Submitted:
19 September 2024
Posted:
20 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
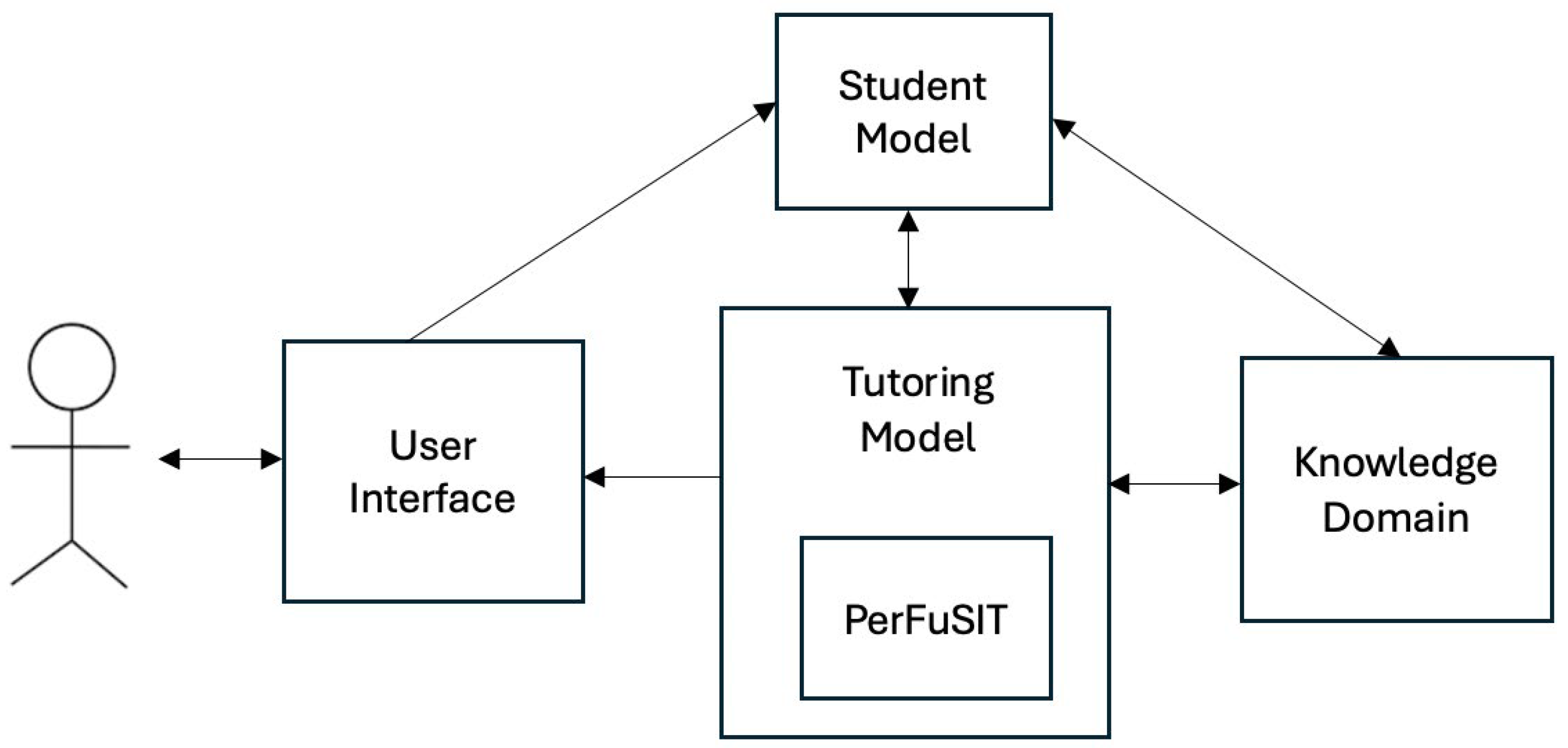
3. PerFuSIT
3.1. Available Tytoring Strategies
- A1: Review the chapter
- A2: Move to the next chapter
- A3: Access supplemental resources
- A4: Practice additional exercises
- A5: Take a break
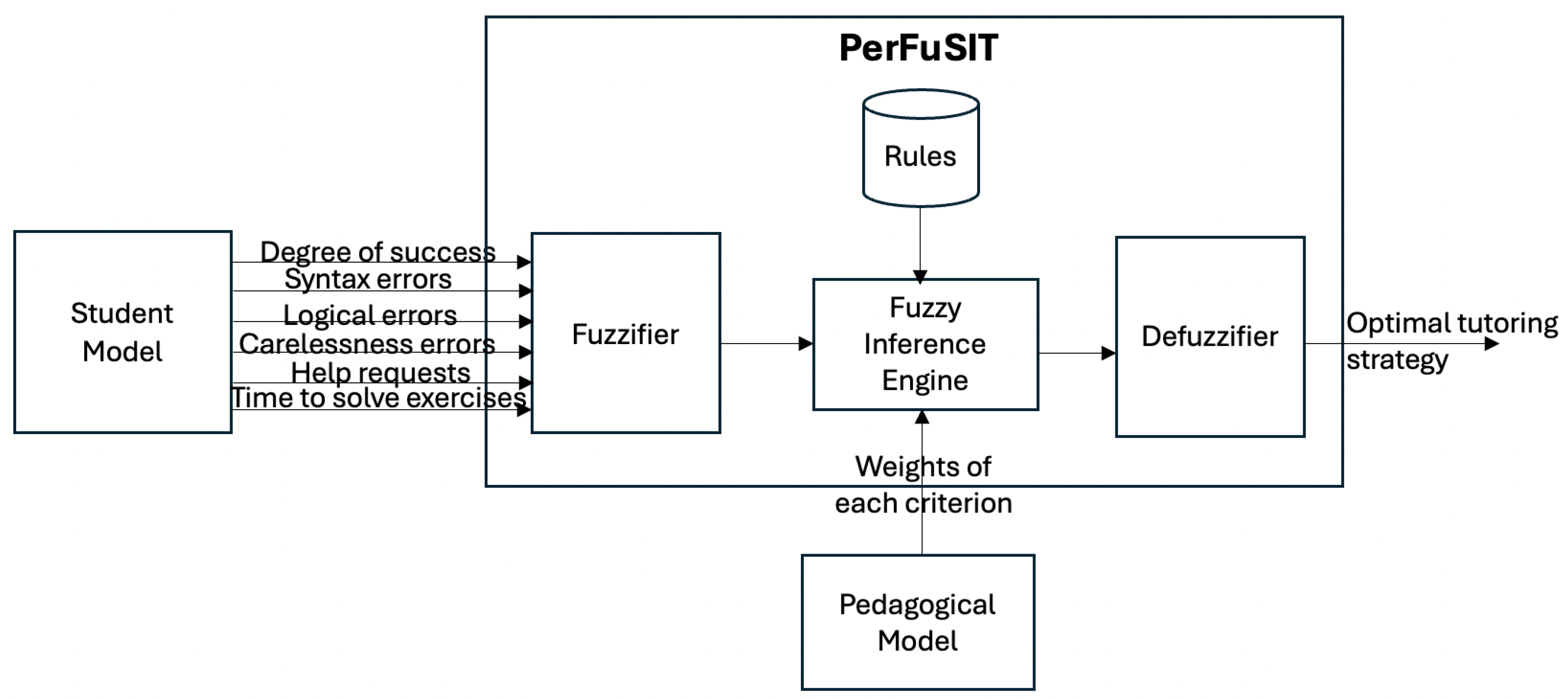
3.2. Input Data and Weights
- a)
- the learner’s degree of success (it is calculated with a maximum value of 100),
- b)
- the learner’s syntax errors (it is calculated as percentage of the overall errors),
- c)
- the learner’s logical errors (it is calculated as percentage of the overall errors),
- d)
- the learner’s errors due to carelessness (it is calculated as percentage of the overall errors),
- e)
- the frequency of help requests (it is calculated as percentage of the total available aids),
- f)
- the mean time the learner needs to solve exercises (it is calculated as percentage of the total available time for solving an exercise).
- Very low (VL): 0.1
- Low (L): 0.3
- Average (A): 0.5
- Μuch (Μ): 0.8
- Very Much (VM): 1
3.3. The Fuzzy Rules
- If ‘degree of success’ is ‘M’ then A1 is ‘A’.
- If ‘degree of success’ is ‘H’ then A3 is ‘VL’.
- If ‘syntax errors’ is ‘L’ then A2 is ‘M’.
- If ‘logical errors’ is ‘VH’ then A5 is ‘M’.
- If ‘carelessness errors’ is ‘VH’ then A5 is ‘VM’.
- If ‘help requests’ is ‘M’ then A1 is ‘L’.
- If ‘time to solve exercises’ is ‘M’ then A3 is ‘A’.
3.4. The Procedure of PerFuSIT Operation
