Submitted:
26 September 2024
Posted:
27 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Principles of Scientific Observation
2.1. Directionality and Orthogonality Principle of Scientific Observation
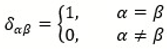
2.2. Observation Interference and the Diagonal Rule
2.3. Low Disturbance Zone
2.4. High Disturbance Zone
2.5. Two Mathematical Paths
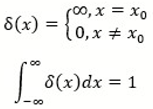
3. Mathematical Foundations of Integration Theory
3.1. Application of Category Theory
3.2. The Mathematical Foundations of Integration Theory
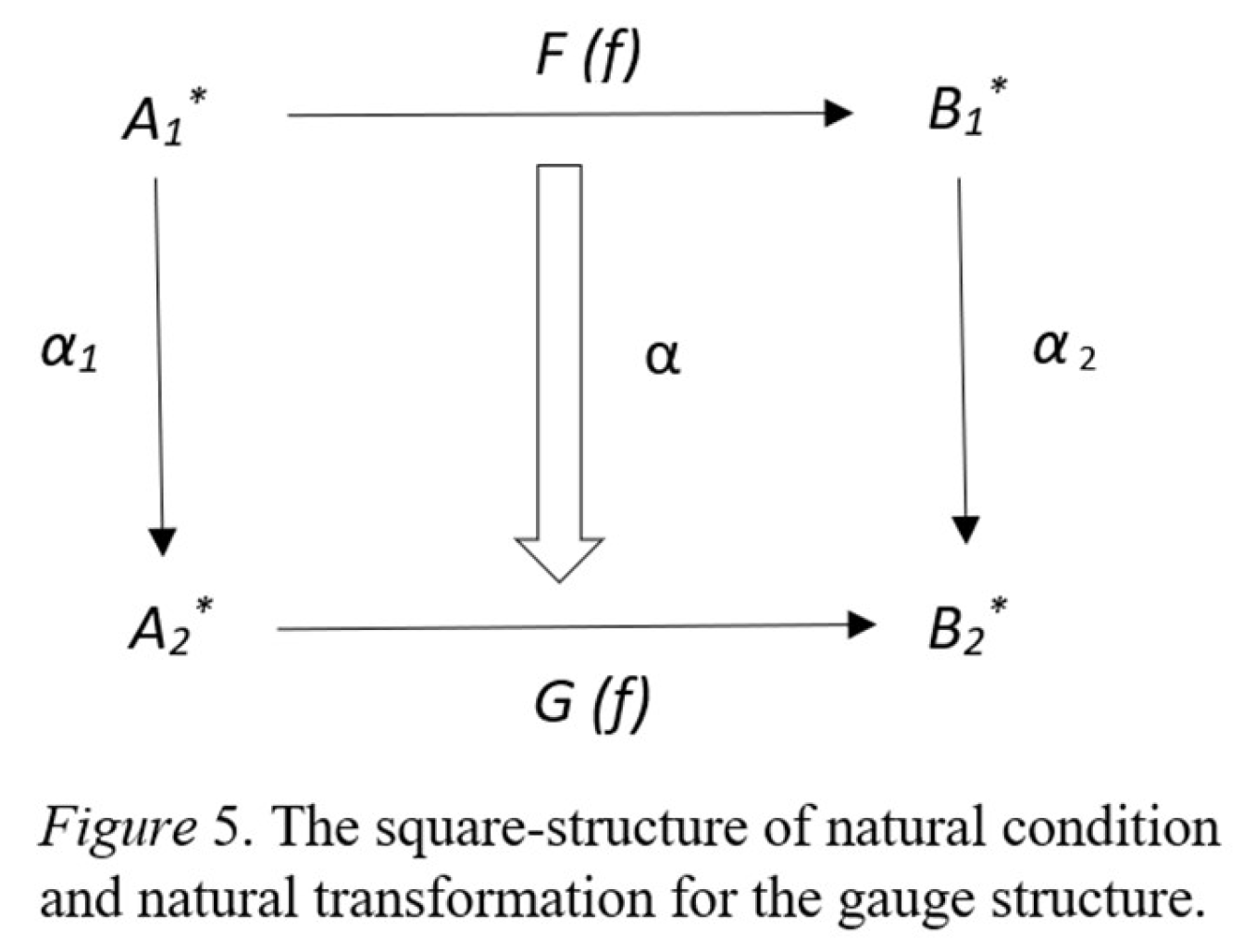
3.3. The Hypothesis of Structural Force
4. Integration Point Cases
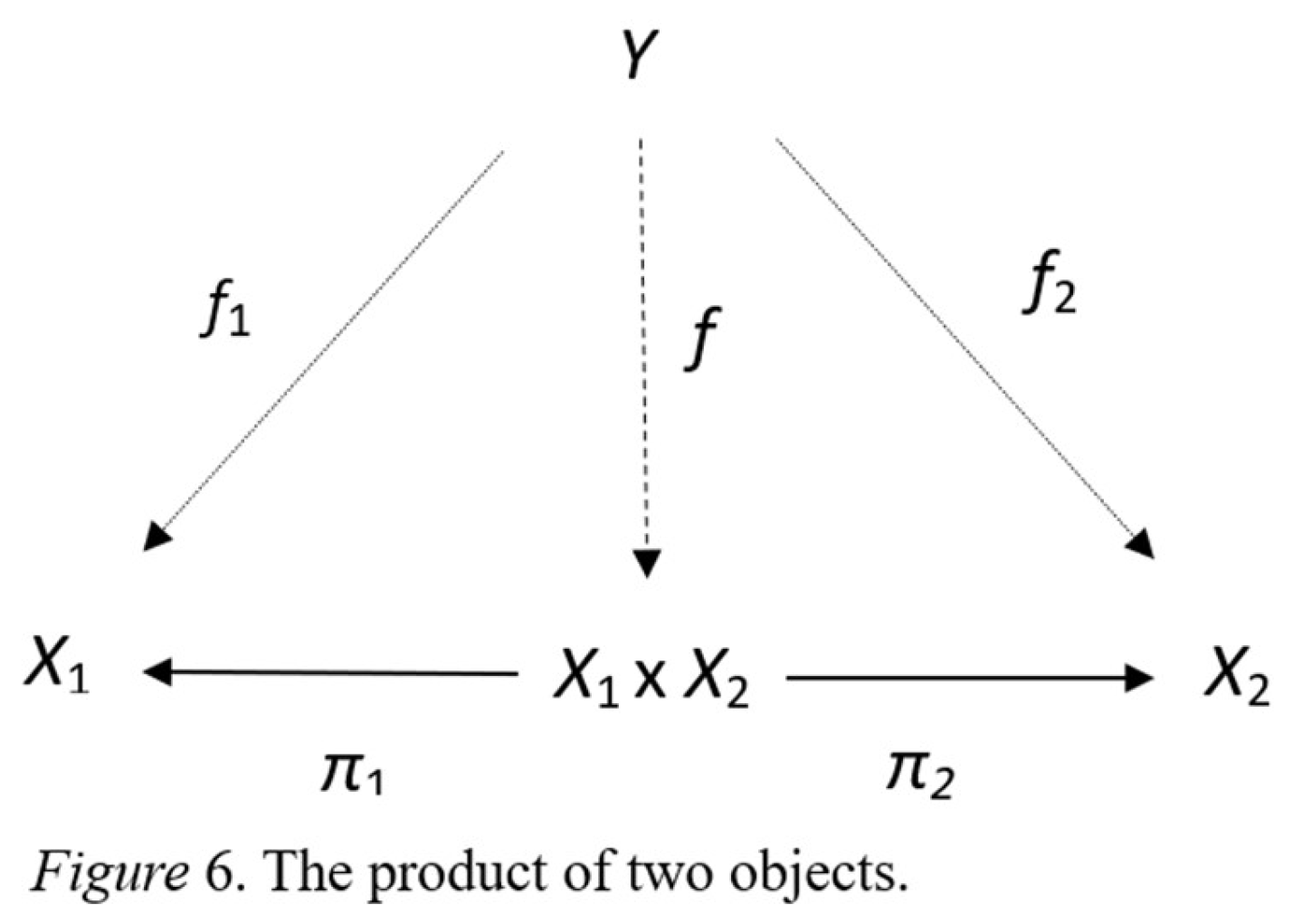
4.1. Two Fields Sharing a Single Integration Point
4.2. Multiple Fields Sharing a Single Integration Point
4.2.1. Standard Dual-Leg Structure of Logic and Formal Language
4.2.2. Syntax Structure and Utility Semantics in Decision Theory
- Selection Set: A collection of choices or options.
