Submitted:
03 August 2024
Posted:
05 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Omics Data Interpretation: AI Technologies for Advanced Analysis
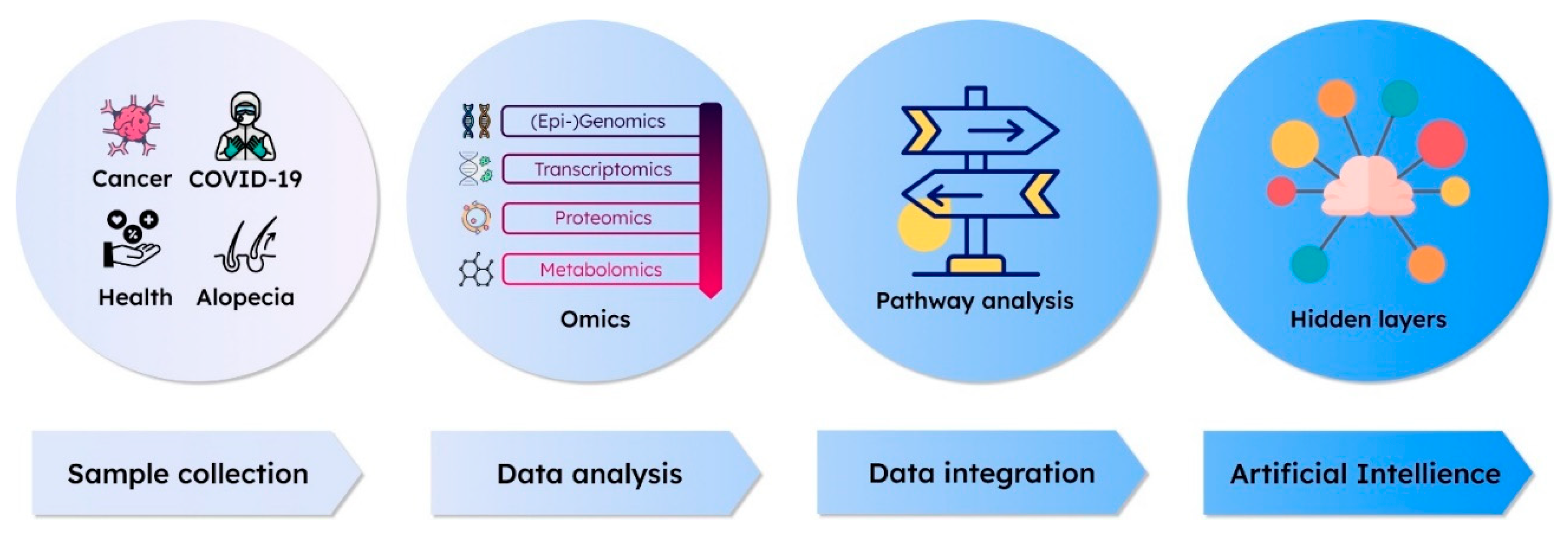
3. Interpretation of Multi-Omics Data with Approaches Using AI Methodology
3.1. Integrating Jointly Profiled Multi-Omics Data
3.2. Statistical Modeling
3.3. Latent Space Approaches
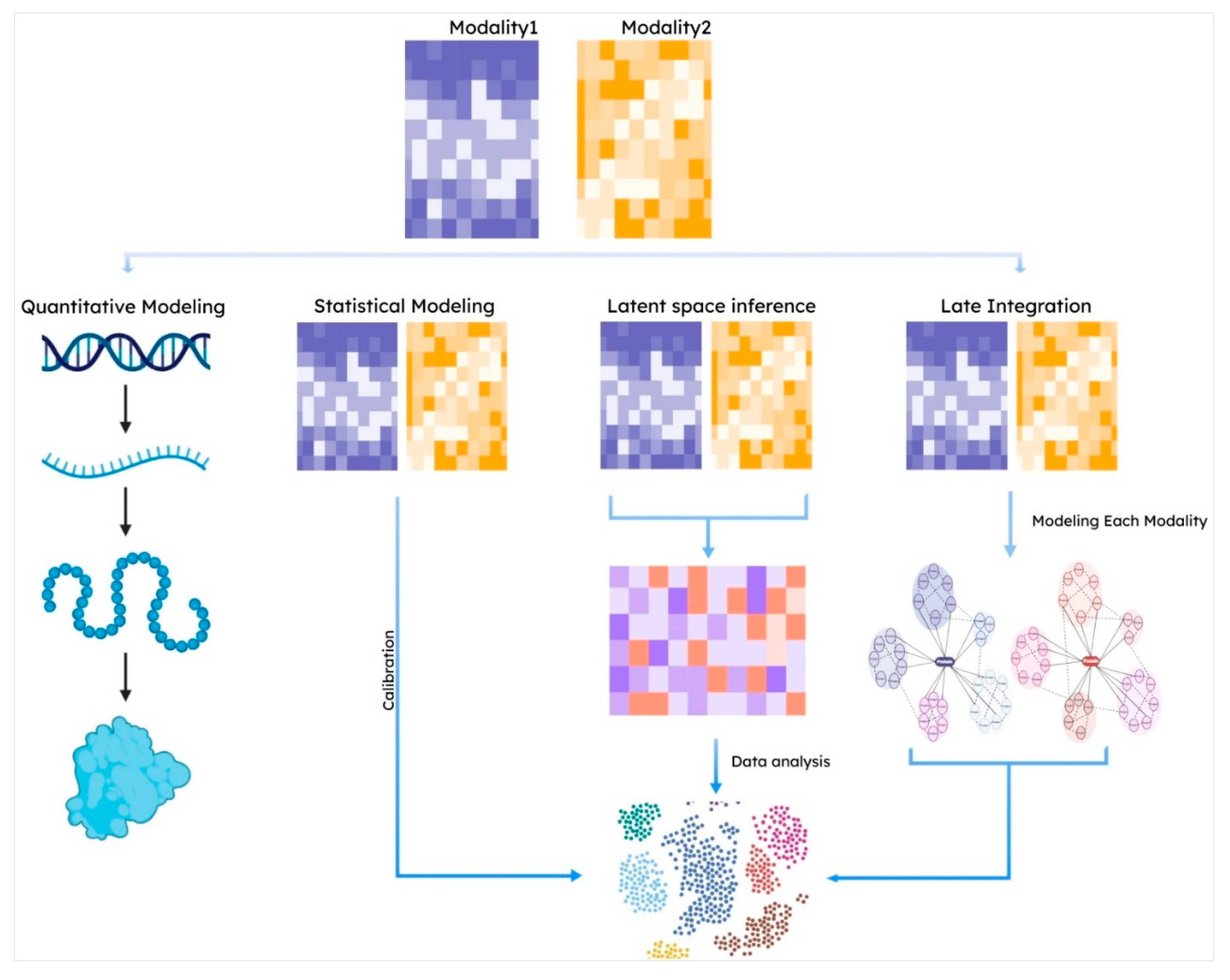
3.4. Late Integration Methods
4. Multi-Omics Approaches in AI application from COVID-19, to Cancer, and Alopecia: Diagnosis, Prog-nosis, and Therapeutics
4.1. COVID-19 Endemic
4.1.1. AI in COVID-19 Diagnosis
4.1.2. AI in Predicting COVID-19 Prognosis and Epidemic Trends
4.1.3. AI in Drug Discovery and Vaccine Development for COVID-19
4.2. Cancer
4.2.1. AI-Assisted Diagnosis for Cancer
4.2.2. Predicting the Prognosis of Cancer
4.2.3. Elucidating Pathophysiology and Drug Discovery for Cancer
4.3. Alopecia
4.3.1. Diagnostic Approaches Combined with Omics Tools
4.3.2. Therapeutic Approaches with Independent Omics Tools in Androgenetic Alopecia
4.3.3. Multi-Omics Integration and Systems Biology in Therapeutic Insights for Androgenic Alopecia
5. The Precision Medicine for Healthy Longevity - Future Perspectives

6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCarthy, J.; Minsky, M.L.; Rochester, N.; Shannon, C.E. A proposal for the dartmouth summer research project on artificial intelligence, august 31, 1955. AI magazine 2006, 27, 12-12.
- Li, R.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J. Machine learning meets omics: applications and perspectives. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2022, 23, bbab460.
- Ahmed, Z.; Wan, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhong, W. Artificial intelligence for omics data analysis. BMC Methods 2024, 1, 4.
- David, L.; Thakkar, A.; Mercado, R.; Engkvist, O. Molecular representations in AI-driven drug discovery: a review and practical guide. Journal of Cheminformatics 2020, 12, 56.
- Lin, J.; Ngiam, K.Y. How data science and AI-based technologies impact genomics. Singapore medical journal 2023, 64, 59-66.
- Xiao, Q.; Zhang, F.; Xu, L.; Yue, L.; Kon, O.L.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, T. High-throughput proteomics and AI for cancer biomarker discovery. Advanced drug delivery reviews 2021, 176, 113844.
- Petrick, L.M.; Shomron, N. AI/ML-driven advances in untargeted metabolomics and exposomics for biomedical applications. Cell Reports Physical Science 2022, 3.