- Step 1: Definitions of the criteria weights for each tutoring strategy
- Step 2: Get the values of the criteria from the log files of the system
- Step 3: Input data fuzzification
- Step 4: Application of the fuzzy rules
- Step 5: Output calculation for each rule
- Step 6: Weights application to the outputs
- Step 7: Results aggregation
- Step 8: Defuzzification of the aggregated result
- Step 9: Rank the results
- Step 10: Selection of the appropriate tutoring strategy
4. Use Case Scenarios
- 1)
- If ‘degree of success’ is ‘M’ then A1 is ‘A’.
- 2)
- If ‘degree of success’ is ‘M’ then A2 is ‘L’.
- 3)
- If ‘degree of success’ is ‘M’ then A3 is ‘A’.
- 4)
- If ‘degree of success’ is ‘M’ then A4 is ‘A’.
- 5)
- If ‘degree of success’ is ‘M’ then A5 is ‘A’.
- 6)
- If ‘degree of success’ is ‘H’ then A1 is ‘L’.
- 7)
- If ‘degree of success’ is ‘H’ then A2 is ‘M’.
- 8)
- If ‘degree of success’ is ‘H’ then A3 is ‘VL’.
- 9)
- If ‘degree of success’ is ‘H’ then A4 is ‘VL’.
- 10)
- If ‘degree of success’ is ‘H’ then A5 is ‘VL’.
- 11)
- If ‘syntax errors’ is ‘VL’ then A1 is ‘VL’.
- 12)
- If ‘syntax errors’ is ‘VL’ then A2 is ‘VM’.
- 13)
- If ‘syntax errors’ is ‘VL’ then A3 is ‘VL’.
- 14)
- If ‘syntax errors’ is ‘VL’ then A4 is ‘VL’.
- 15)
- If ‘syntax errors’ is ‘VL’ then A5 is ‘VL’.
- 16)
- If ‘syntax errors’ is ‘L’ then A1 is ‘VL’.
- 17)
- If ‘syntax errors’ is ‘L’ then A2 is ‘M’.
- 18)
- If ‘syntax errors’ is ‘L’ then A3 is ‘VL’.
- 19)
- If ‘syntax errors’ is ‘L’ then A4 is ‘VL’.
