Submitted:
24 September 2024
Posted:
26 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
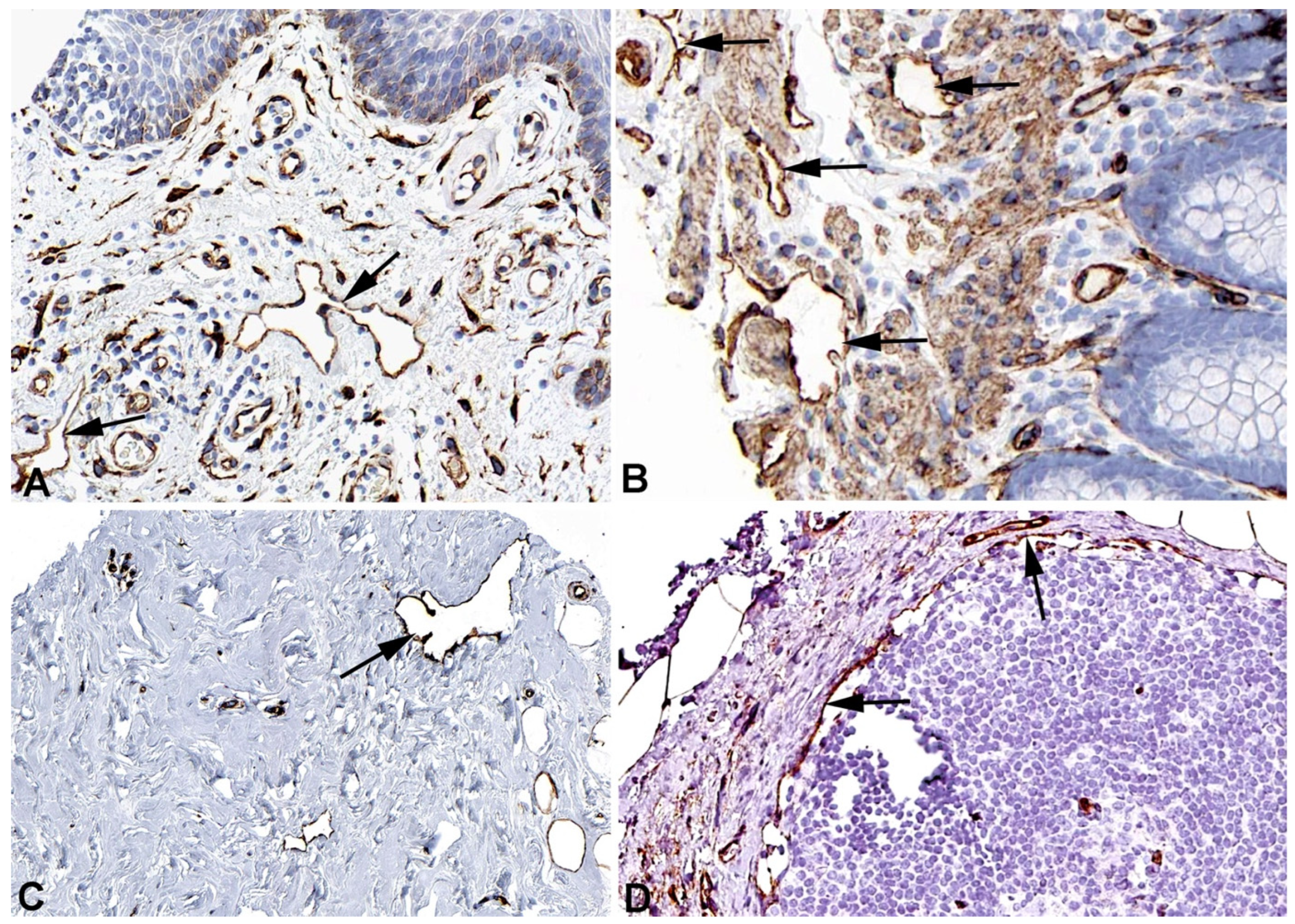
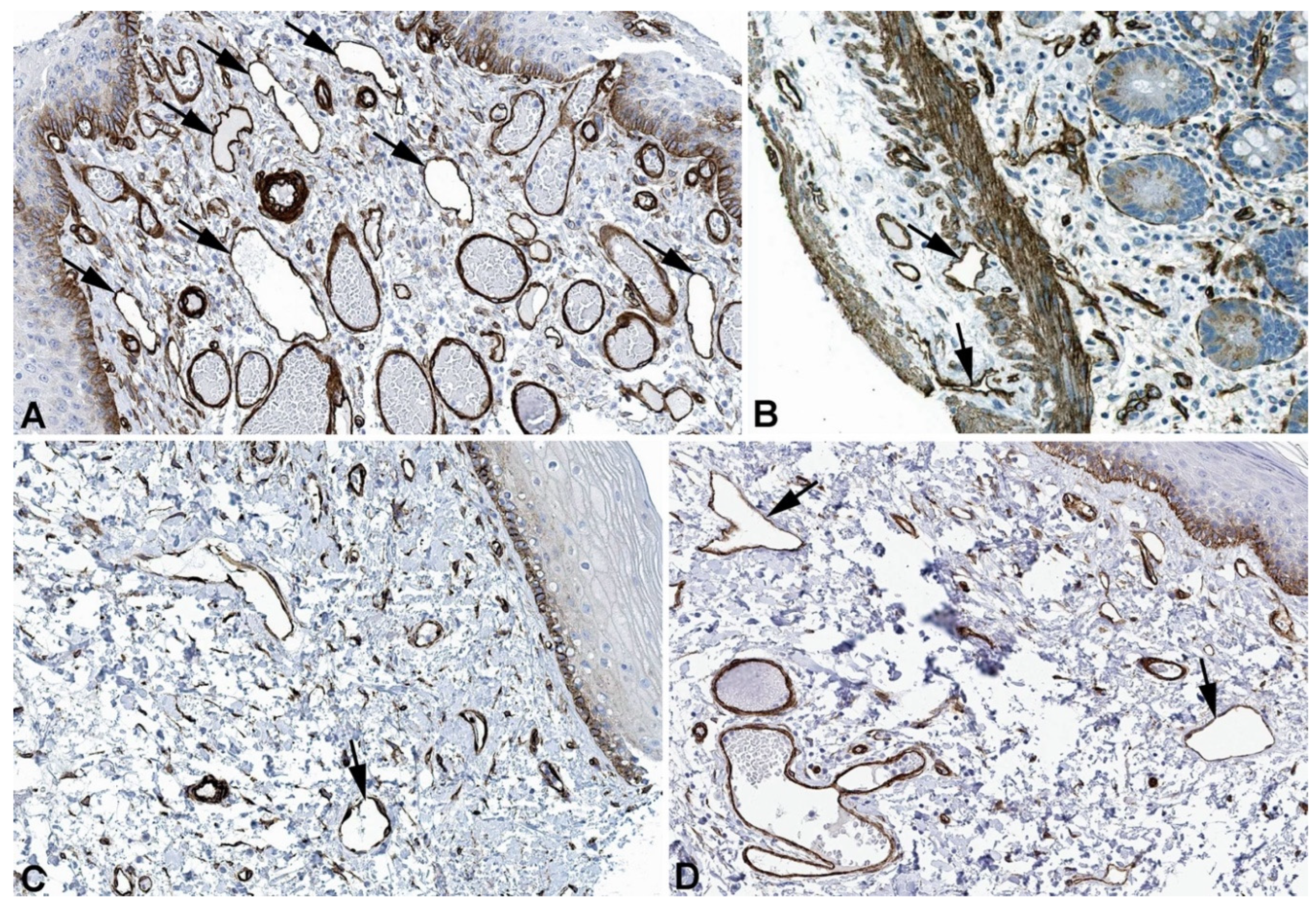
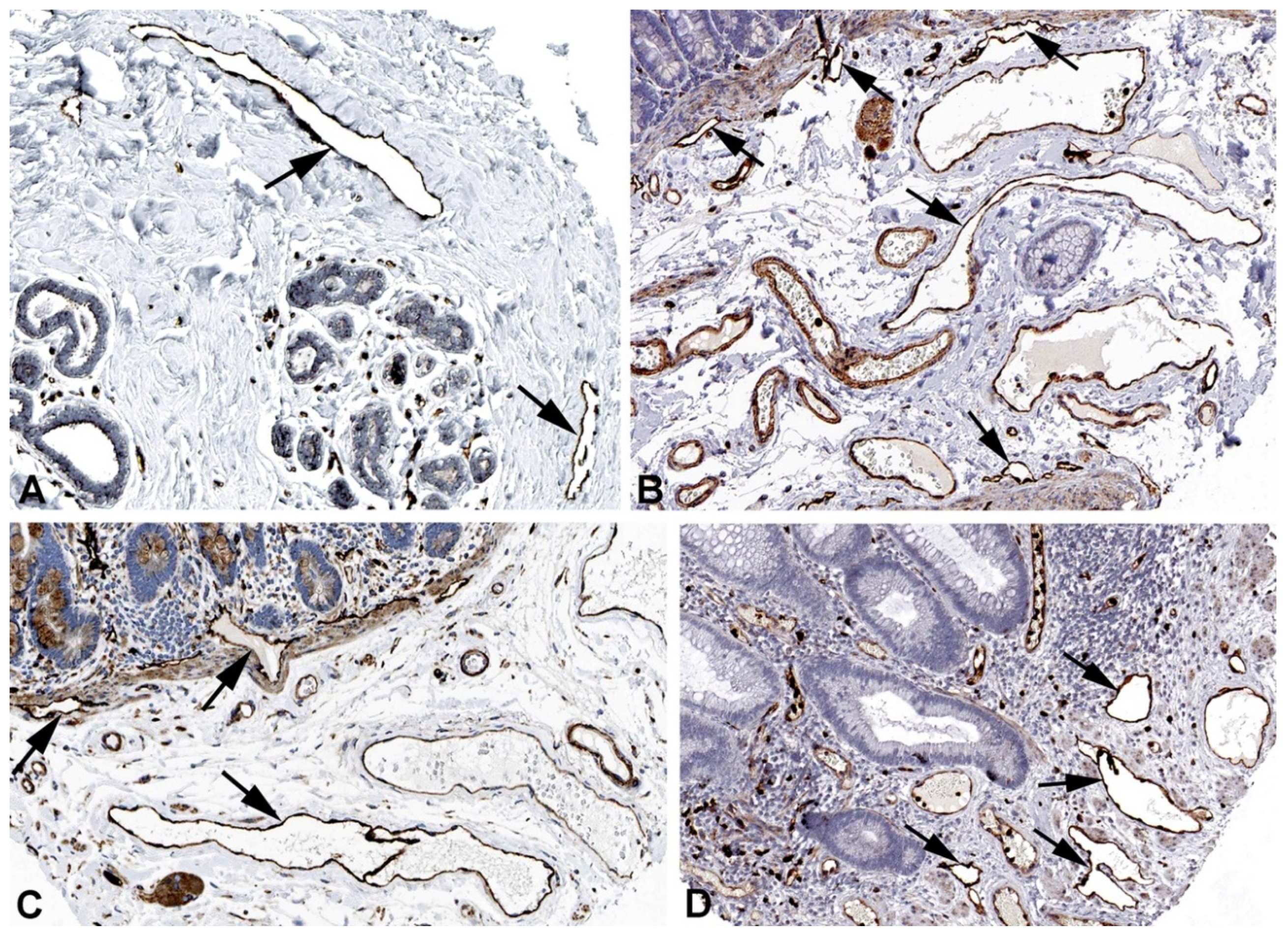
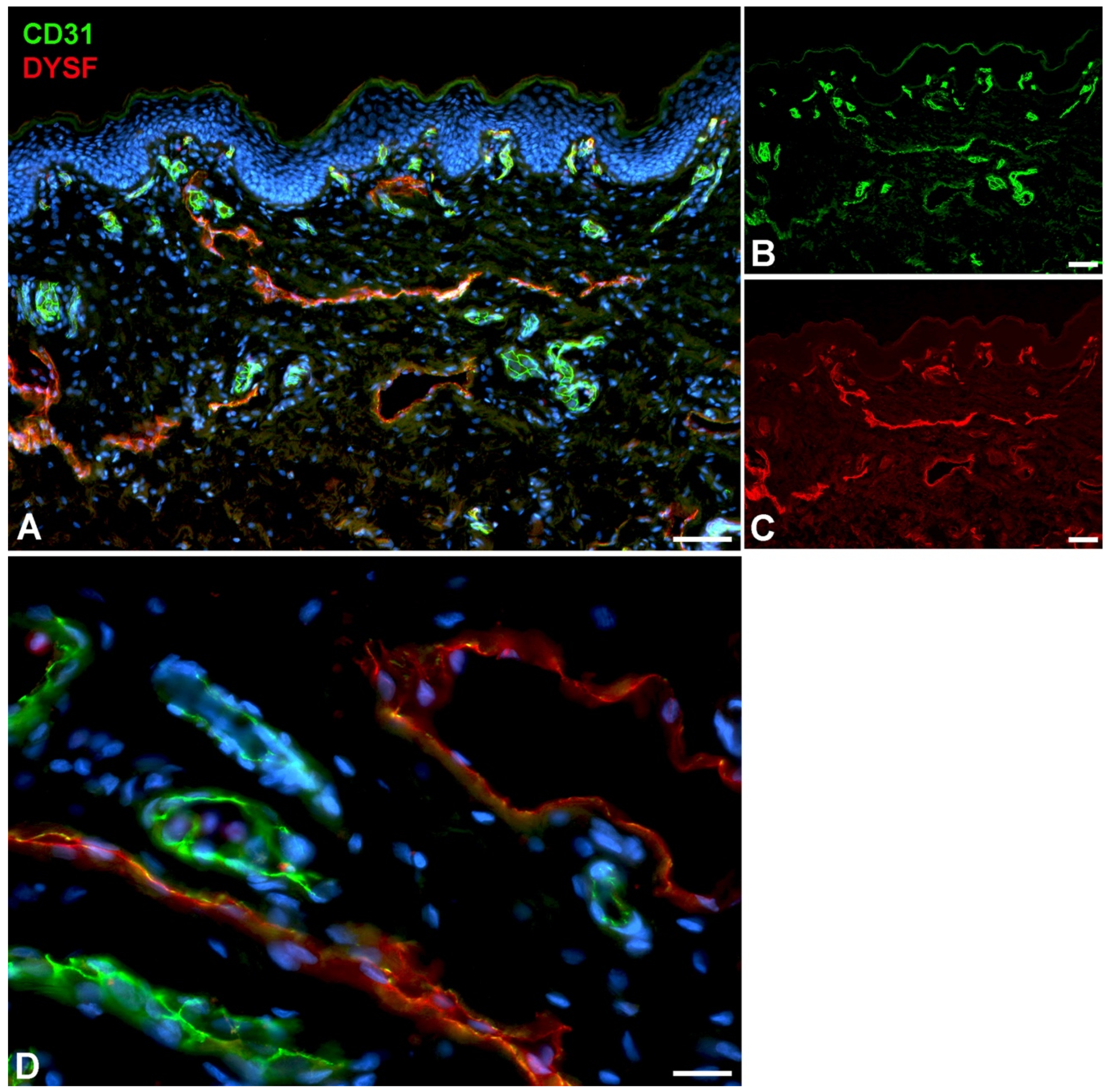
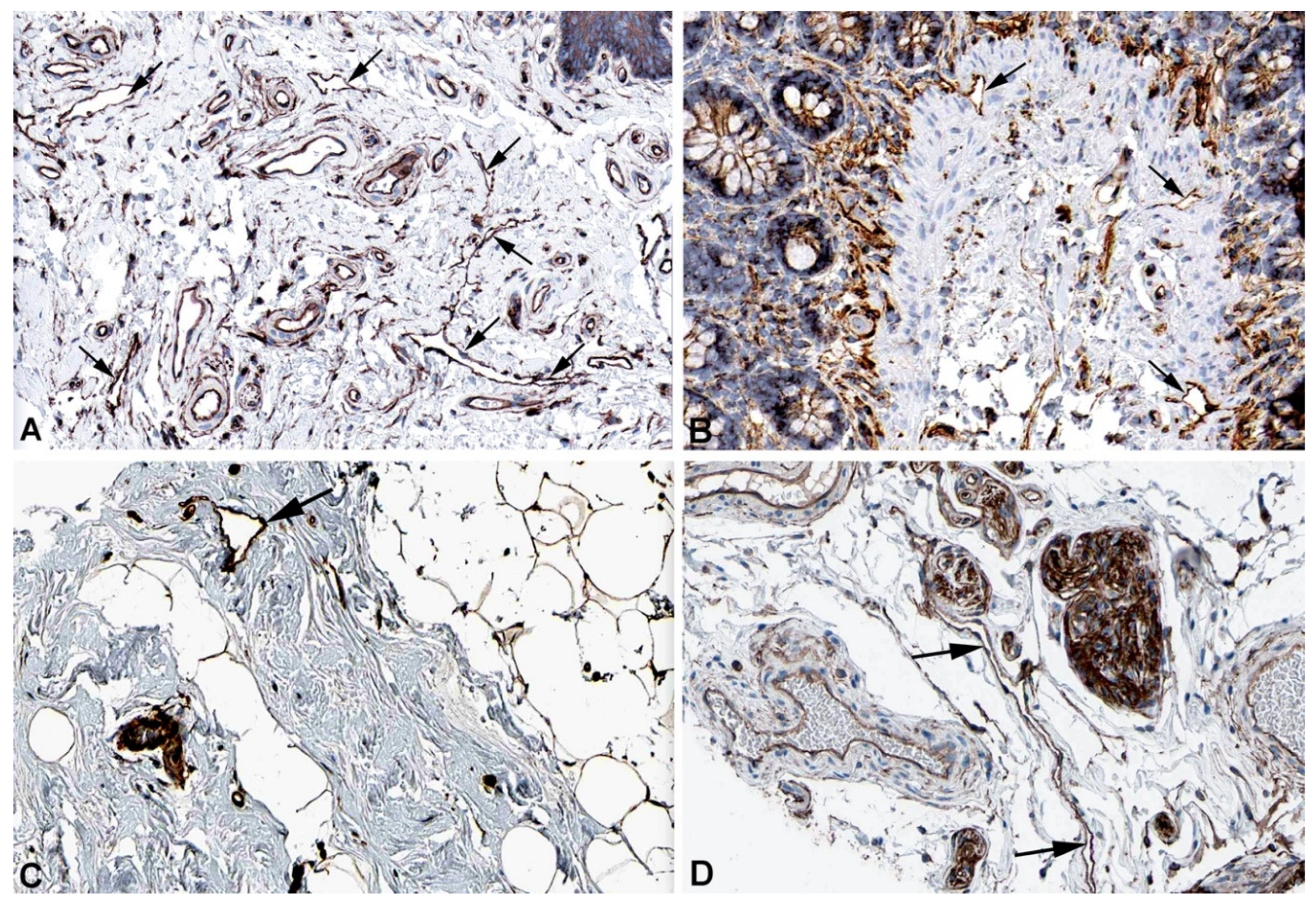
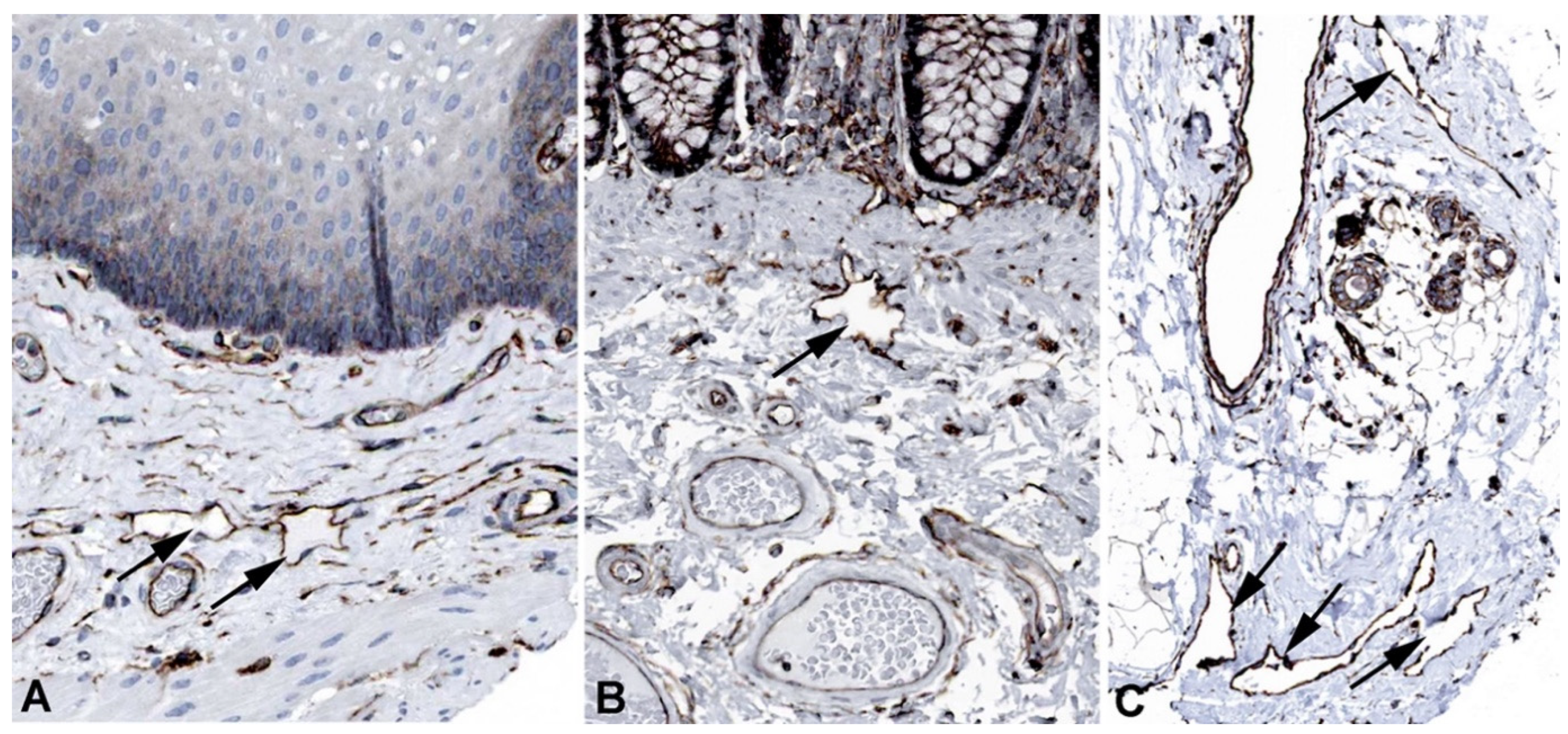
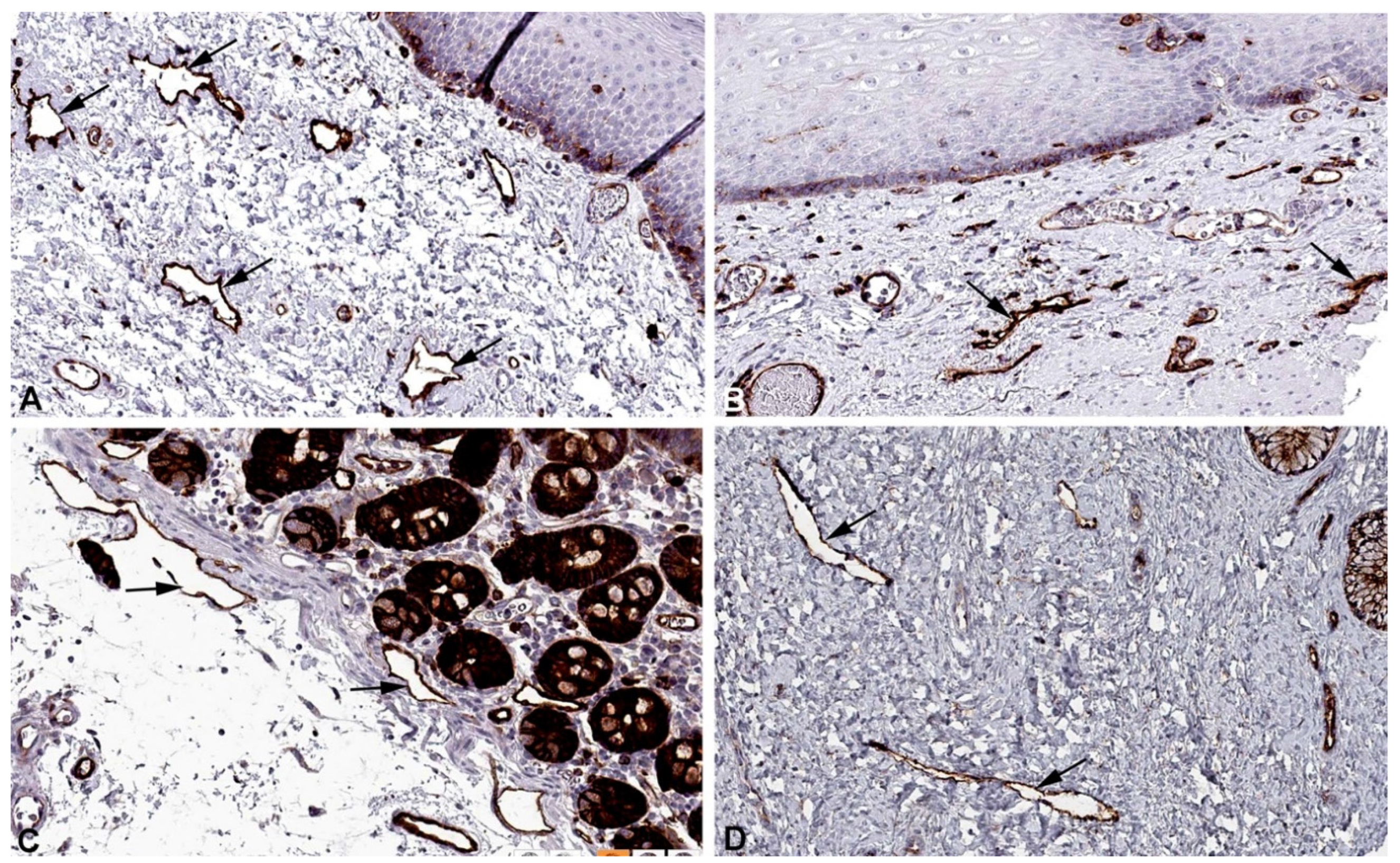
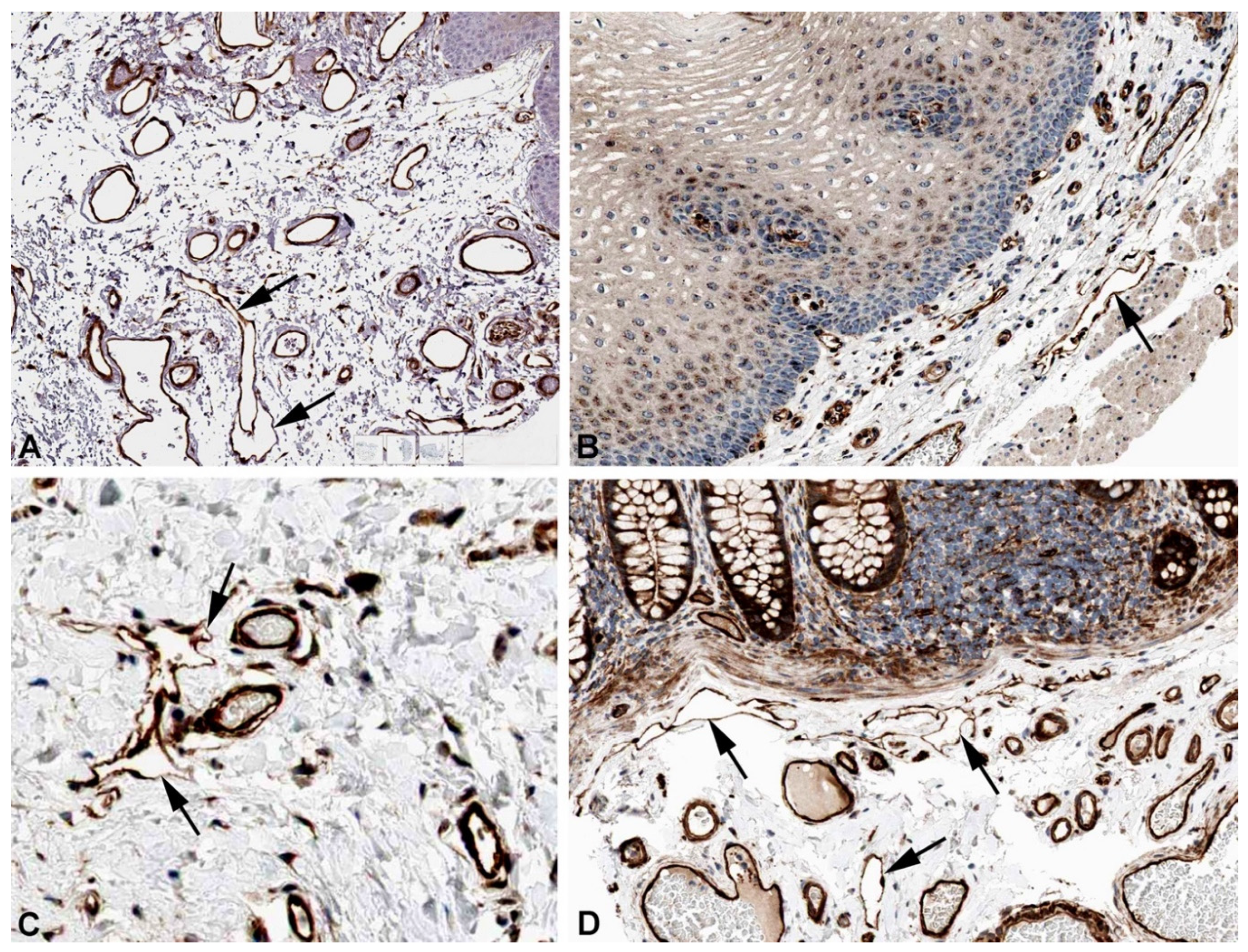
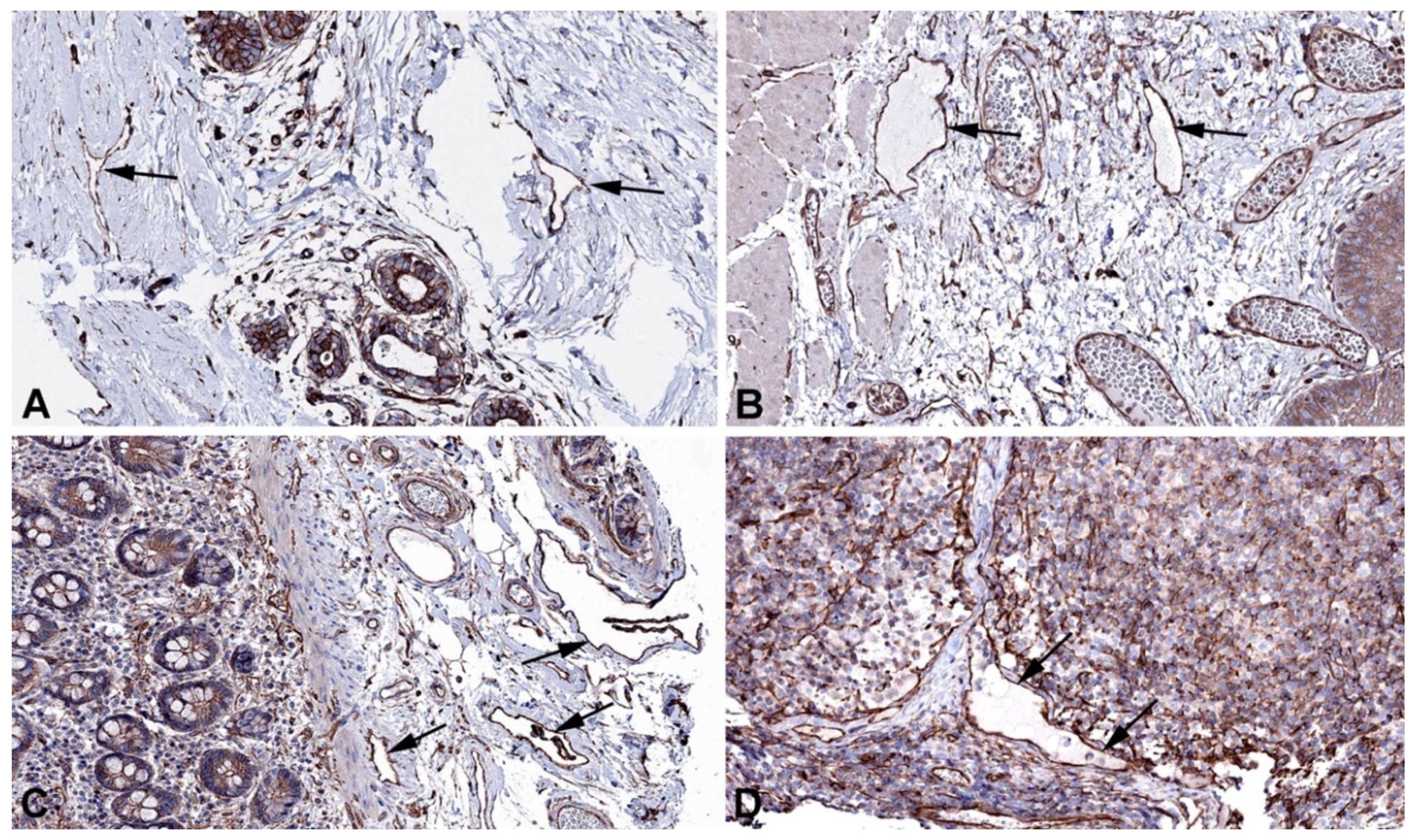
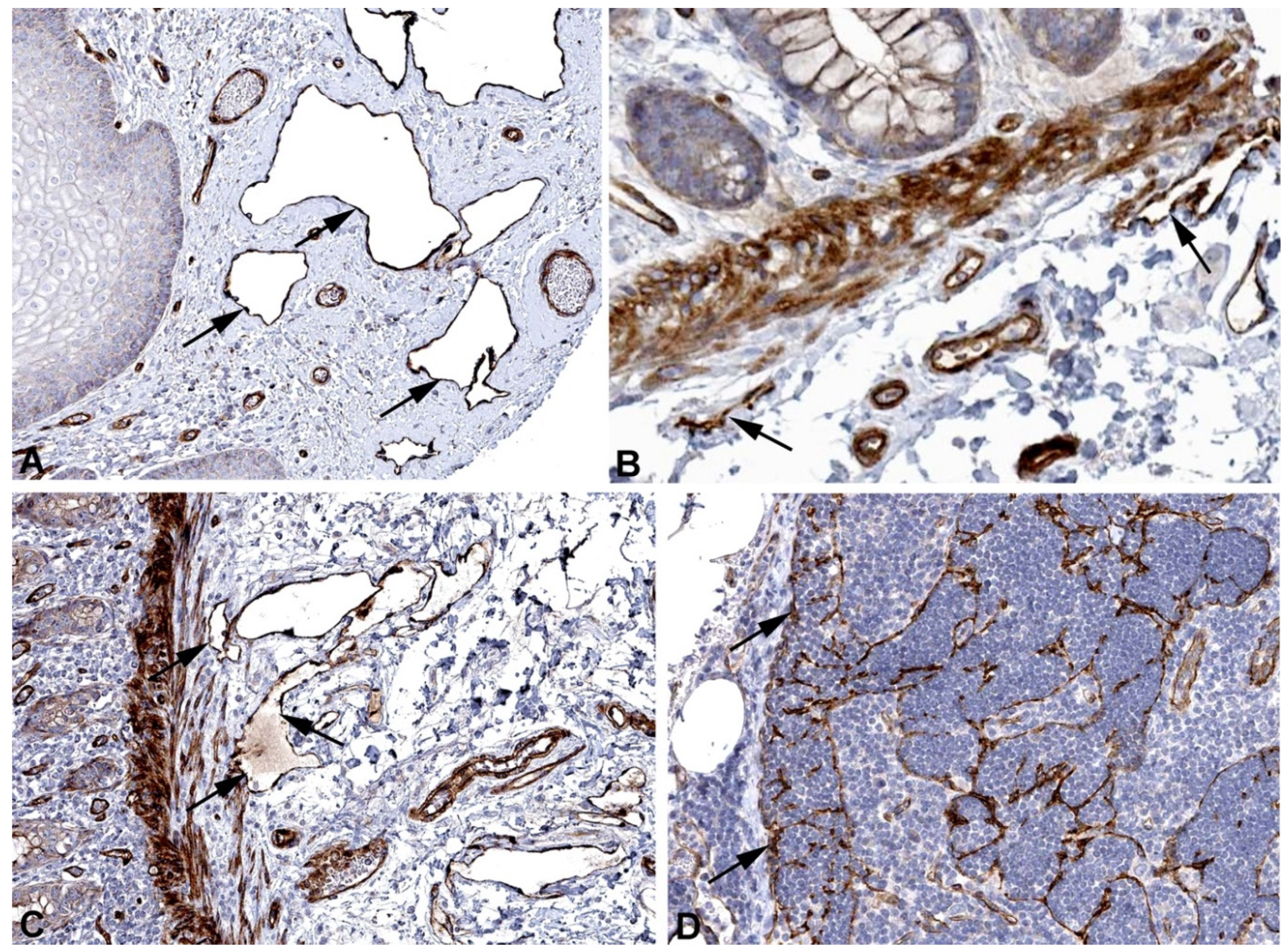
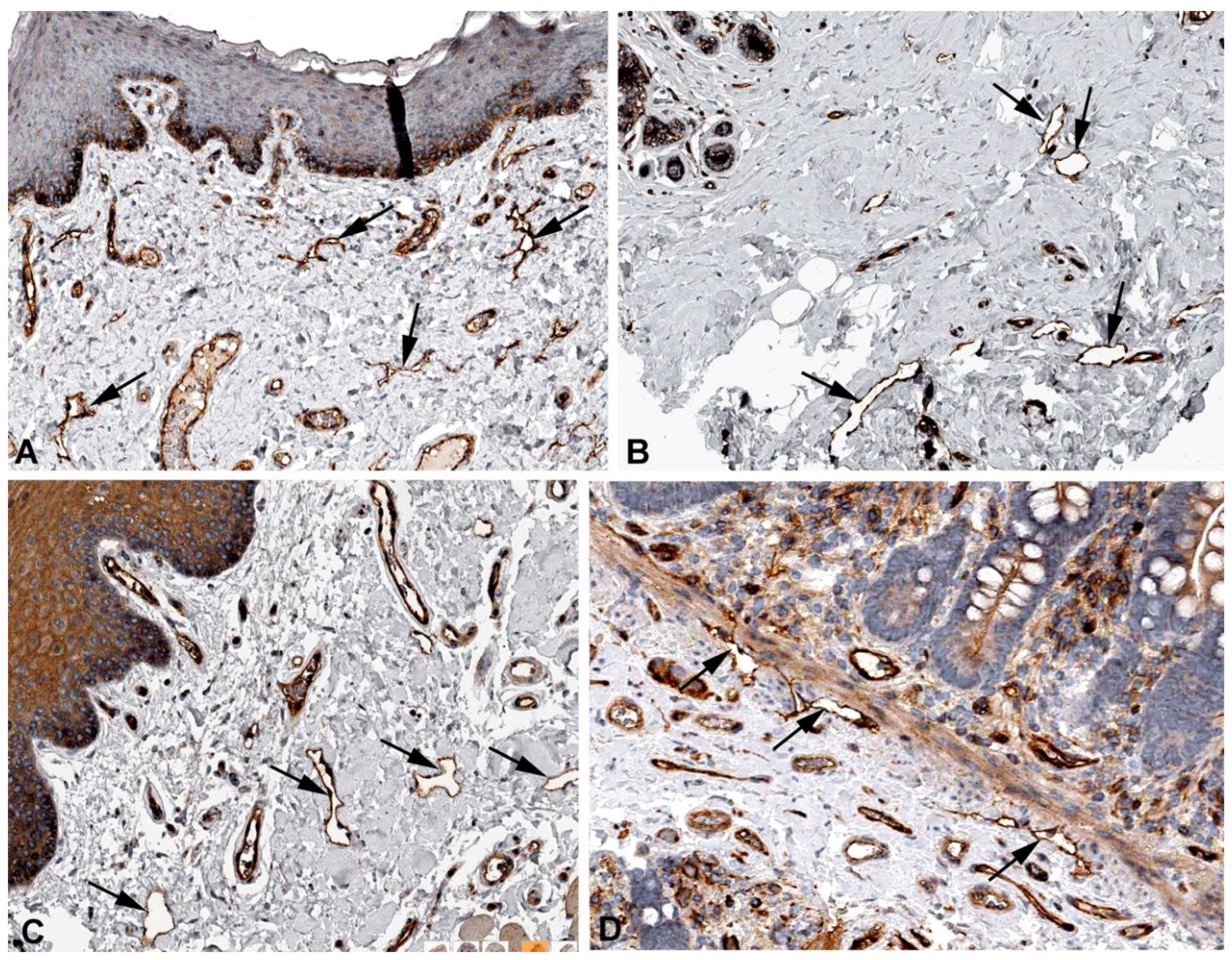
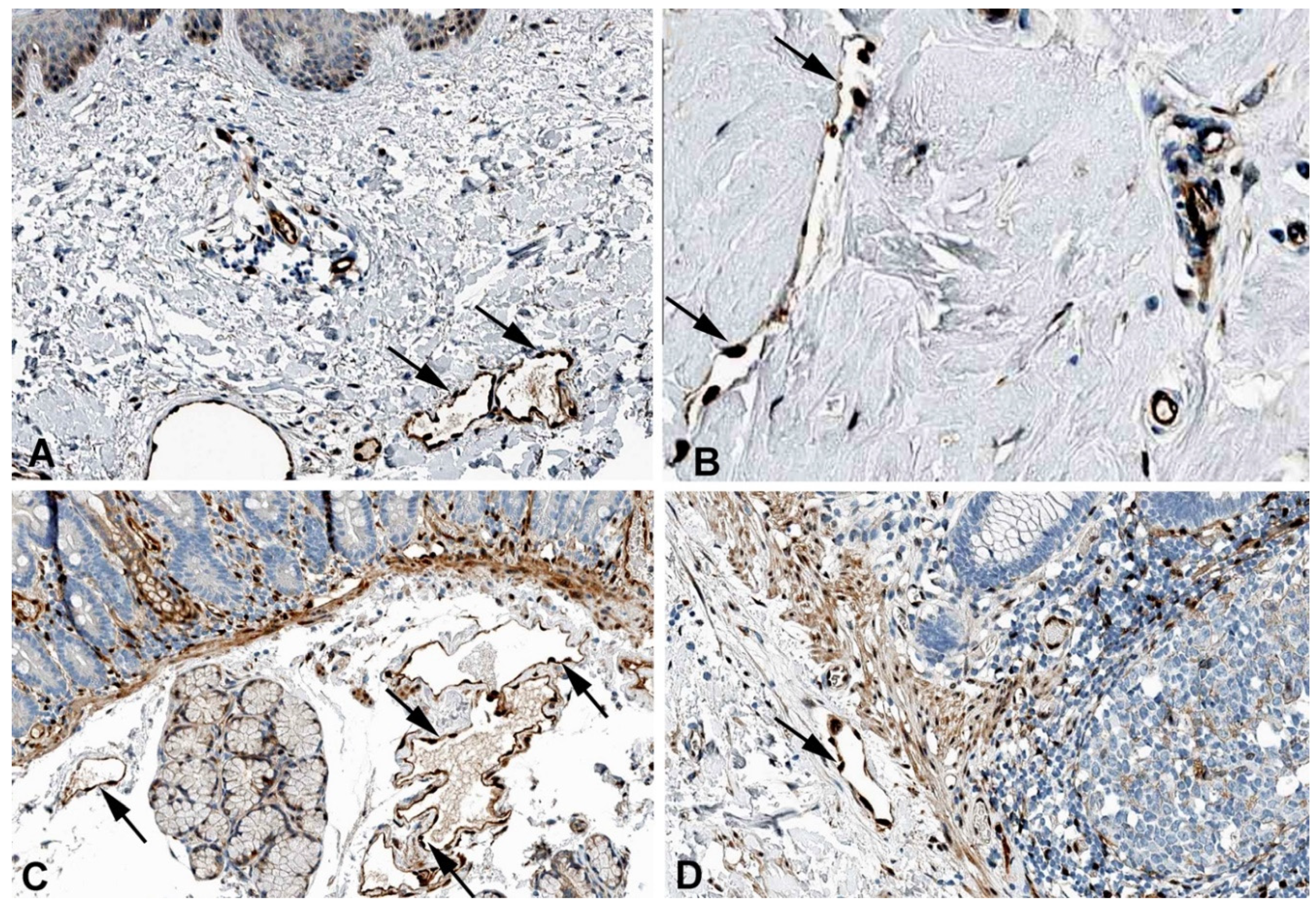
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. RNA Sequencing
4.3. Immunofluorescence (IF)
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest Statement
Abbreviations
References
- Rusznyák, I.; Földi, M.; Szabó, G. Lymphologie. Physiologie und Pathologie der Lymphgefäße und des Lymphkreislaufes; Akadémiai Kiadó, 1969;
