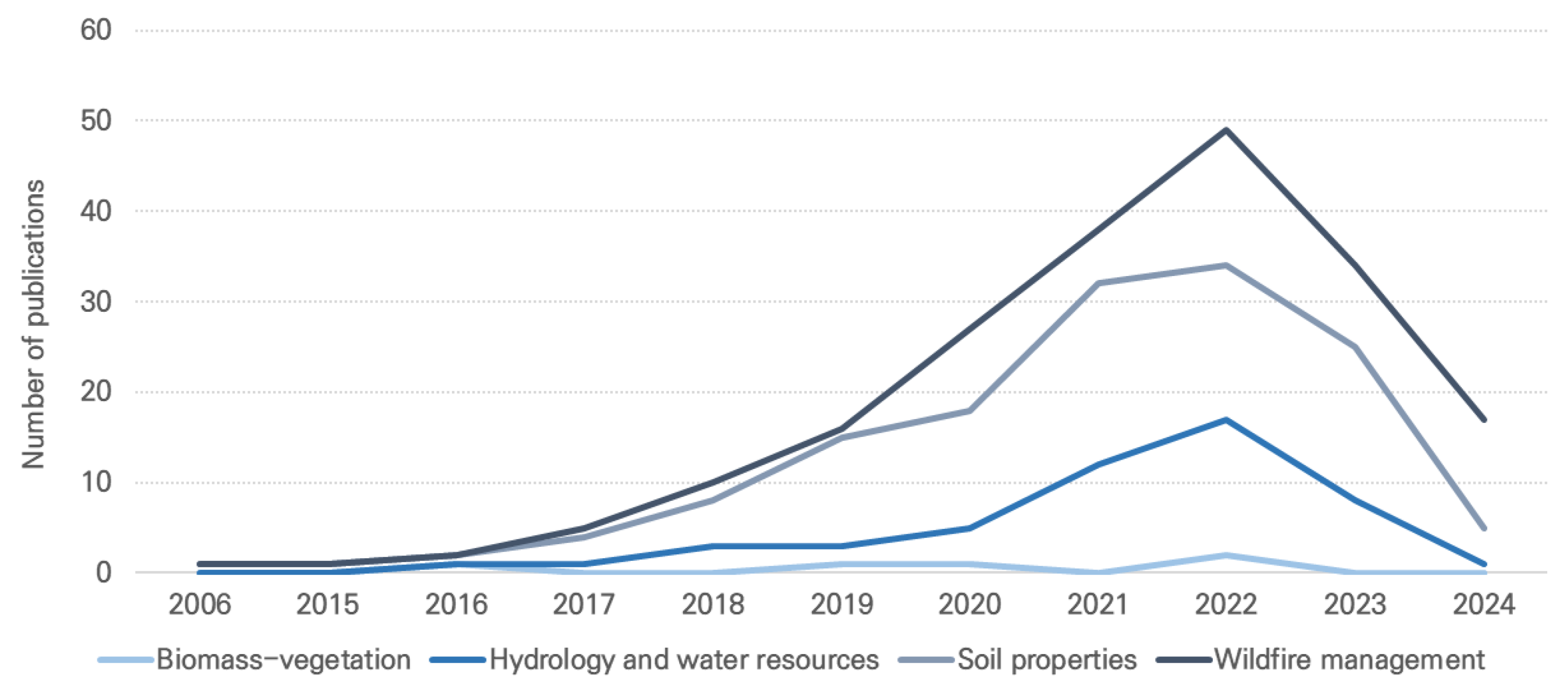
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Types and Frequencies of RS Data Used in Soil and Water Conservation Research
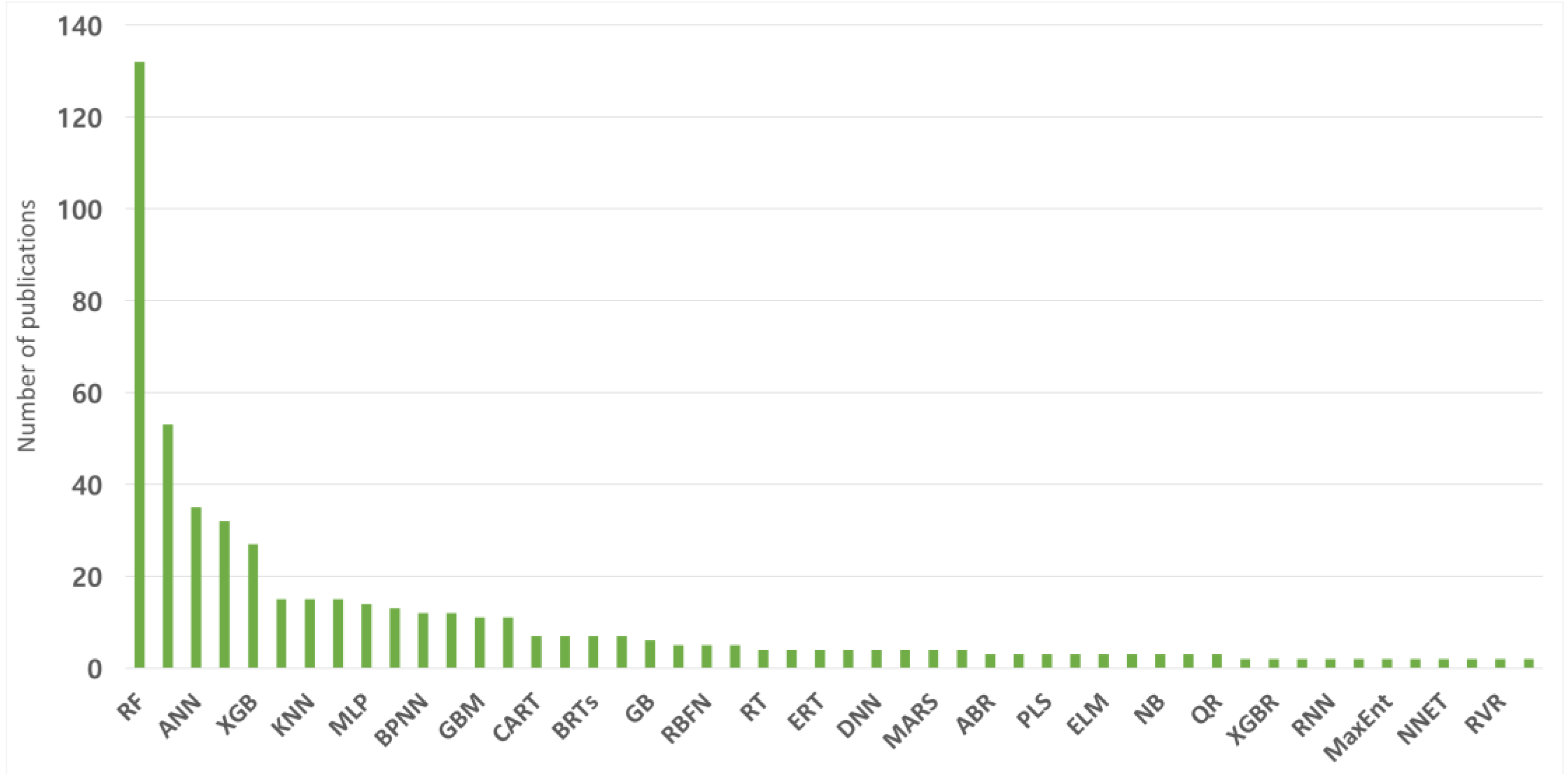
3.2. Types and Frequencies of ML Algorithm Used in Soil and Water Conservation Research
3.3 Field-Specific Observations
3.3.1. Biomass-Vegetation
3.3.2. Soil Properties
3.3.3. Hydrology and Water Resources
3.3.4. Wildfire Management
4. Challenges and Limitations
4.1. Data-Related Challenges
4.2. Technological Limitations
4.3. Implementation Issues
5. Future Directions and Research Opportunities
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| ML | Full of name |
|---|---|
| ABR | Adaptive Boosting Regression |
| AdaBag | Boosting and Bagging |
| AdaBoost | Boosted Classifier |
| ANFIS | Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| ARD | Automatic Relevance Determination |
| BAGGING | Bootstrap Aggregating Regression |
| BAYE | Bayesian |
| B-CART | Bagged Classification and Regression Trees |
| BDT | Bagging Decision Tree |
| BPNN | Back Propagation Neural Network |
| BRTs | Boosted Regression Trees |
| BST | Extreme Gradient Boosting Tree |
| CART | Classification and Regression Trees |
| CB | Cubist |
| CBR | Catboost Regression |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DBN | Deep Belief Network |
| DELM | Deep Extreme Learning Machine |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DMP | Dense Multilayer Perceptron |
| DNN | Deep Neural Networks |
| DR | Dmine Regression |
| DRF | Distributed Random Forest |
| DTr | Decision Tree |
| EBP | Error Back Propagation |
| EFS | Exhaustive Feature Selection |
| ELM | Extreme Learning Machine |
| ELR | Extreme Learning Machine Regression |
| EM | Evaluation metrics |
| EN | Elastic Net |
| EPR | Evolutionary Polynomial Regression |
| ERT | Extremely Randomized Tree |
| ETR | Extreme Tree Regression |
| FCN | Fully Connected Network |
| FNN | Feed forward Neural Networks |
| FR | Frequency Ratio |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Networks |
| GB | Gradient Boosting |
| GBDT | Gradient Boosted Decision Tree |
| GBM | Gradient Boosting Machine |
| GBR | Gradient Boosting Regression |
| GBRT | Gradient Boosting Regression Tree |
| GEP | Genetic Expression Programming |
| GLM | Generalized Linear Model |
| GPR | Gaussian Process Regression |
| GRNN | General Regression Neural Network |
| GSC | Generalized Synthetic Control |
| Isolation Forest | Isolation Forest |
| KNN | K-nearest Neighbors |
| La-R | Lasso Regression |
| LARS | Least Angle Regression |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| LGBM | Light Gradient Boosting Machine |
| Li-R | Linear Regression |
| LMM | Linear Mixed-Effects Model |
| Lo-R | Logistic Regression |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| M5P | M5-pruned |
| MARS | Multivariate Adaptive Regression Spline |
| MaxEnt | Maximum Entropy Model |
| MDN | Mixture Density Network |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| MLPR | Multi-Layer Perceptron Regression |
| MLR | Multiple Linear Regression |
| MR-CNN | Mask Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network |
| MT | M5 Model Tree |
| NB | Naïve Bayes |
| Neu-SICR | Neural Network-Satellite and In situ sensor Collaborated Reconstruction |
| NN | Neural Networks |
| NNET | Feed-Forward Neural Network |
| OLS | Ordinary Least Squares |
| PCR | Principal Component Regression |
| PKR | Polynomial Kernel Regression |
| PLS | Partial Least Squares |
| PLSR | Partial Least Squares Regression |
| PSO-SVR | Particle Swarm Optimization and Support Vector Machine |
| QR | Quantile Regression Forest |
| RBFN | Radial Basin Function Neural Network |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| RPART | Recursive Partitioning and Regression Trees |
| RR | Ridge Regression |
| RT | Regression Tree |
| RTM | Radiative Transfer Models |
| RVR | Relevance Vector Regression |
| SA | Sensitivity Analysis |
| SCA-Elman | Sine Cosine Algorithm-Elman |
| SGB | Stochastic Gradient Boosting |
| SICR | Sensor Collaborated Reconstruction |
| SLR | Stepwise Linear Regression |
| SoLIM | Soil–Landscape Inference Model (Fuzzy logic) |
| SOM | Self-Organizing Maps |
| SR | Simple Regression |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| SVR | Support Vector Regression |
| XGB | EXtreme Gradient Boosting |
| XGBR | Extreme Gradient Boosting Regression |
| YOLO | You Only Look Once |
| RS Techniques | Descriptions | |
|---|---|---|
| Satellite | ALOS-2* |