- Outcome Set: Each choice can produce a set of possible outcomes.
- Characterization: Each outcome is characterized by two properties, desire and feasibility.
4.2.3. Syntax Structure and Utility Semantics in Game Theory
- 4.
- Assumption: Let N be the number of players in the game.
- 5.
- Action Sets: Each player has a set of possible actions, denoted as . This is similar to individual decision theory, with no cognitive difficulty.
- 6.
- Situation: Consider an n-tuple of possible actions (,…,,…,), where each player selects an action from their set of possible actions. This n-tuple is called a situation. A game is the collection of all possible situations, which is the Cartesian product of all players' action sets, denoted as X1n. This is like a film reel composed of individual frames.
4.2.4. Dual-Leg Structure of Set Theory Language
5. Integration Line Case Study
6. Integration Surface Case Studies
6.1. U(1) Dynamics Integration Surface
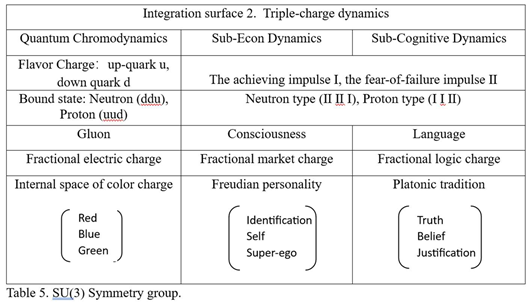
6.2. SU(3) Dynamics Integration Surface
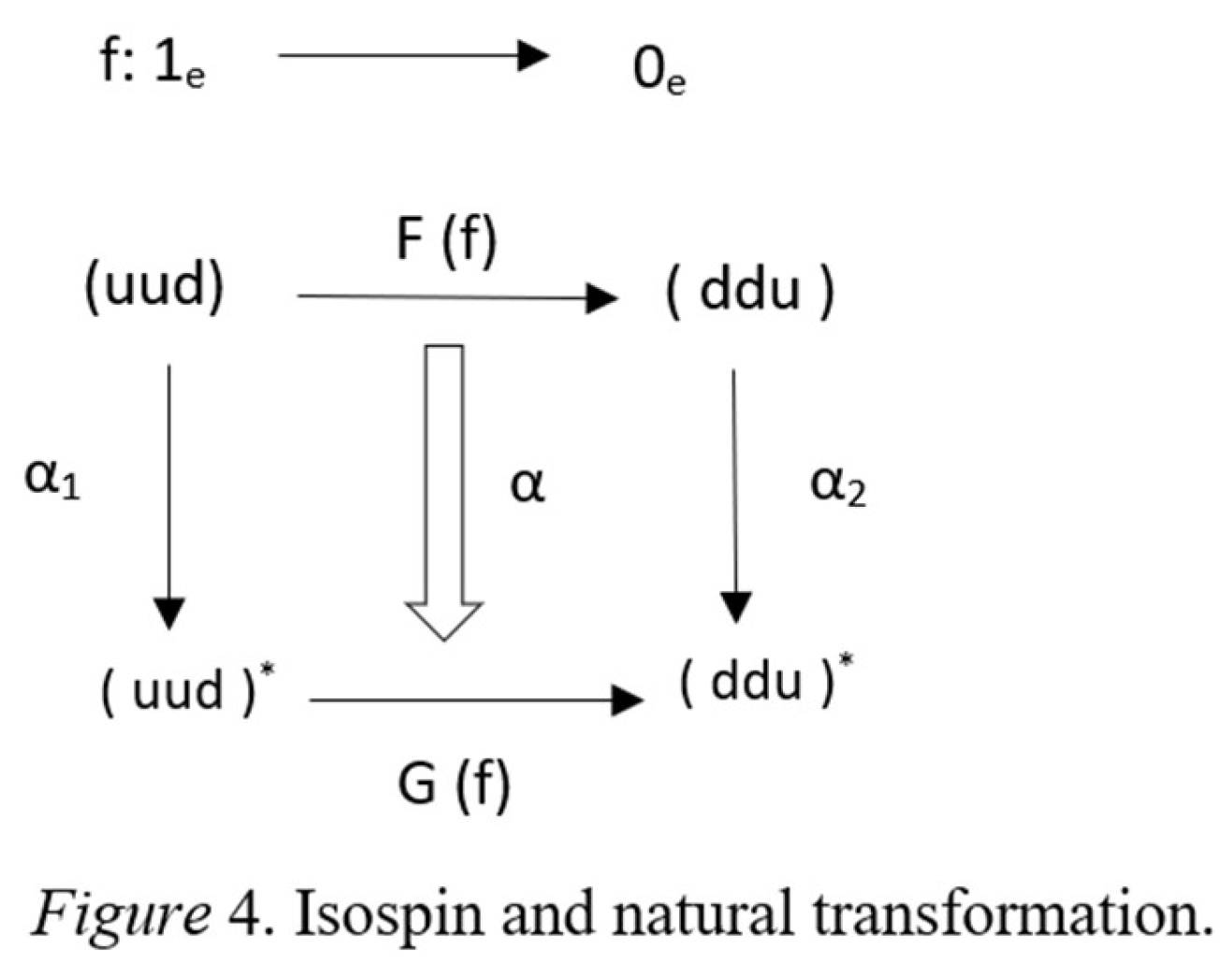
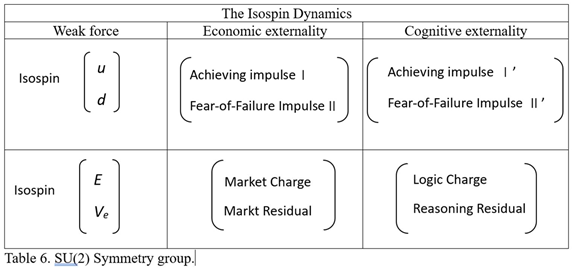
6.3. Isospin Integration Surface
7. Standard Model Integration System
8. General Discussion
References
- Hofstadter, D. (1979/1995). Gödel, Escher, Bach: An Eternal Golden Braid. Basic Basic Books Inc. New York.
- Penrose, R. (2004). The Road to Reality: A Complete Guide to the Laws of the Universe. Alfred A. Knopf.
- Wang, Z. (2008). Elementaty Quantum Field Theory. Peking University Press, Beijing.
- Zee, T. (2003). Quantum Field Theory in a Nutshell. Princeton University Press, Princeton.