- Asellius, G. De lactibus, sive lacteis venis, quarto vasorum mesaraicorum genere, novo invento Gasparis Asellii Cremo. Dissertatio; ex officina Iohannis Maire 1640, Milan 1628;
- Mascagni, P.; Sanctius, C. Vasorum Lymphaticorum Corporis Humani Historia et Ichnographia; Ex typographia Pazzini Carli, 1787;
- Rudbeck, O. Nova exercitatio anatomica, exhibens ductos hepaticos aquosos, et vasa glandularum serosa (1653); Almquist and Wiksells: Uppsala, 1930;
- Witte, M.H.; Jones, K.; Wilting, J.; Dictor, M.; Selg, M.; McHale, N.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Jackson, D.G. Structure Function Relationships in the Lymphatic System and Implications for Cancer Biology. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 159–184. [CrossRef]
- Oliver, G.; Kipnis, J.; Randolph, G.J.; Harvey, N.L. The Lymphatic Vasculature in the 21st Century: Novel Functional Roles in Homeostasis and Disease. Cell 2020, 182, 270–296. [CrossRef]
- Martin-Almedina, S.; Mortimer, P.S.; Ostergaard, P. Development and Physiological Functions of the Lymphatic System: Insights from Human Genetic Studies of Primary Lymphedema. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1809–1871. [CrossRef]
- Wilting, J.; Becker, J. The Lymphatic Vascular System: Much More than Just a Sewer. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 157. [CrossRef]
- Petrova, T.V.; Koh, G.Y. Organ-Specific Lymphatic Vasculature: From Development to Pathophysiology. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 35–49. [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.; Schwoch, S.; Zelent, C.; Sitte, M.; Salinas, G.; Wilting, J. Transcriptome Analysis of Hypoxic Lymphatic Endothelial Cells Indicates Their Potential to Contribute to Extracellular Matrix Rearrangement. Cells 2021, 10, 1008. [CrossRef]
- Podgrabinska, S.; Braun, P.; Velasco, P.; Kloos, B.; Pepper, M.S.; Skobe, M. Molecular Characterization of Lymphatic Endothelial Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2002, 99, 16069–16074. [CrossRef]
