1. Introduction
Schistosomiasis, a neglected tropical disease (NTDs) caused by parasitic flatworms of the genus Schistosoma, poses a persistent threat to public health in various regions. This helminth infection infects an estimate of 250 million people, particularly those living in low and middle-income African countries [
1,
2,
3]. It is a prevalent neglected tropical disease in sub-Saharan Africa. Nigeria has the highest burden of infected individuals with approximately 29 million reported cases, and an additional 101 million individuals at risk of infection [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8]. The transmission of this disease occurs through exposure to freshwater containing cercariae, the infective larval stage that is released from intermediate host snails [
9].
There are 2 major forms of schistosomiasis—intestinal (due to
schistosoma mansoni and S. japonicum) and urogenital (predominantly due to
S. haematobium). Common signs and symptoms of urogenital
S. haematobium include a swollen belly, blood in the urine, stunted growth, cognitive impairment in children and infertility among adults of childbearing age. Notably,
S. haematobium is also associated with squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder, adding a critical dimension to its pathogenicity [
6,
7,
10].
The soil-transmitted helminths (STHs) constitute a group of parasitic nematodes affecting humans, primarily prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, particularly in low- and middle-income countries [
11]. In terms of morbidity, infections caused by soil-transmitted helminths are considered among the most significant neglected tropical diseases, with nearly one billion individuals still harbouring at least one species [
12]. The primary soil-transmitted helminths affecting humans include roundworms, whipworms, and hookworms [
13].
In 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) launched a strategic initiative aimed at eradicating schistosomiasis as a public health concern by 2030. This comprehensive plan involves a multi-faceted approach, including ensuring access to improved drinking water, enhancing sanitation, providing hygiene education, managing the environment, controlling snail populations, administering preventive chemotherapy to vulnerable groups and the use of diagnostic tests for the assessment of schistosomiasis [
14,
15].
Within the specific context of Ekiti state, Nigeria, initiatives to combat schistosomiasis employ diverse strategies, such as the promotion of improved sanitation, dissemination of health education, and the implementation of annual rounds of mass drug administration (MDA) based on prevalence of the disease in each implementing units using praziquantel [
16,
17,
18,
19]. In Ekiti state, MDA has been ongoing since 2015 with annual treatments delivered to populations based on endemicity levels and the WHO guideline on control and elimination of human schistosomiasis treatment guideline. Currently, the operational evaluation and impact assessment of the MDA programs largely depends on the collection and microscopy analysis of urine samples and faecal matters. This approach complies with WHO guidelines on the assessment of schistosomiasis included in the above mentioned WHO guideline. The samples are examined for the presence of parasite eggs and the infection load estimates provide insight into the efficacy of the treatment.
Deep-seated mistrust of health research and a reluctance to participate in surveys involving human samples significantly impact operational assessments that could guide policies and decisions in the control and elimination programs. Consequently, acquisition of human samples (urine and stool samples) for large-scale operational assessments of schistosomiasis in Ekiti state was a challenge.
One significant incident highlighting this challenge occurred in the second quarter of 2013 in Ekiti State, Nigeria as obtained from a series of interviews carried out with staff at the Ekiti State Primary Health Care Development Agency is reported as follows:
Representatives from the Federal Ministry of Health with the research objective to assess the prevalence of schistosomiasis selected five schools from each of the 16 LGA for sample collection and analysis. The head teachers at selected schools were adequately informed of the assessment program. Ethical protocols and procedures were duly followed before sample collection commenced in the selected LGAs.
The project was discontinued when rumoured circulation of the myth or belief that collected urine and stool samples would be used for ritual purposes provoked vehement opposition to the project. Parents demanded the return of all collected samples in some communities. Delayed return of the samples triggered a massive state-wide protest. Some other communities agreed to participate only if collected samples were processed at site. Based on this agreement, the assessment was re-conducted and concluded in 2014. The on-site sample collection created a serious logistic problem. According to the information obtained from Ekiti state NTD department of the Ministry of Health, no extensive impact assessment schistosomiasis-related research has been implemented in Ekiti state since 2014.
Community fears, misconceptions, myths, concerns and suspicions about human sample collection and use is not peculiar to Ekiti state alone. Other similar community misconceptions have been reported in literature [
10,
20].