- van der Lee, M.; Swen, J.J. Artificial intelligence in pharmacology research and practice. Clinical and Translational Science 2023, 16, 31-36.
- Holzinger, A.; Keiblinger, K.; Holub, P.; Zatloukal, K.; Müller, H. AI for life: Trends in artificial intelligence for biotechnology. New Biotechnology 2023, 74, 16-24.
- Misra, B.B.; Langefeld, C.; Olivier, M.; Cox, L.A. Integrated omics: tools, advances and future approaches. Journal of molecular endocrinology 2019, 62, R21-R45.
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Pan, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, G.P. Applications of multi-omics analysis in human diseases. MedComm (2020) 2023, 4, e315. [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, K.; Tomita, M. Merging multiple omics datasets in silico: statistical analyses and data interpretation. Systems Metabolic Engineering: Methods and Protocols 2013, 459-470.
- Zhu, H. Big data and artificial intelligence modeling for drug discovery. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology 2020, 60, 573-589.
- Reel, P.S.; Reel, S.; Pearson, E.; Trucco, E.; Jefferson, E. Using machine learning approaches for multi-omics data analysis: A review. Biotechnology advances 2021, 49, 107739.
- Lee, D.; Kim, S. Knowledge-guided artificial intelligence technologies for decoding complex multiomics interactions in cells. Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics 2022, 65, 239.
- Shakir, H.; Deng, Y.; Rasheed, H.; Khan, T.M.R. Radiomics based likelihood functions for cancer diagnosis. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 9501. [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Sun, J.; Qu, N.; Zhang, G.; Yu, T.; Piao, H. Application of Radiomics for Personalized Treatment of Cancer Patients. Cancer Manag Res 2019, 11, 10851-10858. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Cornman, A.L.; Kellogg, E.H.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Girguis, P.R. Genomic language model predicts protein co-regulation and function. Nature communications 2024, 15, 2880.
- Liang, K.-H. Bioinformatics for biomedical science and clinical applications; Elsevier: 2013.
- Graves, P.R.; Haystead, T.A. Molecular biologist’s guide to proteomics. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews 2002, 66, 39-63.
- Gomez-Cabrero, D.; Abugessaisa, I.; Maier, D.; Teschendorff, A.; Merkenschlager, M.; Gisel, A.; Ballestar, E.; Bongcam-Rudloff, E.; Conesa, A.; Tegnér, J. Data integration in the era of omics: current and future challenges. BMC systems biology 2014, 8, 1-10.
