Submitted:
18 September 2024
Posted:
19 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Location and Material
2.2. Experimental Layout and Treatments
2.3. Plant Height and Chlorophyll Index
2.4. Biomass
2.5. Protein Content in Grain
2.6. Zinc Content
2.7. Translocation Factor
2.8. Zinc Utilization Index
2.9. Zinc Health Risk Index
2.10. Statistical Data Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
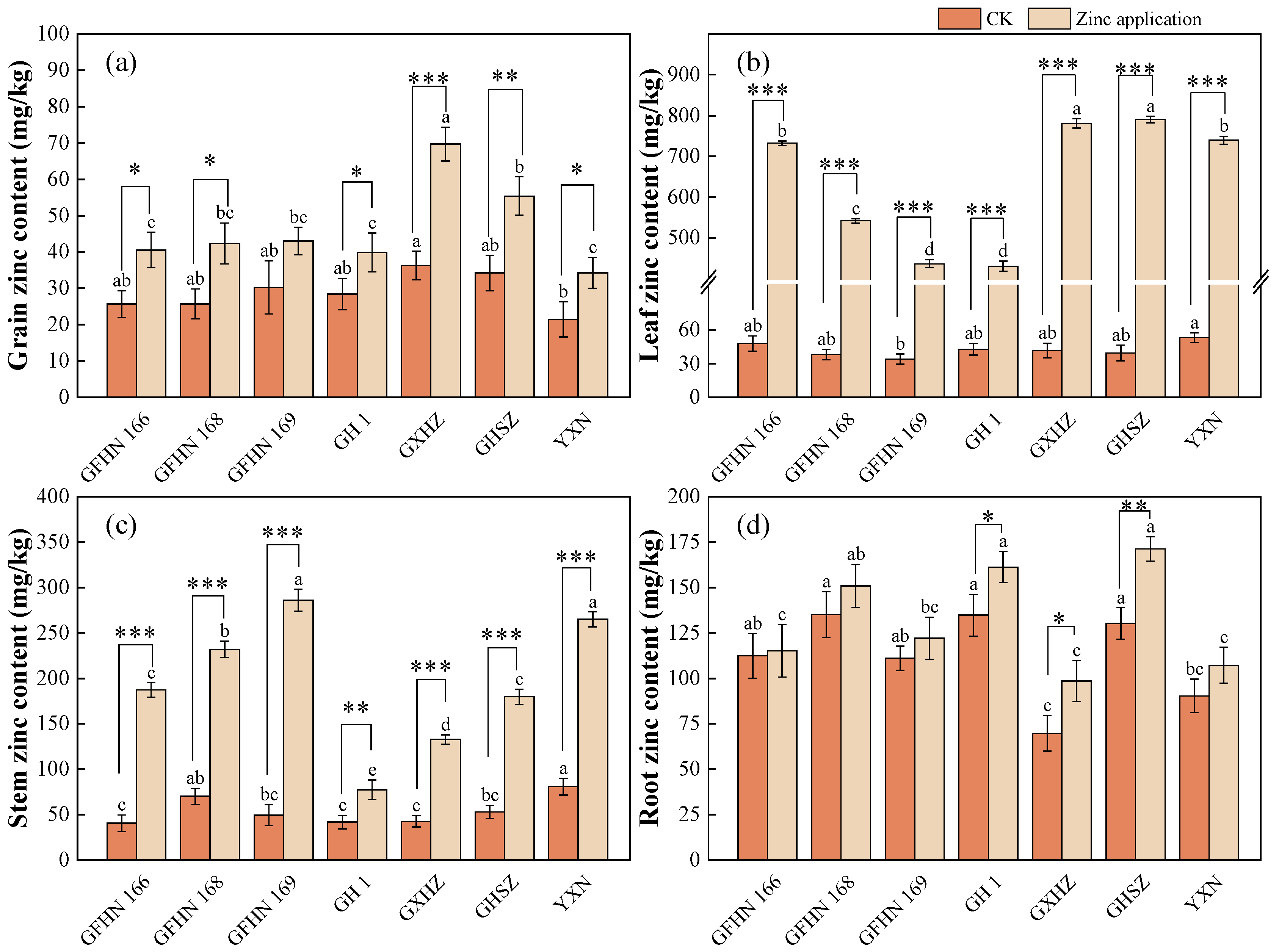
3.1. Zinc Content of Each Organ
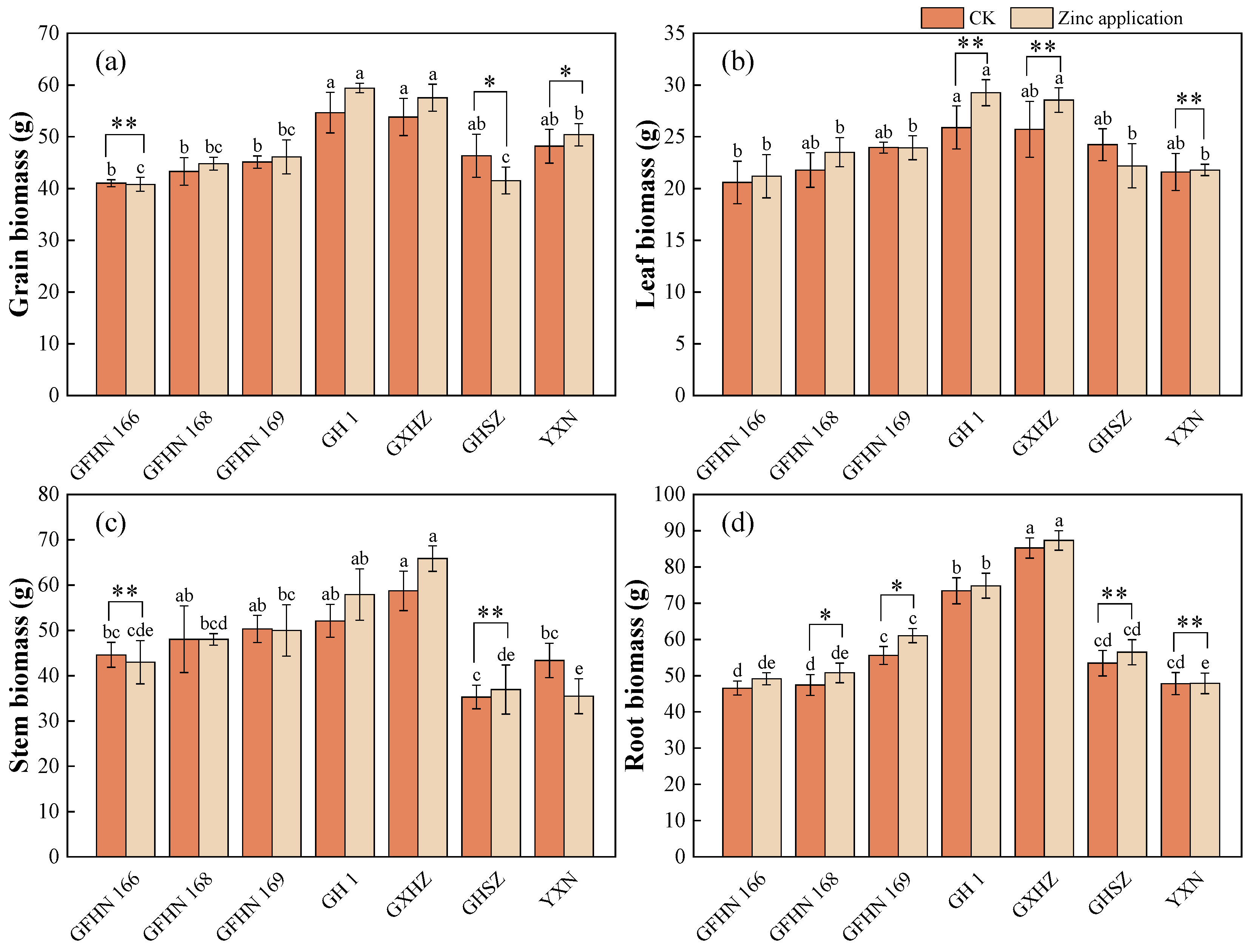
3.2. Biomass of Each Organ
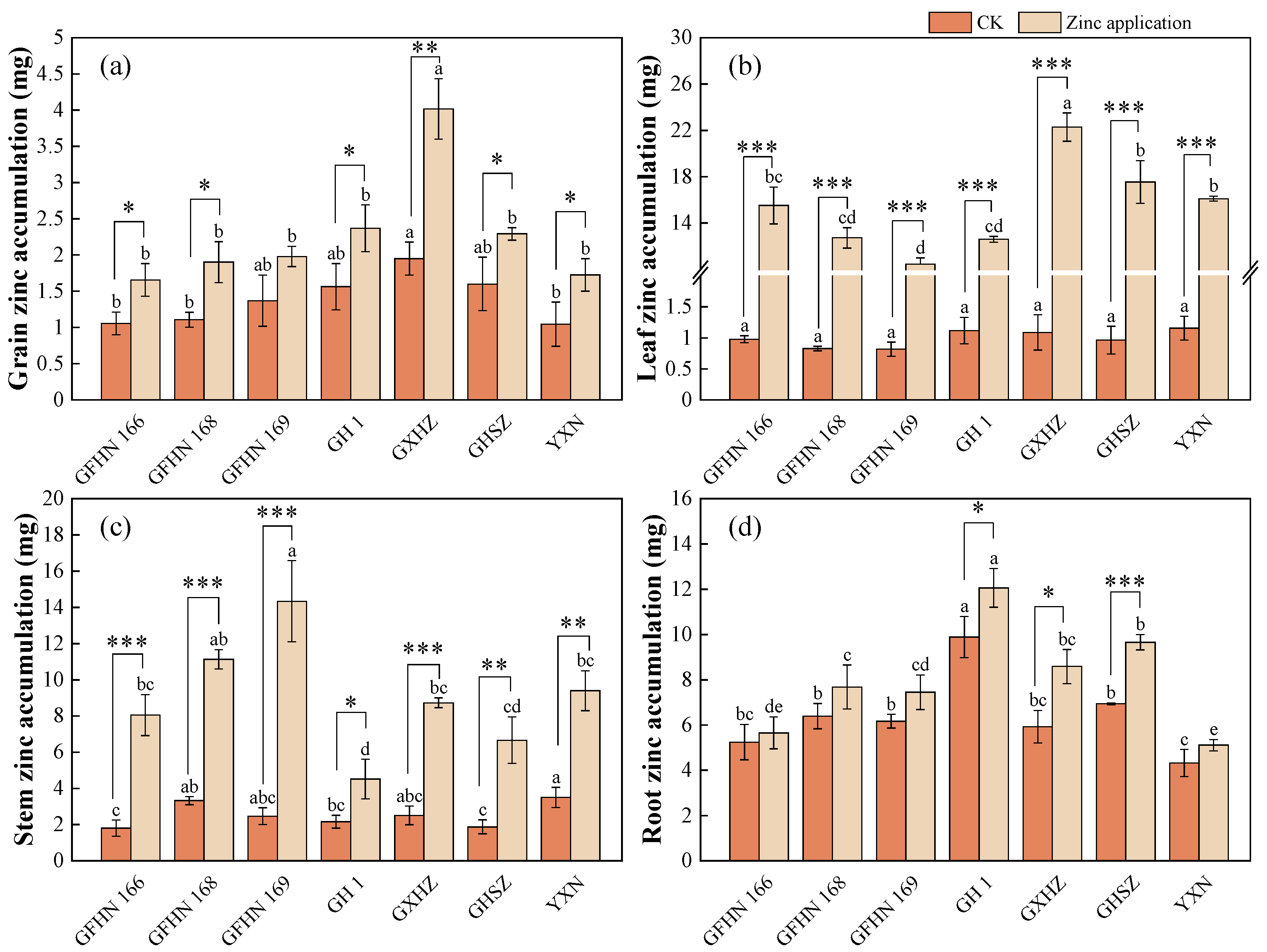
3.3. Zinc Accumulation in Each Organ
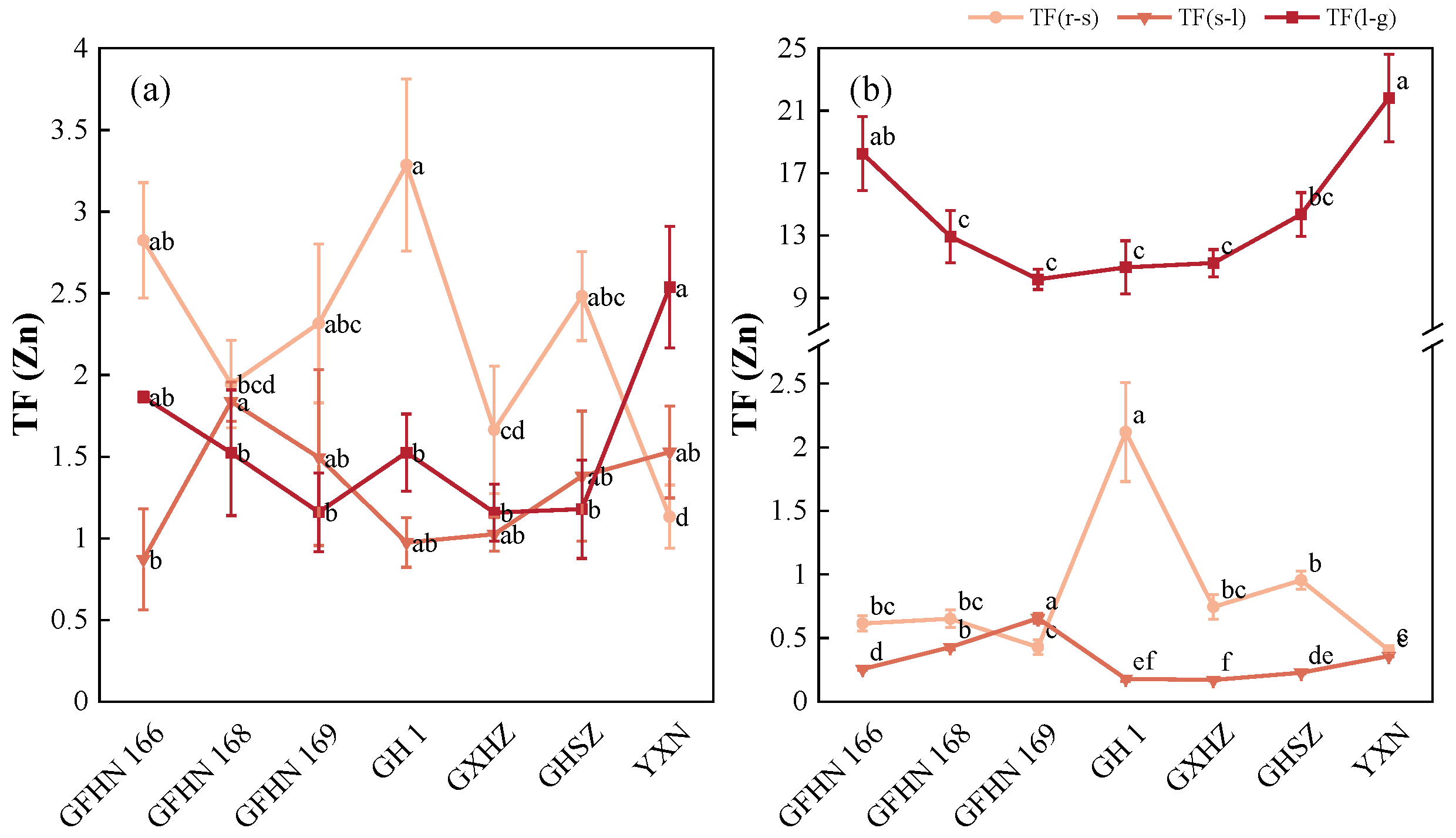
3.4. Translocation Factor
3.5. Zinc Utilization Index
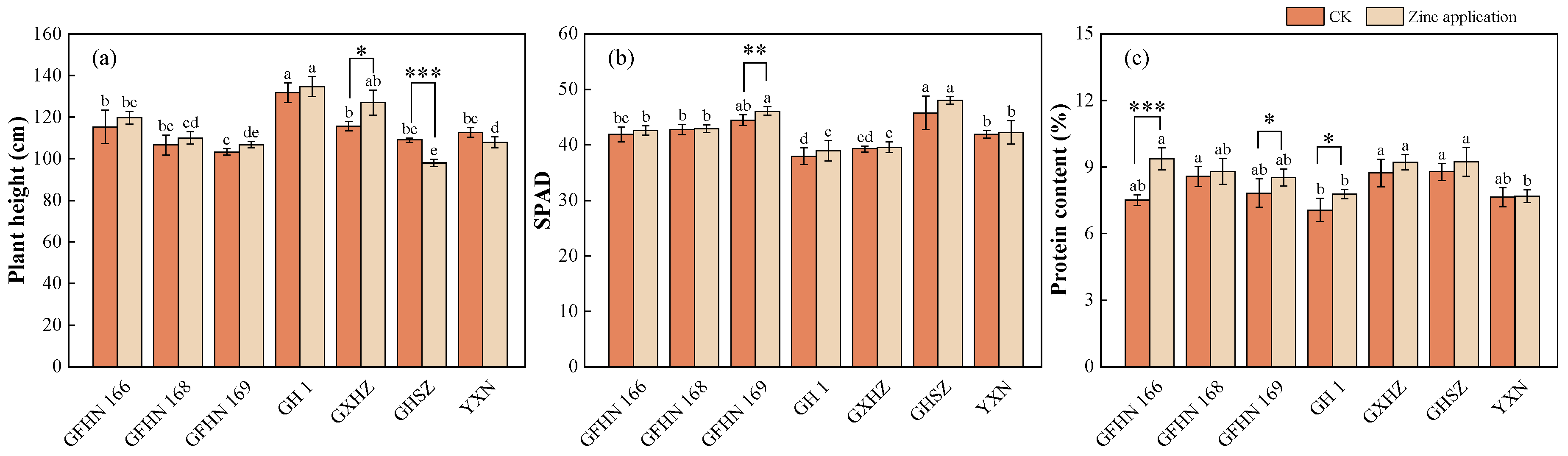
3.6. Plant Height
3.7. SPAD Value
3.8. Protein Content of Grain
3.9. Zinc Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hambidge, M.; Cousins, R.J.; Costello, R.B. Zinc and Health: Current Status and Future Directions: Introduction. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganya, A.; Saravanan, A.; Manivannan, N. Role of Zinc Nutrition for Increasing Zinc Availability, Uptake, Yield, and Quality of Maize (Zea Mays L.) Grains: An Overview. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.E.; Lauren, J.G.; Welch, R.M.; Duxbury, J.M. A Comparison of the Effects of Micronutrient Seed Priming and Soil Fertilization on the Mineral Nutrition of Chickpea (Cicer Arietinum), Lentil (Lens Culinaris), Rice (Oryza Sativa) and Wheat (Triticum Aestivum) in Nepal. Exp. Agric. 