|
| Chinese Environmental 1A |
|
|
| GF-1 |
|
|
| GOES-16 |
|
|
| Himawari-8 |
|
|
| Landsat 4, 5 |
|
|
| Landsat 7 |
|
|
| Landsat 8, 9 |
|
|
| RADARSAT |
|
|
| RapidEye |
|
|
| Sentitel-1 |
|
|
| Sentitel-2 |
|
|
| Sentitel-3 |
|
|
| SMAP |
|
|
| SPOT-4 |
|
|
| SPOT-7 |
|
|
| SRTM |
|
|
| Terra |
|
|
| Triplesat |
|
|
| WorldView-3 |
|
|
| ZH-1 |
|
|
| AGRS |
|
|
| AMSR-E |
|
|
| AVIRIS-NG |
|
|
| ETM+ |
|
|
| Thermal infrared |
|
|
| Leica ADS80 |
|
|
| LiDAR |
|
|
| MERIS |
|
|
| MODIS |
|
|
| PALSAR-2 |
|
|
| SAR |
|
|
| SVC |
|
|
| TDC |
|
|
| Hyperspectral Imager |
|
|
| TM |
|
|
| UAS / UAV |
|
|
| VIIRS |
|
|
References
- Pereira, P. , et al., Soil ecosystem services, sustainability, valuation and management. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 2018. 5: p. 7-13.
- Trap, J.; Bonkowski, M.; Plassard, C.; Villenave, C.; Blanchart, E. Ecological importance of soil bacterivores for ecosystem functions. Plant Soil 2015, 398, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitford, W.G. The importance of the biodiversity of soil biota in arid ecosystems. Biodivers. Conserv. 1996, 5, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, R.P.; Barlow, M.; Byrne, M.P.; Cherchi, A.; Douville, H.; Fowler, H.J.; Gan, T.Y.; Pendergrass, A.G.; Rosenfeld, D.; Swann, A.L.S.; et al. Advances in understanding large-scale responses of the water cycle to climate change. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2020, 1472, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, J.P.; Kettani, M.A. The Control of the Water Cycle. Sci. Am. 1973, 228, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. , Soil conservation and ecosystem services. International soil and water conservation research, 2014. 2(3): p. 36-47.
- Neary, D.G.; Ryan, K.C.; DeBano, L.F. Wildland Fire in Ecosystems: Effects of Fire on Soils and Water, General Technical Report RMRSGTR-42-Vol.4; USDA, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Ogden, UT, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Talukder, M. Increasing water productivity in crop production—A synthesis. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Ishak, M.I.S.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various Natural and Anthropogenic Factors Responsible for Water Quality Degradation: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bungau, S.; Behl, T.; Aleya, L.; Bourgeade, P.; Aloui-Sossé, B.; Purza, A.L.; Abid, A.; Samuel, A.D. Expatiating the impact of anthropogenic aspects and climatic factors on long-term soil monitoring and management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 30528–30550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Tan, M.; Sun, Y. Assessing the impact of urban sprawl on soil resources of Nanjing city using satellite images and digital soil databases. CATENA 2006, 69, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajabbasi, M.A.; Jalalian, A.; Karimzadeh, H.R. Deforestation effects on soil physical and chemical properties, Lordegan, Iran. Plant Soil 1997, 190, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syamsih, D. , Impacts of Deforestation on Soil Quality and Water Resources in Tropical Forest Areas of Sumatra. Journal of Horizon, 2024. 1(1): p. 16-22.
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Lal, R. Principles of Soil Conservation and Management; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, GX, Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Côté, I.M.; Darling, E.S.; Brown, C.J. Interactions among ecosystem stressors and their importance in conservation. Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20152592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, P.W.; Reyes, M.R.; Green, C.H.; Arnold, J.G. The Soil and Water Assessment Tool: Historical Development, Applications, and Future Research Directions. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 1211–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansell, R. , et al., Adaptive grid refinement in numerical models for water flow and chemical transport in soil: a review. Vadose Zone Journal, 2002. 1(2): p. 222-238.
- Kattenberg, A. , et al., Climate models: projections of future climate, in Climate Change 1995: the science of climate change. Contribution of WG1 to the Second Assessment Report of the IPCC. 1996, Cambridge University Press. p. 299-357.
- Kavetski, D., S. W. Franks, and G. Kuczera, Confronting input uncertainty in environmental modelling. Calibration of watershed models, 2003. 6: p. 49-68.