- 20)
- If ‘syntax errors’ is ‘L’ then A5 is ‘VL’.
- 21)
- If ‘logical errors’ is ‘M’ then A1 is ‘A’.
- 22)
- If ‘logical errors’ is ‘M’ then A2 is ‘A’.
- 23)
- If ‘logical errors’ is ‘M’ then A3 is ‘A’.
- 24)
- If ‘logical errors’ is ‘M’ then A4 is ‘M’.
- 25)
- If ‘logical errors’ is ‘M’ then A5 is ‘A’.
- 26)
- If ‘logical errors’ is ‘H’ then A1 is ‘M’.
- 27)
- If ‘logical errors’ is ‘H’ then A2 is ‘VL’.
- 28)
- If ‘logical errors’ is ‘H’ then A3 is ‘M’.
- 29)
- If ‘logical errors’ is ‘H’ then A4 is ‘VM’.
- 30)
- If ‘logical errors’ is ‘H’ then A5 is ‘M’.
- 31)
- If ‘carelessness errors’ is ‘VL’ then A1 is ‘VL’.
- 32)
- If ‘carelessness errors’ is ‘VL’ then A2 is ‘VL’.
- 33)
- If ‘carelessness errors’ is ‘VL’ then A3 is ‘VL’.
- 34)
- If ‘carelessness errors’ is ‘VL’ then A4 is ‘VL’.
- 35)
- If ‘carelessness errors’ is ‘VL’ then A5 is ‘VL’.
- 36)
- If ‘help requests’ is ‘L’ then A1 is ‘VL’.
- 37)
- If ‘help requests’ is ‘L’ then A2 is ‘M’.
- 38)
- If ‘help requests’ is ‘L’ then A3 is ‘L’.
- 39)
- If ‘help requests’ is ‘L’ then A4 is ‘L’.
- 40)
- If ‘help requests’ is ‘L’ then A5 is ‘VL’.
- 41)
- If ‘help requests’ is ‘M’ then A1 is ‘L’.
- 42)
- If ‘help requests’ is ‘M’ then A2 is ‘A’.
- 43)
- If ‘help requests’ is ‘M’ then A3 is ‘A’.
- 44)
- If ‘help requests’ is ‘M’ then A4 is ‘A’.
- 45)
- If ‘help requests’ is ‘M’ then A5 is ‘A’.
- 46)
- If ‘time to solve exercises’ is ‘M’ then A1 is ‘L’.
- 47)
- If ‘time to solve exercises’ is ‘M’ then A2 is ‘A’.
- 48)
- If ‘time to solve exercises’ is ‘M’ then A3 is ‘A’.
- 49)
- If ‘time to solve exercises’ is ‘M’ then A4 is ‘A’.
- 50)
- If ‘time to solve exercises’ is ‘M’ then A5 is ‘L’.
- 51)
- If ‘time to solve exercises’ is ‘H’ then A1 is ‘A’.
- 52)
- If ‘time to solve exercises’ is ‘H’ then A2 is ‘L’.
- 53)
- If ‘time to solve exercises’ is ‘H’ then A3 is ‘M’.
- 54)
- If ‘time to solve exercises’ is ‘H’ then A4 is ‘M’.
- 55)
- If ‘time to solve exercises’ is ‘H’ then A5 is ‘A’.
5. Evaluation
5.1. The Method
5.2. The Test-Bed
5.3. The Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goenaga, S.; Navarro, L.; Quintero M, C.G.; Pardo, M. Imitating human emotions with a nao robot as interviewer playing the role of vocational tutor. Electronics 2020, 9(6), 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minn, S. AI-assisted knowledge assessment techniques for adaptive learning environments. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence 2022, 3, 100050. [Google Scholar]
- Alrakhawi, H.A.; Jamiat, N.U.R.U.L.L.I.Z.A.M.; Abu-Naser, S.S. Intelligent tutoring systems in education: A systematic review of usage, tools, effects and evaluation. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 2023, 101(4), 1205–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Alrakhawi, H.A.; Jamiat, N.; Umar, I.N.; Abu-Naser, S.S. Improvement of Students Achievement by Using Intelligent Tutoring Systems-A Bibliometric Analysis and Reviews. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 2023, 101(11). [Google Scholar]
- Roessingh, J.J.; Poppinga, G.; van Oijen, J.; Toubman, A. Application of artificial intelligence to adaptive instruction-combining the concepts. In Adaptive Instructional Systems: First International Conference, AIS 2019, Held as Part of the 21st HCI International Conference, HCII 2019, Orlando, FL, USA, 26–31 July 2019, Proceedings 21; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 542–556. [Google Scholar]
- Sottilare, R. Agent-based methods in support of adaptive instructional decisions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–21 July 2020; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 164–175. [Google Scholar]
- AlShaikh, F.; Hewahi, N. AI and machine learning techniques in the development of Intelligent Tutoring System: A review. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2021 International Conference on innovation and Intelligence for informatics, computing, and technologies (3ICT), Zallaq, Bahrain, 29–30 September 2021; pp. 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Shan Wang, Fang Wang, Zhen Zhu, Jingxuan Wang, Tam Tran, Zhao Du, Artificial intelligence in education: A systematic literature review. Expert Systems with Applications 2024, 252 Pt A, 124167, ISSN 0957-4174. [CrossRef]
