Submitted:
03 September 2024
Posted:
04 September 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Relevance and Management of Grouper Fisheries in the SEUS
3. Complexities of Managing Grouper Fisheries
3.1. Multispecies Reef Fish Fisheries
3.2. Protogynous Hermaphroditism
3.3. Deepwater Groupers
4. Recovery of Historically Exploited Stocks?
4.1. Nassau Grouper and Red Hind
4.2. Goliath Grouper
5. Climate Change and Anthropogenically Driven Disturbances
6. Ecosystem Based Considerations in Grouper Assessments
7. Using Co-Produced Data to Assess Grouper Stocks
8. Emerging Techniques to Monitor Grouper Populations
9. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coleman, F.C.; Koenig, C.C. The Effects of Fishing, Climate Change, and Other Anthropogenic Disturbances on Red Grouper and Other Reef Fishes in the Gulf of Mexico. Integr Comp Biol 2010, 50, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.D. Red Grouper (Epinephelus Morio) Shape Faunal Communities via Multiple Ecological Pathways. Diversity 2019, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadovy de Mitcheson, Y.; Craig, M.T.; Bertoncini, A.A.; Carpenter, K.E.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Choat, J.H.; Cornish, A.S.; Fennessy, S.T.; Ferreira, B.P.; Heemstra, P.C.; et al. Fishing Groupers towards Extinction: A Global Assessment of Threats and Extinction Risks in a Billion Dollar Fishery. Fish and Fisheries 2013, 14, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.H. Habitats and Biota of the Gulf of Mexico: Before the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. Habitats and Biota of the Gulf of Mexico: Before the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill 2017, 2, 1–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodyear, C.P.; Schirripa, M.J. The Red Grouper Fishery of the Gulf of Mexico. Southeast Fisheries Center. Miami Laboratory Contribution No. MIA-92/93-75.
- Chester, A.J.; Huntsman, G.R.; Tester, P.A.; Manooch III, C.S. South Atlantic Bight Reef Fish Communities as Represented in Hook-and-Line Catches. Bull Mar Sci 1984, 34, 267–279. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, C.M.; Collins, A.B.; Ruzicka, R. Chapter 3: Distribution and Diversity of Coral Habitat, Fishes, and Associated Fisheries in U.S. Waters of the Gulf of Mexico. Interrelationships between corals and fisheries, ed. Bortone, Stephen A. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA. 2014.
- Sledge, J.H. The Gulf of Mexico: A Maritime History. The University of South Carolina Press. 280pp 2019.
- Saul, S. SEDAR12-DW-11 Quantitative Historical Analysis of the United States and Cuban Gulf of Mexico Red Grouper Commercial Fishery. SEDAR. available at . Available online: https://sedarweb.org/documents/s12dw11-quantitative-historical-analysis-of-the-united-states-and-cuban-gulf-of-mexico-red-grouper-commercial-fishery/2006.
- Sadovy, Y.; Flguerola, M.; Roman, A. Age and Growth of Red Hind Epinephelus Guttatus in Puerto Rico and St. Thomas. Fishery Bulletin 1992, 90, 516–528. [Google Scholar]
- Tuohy, E.; Schärer-Umpierre, M.; Penrod, L.; Appeldoorn, R. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of a Nassau Grouper Fish Spawning Aggregation Located on an Isolated Seamount in Puerto Rico. Aquat Conserv 2023, 33, 1116–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadovy, Y.; Eklund, A.-M. Synopsis of Biological Data on the Nassau Grouper, Epinephelus Striatus (Bloch, 1792), and the Jewfish, E. Itajara (Lichtenstein, 1822). NOAA Technical Report NMFS 146. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/30901999.
- Waterhouse, L.; Heppell, S.A.; Pattengill-Semmens, C. V; Mccoy, C.; Bush, P.; Johnson, B.C.; Semmens, B.X. Recovery of Critically Endangered Nassau Grouper (Epinephelus Striatus) in the Cayman Islands Following Targeted Conservation Actions. PNAS 2020, 117, 1587–1595. [CrossRef]
- CFMC Fishery Management Plan, Final Environmental Impact Statement, and Draft Regulatory Impact Review, for the Shallow-Water Reeffish Fishery of Puerto Rico and the U. S. Virgin Islands. Caribbean Fishery Management Council. available at . Available online: https://caribbeanfmc.com/fishery-management/fishery-management-plans1985.
- NOAA Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act. NOAA. available at 2007, 1–178. Available online: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/topic/laws-policies.
- SAFMC Fishery Management Plan, Regulatory Impact Review, and Final Environmental Impact Statement for the Snapper-Grouper Fishery of the South Atlantic Region. South Atlantic Fishery Management Council. available at https://safmc.net/documents/snapper-grouper-fishery-management-plan/ 1983.
- Caillouet Jr., C. W.; Hart, R.A.; Nance, J.M. Growth Overfishing in the Brown Shrimp Fishery of Texas, Louisiana, and Adjoining Gulf of Mexico EEZ. Fish Res 2008, 92, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GMFMC Environmental Impact Statement and Fishery Management Plan for the Reef Fish Resources of the Gulf of Mexico. Gulf of Mexico Fishery Management Council. available at https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/19629 1981.
- Rosemond, R.C.; Nemeth, R.S.; Heppell, S.A. Demographic Recovery of a Reef Fish Population over 30 Years of Spawning Aggregation Site Protection. Front Mar Sci 2022, 9, 931409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, E.A.; Jennings, C.A.; Nemeth, R.S. Sex Structure and Potential Female Fecundity in a Epinephelus Guttatus Spawning Aggregation: Applying Ultrasonic Imaging. J Fish Biol 2005, 66, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggins Jr, L.G.; Catalano, M.J.; Allen, M.S.; Pine III, W.E.; Walters, C.J. Effects of Cryptic Mortality and the Hidden Costs of Using Length Limits in Fishery Management. Fish and Fisheries 2007, 8, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, J.C.; Pine III, W.E.; Allen, M.S.; Ahrens, R.N.M. Effectiveness of Size Limits and Bag Limits for Managing Recreational Fisheries: A Case Study of the Gulf of Mexico Recreational Gag Fishery. Bull Mar Sci 2013, 89, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulver, J.R. Sink or Swim? Factors Affecting Immediate Discard Mortality for the Gulf of Mexico Commercial Reef Fish Fishery. Fish Res 2017, 188, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runde, B.J.; Buckel, J.A. Descender Devices Are Promising Tools for Increasing Survival in Deepwater Groupers. Marine and Coastal Fisheries 2018, 10, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallings, C.D.; Ayala, O.; Cross, T.A.; Sauls, B. Post-Release Survival of Red Snapper (Lutjanus Campechanus) and Red Grouper (Epinephelus Morio) Using Different Barotrauma Mitigation Methods. Fish Res 2023, 264, 106717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runde, B.J.; Michelot, T.; Bacheler, N.M.; Shertzer, K.W.; Buckel, J.A. Assigning Fates in Telemetry Studies Using Hidden Markov Models: An Application to Deepwater Groupers Released with Descender Devices. N Am J Fish Manag 2020, 40, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA Fisheries of the Caribbean, Gulf of Mexico, and South Atlantic; Snapper-Grouper Fishery off the Southern Atlantic Region; Regulatory Amendment 29. NOAA. available at https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2020/06/15/2020-11916/fisheries-of-the-caribbean-gulf-of-mexico-and-south-atlantic-snapper-grouper-fishery-off-the 2020.
- NOAA Fisheries of the Caribbean, Gulf of Mexico, and South Atlantic; Reef Fish Resources of the Gulf of Mexico; Requirement for a Descending Device or Venting Tool. NOAA. available at https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2022/01/14/2022-00720/fisheries-of-the-caribbean-gulf-of-mexico-and-south-atlantic-reef-fish-resources-of-the-gulf-of 2022.
- Coleman, F.C.; Figueira, W.F.; Ueland, J.S.; Crowder, L.B. The Impact of United States Recreational Fisheries on Marine Fish Populations. Science (1979) 2004, 305, 1958–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shertzer, K.; Crosson, S.; Williams, E.; Cao, J.; DeVictor, R.; Dumas, C.; Nesslage, G. Fishery Management Strategies for Red Snapper in the Southeastern U.S. Atlantic: A Spatial Population Model to Compare Approaches. N Am J Fish Manag 2024, 44, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA Fisheries of the Caribbean, Gulf of Mexico, and South Atlantic; Reef Fish Fishery of the Gulf of Mexico; Amendment 53. NOAA. available at https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2021/12/09/2021-26504/fisheries-of-the-caribbean-gulf-of-mexico-and-south-atlantic-reef-fish-fishery-of-the-gulf-of-mexico 2021.