- Hasselhof, V.; Sperling, A.; Buttler, K.; Ströbel, P.; Becker, J.; Aung, T.; Felmerer, G.; Wilting, J. Morphological and Molecular Characterization of Human Dermal Lymphatic Collectors. PloS One 2016, 11, e0164964. [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, N.; He, Y.; D’Addio, M.; Tacconi, C.; Detmar, M.; Dieterich, L.C. Single-Cell Mapping Reveals New Markers and Functions of Lymphatic Endothelial Cells in Lymph Nodes. PLOS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000704. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Angel, C.E.; McIntosh, J.D.; Mansell, C.J.; Chen, C.-J.J.; Cebon, J.; Dunbar, P.R. Mapping the Distinctive Populations of Lymphatic Endothelial Cells in Different Zones of Human Lymph Nodes. PloS One 2014, 9, e94781. [CrossRef]
- Wigle, J.T.; Oliver, G. Prox1 Function Is Required for the Development of the Murine Lymphatic System. Cell 1999, 98, 769–778. [CrossRef]
- Harvey, N.L.; Srinivasan, R.S.; Dillard, M.E.; Johnson, N.C.; Witte, M.H.; Boyd, K.; Sleeman, M.W.; Oliver, G. Lymphatic Vascular Defects Promoted by Prox1 Haploinsufficiency Cause Adult-Onset Obesity. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 1072–1081. [CrossRef]
- Wong, B.W.; Wang, X.; Zecchin, A.; Thienpont, B.; Cornelissen, I.; Kalucka, J.; García-Caballero, M.; Missiaen, R.; Huang, H.; Brüning, U.; et al. The Role of Fatty Acid β-Oxidation in Lymphangiogenesis. Nature 2017, 542, 49–54. [CrossRef]
- Wilting, J.; Papoutsi, M.; Christ, B.; Nicolaides, K.H.; von Kaisenberg, C.S.; Borges, J.; Stark, G.B.; Alitalo, K.; Tomarev, S.I.; Niemeyer, C.; et al. The Transcription Factor Prox1 Is a Marker for Lymphatic Endothelial Cells in Normal and Diseased Human Tissues. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 1271–1273. [CrossRef]