- Hamamoto, R.; Komatsu, M.; Takasawa, K.; Asada, K.; Kaneko, S. Epigenetics analysis and integrated analysis of multiomics data, including epigenetic data, using artificial intelligence in the era of precision medicine. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 62.
- Paik, Y.-K.; Jeong, S.-K.; Omenn, G.S.; Uhlen, M.; Hanash, S.; Cho, S.Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Na, K.; Choi, E.-Y.; Yan, F. The Chromosome-Centric Human Proteome Project for cataloging proteins encoded in the genome. Nature biotechnology 2012, 30, 221-223.
- Baker, M.S.; Ahn, S.B.; Mohamedali, A.; Islam, M.T.; Cantor, D.; Verhaert, P.D.; Fanayan, S.; Sharma, S.; Nice, E.C.; Connor, M. Accelerating the search for the missing proteins in the human proteome. Nature communications 2017, 8, 14271.
- Goh, W.W.B.; Wong, L. Advanced bioinformatics methods for practical applications in proteomics. Briefings in bioinformatics 2019, 20, 347-355.
- Ribbenstedt, A.; Ziarrusta, H.; Benskin, J.P. Development, characterization and comparisons of targeted and non-targeted metabolomics methods. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0207082.
- Picard, M.; Scott-Boyer, M.-P.; Bodein, A.; Périn, O.; Droit, A. Integration strategies of multi-omics data for machine learning analysis. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal 2021, 19, 3735-3746.
- Mann, M.; Kumar, C.; Zeng, W.-F.; Strauss, M.T. Artificial intelligence for proteomics and biomarker discovery. Cell systems 2021, 12, 759-770.
- Alslaity, A.; Chan, G.; Orji, R. A panoramic view of personalization based on individual differences in persuasive and behavior change interventions. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence 2023, 6, 1125191.
- Cao, J.; Cusanovich, D.A.; Ramani, V.; Aghamirzaie, D.; Pliner, H.A.; Hill, A.J.; Daza, R.M.; McFaline-Figueroa, J.L.; Packer, J.S.; Christiansen, L.; et al. Joint profiling of chromatin accessibility and gene expression in thousands of single cells. Science 2018, 361, 1380-1385. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lake, B.B.; Zhang, K. High-throughput sequencing of the transcriptome and chromatin accessibility in the same cell. Nat Biotechnol 2019, 37, 1452-1457. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yu, M.; Huang, H.; Juric, I.; Abnousi, A.; Hu, R.; Lucero, J.; Behrens, M.M.; Hu, M.; Ren, B. An ultra high-throughput method for single-cell joint analysis of open chromatin and transcriptome. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2019, 26, 1063-1070. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Richards, A.; Barrasa, M.I.; Hughes, S.H.; Young, R.A.; Jaenisch, R. Reverse-transcribed SARS-CoV-2 RNA can integrate into the genome of cultured human cells and can be expressed in patient-derived tissues. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2021, 118, e2105968118, doi:doi:10.1073/pnas.2105968118.
- Stoeckius, M.; Hafemeister, C.; Stephenson, W.; Houck-Loomis, B.; Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Swerdlow, H.; Satija, R.; Smibert, P. Simultaneous epitope and transcriptome measurement in single cells. Nat Methods 2017, 14, 865-868. [CrossRef]
- Peterson, V.M.; Zhang, K.X.; Kumar, N.; Wong, J.; Li, L.; Wilson, D.C.; Moore, R.; McClanahan, T.K.; Sadekova, S.; Klappenbach, J.A. Multiplexed quantification of proteins and transcripts in single cells. Nat Biotechnol 2017, 35, 936-939. [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, D. Photoactivated Selective Release of Droplets from Microwell Arrays. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020, 12, 3936-3944. [CrossRef]
- Stuart, T.; Satija, R. Integrative single-cell analysis. Nat Rev Genet 2019, 20, 257-272. [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; McDermaid, A.; Xu, J.; Chang, Y.; Ma, Q. Integrative Methods and Practical Challenges for Single-Cell Multi-omics. Trends Biotechnol 2020, 38, 1007-1022. [CrossRef]
- Sokal, R.R. Distance as a Measure of Taxonomic Similarity. Systematic Zoology 1961, 10, 70-79. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xin, H.; Huang, H.; Duerr, R.H.; Chen, K.; Ding, Y.; Chen, W. BREM-SC: a bayesian random effects mixture model for joint clustering single cell multi-omics data. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, 5814-5824. [CrossRef]
- Flores, J.E.; Claborne, D.M.; Weller, Z.D.; Webb-Robertson, B.-J.M.; Waters, K.M.; Bramer, L.M. Missing data in multi-omics integration: Recent advances through artificial intelligence. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence 2023, 6, 1098308.
- Nicora, G.; Vitali, F.; Dagliati, A.; Geifman, N.; Bellazzi, R. Integrated multi-omics analyses in oncology: a review of machine learning methods and tools. Frontiers in oncology 2020, 10, 1030.
- Xie, G.; Dong, C.; Kong, Y.; Zhong, J.F.; Li, M.; Wang, K. Group lasso regularized deep learning for cancer prognosis from multi-omics and clinical features. Genes 2019, 10, 240.
- Xu, J.; Wu, P.; Chen, Y.; Meng, Q.; Dawood, H.; Dawood, H. A hierarchical integration deep flexible neural forest framework for cancer subtype classification by integrating multi-omics data. BMC bioinformatics 2019, 20, 1-11.
- Koh, H.W.; Fermin, D.; Vogel, C.; Choi, K.P.; Ewing, R.M.; Choi, H. iOmicsPASS: network-based integration of multiomics data for predictive subnetwork discovery. NPJ systems biology and applications 2019, 5, 22.