- NOAA Fisheries of the Caribbean, Gulf of Mexico, and South Atlantic; Reef Fish Resources of the Gulf of Mexico; Amendment 56. NOAA. available at https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2024/05/10/2024-10208/fisheries-of-the-caribbean-gulf-of-mexico-and-south-atlantic-reef-fish-resources-of-the-gulf-of 2024.
- Murua, H. Fish Reproduction Assortment: A Wonderful Diversity. Environ Biol Fishes 2014, 97, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, R.R. Sex Change and the Size-Advantage Model. Trends Ecol Evol 1988, 3, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beverton, R.J.H.; Holt, S.J. On the Dynamics of Exploited Fish Populations. Springer Dordrecht 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barneche, D.R.; Robertson, D.R.; White, C.R.; Marshall, D.J. Fish Reproductive-Energy Output Increases Disproportionately with Body Size. Science (1979) 2018, 360, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hixon, M.A.; Johnson, D.W.; Sogard, S.M. BOFFFFs: On the Importance of Conserving Old-Growth Age Structure in Fishery Populations. ICES Journal of Marine Science 2014, 71, 2171–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa-Salazar, K.R.; Wyanski, D.M.; Bubley, W.J.; Klibansky, N. Effects of Age and Size on Spawning and Egg Production in Gag and Scamp Grouper off the Southeastern United States. ICES Journal of Marine Science 2020, 77, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, L.H.; Murphy, M.D.; Godcharles, M.F.; Mitchell, M.E. Age, Growth, and Reproduction of Jewfish Epinephelus Itajara in the Eastern Gulf of Mexico. Fishery Bulletin 1992, 90, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Murie, D.J.; Parkyn, D.C.; Koenig, C.C.; Coleman, F.C.; Malinowski, C.R.; Cusick, J.A.; Ellis, R.D. Age, Growth, and Functional Gonochorism with a Twist of Diandric Protogyny in Goliath Grouper from the Atlantic Coast of Florida. Fishes 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA Status of Stocks 2023 Annual Report to Congress on the Status of U.S. Fisheries. NOAA. available at https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/s3/2024-04/2023SOS-final.pdf 2024.
- Crabtree, R.E.; Bullock, L.H. Age, Growth, and Reproduction of Black Grouper, Mycteroperca Bonaci, in Florida Waters. Fishery Bulletin 1998, 96, 735–753. [Google Scholar]
- Renán, X.; Brulé, T.; Galindo-Cortes, G.; Colás-Marrufo, T. Age-Based Life History of Three Groupers in the Southern Gulf of Mexico. J Fish Biol 2022, 101, 857–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, M.L.; Potts, J.C.; Carr, D.R. Age, Growth and Natural Mortality of Coney (Cephalopholis Fulva) from the Southeastern United States. PeerJ 2015, 2015, e825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortoletto, E.; Filho, G.; Ester, M.; Simoni, R.; Gomes, M.; Rêgo, D.O.; Lúcia, M.; De Araújo, G.; Guilherme, P.; De Oliveira, V.; et al. Reproductive Biology of Cephalopholis Fulva (Linneus, 1758) Caught in the North Coast of Pernambuco. Panam J Aquat Sci 2019, 14, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, P.J.; Collins, M.R. Age, Growth and Age at Maturity of Gag, Mycteroperca Microlepis, from the Southeastern United States during 1994-1995. Bull Mar Sci 2000, 66, 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Lowerre-Barbieri, S.; Menendez, H.; Bickford, J.; Switzer, T.S.; Barbieri, L.; Koenig, C. Testing Assumptions about Sex Change and Spatial Management in the Protogynous Gag Grouper, Mycteroperca Microlepis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 2020, 639, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEDAR SEDAR 72 Gulf of Mexico Gag Grouper Final Stock Assessment Report. SEDAR, North Charleston SC. 319 pp. available online at: http://sedarweb.org/sedar-72 2021.
- SEDAR SEDAR 71 South Atlantic Gag Stock Assessment Report. SEDAR, North Charleston, SC. 164 pp. available online at: http://sedarweb.org/sedar-71 2021.
- Burton, M.L.; Potts, J.C.; Ostrowski, A.D.; Shertzer, K.W. Age, Growth, and Natural Mortality of Graysby, Cephalopholis Cruentata, from the Southeastern United States. Fishes 2019, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckhurst, B.E.; Dean, J.M. Age Estimates of Two Large Misty Grouper, Epinephelus Mystacinus (Serranidae) from Bermuda with a Comparison of the Age of Tropical Groupers in the Western Atlantic. Gulf Caribb Res 2009, 21, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEDAR SEDAR 61 Stock Assessment Report - Gulf of Mexico Red Grouper. SEDAR, North Charleston, SC. available online at: https://sedarweb.org/assessments/sedar-61 2019.
- SEDAR SEDAR 53 - South Atlantic Red Grouper Assessment Report. SEDAR, North Charleston, SC. 159 pp. available online at: http://sedarweb.org/sedar-53 2017.
- Sadovy, Y.; Rosario, A.; Román, A. Reproduction in an Aggregating Grouper, the Red Hind, Epinephelus Guttatus. Environ Biol Fishes 1994, 41, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, M.L.; Potts, J.C.; Carr, D.R. Age, Growth, and Natural Mortality of Rock Hind, Epinephelus Adscensionis, from the Gulf of Mexico. Bull Mar Sci 2012, 88, 903–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, E.T.; Downes, K.J.; Richardson, A.; Arkhipkin, A.; Brickle, P.; Brown, J.; Mrowicki, R.J.; Shcherbich, Z.; Weber, N.; Weber, S.B. Life-History Strategies of the Rock Hind Grouper Epinephelus Adscensionis at Ascension Island. J Fish Biol 2017, 91, 1549–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi-Carlson, L.A.; Cook, M.; Lyon, H.; Barnett, B.; Bullock, L. A Description of Age, Growth, and Reproductive Life History Traits of Scamps from the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Marine and Coastal Fisheries 2012, 4, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEDAR SEDAR 68 South Atlantic Scamp Stock Assessment Report. SEDAR, North Charleston, SC. 162 pp. available online at: https://sedarweb.org/assessments/sedar-68/ 2022.
- Sanchez, P.J.; Pinsky, J.P.; Rooker, J.R. Bomb Radiocarbon Age Validation of Warsaw Grouper and Snowy Grouper. Fisheries (Bethesda) 2019, 44, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmos, K.J.; Wyanski, D.M.; White, D.B.; Mikell, P.P. Temporal Changes in the Life History of Snowy Grouper (Hyporthodus Niveatus) off North and South Carolina, and Factors That Influence Spawning Dynamics. Fishery Bulletin 2019, 117, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEDAR SEDAR 36 Update South Atlantic Snowy Grouper Stock Assessment Report. SEDAR, North Charleston, SC. 118 pp. available online at https://sedarweb.org/assessments/sedar-36/ 2021.