- Vuković, I.; Kuk, K.; Čisar, P.; Banđur, M.; Banđur, Đ.; Milić, N.; Popović, B. Multi-agent system observer: Intelligent support for engaged e-learning. Electronics 2021, 10(12), 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshyar, D.; Binti Ahmad, R.; Wang, M.; Yousefi, M.; Fathi, M.; Lim, H. Development and evaluation of a game-based bayesian intelligent tutoring system for teaching programming. Journal of Educational Computing Research 2018, 56(6), 775–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.; García-Peñalvo, F.J. Intelligent tutoring systems approach to introductory programming courses. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality, Salamanca, Spain, 21–23 October 2020; pp. 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Chrysafiadi, K.; Virvou, M.; Tsihrintzis, G.A. A fuzzy-based evaluation of E-learning acceptance and effectiveness by computer science students in Greece in the period of COVID-19. Electronics 2023, 12(2), 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Cota, C.; Molina, A.I.; Redondo, M.A.; Lacave, C. Individual differences in computer programming: A systematic review. Behaviour & Information Technology 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lacave, C.; Molina, A.I. The Impact of COVID-19 in Collaborative Programming. Understanding the Needs of Undergraduate Computer Science Students. Electronics 2021, 10, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Schez, J.J.; Glez-Morcillo, C.; Albusac, J.; Vallejo, D. An intelligent tutoring system for supporting active learning: A case study on predictive parsing learning. Information Sciences 2021, 544, 446–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesin, B.; Mangaroska, K.; Akhuseyinoglu, K.; Giannakos, M. Adaptive assessment and content recommendation in online programming courses: On the use of elo-rating. ACM Transactions on Computing Education (TOCE) 2022, 22(3), 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Petegem, C.; Dawyndt, P.; Mesuere, B. Dodona: Learn to code with a virtual co-teacher that supports active learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education V. 2, Turku, Finland, 7–12 June 2023; p. 633. [Google Scholar]
- Day, M.; Penumala, M.R.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, J. Annete: An intelligent tutoring companion embedded into the eclipse IDE. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE First International Conference on Cognitive Machine Intelligence (CogMI), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 12–14 December 2019; pp. 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Brusilovsky, P.; Guerra, J.; Koedinger, K.; Schunn, C. Supporting skill integration in an intelligent tutoring system for code tracing. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning 2023, 39(2), 477–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkot, M.A. Embedding adaptation levels within intelligent tutoring systems for developing programming skills and improving learning efficiency. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2019, 10(12). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, R.E.; de Oliveira Silva, F. Intelligent Tutoring System for Computer Science Education and the Use of Artificial Intelligence: A Literature Review. CSEDU 2022, 1, 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Crow, T.; Luxton-Reilly, A.; Wuensche, B. Intelligent tutoring systems for programming education: A systematic review. In Proceedings of the 20th Australasian Computing Education Conference, Brisbane, Australia, 30 January 2018–2 February 2018; pp. 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros, R.P.; Ramalho, G.L.; Falcão, T.P. A systematic literature review on teaching and learning introductory programming in higher education. IEEE Transactions on Education 2019, 62(2), 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacave, C.; Molina, A.I.; Cruz-Lemus, J.A. Learning Analytics to identify dropout factors of Computer Science studies through Bayesian networks. Behaviour & Information Technology 2018, 37(10–11), 993–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Dirzyte, A.; Perminas, A.; Kaminskis, L.; Žebrauskas, G.; Sederevičiūtė–Pačiauskienė, Ž.; Šliogerienė, J.;... & Gajdosikiene, I. Factors contributing to dropping out of adults’ programming e-learning. Heliyon 2023, 9(12).
- Yulianto, B.; Prabowo, H.; Kosala, R. Comparing the effectiveness of digital contents for improving learning outcomes in computer programming for autodidact students. Journal of e-Learning and Knowledge Society 2016, 12(1). [Google Scholar]
- Zinovieva, I.S.; Artemchuk, V.O.; Iatsyshyn, A.V.; Popov, O.O.; Kovach, V.O.; Iatsyshyn, A.V.;... & Radchenko, O.V. The use of online coding platforms as additional distance tools in programming education. Journal of physics: Conference Series 2021, 1840(1), 012029.
