Submitted:
25 December 2023
Posted:
26 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Motivation and related works
- automation of the administrative process
- maintaining an adaptive learning process
- online review of student progress and assessment
- supporting conventional testing and evaluation.
3. Materials and Methods
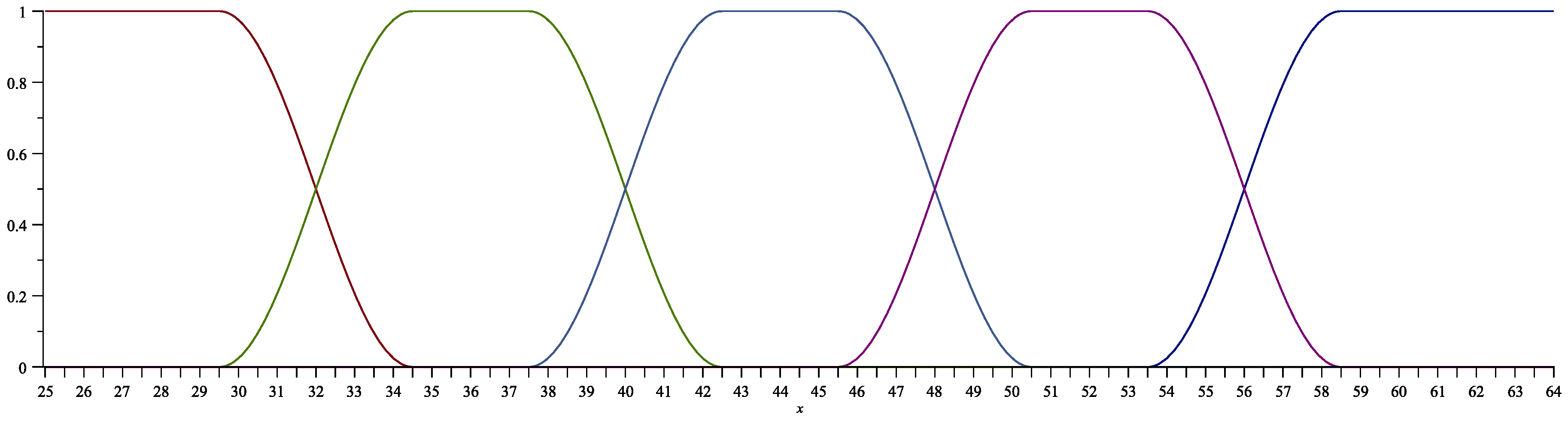
3.1. Application of the fuzzy set theory in student assessment
- An Excellent 6 grade is awarded for test scores from to
- A Very good 5 grade – from to
- A Good 4 grade – from to
- A Satisfactory 3 grade is from to
- A Poor 2 grade is and below.
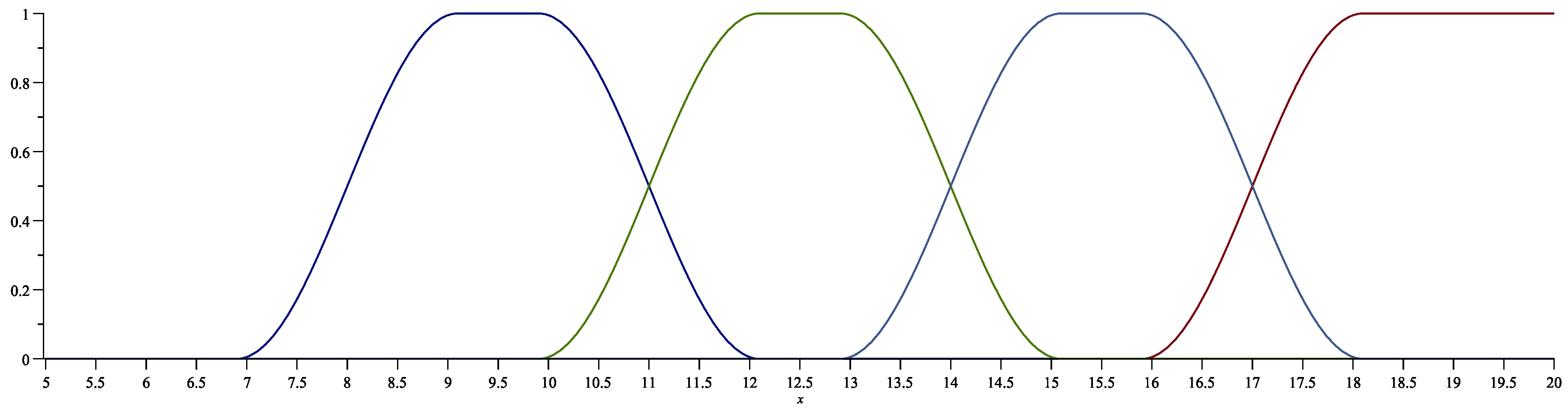
3.2. The test construction
- a)
- red
- b)
- blue
- c)
- black
- d)
- pink.