- Matott, L.S.; Babendreier, J.E.; Purucker, S.T. Evaluating uncertainty in integrated environmental models: A review of concepts and tools. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refsgaard, J.C.; van der Sluijs, J.P.; Højberg, A.L.; Vanrolleghem, P.A. Uncertainty in the environmental modelling process – A framework and guidance. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 1543–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Zhang, K.; Bagheri, M.; Burken, J.G.; Gu, A.; Li, B.; Ma, X.; Marrone, B.L.; Ren, Z.J.; Schrier, J.; et al. Machine Learning: New Ideas and Tools in Environmental Science and Engineering. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12741–12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. Detecting, Extracting, and Monitoring Surface Water From Space Using Optical Sensors: A Review. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogan, J.; Chen, D. Remote sensing technology for mapping and monitoring land-cover and land-use change. Prog. Plan. 2004, 61, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florath, J.; Keller, S. Supervised Machine Learning Approaches on Multispectral Remote Sensing Data for a Combined Detection of Fire and Burned Area. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.Y.; Scanlon, B.R. How can Big Data and machine learning benefit environment and water management: a survey of methods, applications, and future directions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 073001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasgow, H.B.; Burkholder, J.M.; Reed, R.E.; Lewitus, A.J.; Kleinman, J.E. Real-time remote monitoring of water quality: A review of current applications, and advancements in sensor, telemetry, and computing technologies. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 300, 409–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guan, K.; Zhang, C.; Lee, D.; Margenot, A.J.; Ge, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, Y. Using soil library hyperspectral reflectance and machine learning to predict soil organic carbon: Assessing potential of airborne and spaceborne optical soil sensing. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2022, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Yang, G.; Dai, H.; Xu, B.; Yang, H.; Feng, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, X. Modeling maize above-ground biomass based on machine learning approaches using UAV remote-sensing data. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Leigh, L.; Chang, J.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Caffé, M. Above-Ground Biomass Estimation in Oats Using UAV Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Sensors 2022, 22, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quang, N.H.; Quinn, C.H.; Carrie, R.; Stringer, L.C.; Van Hue, L.T.; Hackney, C.R.; Van Tan, D. Comparisons of regression and machine learning methods for estimating mangrove above-ground biomass using multiple remote sensing data in the red River Estuaries of Vietnam. Remote. Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 26, 100725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Cawkwell, F.; Dwyer, E.; Green, S. Modeling Managed Grassland Biomass Estimation by Using Multitemporal Remote Sensing Data—A Machine Learning Approach. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2016, 10, 3254–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Liang, T.; Yi, S.; Yin, J.; Cui, X.; Ge, J.; Hou, M.; Lv, Y.; Sun, Y. Modeling Alpine Grassland Above Ground Biomass Based on Remote Sensing Data and Machine Learning Algorithm: A Case Study in East of the Tibetan Plateau, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2020, 13, 2986–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendzioch, T.; Langhammer, J.; Vlček, L.; Minařík, R. Mapping the Groundwater Level and Soil Moisture of a Montane Peat Bog Using UAV Monitoring and Machine Learning. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygın, F.; Aksoy, H.; Alaboz, P.; Dengiz, O. Different approaches to estimating soil properties for digital soil map integrated with machine learning and remote sensing techniques in a sub-humid ecosystem. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Mousavi, S.R.; Rahmani, A.; Zeraatpisheh, M.; Rahmati, M.; Pakparvar, M.; Mahjenabadi, V.A.J.; Seuntjens, P.; Cornelis, W. Incorporating machine learning models and remote sensing to assess the spatial distribution of saturated hydraulic conductivity in a light-textured soil. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Zhang, J.; He, W.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, R.; Zamanian, K.; Jia, K.; Zhao, X. Combination of Hyperspectral and Machine Learning to Invert Soil Electrical Conductivity. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xue, J.; Peng, J.; Biswas, A.; He, Y.; Shi, Z. Integrating Remote Sensing and Landscape Characteristics to Estimate Soil Salinity Using Machine Learning Methods: A Case Study from Southern Xinjiang, China. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.A.; Metwaly, M.M.; Metwalli, M.R.; AbdelRahman, M.A.E.; Badreldin, N. Integrating Active and Passive Remote Sensing Data for Mapping Soil Salinity Using Machine Learning and Feature Selection Approaches in Arid Regions. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Chan, N.W.; Kung, H.-T.; Ariken, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y. Regional suitability prediction of soil salinization based on remote-sensing derivatives and optimal spectral index. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 775, 145807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Chen, X.; Han, W.; Cui, X.; Ma, W.; Li, G. Estimation of Soil Salt Content at Different Depths Using UAV Multi-Spectral Remote Sensing Combined with Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, S.; Ayoubi, S.; Zeraatpisheh, M.; Dematte, J.A.M. Ground Observations and Environmental Covariates Integration for Mapping of Soil Salinity: A Machine Learning-Based Approach. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, J. Performance Comparison of Machine Learning Algorithms for Estimating the Soil Salinity of Salt-Affected Soil Using Field Spectral Data. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkin, N.; Zhu, L.; Gu, H.; Tusiyiti, A. Method for predicting soil salinity concentrations in croplands based on machine learning and remote sensing techniques. J. Appl. Remote. Sens. 2019, 13, 034520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G. , et al., Soil salinity prediction using Machine Learning and Sentinel–2 Remote Sensing Data in Hyper–Arid areas. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 130: p. 103400.
- Jiang, X.; Duan, H.; Liao, J.; Guo, P.; Huang, C.; Xue, X. Estimation of Soil Salinization by Machine Learning Algorithms in Different Arid Regions of Northwest China. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, Y.U.; Shahbaz, M.; Asif, H.M.S.; Al-Laith, A.; Alsabban, W.H. Spatial Mapping of Soil Salinity Using Machine Learning and Remote Sensing in Kot Addu, Pakistan. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, J. , Yu, D., Ma, X., Zhang, Z., Ge, X. Teng, D.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. Machine learning-based detection of soil salinity in an arid desert region, Northwest China: A comparison between Landsat-8 OLI and Sentinel-2 MSI. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 707, 136092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. , et al., Mapping Multi-Depth Soil Salinity Using Remote Sensing-Enabled Machine Learning in the Yellow River Delta, China. Remote Sensing, 15(24): p. 5640.
- Wei, Q.; Nurmemet, I.; Gao, M.; Xie, B. Inversion of Soil Salinity Using Multisource Remote Sensing Data and Particle Swarm Machine Learning Models in Keriya Oasis, Northwestern China. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, P.V.; Giang, N.V.; Binh, N.A.; Hai, L.V.H.; Pham, T.-D.; Hasanlou, M.; Bui, D.T. Soil Salinity Mapping Using SAR Sentinel-1 Data and Advanced Machine Learning Algorithms: A Case Study at Ben Tre Province of the Mekong River Delta (Vietnam). Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Bhattacharya, B.K.; Setia, R.; Jayasree, G.; Das, B.S. A novel method for detecting soil salinity using AVIRIS-NG imaging spectroscopy and ensemble machine learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2023, 200, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Van, C.P.; Nguyen, T.G.; Dang, D.K.; Pham, T.T.N.; Nguyen, Q.-H.; Bui, Q.-T. Soil salinity prediction using hybrid machine learning and remote sensing in Ben Tre province on Vietnam’s Mekong River Delta. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 74340–74357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, C.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z. Soil Salinity Inversion Model of Oasis in Arid Area Based on UAV Multispectral Remote Sensing. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, S.; Yildirim, A.; Gorji, T.; Hamzehpour, N.; Tanik, A.; Sertel, E. Assessing the performance of machine learning algorithms for soil salinity mapping in Google Earth Engine platform using Sentinel-2A and Landsat-8 OLI data. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 69, 1072–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Ding, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ran, S. Digital mapping of soil salinization based on Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data combined with machine learning algorithms. Reg. Sustain. 2021, 2, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalambukattu, J.G.; Johns, B.; Kumar, S.; Raj, A.D.; Ellur, R. Temporal remote sensing based soil salinity mapping in Indo-Gangetic plain employing machine-learning techniques. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2023, 89, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, M. Remote sensing-based prediction of organic carbon in agricultural and natural soils influenced by salt and sand mining using machine learning. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odebiri, O.; Mutanga, O.; Odindi, J.; Naicker, R. Modelling soil organic carbon stock distribution across different land-uses in South Africa: A remote sensing and deep learning approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2022, 188, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xue, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, N.; Shi, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhuo, Z. Digital Mapping of Soil Organic Carbon with Machine Learning in Dryland of Northeast and North Plain China. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadi, M.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Cherati, A.; Danesh, M.; Mosavi, A.; Scholten, T. Predicting and Mapping of Soil Organic Carbon Using Machine Learning Algorithms in Northern Iran. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, K.; Isong, I.A.; Kebonye, N.M.; Ayito, E.O.; Agyeman, P.C.; Afu, S.M. Using Machine Learning Algorithms to Estimate Soil Organic Carbon Variability with Environmental Variables and Soil Nutrient Indicators in an Alluvial Soil. Land 2020, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Bao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H. An advanced soil organic carbon content prediction model via fused temporal-spatial-spectral (TSS) information based on machine learning and deep learning algorithms. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2022, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraatpisheh, M.; Ayoubi, S.; Jafari, A.; Tajik, S.; Finke, P. Digital mapping of soil properties using multiple machine learning in a semi-arid region, central Iran. Geoderma 2018, 338, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Geng, Y.; Chen, J.; Pan, J.; Haase, D.; Lausch, A. High-resolution digital mapping of soil organic carbon and soil total nitrogen using DEM derivatives, Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data based on machine learning algorithms. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 729, 138244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T. , et al., Prediction of soil organic carbon and the C: N ratio on a national scale using machine learning and satellite data: A comparison between Sentinel-2, Sentinel-3 and Landsat-8 images. Science of the Total Environment, 755: p. 142661.
