Submitted:
16 September 2024
Posted:
18 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Textural Characterization
2.3. Surface wettability
2.4. Electrochemical Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Roughness and Wettability
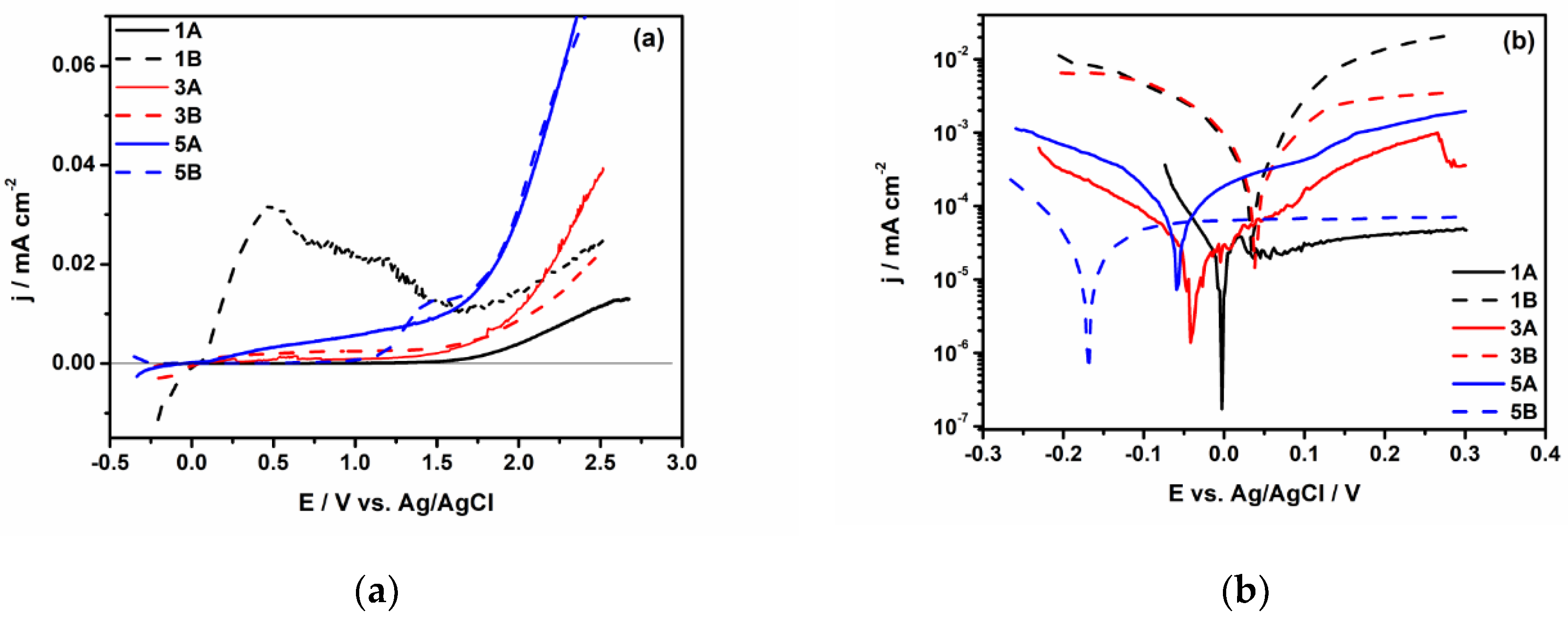
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization
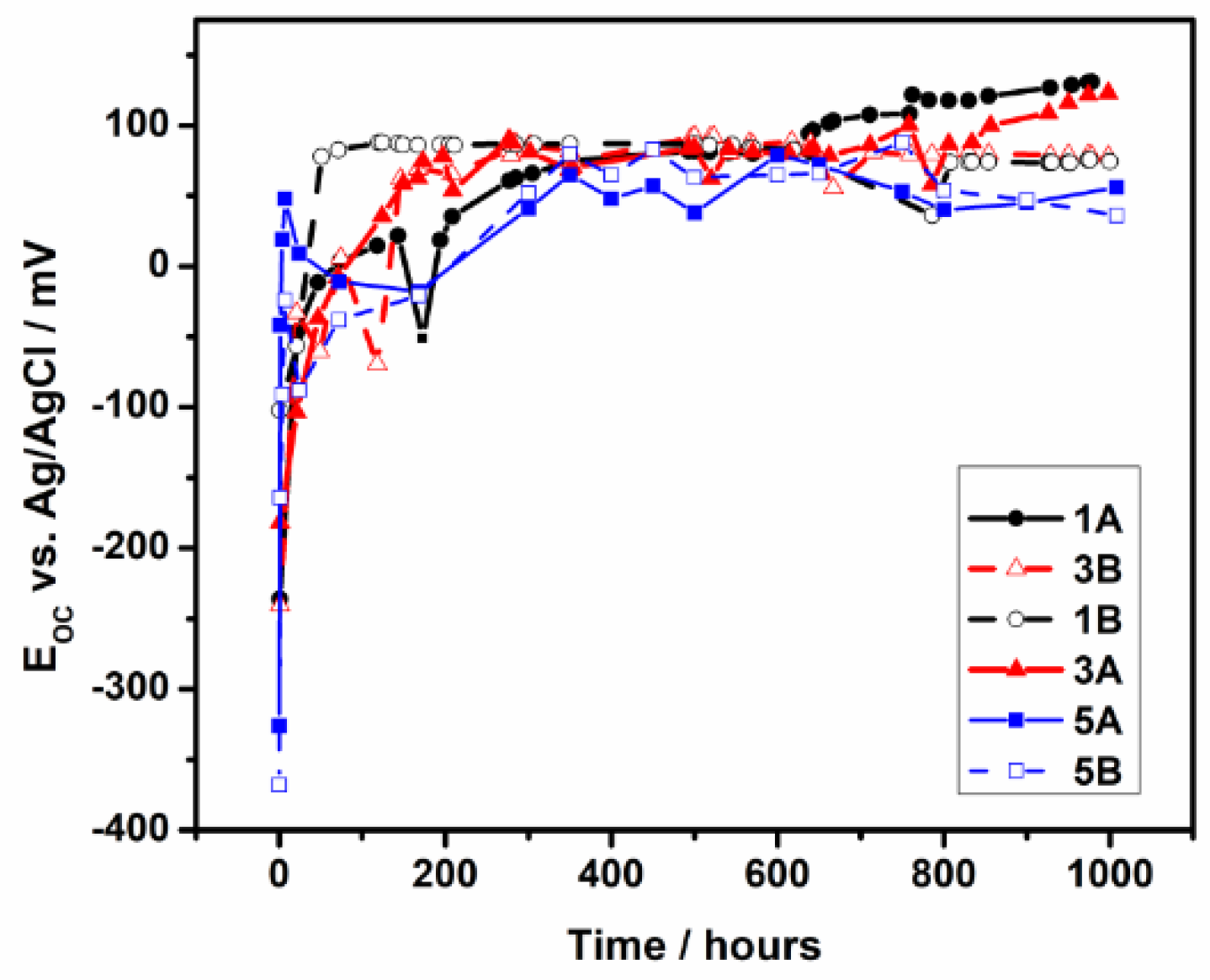
3.2.1. Long-Term Monitoring of the Open Circuit
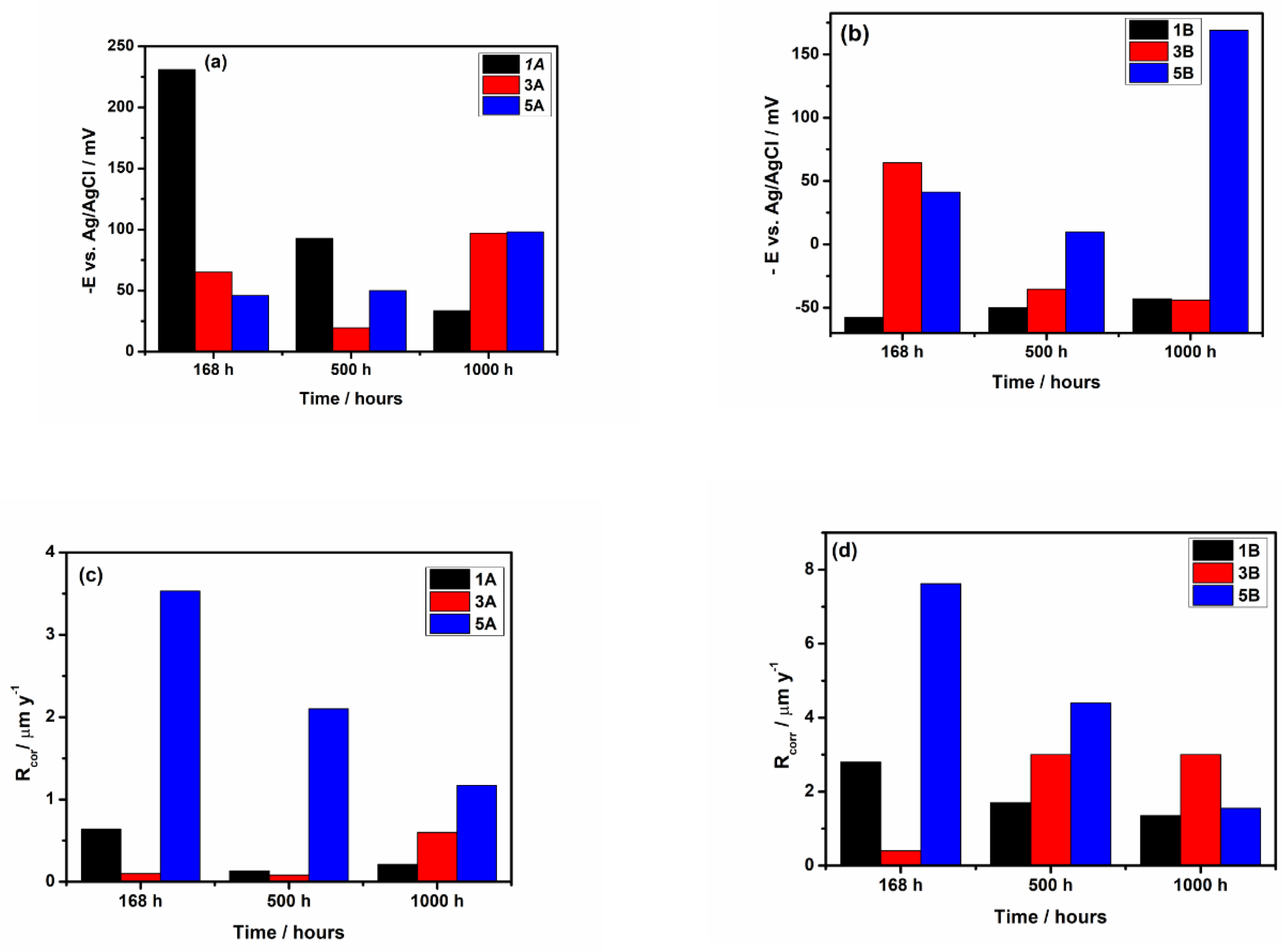
3.2.3. Long-Term Corrosion Evaluation
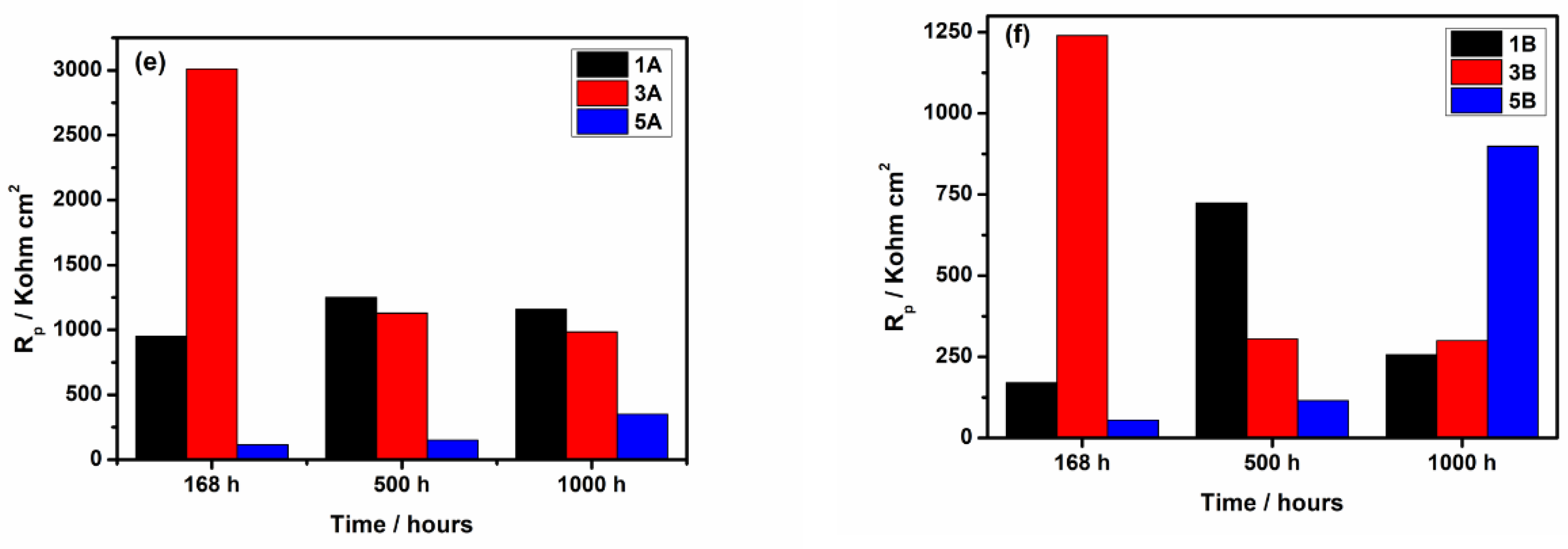
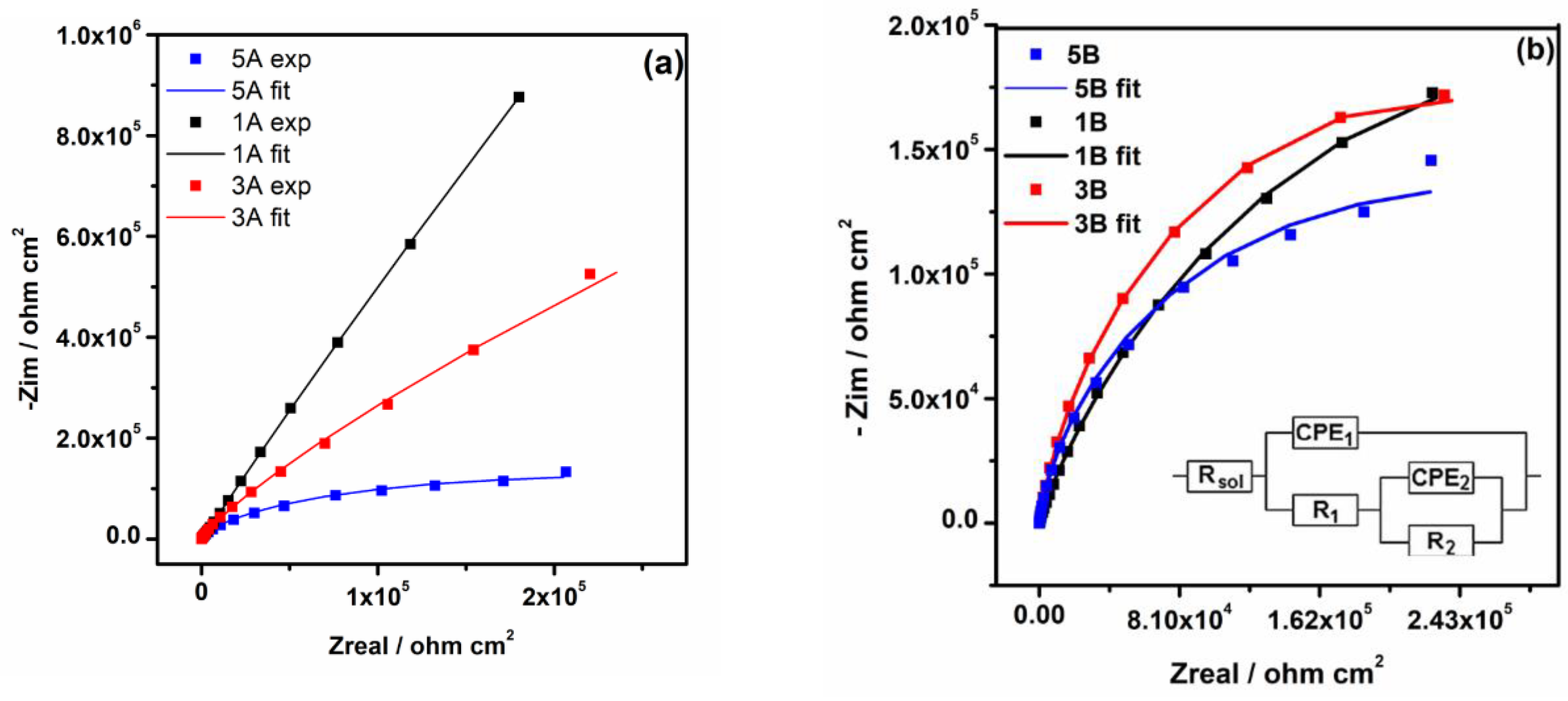
3.2.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
5. Conclusions
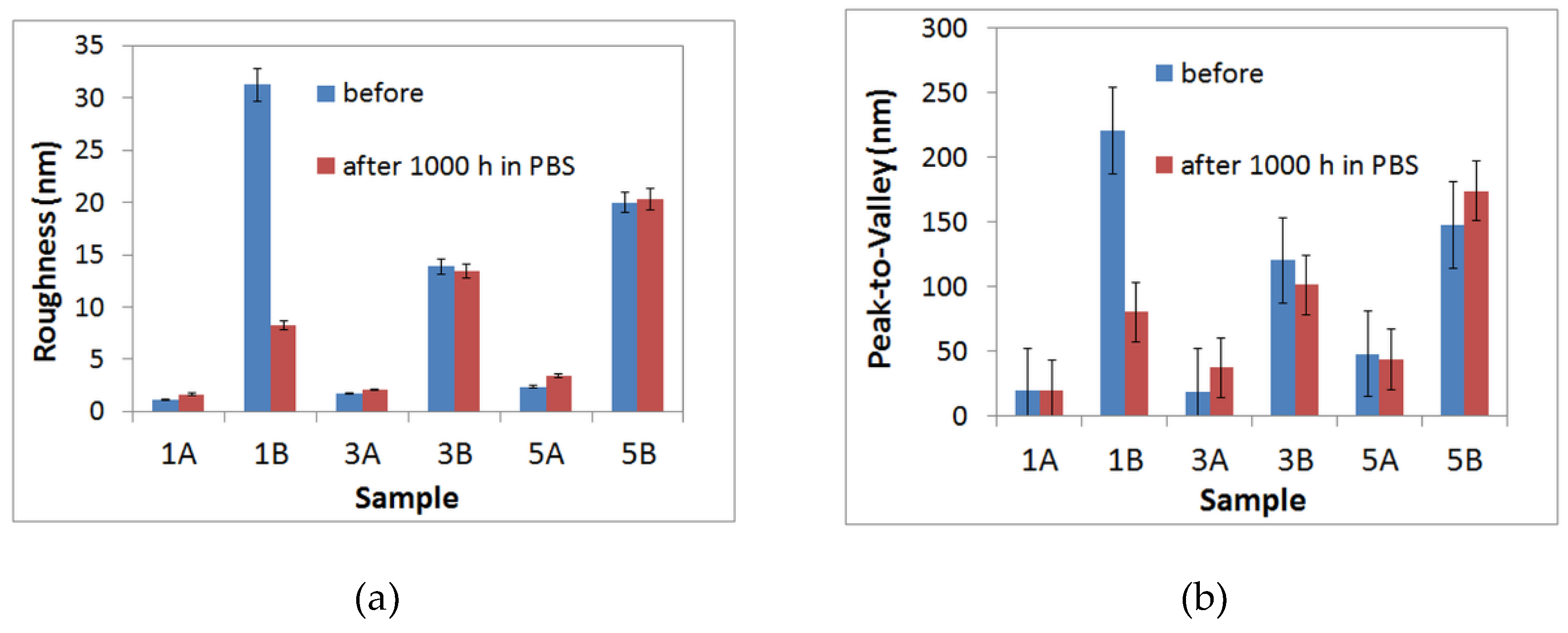
- From AFM investigations before immersion, it was noticed that 1A, 3A and 5A samples show a smooth surface whereas 1B, 3B and 5B samples show a rough surface. After immersion, a similar trend is observed, in spite of the fact that at 1B sample an important decrease of surface roughness is evidenced.
- The moderate values of the contact angles were observed for the all samples (i.e., from 49.1° to 70° for 1A, 3A and 5A samples, and from 54.3° to 73.4° for 1B, 3B and 5B samples), suggesting the hydrophilic character of the surface of all samples which is expected to have a beneficial effect on the osseointegration process.
- The electrochemical tests performed, after 1000 hours of immersion in PBS, revealed that 1A and 3A samples have very good corrosion performance, i.e., 0.21 < Rcorr < 0.6 µm y-1, pointing out that from corrosion point of view they are perfect stable materials. However, the other samples (5A, 1B, 3B