Submitted:
02 September 2024
Posted:
03 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
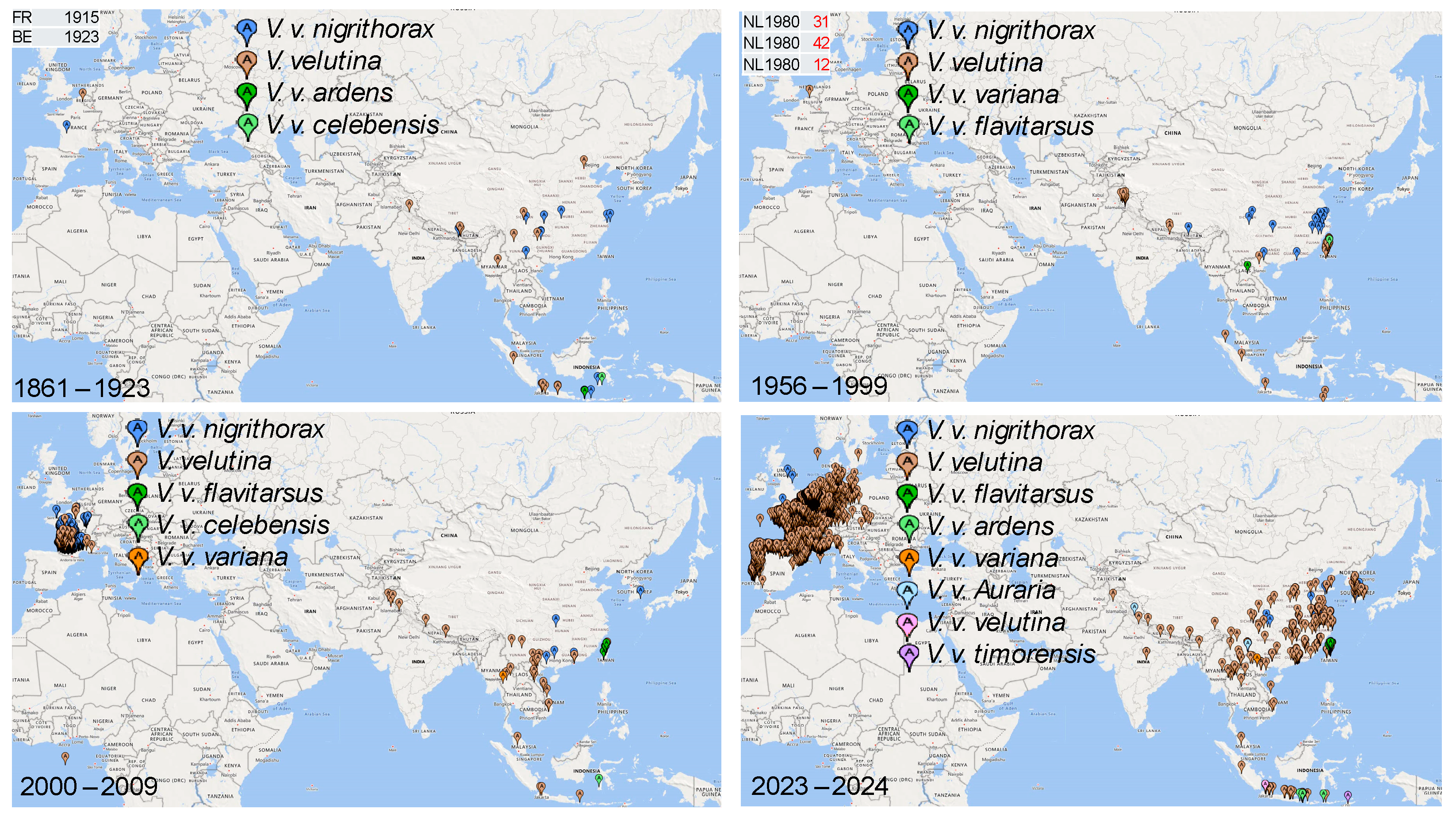
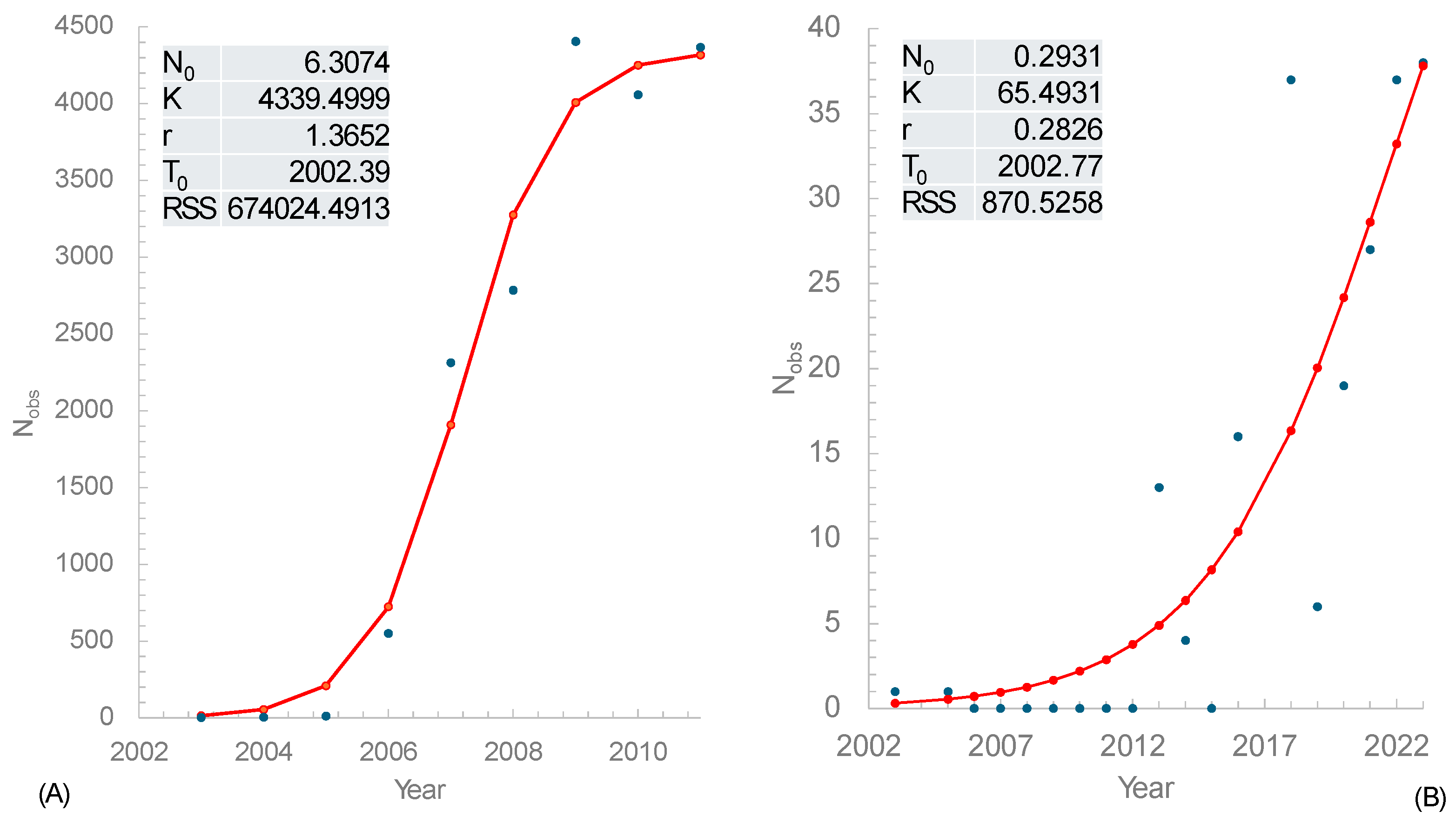
3. Results
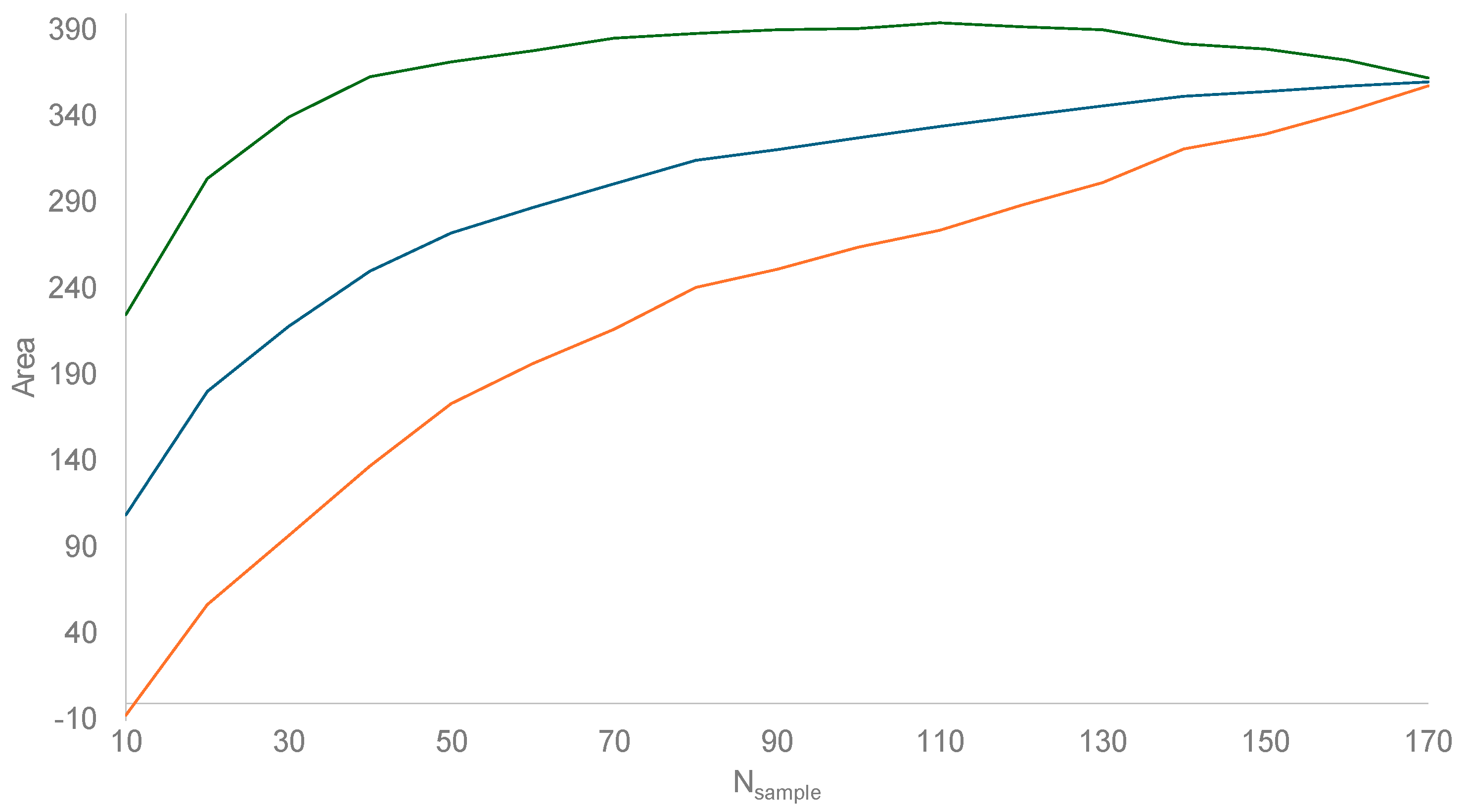
3.1. Estimating Invasion Time () and Instantaneous Rate of Growth (r)
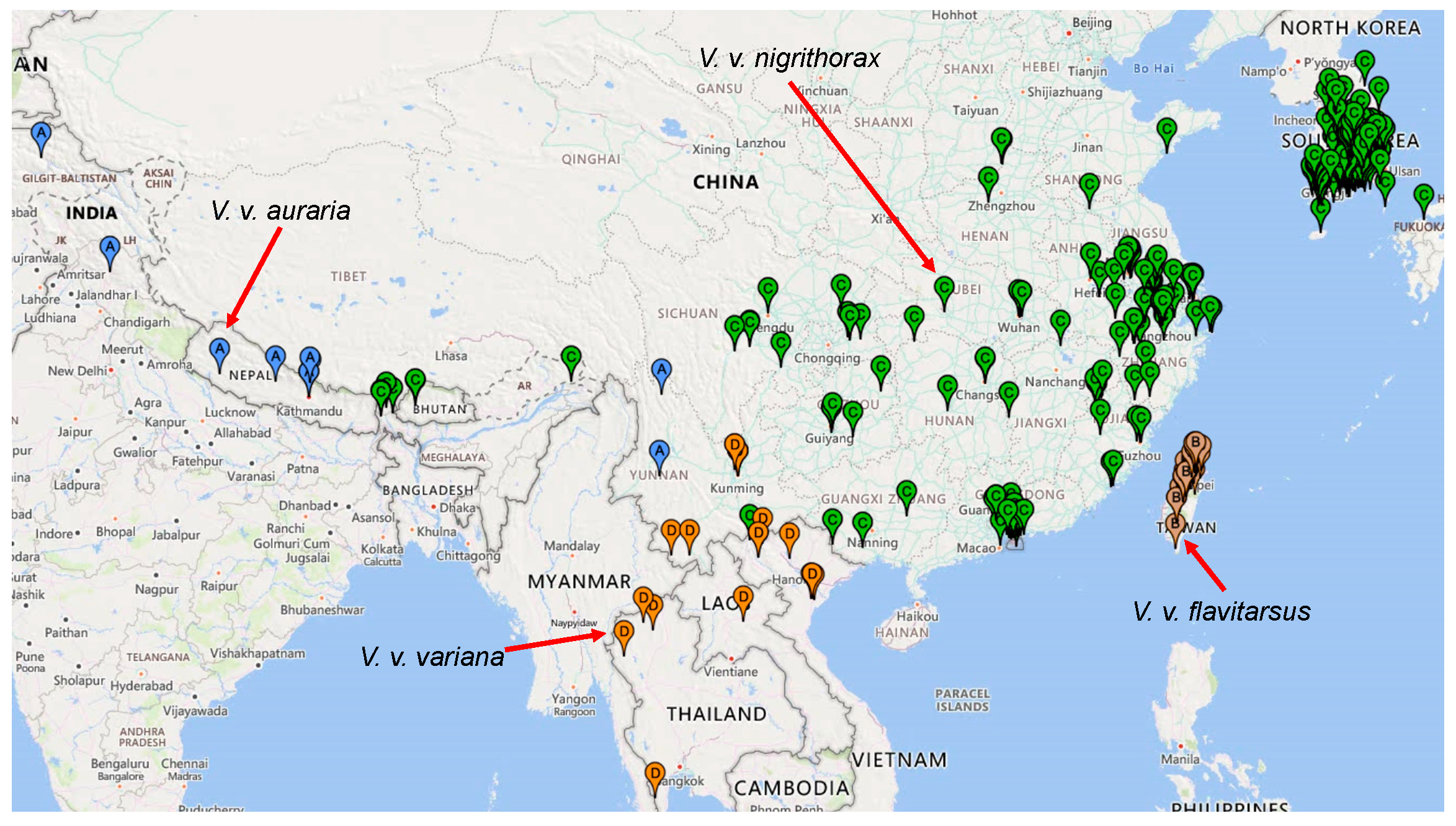
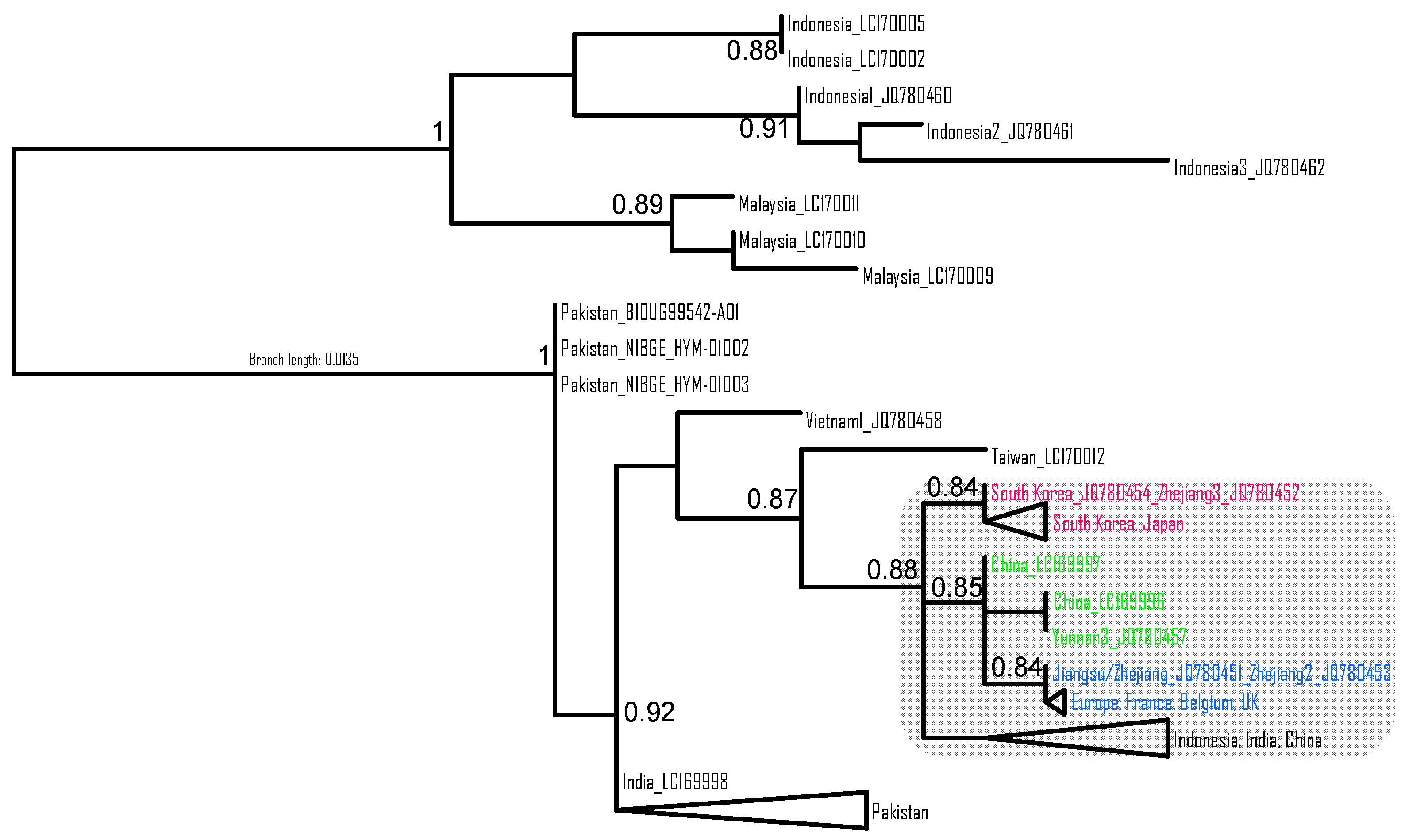
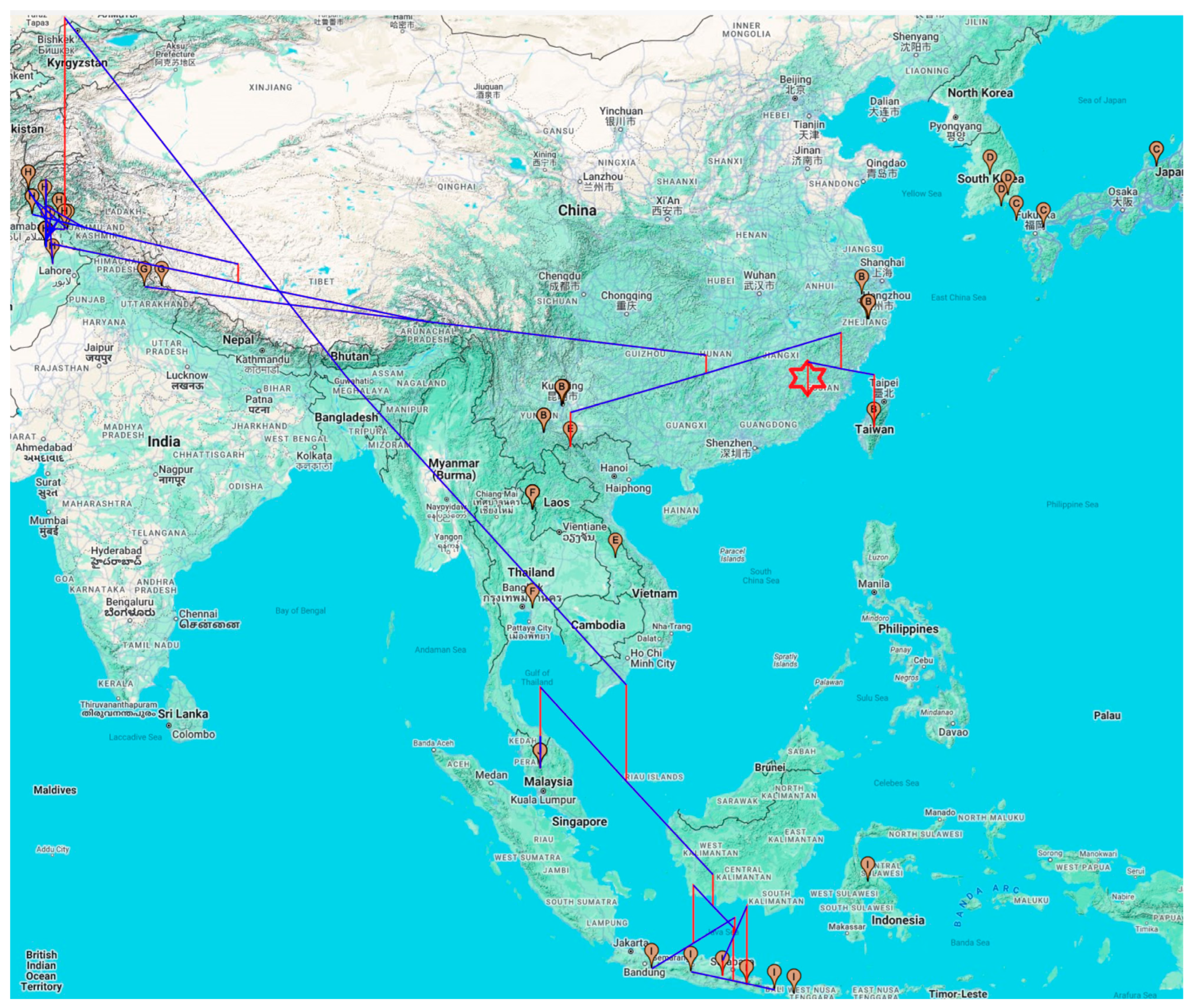
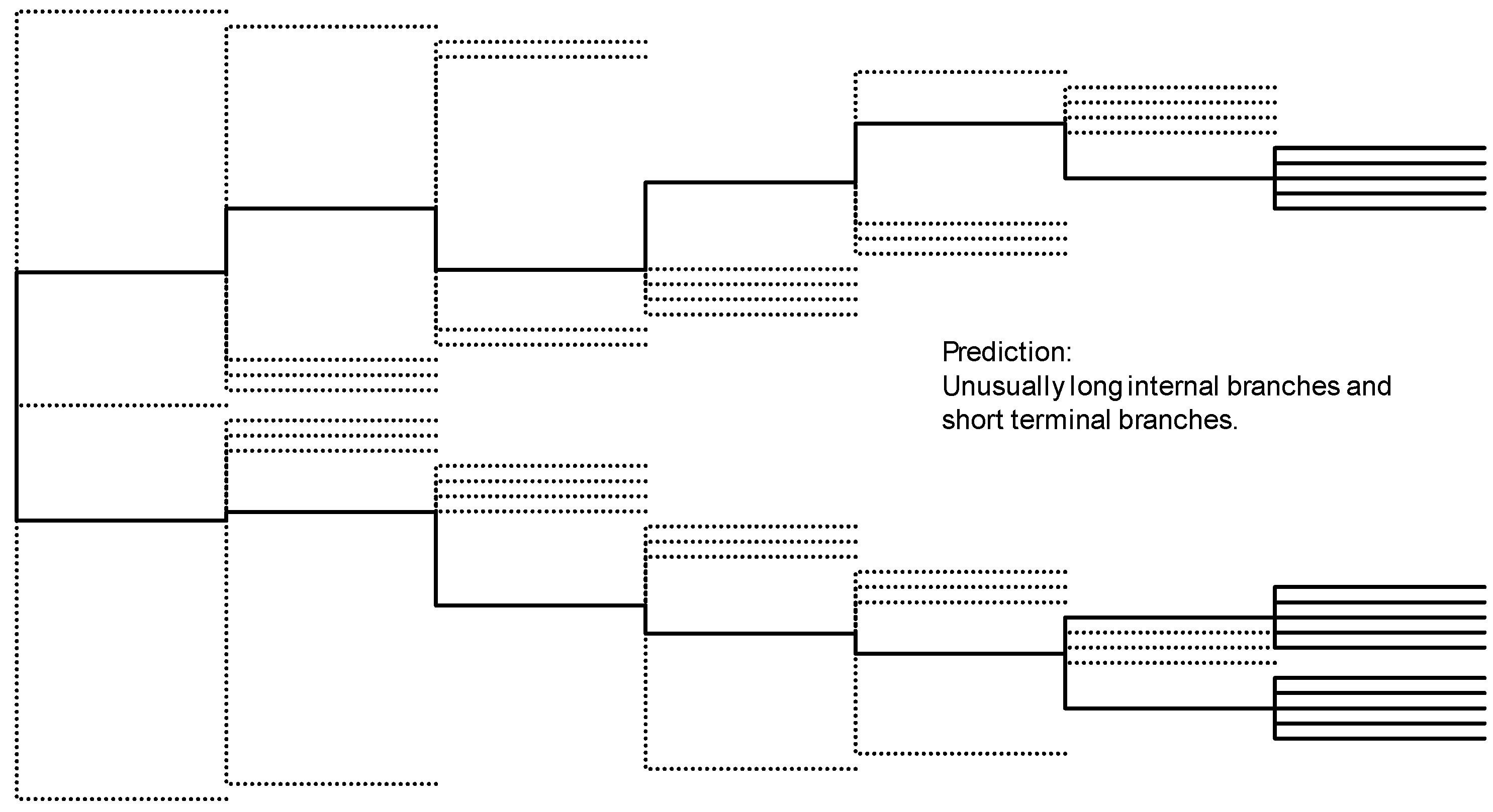
3.2. Phylogeographic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bass, A.; Needham, K.; Bennett, A.M.R. , First record of Vespa crabro Linnaeus (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) in western North America with a review of recorded species of Vespa Linnaeus in Canada. Zootaxa 2022, 5154, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otis, G.W.; Taylor, B.A.; Mattila, H.R. , Invasion