- a)
- set up
- b)
- discovered
- c)
- reformed
- d)
- destroyed
- a)
- the
- b)
- money
- c)
- doesn’t
- d)
- smell
- a)
- He was believed to be crazy so everyone mocked him because he wasn’t sitting down like the others.
- b)
- The others made fun of him because he liked nuts more than anything else.
- c)
- He wasn’t like the others so people thought he was out of his mind and praised him.
- d)
- People thought he was a lunatic and laughed at him because he was different.
- Include a greeting;
- Apologize and say that you lost her cat;
- Explain how exactly it happened;
- Say what you have done about it.
- Close your email.
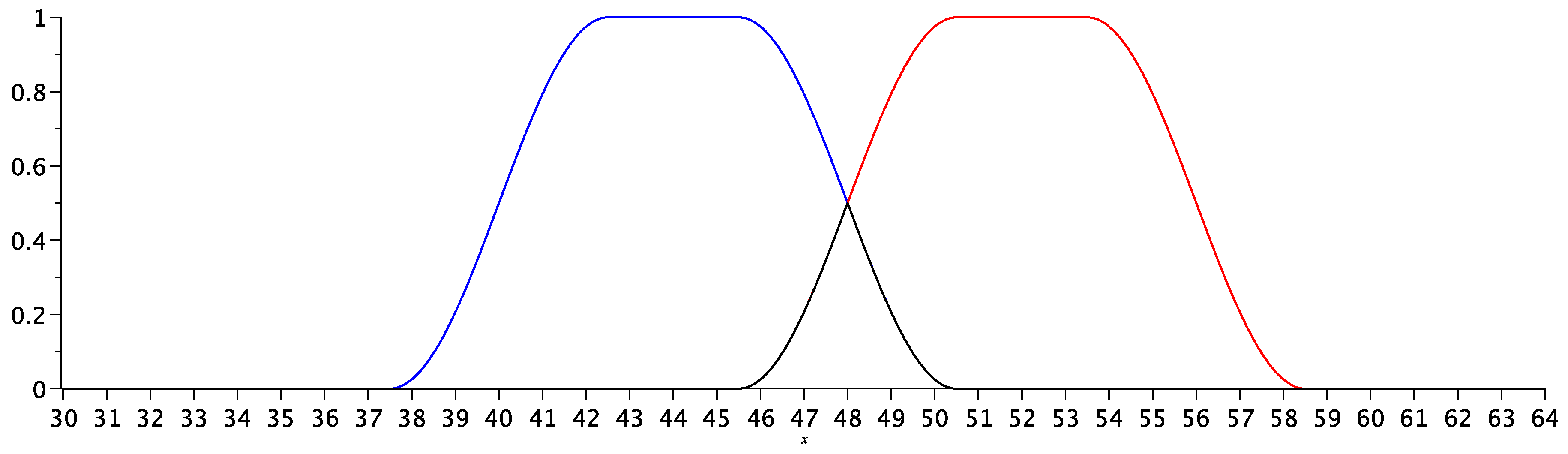
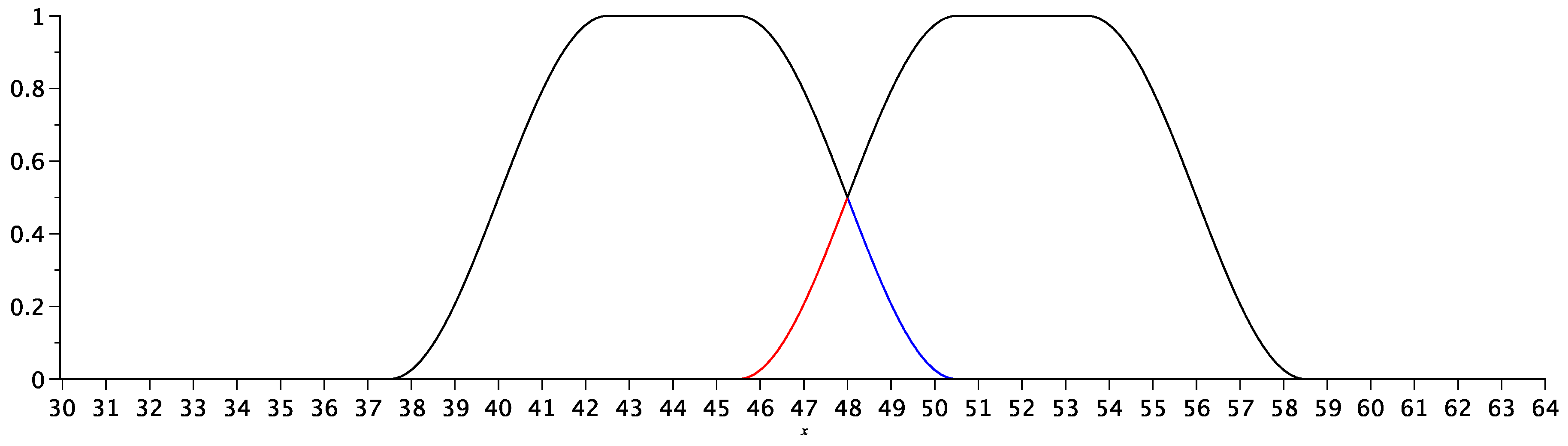
3.3. Illustration of the fuzzy logic usage in recalculating students’ marks
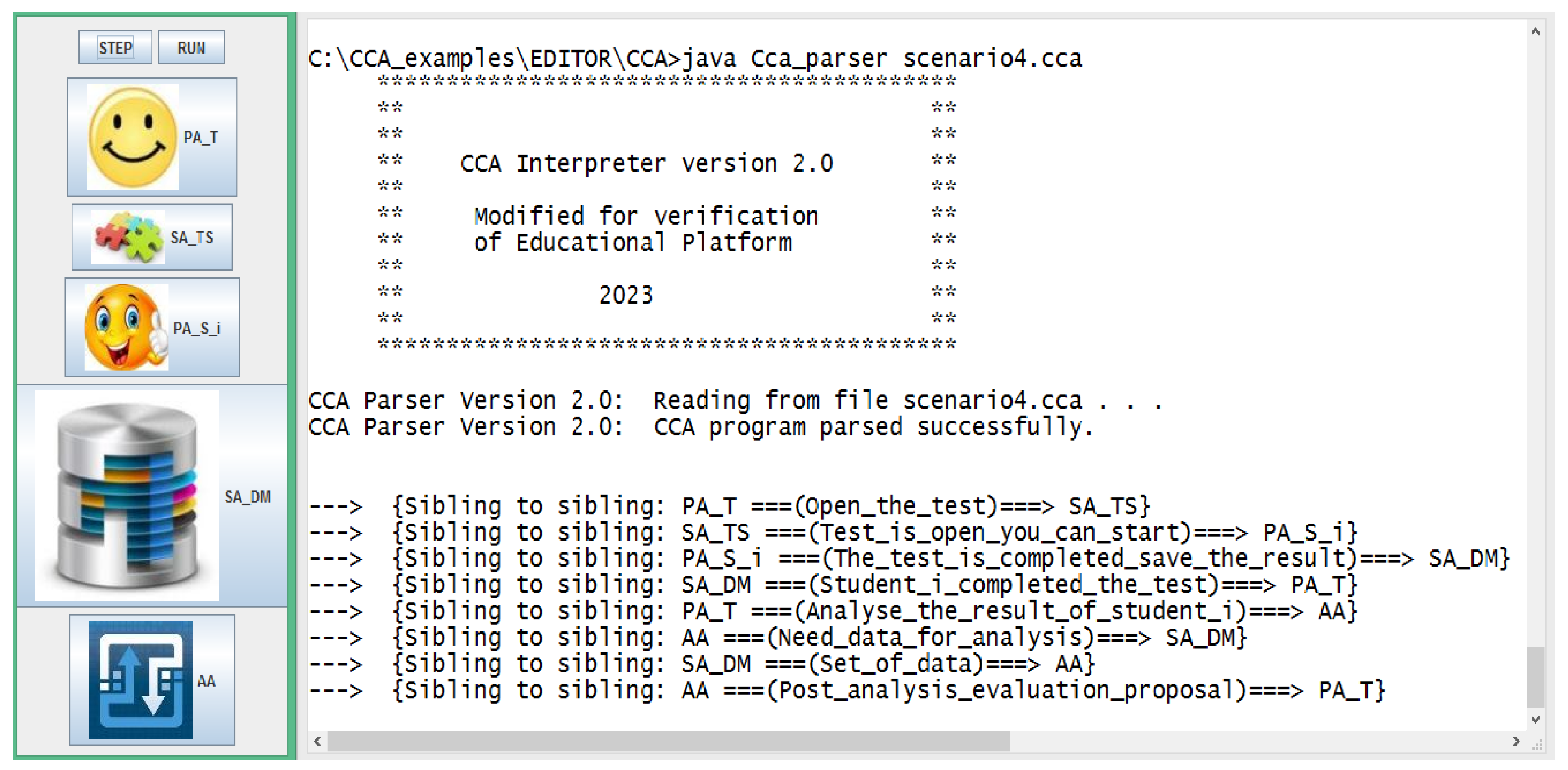
3.4. CCA modeling of the assessment process in a cyber-physical educational environment
- processes P
- capabilities M
- locations
- context expressions k.
- PA_T – a personal assistant to the teacher;
- PA_Si – a personal assistant of the i-th student;
- SA_TS – a specialist assistant serving the Test System in the Education space
- SA_DM – a specialist assistant providing services related to the use of data from the Data Module
- SA_SB – a specialist assistant supporting interaction with Student Books component
- AA – an analytical assistant that provides services related to information analysis by using the described fuzzy set approach.
