Submitted:
02 September 2024
Posted:
03 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
| Notations | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Indices | |
| Index of products, | |
| Index of jobs, | |
| Index of processing operations, | |
| Index of assembly operations, | |
| Index of processing machines, | |
| Index of transportation vehicles, | |
| Index of transportation vehicle load transportation, | |
| Index of assembly machines, | |
| Parameters | |
| The set of processing machines, | |
| The set of transportation vehicles, | |
| The set of assembly machine, | |
| The set of products, | |
| Number of products | |
| Number of jobs | |
| Number of processing operations | |
| Number of assembly operations | |
| Number of processing machines | |
| Number of transportation vehicles | |
| Number of assembly machines | |
| Number of operations on processing machine m and assembly machine k | |
| Number of load transportations by vehicle t | |
| Maximum load capacity of the vehicle | |
| The job indexed by j, the set of all jobs belonging to | |
| The i-th processing operation of , the set of all operations of | |
| The a-th assembly operation and the set of assembly operations of | |
| The set of machines available for processing operation | |
| Unit power consumption of processing machine m and assembly machine k in working mode | |
| Unit power consumption of processing machine m and assembly machine k in standby mode | |
| Unit power consumption of processing machine m in setup mode | |
| Unit power consumption of transportation vehicle t | |
| Distance between the processing shop and the assembly shop | |
| Speed of transportation vehicles when unloaded and speed of transportation vehicle t during the w-th load transportation | |
| Processing time of operation and | |
| Setup time of operation and | |
| Idle time between operation and excluding setup time | |
| Idle time between operation and | |
| Release time of job | |
| Decision variables | |
| Sequence of operations on processing machine m | |
| Sequence of operations on assembly machine k | |
| Sequence of operations on processing stage, transportation stage, and assembly stage | |
| Start time and completion time of operation | |