- Pai, S.; Hui, S.; Isserlin, R.; Shah, M.A.; Kaka, H.; Bader, G.D. netDx: interpretable patient classification using integrated patient similarity networks. Molecular systems biology 2019, 15, e8497.
- Mariette, J.; Villa-Vialaneix, N. Unsupervised multiple kernel learning for heterogeneous data integration. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1009-1015.
- Gönen, M.; Alpaydın, E. Multiple kernel learning algorithms. The Journal of Machine Learning Research 2011, 12, 2211-2268.
- Jin, S.; Zhang, L.; Nie, Q. scAI: an unsupervised approach for the integrative analysis of parallel single-cell transcriptomic and epigenomic profiles. Genome Biol 2020, 21, 25. [CrossRef]
- Argelaguet, R.; Velten, B.; Arnol, D.; Dietrich, S.; Zenz, T.; Marioni, J.C.; Buettner, F.; Huber, W.; Stegle, O. Multi-Omics Factor Analysis-a framework for unsupervised integration of multi-omics data sets. Mol Syst Biol 2018, 14, e8124. [CrossRef]
- Argelaguet, R.; Arnol, D.; Bredikhin, D.; Deloro, Y.; Velten, B.; Marioni, J.C.; Stegle, O. MOFA+: a statistical framework for comprehensive integration of multi-modal single-cell data. Genome Biol 2020, 21, 111. [CrossRef]
- Gayoso, A.; Steier, Z.; Lopez, R.; Regier, J.; Nazor, K.L.; Streets, A.; Yosef, N. Joint probabilistic modeling of single-cell multi-omic data with totalVI. Nat Methods 2021, 18, 272-282. [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Hao, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Mauck, W.M., 3rd; Zheng, S.; Butler, A.; Lee, M.J.; Wilk, A.J.; Darby, C.; Zager, M.; et al. Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell 2021, 184, 3573-3587.e3529. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Mezlini, A.M.; Demir, F.; Fiume, M.; Tu, Z.; Brudno, M.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Goldenberg, A. Similarity network fusion for aggregating data types on a genomic scale. Nat Methods 2014, 11, 333-337. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lin, Y.; Geddes, T.A.; Yang, J.Y.H.; Yang, P. CiteFuse enables multi-modal analysis of CITE-seq data. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 4137-4143. [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Wang, M.; Li, A. A multimodal deep neural network for human breast cancer prognosis prediction by integrating multi-dimensional data. IEEE/ACM transactions on computational biology and bioinformatics 2018, 16, 841-850.
- Sharifi-Noghabi, H.; Zolotareva, O.; Collins, C.C.; Ester, M. MOLI: multi-omics late integration with deep neural networks for drug response prediction. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, i501-i509.
- Kong, W.; Hui, H.W.H.; Peng, H.; Goh, W.W.B. Dealing with missing values in proteomics data. Proteomics 2022, 22, 2200092.
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. Addendum: A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 588, E6. [CrossRef]
- Wiersinga, W.J.; Rhodes, A.; Cheng, A.C.; Peacock, S.J.; Prescott, H.C. Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. Jama 2020, 324, 782-793. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, R.; Li, T.; Zeng, D.; Li, M. Clinical features of familial clustering in patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Virus Res 2020, 286, 198043. [CrossRef]
- Yassine, H.M.; Shah, Z. How could artificial intelligence aid in the fight against coronavirus? Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2020, 18, 493-497. [CrossRef]
- Davenport, T.; Kalakota, R. The potential for artificial intelligence in healthcare. Future Healthc J 2019, 6, 94-98. [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, C.J.P.; Jiang, B.; Chen, J.; Song, J.; Liu, Z.; He, Z.; Wong, S.Y.; Fang, P.H.; Ming, W.K. Artificial Intelligence Versus Clinicians in Disease Diagnosis: Systematic Review. JMIR Med Inform 2019, 7, e10010. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.J.; Kesselheim, A.S.; Vokinger, K.N. Lifecycle Regulation of Artificial Intelligence- and Machine Learning-Based Software Devices in Medicine. Jama 2019, 322, 2285-2286. [CrossRef]
- Abdulaal, A.; Patel, A.; Charani, E.; Denny, S.; Mughal, N.; Moore, L. Prognostic Modeling of COVID-19 Using Artificial Intelligence in the United Kingdom: Model Development and Validation. J Med Internet Res 2020, 22, e20259. [CrossRef]
- Yousefzadeh, M.; Esfahanian, P.; Movahed, S.M.S.; Gorgin, S.; Rahmati, D.; Abedini, A.; Nadji, S.A.; Haseli, S.; Karam, M.B.; Kiani, A.; et al. Correction: ai-corona: Radiologist-assistant deep learning framework for COVID-19 diagnosis in chest CT scans. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0257119. [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.X.; Wang, R.; Xiong, Z.; Hsieh, B.; Chang, K.; Halsey, K.; Tran, T.M.L.; Choi, J.W.; Wang, D.C.; Shi, L.B.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Augmentation of Radiologist Performance in Distinguishing COVID-19 from Pneumonia of Other Origin at Chest CT. Radiology 2021, 299, E225. [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Bai, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, L.; Qin, L.; Gong, S.; Xie, X.; Zhou, C.; Tu, D.; et al. Deep learning for predicting COVID-19 malignant progression. Med Image Anal 2021, 72, 102096. [CrossRef]
- Al-Qaness, M.A.A.; Saba, A.I.; Elsheikh, A.H.; Elaziz, M.A.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Lu, S.; Hemedan, A.A.; Shanmugan, S.; Ewees, A.A. Efficient artificial intelligence forecasting models for COVID-19 outbreak in Russia and Brazil. Process Saf Environ Prot 2021, 149, 399-409. [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, T.; He, Q.; He, Y.; Yue, R.; You, F.; Tang, J. Challenges and strategies to research ethics in conducting COVID-19 research. J Evid Based Med 2020, 13, 173-177. [CrossRef]