- Desmarais, M.C.; Baker, R.S.D. A review of recent advances in learner and skill modeling in intelligent learning environments. User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction 2012, 22, 9–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, H.T.; Trung, N.Q.; Duy, B.T. Responsive student model in an intelligent tutoring system and its evaluation. Education and information technologies 2021, 26(4), 4969–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Noriega, A.; Juárez-Ramírez, R.; Jiménez, S.; Martínez-Ramírez, Y. Knowledge representation in intelligent tutoring system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics 2016; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Le, N.T.; Pinkwart, N. Adding weights to constraints in intelligent tutoring systems: Does it improve the error diagnosis? In Towards Ubiquitous Learning: 6th European Conference of Technology Enhanced Learning, EC-TEL 2011, Palermo, Italy, 20–23 September 2011; Proceedings 6; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 233–247. [Google Scholar]
- McCall, D. Novice Programmer Errors-Analysis and Diagnostics; University of Kent: Kent, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jamaludin, N.H.; Romli, R. Analysis of the Effectiveness of Feedback Provision in Intelligent Tutoring Systems. In International Conference on Computing and Informatics; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 168–179. [Google Scholar]
- Keuning, H.; Jeuring, J.; Heeren, B. A systematic literature review of automated feedback generation for programming exercises. ACM Transactions on Computing Education (TOCE) 2018, 19(1), 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy Sets. Information and Control 1965, 8(3), 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysafiadi, K. The Role of Fuzzy Logic in Artificial Intelligence and Smart Applications. In Fuzzy Logic-Based Software Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- K. Chrysafiadi, S. K. Chrysafiadi, S. Papadimitriou, M. Virvou, Cognitive-based adaptive scenarios in educational games using fuzzy reasoning. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 109111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.X.; Gong, H.P.; Liu, H.C.; Mou, X. Knowledge representation and reasoning using fuzzy Petri nets: A literature review and bibliometric analysis. Artificial Intelligence Review 2023, 56(7), 6241–6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaci, A. Intelligent tutoring system model based on fuzzy logic and constraint-based student model. Neural Computing and Applications 2019, 31(8), 3619–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysafiadi, K.; Virvou, M. Evaluating the learning outcomes of a fuzzy-based Intelligent Tutoring System. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), Washington, DC, USA, 1–3 November 2021; pp. 1392–1397. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, T.-C.; Lee, M.-C.; Su, C.-Y. Designing and implementing a personalized remedial learning system for enhancing the programming learning. Journal of Educational Technology & Society 2013, 16(4), 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter, J.W.; Abdelshiheed, M.; Barnes, T.; Chi, M. Leveraging fuzzy logic towards more explainable reinforcement learning-induced pedagogical policies on intelligent tutoring systems. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ), Incheon, Republic of Korea, 13–17 August 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lasfeto, D.B.; Ulfa, S. Modeling of online learning strategies based on fuzzy expert systems and self-directed learning readiness: The effect on learning outcomes. Journal of Educational Computing Research 2023, 60(8), 2081–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazid, M.A.A.F.M.; Sahabudin, N.A.; Raffei, A.F.M.; Remli, M.A. C Programming Skill Levels Determination Using Fuzzy Logic. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2021 International Conference on Software Engineering & Computer Systems and 4th International Conference on Computational Science and Information Management (ICSECS-ICOCSIM), Pekan, Malaysia, 24–26 August 2021; pp. 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Hurtado, C.; Licea, G.; García-Valdez, M.; Quezada, A.; Castañón-Puga, M. Teaching Computer Programming as Well-Defined Domain for Beginners with Protoboard. In Trends and Innovations in Information Systems and Technologies: Volume 2 8; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 262–271. [Google Scholar]
- Toukiloglou, P.; Xinogalos, S. NanoDoc: Designing an adaptive serious game for programming with working examples support. In European Conference on Games Based Learning, September 2022; Volume 16, No. 1, pp. 628–636.
