Submitted:
17 August 2024
Posted:
20 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
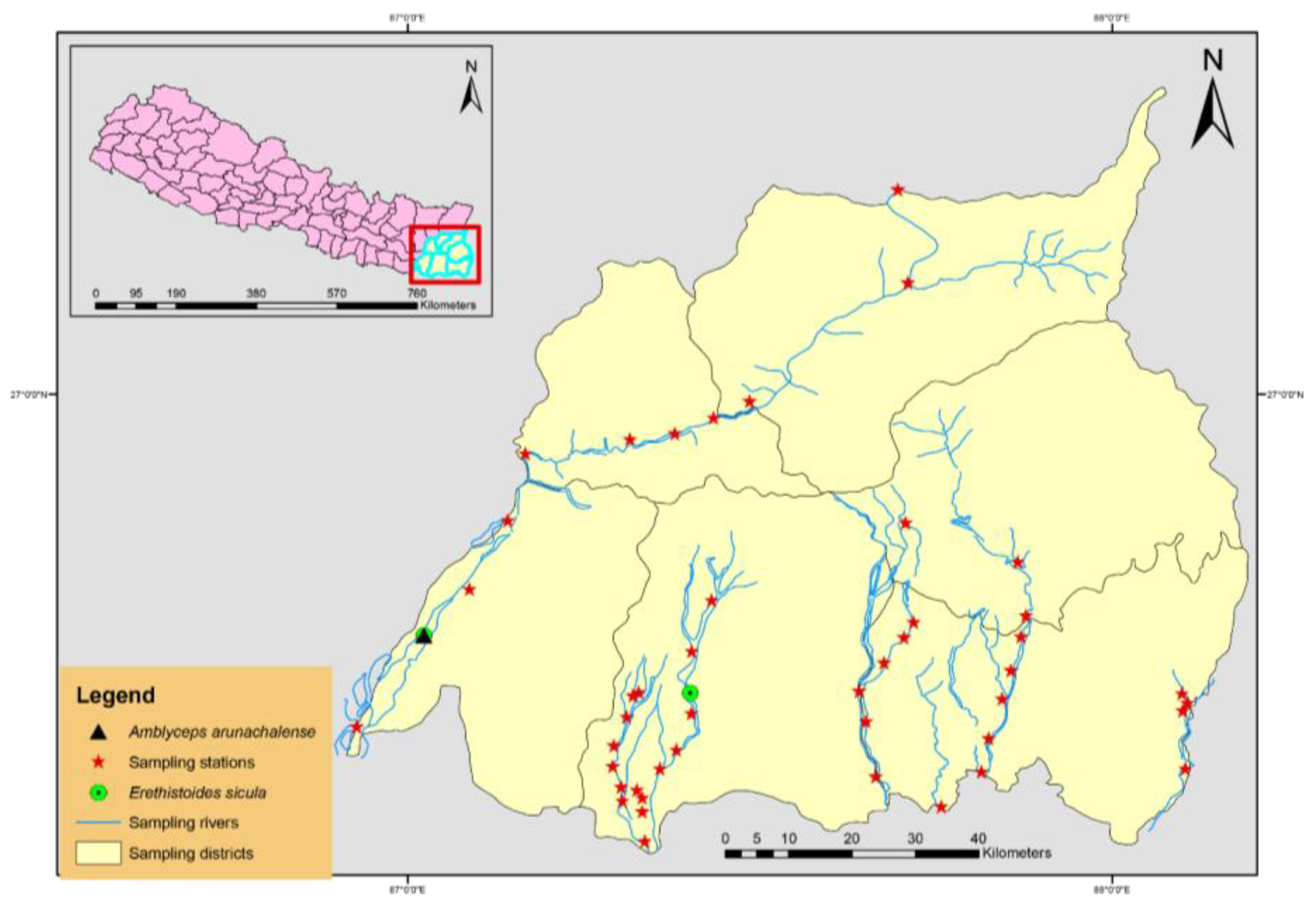
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and PCR
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Catfishes in ERN
3.2. Additional Ichthyofauna for Nepal
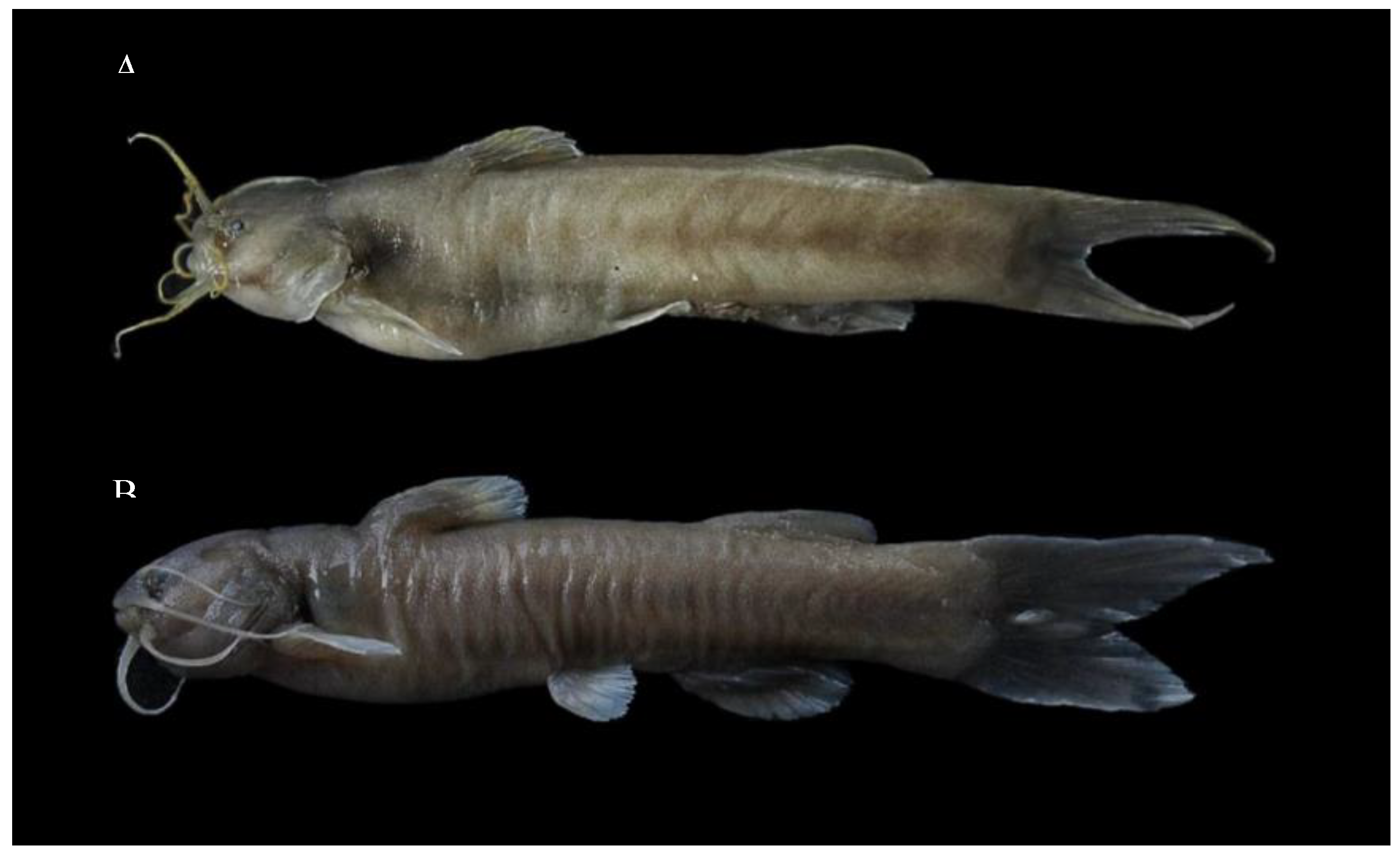