| Release energy consumption, setup energy consumption, processing energy consumption, and idle energy consumption in the processing stage | |
| assembly energy consumption and idle energy consumption in the assembly stage | |
| Energy consumption in the processing stage, transportation stage, and assembly stage | |
| Maximum completion time of a schedule | |
| TEC | Total energy consumption |
2.1. Problem Definition
- In the processing and assembly stages, any machine can only process one operation at a time.
- Once started, processing operations, transportation processes, and assembly operations cannot be interrupted.
- All machines and vehicles are available at time zero.
- Transportation time between machines for consecutive processing (or assembly) operations is not considered.
- Vehicles maintain a constant speed during transportation.
- The initial setup time is included in the release time of the workpiece.
2.2. Mathematical Model
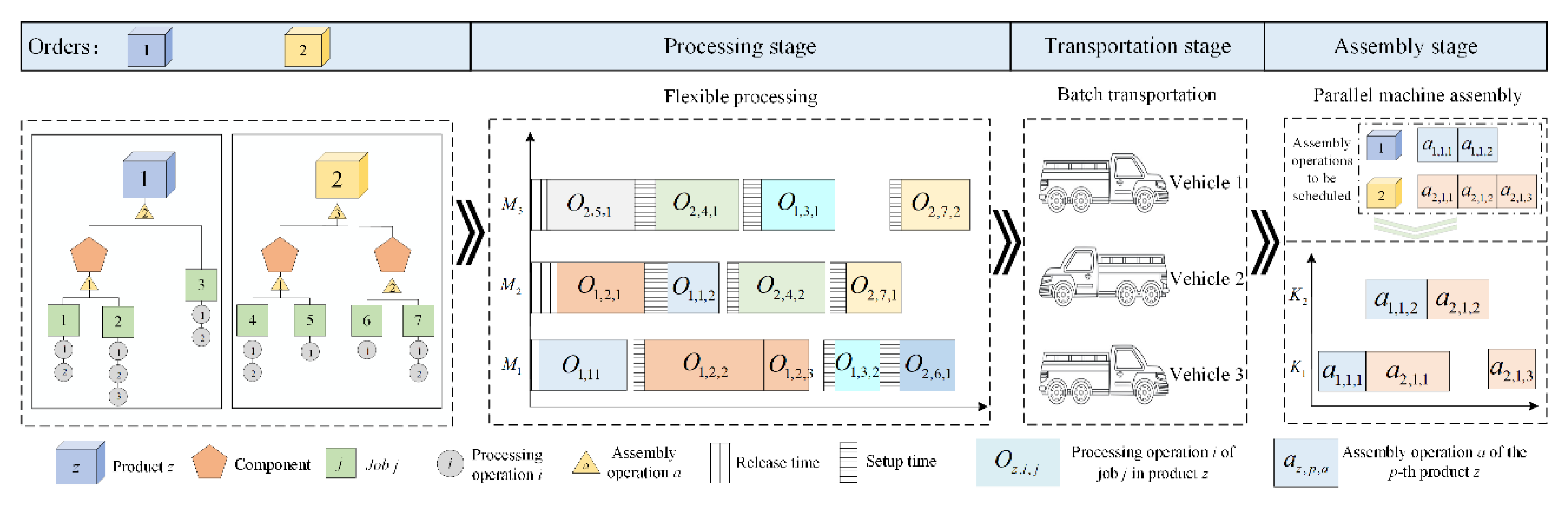
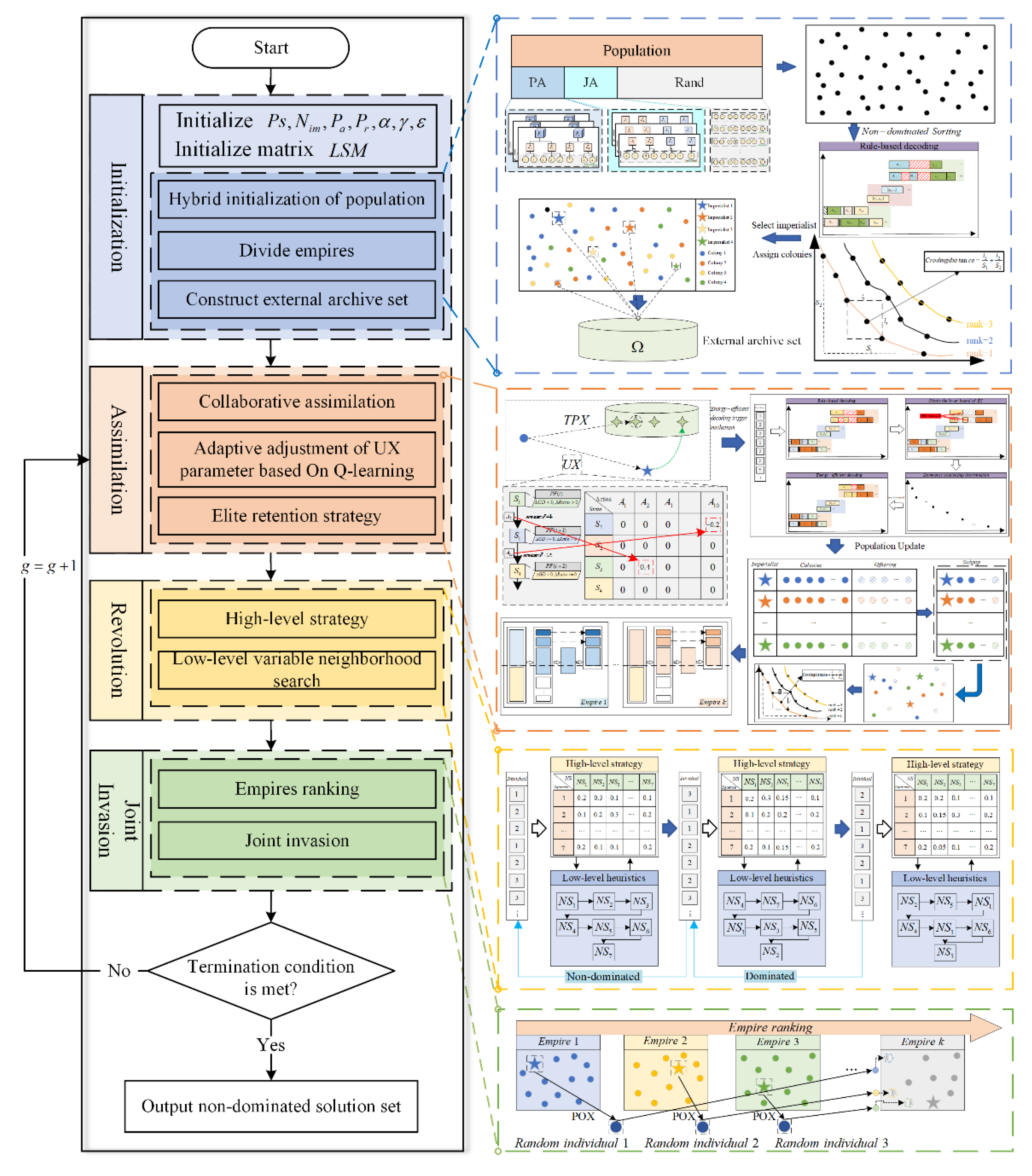
3. Encoding and Decoding Design
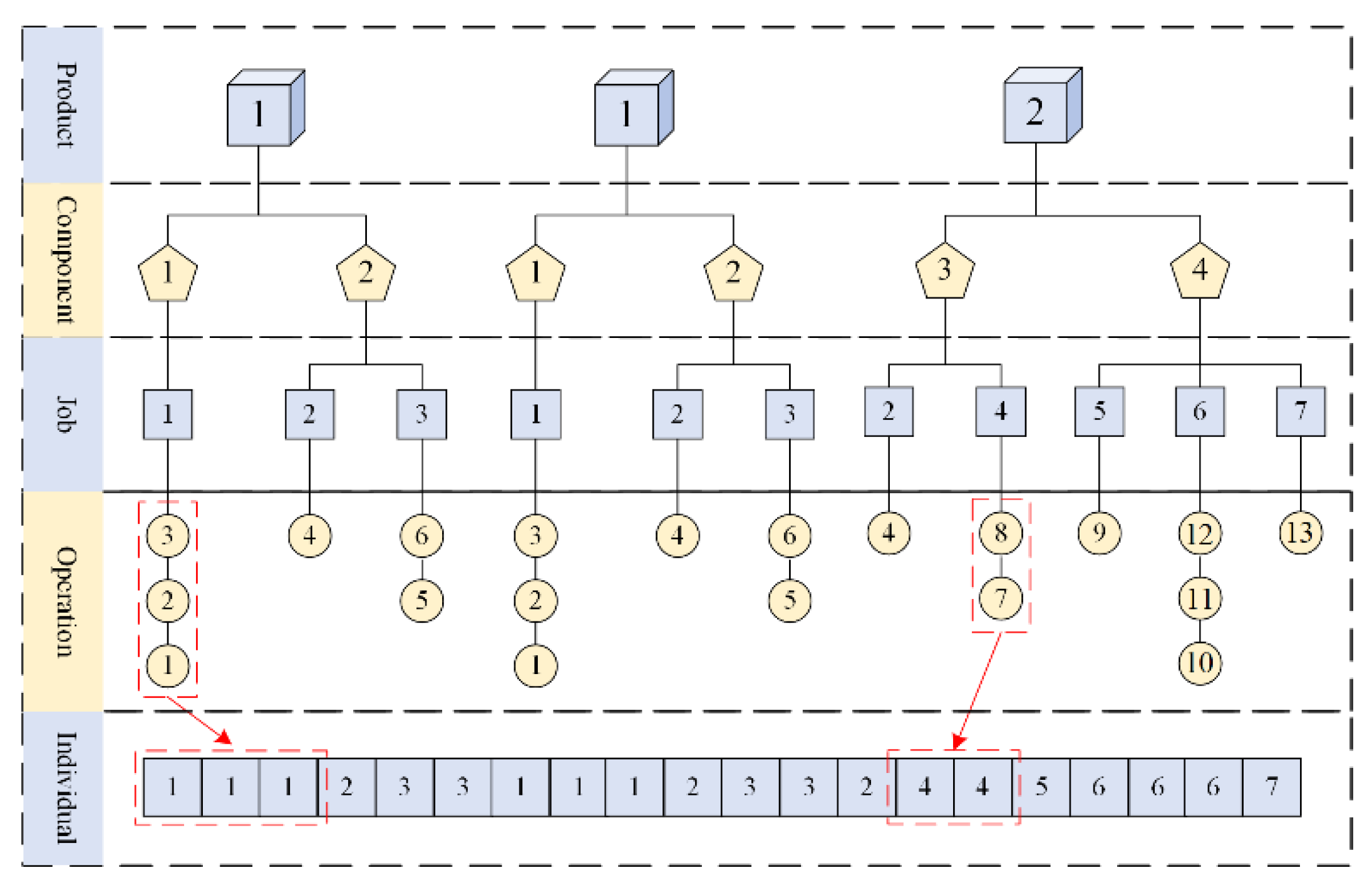
3.1. Encoding
| Algorithm 1 Encoding Method |
 |
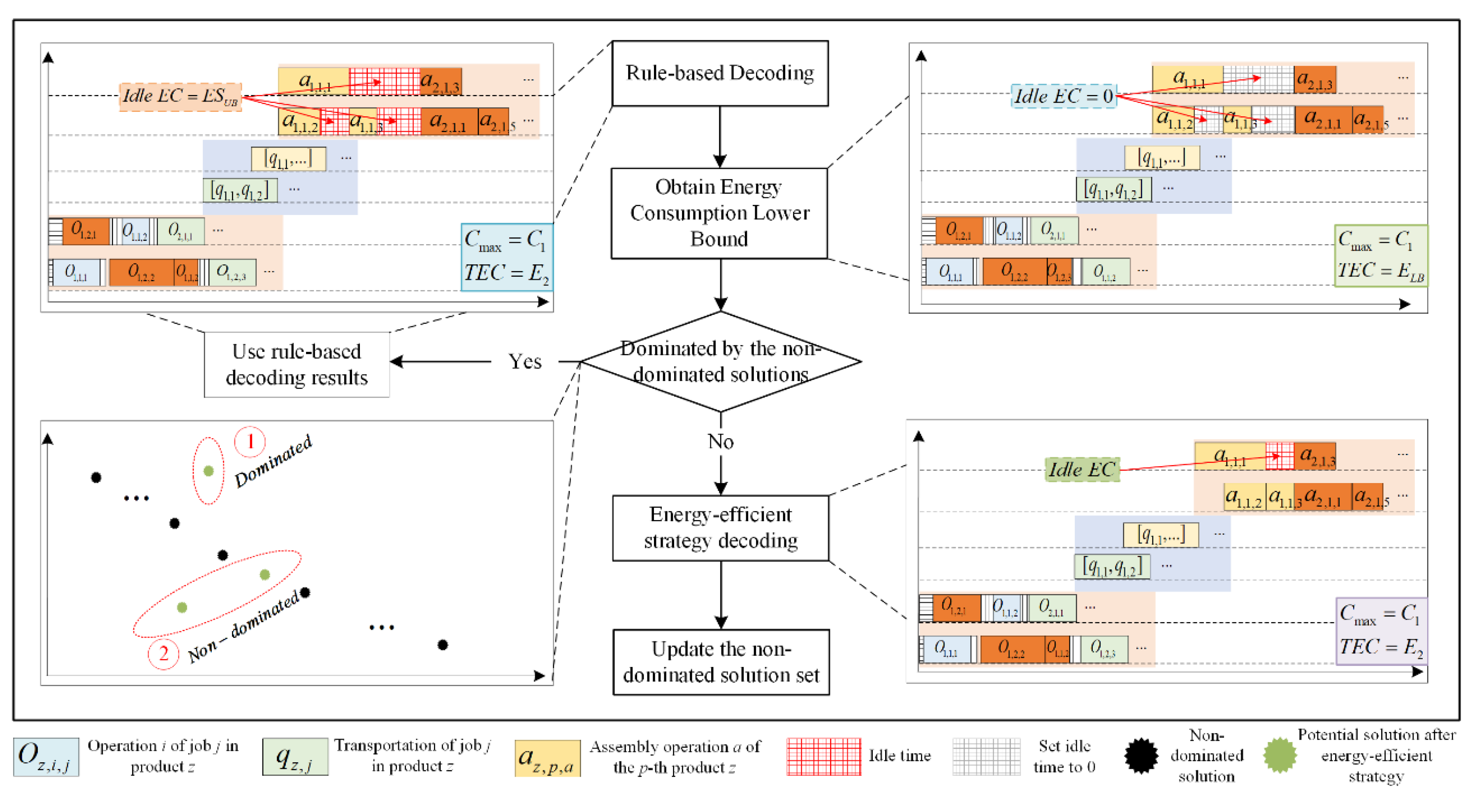
3.2. Decoding Rules
- (1)
- Machine assignment in the processing stage
- (2)
- Jobs transportation sequence and vehicle allocation in the transportation stage
- (3)
- Product assembly sequence and machine assignment in the assembly stage
3.3. Design of Energy-Efficient Strategy Decoding Trigger Mechanism
4. IICA-QL for EEMsMlAJSP
4.1. Initialization of Empires
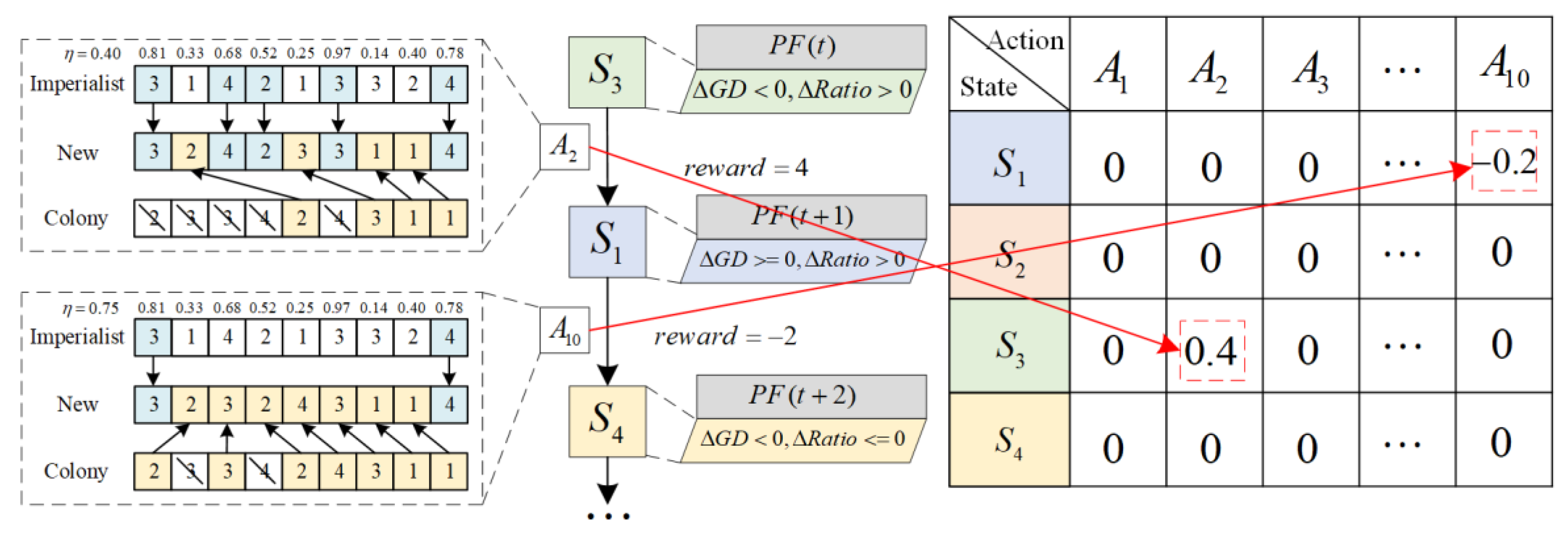
4.2. Assimilation Based on Q-Learning Adaptive Adjustment of Operator Parameter
| Algorithm 2 Assimilation based on Q-learning adaptive adjustment of operator parameter |
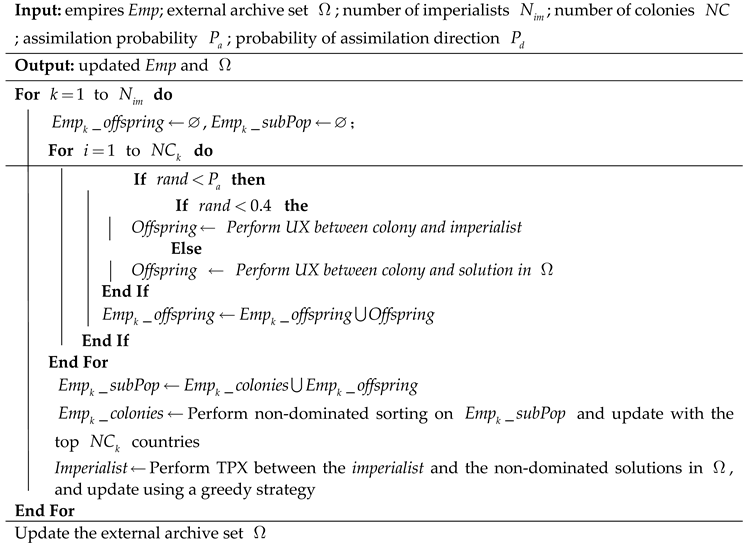 |
4.2.1. Adaptive Adjustment of UX Operator Parameter Based on Q-Learning
4.2.2. Update Strategy
4.3. Revolution Based on Hyper-Heuristic Variable Neighborhood Search
4.3.1. Neighborhood Search (NS) Operations
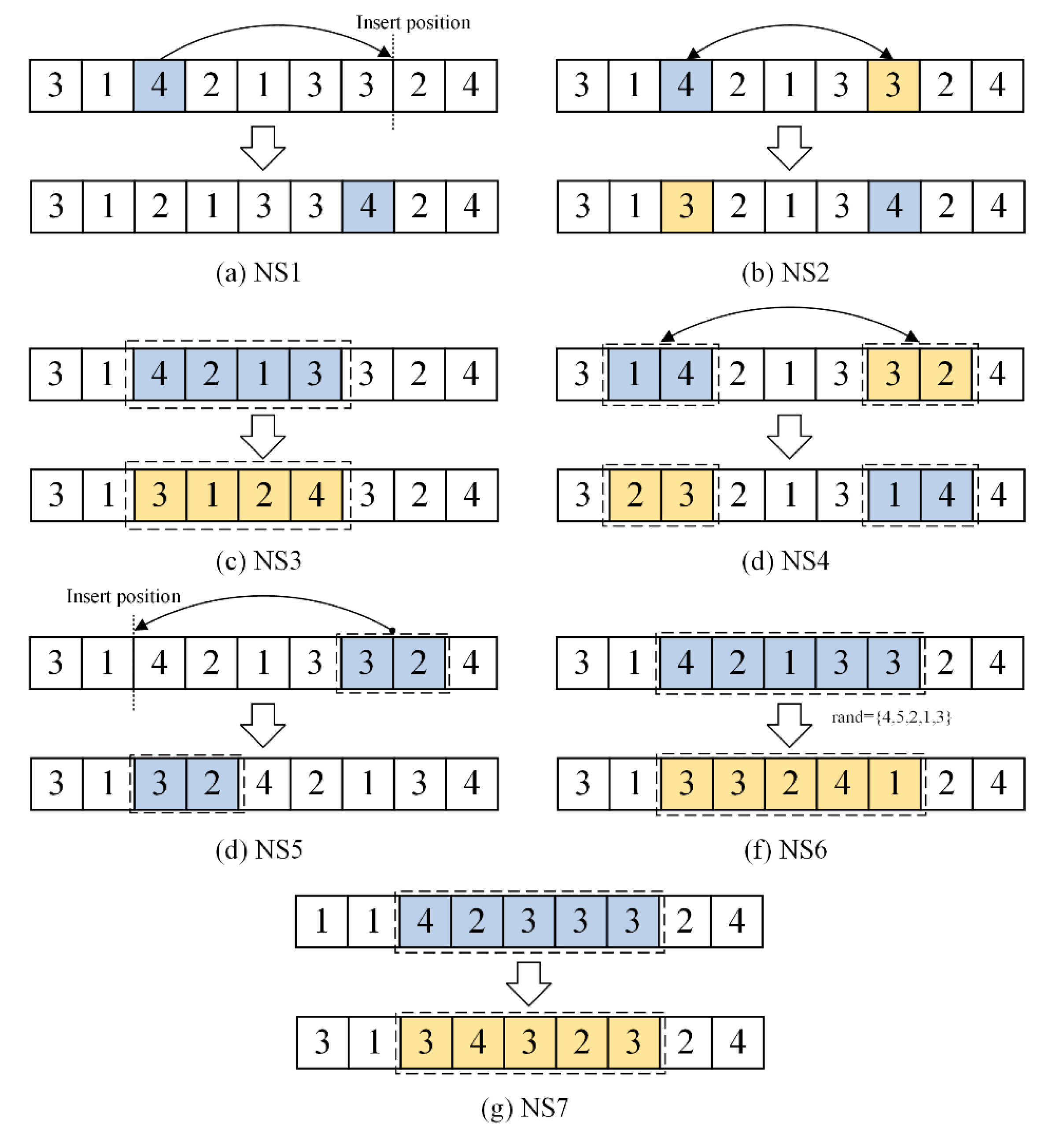
4.3.2. Two-Dimensional Probability Model
| Algorithm 3 Revolution based on hyper-heuristic variable neighborhood search |
 |
4.4. Joint Imperialist Invasion
| Algorithm 4 Joint imperialist invasion |
 |
4.5. Algorithm Description
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
5.1. Performance Metrics