potential of hornets (Hymenoptera: Vespidae: Vespa spp.). Frontiers in Insect Science 2023, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beggs, J.R.; Brockerhoff, E.G.; Corley, J.C.; Kenis, M.; Masciocchi, M.; Muller, F.; Rome, Q.; Villemant, C. , Ecological effects and management of invasive alien Vespidae. BioControl 2011, 56, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaniz, A.J.; Carvajal, M.A.; Vergara, P.M. , Giants are coming? Predicting the potential spread and impacts of the giant Asian hornet (Vespa mandarinia, Hymenoptera:Vespidae) in the USA. Pest Management Science 2021, 77, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez-Penichet, C.; Osorio-Olvera, L.; Gonzalez, V.H.; Cobos, M.E.; Jiménez, L.; DeRaad, D.A.; Alkishe, A.; Contreras-Díaz, R.G.; Nava-Bolaños, A.; Utsumi, K. , et al., Geographic potential of the world's largest hornet, Vespa mandarinia Smith (Hymenoptera: Vespidae), worldwide and particularly in North America. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérubé, C. , Giant alien insect invasion averted. Am. Bee J. 2020, 160, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Gutierrez Illan, J.; Looney, C.; Crowder, D.W. , Assessing the ecological niche and invasion potential of the Asian giant hornet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2020, 117, 24646–24648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, M.; Sakagami, S.F. , A Bionomic Sketch of the Giant Hornet, Vespa mandarinia, a Serious Pest for Japanese Apiculture. Jour. Faa. Sci. Hokkaido Univ. Ser. VI, Zool. 1973, 19, 125–162. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura, M.; Yamane, S. , Biology of the Vespine Wasps. Springer-Verlag: Heidelberg, 1990; p XIX, 323.