- Yang, Y. Psychological Character Periods and Society: Psychological Life and Theoretical Physics I. Science, Economy, Society 2022, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. The Integration Structure of Language and Linguistic Behavior and Its Psychologization Path: Psychological Life and Theoretical Physics II. Science, Economy, Society, 2022; 40. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. (2022). The Content, Methods, and Significance of Economic Dynamics: Economic Dynamics and the Standard Model I. Science, Economy, Society, Vol. 40, No. 5. China. Preprint in English. Yang, Y. Contents, Methods, and Significance of the Economic Dynamics: Economics Dynamics and Standard Model (I). Preprints 2024, 2024080810. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Principles of Market Dynamics: Economic Dynamics and the Standard Model II. Science, Economy, Society, 2023; 41. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Principles of Sub-Economic Dynamics: Economic Dynamics and the Standard Model III. Science, Economy, Society, 2023; 41. [Google Scholar]
- Preprint in English: Yang, Y. Principles of the Sub-Econ Dynamics: The Econ-Dynamics and the Standard Model (Ⅲ). Preprints 2024, 2024071843. Yang, Y. (2023). Principles of Economic Externality Dynamics: Economic Dynamics and the Standard Model V. Science, Economy, Society, Vol. 41, No. 5. China. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Principles of Economic Externality Dynamics Economic Dynamics and the Standard Model (V). Journal of Electrical Electronics Engineering 2024, 3, 01–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Outline of Categorical Dynamics: From Theoretical Physics to Social Sciences. Cognitive Science 2022, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Philosophy Encounters Statistics with the Cognitive Gauge Structure. Cognitive Science 2023, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. (2023). The Content, Methods, and Significance of Higher-Order Cognitive Research. Academic Frontiers, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y., Braine, M.D.S., & O'Brien, D.P. (1998). Some empirical justifications of one mental predicate-logic model. In M.D.S. Braine & D.P. O'Brien (Eds.), Mental Logic, Chapter 12, pp. 333-365. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Yang, Y.; Johnson-Laird, P.N. Illusions in quantified reasoning: How to make impossible seem possible, and vice versa. Memory & Cognition 2000, 28, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G. (2010). Material Structure. Science Press, Beijing.