- (1)
- Solution set Coverage (C-metric). This metric measures the dominance relationship between two solution sets, and is defined as follows:
- (2)
- Generational Distance (GD).
- (3)
- Hypervolume (HV)
5.2. Parameter Settings
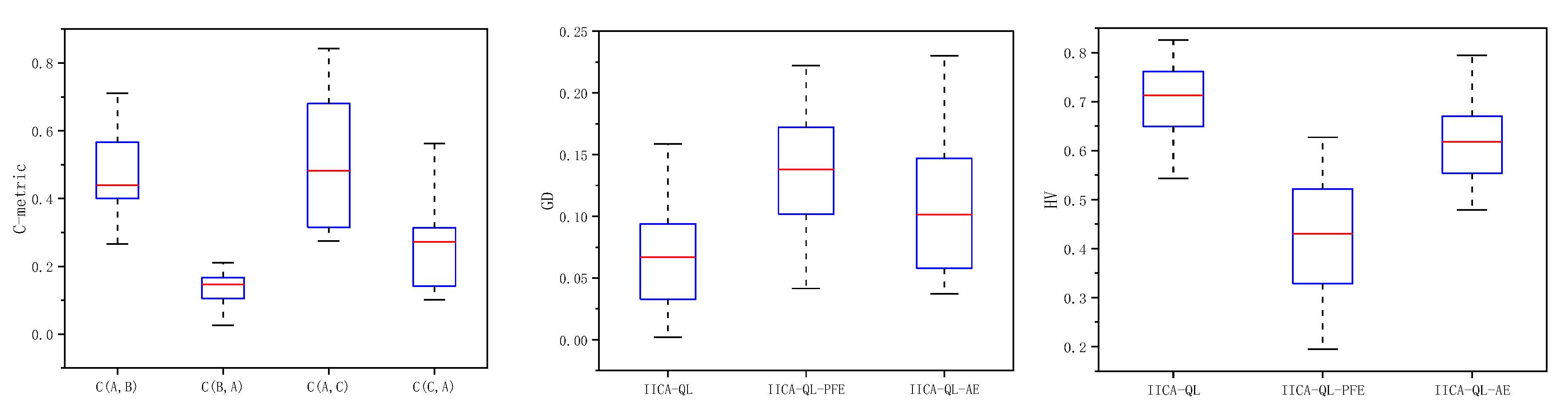
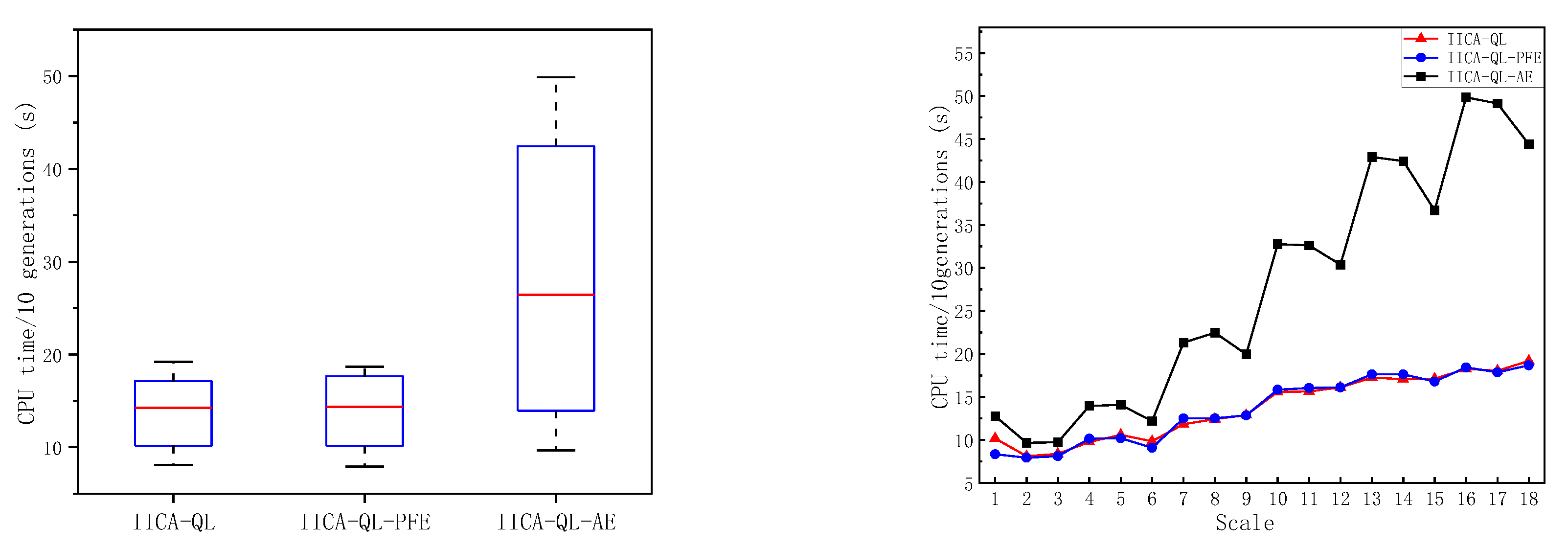
5.3. Effectiveness of the Adaptive Trigger Mechanism for the Energy-Efficient Strategy
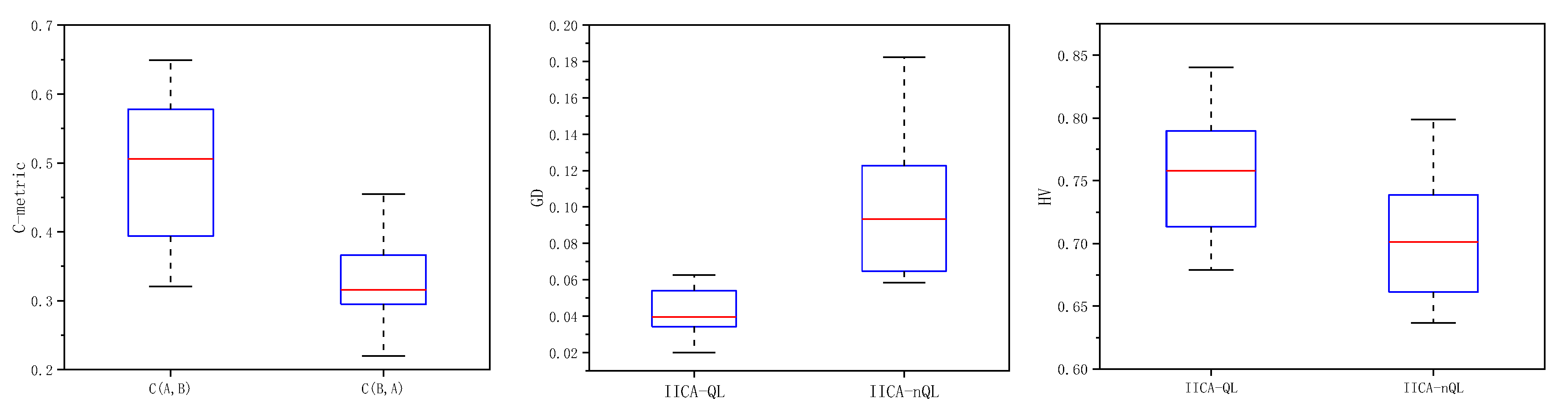
5.4. Effectiveness of Operator Parameter Adaptive Adjustment Based on Q-Learning
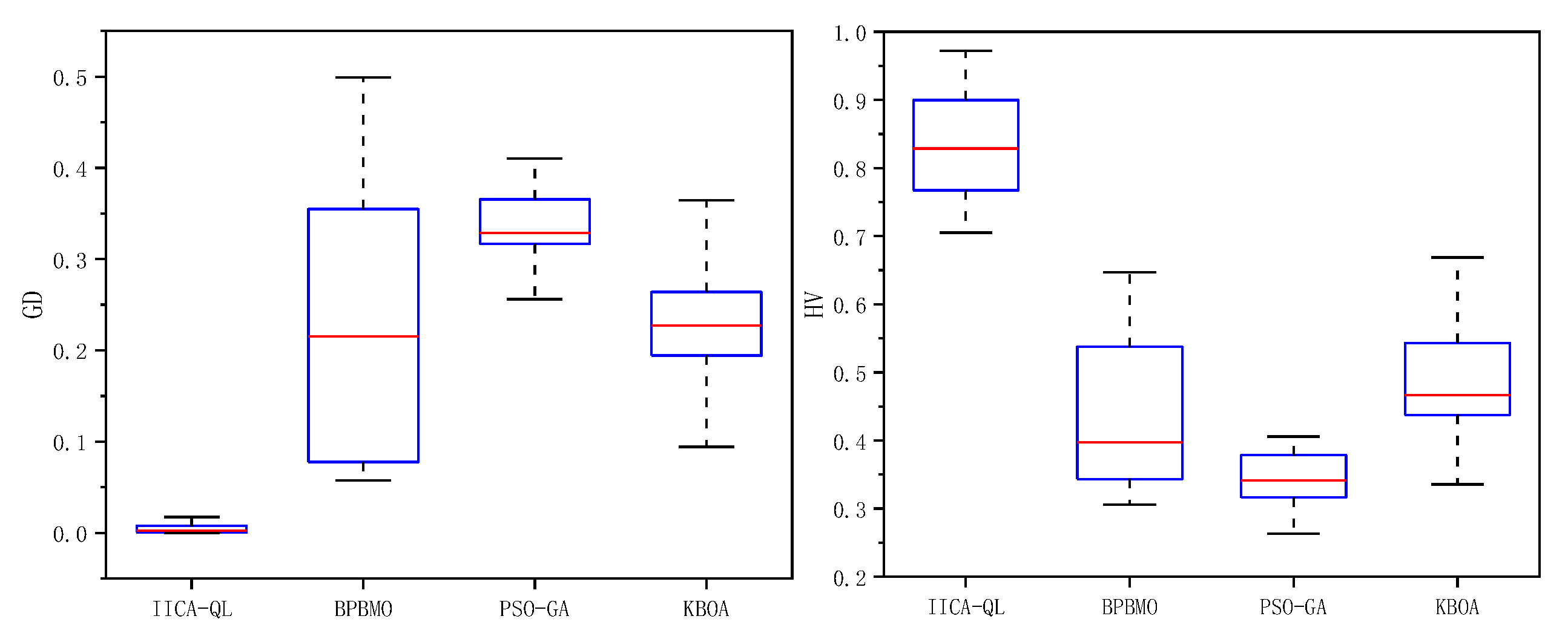
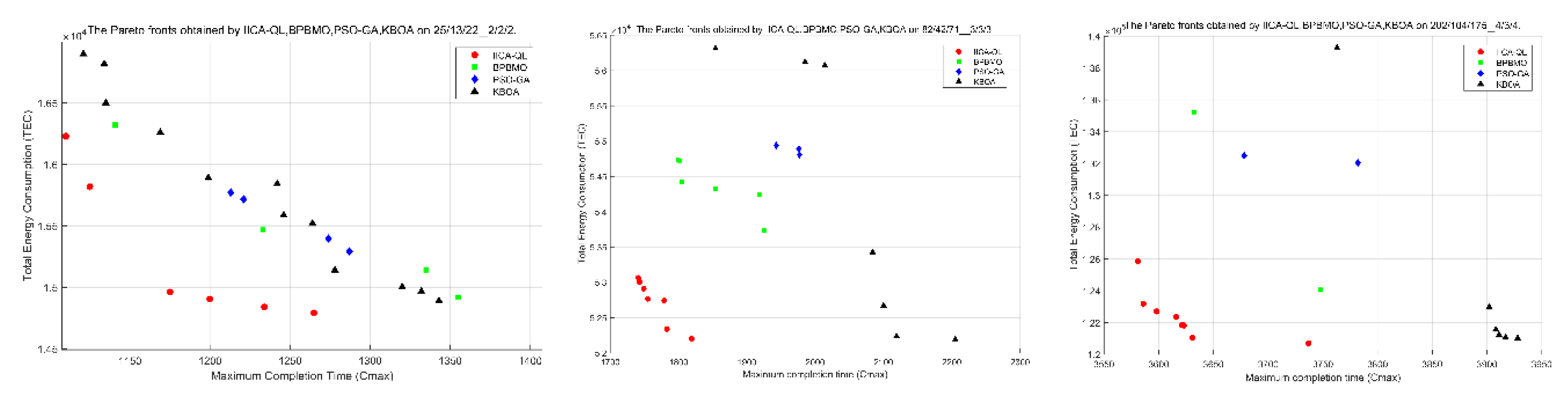
5.5. Comparison with Other Algorithms
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang J, Lei D, Cai J. An adaptive artificial bee colony with reinforcement learning for distributed three-stage assembly scheduling with maintenance. Appl Soft Comput. 2022;117:108371. [CrossRef]
- Cheng L, Tang Q, Liu S, Zhang L. Mathematical model and augmented simulated annealing algorithm for mixed-model assembly job shop scheduling problem with batch transfer. Knowl-Based Syst. 2023;279:110968. [CrossRef]
- Cheng L, Tang Q, Zhang L. Production costs and total completion time minimization for three-stage mixed-model assembly job shop scheduling with lot streaming and batch transfer. Eng Appl Artif Intell. 2024;130:107729. [CrossRef]
- Gong G, Chiong R, Deng Q, et al. A two-stage memetic algorithm for energy-efficient flexible job shop scheduling by means of decreasing the total number of machine restarts. Swarm Evol Comput. 2022;75:101131. [CrossRef]
- Wang JJ, Wang L. A Cooperative Memetic Algorithm With Learning-Based Agent for Energy-Aware Distributed Hybrid Flow-Shop Scheduling. IEEE Trans Evol Comput. 2022;26(3):461-475. [CrossRef]
- Cao S, Li R, Gong W, Lu C. Inverse model and adaptive neighborhood search based cooperative optimizer for energy-efficient distributed flexible job shop scheduling. Swarm Evol Comput. 2023;83:101419. [CrossRef]
- Wang J jing, Wang L. A cooperative memetic algorithm with feedback for the energy-aware distributed flow-shops with flexible assembly scheduling. Comput Ind Eng. 2022;168:108126. [CrossRef]
- Li R, Gong W, Wang L, Lu C, Zhuang X. Surprisingly Popular-Based Adaptive Memetic Algorithm for Energy-Efficient Distributed Flexible Job Shop Scheduling. IEEE Trans Cybern. Published online 2023:1-11. [CrossRef]