- Ong, E.; Wong, M.U.; Huffman, A.; He, Y. COVID-19 Coronavirus Vaccine Design Using Reverse Vaccinology and Machine Learning. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 1581. [CrossRef]
- Naudé, W. Artificial intelligence vs COVID-19: limitations, constraints and pitfalls. AI Soc 2020, 35, 761-765. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 727-733. [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Bernheim, A.; Mei, X.; Zhang, N.; Huang, M.; Zeng, X.; Cui, J.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Fayad, Z.A.; et al. CT Imaging Features of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Radiology 2020, 295, 202-207. [CrossRef]
- Albahri, O.S.; Zaidan, A.A.; Albahri, A.S.; Zaidan, B.B.; Abdulkareem, K.H.; Al-Qaysi, Z.T.; Alamoodi, A.H.; Aleesa, A.M.; Chyad, M.A.; Alesa, R.M.; et al. Systematic review of artificial intelligence techniques in the detection and classification of COVID-19 medical images in terms of evaluation and benchmarking: Taxonomy analysis, challenges, future solutions and methodological aspects. J Infect Public Health 2020, 13, 1381-1396. [CrossRef]
- Swapnarekha, H.; Behera, H.S.; Nayak, J.; Naik, B. Role of intelligent computing in COVID-19 prognosis: A state-of-the-art review. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals 2020, 138, 109947. [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497-506. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Tong, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Fan, H.; et al. Artificial Intelligence for COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021, 8, 704256. [CrossRef]
- Yasaka, K.; Akai, H.; Kunimatsu, A.; Kiryu, S.; Abe, O. Deep learning with convolutional neural network in radiology. Jpn J Radiol 2018, 36, 257-272. [CrossRef]
- Abbasian Ardakani, A.; Acharya, U.R.; Habibollahi, S.; Mohammadi, A. COVIDiag: a clinical CAD system to diagnose COVID-19 pneumonia based on CT findings. Eur Radiol 2021, 31, 121-130. [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Lee, H.-C.; Diao, K.-y.; Huang, M.; Lin, B.; Liu, C.; Xie, Z.; Ma, Y.; Robson, P.M.; Chung, M.; et al. Artificial intelligence–enabled rapid diagnosis of patients with COVID-19. Nature Medicine 2020, 26, 1224-1228. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Das, S.K.; Roy, P.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Identifying COVID19 from Chest CT Images: A Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Based Approach. J Healthc Eng 2020, 2020, 8843664. [CrossRef]
- Momeny, M.; Neshat, A.A.; Hussain, M.A.; Kia, S.; Marhamati, M.; Jahanbakhshi, A.; Hamarneh, G. Learning-to-augment strategy using noisy and denoised data: Improving generalizability of deep CNN for the detection of COVID-19 in X-ray images. Comput Biol Med 2021, 136, 104704. [CrossRef]
- Bressem, K.K.; Adams, L.C.; Erxleben, C.; Hamm, B.; Niehues, S.M.; Vahldiek, J.L. Comparing different deep learning architectures for classification of chest radiographs. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 13590. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gao, L.; Jin, D.; Sun, Y.; Ye, X.; Yu, L.; Hu, Z.; et al. From community-acquired pneumonia to COVID-19: a deep learning-based method for quantitative analysis of COVID-19 on thick-section CT scans. Eur Radiol 2020, 30, 6828-6837. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, T.; Chen, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, S.; Xie, Z. Rapid identification of COVID-19 severity in CT scans through classification of deep features. Biomed Eng Online 2020, 19, 63. [CrossRef]
- Assaf, D.; Gutman, Y.; Neuman, Y.; Segal, G.; Amit, S.; Gefen-Halevi, S.; Shilo, N.; Epstein, A.; Mor-Cohen, R.; Biber, A.; et al. Utilization of machine-learning models to accurately predict the risk for critical COVID-19. Intern Emerg Med 2020, 15, 1435-1443. [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Yao, J.; Chen, A.; Lv, Q.; Zanin, M.; Liu, J.; Wong, S.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Liang, H.; et al. Addendum: Early triage of critically ill COVID-19 patients using deep learning. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 826. [CrossRef]
- Iwendi, C.; Bashir, A.K.; Peshkar, A.; Sujatha, R.; Chatterjee, J.M.; Pasupuleti, S.; Mishra, R.; Pillai, S.; Jo, O. COVID-19 Patient Health Prediction Using Boosted Random Forest Algorithm. Front Public Health 2020, 8, 357. [CrossRef]
- Ayyoubzadeh, S.M.; Ayyoubzadeh, S.M.; Zahedi, H.; Ahmadi, M.; S, R.N.K. Predicting COVID-19 Incidence Through Analysis of Google Trends Data in Iran: Data Mining and Deep Learning Pilot Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill 2020, 6, e18828. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; da Silva, R.G.; Mariani, V.C.; Coelho, L.D.S. Short-term forecasting COVID-19 cumulative confirmed cases: Perspectives for Brazil. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 135, 109853. [CrossRef]
- Alsayed, A.; Sadir, H.; Kamil, R.; Sari, H. Prediction of Epidemic Peak and Infected Cases for COVID-19 Disease in Malaysia, 2020. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17. [CrossRef]
- Mollalo, A.; Rivera, K.M.; Vahedi, B. Artificial Neural Network Modeling of Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Incidence Rates across the Continental United States. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17. [CrossRef]