- Brodmann, J.; Twele, R.; Francke, W.; Yi-bo, L.; Xi-qiang, S.; Ayasse, M. , Orchid mimics honey bee alarm pheromone in order to attract hornets for pollination. Curr Biol 2009, 19, 1368–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monceau, K.; Bonnard, O.; Thiéry, D. , Vespa velutina: a new invasive predator of honeybees in Europe. J. Pest Sci. 2014, 87, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbet-Massin, M.; Salles, J.-M.; Courchamp, F. , The economic cost of control of the invasive yellow-legged Asian hornet. NeoBiota 2020, 55, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Igarashi, T.; Ohno, E.; Sasaki, M. , Unusual thermal defence by a honeybee against mass attack by hornets. Nature 1995, 377, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Okada, I.; Sasaki, M. , Heat production by balling in the Japanese honeybee,Apis cerana japonica as a defensive behavior against the hornet,Vespa simillima xanthoptera (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Experientia 1987, 43, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClenaghan, B.; Schlaf, M.; Geddes, M.; Mazza, J.; Pitman, G.; McCallum, K.; Rawluk, S.; Hand, K.; Otis, G.W. , Behavioral responses of honey bees, Apis cerana and Apis mellifera, to Vespa mandarinia marking and alarm pheromones. Journal of Apicultural Research 2019, 58, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.M.; Takahashi, J.; Spichiger, S.-E.; Kim, I.; van Westendorp, P. , First Reports of Vespa mandarinia (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) in North America Represent Two Separate Maternal Lineages in Washington State, United States, and British Columbia, Canada. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2020, 113, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristoforou, A.; Rortais, A.; Zafeiridou, G.; Theophilidis, G.; Garnery, L.; Thrasyvoulou, A.; Arnold, G. , Smothered to death: Hornets asphyxiated by honeybees. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, R795–R796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Radloff, S.E.; Li, J.J.; Hepburn, H.R.; Yang, M.X.; Zhang, L.J.; Neumann, P. , Bee-hawking by the wasp, Vespa velutina, on the honeybees Apis cerana and A. mellifera. Naturwissenschaften 2007, 94, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, M.E.; Penney, D. , Vespine wasps of the world: behaviour, ecology and taxonomy of the Vespinae.. Siri Scientif Press: Manchester, 2012; p 352.