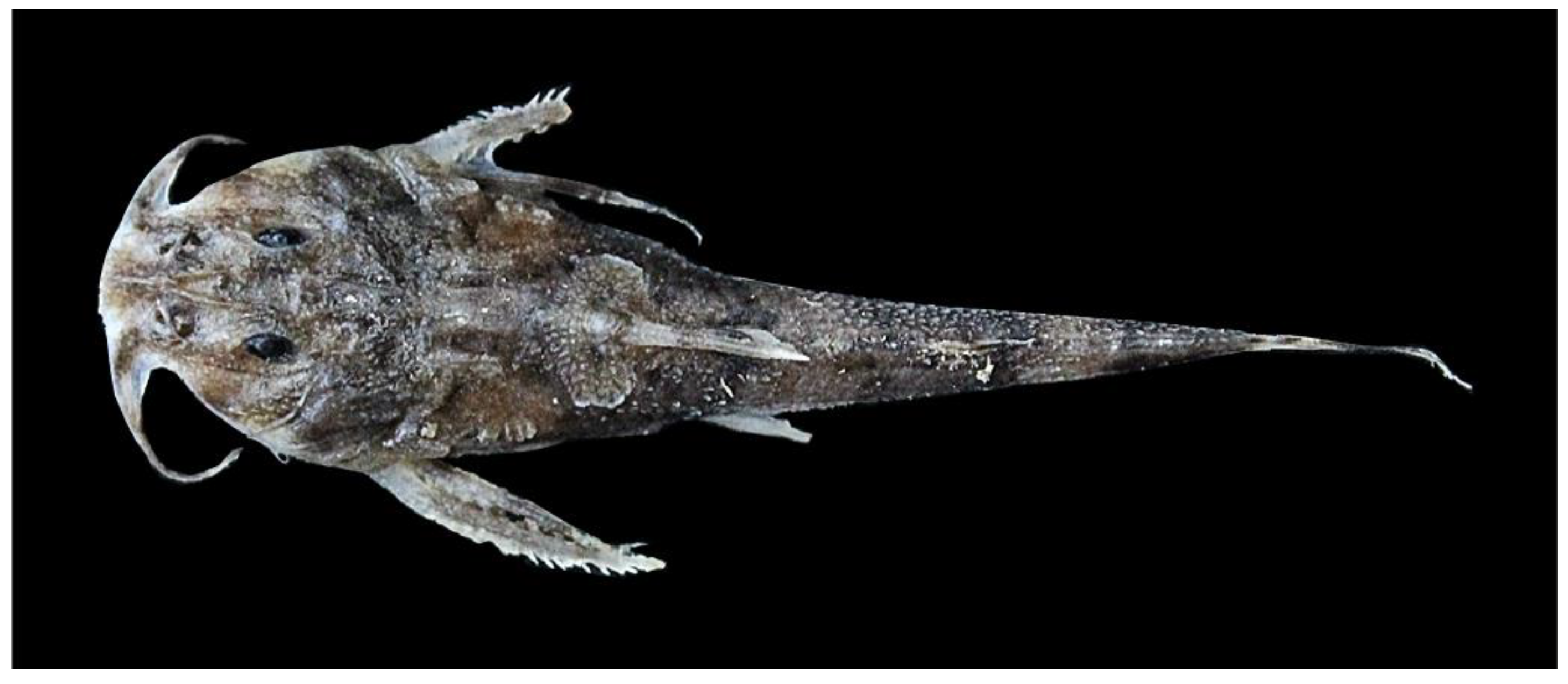
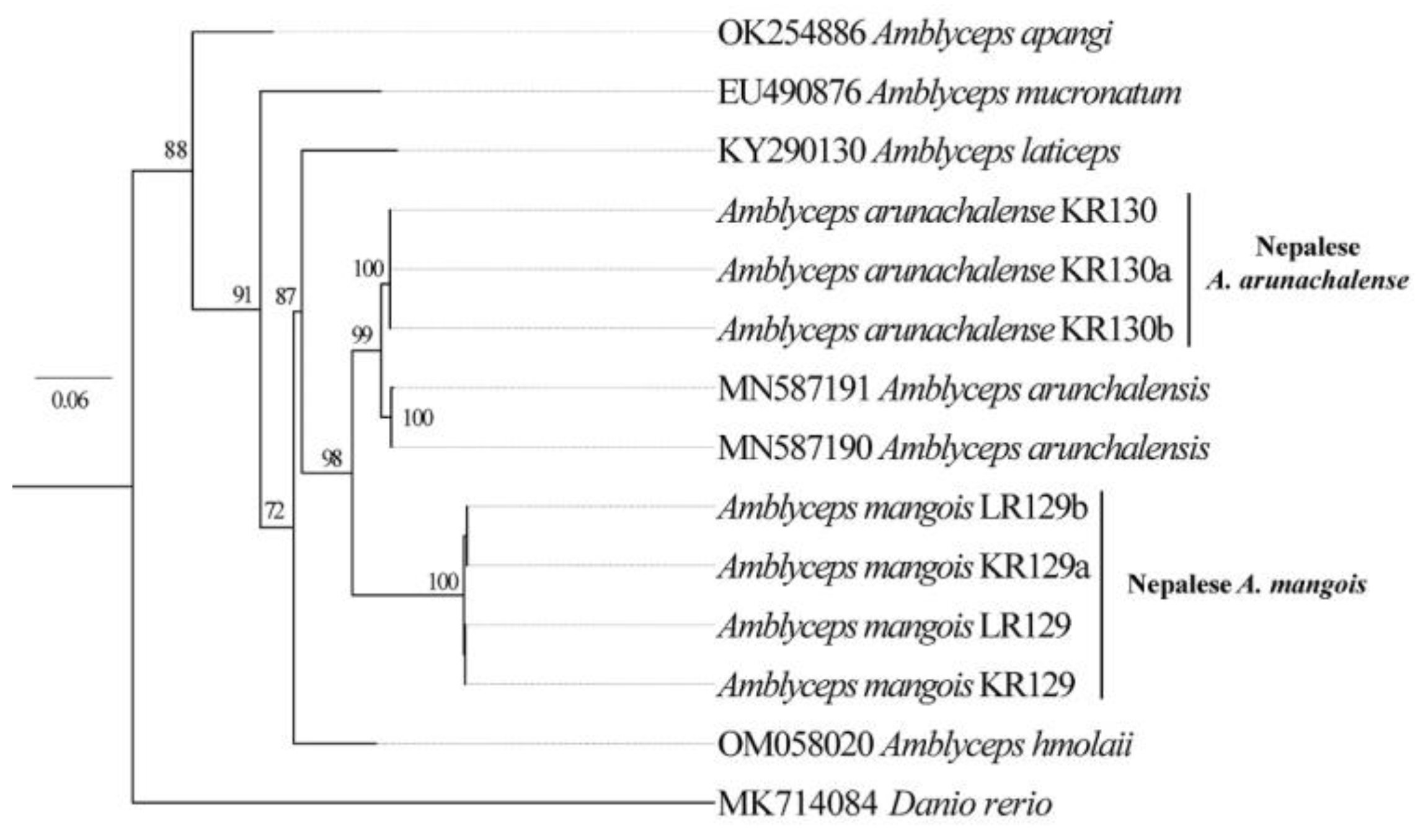

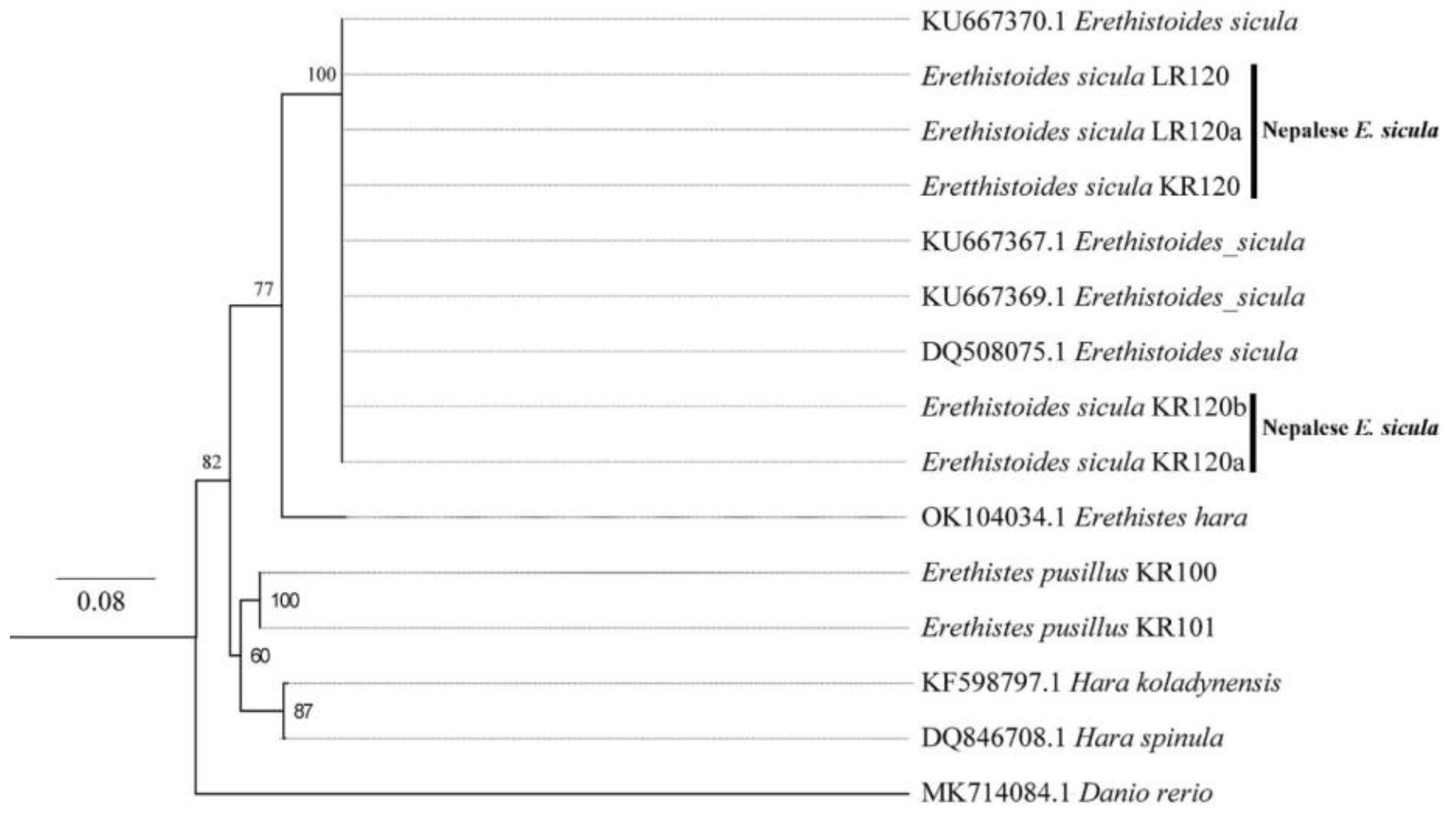

3.3. DNA Barcoding of Catfishes from Eastern Nepal
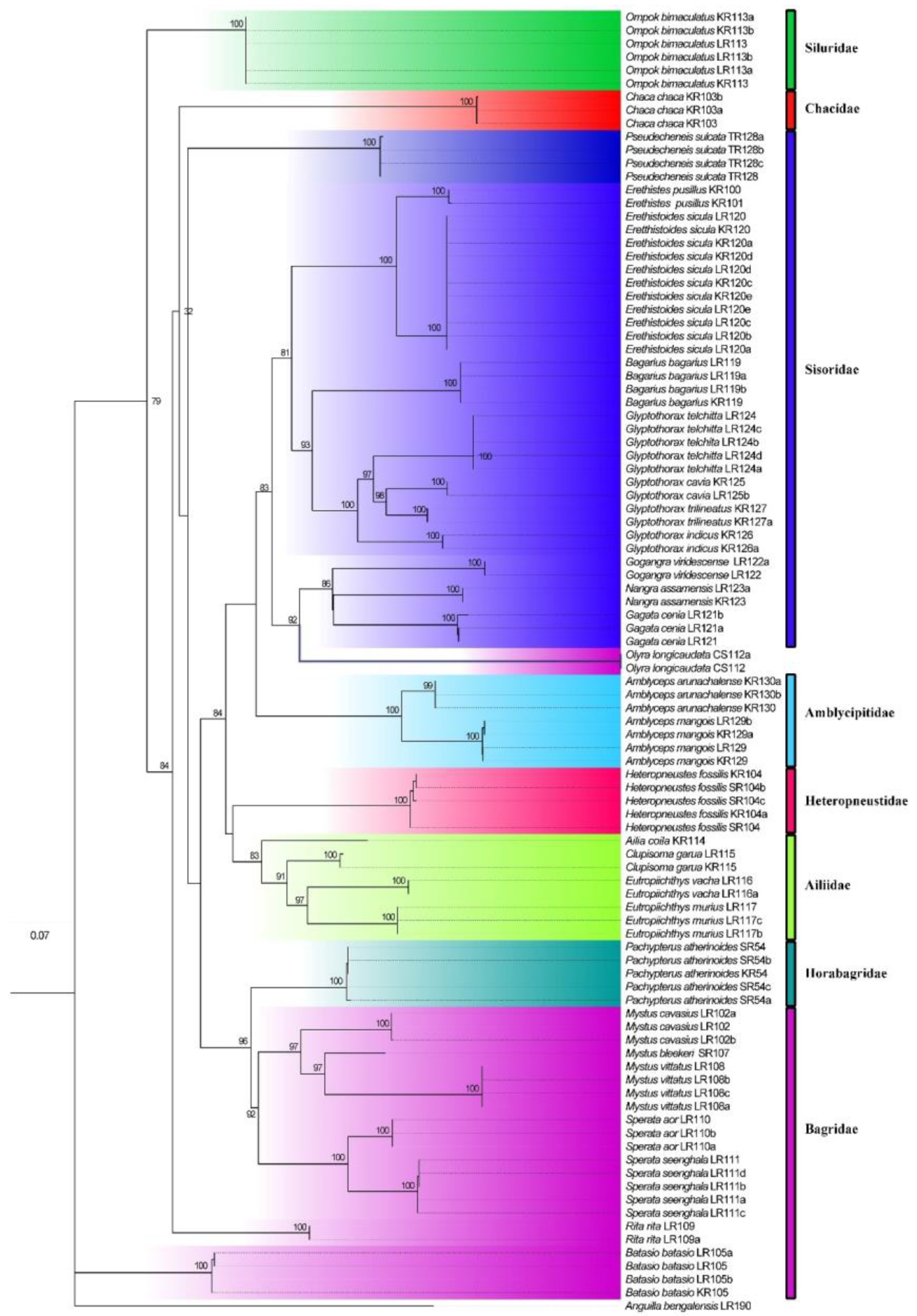
3.4. Phylogenetic Relationship among Catfishes in Eastern Nepal
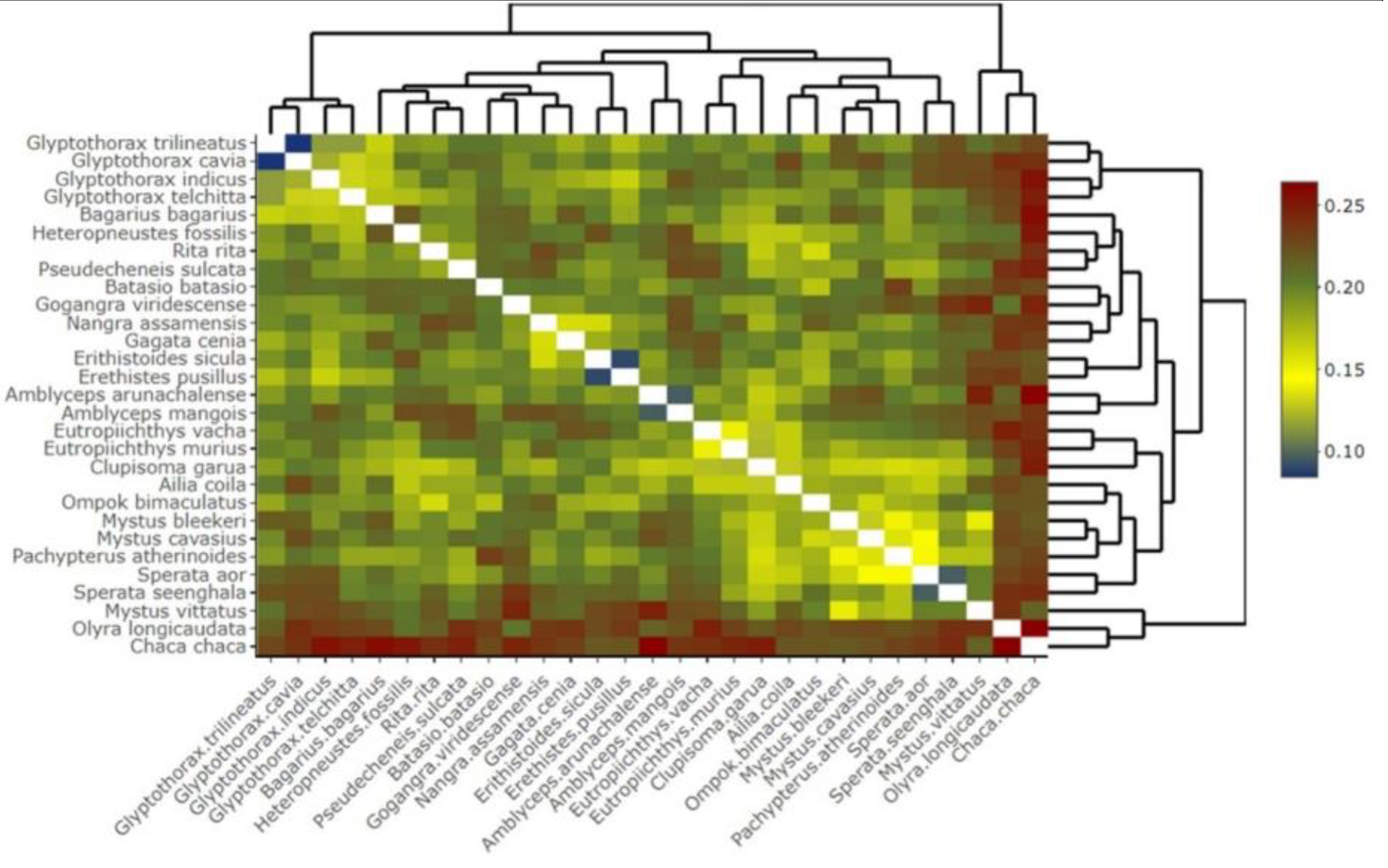