- Shahid, F.; Zameer, A.; Muneeb, M. Predictions for COVID-19 with deep learning models of LSTM, GRU and Bi-LSTM. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110212. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Mehran, M.T.; Haq, Z.U.; Ullah, Z.; Naqvi, S.R.; Ihsan, M.; Abbass, H. Applications of artificial intelligence in COVID-19 pandemic: A comprehensive review. Expert Systems with Applications 2021, 185, 115695. [CrossRef]
- Vaishya, R.; Javaid, M.; Khan, I.H.; Haleem, A. Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications for COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews 2020, 14, 337-339. [CrossRef]
- Amelio, I.; Gostev, M.; Knight, R.A.; Willis, A.E.; Melino, G.; Antonov, A.V. DRUGSURV: a resource for repositioning of approved and experimental drugs in oncology based on patient survival information. Cell Death Dis 2014, 5, e1051. [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.Y.; Peng, T.T.; Yeh, T.K.; Huang, W.Z.; Chang, S.E.; Wu, S.H.; Hung, H.C.; Hsu, T.A.; Lee, S.J.; Song, J.S.; et al. Artificial intelligence approach fighting COVID-19 with repurposing drugs. Biomed J 2020, 43, 355-362. [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Nguyen, D.D.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Wei, G.W. Repositioning of 8565 Existing Drugs for COVID-19. J Phys Chem Lett 2020, 11, 5373-5382. [CrossRef]
- King, B.; Ohyama, M.; Kwon, O.; Zlotogorski, A.; Ko, J.; Mesinkovska, N.A.; Hordinsky, M.; Dutronc, Y.; Wu, W.S.; McCollam, J.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Baricitinib for Alopecia Areata. N Engl J Med 2022, 386, 1687-1699. [CrossRef]
- Stebbing, J.; Krishnan, V.; de Bono, S.; Ottaviani, S.; Casalini, G.; Richardson, P.J.; Monteil, V.; Lauschke, V.M.; Mirazimi, A.; Youhanna, S.; et al. Mechanism of baricitinib supports artificial intelligence-predicted testing in COVID-19 patients. EMBO Mol Med 2020, 12, e12697. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Saravanan, K.M.; Yang, Y.; Hossain, M.T.; Li, J.; Ren, X.; Pan, Y.; Wei, Y. Deep Learning Based Drug Screening for Novel Coronavirus 2019-nCov. Interdiscip Sci 2020, 12, 368-376. [CrossRef]
- Batra, R.; Chan, H.; Kamath, G.; Ramprasad, R.; Cherukara, M.J.; Sankaranarayanan, S. Screening of Therapeutic Agents for COVID-19 Using Machine Learning and Ensemble Docking Studies. J Phys Chem Lett 2020, 11, 7058-7065. [CrossRef]
- Ton, A.T.; Gentile, F.; Hsing, M.; Ban, F.; Cherkasov, A. Rapid Identification of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by Deep Docking of 1.3 Billion Compounds. Mol Inform 2020, 39, e2000028. [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Acharjee, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Baker, M.S.; Srivastava, S. Role of Multiomics Data to Understand Host-Pathogen Interactions in COVID-19 Pathogenesis. J Proteome Res 2021, 20, 1107-1132. [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wan, S.; Yang, Z.; Teschendorff, A.E.; Zou, Q. Tumor origin detection with tissue-specific miRNA and DNA methylation markers. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 398-406. [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, J.P.; Mishra, N.; Tran, F.; Bahmer, T.; Best, L.; Blase, J.I.; Bordoni, D.; Franzenburg, J.; Geisen, U.; Josephs-Spaulding, J.; et al. Longitudinal Multi-omics Analyses Identify Responses of Megakaryocytes, Erythroid Cells, and Plasmablasts as Hallmarks of Severe COVID-19. Immunity 2020, 53, 1296-1314.e1299. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Qian, F.; Sun, L.; Song, Z.G.; Chen, Z.; Feng, J.; et al. Blood molecular markers associated with COVID-19 immunopathology and multi-organ damage. Embo j 2020, 39, e105896. [CrossRef]
- Ponti, G.; Maccaferri, M.; Ruini, C.; Tomasi, A.; Ozben, T. Biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 2020, 57, 389-399. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shen, C.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Wei, J.; Huang, F.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Xing, L.; et al. Plasma IP-10 and MCP-3 levels are highly associated with disease severity and predict the progression of COVID-19. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2020, 146, 119-127.e114. [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Tanaka, T.; Inoue, H.; Ono, C.; Hashimoto, S.; Kioi, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Matsuura, H.; Matsubara, T.; Shimizu, K.; et al. IL-6 trans-signaling induces plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 from vascular endothelial cells in cytokine release syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020, 117, 22351-22356. [CrossRef]
- Whyte, C.S.; Morrow, G.B.; Mitchell, J.L.; Chowdary, P.; Mutch, N.J. Fibrinolytic abnormalities in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and versatility of thrombolytic drugs to treat COVID-19. J Thromb Haemost 2020, 18, 1548-1555. [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, T.; Kubli, S.P.; Yoshinaga, S.K.; Pfeffer, K.; Mak, T.W. An aberrant STAT pathway is central to COVID-19. Cell Death Differ 2020, 27, 3209-3225. [CrossRef]
- Wilk, A.J.; Rustagi, A.; Zhao, N.Q.; Roque, J.; Martínez-Colón, G.J.; McKechnie, J.L.; Ivison, G.T.; Ranganath, T.; Vergara, R.; Hollis, T.; et al. A single-cell atlas of the peripheral immune response in patients with severe COVID-19. Nat Med 2020, 26, 1070-1076. [CrossRef]