- Meng L, Zhang C, Zhang B, Gao K, Ren Y, Sang H. MILP modeling and optimization of multi-objective flexible job shop scheduling problem with controllable processing times. Swarm Evol Comput. 2023;82:101374. [CrossRef]
- Lei D, Li M, Wang L. A Two-Phase Meta-Heuristic for Multiobjective Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problem With Total Energy Consumption Threshold. IEEE Trans Cybern. 2019;49(3):1097-1109. [CrossRef]
- Zhou R, Lei D, Zhou X. Multi-Objective Energy-Efficient Interval Scheduling in Hybrid Flow Shop Using Imperialist Competitive Algorithm. IEEE Access. 2019;7:85029-85041. [CrossRef]
- Lei D, Yuan Y, Cai J, Bai D. An imperialist competitive algorithm with memory for distributed unrelated parallel machines scheduling. Int J Prod Res. 2020;58(2):597-614. [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Yang Z, Wang L, Tang H, Sun L, Guo S. A hybrid imperialist competitive algorithm for energy-efficient flexible job shop scheduling problem with variable-size sublots. Comput Ind Eng. 2022;172:108641. [CrossRef]
- Chen Y, Zhong J, Mumtaz J, Zhou S, Zhu L. An improved spider monkey optimization algorithm for multi-objective planning and scheduling problems of PCB assembly line. Expert Syst Appl. 2023;229:120600. [CrossRef]
- Chen R, Yang B, Li S, Wang S. A self-learning genetic algorithm based on reinforcement learning for flexible job-shop scheduling problem. Comput Ind Eng. 2020;149:106778. [CrossRef]
- Li R, Gong W, Lu C, Wang L. A Learning-Based Memetic Algorithm for Energy-Efficient Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling With Type-2 Fuzzy Processing Time. IEEE Trans Evol Comput. 2023;27(3):610-620. [CrossRef]
- Pan Z, Wang L, Wang J, Yu Y. Distributed Energy-Efficient Flexible Manufacturing With Assembly and Transportation: A Knowledge-Based Bi-Hierarchical Optimization Approach. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng. Published online 2024:1-17. [CrossRef]
- Zou P, Rajora M, Liang SY. A new algorithm based on evolutionary computation for hierarchically coupled constraint optimization: methodology and application to assembly job-shop scheduling. J Sched. 2018;21(5):545-563. [CrossRef]
