Submitted:
26 August 2024
Posted:
26 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection for Lipopeptide Antifungal Activity Meta-Analysis
2.2. Effect Sizes
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Bacillus Strains under Study for Detection of Lipopeptide Biosysntesis Genes
2.5. DNA Extraction of Bacillus Strains
2.6. Detection and Sequence Analysis of Lipopeptide Biosynthesis Genes
2.7. Analysis of Gene Sequences
3. Results
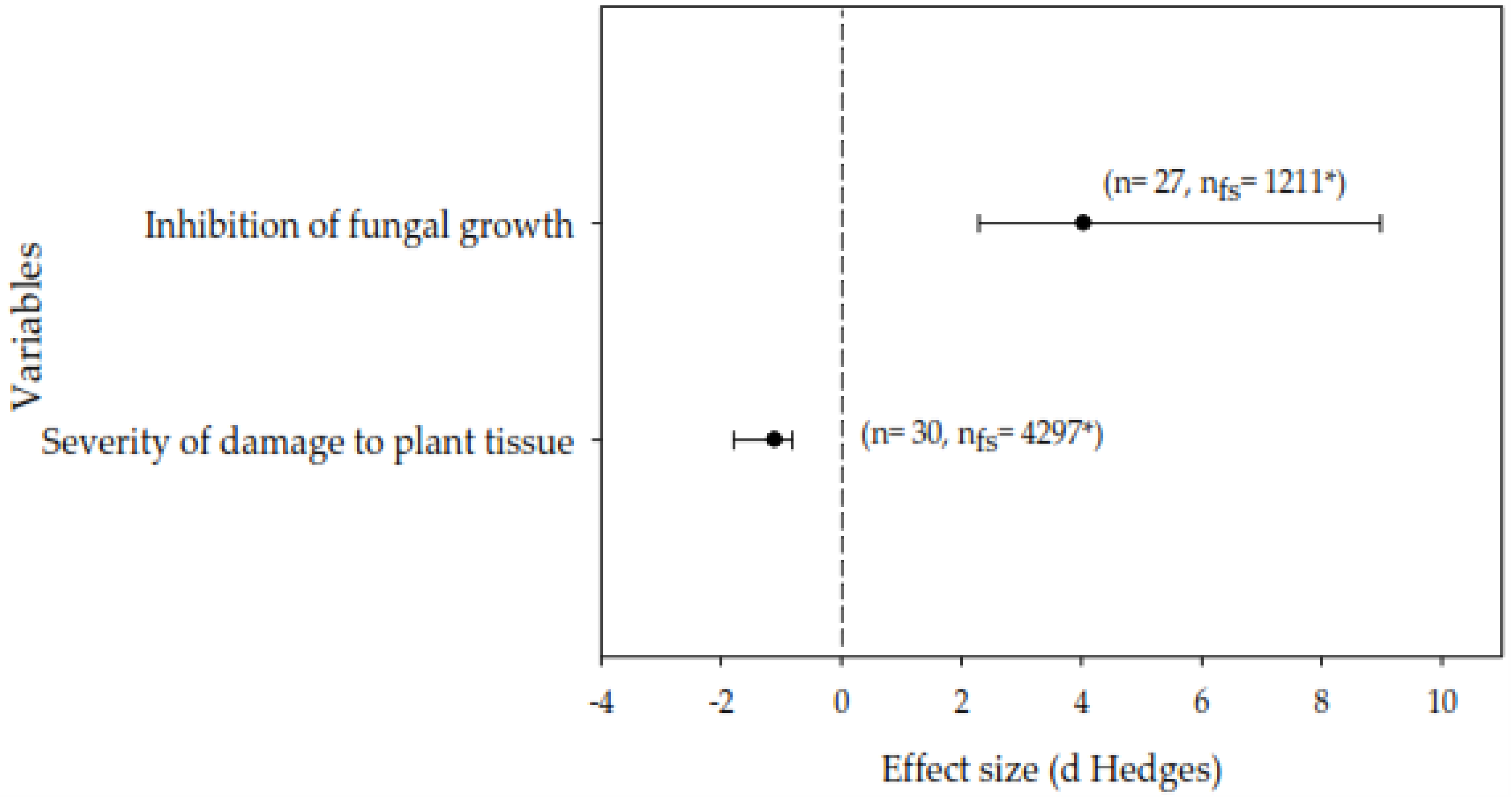
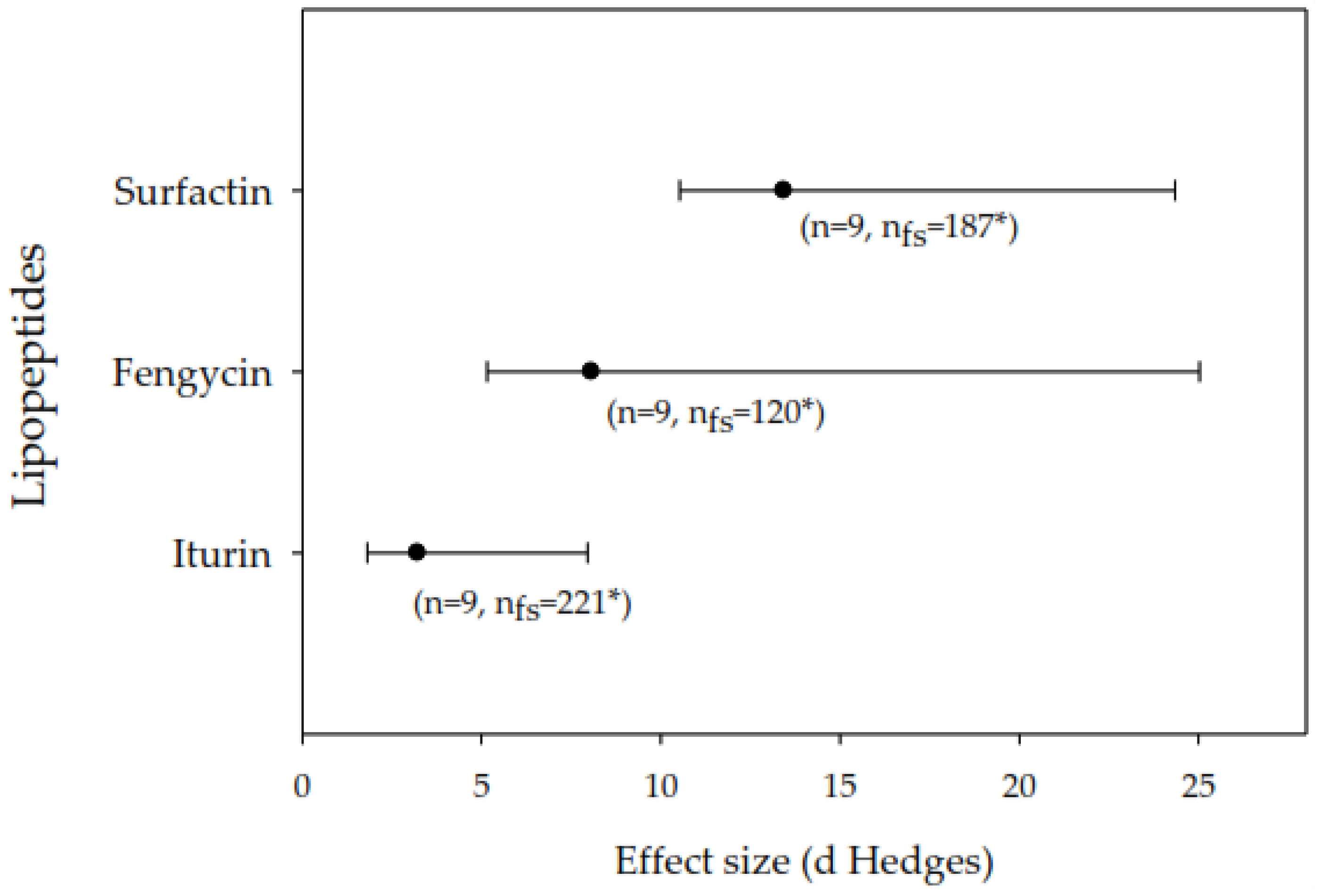
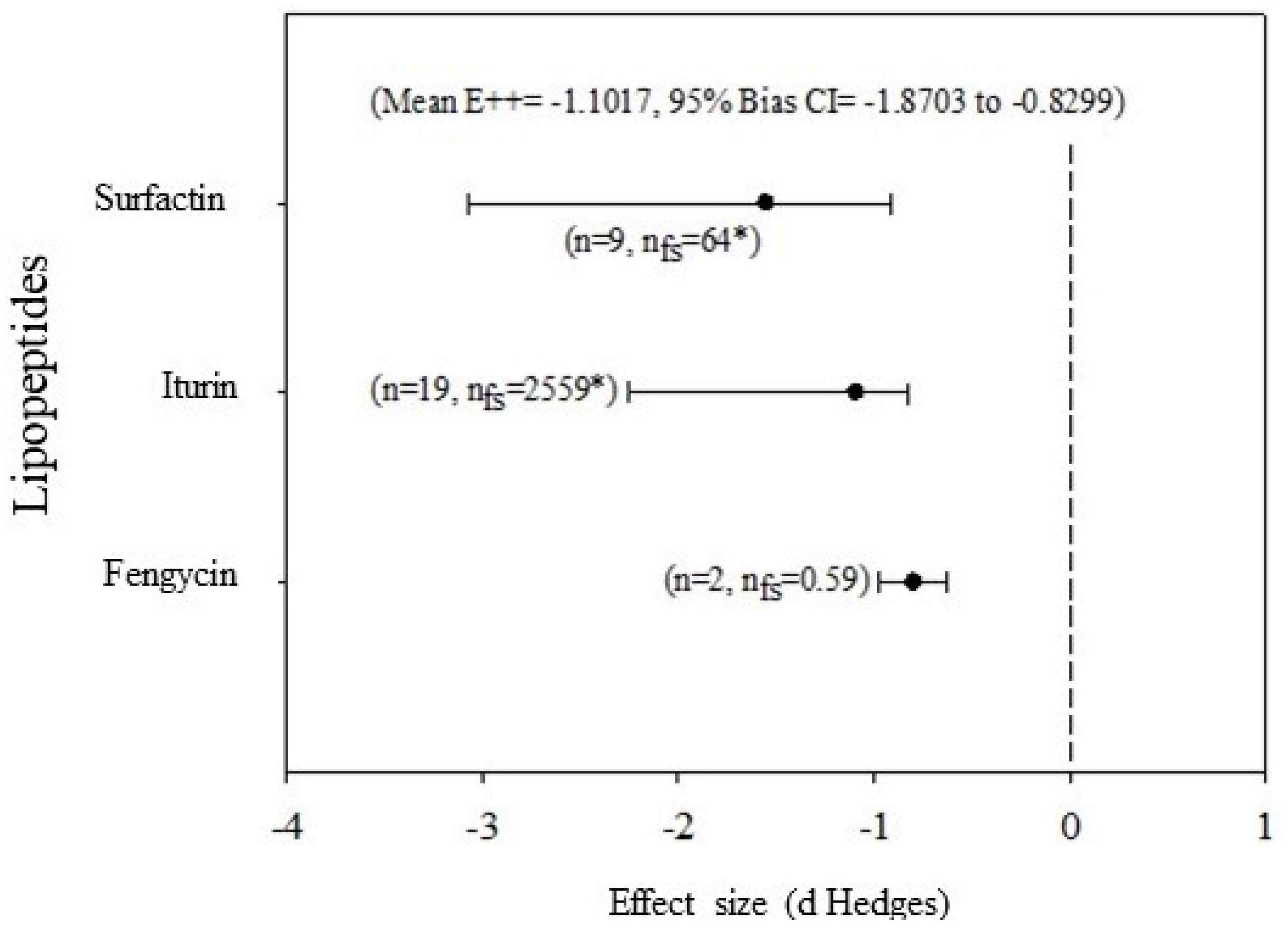
3.1. General Effects of Lipopeptides on Phytopathogenic Fungi
3.2. Meta-Analysis of the Inhibition of Fungal Growth In Vitro and Severity of Damage to Plants
3.3. Detection and Analysis of Lipopeptide Biosynthesis Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Brien, J.; Wright, G.D. An Ecological Perspective of Microbial Secondary Metabolism. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, R.A.; Stajich, J.E.; Yamanaka, Y.; Dietrich, F.S.; Steinbach, W.J.; Perfect, J.R. Phylogenomic Analysis of Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthetases in the Genus Aspergillus. Gene 2006, 383, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpa, E.; Jacques, P.; Wathelet, B.; Paquot, M.; Fuchs, R.; Budzikiewicz, H.; Thonart, P. Influence of Culture Conditions on Lipopeptide Production by Bacillus Subtilis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. - Part A Enzym. Eng. Biotechnol. 2001, 91–93, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munakata, Y.; Heuson, E.; Daboudet, T.; Deracinois, B.; Duban, M.; Hehn, A.; Coutte, F.; Slezack-deschaumes, S. Screening of Antimicrobial Activities and Lipopeptide Production of Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Vetiver Roots. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, D.; De Vicente, A.; Olmos, J.L.; Dávila, J.C.; Pérez-García, A. Effect of Lipopeptides of Antagonistic Strains of Bacillus Subtilis on the Morphology and Ultrastructure of the Cucurbit Fungal Pathogen Podosphaera Fusca. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maget-Dana, R.; Thimon, L.; Peypoux, F.; Ptak, M. Surfactin/Iturin A Interactions May Explain the Synergistic Effect of Surfactin on the Biological Properties of Iturin A. Biochimie 1992, 74, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, A.D.; Li, H.P.; Yuan, Q.S.; Song, X.S.; Yao, W.; He, W.J.; Zhang, J.B.; Liao, Y.C. Antagonistic Mechanism of Iturin A and Plipastatin A from Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens S76-3 from Wheat Spikes against Fusarium Graminearum. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0116871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, N.; Velramar, B.; Velu, R.K. Investigation of Antifungal Activity of Surfactin against Mycotoxigenic Phytopathogenic Fungus Fusarium Moniliforme and Its Impact in Seed Germination and Mycotoxicosis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 155, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, P.A.; McMullen, M.P.; Hershman, D.E.; Madden, L.V. Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Triazole-Based Fungicides on Wheat Yield and Test Weight as Influenced by Fusarium Head Blight Intensity. Disease Control and Pest Management 2010, 100, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athukorala, S.N.P.; Fernando, W.G.D.; Rashid, K.Y. Identification of Antifungal Antibiotics of Bacillus Species Isolated from Different Microhabitats Using Polymerase Chain Reaction and MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. Can. J. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, T. Bacillus Subtilis Antibiotics: Structures, Syntheses and Specific Functions. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 56, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangi, T.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Nakkeeran, S. Antimicrobial Peptide Genes Present in Indigenous Isolates of Bacillus Spp. Exhibiting Antimicrobical Properties. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyne, A.L.; Cleveland, T.E.; Tuzun, S. Molecular Characterization and Analysis of the Operon Encoding the Antifungal Lipopeptide Bacillomycin D. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 234, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verwoert, I.I.G.S.; Verbree, E.C.; Van der Linden, K.H.; Nijkamp, H.J.J.; Stuitje, A.R. Cloning, Nucleotide Sequence, and Expression of the Escherichia Coli FabD Gene, Encoding Malonyl Coenzyme A-Acyl Carrier Protein Transacylase. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 2851–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbidoni, H.R.; De Mendoza, D.; Cronan, J.E. Bacillus Subtilis Acyl Carrier Protein Is Encoded in a Cluster of Lipid Biosynthesis Genes. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 4794–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.H.; Chen, C.L.; Tschen, J.S.M.; Tsay, S.S.; Chang, Y.S.; Liu, S.T. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of Fengycin Synthetase Gene FenB from Bacillus Subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 1338–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosato, V.; Albertini, A.M.; Zotti, M.; Sonda, S.; Bruschi, C.V. Sequence Completion, Identification and Definition of the Fengycin Operon in Bacillus Subtilis 168. Microbiology 1997, 143, 3443–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosmina, P.; Rodriguez, F.; de Ferra, F.; Grandi, G.; Perego, M.; Venema, G.; van Sinderen, D. Sequence and Analysis of the Genetic Locus Responsible for Surfactin Synthesis in Bacillus Subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 1993, 8, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menkhaus, M.; Ullrich, C.; Kluge, B.; Vater, J.; Vollenbroich, D.; Kamp, R.M. Structural and Functional Organization of the Surfactin Synthetase Multienzyme System. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 7678–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.S. The File-Drawer Problem Revisited: A General Weighted Method for Calculating Fail-Safe Numbers in Meta-Analysis. Evolution (N. Y). 