- Andrews, A.H.; Barnett, B.K.; Allman, R.J.; Moyer, R.P.; Trowbridge, H.D. Great Longevity of Speckled Hind (Epinephelus Drummondhayi), a Deep-Water Grouper, with Novel Use of Postbomb Radiocarbon Dating in the Gulf of Mexico. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 2013, 70, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziskin, G.L.; Harris, P.J.; Wyanski, D.M.; Reichert, M.J.M. Indications of Continued Overexploitation of Speckled Hind along the Atlantic Coast of the Southeastern United States. Trans Am Fish Soc 2011, 140, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.B.; Wyanski, D.M.; Eleby, B.M.; Lilyestrom, C.G. Tiger Grouper (Mycteroperca Tigris): Profile of a Spawning Aggregation. Bull Mar Sci 2002, 70, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero-Arango, D.; Brulé, T.; Nóh-Quiñones, V.; Colás-Marrufo, T.; Pérez-Díaz, E. Reproductive Biology of the Tiger Grouper in the Southern Gulf of Mexico. Trans Am Fish Soc 2013, 142, 282–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.; Fitzhugh, G.R.; Franks, J.S. Validation of Yellowedge Grouper, Epinephelus Flavolimbatus, Age Using Nuclear Bomb-Produced Radiocarbon. Environ Biol Fishes 2009, 86, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, L.H.; Godcharles, M.F.; Crabtree, R.E. Reproduction of Yellowedge Grouper, Epinephelus Flavolimbatus, from the Eastern Gulf of Mexico. Bull Mar Sci 1996, 59, 216–224. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, M.L.; Potts, J.C.; Carr, D.R. Age, Growth, and Natural Mortality of Yellowfin Grouper (Mycteroperca Venenosa) from the Southeastern United States. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cagide, A.; García, T. Reproducción de Mycteroperca Bonaci y Mycteroperca Venenosa (Pisces: Serranidae) En La Plataforma Cubana. Rev Biol Trop 1996, 44, 771–780. [Google Scholar]
- Bullock, L.H.; Murphy, M.D. Aspects of the Life History of the Yellowmouth Grouper, Mycteroperca Interstitialis, in the Eastern Gulf of Mexico. Bull Mar Sci 1994, 55, 30–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, P.J.; Rooker, J.R. Age, Growth, and Mortality of Threatened Warsaw Grouper, Hyporthodus Nigritus, in the Gulf of Mexico. Fish Res 2021, 243, 106097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, F.C.; Koenig, C.C.; Collins, L.A. Reproductive Styles of Shallow-Water Groupers (Pisces: Serranidae) in the Eastern Gulf of Mexico and the Consequences of Fishing Spawning Aggregations. Environ Biol Fishes 1996, 47, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, E.A.; White, J.W.; Botsford, L.W. Accurate Assessment of Marine Protected Area Success Depends on Metric and Spatiotemporal Scale of Monitoring. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 2013, 489, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, A.; Pressey, R.L.; Jones, R.E.; Álvarez-Romero, J.G.; Cinner, J.E. Optimizing Enforcement and Compliance in Offshore Marine Protected Areas: A Case Study from Cocos Island, Costa Rica. Oryx 2016, 50, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harford, W.J.; Sagarese, S.R.; Karnauskas, M. Coping with Information Gaps in Stock Productivity for Rebuilding and Achieving Maximum Sustainable Yield for Grouper–Snapper Fisheries. Fish and Fisheries 2019, 20, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, P.B.; Williams, E.H.; Shertzer, K.W. When Can We Reliably Estimate the Productivity of Fish Stocks? Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 2010, 67, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shertzer, K.W.; Conn, P.B. Spawner-Recruit Relationships of Demersal Marine Fishes: Prior Distribution of Steepness. Bull Mar Sci 2012, 88, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA Fisheries of the Caribbean, Gulf of Mexico, and South Atlantic; Reef Fish and Red Drum Fisheries of the Gulf of Mexico; Amendments 48/5. NOAA. available at https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2022/06/08/2022-12339/fisheries-of-the-caribbean-gulf-of-mexico-and-south-atlantic-reef-fish-and-red-drum-fisheries-of-the 2022.
- SEDAR SEDAR 85 Stock Assessment Report - Gulf of Mexico Yellowedge Grouper. SEDAR, North Charleston, SC. 267 pp. available online at: https://sedarweb.org/assessments/sedar-85/ 2023.
- Gulf Fisheries Branch SEDAR 85 Gulf of Mexico Yellowedge Grouper Operational Assessment - Additional Projections. SEDAR. available at https://sedarweb.org/documents/sedar-85-gulf-of-mexico-yellowedge-grouper-operational-assessment-additional-projections/ 2024.
- Brooks, E.N.; Shertzer, K.W.; Gedamke, T.; Vaughan, D.S. Stock Assessment of Protogynous Fish: Evaluating Measures of Spawning Biomass Used to Estimate Biological Reference Points. Fishery Bulletin 2008, 106, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, F.C.; Koenig, C.C.; Huntsman, G.R.; Musick, J.A.; Eklund, A.M.; McGovern, J.C.; Sedberry, G.R.; Chapman, R.W.; Grimes, C.B. Long-Lived Reef Fishes: The Grouper-Snapper Complex. Fisheries (Bethesda) 2000, 25, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, A.B.; Harter, S.L.; Ross, S.W.; Schobernd, C.M.; Runde, B.J.; Rudershausen, P.J.; Johnson, K.H.; Shertzer, K.W.; Bacheler, N.M.; Buckel, J.A.; et al. Four Decades of Reef Observations Illuminate Deep-Water Grouper Hotspots. Fish and Fisheries 2021, 22, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GMFMC Fisherman Feedback: Yellowedge Grouper Response Summary. Gulf of Mexico Fishery Management Council. available at https://gulfcouncil.org/wp-content/uploads/Fisherman-Feedback_Yellowedge-Grouper_2024_Final.pdf 2024.
- Sanchez, P.J.; Zapp Sluis, M.; Pinsky, J.; Miller, N.R.; Rooker, J.R. Population Structure and Regional Connectivity of Young Snowy Grouper in the Gulf of Mexico and Western Atlantic Ocean. Marine and Coastal Fisheries 2022, 14, e10119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA Fisheries of the Caribbean, Gulf of Mexico, and South Atlantic; Snapper-Grouper Fishery off the Southern Atlantic States; Amendment 14. NOAA. available at https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2009/01/13/E9-497/fisheries-of-the-caribbean-gulf-of-mexico-and-south-atlantic-snapper-grouper-fishery-off-the 2009.
- Bacheler, N.M.; Schobernd, C.M.; Harter, S.L.; David, A.W.; Sedberry, G.R.; Kellison, G.T. No Evidence of Increased Demersal Fish Abundance Six Years after Creation of Marine Protected Areas along the Southeast United States Atlantic Coast. Bull Mar Sci 2016, 92, 447–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runde, B.J.; Buckel, J.A.; Rudershausen, P.J.; Mitchell, W.A.; Ebert, E.; Cao, J.; Taylor, J.C. Evaluating the Effects of a Deep-Water Marine Protected Area a Decade after Closure: A Multifaceted Approach Reveals Equivocal Benefits to Reef Fish Populations. Front Mar Sci 2021, 8, 775376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadovy, Y. The Case of the Disappearing Grouper: Epinephelus Striatus, the Nassau Grouper, in the Caribbean and Western Atlantic. Proceedings of the 45th Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute 1999.
- CFMC Amendment Number 1 to the Fishery Management Plan for the Shallow-Water Reeffish Fishery, Preliminary Environmental Assessment and Regulatory Impact Review. Caribbean Fishery Management Council. available at https://caribbeanfmc.com/images/pdf-files/RF%20Amend%201%20ok.pdf 1990.
- NOAA Nassau Grouper Recovery Outline. NOAA. available at. Available online: https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/s3//dam-migration/nassau-grouper-recovery-outline.pdf2018.
- Jackson, A.M.; Semmens, B.X.; De Mitcheson, Y.S.; Nemeth, R.S.; Heppell, S.A.; Bush, P.G.; Aguilar-Perera, A.; Claydon, J.A.B.; Calosso, M.C.; Sealey, K.S.; et al. Population Structure and Phylogeography in Nassau Grouper (Epinephelus Striatus), a Mass-Aggregating Marine Fish. PLoS One 2014, 9, e97508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms-Tuohy, C.; Schärer, M.; Ruiz, H.; Tuohy, E.; Figuerola, M. Identifying Critical Habitats of Juvenile Nassau Grouper (Epinephelus Striatus) in Puerto Rico. Final Report. Caribbean Fishery Management Council. 42pp 2022. [CrossRef]
- Legare, B.; Maize, K.; Nemeth, R. Juvenile Nassau Grouper (Epinephelus Striatus) Utilization of Nearshore Habitats with Evidence of Adult Connectivity to a Spawning Aggregation Site. Proceedings of the 63rd Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute 2011.