- Zhu Z, Zhou X. An efficient evolutionary grey wolf optimizer for multi-objective flexible job shop scheduling problem with hierarchical job precedence constraints. Comput Ind Eng. 2020;140:106280. [CrossRef]
- Li M, Lei D, Cai J. Two-level imperialist competitive algorithm for energy-efficient hybrid flow shop scheduling problem with relative importance of objectives. Swarm Evol Comput. 2019;49:34-43. [CrossRef]
- Fontes DBMM, Homayouni SM, Fernandes JC. Energy-efficient job shop scheduling problem with transport resources considering speed adjustable resources. Int J Prod Res. 2023;0(0):1-24. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Han Y, Gao K, Xiao X, Duan P. Bi-Population Balancing Multi-Objective Algorithm for Fuzzy Flexible Job Shop With Energy and Transportation. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng. Published online 2023:1-17. [CrossRef]
- Ming M, Trivedi A, Wang R, Srinivasan D, Zhang T. A Dual-Population-Based Evolutionary Algorithm for Constrained Multiobjective Optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput. 2021;25(4):739-753. [CrossRef]
- Cheng L, Tang Q, Zhang L, Meng K. Mathematical model and enhanced cooperative co-evolutionary algorithm for scheduling energy-efficient manufacturing cell. J Clean Prod. 2021;326:129248. [CrossRef]
- Wang J jing, Wang L, Xiu X. A cooperative memetic algorithm for energy-aware distributed welding shop scheduling problem. Eng Appl Artif Intell. 2023;120:105877. [CrossRef]
- Ren W, Wen J, Yan Y, Hu Y, Guan Y, Li J. Multi-objective optimisation for energy-aware flexible job-shop scheduling problem with assembly operations. Int J Prod Res. 2021;59(23):7216-7231. [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Notation | Factor level | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| population size | 50 | 100 | 150 | |
| Nim | number of Imperialists | 3 | 5 | 7 |
| assimilation probability | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | |
| revolutionary probability | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | |
| learning rate | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | |
| discount factor | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | |
| greed factor | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.9 | |
| Level | |||||||
| 1 | 0.7855 | 0.7943 | 0.7786 | 0.7912 | 0.7868 | 0.7844 | 0.7851 |