2005, 59, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, R. The File Drawer Problem and Tolerance for Null Results. Psychol. Bull. 1979, 86, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Bautista, M.A.; Cristóbal-Alejo, J.; Tun-Suárez, J.M.; Reyes-Ramírez, A. Actividad in Vitro de Bacillus Spp. En La Inhibición de Crecimiento Micelial de Fusarium Equiseti y Fusarium Solani Aislado de Chile Habanero (Capsicum Chinense Jacq.). Agrociencia 2016, 50, 1123–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Ramarathnam, R.; Bo, S.; Chen, Y.; Fernando, W.G.D.; Xuewen, G.; De Kievit, T. Molecular and Biochemical Detection of Fengycin- and Bacillomycin D-Producing Bacillus Spp., Antagonistic to Fungal Pathogens of Canola and Wheat. Can. J. Microbiol. 2007, 53, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Madan, A. CAP3: A DNA Sequence Assembly Program. Genome Res. 1999, 9, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Bie, X. mei; Lv, F. xia; Zhao, H. zhen; Lu, Z. xin Antifungal Activity and Mechanism of Fengycin in the Presence and Absence of Commercial Surfactin Against Rhizopus Stolonifer. J. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y. feng; Li, Q. qin; Fu, G.; Yuan, G. qing; Miao, J. hua; Lin, W. Identification of Antifungal Substance (Iturin A2) Produced by Bacillus Subtilis B47 and Its Effect on Southern Corn Leaf Blight. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.G.; Lee, H.J.; Bae, J.Y.; Kim, N.H.; Moon, B.J.; Lee, S.W. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of a Biocontrol Bacterium Bacillus Licheniformis N1 on the Strawberry Plants. Plant Pathol. J. 2010, 26, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, I.; Cabrefiga, J.; Montesinos, E. Antimicrobial Peptide Genes in Bacillus Strains from Plant Environments. Int. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, S.; Mihajlović, S.; Draganić, V.; Dimkić, I.; Vukotić, G.; Berić, T.; Fira, D. Screening for the Presence of Biosynthetic Genes for Antimicrobial Lipopeptides in Natural Isolates of Bacillus Sp. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2012, 64, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gond, S.K.; Bergen, M.S.; Torres, M.S.; White, J.F. Endophytic Bacillus Spp. Produce Antifungal Lipopeptides and Induce Host Defence Gene Expression in Maize. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 172, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, G.; Zheng, R.; Sun, C.; Wu, S. Structural and Functional Insights into Iturin W, a Novel Lipopeptide Produced by the Deep-Sea Bacterium Bacillus Sp. Strain Wsm-1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liang, L.; Shao, H.; Ye, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, J. Isolation of the Novel Strain Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens F9 and Identification of Lipopeptide Extract Components Responsible for Activity against Xanthomonas Citri Subsp. Citri. Plants 2022, 11, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steller, S.; Sokoll, A.; Wilde, C.; Bernhard, F.; Franke, P.; Vater, J. Initiation of Surfactin Biosynthesis and the Role of the SrfD-Thioesterase Protein. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 11331–11343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Shiraishi, S.; Suzuki, S. Are Cyclic Lipopeptides Produced by Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens S13-3 Responsible for the Plant Defence Response in Strawberry against Colletotrichum Gloeosporioides? Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 60, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejri, S.; Siah, A.; Coutte, F.; Magnin-Robert, M.; Randoux, B.; Tisserant, B.; Krier, F.; Jacques, P.; Reignault, P.; Halama, P. Biocontrol of the Wheat Pathogen Zymoseptoria Tritici Using Cyclic Lipopeptides from Bacillus Subtilis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 29822–29833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Liu, X.; Fan, X.; Huang, R.; Gao, W.; Wang, S.; Yang, C. Enhanced Production of Antifungal Lipopeptide Iturin A by Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens LL3 through Metabolic Engineering and Culture Conditions Optimization. Microb. Cell Fact. 2019, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.T.; Park, B.K.