and 5B) might be considered very stable materials because a small corrosion rate is noticed (1.35 < Rcorr < 3.01 µm y-1). Based on OCP evolution, this excellent corrosion behavior observed at 1A and 3A samples results from the formation of a stable passive film with remarkable protective properties. Actually, the synergetic effect of the presence of tantalum in alloys composition and of a smooth surface are responsible for the outstanding corrosion resistance of 1A and 3A samples. These findings are supported by the evolution over time of the corrosion parameters estimated for these samples.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sotniazuk, A; Kuczyńska-Zemla.; Kwaśniak, P.; Thomas, M.; Garbacz, H. Corrosion behavior of Ti-29Nb-13Ta-4.6Zr and commercially pure Ti under simulated inflammatory conditions-comparative effect of grain refinement and non-toxic β phase stabilizers. Electrochim. Acta. [CrossRef]
- Vasilescu, C.; Drob, S.I.; Calderon Moreno, J.M.; Osiceanu, P.; Popa, M.; Vasilescu, E. ; Marcu, M; Drob, P. Long-term corrosion resistance of new Ti-Ta-Zr alloy in simulated physiological fluids by electrochemical and surface analysis methods. Corros. Sci, 93. [CrossRef]
- Popa, M.; Calderon Moreno, J. M; Vasilescu, C; Drob, S.I; Neacsu, E.I.; Coer, A.; Hmeljak, J.; Zerjav, G.; Milošev, I. Structural Analysis, Electrochemical Behavior, and Biocompatibility of Novel Quaternary Titanium Alloy with near β Structure. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M.; Nakai, M.; Hieda, J. Development of new metallic alloys for biomaterials applications. Acta Biomater, 3888. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S. K.; Gugulothu, S. B.; Ivanov, E.; Suwas, S.; Chatterjee, K. Additive manufacturing of a low modulus biomedical Ti–Nb–Ta–Zr alloy by directed energy deposition. Bioprinting 2024, 41, e00349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thampi, A.; Ramanathan, S. Corrosion behavior of anodized Ti-Ta binary surface alloys in various physiological fluids for implant applications. Corros. Sci. 2023, 219, 111233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lai, W.; Wang, B.; Tong, X.; You, D.; Li, W.; Wang, X. A novel Ti42.5Zr42.5Nb5Ta10 multi-principal element alloy with excellent properties for biomedical applications. Intermetallics, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawajreh, G. Al.; Gonzalez, G.; Romero-Resendiz, L.; Vidilli, A.; Otani, L.B.; Amigo, V. Effect of the Ti/Ta ratio on the feasibility of porous Ti25+x-Nb25-Zr25-Ta25-x (X = 0, 5, and 10) alloys for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 24, 4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselme, K. Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials 2020, 21, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallab, N.; Bundy, K.; O’Connor, K.; Clark, R.; Moses, R. Cell adhesion to biomaterials: correlation between surface charge, surface roughness, adsorbed protein and cell morphology. J. Long-Term Eff. Med. Implants. 1995, 53, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ponsonnet, L.; Reybier, K.; Jaffrezic, N.; Comte, V.; Lagneau, C.; Lissac, M.; Martelet, C. Relationship between surface properties (roughness, wettability) of titanium and titanium alloys