- Kaipainen, A.; Korhonen, J.; Mustonen, T.; van Hinsbergh, V.W.; Fang, G.H.; Dumont, D.; Breitman, M.; Alitalo, K. Expression of the Fms-like Tyrosine Kinase 4 Gene Becomes Restricted to Lymphatic Endothelium during Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1995, 92, 3566–3570. [CrossRef]
- Banerji, S.; Ni, J.; Wang, S.X.; Clasper, S.; Su, J.; Tammi, R.; Jones, M.; Jackson, D.G. LYVE-1, a New Homologue of the CD44 Glycoprotein, Is a Lymph-Specific Receptor for Hyaluronan. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 144, 789–801. [CrossRef]
- Breiteneder-Geleff, S.; Soleiman, A.; Kowalski, H.; Horvat, R.; Amann, G.; Kriehuber, E.; Diem, K.; Weninger, W.; Tschachler, E.; Alitalo, K.; et al. Angiosarcomas Express Mixed Endothelial Phenotypes of Blood and Lymphatic Capillaries: Podoplanin as a Specific Marker for Lymphatic Endothelium. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 385–394. [CrossRef]
- Mattonet, K.; Wilting, J.; Jeltsch, M. Genetic Causes of Primary Lymphedema [German: Die Genetischen Ursachen Des Primären Lymphödems]. In; 2015; pp. 210–229.