In this study, we report the awareness campaign, community mobilisation strategies and approaches used amidst misinformation about sample collection during the granular operational assessment of schistosomiasis and STH in Ekiti state in Southwest Nigeria in the year 2023. The primary objective of the granular operational assessment was to determine the prevalence and intensity of, S. haematobium, S. mansoni and STH at the Ward administrative level.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Consideration and Approval
The ethical approval was received from the Research Ethics Committee (Ekiti State Ministry of Health and Human Services, HREC) under approval number: MOH/EKHREC/EA/P/59 and all research was performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations received from the Federal Capital Territory (FCT, Nigeria) Health Research Ethics Committee (FCT, HREC) under approval number: FHREC/2022/01/102/05-07-22. The project was introduced in detail to the NTD Unit.
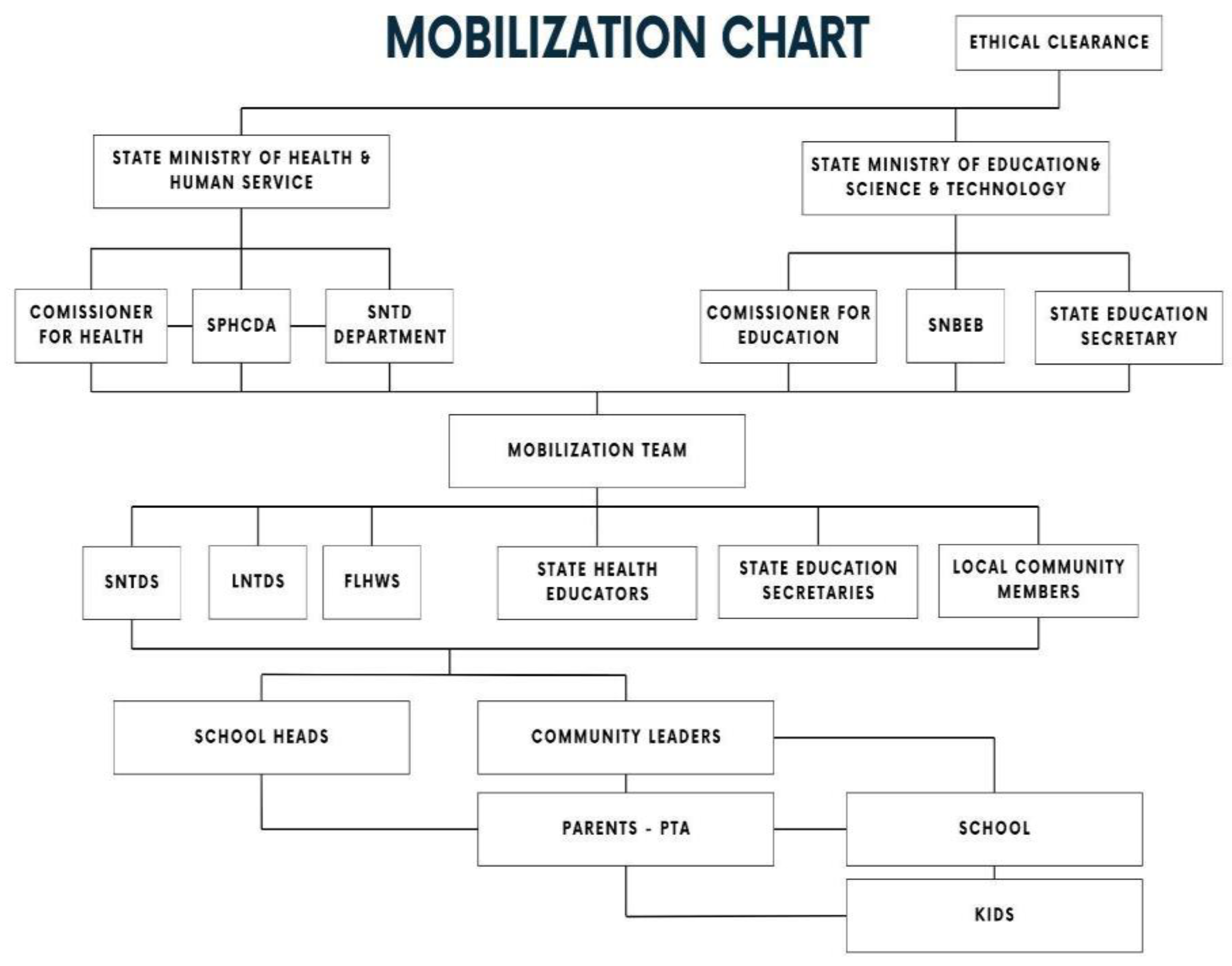
2.2. Collaborative Strategy Development for Community Mobilisation
A collaborative strategy meeting to develop a strategic approach to community mobilisation was convened by the Ekiti State ministry of Health and Human Services, Neglected Tropical Disease Department. The mobilisation approach identified stakeholders at different arms and levels of government with the potential to engage the community and address potential fears and concerns due to the sample collection and overall objective of the study. Community stakeholders were identified as trusted local community members that could potentially facilitate community acceptance of the project; and raise community ownership and participations. This proposed involvement intended to ensure community members were provided with correct information about the operational mapping exercise and its communal benefit. Use of image-based awareness campaign techniques as proposed by [
18] as also used. During the strategy meeting, critical hotspots of potential resistance to the project based on the previous mapping were identified. Four challenging Local Government Areas (LGAs) were identified: Ikere, Ise Orun, Ekiti-Southwest & Emure. These were earmarked for intense awareness campaigns and community mobilisation. These LGAs were also strategically reserved as the last regions for sample collection as success in other communities could be used as part of the mobilisation strategies in these LGAs. Training plans, community media outreach strategies and advocacy visits to religious, community and traditional leaders and their institutions were incorporated into the strategy. Another important stakeholder of interest was the Ekiti State University Teaching Hospital. The involvement of the department of Community Medicine also enhanced trust and increased community participation.
2.3. Community Mobilisation
A quick sampling technique was used to categorise the communities based on their envisaged preference. A-priori knowledge of community preferences, beliefs, culture, and sensitivity enhanced easy data collection and entry during the study. The mobilisation protocol for local community leaders was adapted for the following categories:
2.3.1. Mobilisation of Community Leaders