and cell behavior. Mater. Scie. Eng. C. 2003, 23, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Chibowski, E. , Szcześ, A. Surface properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy part I: Surface roughness and apparent surface free energy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2017, 70, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, E.S.; Matos, A.O.; Beline, T.; Marques, I.S.V.; Mathew, M.T.; Rangel, N.C. Cruz; Mesquita, M.F.; Consani, R.X.; Barao, V.A.R. Surface-treated commercially pure titanium for biomedical applications: Electrochemical, structural, mechanical and chemical characterizations. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2016, 65, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sittig, C.; Textor, M.; Spencer, N. D.; Wieland, M.; Vallotton, P.-H. Surface characterization of implant materials c.p. Ti, Ti-6Al-7Nb and Ti-6Al-4V with different pretreatments. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 1999, 10, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elaziem, W.; Darwish, M.A.; Hamadad, A.; Daoush, W.M. Titanium-Based alloys and composites for orthopedic implants Applications: A comprehensive review. Mater. Des. 2024, 241, 112850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Juma, T.; Li, X.; Ding, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, T. β duplex phase Ti–Zr–Nb–Ag alloys with impressive mechanical properties, excellent antibacterial and good biocompatibility. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 5008–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilescu, C.; Osiceanu, P.; Calderon Moreno, J.M.; Drob, S.I.; Preda, S.; Popa, M.; Dan, I.; Marcu, M.; Prodana, M.; Popovici, I.A.; Ionita, D.; Vasilescu, E. Microstructure, surface characterization and long-term stability of new quaternary Ti-Zr-Ta-Ag alloy for implant use. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2017, 71, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banu, A.; Preda, L.; Marcu, M.; Dinca, L.L.; Maxim, M.E.; Dobri, G. Electrochemical behavior of SLM Ti-6Al-4V alloy after long time of immersion in lactic acid environment. Met. Mater. Trans. A, 2022, 53, 2060–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanovic, M.B.; Tasic, Ž. Z.; Simonovic ́, A.T.; Petrovic ́ Mihajlovic, M.B.; Antonijević, M.M. Corrosion Behavior of Titanium in Simulated Body Solutions with the Addition of Biomolecules. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12768–12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobri, G.; Berceanu, A.; Paraschiv, A.; Geanta, V.; Ciuca, S.; Banu, A. The effect of tantalum content on microstructure and Vickers hardness of TiNbZrTaAg alloy. U.P.B. 85, 2023; 85. [Google Scholar]
- Dobri, G.; Banu, A.; Donath, C.; Marcu, M. The Influence of the Tantalum Content on the Main Properties of the TixTa9Nb8Zr2Ag Alloy. Metals 2023, 13, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Neumann, A. W. Equation of State for Interfacial Tensions of Solid-Liquid Systems, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1992, 39, 299–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10271/2001-Dental Metallic Materials-Corrosion Test Methods. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001.