- Modaghegh, M.H.S.; Tanzadehpanah, H.; Kamyar, M.M.; Manoochehri, H.; Sheykhhasan, M.; Forouzanfar, F.; Mahmoudian, R.A.; Lotfian, E.; Mahaki, H. The Role of Key Biomarkers in Lymphatic Malformation: An Updated Review. J. Gene Med. 2024, 26, e3665. [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, T.; Boon, L.M.; Vikkula, M.; Alitalo, K. Lymphatic Malformations: Genetics, Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Circ. Res. 2021, 129, 136–154. [CrossRef]
- Petkova, M.; Ferby, I.; Mäkinen, T. Lymphatic Malformations: Mechanistic Insights and Evolving Therapeutic Frontiers. J. Clin. Invest. 2024, 134, e172844. [CrossRef]
- Wilting, J.; Felmerer, G.; Becker, J. Control of the Extracellular Matrix by Hypoxic Lymphatic Endothelial Cells: Impact on the Progression of Lymphedema? Dev. Dyn. 2023, 252, 227–238. [CrossRef]
- Thul, P.J.; Lindskog, C. The Human Protein Atlas: A Spatial Map of the Human Proteome. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 2018, 27, 233–244. [CrossRef]
- Casley-Smith, J.R.; Florey, H.W. The Structure of Normal Small Lymphatics. Q. J. Exp. Physiol. Cogn. Med. Sci. 1961, 46, 101–106. [CrossRef]
- Sabesin, S.M.; Frase, S. Electron Microscopic Studies of the Assembly, Intracellular Transport, and Secretion of Chylomicrons by Rat Intestine. J. Lipid Res. 1977, 18, 496–511.
- Zhang, F.; Zarkada, G.; Han, J.; Li, J.; Dubrac, A.; Ola, R.; Genet, G.; Boyé, K.; Michon, P.; Künzel, S.E.; et al. Lacteal Junction Zippering Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity. Science 2018, 361, 599–603. [CrossRef]
- Arif, S.; Richer, M.; Larochelle, S.; Moulin, V.J. Microvesicles Derived from Dermal Myofibroblasts Modify the Integrity of the Blood and Lymphatic Barriers Using Distinct Endocytosis Pathways. J. Extracell. Biol. 2024, 3, e151. [CrossRef]
- Bansal, D.; Miyake, K.; Vogel, S.S.; Groh, S.; Chen, C.-C.; Williamson, R.; McNeil, P.L.; Campbell, K.P. Defective Membrane Repair in Dysferlin-Deficient Muscular Dystrophy. Nature 2003, 423, 168–172. [CrossRef]
- McMahon, A.P.; Giebelhaus, D.H.; Champion, J.E.; Bailes, J.A.; Lacey, S.; Carritt, B.; Henchman, S.K.; Moon, R.T. cDNA Cloning, Sequencing and Chromosome Mapping of a Non-Erythroid Spectrin, Human Alpha-Fodrin. Differ. Res. Biol. Divers. 1987, 34, 68–78. [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.G.; Scarpa, A.; Eddy, R.L.; Byers, M.G.; Harris, A.S.; Morrow, J.S.; Watkins, P.; Shows, T.B.; Forget, B.G. Cloning of a Portion of the Chromosomal Gene and cDNA for Human Beta-Fodrin, the Nonerythroid Form of Beta-Spectrin. Genomics 1993, 17, 287–293. [CrossRef]
- Liem, R.K.H. Cytoskeletal Integrators: The Spectrin Superfamily. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a018259. [CrossRef]
- Leak, L.V.; Liotta, L.A.; Krutzsch, H.; Jones, M.; Fusaro, V.A.; Ross, S.J.; Zhao, Y.; Petricoin, E.F. Proteomic Analysis of Lymph. Proteomics 2004, 4, 753–765. [CrossRef]
- Posner, M.G. Multimerin-1 and Cancer: A Review. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20211248. [CrossRef]
- Hayward, C.P.; Hassell, J.A.; Denomme, G.A.; Rachubinski, R.A.; Brown, C.; Kelton, J.G. The cDNA Sequence of Human Endothelial Cell Multimerin. A Unique Protein with RGDS, Coiled-Coil, and Epidermal Growth Factor-like Domains and a Carboxyl Terminus Similar to the Globular Domain of Complement C1q and Collagens Type VIII and X. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 18246–18251. [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.C.; Kato, S. Histochemical Analysis of Lymphatic Endothelial Cells in Lymphostasis. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2001, 55, 70–80. [CrossRef]
- Umekage, T.; Kato, K. A Mouse Brain cDNA Encodes a Novel Protein with the Protein Kinase C Phosphorylation Site Domain Common to MARCKS. FEBS Lett. 1991, 286, 147–151. [CrossRef]
- Stumpo, D.J.; Eddy, R.L.; Haley, L.L.; Sait, S.; Shows, T.B.; Lai, W.S.; Young, W.S.; Speer, M.C.; Dehejia, A.; Polymeropoulos, M.; et al. Promoter Sequence, Expression, and Fine Chromosomal Mapping of the Human Gene (MLP) Encoding the MARCKS-like Protein: Identification of Neighboring and Linked Polymorphic Loci for MLP and MACS and Use in the Evaluation of Human Neural Tube Defects. Genomics 1998, 49, 253–264. [CrossRef]
- Björkblom, B.; Padzik, A.; Mohammad, H.; Westerlund, N.; Komulainen, E.; Hollos, P.; Parviainen, L.; Papageorgiou, A.C.; Iljin, K.; Kallioniemi, O.; et al. C-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Phosphorylation of MARCKSL1 Determines Actin Stability and Migration in Neurons and in Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 3513–3526. [CrossRef]
- Jonsdottir, K.; Zhang, H.; Jhagroe, D.; Skaland, I.; Slewa, A.; Björkblom, B.; Coffey, E.T.; Gudlaugsson, E.; Smaaland, R.; Janssen, E.A.M.; et al. The Prognostic Value of MARCKS-like 1 in Lymph Node-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 135, 381–390. [CrossRef]
- Maguchi, M.; Nishida, W.; Kohara, K.; Kuwano, A.; Kondo, I.; Hiwada, K. Molecular Cloning and Gene Mapping of Human Basic and Acidic Calponins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 217, 238–244. [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Jin, J.-P. Calponin Isoforms CNN1, CNN2 and CNN3: Regulators for Actin Cytoskeleton Functions in Smooth Muscle and Non-Muscle Cells. Gene 2016, 585, 143–153. [CrossRef]
- Ciuba, K.; Hawkes, W.; Tojkander, S.; Kogan, K.; Engel, U.; Iskratsch, T.; Lappalainen, P. Calponin-3 Is Critical for Coordinated Contractility of Actin Stress Fibers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17670. [CrossRef]
- Maddala, R.; Mongan, M.; Xia, Y.; Rao, P.V. Calponin-3 Deficiency Augments Contractile Activity, Plasticity, Fibrogenic Response and Yap/Taz Transcriptional Activation in Lens Epithelial Cells and Explants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1295. [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kim, J.; Ahn, J.H.; Hong, Y.-K.; Mäkinen, T.; Lim, D.-S.; Koh, G.Y. YAP and TAZ Negatively Regulate Prox1 During Developmental and Pathologic Lymphangiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 225–242. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Jiang, H.; Zou, Y.; Ren, J.; Li, Z.; He, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X.; Mou, D.; Cai, Y. The YAP Signaling Pathway Promotes the Progression of Lymphatic Malformations through the Activation of Lymphatic Endothelial Cells. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 110–117.