3.5. Genetic Divergence among Catfishes of Eastern Nepal
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nelson JS, Grande TC, Wilson MVH (2016). Fishes of the World. 5th Edition, John Wiley and Sons, Hoboken. [CrossRef]
- Fricke R, Eschmeyer WN, Laan RV (2024). Eschmeyer’s catalog of fishes: Genera, Species. Electronic version accessed 9 July 2024.
- Grande L, Eastman JT (1986). A review of Antarctic ichthyofaunas in the light of new fossil discoveries. Palaeontology, 29(1):113–137.
- Diogo R (2004). Osteology and myology of the cephalic region and pectoral girdle of Batrochoglanis raninus, with a discussion on the synapomorphies and phylogenetic relationships of the Pseudopimelodinae and Pimelodidae (Teleostei: Siluriformes). Animal Biology, 54(3):261–280.
- Malabarba LR, & Malabarba MC (2020). Phylogeny and classification of Neotropical fish. In B. Baldisserotto, E. C. Urbinati, & J. E. P. Cyrino (Eds.), Biology and Physiology of Freshwater Neotropical Fish (pp. 1-19). Academic Press. [CrossRef]
- Ballen GA, De Pinna MCC (2022). A standardized terminology of spines in the order Siluriformes (Actinopterygii: Ostariophysi). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 194(2): 601–625. [CrossRef]
- Shrestha TK (2019). Ichthyology of Nepal, a study of fishes of the Himalayan waters. Prism Color Scanning and Press Supportive Pvt. Ltd, Kathmandu, Nepal, 400 pp.