- Volger, E. A. Water and the acute biological response to surfaces. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1999, (10), 1015–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamek, G.; Kozlowski, M.; Junka, A.; Siwak, P.; Jakubowicz, J. Preparation and Properties of Bulk and Porous Ti-Ta-Ag Biomedical Alloys. Materials 2022, 15, 4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozdemir, Z.; Basim, G.B. Effect of chemical mechanical polishing on surface nature of titanium implants FT-IR and wettability data of titanium implants surface after chemical mechanical polishing implementation. Data Brief 2017, 10, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilescu, C.; Drob, S.I.; Osiceanu, P.; Calderon-Moreno, J.M.; Predoana, M.; Ionita, D.; Demetrescu, I.; Marcu, M.; Popovici, I.A.; Vasilescu, E. Microstructure, Surface characterization and electrochemical behavior of new Ti-Zr-Ta-Ag alloy in simulated human electrolyte. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. /: 513-523, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Monteiro, E.; de Souza Soares, M.F.; Fernandes Nunes, L.; Carvalho Santana, A.I. ; de Biasi,S.R.; Nelson Elias, C. Comparison of the wettability and corrosion resistance of two biomedical Ti alloys free of toxic elements with those of the commercial ASTM F136 (Ti-6Al-4V) alloy. J. Mater. Research Tech, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbaix, M. Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions, 2nd Ed. H: National Association of Corrosion, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.-W.; Chen, L-Y. ; Chu, Y.-H.; Zhang, L.; Li, R.; Lu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.-C. Metastable pitting corrosion behavior and characteristics of passive film of laser powder bed fusion produced Ti–6Al–4V in NaCl solutions with different concentrations. Corros. Sci. 2023, 215, 111017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8044/2020; Corrosion of metals and alloys — Basic terms and definitions. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Burnat, B.; Walkowiak-Przybylo, M.; Blaszczyk, T.; Klimek, L. Corrosion behaviour of polished and sandblasted titanium alloys in PBS solution. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2013, 15, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamilselvi, S.; Rajendran, N. In vitro corrosion behaviour of Ti-5Al-2Nb-1Ta alloy in Hank’s solution. Mater. Corros. 2007, 58, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frauchiger, T.; Taborelli, M.; Aronsson, B.-O.; Descouts, P. Ion adsorption on titanium surfaces exposed to a physiological solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1999, 143, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szesz, E.M.; de Souza, G.B.; de Lima, G.G.; da Silva, B.A.; Kuromoto, N.K.; Lepienski, C.M. Improved tribo-mechanical behavior of CaP-containing TiO2 layers produced on titanium by shot blasting and micro-arc oxidation. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 2265–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M. ; Zhu, J-N.; Popovich, V.A.; Borisov, E.; Mol, J.M.C.; Gonzalez-Garcia, Y. Passive film formation and corrosion resistance of laser-powder bed fusion fabricated NiTi shape memory alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotniczuk, A.; Gilbert, J.L.; Liu, Y.; Matczuk, M.; Chrominski, W.; Kalita, D.; Pisarek, M.; Gerbacz, H. Corrosion resistance of β-phase titanium alloys under simulated inflammatory conditions: Exploring the relevance of biocompatible alloying elements. Corros. Sci. 2023, 220, 111271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Dai, J.; Li, H.-B.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Qu, J.-D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.-C.; Zhang, T. Sn microalloying enhances corrosion resistance of stainless steel by accelerating heterogeneous nucleation of passive film. Corros. Sci. 2022, 201, 10279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudic, S.; Vrsalović, L.; Kvrgić, D.; Nagode, A. Electrochemical Behaviour of Ti and Ti-6Al-4V Alloy in Phosphate Buffered Saline Solution. Materials 2021, 14, 7495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Hernández, H.J.; Olmos, L.; Solorio, V.M.; Bouvard, D.; Villalobos-Brito, J.; Chávez, J.; Jimenez, O. Powder Metallurgy Fabrication and Characterization of Ti6Al4V/xCu Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Metals 