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, W.J.; Moon, J.S.; Cho, M.S.; Park, H.Y.; Hwang, I.; Kim, S.U. Organization and Characterization of Genetic Regions in Bacillus Subtilis Subsp. Krictiensis ATCC55079 Associated with the Biosynthesis of Iturin and Surfactin Compounds. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0188179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Inhibition of fungal growth | Severity of damage to plant tissue | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Df | Q.B. | Q | Df | Q.B. | Q | ||
| Complete model | 26 | 210.9195 | <0.0000 | 29 | 465.4113 | <0.0000 | |
| Lipopeptides | 2 | 43.1895 | <0.0000 | 2 | 2.3683 | <0.3060 | |
| Concentration | 1 | 31.9641 | <0.0000 | 3 | 23.6973 | <0.0000 | |
| Strains | Genes for antimicrobial lipopeptides | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ituA | fenD | srfA | |
| Bacillus sp. CBRF5 | + | - | - |
| B. amyloliquefaciens CBRF6 | + | - | + |
| B. subtilis CBRF15 | - | + | - |
| Bacillus sp. CBRM9 | + | - | - |
| B. subtilis CBSN67 | + | - | - |
| Homology | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cepa | Lipopeptide /Gene1 | GenBank | UniProt | ||||
| Protein | Identity (%) | Function | Protein | Identity (%) | Protein | ||
| CBRF5 | Iturin A/ fabD |
malonyl-CoA transacylase | 100 | WP_253612942.1 | ACP-S-m Transferase | 100 | Q5NKN8 |
| CBRF6 | Iturin A/ fabD |
malonyl-CoA transacylase | 100 | WP_253612942.1 | ACP-S-m Transferase | 100 | Q5NKN8 |
| CBSN67 | Iturin A/ fabD |
ACP-S-m transferase | 100 | WP_268428834.1 | Malonyl-CoA transacylase | 99.5 | A0A9W5LIK4 |
| CBRM9 | Iturin A/ ituD |
Iturin A synthetase D |
100 | AVN84851.1 | Iturin A synthetase D | 100 | A0A2P1IM41 |
| CBRF15 | Fengycin/ fabD | ACP-S- m transferase | 84.43 | MDA2462581.1 | ACP-S- m transferase | 84.4 | A0A9X7HYE2 |
| CBRF6 | Surfactin/ srf |
Surfactin synthetase |
100 | AEU04020.1 | Surfactin synthetase | 100 | G9JLX1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