| 2 | 0.7986 | 0.7814 | 0.7923 | 0.7838 | 0.7926 | 0.7856 | 0.7974 |
| 3 | 0.7786 | 0.7869 | 0.7917 | 0.7877 | 0.7832 | 0.7926 | 0.7801 |
| Delta | 0.0200 | 0.0130 | 0.0138 | 0.0074 | 0.0094 | 0.0083 | 0.0174 |
| Rank | 1 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 2 |
| O/J/A_M/T/K | C-metric | GD | HV | |||||||
| C(A,B) | C(B,A) | C(A,C) | C(C,A) | A | B | C | A | B | C | |
| 25/13/22_2/2/2 | 0.3839 | 0.0400 | 0.2750 | 0.1600 | 0.0020 | 0.1062 | 0.0373 | 0.5436 | 0.5218 | 0.6807 |
| 25/13/22_3/2/2 | 0.6563 | 0.1050 | 0.2900 | 0.1409 | 0.0339 | 0.1394 | 0.0548 | 0.6450 | 0.5321 | 0.6181 |
| 25/13/22_3/3/3 | 0.4100 | 0.2100 | 0.3000 | 0.2000 | 0.0717 | 0.1468 | 0.1030 | 0.6490 | 0.5082 | 0.5965 |
| 44/23/39_2/2/2 | 0.5657 | 0.1820 | 0.3150 | 0.3000 | 0.0574 | 0.1509 | 0.0588 | 0.5470 | 0.3884 | 0.6212 |
| 44/23/39_3/2/2 | 0.4458 | 0.1650 | 0.3700 | 0.3450 | 0.0731 | 0.2145 | 0.1015 | 0.7129 | 0.3520 | 0.6705 |
| 44/23/39_3/3/3 | 0.5582 | 0.1350 | 0.3400 | 0.3133 | 0.1082 | 0.2129 | 0.0442 | 0.7045 | 0.3352 | 0.7143 |
| 82/42/71_2/2/2 | 0.4906 | 0.3996 | 0.5576 | 0.2904 | 0.1522 | 0.1231 | 0.1915 | 0.6359 | 0.5231 | 0.5631 |
| 82/42/71_3/2/2 | 0.7106 | 0.0514 | 0.4873 | 0.2845 | 0.0939 | 0.2222 | 0.0962 | 0.7420 | 0.4404 | 0.6939 |
| 82/42/71_3/3/3 | 0.4310 | 0.0681 | 0.2775 | 0.5630 | 0.1586 | 0.1963 | 0.0408 | 0.6667 | 0.2430 | 0.7947 |
| 135/70/120_3/3/3 | 0.4000 | 0.1630 | 0.5083 | 0.2593 | 0.0631 | 0.1542 | 0.0957 | 0.6700 | 0.3284 | 0.5469 |
| 135/70/120_4/3/3 | 0.2657 | 0.3518 | 0.4769 | 0.3038 | 0.1423 | 0.0738 | 0.1619 | 0.7283 | 0.6271 | 0.6485 |
| 135/70/120_4/3/4 | 0.3667 | 0.1672 | 0.5594 | 0.3510 | 0.0932 | 0.1349 | 0.1270 | 0.7616 | 0.4698 | 0.6264 |
| 173/88/151_3/3/3 | 0.6350 | 0.0258 | 0.7278 | 0.1113 | 0.0119 | 0.1721 | 0.1469 | 0.7686 | 0.1946 | 0.4786 |
| 173/88/151_4/3/3 | 0.6333 | 0.1595 | 0.8169 | 0.1060 | 0.0669 | 0.0912 | 0.2302 | 0.7864 | 0.4832 | 0.4958 |
| 173/88/151_4/3/4 | 0.3667 | 0.1445 | 0.7105 | 0.1496 | 0.0328 | 0.0415 | 0.1221 | 0.8258 | 0.5409 | 0.6232 |
| 202/104/175_3/3/3 | 0.4300 | 0.1385 | 0.3846 | 0.3389 | 0.0611 | 0.1018 | 0.0579 | 0.7153 | 0.2788 | 0.5539 |
| 202/104/175_4/3/3 | 0.4333 | 0.1494 | 0.8427 | 0.1018 | 0.0283 | 0.0734 | 0.1721 | 0.7675 | 0.4303 | 0.5742 |