- Zhang J,Hanner R (2012). Molecular approach to the identification of fish in the South China Sea. PLoS One, 7(2): e30621. [CrossRef]
- Pandey PK, Singh YS, Tripathy PS, Kumar R, Abujam SK, Parhi J (2020). DNA barcoding and phylogenetics of freshwater fish fauna of Ranganadi River, Arunachal Pradesh. Gene, 754:144860. [CrossRef]
- Shen Y, Guan L, Wang D, Gan X (2016). DNA barcoding and evaluation of genetic diversity in Cyprinidae fish in the midstream of the Yangtze River. Ecology and Evolution, 6(9):2702–2713. [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho DC, Oliveira DA, Pompeu PS, Leal CG, OliveiraC, Hanner R(2011). Deep barcode divergence in Brazilian freshwater fishes: the case of the São Francisco River basin. Mitochondrial DNA, 22:80–86. [CrossRef]
- Steinke D, Zemlak TS, Hebert PDN (2009). Barcoding Nemo: DNA-based identifications for the ornamental fish trade. PLoS One, 4(7): e6300. [CrossRef]
- Rosso JJ, Mabragaña E, Castro MG, de Astarloa JM (2012). DNA barcoding Neotropical fishes: recent advances from the Pampa Plain, Argentina. Molecular Ecology Resources, 12(6): 999–1011. [CrossRef]
- Chen W, Ma X, Shen Y, Mao Y, He, S(2015). The fish diversity in the upper reaches of the Salween River, Nujiang River, revealed by DNA barcoding. Scientific Reports, 5: 17437. [CrossRef]
- Hebert PD, Cywinska A, Ball SL, de Waard JR (2003). Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proceedings of the Royal Society: Biological Sciences, 270(1512): 313–321. [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S., Chandra, K., Tyagi, K., Pakrashi, A., and Kumar, V., 2019. DNA barcoding of freshwater fishes from Brahmaputra River in Eastern Himalaya biodiversity hotspot. Mitochondrial DNA Part B, 4(2), 2411–2419. [CrossRef]
- Ward RD(2009). DNA barcode divergence among species and genera of birds and fishes. Molecular Ecology Resources, 9(4): 1077-1085. [CrossRef]
- Limbu JH, Subba S, GurungJK, Tumbahangfe J, Subba BR (2021b). Correlation of fish assemblages with habitat and environmental variables in the Phewa Khola stream of Mangsebung rural municipality, Ilam, Nepal. Journal of Animal Diversity, 3(1): 27–36. [CrossRef]
- Khatri, K., B.R. Jha, S. Gurung & U.R. Khadka (2024). Freshwater fish diversity and IUCN Red List status of glacial-fed (Bheri) and spring-fed (Babai) rivers in the wake of inter-basin water transfer. Journal of Threatened Taxa, 16(1): 24535–24549. [CrossRef]
- Talwar PK, Jhingran AG (1991). Inland Fisheries of India and Adjacent Countries. Volume I and II. Oxford and IBH Publishing Corporation. India, 1158pp.
- Jayaram KC (2010). The freshwater fishes of Indian region. Narendra Publishing House, Delhi, India, 614pp.
- 22. Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021). MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 38(7), 3022–3027. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen LT, Schmidt HA, von Haeseler A, & Minh BQ (2015). IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 32(1): 268–274. [CrossRef]
- Zhang D, F. Gao, I. Jakovlić, H. Zou, J. Zhang, W.X. Li, and G.T. Wang (2020). PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Molecular Ecology Resources, 20(1): 348–355. [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S., Minh, B. Q., Wong, T. K., von Haeseler, A., & Jermiin, L. S. (2017). ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nature Methods, 14: 587–589.
- Galili T, O'Callaghan A, Sidi J, & Sievert C (2018). heatmaply: an R package for creating interactive cluster heatmaps for online publishing. Bioinformatics, 34(9): 1600-1602. [CrossRef]
- R Core Team (2024). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/.
- Puillandre N, Lambert A, Brouillet S, Achaz G(2012). ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for primary species delimitation. Molecular Ecology, 21: 1864–1877. [CrossRef]
- Ng HH (2005). Erethistoides sicula , a new catfish (Teleostei: Erethistidae) from India. Zootaxa, 1021, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Vishwanath W, Linthoingambi I (2007). Redescription of catfish Amblyceps arunachalensis nath & dey and Amblyceps apangi nath & dey (teleostei: amblycipitidae). Zoos Print Journal 22(4): 2662-2664.