2005, 41, 427–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.S. Zinc: The Missing Link in Combating Micronutrient Malnutrition in Developing Countries. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2006, 65, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotz, C. Dietary Indicators for Assessing the Adequacy of Population Zinc Intakes. Food Nutr. Bull. 2007, 28, 430–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swamy, B.P.M.; Rahman, M.A.; Inabangan-Asilo, M.A.; Amparado, A.; Manito, C.; Chadha-Mohanty, P.; Reinke, R.; Slamet-Loedin, I.H. Advances in Breeding for High Grain Zinc in Rice. Rice 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, R.M.; Graham, R.D. ; Ismail Cakmak Linking Agricultural Production Practices to Improving Human Nutrition and Health. ICN2 Second Int. Conf. Nutr. better Nutr. better lives 2014, 7–31. [Google Scholar]
- Harding, K.L.; Aguayo, V.M.; Webb, P. Hidden Hunger in South Asia: A Review of Recent Trends and Persistent Challenges. Public Health Nutr. 2018, 21, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouis, H.E. Micronutrient Fortification of Plants through Plant Breeding: Can It Improve Nutrition in Man at Low Cost? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phattarakul, N.; Rerkasem, B.; Li, L.J. Biofortification of Rice Grain with Zinc through Zinc Fertilization in Different Countries. 2012, 131–141. [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, F.; Ahmad, R.; Ashraf, M.Y.; Waraich, E.A.; Khan, S.Z. Effect of Selenium Foliar Spray on Physiological and Biochemical Processes and Chemical Constituents of Wheat under Drought Stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Minyan, W.; Lianghuan, W.; Jiangguo, W.; Chunhai, S. Impacts of Combination of Foliar Iron and Boron Application on Iron Biofortification and Nutritional Quality of Rice Grain. J. Plant Nutr. 2008, 31, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 28050-2011;National Food Safety Standards General Principles for Nutrition Labeling of Prepackaged Foods,China,2011. 2013.
- Berbudi, A.; Rahmadika, N.; Tjahjadi, A.I.; Ruslami, R. Type 2 Diabetes and Its Impact on the Immune System. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2019, 16, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goufo, P.; Trindade, H. Rice Antioxidants: Phenolic Acids, Flavonoids, Anthocyanins, Proanthocyanidins, Tocopherols, Tocotrienols, c-Oryzanol, and Phytic Acid. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 2, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, D.K.; Srivastav, P.P. Bioactive Compounds of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.): Review on Paradigm and Its Potential Benefit in Human Health. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengkumsri, N.; Chaiyasut, C.; Saenjum, C.; Sirilun, S.; Peerajan, S.; Suwannalert, P.; Sirisattha, S.; Sivamaruthi, B.S. Physicochemical and Antioxidative Properties of Black, Brown and Red Rice Varieties of Northern Thailand. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 35, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fongfon, S.; Prom-U-thai, C.; Pusadee, T.; Jamjod, S. Responses of Purple Rice Genotypes to Nitrogen and Zinc Fertilizer Application on Grain Yield, Nitrogen, Zinc, and Anthocyanin Concentration. Plants 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaksomsak, P.; Rerkasem, B.; Prom-U-Thai, C. Variation in Nutritional Quality of Pigmented Rice Varieties under Different Water Regimes. Plant Prod. Sci. 2021, 24, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Ullah, A.; Rehman, A.; Nawaz, A.; Nadeem, A.; Wakeel, A.; Nadeem, F.; Siddique, K.H.M. Application of Zinc Improves the Productivity and Biofortification of Fine Grain Aromatic Rice Grown in Dry Seeded and Puddled Transplanted Production Systems. F. Crop. Res. 2018, 216, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, C.; Lu, T.L.D. The Origins and Dispersal of Rice Cultivation. Antiquity 1998, 72, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaszmann, J.C. Isozymes and Classification of Asian Rice Varieties. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1987, 74, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Shen, S.; Sun, J.; Wang, M.; Liao, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Xiao, F.; et al. Evaluation of Genetic Diversity of Rice Landraces (Oryza Sativa L.) in Yunnan, China. Breed. Sci. 2007, 57, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Sun, J.; Qi, Y.; Wang, F.; Wei, X.; Han, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. Genetic Structure and Differentiation of Oryza Sativa L. in China Revealed by Microsatellites. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 119, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Caiji, Z.; Yang, J.; Cui, D.; Cao, G.; Ma, X.; Han, B.; Xue, D.; et al. Influence of Ethnic Traditional Cultures on Genetic Diversity of Rice Landraces under On-Farm Conservation in Southwest China. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2016, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Cui, P.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. The Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Enhancing Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Yield and Quality. Agric. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impa, S.M.; Johnson-Beebout, S.E. Mitigating Zinc Deficiency and Achieving High Grain Zn in Rice through Integration of Soil Chemistry and Plant Physiology Research; 2012; Vol. 361; ISBN 1110401213.