| 202/104/175_4/3/4 | 0.4500 | 0.1076 | 0.6800 | 0.1413 | 0.0248 | 0.1309 | 0.0936 | 0.7295 | 0.2392 | 0.5453 |
| Mean | 0.4796 | 0.1535 | 0.4955 | 0.2478 | 0.0709 | 0.1381 | 0.1075 | 0.7000 | 0.4131 | 0.6137 |
| O/J/A_M/T/K | CPU time / 10 generations (s) | ||
| IICA-QL | IICA-QL-PFE | IICA-QL-AE | |
| 25/13/22_2/2/2 | 10.1695 | 8.3333 | 12.7660 |
| 25/13/22_3/2/2 | 8.1006 | 7.9235 | 9.6667 |
| 25/13/22_3/3/3 | 8.3721 | 8.1081 | 9.7297 |
| 44/23/39_2/2/2 | 9.7696 | 10.1435 | 13.9474 |
| 44/23/39_3/2/2 | 10.5785 | 10.1992 | 14.0659 |
| 44/23/39_3/3/3 | 9.8452 | 9.0857 | 12.1839 |
| 82/42/71_2/2/2 | 11.8182 | 12.5000 | 21.3115 |
| 82/42/71_3/2/2 | 12.4211 | 12.5199 | 22.4762 |
| 82/42/71_3/3/3 | 12.8855 | 12.8571 | 19.9659 |
| 135/70/120_3/3/3 | 15.5887 | 15.8373 | 32.7723 |
| 135/70/120_4/3/3 | 15.6354 | 16.0340 | 32.6225 |
| 135/70/120_4/3/4 | 16.1133 | 16.1133 | 30.3883 |
| 173/88/151_3/3/3 | 17.2385 | 17.6320 | 42.9167 |
| 173/88/151_4/3/3 | 17.0788 | 17.6345 | 42.4398 |
| 173/88/151_4/3/4 | 17.1053 | 16.7922 | 36.7059 |
| 202/104/175_3/3/3 | 18.2660 | 18.4342 | 49.8577 |
| 202/104/175_4/3/3 | 18.0452 | 17.8635 | 49.1385 |
| 202/104/175_4/3/4 | 19.1857 | 18.6786 | 44.3970 |
| Mean | 13.7898 | 13.7050 | 27.6306 |
| O/J/A_M/T/K | C-metric | GD | HV | |||
| IICA-QL(A) | IICA-nQL (B) | IICA-QL | IICA-nQL | IICA-QL | IICA-nQL | |
| C(A,B) | C(B,A) | |||||
| 25/13/22_2/2/2 | 0.3206 | 0.3050 | 0.0471 | 0.0585 | 0.6789 | 0.6848 |
| 25/13/22_3/2/2 | 0.3767 | 0.2617 | 0.0540 | 0.0669 | 0.6966 | 0.6940 |
| 25/13/22_3/3/3 | 0.3937 | 0.2950 | 0.0861 | 0.1289 | 0.7014 | 0.6438 |
| 44/23/39_2/2/2 | 0.3283 | 0.3679 | 0.0627 | 0.0633 | 0.7132 | 0.6424 |
| 44/23/39_3/2/2 | 0.3922 | 0.3344 | 0.0373 | 0.1339 | 0.7103 | 0.6975 |
| 44/23/39_3/3/3 | 0.5367 | 0.3250 | 0.0622 | 0.1823 | 0.7490 | 0.6484 |
| 82/42/71_2/2/2 | 0.5235 | 0.2410 | 0.0253 | 0.1227 | 0.7581 | 0.6368 |
| 82/42/71_3/2/2 | 0.4920 | 0.3293 | 0.0297 | 0.0703 | 0.7999 | 0.7471 |
| 82/42/71_3/3/3 | 0.4343 | 0.3915 | 0.0928 | 0.1081 | 0.7274 | 0.7228 |
| 135/70/120_3/3/3 | 0.6492 | 0.3096 | 0.0351 | 0.0767 | 0.7898 | 0.7387 |
| 135/70/120_4/3/3 | 0.5101 | 0.3000 | 0.0383 | 0.0632 | 0.7579 | 0.7362 |
| 135/70/120_4/3/4 | 0.5018 | 0.4549 | 0.0406 | 0.0647 | 0.7681 | 0.7496 |
| 173/88/151_3/3/3 | 0.5481 | 0.3214 | 0.0431 | 0.0605 | 0.7361 | 0.7087 |