- Wong EHK, HannerRH (2008). DNA barcoding detects market substitution in North American seafood. Food Research International, 41:828–837. [CrossRef]
- Lakra WS, Singh M, Goswami M, Gopalakrishnan A, Lal KK, Mohindra V, Ayyappan S (2015). DNA barcoding Indian freshwater fishes. Mitochondrial DNA, 27: 4510–4517. [CrossRef]
- Shen Y, Guan L, Wang D, Gan X (2016). DNA barcoding and evaluation of genetic diversity in Cyprinidae fish in the midstream of the Yangtze River. Ecology and Evolution, 6(9): 2702–2713. [CrossRef]
- Ude GN, Igwe DO, Brown C. et al. (2020). DNA barcoding for identification of fish species from freshwater in Enugu and Anambra States of Nigeria. Conservation Genetic Resources, 12: 643–658. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Lu B, Zan R, Chai J, Ma W et al. (2016). Phylogenetic Relationships of Five Asian Schilbid Genera Including Clupisoma (Siluriformes: Schilbeidae). PLoS One, 11(1): e0145675. [CrossRef]
- Karinthanyakit W, Jondeung A (2012). Molecular phylogenetic relationships of pangasiid and schilbid catfish in Thailand. Journal of Fish Boilogy, 80(7): 2549–2570. [CrossRef]
- Song J, Hou F, Zhang X, Yue B, Song Z (2014). Mitochondrial genetic diversity and population structure of a vulnerable freshwater fish, rock carp (Procypris rabaudi) in upper Yangtze River drainage. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 55: 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2014.02.008. [CrossRef]
- Araújo RG, Silva RDF, Sampaio I & Guimarães-Costa A (2019). Does DNA barcoding offer meaningful insights into the diversity of the parrotfish of the genus Sparisoma (Scaridae)? Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 35: 1029–1033. [CrossRef]
- Kumar A, Adhavan DAV & Prakash S (2020). DNA barcoding revealed first record of the ‘fine spotted whipray’ Himantura tutul (Myliobatoidei: Dasyatidae) in the Indian coastal waters. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 36(4): 515-518. [CrossRef]
- Limbu J, Rajbanshi D, Subba A, Khanal L, Yang JQ & Li C (2024). First record of the non-native vermiculated sailfin catfish Pterygoplichthys disjunctivus (Weber, 1991) from Lohandra River, Eastern Nepal. BioInvasions Records, 13(2): 557-564. [CrossRef]
| S.N. | Family | Species | IUCN, 2022 | GenBank Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amblycipitidae | Amblyceps mangois (Hamilton 1822) | LC | OR793874–OR793877 |
| 2 | *Amblyceps arunachalense Nath & Dey 1989 | EN | OR801071–OR801073 | |
| 3 | Ailiidae | Ailia coila (Hamilton 1822) | NT | OR793880 |
| 4 | Clupisoma garua (Hamilton 1822) | LC | OR726087, OR799676 | |
| 5 | Eutropiichthys vacha (Hamilton 1822) | LC | OR733549, OR799677 | |
| 6 | Eutropiichthys murius (Hamilton 1822) | LC | OR794001–OR794003, | |
| 7 | Bagridae | Batasio batasio (Hamilton 1822) | LC | OR793868–OR793871 |
| 8 | Mystus bleekeri (Day 1877) | LC | OR726099 | |
| 9 | Mystus vittatus (Bloch 1794) | LC | OR801519–OR801522 | |
| 10 | Mystus cavasius (Hamilton 1822) | LC | OR793864–OR793867 | |
| 11 | Rita rita (Hamilton 1822) | LC | OR801529–OR801531 | |
| 12 | Sperata aor (Hamilton 1822) | LC | OR801372–OR801374 | |
| 13 | Sperata seenghala (Sykes 1839) | LC | OR801376–OR801381 | |
| 14 | Olyra longicaudata McClelland 1842 | LC | OR801375, OR801515 | |
| 15 | Siluridae | Ompok bimaculatus (Bloch 1794) | NT | OR801463–OR801468 |
| 16 | Sisoridae | Bagarius bagarius (Hamilton 1822) | VU | OR801523–OR801526 |
| 17 | Erethistes pusillus Müller & Troschel 1849 | LC | OR801436–OR801437 | |
| 18 | *Erethistoides sicula Ng 2005 | DD | OR801443–OR801454 | |
| 19 | Gagata cenia (Hamilton 1822) | LC | OR801457–OR801459 | |
| 20 | Gogangra viridescens (Hamilton 1822) | LC | OR801461–OR801462 | |
| 21 | Nangra assamensis Sen & Biswas 1994 | LC | OR801527, OR801553 | |
| 22 | Glyptothorax telchitta (Hamilton 1822) | LC | OR801537–OR801541 | |
| 23 | Glyptothorax cavia (Hamilton 1822) | LC | OR801516–OR801517 | |
| 24 | Glyptothorax trilineatus Blyth 1860 | LC | OR801440–OR801441 | |
| 25 | Glyptothorax indicus Talwar 1991 | LC | OR801455–OR801456 | |
| 26 | Pseudecheneis sulcata (McClelland 1842) | LC | OR801199–OR801203 | |
| 27 | Heteropneustidae | Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch 1794) | LC | OR801151–OR801155 |
| 28 | Horabagridae | Pachypterus atherinoides (Bloch 1794) | LC | OR801194–OR801198 |
| 29 | Chacidae | Chaca chaca (Hamilton 1822) | LC | OR801438–OR801439 |
| Taxonomic level | Min (%) | Mean (%) | Max (%) | SE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K2P distance | |||||
| Within species | 0.00 | 0.52 | 5.0 | 0.0023 | |
| Within genus | 0.00 | 2.6 | 17.0 | 0.0098 | |
| Within family | 0.00 | 8 | 21.0 | 0.0031 | |
| P-distance | |||||
| Within species | 0.00 | 0.45 | 4.0 | 0.0011 | |
| Within genus | 0.00 | 2.12 | 14.0 | 0.0073 | |
| Within family | 0.00 | 7.25 | 15.0 | 0.0014 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