- Toukiloglou, P.; Xinogalos, S. NanoDoc: Designing an adaptive serious game for programming with working examples support. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Games Based Learning, Lisbon, Portugal, 6–7 October 2022; No. 1; Volume 16, pp. 628–636. [Google Scholar]
- Vahldick, A.; Mendes, A.J.; Marcelino, M.J. Dynamic difficulty adjustment through a learning analytics model in a casual serious game for computer programming learning. EAI Endorsed Transactions on Serious Games 2017, 4(13). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, F.; Redondo, M.A.; Ortega, M. Using fuzzy logic applied to software metrics and test cases to assess programming assignments and give advice. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2012, 35(2), 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysafiadi, K.; Virvou, M. Fuzzy logic for adaptive instruction in an e-learning environment for computer programming. IEEE transactions on Fuzzy Systems 2014, 23(1), 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallant, J. SPSS survival manual: A step by step guide to data analysis using IBM SPSS; Routledge: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
| Fuzzy set | partition | Membership function |
| Very Low (VL) | (0, 0, 20) | |
| Low (L) | (10, 30, 50) | |
| Average (A) | (30, 50, 80) | |
| Much (M) | (50, 80, 90) | |
| Very Much (VM) | (80, 100, 100) |
| Fuzzy set | partition | Membership function |
| Very Low (VL) | (0, 0, 20) | |
| Low (L) | (10, 30, 50) | |
| Medium (M) | (30, 50, 80) | |
| High (H) | (50, 80, 90) | |
| Very High (VH) | (80, 100, 100) |
| degree | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| A1 | VM | M | A | L | VL |
| A2 | VL | VL | L | M | VM |
| A3 | M | M | A | VL | VL |
| A4 | L | L | A | VL | VL |
| A5 | M | M | A | VL | VL |
| syntax | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| A1 | VL | VL | A | M | VM |
| A2 | VM | M | A | VL | VL |
| A3 | VL | VL | L | A | A |
| A4 | VL | VL | A | M | M |
| A5 | VL | VL | A | M | M |
| logical | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| A1 | VL | VL | A | M | VM |
| A2 | VM | M | A | VL | VL |
| A3 | VL | L | A | M | VM |
| A4 | VL | L | M | VM | VM |
| A5 | VL | VL | A | M | M |
| carelessness | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| A1 | VL | VL | VL | L | L |
| A2 | VL | VL | VL | VL | VL |
| A3 | VL | VL | VL | VL | VL |
| A4 | VL | VL | M | M | M |
| A5 | VL | VL | M | VM | VM |
| Help requests | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| A1 | VL | VL | L | A | A |
| A2 | M | M | A | L | VL |
| A3 | VL | L | A | M | VM |
| A4 | VL | L | A | M | VM |
| A5 | VL | VL | L | M | M |
| Time | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| A1 | VL | VL | L | A | A |
| A2 | M | A | A | L | L |
| A3 | VL | VL | A | M | VM |
| A4 | VL | VL | A | M | VM |
| A5 | VL | VL | L | A | M |
| degree of success | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| A1 | VM | M | A | L | VL |
| A2 | VL | VL | L | M | VM |
| A3 | M | M | A | VL | VL |
| A4 | L | L | A | VL | VL |
| A5 | M | M | A | VL | VL |
| Syntax errors | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| A1 | VL | VL | A | M | VM |
| A2 | VM | M | A | VL | VL |
| A3 | VL | VL | L | A | A |
| A4 | VL | VL | A | M | M |
| A5 | VL | VL | A | M | M |
| Logical errors | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| A1 | VL | VL | A | M | VM |
| A2 | VM | M | A | VL | VL |
| A3 | VL | L | A | M | VM |
| A4 | VL | L | M | VM | VM |
| A5 | VL | VL | A | M | M |
| Carelessness errors | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| A1 | VL | VL | VL | L | L |
| A2 | VL | VL | VL | VL | VL |
| A3 | VL | VL | VL | VL | VL |
| A4 | VL | VL | M | M | M |
| A5 | VL | VL | M | VM | VM |
| Help requests | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| A1 | VL | VL | L | A | A |
| A2 | M | M | A | L | VL |
| A3 | VL | L | A | M | VM |
| A4 | VL | L | A | M | VM |
| A5 | VL | VL | L | M | M |
| Time to solve exercises | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| A1 | VL | VL | L | A | A |
| A2 | M | A | A | L | L |
| A3 | VL | VL | A | M | VM |
| A4 | VL | VL | A | M | VM |
| A5 | VL | VL | L | A | M |
| degree | syntax | logical | carelessness | Help requests | time | |
| Maria | 62% | 18% | 60% | 5% | 32% | 58% |
| John | 75% | 32% | 15% | 12% | 60% | 76% |
| Alex | 86% | 45% | 23% | 35% | 12% | 65% |
| Kate | 58% | 40% | 20% | 7% | 80% | 10% |
| Jason | 65% | 25% | 62% | 48% | 35% | 85% |
| degree | syntax | logical | carelessness | Help requests | time | |
| Maria | (0, 0, 0.6, 0.4, 0) | (0.1, 0.4, 0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0.67, 0.33, 0) | (0.75, 0, 0, 0, 0) | (0, 0.9, 0.1, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0.73, 0.27, 0) |