| 173/88/151_4/3/3 | 0.6261 | 0.3101 | 0.0342 | 0.1021 | 0.7803 | 0.7031 |
| 173/88/151_4/3/4 | 0.4405 | 0.4014 | 0.0472 | 0.1128 | 0.8402 | 0.7989 |
| 202/104/175_3/3/3 | 0.5780 | 0.2200 | 0.0200 | 0.1030 | 0.7784 | 0.6613 |
| 202/104/175_4/3/3 | 0.6417 | 0.2254 | 0.0232 | 0.1256 | 0.8142 | 0.6995 |
| 202/104/175_4/3/4 | 0.6208 | 0.3661 | 0.0353 | 0.0846 | 0.8250 | 0.7784 |
| Mean | 0.4952 | 0.3200 | 0.0452 | 0.0960 | 0.7569 | 0.7051 |
| O/J/A_M/T/K | GD | HV | ||||||
| IICA-QL | BPBMO | PSO-GA | KBOA | IICA-QL | BPBMO | PSO-GA | KBOA | |
| 25/13/22_2/2/2 | 0.0028 | 0.2698 | 0.3198 | 0.2026 | 0.7888 | 0.4022 | 0.3688 | 0.5433 |
| 25/13/22_3/2/2 | 0.0174 | 0.1952 | 0.3166 | 0.2087 | 0.8628 | 0.5660 | 0.4059 | 0.5858 |
| 25/13/22_3/3/3 | 0.0021 | 0.4099 | 0.3654 | 0.2204 | 0.8997 | 0.3544 | 0.3958 | 0.5970 |
| 44/23/39_2/2/2 | 0.0034 | 0.3417 | 0.3449 | 0.2514 | 0.8786 | 0.3625 | 0.3508 | 0.4630 |
| 44/23/39_3/2/2 | 0.0017 | 0.4248 | 0.5155 | 0.3644 | 0.9560 | 0.4654 | 0.3790 | 0.5477 |
| 44/23/39_3/3/3 | 0 | 0.4992 | 0.3343 | 0.1943 | 0.9531 | 0.3060 | 0.3785 | 0.6688 |
| 82/42/71_2/2/2 | 0.0013 | 0.2599 | 0.4022 | 0.2959 | 0.8988 | 0.5376 | 0.3174 | 0.4242 |
| 82/42/71_3/2/2 | 0.0127 | 0.1507 | 0.3259 | 0.1707 | 0.8421 | 0.4690 | 0.3655 | 0.4644 |
| 82/42/71_3/3/3 | 0.0075 | 0.3547 | 0.3316 | 0.0941 | 0.7589 | 0.3434 | 0.3313 | 0.4765 |
| 135/70/120_3/3/3 | 0.0003 | 0.0777 | 0.3235 | 0.2528 | 0.7709 | 0.3298 | 0.2637 | 0.4445 |
| 135/70/120_4/3/3 | 0.0005 | 0.3859 | 0.4102 | 0.4588 | 0.9723 | 0.4449 | 0.3878 | 0.3356 |
| 135/70/120_4/3/4 | 0.0010 | 0.2352 | 0.4640 | 0.2639 | 0.9323 | 0.6075 | 0.3326 | 0.2695 |
| 173/88/151_3/3/3 | 0.0031 | 0.1326 | 0.2997 | 0.2859 | 0.8063 | 0.3339 | 0.3163 | 0.4845 |
| 173/88/151_4/3/3 | 0 | 0.0733 | 0.2559 | 0.1525 | 0.7225 | 0.3928 | 0.3541 | 0.4779 |
| 173/88/151_4/3/4 | 0.0117 | 0.0677 | 0.3560 | 0.2144 | 0.7672 | 0.6232 | 0.3032 | 0.3667 |
| 202/104/175_3/3/3 | 0 | 0.0676 | 0.2872 | 0.2337 | 0.8153 | 0.3370 | 0.2904 | 0.4662 |
| 202/104/175_4/3/3 | 0.0049 | 0.0878 | 0.2991 | 0.1570 | 0.7052 | 0.3648 | 0.2861 | 0.4667 |
| 202/104/175_4/3/4 | 0.0217 | 0.0575 | 0.3204 | 0.2630 | 0.7515 | 0.6474 | 0.3274 | 0.4378 |
| Mean | 0.0051 | 0.2273 | 0.3485 | 0.2380 | 0.8379 | 0.4382 | 0.3419 | 0.4733 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