- Aguilar-Perera, A.; Schärer, M.T.; Nemeth, M. Occurrence of Juvenile Nassau Grouper, Epinephelus Striatus (Teleostei: Serranidae), off Mona Island, Puerto Rico: Considerations of Recruitment Potential. Caribb J Sci 2006, 42, 264–267. [Google Scholar]
- Coffill-Rivera, M.E.; Neal, J.W.; Rodríguez-Ferrer, G.; Lilyestrom, C.G. Using Lessons Learned from a Multidecadal Intercept Survey of Puerto Rico Spear Fishers to Improve Data Collection in the U.S. Caribbean. N Am J Fish Manag 2024, 44, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, R.; De Mitcheson, Y.S.; Aguilar-Perera, A. The Role of Local Ecological Knowledge in the Conservation and Management of Reef Fish Spawning Aggregations. Reef Fish Spawning Aggregations: Biology, Research and Management 2012, 331–369. [CrossRef]
- Beets, J.; Friedlander, A. Stock Analysis and Management Strategies for Red Hind, Epinephelus Guttatus in the U.S. Virgin Islands. Proceedings of the 42nd Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute 1992, 66–79.
- Sadovy, Y.; Figuerola, M. The Status of the Red Hind Fishery in Puerto Rico and St. Thomas as Determined by Yield-per-Recruit Analysis. Proceedings of the 42nd Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute 1992, 23–38.
- Sabat, A.M.; Hernández, E.A.; Toledo, C.G. Demographic Analysis of the Effect of Fishing Mortality on the Red Hind (Epinephelus Guttatus) Population in Western Puerto Rico. Proceedings of the 51st Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute 2000, 169–181.
- Eristhee, N.; Kadison, E.; Murray, P.A.; Llewellyn, A. Preliminary Investigations into the Red Hind Fishery in the British Virgin Islands. 57th Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute 2006, 374–384.
- Nemeth, R.S. Population Characteristics of a Recovering US Virgin Islands Red Hind Spawning Aggregation Following Protection. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 2005, 286, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, R.S.; Blondeau, J.; Herzlieb, S.; Kadison, E. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Movement and Migration at Spawning Aggregations of Red Hind, Epinephelus Guttatus, in the U.S. Virgin Islands. Environ Biol Fishes 2007, 78, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, R.S.; Kadison, E.; Jossart, J.; Shivji, M.; Wetherbee, B.M.; Matley, J.K. Acoustic Telemetry Provides Insights for Improving Conservation and Management at a Spawning Aggregation Site of the Endangered Nassau Grouper (Epinephelus Striatus). Front Mar Sci 2023, 10, 1154689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, C.R.; Ray, G.C. A Field Guide to Atlantic Coast Fishes: North America. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt 1986. [Google Scholar]
- McClenachan, L. Historical Declines of Goliath Grouper Populations in South Florida, USA. Endanger Species Res 2009, 7, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardinger, L.C.; Carvalho Marenzi, R.; Andrade Bertoncini, Á.; Pereira Medeiros, R.; Hostim-Silva, M. Local Ecological Knowledge on the Goliath Grouper Epinephelus Itajara (Teleostei: Serranidae) in Southern Brazil. Neotropical Ichthyology 2006, 4, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiros, J.P.; Coleman, F.C. West African Goliath Grouper: Where Are They between Senegal and Angola? Fishes 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, C.C.; Coleman, F.C.; Kingon, K. Pattern of Recovery of the Goliath Grouper Epinephelus Itajara Population in the Southeastern US. Bull Mar Sci 2011, 87, 891–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, C.C.; Coleman, F.C.; Malinowski, C.R. Atlantic Goliath Grouper of Florida: To Fish or Not to Fish. Fisheries (Bethesda) 2020, 45, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, C.; Coleman, F.; Koenig, C.; Locascio, J.; Murie, D. Are Atlantic Goliath Grouper, Epinephelus Itajara, Establishing More Northerly Spawning Sites? Evidence from the Northeast Gulf of Mexico. Bull Mar Sci 2019, 95, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shideler, G.S.; Carter, D.W.; Liese, C.; Serafy, J.E. Lifting the Goliath Grouper Harvest Ban: Angler Perspectives and Willingness to Pay. Fish Res 2015, 161, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, F.C.; Nunes, J.A.C.C.; Bertoncini, Á.A.; Bueno, L.S.; Freitas, M.O.; Borgonha, M.; Leite, J.R.; Lima-Júnior, M.J.C.A.; Ferreira, B.; Bentes, B.; et al. Controversial Opening of a Limited Fishery for Atlantic Goliath Grouper in the United States: Implications for Population Recovery. Mar Policy 2023, 155, 105752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindegren, M.; Brander, K. Adapting Fisheries and Their Management To Climate Change: A Review of Concepts, Tools, Frameworks, and Current Progress Toward Implementation. Reviews in Fisheries Science and Aquaculture 2018, 26, 400–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellinger, E.L.; Szuwalski, C.; Punt, A.E. The Robustness of Our Assumptions about Recruitment: A Re-Examination of Marine Recruitment Dynamics with Additional Data and Novel Methods. Fish Res 2024, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szuwalski, C.S.; Vert-Pre, K.A.; Punt, A.E.; Branch, T.A.; Hilborn, R. Examining Common Assumptions about Recruitment: A Meta-Analysis of Recruitment Dynamics for Worldwide Marine Fisheries. Fish and Fisheries 2015, 16, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimova, A.; Núñez-Riboni, I.; Kempf, A.; Taylor, M.H. Spatially-Resolved Influence of Temperature and Salinity on Stock and Recruitment Variability of Commercially Important Fishes in the North Sea. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0161917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogstad, B.; Dingsør, G.E.; Ingvaldsen, R.B.; Gjøsæter, H. Changes in the Relationship between Sea Temperature and Recruitment of Cod, Haddock and Herring in the Barents Sea. Marine Biology Research 2013, 9, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.M.; Sadler, P.; Hoenig, J.M. Evaluating a Possible New Paradigm for Recruitment Dynamics: Predicting Poor Recruitment for Striped Bass (Morone Saxatilis) from an Environmental Variable. Fish Res 2022, 252, 106329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brulé, T.; Renán, X.; Colás-Marrufo, T. Potential Impact of Climate Change on Fish Reproductive Phenology: A Case Study in Gonochoric and Hermaphrodite Commercially Important Species from the Southern Gulf of Mexico. Fishes 2022, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lema, S.C.; Luckenbach, J.A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Housh, M.J. Fish Reproduction in a Warming World: Vulnerable Points in Hormone Regulation from Sex Determination to Spawning. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2024, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, L.A.; Chalde, T.; Elisio, M.; Strüssmann, C.A. Effects of Global Warming on Fish Reproductive Endocrine Axis, with Special Emphasis in Pejerrey Odontesthes Bonariensis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 2013, 192, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzhugh, G.R.; Koenig, C.C.; Coleman, F.C.; Grimes, C.B.; Sturges III, W. Spatial and Temporal Patterns in Fertilization of Young Gag (Mycteroperca Microlepis) along the West Florida Shelf. Bull Mar Sci 2005, 77, 377–396. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, M.R.; C Hatfield, E.M.; Dickey-Collas, M.; Falkenhaug, T.; Gallego, A.; Gröger, J.; Licandro, P.; Llope, M.; Munk, P.; Röckmann, C.; et al. Recruitment in a Changing Environment: The 2000s North Sea Herring Recruitment Failure. ICES Journal of Marine Science 2009, 66, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacheler, N.M.; Ballenger, J.C. Decadal-Scale Decline of Scamp (Mycteroperca Phenax) Abundance along the Southeast United States Atlantic Coast. Fish Res 2018, 204, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacheler, N.M.; Klibansky, N.; Bubley, W.J.; Smart, T.I. Low Recruitment Drives the Decline of Red Porgy (Pagrus Pagrus) along the Southeast USA Atlantic Coast: Inferences from Fishery-Independent Trap and Video Monitoring. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0286078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, K.J.; Shertzer, K.W.; Craig, J.K.; Williams, E.H. Correlations in Recruitment Patterns of Atlantic Reef Fishes off the Southeastern United States Based on Multi-Decadal Estimates from Stock Assessments. Reg Stud Mar Sci 2023, 57, 102736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, C.W.; Falk-Petersen, J. Habitat-Fisheries Interactions: A Missing Link? ICES Journal of Marine Science 2008, 65, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minello, T.J.; Able, K.W.; Weinstein, M.P.; Hays, C.G. Salt Marshes as Nurseries for Nekton: Testing Hypotheses on Density, Growth and Survival through Meta-Analysis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 2003, 246, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.B.; Heck, K.L.; Able, K.W.; Childers, D.L.; Eggleston, D.B.; Gillanders, B.M.; Halpern, B.; Hays, C.G.; Hoshino, K.; Minello, T.J.; et al. The Identification, Conservation, and Management of Estuarine and Marine Nurseries for Fish and Invertebrates. Bioscience 2001, 51, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, B.G.W.; Van Den Brink, F.W.B.; Nienhuis, P.H. Habitat Loss as the Main Cause of the Slow Recovery of Fish Faunas of Regulated Large Rivers in Europe: The Transversal Floodplain Gradient. River Res Appl 2004, 20, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamp, T.; West, E.; Robbins, T.; Plenty, S.; Sheehan, E. Large-Scale Historic Habitat Loss in Estuaries and Its Implications for Commercial and Recreational Fin Fisheries. ICES Journal of Marine Science 2022, 79, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, J.L.; Peebles, E.B. Lifetime-Scale Ontogenetic Movement and Diets of Red Grouper Inferred Using a Combination of Instantaneous and Archival Methods. Environ Biol Fishes 2022, 105, 1887–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, R.H.; Zheng, L.; Peebles, E. Gag Grouper Larvae Pathways on the West Florida Shelf. Cont Shelf Res 2014, 88, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, C.C.; Coleman, F.C.; Eklund, A.-M.; Schull, J.; Ueland, J. Mangroves Are Essential Nursery Habitat for Goliath Grouper (Epinephelus Itajara). Bull Mar Sci 2007, 80, 567–586. [Google Scholar]
- Casey, J.P.; Poulakis, G.R.; Stevens, P.W. Habitat Use by Juvenile Gag, Mycteroperca Microlepis (Pisces: Serranidae), in Subtropical Charlotte Harbor, Florida (USA). Gulf Caribb Res 2007, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switzer, T.S.; Keenan, S.F.; Stevens, P.W.; McMichael, R.H.; MacDonald, T.C. Incorporating Ecology into Survey Design: Monitoring the Recruitment of Age-0 Gags in the Eastern Gulf of Mexico. N Am J Fish Manag 2015, 35, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardou, R.; Osland, M.J.; Scyphers, S.; Shepard, C.; Aerni, K.E.; Alemu I, J.B.; Crimian, R.; Day, R.H.; Enwright, N.M.; Feher, L.C.; et al. Rapidly Changing Range Limits in a Warming World: Critical Data Limitations and Knowledge Gaps for Advancing Understanding of Mangrove Range Dynamics in the Southeastern USA. Estuaries and Coasts 2023 46:5 2023, 46, 1123–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, R.C. Scaling up: Predicting the Impacts of Climate Change on Seagrass Ecosystems. Estuaries and Coasts 2021, 44, 558–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.W.; Flaherty-Walia, K.; Scolaro, S.; Burke, M.C.; Furman, B.T.; Karlen, D.J.; Pratt, C.; Anastasiou, C.J.; Sherwood, E.T. Hot and Fresh: Evidence of Climate-Related Suboptimal Water Conditions for Seagrass in a Large Gulf Coast Estuary. Estuaries and Coasts 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarbro, L.A.; Carlson, P.R.; Johnsey, E. Extensive and Continuing Loss of Seagrasses in Florida’s Big Bend (USA). Environ Manage 2024, 73, 876–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodemann, J.R.; James, W.R.; Rehage, J.S.; Baktoft, H.; Costa, S. V.; Ellis, R.D.; Gonzalez, L.; Santos, R.O. Residency and Fine-Scale Habitat Use of Juvenile Goliath Grouper (Epinephelus Itajara) in a Mangrove Nursery. Bull Mar Sci 2023, 99, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, D.P.; Berens McCabe, E.J.; Camilleri, S.A.; Gannon, J.G.; Brueggen, M.K.; Barleycorn, A.A.; Palubok, V.I.; Kirkpatrick, G.J.; Wells, R.S. Effects of Karenia Brevis Harmful Algal Blooms on Nearshore Fish Communities in Southwest Florida. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 2009, 378, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, M.; Kaplan, D.; Milbrandt, E.C.; Tomasko, D.; Huffaker, R.; Angelini, C. Nitrogen-Enriched Discharges from a Highly Managed Watershed Intensify Red Tide (Karenia Brevis) Blooms in Southwest Florida. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 827, 154149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagarese, S.R.; Gray, A.M.; Ainsworth, C.H.; Chagaris, D.D.; Mahmoudi, B. SEDAR42-AW-01 Red Tide Mortality on Red Grouper (Epinephelus Morio) between 1980 and 2009 on the West Florida Shelf. SEDAR, North Charleston, SC. 12 pp. available at https://sedarweb.org/documents/sedar-42-aw-01-red-tide-mortality-on-red-grouper-epinephelus-morio-between-1980-and-2009-on-the-west-florida-shelf/ 2015.
- Walter III, J.F.; Sagarese, S.R.; Harford, W.J.; Grüss, A.; Stumpf, R.P.; Christman, M.C. SEDAR42-RW-02 Assessing the Impact of the 2014 Red Tide Event on Red Grouper (Epinephelus Morio) in the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. SEDAR, North Charleston, SC. 13 pp. available at https://sedarweb.org/documents/sedar-42-rw-02-assessing-the-impact-of-the-2014-red-tide-event-on-red-grouper-epinephelus-morio-in-the-northeastern-gulf-of-mexico/ 2015.
- Ainsworth, C.H.; Paris, C.B.; Perlin, N.; Dornberger, L.N.; Patterson III, W.F.; Chancellor, E.; Murawski, S.; Hollander, D.; Daly, K.; Romero, I.C.; et al. Impacts of the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill Evaluated Using an End-to-End Ecosystem Model. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0190840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, S.A.; Schwing, P.T.; Patterson III, W.F.; Sutton, T.T.; Montagna, P.A.; Milligan, R.J.; Joye, S.B.; Thomas, L.; Kilborn, J.P.; Paris, C.B.; et al. Vulnerability and Resilience of Living Marine Resources to the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill: An Overview. Front Mar Sci 2023, 10, 1202250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson III, W.F.; Robinson, K.L.; Barnett, B.K.; Campbell, M.D.; Chagaris, D.C.; Chanton, J.P.; Daly, K.L.; Hanisko, D.S.; Hernandez, F.J.; Murawski, S.A.; et al. Evidence of Population-Level Impacts and Resiliency for Gulf of Mexico Shelf Taxa Following the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. Front Mar Sci 2023, 10, 1198163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokesbury, K.D.E.; Cassidy, K.; Lowery, T.M. Constructing a Baseline Groundfish Trawl Survey for an Offshore Windfarm Development Area. Marine and Coastal Fisheries 2023, 15, e10267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jech, J.M.; Lipsky, A.; Moran, P.; Matte, G.; Diaz, G. Fish Distribution in Three Dimensions around the Block Island Wind Farm as Observed with Conventional and Volumetric Echosounders. Marine and Coastal Fisheries 2023, 15, e10265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoeck, R. V.; Rowell, T.J.; Dean, M.J.; Rice, A.N.; Van Parijs, S.M. Comparing Atlantic Cod Temporal Spawning Dynamics across a Biogeographic Boundary: Insights from Passive Acoustic Monitoring. Marine and Coastal Fisheries 2023, 15, e10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO The Ecosystem Approach to Fisheries. FAO Technical Guidelines for Responsible Fisheries. No. 4, suppl. 2. Rome, FAO. 112 p. available at https://www.fao.org/in-action/globefish/publications/details-publication/en/c/346126/ 2003, 112.
- Howell, D.; Schueller, A.M.; Bentley, J.W.; Buchheister, A.; Chagaris, D.; Cieri, M.; Drew, K.; Lundy, M.G.; Pedreschi, D.; Reid, D.G.; et al. Combining Ecosystem and Single-Species Modeling to Provide Ecosystem-Based Fisheries Management Advice within Current Management Systems. Front Mar Sci 2021, 7, 607831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, M.A.; Link, J.S.; Grezlik, M.; Cadrin, S.; Fay, G.; Lynch, P.; Townsend, H.; Methot, R.D.; Adams, G.D.; Blackhart, K.; et al. Increasing the Uptake of Multispecies Models in Fisheries Management. ICES Journal of Marine Science 2023, 80, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA NOAA Fisheries Policy 01-120: Ecosystem-Based Fisheries Management Policy. NOAA. available at https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/resource/document/ecosystem-based-fisheries-management-policy 2016.