- Garg, M.; Sharma, N.; Sharma, S.; Kapoor, P.; Kumar, A.; Chunduri, V.; Arora, P. Biofortified Crops Generated by Breeding, Agronomy, and Transgenic Approaches Are Improving Lives of Millions of People around the World. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.F.; Li, X.J.; Yan, W.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, C.Y.; Huang, M.; Sun, J.B.; Qi, S.J.; Ding, Z.H.; Cui, Z.L. Biofortification of Different Maize Cultivars with Zinc, Iron and Selenium by Foliar Fertilizer Applications. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szerement, J.; Szatanik-Kloc, A.; Mokrzycki, J.; Mierzwa-Hersztek, M. Agronomic Biofortification with Se, Zn, and Fe: An Effective Strategy to Enhance Crop Nutritional Quality and Stress Defense—A Review; Springer International Publishing, 2022; Vol. 22; ISBN 0123456789.
- Cakmak, I.; Kutman, U.B. Agronomic Biofortification of Cereals with Zinc: A Review. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, M.B.; Giráldez, M.I.; Fernández-Caliani, J.C. Assessing the Environmental Availability of Heavy Metals in Geogenically Contaminated Soils of the Sierra de Aracena Natural Park (SW Spain). Is There a Health Risk? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 560–561, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasal, P.C.; Shivay, Y.S.; Pooniya, V.; Choudhary, M.; Verma, R.K. Zinc Partitioning in Basmati Rice Varieties as Influenced by Zn Fertilization. Crop J. 2018, 6, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; Baligar, V.C. Lowland Rice Response to Nitrogen Fertilization. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2001, 32, 1405–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Shivay, Y.S. Effects of Secondary Micronutrients on Nitrogen Recovery Efficiency in Different Crops. Indian J. Fert 2015, 11, 51–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Liang-ji, D.; Fan-fan, J.I.A.; Han, L.I. Enrichment Characteristic and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Wheat and Rice Organs under Mushroom Residue or Swine Manure Recycling Solaar M6 Thermo Fisher Scientific Cd Solaar M6 Thermo Fisher Scientific Cu 、 Pb Solaar M6 Thermo Fisher Scien - Cd Sol. 2017, 230–240. [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Singh, A.K. Human Health Risk Assessment Due to Dietary Intake of Heavy Metals through Rice in the Mining Areas of Singhbhum Copper Belt, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14945–14956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradfield, S.J.; Kumar, P.; White, J.C.; Ebbs, S.D. Zinc, Copper, or Cerium Accumulation from Metal Oxide Nanoparticles or Ions in Sweet Potato: Yield Effects and Projected Dietary Intake from Consumption. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 110, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, C.; Pan, B.; Li, W. Study on the Effect of Ultraviolet Absorber UV-531 on the Performance of SBS-Modified Asphalt. Materials (Basel). 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Struik, P.C.; Lingna, J.; Van Keulen, H.; Ming, Z.; Stomph, T.J. Uptake and Distribution of Root-Applied or Foliar-Applied 65Zn after Flowering in Aerobic Rice. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2007, 150, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Mao, K.; Zhang, H.; Junaid, M.; Xu, N.; Rasool, A.; Feng, X.; Yang, Z. Comprehensive Review of the Basic Chemical Behaviours, Sources, Processes, and Endpoints of Trace Element Contamination in Paddy Soil-Rice Systems in Rice-Growing Countries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanam, R.; Kumar, A.; Nayak, A.K.; Shahid, M.; Tripathi, R.; Vijayakumar, S.; Bhaduri, D.; Kumar, U.; Mohanty, S.; Panneerselvam, P.; et al. Metal(Loid)s (As, Hg, Se, Pb and Cd) in Paddy Soil: Bioavailability and Potential Risk to Human Health. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Struik, P.C.; Van Keulen, H.; Zhao, M.; Jin, L.N.; Stomph, T.J. Does Increased Zinc Uptake Enhance Grain Zinc Mass Concentration in Rice? Ann. Appl. Biol. 2008, 153, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Ram, H.; Kumar, B. Mechanism of Zinc Absorption in Plants: Uptake, Transport, Translocation and Accumulation. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Rengel, Z.; Graham, R.D. Root Morphology of Wheat Genotypes Differing in Zinc Efficiency. J. Plant Nutr. 1995, 18, 2761–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Shohag, M.J.I.; Yang, X. Biofortification and Bioavailability of Rice Grain Zinc as Affected by Different Forms of Foliar Zinc Fertilization. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadi, R.; Dastan, S.; Yasari, E. Role of Zinc Fertilizer on Grain Yield and Some Qualities Parameters in Iranian Rice Genotypes. Sch. Res. Libr. Ann. Biol. Res. 2012, 3, 4519–4527. [Google Scholar]
- Tuiwong, P.; Lordkaew, S.; Veeradittakit, J.; Jamjod, S.; Prom-u-thai, C. Efficacy of Nitrogen and Zinc Application at Different Growth Stages on Yield, Grain Zinc, and Nitrogen Concentration in Rice. Agronomy 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golada, S.; Debbarma, V. Influence of Varieties and Foliar Application of Zinc on Growth, Yield and Economics of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2023, 35, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khampuang, K.; Lordkaew, S.; Dell, B. Foliar Zinc Application Improved Grain Zinc Accumulation and Bioavailable Zinc in Unpolished and Polished Rice. Plant Prod. Sci. 2020, 00, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, A.; Ghazanfar, M.; Khan, J.S.; Pervaiz, S.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Alamri, S. Zinc Absorption through Leaves and Subsequent Translocation to the Grains of Bread Wheat after Foliar Spray. Agric. 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, J.J.; Norvell, W.A.; Welch, R.M.; Sullivan, L.A.; Kochian, L. V. Characterization of Zinc Uptake, Binding, and Translocation in Intact Seedlings of Bread and Durum Wheat Cultivars. Plant Physiol. 1998, 118, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengel, Z.; Römheld, V. Root Exudation and Fe Uptake and Transport in Wheat Genotypes Differing in Tolerance to Zn Deficiency. Plant Soil 2000, 222, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Nishizawa, N.K. Iron Uptake, Translocation, and Regulation in Higher Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, T.R. Historical Changes in Harvest Index and Crop Nitrogen Accumulation. Crop Sci. 1998, 38, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yuan, H.; Ji, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Chen, L.; Guo, Z. Effect of ZnO Nanoparticles on the Productivity, Zn Biofortification, and Nutritional Quality of Rice in a Life Cycle Study. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 163, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, G.K.; Genc, Y.; Graham, R.D. A Simple Method to Evaluate Genetic Variation in Grain Zinc Concentration by Correcting for Differences in Grain Yield. Plant Soil 2008, 306, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impa, S.M.; Morete, M.J.; Ismail, A.M.; Schulin, R.; Johnson-Beebout, S.E. Zn Uptake, Translocation and Grain Zn Loading in Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Genotypes Selected for Zn Deficiency Tolerance and High Grain Zn. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 2739–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, C.; Sanders, D.; Krämer, U.; Podar, D. Zinc in Plants: Integrating Homeostasis and Biofortification. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattha, M.B.; Ali, Q.; Subhani, M.N.; Ashfaq, M.; Ahmad, S.; Iqbal, Z.; Ijaz, M.; Ayub, M.A.; Anwar, M.R.; Aljabri, M.; et al. Foliar Applied Zinc on Different Growth Stages to Improves the Growth, Yield, Quality and Kernel Bio- Bio - Fortification of Fine Rice. 2023, 51, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Faizan, M.; Faraz, A.; Yusuf, M.; Khan, S.T.; Hayat, S. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle-Mediated Changes in Photosynthetic Efficiency and Antioxidant System of Tomato Plants. Photosynthetica 2018, 56, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monostori, I.; Árendás, T.; Hoffman, B.; Galiba, G.; Gierczik, K.; Szira, F.; Vágújfalvi, A. Relationship between SPAD Value and Grain Yield Can Be Affected by Cultivar, Environment and Soil Nitrogen Content in Wheat. Euphytica 2016, 211, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.W.; He, L.X.; Du, B.; Wang, Z.M.; Zheng, A.X.; Lai, R.F.; Tang, X.R. Foliar Application of Selenium (Se) at Heading Stage Induces Regulation of Photosynthesis, Yield Formation, and Quality Characteristics in Fragrant Rice. Photosynthetica 2019, 57, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathpal, B.; Srivastava, P.C.; Shankhdhar, D.; Shankhdhar, S.C. Improving Key Enzyme Activities and Quality of Rice under Various Methods of Zinc Application. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2015, 21, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BIAN, J. long; REN, G. lei; HAN, C.; XU, F. fu; QIU, S.; TANG, J. hua; ZHANG, H. cheng; WEI, H. yan; GAO, H. Comparative Analysis on Grain Quality and Yield of Different Panicle Weight Indica-Japonica Hybrid Rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Cultivars. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheyri, N.; Norouzi, H.A.; Mobasser, H.R.; Torabi, B. Effects of Silicon and Zinc Nanoparticles on Growth, Yield, and Biochemical Characteristics of Rice. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 3084–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; Andrews, J.; Fugice, J.; Singh, U.; Bindraban, P.S.; Elmer, W.H.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; White, J.C. Facile Coating of Urea With Low-Dose ZnO Nanoparticles Promotes Wheat Performance and Enhances Zn Uptake Under Drought Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Place of Origin | Color | Life Cycle (day) | Breed type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GFHN 166 | Guangxi | Black | 122 | Indica-type conventional glutinous rice |
| GFHN 168 | Guangxi | Black | 124 | Indica-type conventional glutinous rice |
| GFHN 169 | Guangxi | Black | 126 | Indica-type conventional glutinous rice |
| GH 1 | Guizhou | Red | 150 | Indica-type conventional non-glutinous rice |
| GXHZ | Guangxi | Red | 122 | Indica-type conventional non-glutinous rice |
| GHSZ | Guangxi | Black | 127 | Indica-type conventional non-glutinous rice |
| YXN | Jiangsu | Purple | 125 | Indica-type conventional non-glutinous rice |
| Category | Gender | DRI (kg/d) | TF (d/a) | EA (a) | AA (a) | BW (kg) | IT (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | Male | 2.5×10−1 | 365 | 81.2 | 46.2 | 72.0 | 12775 |
| Female | 1.9×10−1 | 350 | 85.6 | 48.4 | 58.7 | 13578 | |
| Child | Male | 1.2×10−1 | 300 | 6 | 3.6 | 20.7 | 876 |
| Female | 8.5×10−2 | 300 | 6 | 3.6 | 19.5 | 876 |
| Treatment | Grain zinc content (mg/kg) | Grain biomass (g) | Grain zinc accumulation (mg) | Plant height (cm) | SPAD | Grain protein content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 28.87±3.33b | 45.73±2.88b | 1.38±0.18a | 113.48±0.92a | 41.95±0.54b | 8.25±0.27a |
| Zinc application | 41.55±1.94a | 51.87±0.82a | 2.28±0.14a | 114.86±1.31a | 42.85±0.13a | 8.49±0.18a |
| Cultivar | Harvest Index (HI)% |
Zinc Harvest Index (ZnHI)% |
Zinc Use Efficiency (ZnUE)% |
|---|---|---|---|
| GFHN 166 | 26.48 | 3.77 | 14.24 |
| GFHN 168 | 26.82 | 4.38 | 16.33 |
| GFHN 169 | 25.47 | 4.84 | 19.02 |
| GH1 | 26.84 | 5.62 | 20.93 |
| GXHZ | 24.06 | 6.44 | 26.79 |
| GHSZ | 26.44 | 4.63 | 17.50 |
| YXN | 32.39 | 2.99 | 9.23 |
| cultivars | Adult | Young child | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Male | Female | |
| GFHN 166 | 0.47±0.06c | 0.42±0.05c | 0.64±0.08c | 0.48±0.06c |
| GFHN 168 | 0.49±0.07bc | 0.44±0.06bc | 0.67±0.09bc | 0.51±0.07bc |
| GFHN 169 | 0.50±0.04bc | 0.44±0.04bc | 0.68±0.06bc | 0.51±0.05bc |
| GH 1 | 0.46±0.06c | 0.41±0.06c | 0.63±0.09c | 0.48±0.06c |
| GXHZ | 0.81±0.05a | 0.72±0.05c | 0.91±0.07a | 0.83±0.06a |
| GHSZ | 0.64±0.06b | 0.57±0.05b | 0.88±0.08b | 0.66±0.06b |
| YXN | 0.40±0.05c | 0.35±0.04c | 0.54±0.07c | 0.41±0.05c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