Community leaders were subdivided into four main categories: (1) political actors; (2) Traditional Leaders; (3) Religious leaders; and (4) Market & community youth leaders. Traditional palaces, mosques, churches, and town halls were strategically visited, and leaders informed, utilising an image-based information approach showing the target parasites as reported in [
18].
2.3.2. Mobilisation of School Heads and Parents Teachers Association
A school mobilisation protocol included advocacy to the school heads and the chairpersons of the Parents Teachers Association (PTA). To gain the buy-in of the target leaders, Local Government Education Secretaries were included in the mobilisation team. School mobilisation was done one week after the intensive community mobilisation. Training was then organised for all School heads within a community to ensure that the entire community is well informed. Parental consent forms were then issued to the head teachers for distribution to their students.
2.3.3. Community Publicity and Awareness Campaign
An extensive awareness campaign was conducted in town squares and marketplace. The mobilisation team planned the advocacy outreach to secure the collaboration of community market and youth leaders. Women market leaders were identified, and they were trained to reach out to parents of the target school age children
3. Results
Based on the reference standard sample collection of 50 samples per community, 17,700 urine and stool samples were expected [
21]. A total of 15,340 urine and stool samples were collected, and the sample collection process occurred in 34 days.
The participant response rate at community level was 86.7% as shown in
Table 1. Participant response rate is computed based on the ratio of the total number of actual participants (7670) to the total number of expected participants (8850).
More than 80% Compliance rate was achieved in 11 out of the 16 LGA. The remaining 5 LGAs demonstrated > 50% compliance rate.
The 4 sensitive LGAs: Ikere, Ise Orun, Ekiti Southwest and Emure interestingly demonstrated satisfactory compliance rates of 100%, 100%, 100% and 64% respectively as shown in
Table 2.
The overall community compliance rate was 93%. An exceptional 100% compliance was observed in the following LGA’s: Ekiti East, Ilejemeje, Ikere, Ekiti South West, Ise/Orun and Ado Ekiti. The 100% compliance in the highlighted communities emphasise the need for clearly planned & effective mobilisation strategies which should be designed to include both high & low-level stakeholders in the community of interest. Sample collection was successful in 166 out of the 177 communities in the state. Nine communities declined participation in the project and 2 other communities demanded for the return of collected samples
4. Discussion
Community mobilisation remains an essential aspect of community health programs. The importance of clear communication and partnerships with all stakeholders at all levels as demonstrated in this study cannot be overemphasized. For this assessment, a top-bottom and bottom-up approach was used. The top-bottom approach includes the involvement of high-level stakeholders in the state ministries of health & education to disseminate information that would support and enhance community acceptance. This approach established the necessary trust needed to validate the integrity, safety, and benefit of the project to the community members. The bottom-up method involves the use of front-line health care workers to enhance community participation.