- Anstead, K.A.; Drew, K.; Chagaris, D.; Schueller, A.M.; McNamee, J.E.; Buchheister, A.; Nesslage, G.; Uphoff, J.H.; Wilberg, M.J.; Sharov, A.; et al. The Path to an Ecosystem Approach for Forage Fish Management: A Case Study of Atlantic Menhaden. Front Mar Sci 2021, 8, 607657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüss, A.; Rose, K.A.; Simons, J.; Ainsworth, C.H.; Babcock, E.A.; Chagaris, D.D.; De Mutsert, K.; Froeschke, J.; Himchak, P.; Kaplan, I.C.; et al. Recommendations on the Use of Ecosystem Modeling for Informing Ecosystem-Based Fisheries Management and Restoration Outcomes in the Gulf of Mexico. Marine and Coastal Fisheries 2017, 9, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seara, T.; Williams, S.M.; Acevedo, K.; Garcia-Molliner, G.; Tzadik, O.; Duval, M.; Cruz-Motta, J.J. Development and Analyses of Stakeholder Driven Conceptual Models to Support the Implementation of Ecosystem-Based Fisheries Management in the U.S. Caribbean. PLoS One 2024, 19, e0304101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagaris, D.; Sagarese, S.; Farmer, N.; Mahmoudi, B.; de Mutsert, K.; VanderKooy, S.; Patterson, W.F.; Kilgour, M.; Schueller, A.; Ahrens, R.; et al. Management Challenges Are Opportunities for Fisheries Ecosystem Models in the Gulf of Mexico. Mar Policy 2019, 101, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagaris, D.; Drew, K.; Schueller, A.; Cieri, M.; Brito, J.; Buchheister, A. Ecological Reference Points for Atlantic Menhaden Established Using an Ecosystem Model of Intermediate Complexity. Front Mar Sci 2020, 7, 606417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagaris, D.; Sinnickson, D. SEDAR61-WP-06 An Index of Red Tide Mortality on Red Grouper in the Eastern Gulf of Mexico. SEDAR, North Charleston, SC. 16 pp. available at https://sedarweb.org/documents/sedar-61-wp-06-an-index-of-red-tide-mortality-on-red-grouper-in-the-eastern-gulf-of-mexico/ 2018.
- Vilas, D.; Chagaris, D.; Buczkowski, J. SEDAR72-WP-01 Red Tide Mortality on Gag Grouper from 2002-2018 Generated by an Ecospace Model of the West Florida Shelf. SEDAR, North Charleston, SC. 17 pp. available at https://sedarweb.org/documents/sedar-72-wp-01-red-tide-mortality-on-gag-grouper-from-2002-2018-generated-by-an-ecospace-model-of-the-west-florida-shelf/ 2020.
- Pita, C.; Pierce, G.J.; Theodossiou, I. Stakeholders’ Participation in the Fisheries Management Decision-Making Process: Fishers’ Perceptions of Participation. Mar Policy 2010, 34, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinson, S.; Wilson, D.C.; Galiay, P.; Deas, B. Engaging Stakeholders in Fisheries and Marine Research. Mar Policy 2011, 35, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, J.W.; Hines, D.E.; Borrett, S.R.; Serpetti, N.; Hernandez-Milian, G.; Fox, C.; Heymans, J.J.; Reid, D.G. Combining Scientific and Fishers’ Knowledge to Co-Create Indicators of Food Web Structure and Function. ICES Journal of Marine Science 2019, 76, 2218–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, S.J.; Nguyen, V.M.; Chapman, J.M.; Reid, A.J.; Landsman, S.J.; Young, N.; Hinch, S.G.; Schott, S.; Mandrak, N.E.; Semeniuk, C.A.D. Knowledge Co-Production: A Pathway to Effective Fisheries Management, Conservation, and Governance. Fisheries (Bethesda) 2021, 46, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.E.; Armitage, D.; Eurich, J.G.; Kleisner, K.M.; Pecl, G.T.; Tokunaga, K. Co-Production of Knowledge and Strategies to Support Climate Resilient Fisheries. ICES Journal of Marine Science 2023, 80, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.B.; Fluech, B.; Siders, Z.A.; Sipos, M.; Zangroniz, A. Diving for Data: Florida Sea Grant’s Great Goliath Grouper Count. Oceanography 2024, 37, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEDAR SEDAR 47 Stock Assessment Report - Southeastern U.S. Goliath Grouper. SEDAR, North Charleston, SC. available at https://sedarweb.org/assessments/sedar-47/ 2016.