| John | (0, 0, 0.167, 0.83,0) | (0, 0.9, 0.1, 0, 0) | (0.25, 0.25, 0, 0, 0) | (0.4, 0.1, 0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0.67, 0.33, 0) | (0, 0, 0.13, 0.87, 0) |
| Alex | (0, 0, 0, 0.4, 0.3) | (0, 0.25, 0.75, 0, 0) | (0, 0.65, 0, 0, 0) | (0, 0.75, 0.25, 0, 0) | (0.4, 0.1, 0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0.5, 0.5, 0) |
| Kate | (0, 0, 0.73, 0.267, 0) | (0, 0.5, 0.5, 0, 0) | (0, 0.5, 0, 0, 0) | (0.65, 0, 0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0, 1, 0) | (0.5, 0, 0, 0, 0) |
| Jason | (0, 0, 0.5, 0.5, 0) | (0, 0.75, 0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0.6, 0.4, 0) | (0, 0.1, 0.9, 0, 0) | (0, 0.75, 0.25, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0, 0.5, 0.25) |
| degree | syntax | logical | carelessness | Help requests | time | |
| Maria | ‘M’ with μM(x)=0.6 & ‘H’ with μH(x)=0.4 |
‘VL’ with μVL(x)=0.1 & ‘L’ with μL(x)=0.4 |
‘M’ with μM(x)=0.67 & ‘H’ with μH(x)=0.33 |
‘VL’ with μVL(x)=0.75 | ‘L’ with μL(x)=0.9 & ‘M’ with μM(x)=0.1 |
‘M’ with μM(x)=0.73 & ‘H’ with μH(x)=0.27 |
| John | ‘M’ with μM(x)=0.167 & ‘H’ with μH(x)=0.83 |
‘L’ with μL(x)=0.9 & ‘M’ with μM(x)=0.1 |
‘VL’ with μVL(x)=0.25 & ‘L’ with μL(x)=0.25 |
‘VL’ with μVL(x)=0.4 & ‘L’ with μL(x)=0.1 |
‘M’ with μM(x)=0.67 & ‘H’ with μH(x)=0.33 |
‘M’ with μM(x)=0.13 & ‘H’ with μH(x)=0.87 |
| Alex | ‘H’ with μH(x)=0.4 & ‘VH’ with μVH(x)=0.3 |
‘L’ with μL(x)=0.25 & ‘M’ with μM(x)=0.75 |
‘L’ with μL(x)=0.65 | ‘L’ with μL(x)=0.75 & ‘M’ with μM(x)=0.25 |
‘VL’ with μVL(x)=0.4 & ‘L’ with μL(x)=0.1 |
‘M’ with μM(x)=0.5 & ‘H’ with μH(x)=0.5 |
| Kate | ‘M’ with μM(x)=0.73 & ‘H’ with μH(x)=0.267 |
‘L’ with μL(x)=0.5 & ‘M’ with μM(x)=0.5 |
‘L’ with μL(x)=0.5 | ‘VL’ with μM(x)=0.65 | ‘H’ with μH(x)=1 | ‘VL’ with μVL(x)=0.5 |
| Jason | ‘M’ with μM(x)=0.4 & ‘H’ with μH(x)=0.5 |
‘L’ with μL(x)=0.75 | ‘M’ with μM(x)=0.6 & ‘H’ with μH(x)=0.4 |
‘L’ with μL(x)=0.1 & ‘M’ with μM(x)=0.9 |
‘L’ with μL(x)=0.75 & ‘M’ with μM(x)=0.25 |
‘H’ with μH(x)=0.5 & ‘VH’ with μVH(x)=0.25 |
| Degree | syntax | logical | carelessness | Help requests | time | |
| A1 | A with μA=0.6 | VL with μVL=0.08 | A with μA=0.536 | VL with μVL=0.075 | VL with μVL=0.9 | L with μL=0.219 |
| L with μL=0.4 | VL with μL=0.32 | M with μM=0.264 | L with μL=0.1 | A with μA=0.081 | ||
| A2 | L with μL=0.6 | VM with μVM=0.08 | A with μA=0.536 | VL with μVL=0.075 | M with μM=0.9 | A with μA=0.219 |
| M with μM=0.4 | M with μM=0.32 | VL with μVL=0.264 | A with μA=0.1 | L with μL=0.081 | ||
| A3 | A with μA=0.48 | VL with μVL=0.03 | A with μA=0.67 | VL with μVL=0.075 | L with μL=0.9 | A with μA=0.219 |
| VL with μVL=0.32 | VL with μVL=0.12 | M with μM=0.33 | A with μA=0.1 | M with μM=0.081 | ||
| A4 | A with μA=0.48 | VL with μVL=0.03 | M with μM=0.67 | VL with μVL=0.225 | L with μL=0.45 | A with μA=0.584 |
| VL with μVL=0.32 | VL with μVL=0.12 | VM with μVM=0.33 | A with μA=0.05 | M with μM=0.216 | ||
| A5 | A with μA=0.3 | VL with μVL=0.05 | A with μA=0.335 | VL with μVL=0.75 | VL with μVL=0.45 | L with μL=0.584 |
| VL with μVL=0.2 | VL with μVL=0.2 | M with μM=0.165 | L with μL=0.05 | A with μA=0.216 |
| Degree | syntax | logical | carelessness | Help requests | time | |
| A1 | A with μA=0.167 | VL with μVL=0.72 | VL with μVL=0.2 | VL with μVL=0.04 | L with μL=0.67 | L with μL=0.039 |
| L with μL=0.83 | A with μA=0.08 | VL with μVL=0.2 | VL with μVL=0.01 | A with μA=0.33 | A with μA=0.261 | |
| A2 | L with μL=0.167 | M with μM=0.72 | VM with μVM=0.2 | VL with μVL=0.04 | A with μA=0.67 | A with μA=0.039 |
| M with μM=0.83 | A with μA=0.08 | M with μM=0.2 | VL with μVL=0.01 | L with μL=0.33 | L with μL=0.261 | |
| A3 | A with μA=0.134 | VL with μVL=0.27 | VL with μVL=0.25 | VL with μVL=0.04 | A with μA=0.67 | A with μA=0.039 |
| VL with μVL=0.664 | L with μL=0.03 | L with μL=0.25 | VL with μVL=0.01 | M with μM=0.33 | M with μM=0.261 | |
| A4 | A with μA=0.134 | VL with μVL=0.27 | VL with μVL=0.25 | VL with μVL=0.12 | A with μA=0.335 | A with μA=0.104 |
| VL with μVL=0.664 | A with μA=0.03 | L with μL=0.25 | VL with μVL=0.03 | M with μM=0.165 | M with μM=0.7 | |
| A5 | A with μA=0.084 | VL with μVL=0.45 | VL with μVL=0.125 | VL with μVL=0.4 | L with μL=0.335 | L with μL=0.104 |
| VL with μVL=0.415 | A with μA=0.05 | L with μL=0.125 | VL with μVL=0.1 | M with μM=0.165 | A with μA=0.7 |
| Degree | syntax | logical | carelessness | Help requests | time | |
| A1 | L with μL=0.4 | VL with μVL=0.2 | VL with μVL=0.52 | VL with μVL=0.075 | VL with μVL=0.4 | L with μL=0.15 |
| VL with μVL=0.3 | A with μA=0.6 | VL with μVL=0.025 | VL with μVL=0.1 | A with μA=0.15 | ||
| A2 | M with μM=0.4 | M with μM=0.2 | M with μML=0.52 | VL with μVL=0.075 | M with μM=0.4 | A with μA=0.15 |