- Cacciapuoti, S.; De Rosa, A.; Gelzo, M.; Megna, M.; Raia, M.; Pinchera, B.; Pontarelli, A.; Scotto, R.; Scala, E.; Scarano, F.; et al. Immunocytometric analysis of COVID patients: A contribution to personalized therapy? Life Sci 2020, 261, 118355. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G.Q. Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: interleukin-6 receptor antagonist tocilizumab may be the key to reduce mortality. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2020, 55, 105954. [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Thomas, T.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Hill, R.C.; Francis, R.O.; Hudson, K.E.; Zimring, J.C.; Hod, E.A.; Spitalnik, S.L.; Hansen, K.C. Serum Proteomics in COVID-19 Patients: Altered Coagulation and Complement Status as a Function of IL-6 Level. J Proteome Res 2020, 19, 4417-4427. [CrossRef]
- Urwyler, P.; Moser, S.; Charitos, P.; Heijnen, I.; Rudin, M.; Sommer, G.; Giannetti, B.M.; Bassetti, S.; Sendi, P.; Trendelenburg, M.; et al. Treatment of COVID-19 With Conestat Alfa, a Regulator of the Complement, Contact Activation and Kallikrein-Kinin System. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 2072. [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Harbord, R.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Timpson, N.; Davey Smith, G. Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat Med 2008, 27, 1133-1163. [CrossRef]
- Ponsford, M.J.; Gkatzionis, A.; Walker, V.M.; Grant, A.J.; Wootton, R.E.; Moore, L.S.P.; Fatumo, S.; Mason, A.M.; Zuber, V.; Willer, C.; et al. Cardiometabolic Traits, Sepsis, and Severe COVID-19: A Mendelian Randomization Investigation. Circulation 2020, 142, 1791-1793. [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 2023, 73, 17-48. [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Soerjomataram, I. The ever-increasing importance of cancer as a leading cause of premature death worldwide. Cancer 2021, 127, 3029-3030. [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, E.A.; Poverennaya, E.V.; Ilgisonis, E.V.; Pyatnitskiy, M.A.; Kopylov, A.T.; Zgoda, V.G.; Lisitsa, A.V.; Archakov, A.I. The Size of the Human Proteome: The Width and Depth. Int J Anal Chem 2016, 2016, 7436849. [CrossRef]
- Perkins, D.O.; Jeffries, C.; Sullivan, P. Expanding the ‘central dogma’: the regulatory role of nonprotein coding genes and implications for the genetic liability to schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2005, 10, 69-78. [CrossRef]
- Tsakiroglou, M.; Evans, A.; Pirmohamed, M. Leveraging transcriptomics for precision diagnosis: Lessons learned from cancer and sepsis. Front Genet 2023, 14, 1100352. [CrossRef]
- Janes, K.A.; Yaffe, M.B. Data-driven modelling of signal-transduction networks. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006, 7, 820-828. [CrossRef]
- Haga, Y.; Minegishi, Y.; Ueda, K. Frontiers in mass spectrometry-based clinical proteomics for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Cancer Sci 2023, 114, 1783-1791. [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Li, X.; Gan, Y.; Han, S.; Rong, P.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Zhou, L. Artificial intelligence assists precision medicine in cancer treatment. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 998222. [CrossRef]
- Sirinukunwattana, K.; Ahmed Raza, S.E.; Yee-Wah, T.; Snead, D.R.; Cree, I.A.; Rajpoot, N.M. Locality Sensitive Deep Learning for Detection and Classification of Nuclei in Routine Colon Cancer Histology Images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2016, 35, 1196-1206. [CrossRef]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernández, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 16878. [CrossRef]
- Korbar, B.; Olofson, A.M.; Miraflor, A.P.; Nicka, C.M.; Suriawinata, M.A.; Torresani, L.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Hassanpour, S. Deep Learning for Classification of Colorectal Polyps on Whole-slide Images. J Pathol Inform 2017, 8, 30. [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, K.; Foote, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, P.C.; Wulczyn, E.; Tan, F.; Olson, N.; Smith, J.L.; Mohtashamian, A.; Wren, J.H.; et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for improving Gleason scoring of prostate cancer. NPJ Digit Med 2019, 2, 48. [CrossRef]
- Ramón, Y.C.S.; Sesé, M.; Capdevila, C.; Aasen, T.; De Mattos-Arruda, L.; Diaz-Cano, S.J.; Hernández-Losa, J.; Castellví, J. Clinical implications of intratumor heterogeneity: challenges and opportunities. J Mol Med (Berl) 2020, 98, 161-177. [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.Y.; Jung, C.K.; Woo, J.I.; Lee, S.; Cho, J.; Kim, S.W.; Kwak, T.Y. Artificial Intelligence in Pathology. J Pathol Transl Med 2019, 53, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.M.; Majid, M.; Qayyum, A.; Awais, M.; Alnowami, M.; Khan, M.K. Medical Image Analysis using Convolutional Neural Networks: A Review. J Med Syst 2018, 42, 226. [CrossRef]
- McKinney, S.M.; Sieniek, M.; Godbole, V.; Godwin, J.; Antropova, N.; Ashrafian, H.; Back, T.; Chesus, M.; Corrado, G.S.; Darzi, A.; et al. International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening. Nature 2020, 577, 89-94. [CrossRef]
- Elkhader, J.; Elemento, O. Artificial intelligence in oncology: From bench to clinic. Semin Cancer Biol 2022, 84, 113-128. [CrossRef]
- Biswas, N.; Chakrabarti, S. Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Based Systems Biology Approaches in Multi-Omics Data Analysis of Cancer. Frontiers in Oncology 2020, 10. [CrossRef]