The familiarity between the frontline workers and the community probably increased the success of sample collection. Mass awareness and mobilisation may have diminished fears, mistrust, prevailing rumours, myths, and misconceptions associated with collections of intimate samples such as stool, urine & blood.
Our proposed strategy facilitated the successful collection of 15,340 urine and stool samples from school age children (5-14 years) with parental consent. The achieved participation and compliance rate reported in this report demonstrates the promising potential of our proposed mobilisation strategy for health-related research & campaign in sensitive communities.
Despite various mobilisation strategies, certain parents openly expressed their refusal for their children to participate in the assessment project. Some children returned unsigned consent forms; some parents withdrew their children from school during the sample collection exercise while others prevented the sample collection process. All these practical issues account for the 86.7% response rate of participants estimated at community level.
While 100% response rate was recorded in some urban communities, community mobilisation and sample collection were most challenging in rural low-density areas. Potential impediments include lack of access to state radio & television media where awareness messages about the exercise were disseminated, low level of outreach to community members who were away from their homes during the day.
Overall, a total of 11 communities were unwilling to participate in the exercise. Community members in 9 of these (11) communities made their intentions clear during community mobilisation, asserting their refusal to allow the collection of samples from their children.
Demand for the return of samples that were collected and transported to the laboratory by parents in 2 communities was a serious challenge. Parents in those communities suddenly became agitated and staged a protest to demand the return of the collected samples despite their previous approval. The frontline healthcare workers prevented the further escalation of the situation by appealing for the intervention of the community leaders. The situation was resolved, and samples collected from the community were returned accordingly. These multifaceted challenges underscore the intricate nature of conducting health assessments within communities marked by deep-seated mistrust and resistance.
The 2013/2014 mobilisation strategy mobilised the involvement of the school authority. However, high-level stakeholder engagement, community mobilisation, Parent Teachers Association awareness & mobilisation were excluded. Aside from complementing the identified gaps in the previous survey, our proposed mobilisation strategy sought to strengthen the Ekiti State Ministry of Health NTD Department to take ownership of the project and design a top-bottom, bottom-top approach for effective awareness campaign & mobilisation. The local knowledge of practical challenges peculiar to each community enabled the design of a well-thought through strategy that identified and engaged the right stakeholders for effective project dissemination at all levels. Allowing local context ownership of the project was critical to the success of the project.
To further improve on the participation of other communities we suggest a multiple iteration of awareness campaign in the local community which will involve local political actors, government officials and state ministry of health. Discussion must be evidence-based. Results, community impact and benefits derived from previous projects should be clearly presented to sensitise and stimulate participation.
To address the challenges identified in this schistosomiasis assessment and to establish a foundation for sustainable and community-driven health initiatives we recommend the following: A clear community feedback mechanism, in which community members who gave their samples should receive timely and comprehensible feedback on the outcomes of the assessment. This could ensure a two-way communication channel, foster trust, and reinforce the notion that community participation yields tangible and meaningful results. Feedback sessions can be organised at community centres, involving local leaders to enhance the credibility of the information shared. We strongly recommend the use of Image-based awareness campaign method. The use of images as part of the IEC material would enable the community members to appreciate the need for the assessment and the potential health benefit for their children and the selected community.
Limitations of this Study
The limitation of this study is that the contribution of each specific activity (media campaign, engagement of community & religious leaders, involvement of parent teachers’ association etc.) to the whole strategy could not be estimated. Hence the effectiveness of each strategy in our developed model could not be quantified.
5. Conclusions
After comprehensive design and implementation of a community mobilisation for the schistosomiasis and STH sampling, an 86.67 % response rate was achieved in a set of communities that were previously refractory to these programs.
The successful mobilisation was achieved after involvement and continuous engagement of the relevant stakeholders both at the state and community level. Regular consultation and several feedback iterations during the awareness campaign, community mobilisation and sample collection process appear to have been successful.