- Farmer, N.A.; Heyman, W.D.; Karnauskas, M.; Kobara, S.; Smart, T.I.; Ballenger, J.C.; Reichert, M.J.M.; Wyanski, D.M.; Tishler, M.S.; Lindeman, K.C.; et al. Timing and Locations of Reef Fish Spawning off the Southeastern United States. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0172968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyman, W.D.; Grüss, A.; Biggs, C.R.; Kobara, S.; Farmer, N.A.; Karnauskas, M.; Lowerre-Barbieri, S.; Erisman, B. Cooperative Monitoring, Assessment, and Management of Fish Spawning Aggregations and Associated Fisheries in the U.S. Gulf of Mexico. Mar Policy 2019, 109, 103689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punt, A.E.; Butterworth, D.S.; de Moor, C.L.; De Oliveira, J.A.A.; Haddon, M. Management Strategy Evaluation: Best Practices. Fish and Fisheries 2016, 17, 303–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, M.D.; Shertzer, K.W.; Cao, J. Exploring Tradeoffs in Southeast United States Marine Fisheries Management Using Management Strategy Evaluation. Fish Res 2024, 275, 107028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson III, W.F.; Barnett, B.K.; TinHan, T.C.; Lowerre-Barbieri, S.K. Eye Lens Δ14C Validates Otolith-Derived Age Estimates of Gulf of Mexico Reef Fishes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 2021, 78, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson III, W.F.; Chamberlin, D.W. Application of the Bomb Radiocarbon Chronometer with Eye Lens Core Δ14C for Age Validation in Deepwater Reef Fishes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 2023, 80, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.N.; Fields, A.T.; Patterson, W.F.; Barnett, B.K.; Hollenbeck, C.M.; Portnoy, D.S. Novel Epigenetic Age Estimation in Wild-Caught Gulf of Mexico Reef Fishes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 2022, 79, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.N.; Fields, A.T.; Chamberlin, D.W.; Patterson, W.F.; Portnoy, D.S. Epigenetic Age Estimation in a Long-Lived, Deepwater Scorpionfish: Insights into Epigenetic Clock Development. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 2024, 81, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appeldoorn-Sanders, E.; Schärer-Umpierre, M.T.; Cruz-Motta, J.J. Passive Acoustics as a Tool to Quantify/Characterize Vessel Activity at Fish Spawning Aggregation Sites. Ocean Coast Manag 2022, 226, 106270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, C.; Schärer-Umpierre, M.; Nemeth, R.S.; Appeldoorn, R.; Chérubin, L.M. Spatial Distribution of Spawning Groupers on a Caribbean Reef from an Autonomous Surface Platform. Fish Res 2023, 266, 106794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appeldoorn-Sanders, E.; Zayas-Santiago, C.; Schärer-Umpierre, M. Characterization and Temporal Patterns of Red Hind Grouper, Epinephelus Guttatus, Choruses at a Single Aggregation Site over a 10-Year Period. Environ Biol Fishes 2023, 106, 1953–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chérubin, L.M.; Dalgleish, F.; Ibrahim, A.K.; Schärer-Umpierre, M.; Nemeth, R.S.; Matthews, A.; Appeldoorn, R. Fish Spawning Aggregations Dynamics as Inferred from a Novel, Persistent Presence Robotic Approach. Front Mar Sci 2020, 6, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.A.; Herbig, J.L.; Morley, D.; Wile, A.; Barbera, P.; Acosta, A. Grouper Tales: Use of Acoustic Telemetry to Evaluate Grouper Movements at Western Dry Rocks in the Florida Keys. Marine and Coastal Fisheries 2020, 12, 290–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, N.A.; Ault, J.S. Grouper and Snapper Movements and Habitat Use in Dry Tortugas, Florida. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 2011, 433, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharp, R.M.; Hostetter, N.J.; Paxton, A.B.; Taylor, J.C.; Buckel, J.A. Artificial Structure Selection by Economically Important Reef Fishes at North Carolina Artificial Reefs. Front Mar Sci 2024, 11, 1373494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, J.L.; Ostroff, J.L.; Peebles, E.B. Isotopic Characterization of Lifetime Movement by Two Demersal Fishes from the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 2021, 657, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, P.J.; Koenig, C.C.; Zdanowicz, V.S. Elemental Composition of Otoliths Used to Trace Estuarine Habitats of Juvenile Gag Mycteroperca Microlepis along the West Coast of Florida. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 2004, 267, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Colmenares, G.M.; Gonzalez Montes, A.J.; Harms-Tuohy, C.A.; Schizas, N. V. Using EDNA Sampling for Species-Specific Fish Detection in Tropical Oceanic Samples: Limitations and Recommendations for Future Use. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacheler, N.M.; Gillum, Z.D.; Gregalis, K.C.; Pickett, E.P.; Schobernd, C.M.; Schobernd, Z.H.; Teer, B.Z.; Smart, T.I.; Bubley, W.J. Comparison of Video and Traps for Detecting Reef Fishes and Quantifying Species Richness in the Continental Shelf Waters of the Southeast USA. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 2022, 698, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switzer, T.S.; Keenan, S.F.; Thompson, K.A.; Shea, C.P.; Knapp, A.R.; Campbell, M.D.; Noble, B.; Gardner, C.; Christman, M.C. Integrating Assemblage Structure and Habitat Mapping Data into the Design of a Multispecies Reef Fish Survey. Marine and Coastal Fisheries 2023, 15, e10245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.P.; Drymon, J.M.; Hightower, C.L.; Spearman, T.; Bosarge, G.S.; Jefferson, A. Distribution and Age Composition of Red Snapper across the Inner Continental Shelf of the North-Central Gulf of Mexico. Trans Am Fish Soc 2018, 147, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.D.; Rademacher, K.R.; Noble, B.; Salisbury, J.; Felts, P.; Moser, J.; Caillouet, R.; Hendon, M.; Driggers, W.B. Status and Trends of Marbled Grouper in the North-Central Gulf of Mexico. Marine and Coastal Fisheries 2019, 11, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, S.E.; Dixon, O.F.L.; de Silva, C.; Kohler, J.K.; Shipley, O.N.; Phillips, B.T.; Fernandes, T.F.; Austin, T.; Ormond, R.F.; Gore, M.A.; et al. Depth Range Extension for the Misty Grouper Hyporthodus Mystacinus Documented via Deep-Sea Landers throughout the Greater Caribbean. Fishes 2024, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.C.; Appeldoorn, R.S.; Schärer-Umpierre, M.T.; Cruz-Motta, J.J. Recovery When You Are on Your Own: Slow Population Responses in an Isolated Marine Reserve. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0223102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, M.W.; Bernard, A.M. A Bank Divided: Quantifying a Spatial and Temporal Connectivity Break between the Campeche Bank and the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Mar Biol 2017, 164, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

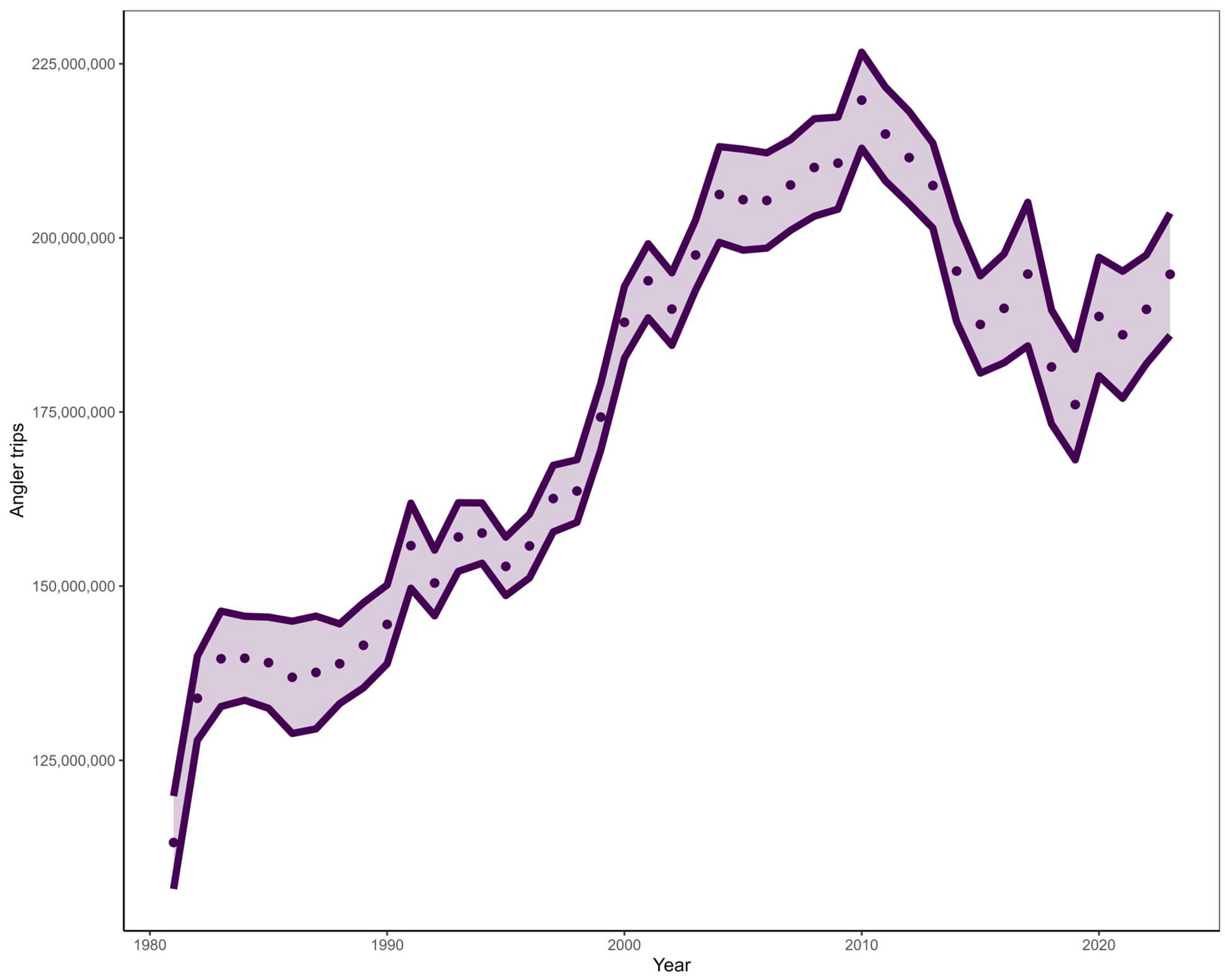

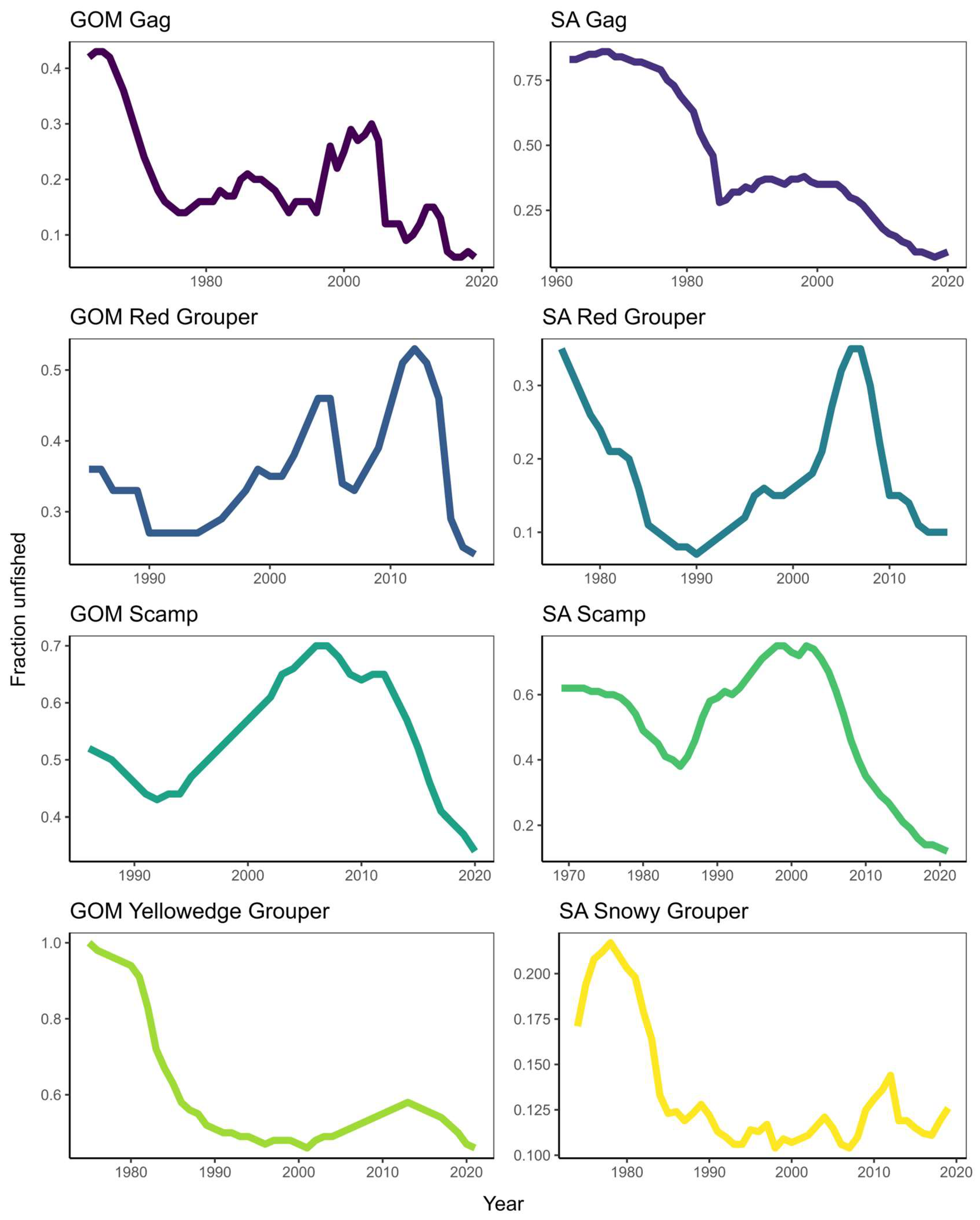

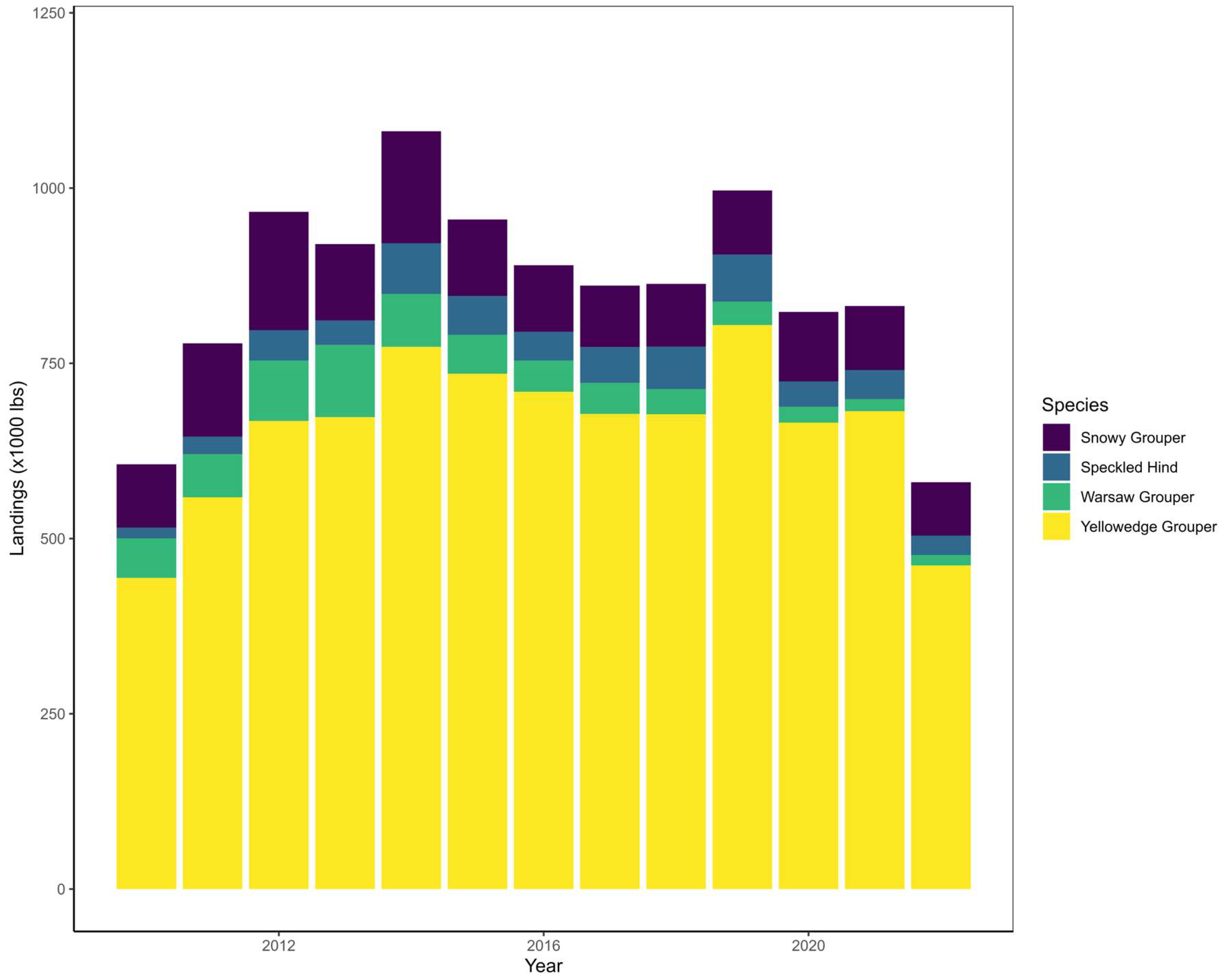

| Common name | Scientific name | Longevity (y) | Reproductive strategy | Managed? | Overfished and/or overfishing? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atlantic Goliath Grouper | Epinephelus itajara | >30 [39] | G, DPH [40] | CAB, GOM, SA | CAB [41] |
| Black Grouper | Mycteroperca bonaci | >20 [42] | MPH [43] | CAB,GOM, SA | - |
| Coney | Cephalopholis fulva | >10 [44] | MPH [45] | CAB, SA | - |
| Gag | Mycteroperca microlepis | >20 [46] | MPH [47] | GOM, SA | GOM [48], SA [49] |
| Graysby | Cephalopholis cruentata | >20 [50] | MPH [50] | CAB, SA | - |
| Marbled Grouper | Dermatolepis inermis | - | - | - | - |
| Misty Grouper | Hyporthodus mystacinus | >100 [51] | - | SA | - |
| Nassau Grouper | Epinephelus striatus | >20 [12] | G [12] | CAB, GOM, SA | - |
| Red Grouper | Epinephelus morio | >20 [52] | MPH [43] | CAB, GOM, SA | SA [53] |
| Red Hind | Epinephelus guttatus | >10 [10] | MPH [54] | CAB, SA | - |
| Rock Hind | Epinephelus adscensionis | >30 [55] | MPH [56] | CAB, SA | - |
| Scamp | Mycteroperca phenax | >30 [57] | MPH [57] | GOM, SA | SA [58] |
| Snowy Grouper | Hyporthodus niveatus | >50 [59] | MPH [60] | GOM, SA | SA [61] |
| Speckled Hind | Epinephelus drummondhayi | >40 [62] | MPH [63] | GOM, SA | - |
| Tiger Grouper | Mycteroperca tigris | >10 [64] | MPH [65] | CAB | - |
| Yellowedge Grouper | Hyporthodus flavolimbatus | >80 [66] | MPH [67] | CAB, GOM, SA | - |
| Yellowfin Grouper | Mycteroperca venenosa | >30 [68] | MPH [69] | CAB | - |
| Yellowmouth Grouper | Mycteroperca interstitialis | >20 [70] | MPH [70] | GOM, SA | - |
| Warsaw Grouper | Hyporthodus nigritus | >90 [71] | - | GOM, SA | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