- Smith-Pardo, A.H.; Carpenter, J.M.; Kimsey, L. , The Diversity of Hornets in the Genus Vespa (Hymenoptera: Vespidae; Vespinae), Their Importance and Interceptions in the United States. Insect Systematics and Diversity 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, M. , Taxonomy, distribution and nesting biology of the Vespa bicolor group (Hym., Vespinae). Entomologist’s Monthly Magazine 1994, 130, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Perrard, A.; Arca, M.; Rome, Q.; Muller, F.; Tan, J.; Bista, S.; Nugroho, H.; Baudoin, R.; Baylac, M.; Silvain, J.-F. , et al., Geographic Variation of Melanisation Patterns in a Hornet Species: Genetic Differences, Climatic Pressures or Aposematic Constraints? PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e94162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Vecht, J. , The Vespinae of the Indo-Malayan and Papuan Areas (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Zoologische Verhandelingen 1957, 34, 1–82. [Google Scholar]
- Villemant, C.; Muller, F.; Haubois, S. ; A., P.; Darrouzet, E.; Rome, Q. In Bilan dês travaux (MNHN et IRBI) sur l’invasion en France de Vespa velutina, le frelon asiatique prédateur d’abeilles., Journée Scientifique Apicole JSA, Arles, 11 fevrier 2011, Arles, Nantes, France, 2011; Barbançon, J.-M.; L’hostis, M., Eds. Arles, Nantes, France, pp 3-12.
- Ueno, T. In Establishment of the Invasive Hornet Vespa velutina ( Hymenoptera : Vespidae ) in Japan, 2014.
- Kim, J.K.; Moon, T.Y.; Yoon, I.B. , Systematics of Vespine wasps from Korea, 1. Genus Vespa Linnaeus (Vespidae, Hymenoptera). Korean Journal of Entomology 1994, 24, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.-B.; Martin, S.J.; Lee, J.-W. , Distribution, spread and impact of the invasive hornet Vespa velutina in South Korea. Entomological Research 2011, 41, 276–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabín-García, L.B.; Bartolomé, C.; Guerra-Tort, C.; Rojas-Nossa, S.V.; Llovo, J.; Maside, X. , Identification of pathogens in the invasive hornet Vespa velutina and in native Hymenoptera (Apidae, Vespidae) from SW-Europe. Scientific reports 2021, 11, 11233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macià, F.X.; Menchetti, M.; Corbella, C.; Grajera, J.; Vila, R. , Exploitation of the invasive Asian Hornet Vespa velutina by the European Honey Buzzard Pernis apivorus. Bird Study 2019, 66, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, M.; Aris-Brosou, S.; Xia, X. , Testing alternative hypotheses on the origin and speciation of Hawaiian katydids. BMC ecology and evolution 2022, 22, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, A.; Xia, X. , Phylogeographic Reconstruction to Trace the Source Population of Asian Giant Hornet Caught in Nanaimo in Canada and Blaine in the USA. Life 2024, 14, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, D.N.; Brown, M.A.; Datta, S.; Cuthbertson, A.G.S.; Budge, G.E.; Keeling, M.J. , Invasion dynamics of Asian hornet, Vespa velutina (Hymenoptera: Vespidae): a case study of a commune in south-west France. Applied Entomology and Zoology 2017, 52, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBIF.org 2024, GBIF Occurrence Download. [CrossRef]
- HAXAIRE, J.; BOUGUET, J.-P.; TAMISIER, J.-P. , Vespa velutina Lepeletier, 1836, une redoutable nouveauté pour la faune de France (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Bulletin de la Société entomologique de France 2006, 111, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemant, C.; Streito, J.-C.; Haxaire, J. , Premier bilan de l'invasion de Vespa velutina Lepeletier en France (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). bsef 2006, 111, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rortais, A.; Villemant, C.; Gargominy, O.; Rome, Q.; Haxaire, J.; Papachristoforou, A.; Arnold, G. , A new enemy of honeybees in Europe: The Asian hornet Vespa velutina. Atlas of Biodiversity Risks–from Europe to globe, from stories to maps. Sofia & Moscow: Pensoft 2010, 11, 181–181. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D. , BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Molecular ecology notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockland, P.-E. Statecraft and Insect Oeconomies in the Global French Enlightenment (1670-1815). Columbia University, 2018.
- Arca, M.; Mougel, F.; Guillemaud, T.; Dupas, S.; Rome, Q.; Perrard, A.; Muller, F.; Fossoud, A.; Capdevielle-Dulac, C.; Torres-Leguizamon, M. , et al., Reconstructing the invasion and the demographic history of the yellow-legged hornet, Vespa velutina, in Europe. Biological Invasions 2015, 17, 2357–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Takahashi, R.; Kiyoshi, T.; Nakamura, M.; Minoshima, Y.N.; Takahashi, J. , The origin and genetic diversity of the yellow-legged hornet, Vespa velutina introduced in Japan. Insectes Sociaux 2017, 64, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. , How Trustworthy Are Genomic Sequences of SARS-CoV-2 in GenBank? In Preprints, Preprints: 2024.