- Lee, S.; Finn, L.; Sze, R.W.; Perkins, J.A.; Sie, K.C. Gorham Stout Syndrome (Disappearing Bone Disease): Two Additional Case Reports and a Review of the Literature. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2003, 129, 1340–1343. [CrossRef]
- Leite, I.; Hernández-Martín, A.; Colmenero, I.; López-Gutiérrez, J.C.; Torrelo, A. Invasive Lymphatic Malformation (Gorham-Stout) of the Pelvis with Prominent Skin Involvement. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2013, 30, 374–378. [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarpour, N.; Baselga, E.; Boon, L.M.; Diociaiuti, A.; Dompmartin, A.; Dvorakova, V.; El Hachem, M.; Gasparella, P.; Haxhija, E.; Kyrklund, K.; et al. The VASCERN-VASCA Working Group Diagnostic and Management Pathways for Lymphatic Malformations. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 65, 104637. [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Fu, H.; Zhou, X.; Duan, Y.; Yin, N.; Huang, J.; Liu, X. ANKRD37 Inhibits Trophoblast Migration and Invasion by Regulating the NF-κB Pathway in Preeclampsia. J. Gene Med. 2022, 24, e3416. [CrossRef]
- Benita, Y.; Kikuchi, H.; Smith, A.D.; Zhang, M.Q.; Chung, D.C.; Xavier, R.J. An Integrative Genomics Approach Identifies Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1 (HIF-1)-Target Genes That Form the Core Response to Hypoxia. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 4587–4602. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Kakinuma, N.; Wang, Y.; Kiyama, R. Kank Proteins: A New Family of Ankyrin-Repeat Domain-Containing Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1780, 128–133. [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.S.; Seiwert, A.; Szeto, I.Y.Y.; Fässler, R. Tissue Distribution and Subcellular Localization of the Family of Kidney Ankyrin Repeat Domain (KANK) Proteins. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 398, 112391. [CrossRef]
- Janeway, C.; Travers, P.; Walport, M.; Shlomchik, M. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease; Garland Pub. New York, 2001; Vol. 2;.
- Okada, N.; Harada, R.; Fujita, T.; Okada, H. A Novel Membrane Glycoprotein Capable of Inhibiting Membrane Attack by Homologous Complement. Int. Immunol. 1989, 1, 205–208. [CrossRef]
- Nevo, Y.; Ben-Zeev, B.; Tabib, A.; Straussberg, R.; Anikster, Y.; Shorer, Z.; Fattal-Valevski, A.; Ta-Shma, A.; Aharoni, S.; Rabie, M.; et al. CD59 Deficiency Is Associated with Chronic Hemolysis and Childhood Relapsing Immune-Mediated Polyneuropathy. Blood 2013, 121, 129–135. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wu, Y.; Fu, X.; Liang, S.; Peng, M.; Guo, J.; Liu, M. Revisiting the Relationship between Complement and Ulcerative Colitis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2023, 98, e13329. [CrossRef]
- Dejana, E. The Role of Wnt Signaling in Physiological and Pathological Angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 943–952. [CrossRef]
- Lutze, G.; Haarmann, A.; Demanou Toukam, J.A.; Buttler, K.; Wilting, J.; Becker, J. Non-Canonical WNT-Signaling Controls Differentiation of Lymphatics and Extension Lymphangiogenesis via RAC and JNK Signaling. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4739. [CrossRef]
- Kurooka, H.; Kato, K.; Minoguchi, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Ikeda, J.; Habu, S.; Osawa, N.; Buchberg, A.M.; Moriwaki, K.; Shisa, H.; et al. Cloning and Characterization of the Nucleoredoxin Gene That Encodes a Novel Nuclear Protein Related to Thioredoxin. Genomics 1997, 39, 331–339. [CrossRef]
- Person, A.D.; Beiraghi, S.; Sieben, C.M.; Hermanson, S.; Neumann, A.N.; Robu, M.E.; Schleiffarth, J.R.; Billington, C.J.; van Bokhoven, H.; Hoogeboom, J.M.; et al. WNT5A Mutations in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Robinow Syndrome. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 327–337. [CrossRef]
- White, J.J.; Mazzeu, J.F.; Coban-Akdemir, Z.; Bayram, Y.; Bahrambeigi, V.; Hoischen, A.; van Bon, B.W.M.; Gezdirici, A.; Gulec, E.Y.; Ramond, F.; et al. WNT Signaling Perturbations Underlie the Genetic Heterogeneity of Robinow Syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 27–43. [CrossRef]
- von Recklinghausen, F. Die Lymphgefässe und ihre Beziehung zum Bindegewebe; A. Hirschwald, 1862;
- Trzewik, J.; Mallipattu, S.K.; Artmann, G.M.; Delano, F.A.; Schmid-Schonbein, G.W. Evidence for a Second Valve System in Lymphatics: Endothelial Microvalves. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 1711–1717. [CrossRef]
- Baluk, P.; Fuxe, J.; Hashizume, H.; Romano, T.; Lashnits, E.; Butz, S.; Vestweber, D.; Corada, M.; Molendini, C.; Dejana, E. Functionally Specialized Junctions between Endothelial Cells of Lymphatic Vessels. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2349–2362.

| gene_id | gene_name | chromos. | start | end | width | strand | gene_biotype | HDLEC-5 | HDLEC-6 | HDLEC-7 | Hypox-5 | Hypox-6 | Hypox-7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSG00000186352 | ANKRD37 | 4 | 1.85E+08 | 1.85E+08 | 4608 | + | protein_cod. | 92.68 | 117.12 | 124.35 | 312.56 | 549.57 | 650.6 |
| ENSG00000105974 | CAV1 | 7 | 1.17E+08 | 1.17E+08 | 36184 | + | protein_cod. | 28254.02 | 22816.55 | 40041.39 | 41886.36 | 29070.25 | 44229.96 |
| ENSG00000105971 | CAV2 | 7 | 1.16E+08 | 1.17E+08 | 221162 | + | protein_cod. | 5923.02 | 6362.42 | 8338.77 | 8258.02 | 7425.45 | 10627.94 |
| ENSG00000085063 | CD59 | 11 | 33703010 | 33736491 | 33482 | - | protein_cod. | 25996.8 | 30542.27 | 33419.64 | 25877.99 | 36425.42 | 34222.24 |
| ENSG00000117519 | CNN3 | 4 | 94896949 | 94927223 | 30275 | - | protein_cod. | 16690.62 | 24868.18 | 11453.55 | 14356.97 | 20710.53 | 8937.79 |
| ENSG00000135636 | DYSF | 2 | 71453722 | 71686768 | 233047 | + | protein_cod. | 2655.52 | 1698.22 | 4384.61 | 3353.58 | 2204.57 | 5193.08 |
| ENSG00000186994 | KANK3 | 19 | 8322584 | 8343262 | 20679 | - | protein_cod. | 2257.23 | 4007.72 | 2948.58 | 3945.85 | 4201.93 | 5177.89 |
| ENSG00000175130 | MARCKSL1 | 1 | 32333839 | 32336233 | 2395 | - | protein_cod. | 8786.11 | 9698.24 | 8003.97 | 8408.33 | 7819.15 | 4811.13 |
| ENSG00000138722 | MMRN1 | 4 | 89879532 | 89954629 | 75098 | + | protein_cod. | 19949464 | 204322.7 | 16868.85 | 263839.6 | 303443.4 | 38908.39 |
| ENSG00000138119 | MYOF | 10 | 93306429 | 93482334 | 175906 | - | protein_cod. | 12506.28 | 4986.79 | 5959.34 | 11865.43 | 2877.56 | 11681.51 |
| ENSG00000167693 | NXN | 17 | 799310 | 979776 | 180467 | - | protein_cod. | 5646.52 | 7277.79 | 2263.45 | 4812.87 | 5743.42 | 2401.48 |
| ENSG00000115155 | OTOF | 2 | 26457203 | 26558698 | 101496 | - | protein_cod. | 1187.21 | 1087.97 | 463.93 | 498.71 | 109.01 | 146 |
| ENSG00000197694 | SPTAN1 | 9 | 1.29E+08 | 1.29E+08 | 81105 | + | protein_cod. | 10798.23 | 8180.84 | 6609.8 | 8411.32 | 9523.71 | 8408.68 |
| ENSG00000115306 | SPTBN1 | 2 | 54456317 | 54671446 | 215130 | + | protein_cod. | 23119.16 | 28282.09 | 11418.88 | 25384.26 | 39159.74 | 14476.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