- Abdoli, P.; Khanmirzaei, A.; Hamzeh, S.; Rezaei, S.; Moghimi, S. Use of remote sensing data to predict soil organic carbon in some agricultural soils of Iran. Remote. Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2023, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Coops, N.; Johnson, M.; Krzic, M.; Chandna, A.; Smukler, S. Mapping soil organic carbon and clay using remote sensing to predict soil workability for enhanced climate change adaptation. Geoderma 2020, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzehpour, N.; Shafizadeh-Moghadam, H.; Valavi, R. Exploring the driving forces and digital mapping of soil organic carbon using remote sensing and soil texture. CATENA 2019, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matinfar, H.R.; Maghsodi, Z.; Mousavi, S.R.; Rahmani, A. Evaluation and Prediction of Topsoil organic carbon using Machine learning and hybrid models at a Field-scale. CATENA 2021, 202, 105258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Ding, J.; Ge, X.; Li, X.; Han, L.; Wang, Z. Estimation of Soil Organic Carbon Content in the Ebinur Lake Wetland, Xinjiang, China, Based on Multisource Remote Sensing Data and Ensemble Learning Algorithms. Sensors 2022, 22, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Waters, C.; Orgill, S.; Gray, J.; Cowie, A.; Clark, A.; Liu, D.L. High resolution mapping of soil organic carbon stocks using remote sensing variables in the semi-arid rangelands of eastern Australia. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 630, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, C.; Chen, N.; Zhang, X.; Gong, J. A Machine Learning Based Reconstruction Method for Satellite Remote Sensing of Soil Moisture Images with In Situ Observations. Remote. Sens. 2017, 9, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraatpisheh, M.; Ayoubi, S.; Mirbagheri, Z.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Xu, M. Spatial prediction of soil aggregate stability and soil organic carbon in aggregate fractions using machine learning algorithms and environmental variables. Geoderma Reg. 2021, 27, e00440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjenabadi, V.A.J.; Mousavi, S.R.; Rahmani, A.; Karami, A.; Rahmani, H.A.; Khavazi, K.; Rezaei, M. Digital mapping of soil biological properties and wheat yield using remotely sensed, soil chemical data and machine learning approaches. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.; Fulton, J.; Klopfenstein, A.; Douridas, N.; Shearer, S. Integration of high resolution remotely sensed data and machine learning techniques for spatial prediction of soil properties and corn yield. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 153, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhovich, D.I. , et al., Recognition of the bare soil using deep machine learning methods to create maps of arable soil degradation based on the analysis of multi-temporal remote sensing data. Remote Sensing, 2022. 14(9): p. 2224.
- Alexakis, D.D.; Tapoglou, E.; Vozinaki, A.-E.K.; Tsanis, I.K. Integrated Use of Satellite Remote Sensing, Artificial Neural Networks, Field Spectroscopy, and GIS in Estimating Crucial Soil Parameters in Terms of Soil Erosion. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, D.; Adermann, E.; Pizzolato, M.; Pechenkin, R.; Rodríguez, C.G.; Taravat, A. Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms for Soil Erosion Modelling Based on Remotely Sensed Data. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.T.; Do, T.A.T.; Tran, H.D.; Do, A.N.T. Classifying forest cover and mapping forest fire susceptibility in Dak Nong province, Vietnam utilizing remote sensing and machine learning. Ecol. Informatics 2023, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygın, F.; Aksoy, H.; Alaboz, P.; Birol, M.; Dengiz, O. Estimation of soil erodability parameters based on different machine algorithms integrated with remote sensing techniques. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, R.F.; Lurbe, C.B.; Hornbuckle, J. Machine learning approach to estimate soil matric potential in the plant root zone based on remote sensing data. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 931491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleymanov, A.; Suleymanov, R.; Kulagin, A.; Yurkevich, M. Mercury Prediction in Urban Soils by Remote Sensing and Relief Data Using Machine Learning Techniques. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, I.; Yeo, I.-Y.; Walker, J.; Willgoose, G. Estimating catchment scale soil moisture at a high spatial resolution: Integrating remote sensing and machine learning. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Shangguan, W.; Li, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, F.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, R. A Spatial Downscaling Method for Remote Sensing Soil Moisture Based on Random Forest Considering Soil Moisture Memory and Mass Conservation. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeian, E.; Paheding, S.; Siddique, N.; Devabhaktuni, V.K.; Tuller, M. Estimation of root zone soil moisture from ground and remotely sensed soil information with multisensor data fusion and automated machine learning. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2021, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Cui, Y. Evaluating Downscaling Factors of Microwave Satellite Soil Moisture Based on Machine Learning Method. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senyurek, V.; Lei, F.; Boyd, D.; Kurum, M.; Gurbuz, A.C.; Moorhead, R. Machine Learning-Based CYGNSS Soil Moisture Estimates over ISMN sites in CONUS. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, S.N.; Fryjoff-Hung, A.; Anderson, A.; Viers, J.H.; Ghezzehei, T.A. Advances in soil moisture retrieval from multispectral remote sensing using unoccupied aircraft systems and machine learning techniques. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 2739–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisekka, I.; Peddinti, S.R.; Kustas, W.P.; McElrone, A.J.; Bambach-Ortiz, N.; McKee, L.; Bastiaanssen, W. Spatial–temporal modeling of root zone soil moisture dynamics in a vineyard using machine learning and remote sensing. Irrig. Sci. 2022, 40, 761–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greifeneder, F.; Notarnicola, C.; Wagner, W. A Machine Learning-Based Approach for Surface Soil Moisture Estimations with Google Earth Engine. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jing, W.; Yue, X. Comparison of Different Machine Learning Approaches for Monthly Satellite-Based Soil Moisture Downscaling over Northeast China. Remote. Sens. 2017, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Hu, S.; Xiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, T. Multilayer Soil Moisture Mapping at a Regional Scale from Multisource Data via a Machine Learning Method. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Min, L.; Guo, Z.; Li, N. Retrieval of Farmland Surface Soil Moisture Based on Feature Optimization and Machine Learning. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abowarda, A.S.; Bai, L.; Zhang, C.; Long, D.; Li, X.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Z. Generating surface soil moisture at 30 m spatial resolution using both data fusion and machine learning toward better water resources management at the field scale. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2021, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, X. Remote sensing-based retrieval of soil moisture content using stacking ensemble learning models. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 34, 911–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.; Park, S.; Rhee, J.; Baik, J.; Choi, M. Downscaling of AMSR-E soil moisture with MODIS products using machine learning approaches. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, L.; Mishra, A.K. Multi-layer high-resolution soil moisture estimation using machine learning over the United States. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2021, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, S.N.; Fryjoff-Hung, A.; Anderson, A.; Viers, J.H.; Ghezzehei, T.A. Machine Learning Based Soil Moisture Retrieval from Unmanned Aircraft System Multispectral Remote Sensing. IGARSS 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, United StatesDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 4598–4601.