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morales-Salas, R.E.; Infante-Moro, J.C.; Gallardo-Pérez, J. Evaluation of virtual learning environments. A management to improve. International Journal of Educational Research and Innovation 2020, 2020, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanov, S.; Glushkova, T.; Stoyanova-Doycheva, A.; Krasteva, I. The virtual education space: Concept, architecture, application. Informatics and Education 2021, 36, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, J.; Krasteva, I.; V., I.; Doychev, E. BLISS-A CPSS-like Application for Lifelong Learning. IEEE International Symposium on INnovations in Intelligent SysTems and Applications, INISTA 2019 - Proceedings, 2019, p. Article number 8778363. [CrossRef]
- National Science Foundation (US). Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), 2008. Available online: https://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2008/nsf08611/nsf08611.htm (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Han, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, F.Y. Metaverses and DeMetaverses: From digital twins in CPS to parallel intelligence in CPSS. IEEE Intelligent Systems 2022, 37, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürdür Broo, D.; Boman, U.; Törngren, M. Cyber-physical systems research and education in 2030: Scenarios and strategies. Journal of Industrial Information Integration 2021, 21, 100192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine.. A 21st century cyber-physical systems education, 2017. Available online: https://nap.nationalacademies.org/catalog/23686/a-21st-century-cyber-physical-systems-education (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Stoyanov, S.; Stoyanova-Doycheva, A.; Glushkova, T.; Doychev, E. Virtual physical space – An architecture supporting internet of things applications. 2018 20th International Symposium on Electrical Apparatus and Technologies (SIELA), Bourgas, Bulgaria, 2018, p. Article number 8447156. [CrossRef]
- Stoyanov, S.; Glushkova, T.; Stoyanova-Doycheva, A.; Todorov, J.; Toskova, A. A Generic Architecture for Cyber-Physical-Social Space Applications. Intelligent Systems: Theory, Research and Innovation in Applications. Studies in Computational Intelligence 2020, 864, 319–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnev, A.; Pavlov, N.; Golev, A.; Stieger, M.; Gardjeva, T. New electronic education services using the Distributed E–Learning Platform (DisPeL). International Electronic Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics (IEJPAM) 2014, 7, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of Europe. Common European framework of reference for languages: Learning, teaching, assessment. Cambridge, U.K: Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge, 2011. Available online: https://rm.coe.int/CoERMPublicCommonSearchServices/DisplayDCTMContent?documentId=0900001680459f97 (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Ivanova, V.; Zlatanov, B. Application of fuzzy logic in online test evaluation in English as a foreign language at university level. AIP Conference Proceedings 2019, 2172, 040009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L. Fuzzy Sets. Information and Control 1965, 8, 338–353.