- Xia, X. , DAMBE6: New Tools for Microbial Genomics, Phylogenetics, and Molecular Evolution. J Hered 2017, 108, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrard, A.; Pickett, K.; Villemant, C.; Kojima, J.-i.; Carpenter, J.M. , Phylogeny of hornets: a total evidence approach (Hymenoptera, Vespidae, Vespinae, Vespa). Journal of Hymenoptera Research 2013, 32, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtgam, S.; Jongjitvimol, T. , Genetic Evolution of Asian Predatory Wasp, Vespa velutina, in Northernof Thailand Based on Cytochrome Oxidase Subunit I DNA Barcoding. NU. International Journal of Science 2020, 17, 101–113. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamadzade Namin, S.; Jung, C. , Genetic diversity of genus Vespa including an invaded species of V. velutina (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) in Korea inferred from DNA barcoding data. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology 2020, 23, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, H.R.; Nguyen, L.T.P.; Perrard, A.; Bain, M.; Otis, G.W. , Biology of the southern giant hornet, Vespa soror: nest architecture, morphological differences among castes, and the genetic structure of colonies. Frontiers in Insect Science 2023, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Asimenos, G.; Toh, H. , Multiple alignment of DNA sequences with MAFFT. Methods Mol Biol 2009, 537, 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. , New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z. , Statistical properties of the maximum likelihood method of phylogenetic estimation and comparison with distance matrix method. Syst Biol 1994, 43, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. , Information-theoretic indices and an approximate significance test for testing the molecular clock hypothesis with genetic distances. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2009, 52, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. , A Mathematical Primer of Molecular Phylogenetics. CRC Press: New York, 2020; p 380.
- Hasegawa, M.; Kishino, H.; Yano, T. , Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. , Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Molecular Biology and Evolution 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar]
- Tavaré, S. , Some Probabilistic and Statistical Problems in the Analysis of DNA Sequences. American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, 1986; Vol. 17, p 57-86.
- Lanave, C.; Preparata, G.; Saccone, C.; Serio, G. , A new method for calculating evolutionary substitution rates. J. Mol. Evol. 1984, 20, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.L. , An efficient algorith for determining the convex hull of a finite planar set. Information Processing Letters 1972, 1, 132–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. , PGT: Visualizing temporal and spatial biogeographic patterns. Global Ecology & Biogeography 2019, 28, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar]
- French Government, Stéphane Le Foll et Delphine Batho annoncent le classement du frelon asiatique en espèce envahissante et nuisible. le Ministre de l’Agriculture; de l’Agroalimentaire et de la Forêt; la Ministre de l’Ecologie; du Développement Durable et de l’Energie, Eds. Ministere de 'Agriculture et de la Souverainete alimentaire: 2012.
- KIM, J.-K.; CHOI, M.; MOON, T.-Y. , Occurrence of Vespa velutina Lepeletier from Korea, and a revised key for Korean Vespa species (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Entomological Research 2006, 36, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carisio, L.; Cerri, J.; Lioy, S.; Bianchi, E.; Bertolino, S.; Porporato, M. , Impacts of the invasive hornet Vespa velutina on native wasp species: a first effort to understand population-level effects in an invaded area of Europe. Journal of Insect Conservation 2022, 26, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Takahashi, J. , Discovery of a worker of Vespa velutina (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) from Tsushima Island, Japan. 2014.
- Minoshima, Y.N.; Yamane, S.; Ueno, T. , An invasive alien hornet, Vespa velutina nigrithorax du Buysson (Hymenoptera, Vespidae), found in Kitakyushu, Kyushu Island: a first record of the species from mainland Japan. Jpn J Syst Entomol 2015, 21, 259–261. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, C.; Ferragut, J.F.; Leza, M.; Jurado-Rivera, J.A. , Invasion genetics of the yellow-legged hornet Vespa velutina in the Westernmost Mediterranean archipelago. Journal of Pest Science 2024, 97, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberloff, D.; Martin, J.-L.; Genovesi, P.; Maris, V.; Wardle, D.A.; Aronson, J.; Courchamp, F.; Galil, B.; García-Berthou, E.; Pascal, M. , et al., Impacts of biological invasions: what's what and the way forward. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, A.S.; Carvalho, J.; Gomes, A.; Santarém, F. , Climate and land-use drivers of invasion: predicting the expansion of Vespa velutina nigrithorax into the Iberian Peninsula. Insect Conservation and Diversity 2016, 9, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Okuyama, H.; Minoshima, Y.N.; Takahashi, J.I. , Complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the alien hornet Vespa velutina (Insecta: Hymenoptera) invading Kyushu Island, Japan. Mitochondrial DNA. Part B, Resources 2018, 3, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, Y.; Morita, K.; Sugiura, T.; Okada, Y. , Cutaneous hemorrhage or necrosis findings after Vespa mandarinia (wasp) stings may predict the occurrence of multiple organ injury: A case report and review of literature. Clin. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haro, L.; Labadie, M.; Chanseau, P.; Cabot, C.; Blanc-Brisset, I.; Penouil, F. , Medical consequences of the Asian black hornet (Vespa velutina) invasion in Southwestern France. Toxicon 2010, 55, 650–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAYR, E. , Systematics and the Origin of Species. Columbia University Press: New York, 1942.
- Templeton, A.R. , The theory of speciation via the founder principle. Genetics 1980, 94, 1011–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. , Statistical genetics and evolution. Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 1942, 48, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish Kumar, P.; Srinivasan, G. , Taxonomic Studies of Hornet Wasps (Hymenoptera : Vespidae) Vespa Linnaeus of India. Records of the Zoological Survey of India 2010, 110, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, J.M.; Kojima, J. , Checklist of the Species in the Subfamily Vespinae (Insecta: Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Nat. Hist. Bull Ibaraki Univ. 1997, 1, 51–92. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