- von Neuman, J. (1955/1983), The Mathematical Foundations of Quantum Mechanics. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey.

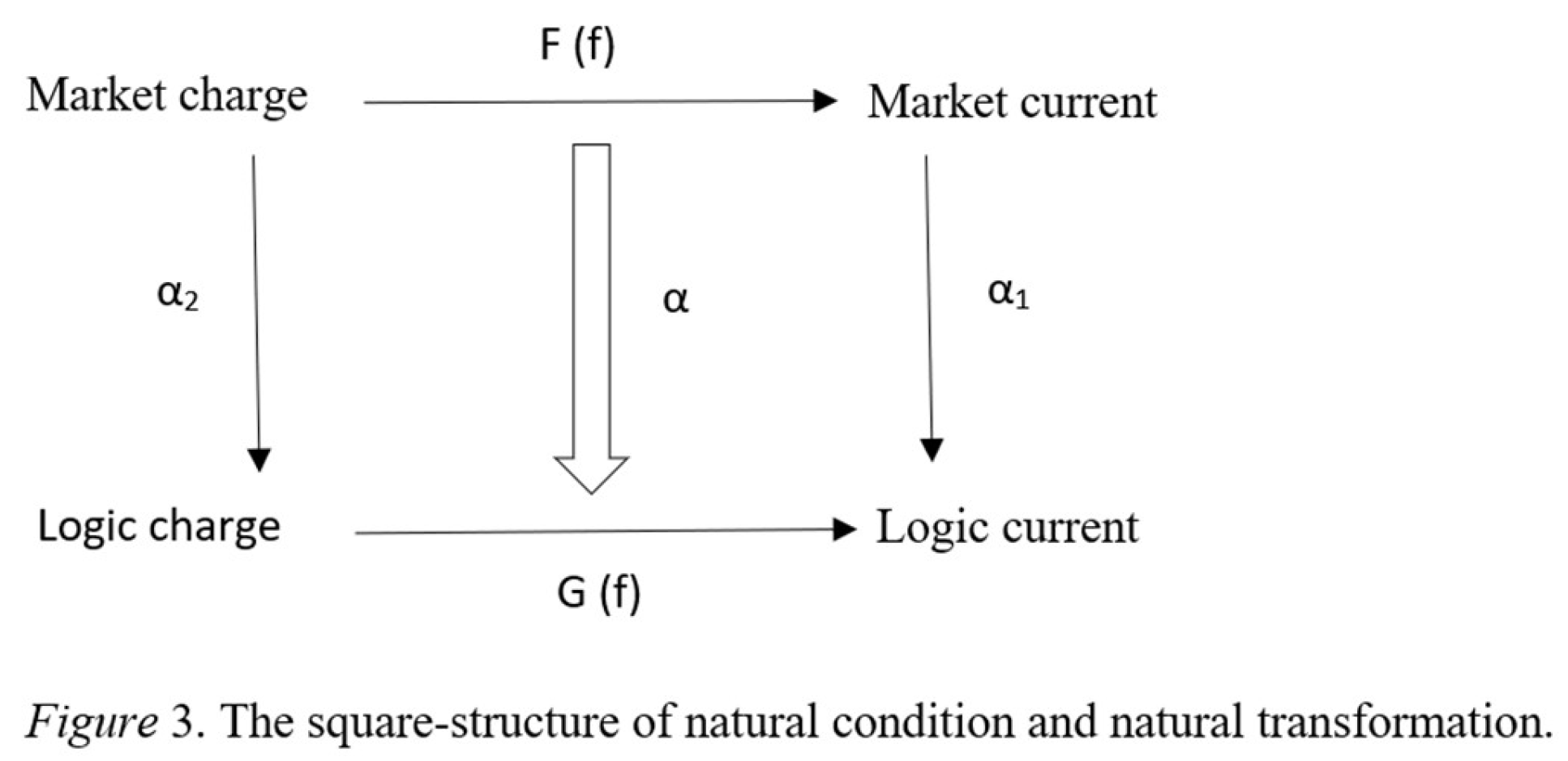
| Gauge Structure | ||
| Gauge Structure | Philosophy | Statistics |
| Global Gauge Potential | Metaphysics | Population |
| Global Gauge Field Strength | Add-on Philosophy | Population Mean |
| Local Gauge Potential | Cognitive Philosophy, Individual Philosophical Ability | Stochastic Sampling |
| Local Gauge Field Strength | Cognitive Philosophy, Individual Philosophical Expression | Sample Probability |
| One more integration point | |
| Syntax/Semantics Two-leg mechanism | Logic, decision theory, game theory, set theory, etc. |
| Integration line | |
| Psychological life characteristic phase | Theoretical physics |
| Embracing phase | Newtonian mechanics |
| Phase of conflict | Quantum mechanics and special relativity |
| Re-entry phase | Proper time, momentum cone Gauge field theory concept |
| Citizenship phase | gauge field theory model |
| Emotional phase | general relativity |
| Single Charge Dynamics | ||
| Quantum Electrodynamics | Market Dynamics | Reasoning Dynamics |
| Electric Charge | Market Charge | Logical Charge |
| Spin Up Spin Down |
Buying Not Buying |
Valid / Yes Invalid / No |
| Magnetic Field | Economic Cognitive Field |
Reasoning Cognitive Field |
| Global Gauge Potential | Economic Rationality or Rational Man | Logician or Logic |
| Global Gauge Field Strength | Perfect Competitive Market |
A Specific Logical System or A Set of Reasoning Experiment items |
| Local Gauge Potential | Individual Consumer Budget | Reasoner Ability |
| Local Gauge Field Strength | Individual Consumer Consumption | Reasoner Performance |
| Light Cone | Money Cone | Language Cone |
 |
 |
| Three Standard models | ||||
| Integration Surface | Integration Surface 1 | Integration Surface 2 | Integration Surface 3 | Integration Surface 4 |
| Standard Model | Quantum Electrodynamics | Quantum Chromodynamics | Weak Force Model | Higgs Mechanism |
| Economic Dynamics | Market Dynamics | Subeconomic Dynamics | Economic Externality Dynamics | Ordinary Rationality Mechanism |
| Epistemic Dynamics | Reasoning Dynamics | Subcognitive Dynamics | Cognitive Externality Dynamics | |
| Number Of Charges | Single Charge Dynamics | Three Charge Dynamics | Isospinal Dynamics | Complex Scalar Field |
| Gauge Symmetry Group | U (1) Symmetry Group | SU (3) Symmetry Group | SU (2) Symmetry Group | Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