- Fahad, S.; Shah, A. Intelligent testing using fuzzy logic: Applying fuzzy logic to examination of students. Innovations in E-learning, Instruction Technology, Assessment, and Engineering Education 2007, pp. 95–98. [CrossRef]
- Gokmena, G.; Akinci, T.; Tektau, M.; Onat, N.; Kocyigit, G.; Tektau, N. Evaluation of student performance in laboratory applications using fuzzy logic. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences 2010, 2, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, S.; Diniz, J. FuzzyQoI model: A fuzzy logic-based modelling of users’ quality of interaction with a learning management system under blended learning. Computers & Education 2013, 69, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troussas, C.; Krouska, A.; Sgouropoulou, C. Collaboration and fuzzy–modeled personalization for mobile game–based learning in higher education. Computers & Education 2020, 144, 103698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldana-Burgos, L.; Gaona-García, P.; Montenegro-Marín, C. A Fuzzy Logic Implementation to Support Second Language Learning Through 3D Immersive Scenarios. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies 2023, 320, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandwalkar, B.; Pardeshi, S.; Shahade, M.; Awate, A. Descriptive Handwritten Paper Grading System using NLP and Fuzzy Logic. International Journal of Performability Engineering 2023, 19, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimzhanova, S.; Atanov, S.; Moldamurat, K.; Baymuhambetova, B.; Brimzhanova, K.; Seitmetova, A. An intelligent testing system development based on the shingle algorithm for assessing humanities students’ academic achievements. Education and Information Technologies 2022, 27, 10785–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doz, D.; Cotič, M.; Felda, D. Random Forest Regression in Predicting Students’ Achievements and Fuzzy Grades. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doz, D.; Felda, D.; Cotič, M. Demographic Factors Affecting Fuzzy Grading: A Hierarchical Linear Regression Analysis. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doz, D.; Felda, D.; Cotič, M. Assessing Students’ Mathematical Knowledge with Fuzzy Logic. Education Sciences 2022, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doz, D.; Felda, D.; Cotič, M. Combining Students’ grades and Achievements on the National assessment of Knowledge: A fuzzy Logic Approach. Axioms 2022, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doz, D.; Felda, D.; Cotič, M. Using Fuzzy Logic to Assess Students’ Mathematical Knowledge. in Proc. Nauka i obrazovanje – izazovi i perspektive, 2022, pp. 263–278. [CrossRef]
- Özseven, B.E.; Çağman, N. A Novel Student Performance Evaluation Model Based on Fuzzy Logic for Distance Learning. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies 2022, 6, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özseven, B.E.; Çağman, N. A novel evaluation model based on fuzzy logic for distance learning. [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, A. Fuzzy Logic and Education: Teaching the Basics of Fuzzy Logic through an Example (by Way of Cycling). Education Sciences 2013, 3, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, V.; Zlatanov, B. Implementation of fuzzy functions aimed at fairer grading of students’ tests. Education Sciences 2019, 8, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewe, F.; Zedan, H.; Cau, A. The calculus of context-aware ambients. Journal of Computer and System Sciences 2011, 77, 597–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | |
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 | |
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [4, 6], 3, 42.80, 19, 5, 4 | ||
| [4, 6], 4, 42.80, 19, 5, 4 | ||
| [2, 5], 12, 29.20, 16, 3, 2 | ||
| [5, 5], 13, 50.80, 14, 5, 5 | [2, 5], 14, 29.20, 16, 3, 2 | |
| [5, 5], 19, 53.20, 16, 5, 5 | ||
| [6, 6], 20, 58.80, 19, 6, 6 | ||
| [3, 3], 31, 34.80, 9, 3, 3 | ||
| [5, 6], 62, 50.80, 19, 6, 5 | ||
| [4, 5], 69, 42.80, 14, 4, 4 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