- Chen, Q.; Miao, F.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Tang, Z.; Yang, L.; Qi, S. Downscaling of Satellite Remote Sensing Soil Moisture Products Over the Tibetan Plateau Based on the Random Forest Algorithm: Preliminary Results. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouraki, A. , et al., Spatial-temporal modeling of soil moisture using optical and thermal remote sensing data and machine learning algorithms. Iranian Journal of Soil and Water Research, 2023. 54(4): p. 637-653.
- Chen, L.; Xing, M.; He, B.; Wang, J.; Shang, J.; Huang, X.; Xu, M. Estimating Soil Moisture Over Winter Wheat Fields During Growing Season Using Machine-Learning Methods. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2021, 14, 3706–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdu, I.; Yule, I.; Dehghan-Shear, M.H. Modelling of Near-Surface Soil Moisture Using Machine Learning and Multi-Temporal Sentinel 1 Images in New Zealand. IGARSS 2018 - 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 1422–1425.
- Santi, E.; Dabboor, M.; Pettinato, S.; Paloscia, S. Combining Machine Learning and Compact Polarimetry for Estimating Soil Moisture from C-Band SAR Data. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S. , et al. AMSR2 soil moisture downscaling using multisensor products through machine learning approach. in 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). 2015. IEEE.
- Bueno, M. , et al., Watershed scale soil moisture estimation model using machine learning and remote sensing in a data-scarce context. Scientia Agropecuaria, 2024. 15(1): p. 103-120.
- Cui, Y.; Chen, X.; Xiong, W.; He, L.; Lv, F.; Fan, W.; Luo, Z.; Hong, Y. A Soil Moisture Spatial and Temporal Resolution Improving Algorithm Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data and GRNN Model. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; She, D.; Zhang, L.; Guo, M.; Liu, X. Spatial Downscaling Methods of Soil Moisture Based on Multisource Remote Sensing Data and Its Application. Water 2019, 11, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Wang, H.; Magagi, R.; Goita, K.; Wang, K. Spatial Gap-Filling of SMAP Soil Moisture Pixels Over Tibetan Plateau via Machine Learning Versus Geostatistics. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2021, 14, 9899–9912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, A.A.; Zha, Y.; Shi, L.; Ali, S.; Wang, X.; Zafar, Z.; Afzal, Z.; Tariq, M.A.U.R. Spatial Downscaling and Gap-Filling of SMAP Soil Moisture to High Resolution Using MODIS Surface Variables and Machine Learning Approaches over ShanDian River Basin, China. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, L.; Zhuang, Q.; Chen, D.; Sun, T. Mapping Cropland Soil Nutrients Contents Based on Multi-Spectral Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-Q.; Zhao, X.; Su, H.-Y.; Li, B.; Hu, Y.-M.; Cui, X.-S. Predicting Spatial Variations in Soil Nutrients with Hyperspectral Remote Sensing at Regional Scale. Sensors 2018, 18, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengl, T.; Leenaars, J.G.B.; Shepherd, K.D.; Walsh, M.G.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Mamo, T.; Tilahun, H.; Berkhout, E.; Cooper, M.; Fegraus, E.; et al. Soil nutrient maps of Sub-Saharan Africa: assessment of soil nutrient content at 250 m spatial resolution using machine learning. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2017, 109, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Das, K.; Hazra, J. Soil Nutrients Prediction Using Remote Sensing Data in Western India: An Evaluation of Machine Learning Models. IGARSS 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, United StatesDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 4677–4680.
- Liu, Y.; Lin, J.; Yue, H. Soil respiration estimation in desertified mining areas based on UAV remote sensing and machine learning. Earth Sci. Informatics 2023, 16, 3433–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, J.; Oommen, T.; Jayakumar, P.; Alger, R. Characterizing Soil Stiffness Using Thermal Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkuor, G.; Hounkpatin, O.K.L.; Welp, G.; Thiel, M. High Resolution Mapping of Soil Properties Using Remote Sensing Variables in South-Western Burkina Faso: A Comparison of Machine Learning and Multiple Linear Regression Models. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0170478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeitalarposhti, R.; Shafizadeh-Moghadam, H.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Demyan, M.S. Digital Soil Texture Mapping and Spatial Transferability of Machine Learning Models Using Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, and Terrain-Derived Covariates. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Thomasson, J.A.; Boggess, J.E.; Sui, R. Soil texture classification with artificial neural networks operating on remote sensing data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2006, 54, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, Y.U.; Shahbaz, M.; Asif, H.S.; Al-Laith, A.; Alsabban, W.; Aziz, M.H. Identification of soil type in Pakistan using remote sensing and machine learning. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2022, 8, e1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heil, J.; Jörges, C.; Stumpe, B. Fine-Scale Mapping of Soil Organic Matter in Agricultural Soils Using UAVs and Machine Learning. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. , et al., Mapping regional soil organic matter based on sentinel-2a and modis imagery using machine learning algorithms and google earth engine. Remote Sensing, 2021. 13(15): p. 2934.
- Chen, D.; Chang, N.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, W. Mapping dynamics of soil organic matter in croplands with MODIS data and machine learning algorithms. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 669, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Luo, J.; Dong, W.; Sun, Y.; Xia, L.; Zhang, X. Geo-Object-Based Soil Organic Matter Mapping Using Machine Learning Algorithms With Multi-Source Geo-Spatial Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2019, 12, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueiras, R.; Almeida, T.S.; Mantovani, E.C.; Dias, S.H.B.; Fernandes-Filho, E.I.; da Cunha, F.F.; Venancio, L.P. Soil water content and actual evapotranspiration predictions using regression algorithms and remote sensing data. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Raza, M.; Kwon, K.D. Land use and land cover changes in the Haean Basin of Korea: Impacts on soil erosion. Episodes 2019, 42, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Saft, M.; Hou, X.; Webb, J.A.; Hairsine, P.B.; Western, A.W. How does wildfire and climate variability affect streamflow in forested catchments? A regional study in eastern Australia. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, H.; Roshani; Masroor; Sajjad, H. Integrating remote sensing derived indices and machine learning algorithms for precise extraction of small surface water bodies in the lower Thoubal river watershed, India. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, T.D.; Subedi, A.; Lee, D.H. Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithms for Surface Water Extraction in a Landsat 8 Scene of Nepal. Sensors 2019, 19, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Guo, H.; Dai, W.; Nie, B.; Qiao, B.; Zhu, L. Bathymetric mapping and estimation of water storage in a shallow lake using a remote sensing inversion method based on machine learning. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 789–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkordi, A.T.; Ghasemi, H.; Zoej, M.J.V. Machine Learning-Based Estimation of Suspended Sediment Concentration along Missouri River using Remote Sensing Imageries in Google Earth Engine. 2021 7th International Conference on Signal Processing and Intelligent Systems (ICSPIS). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, IranDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 1–5.
- Izadi, M.; Sultan, M.; El Kadiri, R.; Ghannadi, A.; Abdelmohsen, K. A Remote Sensing and Machine Learning-Based Approach to Forecast the Onset of Harmful Algal Bloom. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. , et al., Improving remote sensing estimation of Secchi disk depth for global lakes and reservoirs using machine learning methods. GIScience & Remote Sensing, 2022. 59(1): p. 1367-1383.