2023, 13(5), 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Mahobia, G.S.; Mandal, S.; Singh, V.; Chattopadhyay, K. Enhanced corrosion resistance of the surface modified Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloy by ultrasonic shot peening. Corros. Sci. 2021, 189, 09597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
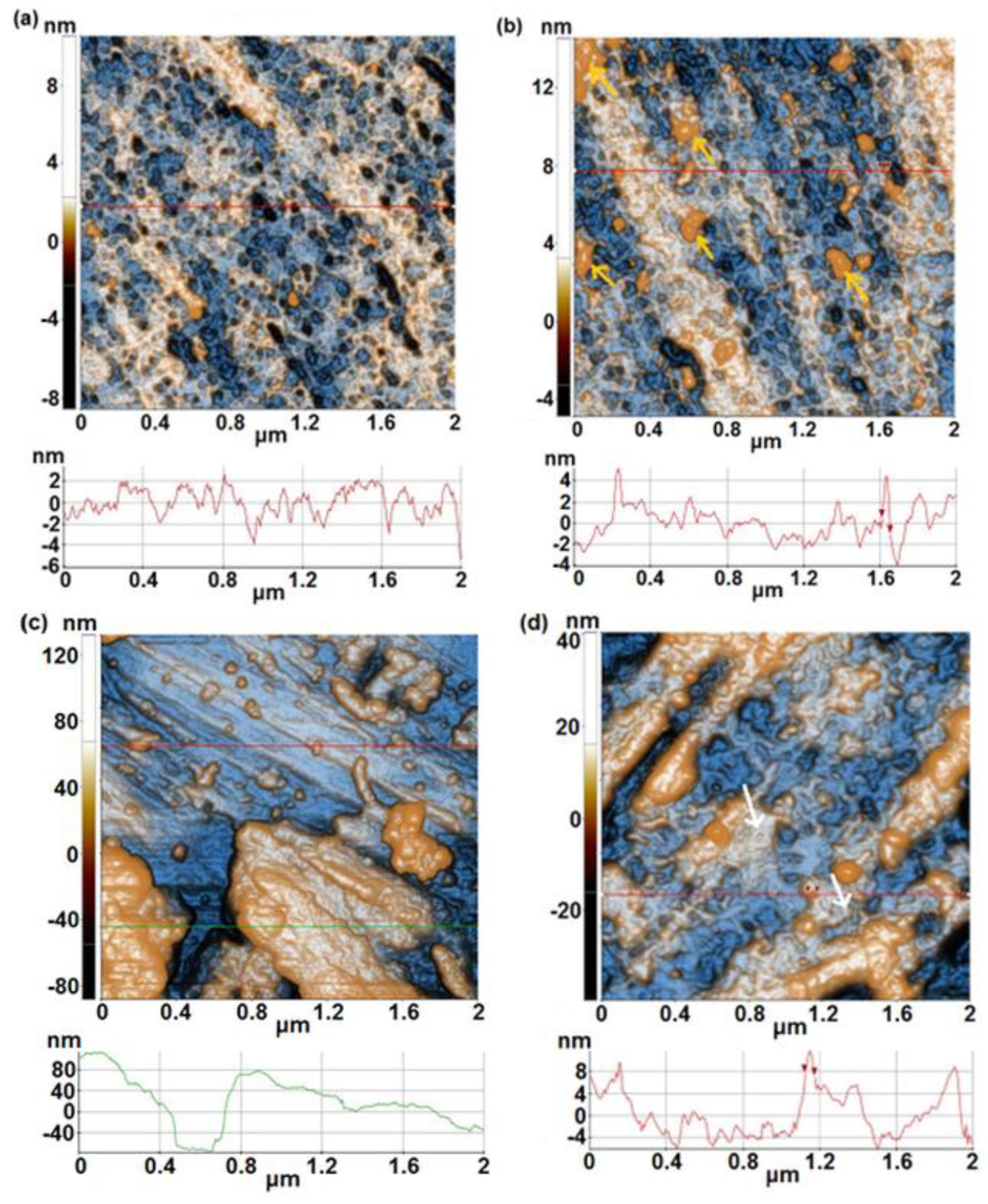
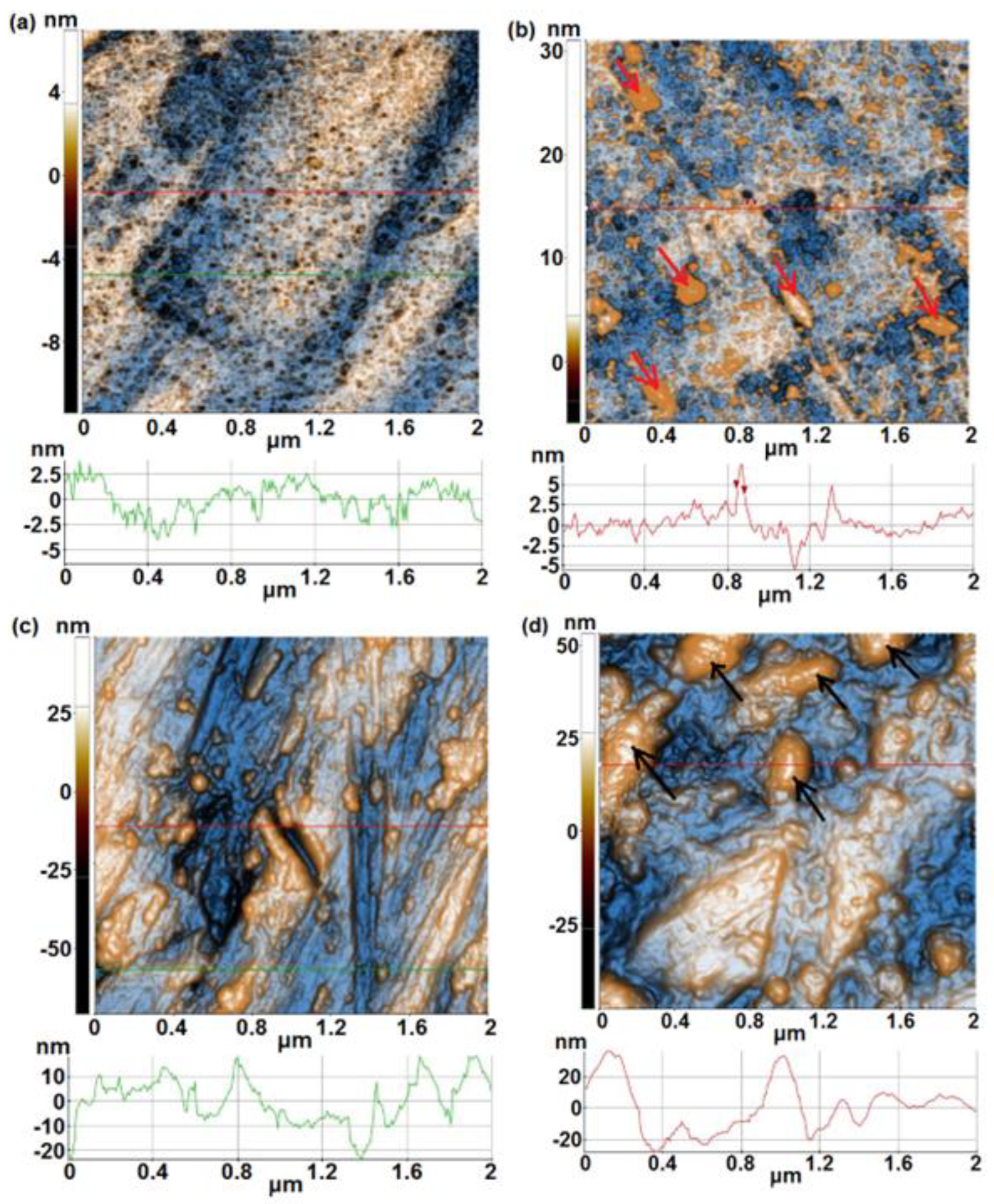
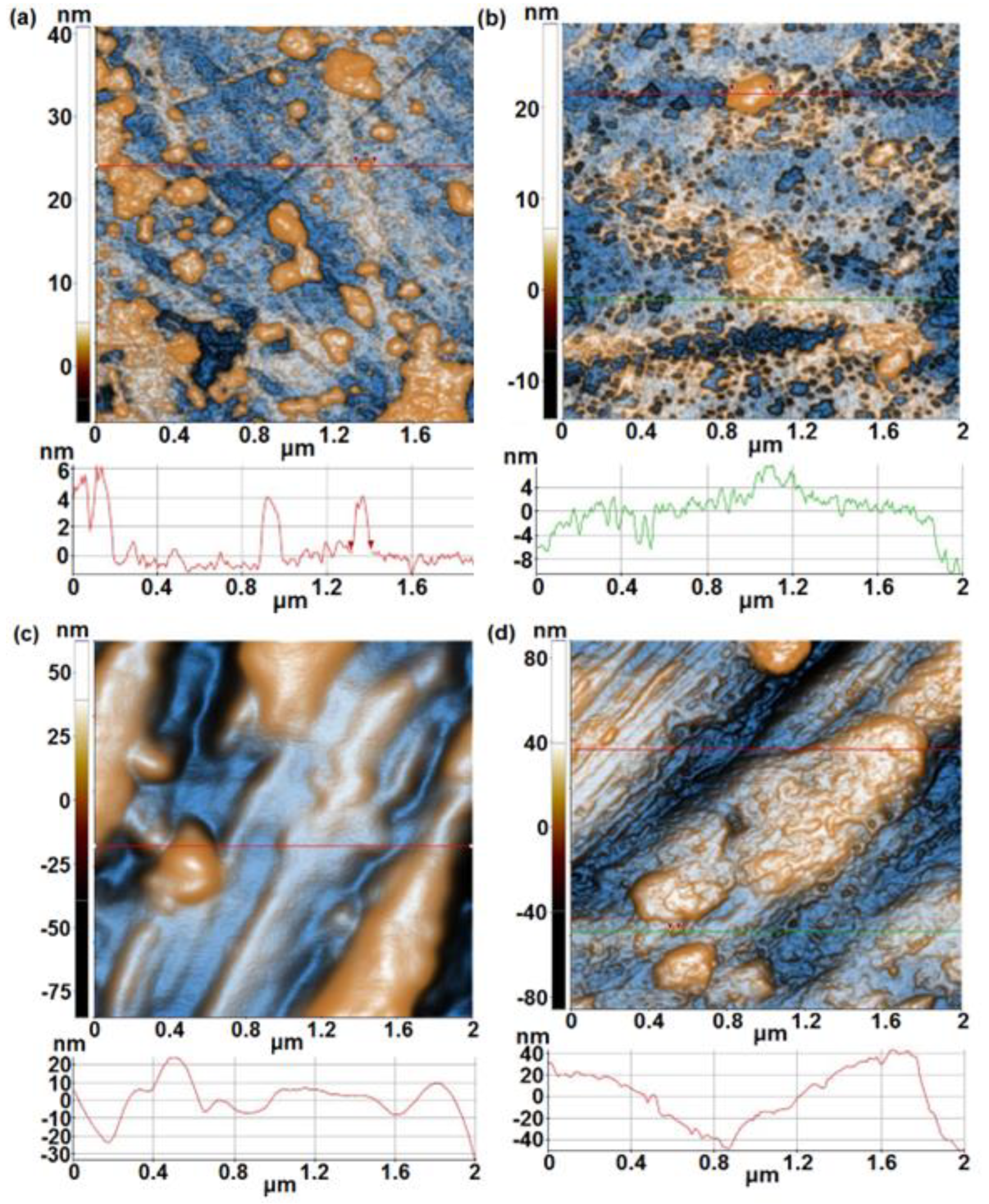
| Alloy | Sample | % Ti | % Ta | % Nb | % Zr | % Ag | Surface |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti20Ta9Nb8Zr2Ag | 1A | Balance | 20.02±0.64 | 9.01±0.16 | 7.88±0.17 | 1.92±0.08 | smooth |
| Ti20Ta9Nb8Zr2Ag | 1B | Balance | 20.02±0.64 | 9.01±0.16 | 7.88±0.17 | 1.92±0.08 | rough |
| Ti10Ta9Nb8Zr2Ag | 3A | Balance | 8.94±0.36 | 10.20±0.68 | 7.95±0.28 | 1.91±0.09 | smooth |
| Ti10Ta9Nb8Zr2Ag | 3B | Balance | 8.94±0.36 | 10.20±0.68 | 7.95±0.28 | 1.91±0.09 | rough |
| Ti9Nb8Zr2Ag | 5A | Balance | 0.0 | 9.22±0.41 | 8.28±0.19 | 1.86±0.16 | smooth |
| Ti9Nb8Zr2Ag | 5B | Balance | 0.0 | 9.22±0.41 | 8.28±0.19 | 1.86±0.16 | rough |
| Sample | θ [ o ] (Before immersion) |
θ [ o ] (After immersion) |
SFE [mN/m] (Before immersion) |
SFE [mN/m] (After immersion) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | 74.3±2.09 | 62.6±3.65 | 38.68±0.89 | 45.87±2.21 |
| 1B | 71.6±1.52 | 54.3±2.82 | 40.35±0.94 | 50.84±1.66 |
| 3A | 67.2±0.48 | 49.1±3.95 | 43.07±0.29 | 53.93±2.27 |
| 3B | 66.7±2.65 | 73.4±4.19 | 43.37±1.62 | 39.24±0.26 |
| 5A | 86.2±4.22 | 70.8±4.12 | 31.27±2.63 | 40.85±2.54 |
| 5B | 82.5±2.49 | 67.3±5.49 | 33.58±1.55 | 43.00±3.37 |
| Sample | Ecor, mV |
Jcor, nA cm-2 |
Rcor, µm y-1 |
Rp, kΩ cm2 |
Δ Epass, V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | -33 ± 1 | 17.2 ± 0.02 | 0.21± 0.01 | 1160 ± 2.5 | 2.4 ± 0.05 |
| 1B | 43 ± 2 | 107 ± 0.15 | 1.35 ± 0.1 | 257 ± 1.0 | - |
| 3A | -97 ± 5 | 53 ± 0.11 | 0.6 ± 0.05 | 456 ± 1.5 | 2.05 ± 0.02 |
| 3B | 44 ± 2 | 228 ± 0.24 | 3.01 ± 0.25 | 305 ± 1.5 | 2.04 ± 0.02 |
| 5A | -98 ± 5 | 134 ± 0.18 | 2.1± 0.2 | 151 ± 1.0 | 1.65 ± 0.01 |
| 5B | -169 ± 5 | 68.6 ± 0.15 | 1.55 ± 0.1 | 899 ± 2.0 | 1.62 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