| VM with μVM=0.3 | A with μA=0.06 | VL with μVL=0.025 | M with μM=0.1 | L with μL=0.15 | ||
| A3 | VL with μVL=0.32 | VL with μVL=0.075 | L with μL=0.65 | VL with μVL=0.075 | VL with μVL=0.4 | A with μA=0.15 |
| VL with μVL=0.24 | L with μL=0.225 | VL with μVL=0.025 | L with μL=0.1 | M with μM=0.15 | ||
| A4 | VL with μVL=0.32 | VL with μVL=0.075 | L with μL=0.65 | VL with μVL=0.225 | VL with μVL=0.2 | A with μA=0.4 |
| VL with μVL=0.24 | A with μA=0.225 | M with μM=0.075 | L with μL=0.05 | M with μM=0.4 | ||
| A5 | VL with μVL=0.2 | VL with μVL=0.125 | VL with μVL=0.325 | VL with μVL=0.75 | VL with μVL=0.2 | L with μL=0.4 |
| VL with μVL=0.15 | A with μA=0.375 | M with μM=0.25 | VL with μVL=0.05 | A with μA=0.4 |
| Degree | syntax | logical | carelessness | Help requests | time | |
| A1 | A with μA=0.73 | VL with μVL=0.4 | VL with μVL=0.4 | VL with μVL=0.065 | A with μA=0.8 | VL with μVL=0.15 |
| L with μL=0.267 | A with μA=0.4 | |||||
| A2 | L with μL=0.73 | M with μM=0.4 | M with μM=0.4 | VL with μVL=0.065 | L with μL=0.8 | M with μM=0.15 |
| M with μM=0.267 | A with μA=0.4 | |||||
| A3 | A with μA=0.584 | VL with μVL=0.15 | L with μL=0.5 | VL with μVL=0.065 | M with μM=0.8 | VL with μVL=0.15 |
| VL with μVL=0.214 | L with μL=0.15 | |||||
| A4 | A with μA=0.584 | VL with μVL=0.15 | L with μL=0.5 | VL with μVL=0.195 | M with μM=0.5 | VL with μVL=0.4 |
| VL with μVL=0.214 | A with μA=0.15 | |||||
| A5 | A with μA=0.365 | VL with μVL=0.25 | VL with μVL=0.25 | VL with μVL=0.65 | M with μM=0.5 | VL with μVL=0.4 |
| VL with μVL=0.133 | A with μA=0.25 |
| Degree | syntax | logical | carelessness | Help requests | time | |
| A1 | A with μA=0.4 | VL with μVL=0.6 | A with μA=0.48 | VL with μVL=0.01 | VL with μVL=0.6 | A with μA=0.15 |
| L with μL=0.5 | M with μM=0.32 | VL with μVL=0.09 | L with μL=0.2 | A with μA=0.075 | ||
| A2 | L with μL=0.4 | M with μM=0.6 | A with μA=0.48 | VL with μVL=0.01 | M with μM=0.6 | L with μL=0.15 |
| M with μM=0.5 | VL with μVL=0.32 | VL with μVL=0.09 | A with μA=0.2 | L with μL=0.075 | ||
| A3 | A with μA=0.32 | VL with μVL=0.225 | A with μA=0.6 | VL with μVL=0.01 | L with μL=0.6 | M with μM=0.15 |
| VL with μVL=0.4 | M with μM=0.4 | VL with μVL=0.09 | A with μA=0.2 | VM with μVM=0.075 | ||
| A4 | A with μA=0.32 | VL with μVL=0.225 | M with μM=0.6 | VL with μVL=0.03 | L with μL=0.375 | M with μM=0.4 |
| VL with μVL=0.4 | VM with μVM=0.4 | M with μM=0.27 | A with μA=0.125 | VM with μVM=0.2 | ||
| A5 | A with μA=0.2 | VL with μVL=0.375 | A with μA=0.3 | VL with μVL=0.1 | VL with μVL=0.375 | A with μA=0.4 |
| VL with μVL=0.25 | M with μM=0.2 | M with μM=0.9 | L with μL=0.125 | M with μM=0.2 |
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | |
| Maria |
|
|
|
|
|
| John |
|
|
|
|
|
| Alex |
|
|
|
|
|
| Kate |
|
|
|
|
|
| Jason |
|
|
|
|
|
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | |
| Maria | 40.06 | 51.81 | 43.26 | 52.94 | 35.95 |
| John | 32.64 | 59.38 | 43.51 | 47.42 | 42.37 |
| Alex | 38.38 | 57.29 | 34.05 | 43.62 | 44.79 |
| Kate | 41.67 | 46.45 | 50.99 | 45.94 | 47.36 |
| Jason | 40.94 | 48.77 | 44.91 | 52.96 | 53.44 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | Female | |||
| PerFuSIT_group | 32 | 25 | ||
| No_PerFuSIT_group | 35 | 22 | ||
| Age | ||||
| 18-20 | 21-23 | 23+ | ||
| PerFuSIT_group | 37 | 13 | 7 | |
| No_PerFuSIT_group | 39 | 13 | 5 | |
| Background on computer programming | ||||
| none | low | medium | high | |
| PerFuSIT_group | 24 | 28 | 5 | 0 |
| No_PerFuSIT_group | 26 | 25 | 4 | 2 |
| Experience in using computers | ||||
| none | low | medium | high | |
| PerFuSIT_group | 0 | 0 | 4 | 53 |
| No_PerFuSIT_group | 0 | 0 | 7 | 50 |
| Experience in interacting with tutoring systems | ||||
| none | low | medium | high | |
| PerFuSIT_group | 17 | 10 | 23 | 7 |
| No_PerFuSIT_group | 14 | 16 | 18 | 9 |
| No_PerFuSIT_group | PerFuSIT_group | |
| Mean | 7.01754386 | 8.50877193 |
| Variance | 1.946115288 | 1.468671679 |
| Observations | 57 | 57 |
| Pooled Variance | 1.707393484 | |
| Hypothesized Mean Difference | 0 | |
| df | 112 | |
| t Stat | -6.092558252 | |
| P(T<=t) one-tail | 8.03134E-09 | |
| t Critical one-tail | 1.658572629 | |
| P(T<=t) two-tail | 1.60627E-08 | |
| t Critical two-tail | 1.981371815 |
| No_PerFuSIT_group | PerFuSIT_group | |
| Mean | 54.1052632 | 45.8245614 |
| Variance | 253.845865 | 184.9686717 |
| Observations | 57 | 57 |
| Pooled Variance | 219.407268 | |
| Hypothesized Mean Difference | 0 | |
| df | 112 | |
| t Stat | 2.98444835 | |
| P(T<=t) one-tail | 0.00174425 | |
| t Critical one-tail | 1.65857263 | |
| P(T<=t) two-tail | 0.00348849 | |
| t Critical two-tail | 1.98137181 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