- Mohsen, A.; Kovács, F.; Kiss, T. Remote Sensing of Sediment Discharge in Rivers Using Sentinel-2 Images and Machine-Learning Algorithms. Hydrology 2022, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, I.; Hossain, S.A.; Roy, S.K.; Karmakar, J.; Jose, F.; De, T.K.; Nguyen, T.T.; Elkhrachy, I.; Nguyen, N.-M. Assessing intra and interannual variability of water quality in the Sundarban mangrove dominated estuarine ecosystem using remote sensing and hybrid machine learning models. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; A, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Q.; Tang, R. Study on remote sensing inversion and temporal-spatial variation of Hulun lake water quality based on machine learning. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2023, 260, 104282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Fu, B.; Li, S.; Lao, Z.; Deng, T.; He, W.; He, H.; Chen, Z. Monitoring multi-water quality of internationally important karst wetland through deep learning, multi-sensor and multi-platform remote sensing images: A case study of Guilin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Sun, S.; Jiang, Q.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H. Retrieval of Total Phosphorus Concentration in the Surface Water of Miyun Reservoir Based on Remote Sensing Data and Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovskaya, R.; Krivoguz, D.; Chernyi, S.; Kozhurin, E.; Khorosheltseva, V.; Zinchenko, E. Surface Water Salinity Evaluation and Identification for Using Remote Sensing Data and Machine Learning Approach. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Mumtaz, R.; Anwar, Z.; Shaukat, A.; Arif, O.; Shafait, F. A Multi–Step Approach for Optically Active and Inactive Water Quality Parameter Estimation Using Deep Learning and Remote Sensing. Water 2022, 14, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Guo, H.; Huang, J.J.; Tian, S.; Xu, W.; Mai, Y. An ensemble machine learning model for water quality estimation in coastal area based on remote sensing imagery. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggesse, E.S.; Zimale, F.A.; Sultan, D.; Enku, T.; Srinivasan, R.; Tilahun, S.A. Predicting Optical Water Quality Indicators from Remote Sensing Using Machine Learning Algorithms in Tropical Highlands of Ethiopia. Hydrology 2023, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; Ding, Z.; Wang, D.; Deng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, T.; Li, W.; Lu, Z.; Wang, G. Comparing deep learning with several typical methods in prediction of assessing chlorophyll-a by remote sensing: a case study in Taihu Lake, China. Water Supply 2021, 21, 3710–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Qin, B. Monitoring water quality using proximal remote sensing technology. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 803, 149805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Liu, H.; Qian, L.; Bauer, J.; Xue, X.; Yu, G.; He, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Bi, Y.; Norra, S. Water quality monitoring and assessment based on cruise monitoring, remote sensing, and deep learning: A case study of Qingcaosha Reservoir. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyek, A.; Arias-Rodriguez, L.F.; Perosa, F. Holistic Approach for Estimating Water Quality Ecosystem Services of Danube Floodplains: Field Measures, Remote Sensing, and Machine Learning. Hydrobiology 2022, 1, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Ding, J. Evaluation of water quality based on a machine learning algorithm and water quality index for the Ebinur Lake Watershed, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Ning, Z.; Chen, M.; Wu, D.; Hao, C.; Zhang, D.; Bai, R.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; et al. Satellite and Machine Learning Monitoring of Optically Inactive Water Quality Variability in a Tropical River. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.T., V. Sagan, and J.J. Sloan, Deep learning-based water quality estimation and anomaly detection using Landsat-8/Sentinel-2 virtual constellation and cloud computing. GIScience & Remote Sensing, 57(4): p. 510-525.
- Najafzadeh, M.; Basirian, S. Evaluation of River Water Quality Index Using Remote Sensing and Artificial Intelligence Models. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, P.M. and S. Keller. Machine learning regression on hyperspectral data to estimate multiple water parameters. in 2018 9th Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS). 2018. IEEE.
- Arias-Rodriguez, L.F.; Duan, Z.; Sepúlveda, R.; Martinez-Martinez, S.I.; Disse, M. Monitoring Water Quality of Valle de Bravo Reservoir, Mexico, Using Entire Lifespan of MERIS Data and Machine Learning Approaches. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Yu, G.; Sun, S.; Dou, Y.; Li, H.; Qiao, Z. Monitoring Water Quality of the Haihe River Based on Ground-Based Hyperspectral Remote Sensing. Water 2021, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yin, G.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Hao, F.; Fu, Y. UAV Multispectral Image-Based Urban River Water Quality Monitoring Using Stacked Ensemble Machine Learning Algorithms—A Case Study of the Zhanghe River, China. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Pahlevan, N.; Melack, J.; Shen, M.; Xue, K. A machine learning approach to estimate chlorophyll-a from Landsat-8 measurements in inland lakes. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adusei, Y.Y.; Quaye-Ballard, J.; Adjaottor, A.A.; Mensah, A.A. Spatial prediction and mapping of water quality of Owabi reservoir from satellite imageries and machine learning models. Egypt. J. Remote. Sens. Space Sci. 2021, 24, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Rodriguez, L.F.; Tüzün, U.F.; Duan, Z.; Huang, J.; Tuo, Y.; Disse, M. Global Water Quality of Inland Waters with Harmonized Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 Using Cloud-Computed Machine Learning. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blix, K.; Pálffy, K.; Tóth, V.R.; Eltoft, T. Remote Sensing of Water Quality Parameters over Lake Balaton by Using Sentinel-3 OLCI. Water 2018, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, J.; Dou, X.; Xing, Q. Using Machine Learning Algorithms With In Situ Hyperspectral Reflectance Data to Assess Comprehensive Water Quality of Urban Rivers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.P.; Oliveira, B.A.; Andrade, M.L.; Starling, M.C.V.; Pereira, A.H.; Maillard, P.; Nogueira, K.; dos Santos, J.A.; Amorim, C.C. Integrating remote sensing and machine learning to detect turbidity anomalies in hydroelectric reservoirs. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 902, 165964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Song, K.; Wen, Z.; Liu, G.; Shang, Y.; Lyu, L.; Du, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, S.; Tao, H.; et al. Remote Sensing of Turbidity for Lakes in Northeast China Using Sentinel-2 Images With Machine Learning Algorithms. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2021, 14, 9132–9146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, H.J.; Lutz, D.A.; Steele, B.G.; Cottingham, K.L.; Weathers, K.C.; Ducey, M.J.; Palace, M.; Johnson, K.M.; Chipman, J.W. Remote Sensing of Lake Water Clarity: Performance and Transferability of Both Historical Algorithms and Machine Learning. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Xu, K.; Cheng, S.; Zhao, L.; Yang, K. Regional Remote Sensing of Lake Water Transparency Based on Google Earth Engine: Performance of Empirical Algorithm and Machine Learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrì, S.; Ottaviani, E.; Prampolini, E.; Besio, G.; Fabiano, B.; Federici, B. Application of machine learning techniques to derive sea water turbidity from Sentinel-2 imagery. Remote. Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2023, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Si, W.; Wei, L.; Li, Z.; Xia, Z.; Ye, S.; Xia, Y. Retrieval of Water Quality from UAV-Borne Hyperspectral Imagery: A Comparative Study of Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosre, J.; Suárez, F. Actual Evapotranspiration Estimates in Arid Cold Regions Using Machine Learning Algorithms with In Situ and Remote Sensing Data. Water 2021, 13, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loggenberg, K. , et al., Modelling water stress in a Shiraz vineyard using hyperspectral imaging and machine learning. Remote Sensing, 10(2): p. 202.
- Elkhrachy, I. Flash Flood Water Depth Estimation Using SAR Images, Digital Elevation Models, and Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, Q.; Tang, Z. Using Sentinel-2 Imagery and Machine Learning Algorithms to Assess the Inundation Status of Nebraska Conservation Easements during 2018–2021. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Hu, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Z.; Hu, B.; Du, Z.; Liu, R. Estimating spatial and temporal variation in ocean surface pCO2 in the Gulf of Mexico using remote sensing and machine learning techniques. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 745, 140965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, C.; Swain, K.C.; Moghimi, A.; Foroughnia, F.; Swain, S.K. Integrating geospatial, remote sensing, and machine learning for climate-induced forest fire susceptibility mapping in Similipal Tiger Reserve, India. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar, B.; Ueda, N.; Idrees, M.O.; Janizadeh, S.; Ahmadi, K.; Shabani, F. Forest Fire Susceptibility Prediction Based on Machine Learning Models with Resampling Algorithms on Remote Sensing Data. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piralilou, S.T.; Einali, G.; Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Nachappa, T.G.; Gholamnia, K.; Blaschke, T.; Ghamisi, P. A Google Earth Engine Approach for Wildfire Susceptibility Prediction Fusion with Remote Sensing Data of Different Spatial Resolutions. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhan, J.; Li, S.; Shama, A.; Zhan, R.; Wang, T.; Lv, J.; Bao, X.; Wu, R. Wildfire Risk Assessment in Liangshan Prefecture, China Based on An Integration Machine Learning Algorithm. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Jin, Y.; Harrison, S.P.; Quilodrán-Casas, C.; Prentice, I.C.; Guo, Y.-K.; Arcucci, R. Parameter Flexible Wildfire Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniques: Forward and Inverse Modelling. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulova, A.; Arsanjani, J.J. Exploratory Analysis of Driving Force of Wildfires in Australia: An Application of Machine Learning within Google Earth Engine. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saim, A.A. and M.H. Aly, Machine learning for modeling wildfire susceptibility at the state level: an example from Arkansas, USA. Geographies, 2022. 2(1): p. 31-47.