From the lessons and practises learned from the granular schistosomiasis assessment project’s community mobilisation approach, other health-care assessment programs and large community-based outreaches can significantly benefit by improving and applying the outlined techniques.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.A., L.M.B., D.B.; Methodology, T.A., L.M.B., D.B., G.V., J.S., A.A.; Data collection, S.A., T.A.; Data validation, T.A., S.P., O.O., B.P.; Formal analysis and investigation, T.A., S.P., O.O.; Writing—original draft preparation, T.A.; Writing—review and editing, T.A., L.M.B., M.A., D.B., LA., J.A.E., J.C.D., G.V., J.S., O.A., A.A., O.O., S.A., P.A.; Supervision, O.A, S.A., P.A., J.S., S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the END Fund, New York, United States of America.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study involved human participants. The ethical approval was received from the Research Ethics Committee (Ekiti State Ministry of Health and Human Services, HREC) under approval number: MOH/EKHREC/EA/P/59 and all research was performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the NTD Division of the Ekiti state ministry of health, Ekiti State Teaching Hospital and College of Medicine, Ekiti State University, Ado Ekiti, Ekiti state as well as the NTD Division of the Federal Ministry of Health, FCT Abuja, and Mission to Save the Helpless (MITOSATH) for their collaborative efforts on schistosomiasis and STH and in making this research a successful one. We also appreciate the head of each community that participated in this work. Authors also appreciate the support of Flexible Optical, Rijswijk, and Delft Global Initiative - Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Murray, C.J.; Vos, T.; Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Flaxman, A.D.; Michaud, C.; Haring, D. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2197–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.S.; Biedermann, P.; Ekpo, U.F.; Garba, A.; Mathieu, E.; Midzi, N.; Vounatsou, P. Spatial distribution of schistosomiasis and treatment needs in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review and geostatistical analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, N.C.; Bezerra FS, M.; Colley, D.G.; Fleming, F.M.; Homeida, M.; Kabatereine, N.; Garba, A. Review of 2022 WHO guidelines on the control and elimination of schistosomiasis. Lancet Infect. Diseases 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotez, P.J.; Kamath, A. Neglected tropical diseases in sub-Saharan Africa: review of their prevalence, distribution, and disease burden. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, D.P.; Dunne, D.W.; Sacko, M.; Utzinger, J.; Vennervald, B.J.; Zhou, X.N. Schistosomiasis. Nat Rev Dis Primer. Schistosomiasis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, T.C.A.; Moreira, P.R.R. Neuroschistosomiasis: clinical symptoms and pathogenesis. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downs, J.A.; Mguta, C.; Kaatano, G.M.; Mitchell, K.B.; Bang, H.; Simplice, H.; Fitzgerald, D.W. Urogenital schistosomiasis in women of reproductive age in Tanzania's Lake Victoria region. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawaki, S.; Al-Mekhlafi, H.M.; Ithoi, I.; Ibrahim, J.; Abdulsalam, A.M.; Ahmed, A.; Atroosh, W.M. The menace of schistosomiasis in Nigeria: knowledge, attitude, and practices regarding schistosomiasis among rural communities in Kano state. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colley, D.G.; Bustinduy, A.L.; Secor, W.E.; King, C.H. Human schistosomiasis. Lancet 2014, 383, 2253–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedrow, V.A.; Zelaya, C.E.; Kennedy, C.E.; Morin, S.F.; Khumalo-Sakutukwa, G.; Sweat, M.D.; Celentano, D.D. No “magic bullet”: Exploring community mobilization strategies used in a multi-site community based randomized controlled trial: Project accept (HPTN 043). AIDS Behav. 2012, 16, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethony, J.; Brooker, S.; Albonico, M.; Geiger, S.M.; Loukas, A.; Diemert, D.; Hotez, P.J. Soil-transmitted helminth infections: ascariasis, trichuriasis, and hookworm. Lancet 2006, 367, 1521–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loukas, A.; Maizels, R.M.; Hotez, P.J. The yin and yang of human soil-transmitted helminth infections. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkins, D.B.; Haswell-Elkins, M.; Anderson, R.M. The epidemiology and control of intestinal helminths in the Pulicat Lake region of Southern India. I. Study design and pre-and post-treatment observations on Ascaris lumbricoides infection. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1986, 80, 774–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO guideline on control and elimination of human schistosomiasis; World Health Organization, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, K.R.; Cantera, J.L.; Storey, H.L.; Leader, B.T.; de Los Santos, T. Diagnostic tests to support late-stage control programs for schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminthiases. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluwafemi, F.S.; Oluwadare, T.; Fasuba, B.; Faeji, C.O.; Kukoyi, O.; Oni, I.O.; Uzoayia, S.O. Prevalence of Urinary Schistosomiasis Among School Children In Ago Aduloju Community, Ado LGA of Ekiti State, Nigeria. Niger. J. Parasitol. 2022, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savioli, L.; Gabrielli, A.F.; Montresor, A.; Chitsulo, L.; Engels, D. Schistosomiasis control in Africa: 8 years after World Health Assembly Resolution 54· 19. Parasitology 2009, 136, 1677–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makau-Barasa, L.; Assefa, L.; Aderogba, M.O.; Bell, D.; Solomon, J.; Abba, A.; Agbana, T. Image-Based Awareness Campaign and Community Mobilization in the Control of Schistosomiasis. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osakunor DN, M.; Mduluza, T.; Midzi, N.; Chase-Topping, M.; Mutsaka-Makuvaza, M.J.; Chimponda, T.; Mutapi, F. Dynamics of paediatric urogenital schistosome infection, morbidity and treatment: a longitudinal study among preschool children in Zimbabwe. BMJ Glob. Health 2018, 3, e000661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacQueen, K.M.; Bhan, A.; Frohlich, J.; Holzer, J.; Sugarman, J.; Ethics Working Group of the HIV Prevention Trials Network. Evaluating community engagement in global health research: the need for metrics. BMC Med. Ethics 2015, 16, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Guide for mapping neglected tropical diseases amenable to preventive chemotherapy in the african region; World Health Organization Regional Office for Africa, 2014; Available online: https://www.eliminateschisto.org/sites/gsa/files/content/attachments/2020-02-13/AFRO%20NTD%20Mapping%20Guide%20vFeb2014_Revised%20March%202018.pdf (accessed on 2023 Sep 26).
Table 1.
Percentage compliance for all the 16 LGAs in Ekiti state.
Table 1.
Percentage compliance for all the 16 LGAs in Ekiti state.
| LGA |
Total number of wards |
Total number of expected participants |
Total number of actual participants |
Average number of participants |
Percentage compliance
(%) |
| Ikole |
12 |
600 |
527 |
43.9 |
87.8 |
| Oye |
12 |
600 |
418 |
34.8 |
70.7 |
| Emure |
10 |
500 |
320 |
32.0 |
64.0 |
| Ado |
13 |
650 |
658 |
50.6 |
100.0 |
| Ikere |
11 |
550 |
550 |
50.0 |
100.0 |
| Ekiti East |
12 |
600 |
618 |
51.5 |
100.0 |
| Moba |
11 |
550 |
420 |
38.2 |
76.4 |
| Ilejemeje |
10 |
500 |
546 |
54.6 |
100.0 |
| Ekiti South West |
11 |
550 |
556 |
50.5 |
100.0 |
| Ise/Orun |
10 |
500 |
517 |
51.7 |
100.0 |
| Ekiti West |
11 |
550 |
469 |
42.6 |
85.3 |
| Irepodun/Ifelodun |
11 |
550 |
396 |
36.0 |
72.0 |
| Efon |
10 |
500 |
416 |
41.6 |
83.2 |
| Ijero |
12 |
600 |
303 |
25.3 |
50.5 |
| Gbonyin |
10 |
500 |
447 |
44.7 |
89.4 |
| Ido/Osi |
11 |
550 |
509 |
46.2 |
92.5 |
| Total Percentage Compliance Across the 16 LGAs |
86.7 |
Table 2.
Percentage compliance of 4 sensitive 16 LGAs.
Table 2.
Percentage compliance of 4 sensitive 16 LGAs.
| LGA |
Total number of wards |
Total number of expected participants |
Total number of actual participants |
Average number of participants |
Percentage compliance
(%) |
| Emure |
10 |
500 |
320 |
32.0 |
64.0 |
| Ikere |
11 |
550 |
550 |
50.0 |
100.0 |
| Ekiti South West |
11 |
550 |
556 |
50.5 |
100.0 |
| Ise/Orun |
10 |
500 |
517 |
51.7 |
100.0 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).