- Pérez-Porras, F.-J.; Triviño-Tarradas, P.; Cima-Rodríguez, C.; Meroño-De-Larriva, J.-E.; García-Ferrer, A.; Mesas-Carrascosa, F.-J. Machine Learning Methods and Synthetic Data Generation to Predict Large Wildfires. Sensors 2021, 21, 3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCandless, T.C.; Kosovic, B.; Petzke, W. Enhancing wildfire spread modelling by building a gridded fuel moisture content product with machine learning. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol. 2020, 1, 035010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaqat, W.; Iqbal, M.; Kanwal, R.; Song, W. Study of Driving Factors Using Machine Learning to Determine the Effect of Topography, Climate, and Fuel on Wildfire in Pakistan. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, N.; Nelson, P.V.; Low, R.D. A Novel Approach for Predicting Large Wildfires Using Machine Learning towards Environmental Justice via Environmental Remote Sensing and Atmospheric Reanalysis Data across the United States. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W. , et al., Wildfire risk assessment using deep learning in Guangdong Province, China. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2024. 128: p. 103750.
- Shirazi, Z.; Wang, L.; Bondur, V.G. Modeling Conditions Appropriate for Wildfire in South East China – A Machine Learning Approach. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, M.C.; Chang, K.-T.; Chen, C.-F.; Chiang, S.-H.; Santos, J.L. Modelling the spatial variability of wildfire susceptibility in Honduras using remote sensing and geographical information systems. Geomatics, Nat. Hazards Risk 2017, 8, 876–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisig, J.; Olson, E.; Pebesma, E. Predicting Wildfire Fuels and Hazard in a Central European Temperate Forest Using Active and Passive Remote Sensing. Fire 2022, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. Saliency Detection and Deep Learning-Based Wildfire Identification in UAV Imagery. Sensors 2018, 18, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. , et al., M4SFWD: A Multi-Faceted synthetic dataset for remote sensing forest wildfires detection. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024. 248: p. 123489.
- Velayati, A.H.; Boloorani, A.D.; Kiavarz, M.; Samani, N.N.; Alavipanah, S.K. Spatiotemporal analysis of wildfire in the Tigris and Euphrates basin: A remote sensing based wildfire potential mapping. Remote. Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2024, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, N.; Millard, K.; Darling, S. Wildfire likelihood in Canadian treed peatlands based on remote-sensing time-series of surface conditions. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2023, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Wang, T.; Huang, H.; Zheng, X.; Li, T.; Guo, Z. A self-adaptive wildfire detection algorithm by fusing physical and deep learning schemes. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinformation 2024, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, L. Beyond being wise after the event: Combining spatial, temporal and spectral information for Himawari-8 early-stage wildfire detection. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinformation 2023, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, D.J.; Zhu, Y.; Brown, C.F.; Jin, Y. Satellite detection of canopy-scale tree mortality and survival from California wildfires with spatio-temporal deep learning. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2023, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, L.N.; Tran, V.N.; Nguyen, G.V.; Yeon, M.; Do, M.T.-T.; Lee, G. Enhancing wildfire mapping accuracy using mono-temporal Sentinel-2 data: A novel approach through qualitative and quantitative feature selection with explainable AI. Ecol. Informatics 2024, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, F.; Hu, R.L.; Goyal, N.; Sankar, T.; Ihme, M.; Chen, Y.-F. Next Day Wildfire Spread: A Machine Learning Dataset to Predict Wildfire Spreading From Remote-Sensing Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, S.M.B. , et al., Remote sensing applications for mapping large wildfires based on machine learning and time series in northwestern Portugal. Fire, 2023. 6(2): p. 43.
- Iban, M.C.; Sekertekin, A. Machine learning based wildfire susceptibility mapping using remotely sensed fire data and GIS: A case study of Adana and Mersin provinces, Turkey. Ecol. Informatics 2022, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajane, M.; Costache, R.; Karimi, F.; Pham, Q.B.; Essahlaoui, A.; Nguyen, H.; Laneve, G.; Oudija, F. Application of remote sensing and machine learning algorithms for forest fire mapping in a Mediterranean area. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiec, P.; Gadal, S. A Comparison of Two Machine Learning Classification Methods for Remote Sensing Predictive Modeling of the Forest Fire in the North-Eastern Siberia. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, P.K.; Kinoshita, A.M. Estimating Evapotranspiration in a Post-Fire Environment Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Remote. Sens. 2018, 10, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, A.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, C.-W. Creation of Wildfire Susceptibility Maps in Plumas National Forest Using InSAR Coherence, Deep Learning, and Metaheuristic Optimization Approaches. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S. , et al., Wildfire severity mapping using sentinel satellite data based on machine learning approaches. Korean Journal of Remote Sensing, 36(5_3): p. 1109-1123.
- Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Kamran, K.V.; Blaschke, T.; Aryal, J.; Naboureh, A.; Einali, J.; Bian, J. Spatial Prediction of Wildfire Susceptibility Using Field Survey GPS Data and Machine Learning Approaches. Fire 2019, 2, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamnia, K.; Nachappa, T.G.; Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Blaschke, T. Comparisons of Diverse Machine Learning Approaches for Wildfire Susceptibility Mapping. Symmetry 2020, 12, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Napoli, M. , et al., Landslide susceptibility assessment of wildfire burnt areas through earth-observation techniques and a machine learning-based approach. Remote Sensing, 12(15): p. 2505.
- Zikiou, N.; Rushmeier, H.; Capel, M.I.; Kandakji, T.; Rios, N.; Lahdir, M. Remote Sensing and Machine Learning for Accurate Fire Severity Mapping in Northern Algeria. Remote. Sens. 2024, 16, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, N.; Razavi-Termeh, S.V.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Al-Kindi, K.M.; Abuhmed, T.; Nazeri, B.; Choi, S.-M. Wildfire Susceptibility Mapping Using Deep Learning Algorithms in Two Satellite Imagery Dataset. Forests 2023, 14, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmuel, A.; Heifetz, E. Global Wildfire Susceptibility Mapping Based on Machine Learning Models. Forests 2022, 13, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.A.; Brothers, K.L.; Jones, S.D.; Colwell, J.; Winters, J. Wildland Fire Tree Mortality Mapping from Hyperspatial Imagery Using Machine Learning. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, J.S.; Petzke, W.; Jiménez, P.A.; Brummet, T.; Knievel, J.C.; James, E.; Kosović, B.; Gagne, D.J. Machine Learning and VIIRS Satellite Retrievals for Skillful Fuel Moisture Content Monitoring in Wildfire Management. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syifa, M.; Panahi, M.; Lee, C.W. Mapping of Post-Wildfire Burned Area Using a Hybrid Algorithm and Satellite Data: The Case of the Camp Fire Wildfire in California, USA. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.A.; Pivot, F.C.; Tan, Q.; Cantin, A.S.; Wooster, M.J.; Johnston, J.M. A Machine Learning Approach to Waterbody Segmentation in Thermal Infrared Imagery in Support of Tactical Wildfire Mapping. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Y.; Zhang, P.; Nascetti, A.; Bevington, A.R.; Wulder, M.A. Near Real-Time Wildfire Progression Monitoring with Sentinel-1 SAR Time Series and Deep Learning. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Zhang, F.; Fu, S.; Wei, X.; Ma, Y.; Wu, K. High Spatiotemporal Resolution PM2.5 Concentration Estimation with Machine Learning Algorithm: A Case Study for Wildfire in California. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastick, N.J.; Wylie, B.K.; Rigge, M.B.; Dahal, D.; Boyte, S.P.; Jones, M.O.; Allred, B.W.; Parajuli, S.; Wu, Z. Rapid Monitoring of the Abundance and Spread of Exotic Annual Grasses in the Western United States Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. AGU Adv. 2021, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Burriel, F.; Delicado, P.; Prata, A.T.; Cucchietti, F.M. Estimating heterogeneous wildfire effects using synthetic controls and satellite remote sensing. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolè, A.; Rita, A.; Spatola, M.F.; Borghetti, M. Biogeographic variability in wildfire severity and post-fire vegetation recovery across the European forests via remote sensing-derived spectral metrics. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 823, 153807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Hernández, J.; Pereira, J.C.; Stovall, A.; Pascual, A. Impact of fire severity on forest structure and biomass stocks using NASA GEDI data. Insights from the 2020 and 2021 wildfire season in Spain and Portugal. Sci. Remote. Sens. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; He, B.; Li, Y.; Fan, C.; Yin, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y. Estimation of potential wildfire behavior characteristics to assess wildfire danger in southwest China using deep learning schemes. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 120005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, S.; Reinke, K.; Jones, S. Mapping the recovery of Mountain Ash (Eucalyptus regnans) and Alpine Ash (E. delegatensis) using satellite remote sensing and a machine learning classifier. Remote. Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2024, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Guisuraga, J.M.; Fernández-Manso, A.; Quintano, C.; Fernández-García, V.; Cerrillo, A.; Marqués, G.; Cascallana, G.; Calvo, L. FIREMAP: Cloud-based software to automate the estimation of wildfire-induced ecological impacts and recovery processes using remote sensing techniques. Ecol. Informatics 2024, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.

| Research fields | Subcategorized subjects | Number of publications |
|---|---|---|
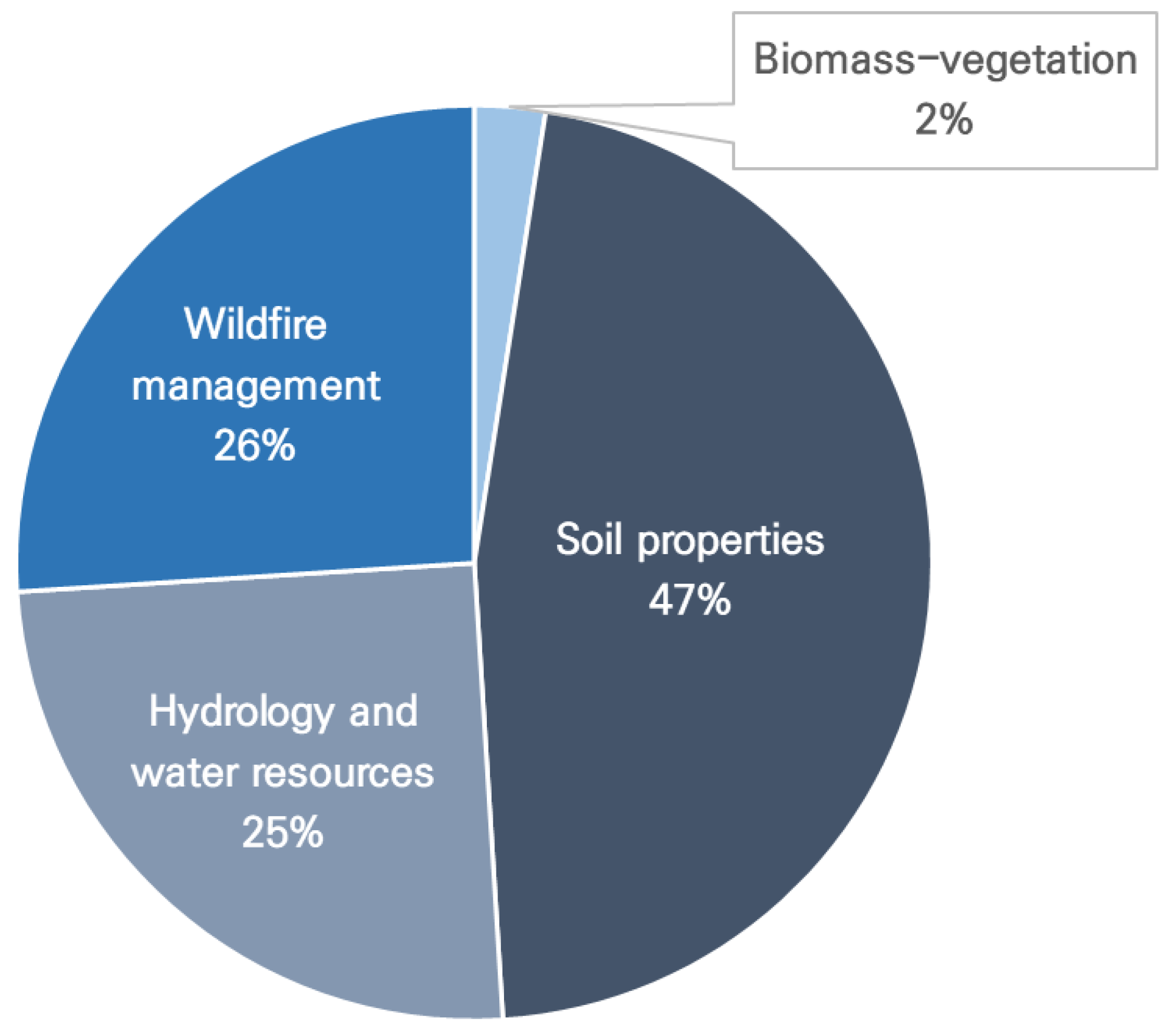
| Biomass-vegetation | Above-ground biomass[29,30,31], grassland biomass[32], ground biomass[33,34] | 5 |
| Soil properties | Soil conductivity[35,36,37], soil salinity[28,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57], SOC [58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72], soil aggregate stability[73,74], soil chemistry[75,76], soil degradation[77], soil erodibility[78,79,80,81], soil matric potential[82], soil mercury[83], soil moisture[84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110], soil nutrients[111,112,113], soil total nitrogen[114], soil respiration[115], soil stiffness[116], soil texture[117,118,119], soil types[120], soil organic matter[121,122,123,124], soil water content and evapotranspiration[125] | 93 |
| Hydrology and water resources | Groundwater level[126], streamflow[127], surface water[128,129], water storage[130], sediment concentration[131], algal blooms[132], Secchi disk depth[133], sediment discharge[134], waters quality[135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159], turbidity[160,161,162,163,164,165], evapotranspiration[166,167], flash flood water depth[168], inundation status[169], ocean surface CO2[170] | 50 |
| Wildfire management | Wildfire prediction[171,172,173,174,175,176,177,178,179,180,181,182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189,190,191,192], wildfire monitoring[25,193,194,195,196,197,198,199,200,201,202,203,204,205,206,207,208,209,210,211,212,213,214,215,216,217,218], wildfire recovery[219,220] | 52 |
| Research fields | Number of publications | Top three most commonly used RS data | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithms | Frequency of usages | ||
| Biomass-vegetation | 5 | (1) MODIS, UAV | 2 |
| (2) Landsat 8, Sentinel-2, ALOS-2, STRM | 1 | ||
| N/A | N/A | ||
| Soil properties | 93 | (1) Landsat 8 | 32 |
| (2) Sentinel-2 | 28 | ||
| (3) MODIS | 22 | ||
| Hydrology and water resources | 50 | (1) Landsat 8 | 18 |
| (2) Sentinel-2 | 16 | ||
| (3) Rapid Eye | 7 | ||
| Wildfire management | 52 | (1) MODIS | 20 |
| (2) Sentinel-2 | 15 | ||
| (3) Landsat 8 | 10 | ||
| Research fields | Number of publications | Top three most commonly used RS data | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithms | Frequency of usages | ||
| Biomass-vegetation | 5 | (1) RF, ANN | 3 |
| (2) SVM, MLR | 2 | ||
| (3) ANFIS, PLS, KNN, MARS | 1 | ||
| Soil properties | 93 | (1) RF | 67 |
| (2) ANN | 23 | ||
| (3) SVM | 21 | ||
| Hydrology and water resources | 50 | (1) RF | 32 |
| (2) SVM, SVR | 14 | ||
| (3) XGB | 9 | ||
| Wildfire management | 52 | (1) RF | 30 |
| (2) SVM | 16 | ||
| (3) MLP | 7 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