- El-Manzalawy, Y.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Shivakumar, M.; Kim, D.; Honavar, V. Min-redundancy and max-relevance multi-view feature selection for predicting ovarian cancer survival using multi-omics data. BMC Med Genomics 2018, 11, 71. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhan, X.; Xiang, S.; Johnson, T.S.; Helm, B.; Yu, C.Y.; Zhang, J.; Salama, P.; Rizkalla, M.; Han, Z.; et al. SALMON: Survival Analysis Learning With Multi-Omics Neural Networks on Breast Cancer. Front Genet 2019, 10, 166. [CrossRef]
- Costello, J.C.; Heiser, L.M.; Georgii, E.; Gönen, M.; Menden, M.P.; Wang, N.J.; Bansal, M.; Ammad-ud-din, M.; Hintsanen, P.; Khan, S.A.; et al. A community effort to assess and improve drug sensitivity prediction algorithms. Nat Biotechnol 2014, 32, 1202-1212. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Song, N.; Shen, R.; Arora, A.; Machiela, M.J.; Song, L.; Landi, M.T.; Ghosh, D.; Chatterjee, N.; Baladandayuthapani, V.; et al. Integrating Clinical and Multiple Omics Data for Prognostic Assessment across Human Cancers. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 16954. [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthi, B.V.S.K.; Nepal, S.; Varambally, S. Genomic and Epigenomic Alterations in Cancer. The American Journal of Pathology 2016, 186, 1724-1735. [CrossRef]
- Ushijima, T.; Clark, S.J.; Tan, P. Mapping genomic and epigenomic evolution in cancer ecosystems. Science 2021, 373, 1474-1479. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Wu, C.C.; Peng, P.H.; Liang, Y.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Chien, K.Y.; Chen, J.T.; Lin, S.J.; Tang, R.P.; Hsieh, L.L.; et al. Identification of secretory gelsolin as a plasma biomarker associated with distant organ metastasis of colorectal cancer. J Mol Med (Berl) 2012, 90, 187-200. [CrossRef]
- Fayazfar, S.; Zali, H.; Arefi Oskouie, A.; Asadzadeh Aghdaei, H.; Rezaei Tavirani, M.; Nazemalhosseini Mojarad, E. Early diagnosis of colorectal cancer via plasma proteomic analysis of CRC and advanced adenomatous polyp. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench 2019, 12, 328-339.
- Thorsen, S.F.; Gromova, I.; Christensen, I.J.; Fredriksson, S.; Andersen, C.L.; Nielsen, H.J.; Stenvang, J.; Moreira, J.M.A. Gel-Based Proteomics of Clinical Samples Identifies Potential Serological Biomarkers for Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 6082.
- Mishra, S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Suman, S.; Kumar, V.; Shukla, Y. Circulating miRNAs revealed as surrogate molecular signatures for the early detection of breast cancer. Cancer Lett 2015, 369, 67-75. [CrossRef]
- Ger, M.; Kaupinis, A.; Nemeikaite-Ceniene, A.; Sarlauskas, J.; Cicenas, J.; Cenas, N.; Valius, M. Quantitative proteomic analysis of anticancer drug RH1 resistance in liver carcinoma. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics 2016, 1864, 219-232. [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; George, B.; Rai, V. Artificial Intelligence to Decode Cancer Mechanism: Beyond Patient Stratification for Precision Oncology. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 1177. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Bartolomé, S.; Binz, P.A.; Albar, J.P. The Minimal Information about a Proteomics Experiment (MIAPE) from the Proteomics Standards Initiative. Methods Mol Biol 2014, 1072, 765-780. [CrossRef]
- Abbatiello, S.; Ackermann, B.L.; Borchers, C.; Bradshaw, R.A.; Carr, S.A.; Chalkley, R.; Choi, M.; Deutsch, E.; Domon, B.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; et al. New Guidelines for Publication of Manuscripts Describing Development and Application of Targeted Mass Spectrometry Measurements of Peptides and Proteins. Mol Cell Proteomics 2017, 16, 327-328. [CrossRef]
- Mertins, P.; Mani, D.R.; Ruggles, K.V.; Gillette, M.A.; Clauser, K.R.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Qiao, J.W.; Cao, S.; Petralia, F.; et al. Proteogenomics connects somatic mutations to signalling in breast cancer. Nature 2016, 534, 55-62. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gonzàlez-Porta, M.; Santos, S.; Brazma, A.; Marioni, J.C.; Aebersold, R.; Venkitaraman, A.R.; Wickramasinghe, V.O. Impact of Alternative Splicing on the Human Proteome. Cell Rep 2017, 20, 1229-1241. [CrossRef]
- Mo, Q.; Li, R.; Adeegbe, D.O.; Peng, G.; Chan, K.S. Integrative multi-omics analysis of muscle-invasive bladder cancer identifies prognostic biomarkers for frontline chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Commun Biol 2020, 3, 784. [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Ji, J.; Gleason, K.J.; Yang, F.; Martignetti, J.A.; Chen, L.S.; Wang, P. Insights into Impact of DNA Copy Number Alteration and Methylation on the Proteogenomic Landscape of Human Ovarian Cancer via a Multi-omics Integrative Analysis. Mol Cell Proteomics 2019, 18, S52-s65. [CrossRef]
- Champion, M.; Brennan, K.; Croonenborghs, T.; Gentles, A.J.; Pochet, N.; Gevaert, O. Module Analysis Captures Pancancer Genetically and Epigenetically Deregulated Cancer Driver Genes for Smoking and Antiviral Response. EBioMedicine 2018, 27, 156-166. [CrossRef]
- Porta Siegel, T.; Hamm, G.; Bunch, J.; Cappell, J.; Fletcher, J.S.; Schwamborn, K. Mass Spectrometry Imaging and Integration with Other Imaging Modalities for Greater Molecular Understanding of Biological Tissues. Mol Imaging Biol 2018, 20, 888-901. [CrossRef]
- Addie, R.D.; Balluff, B.; Bovée, J.V.; Morreau, H.; McDonnell, L.A. Current State and Future Challenges of Mass Spectrometry Imaging for Clinical Research. Anal Chem 2015, 87, 6426-6433. [CrossRef]
- Delcourt, V.; Franck, J.; Leblanc, E.; Narducci, F.; Robin, Y.M.; Gimeno, J.P.; Quanico, J.; Wisztorski, M.; Kobeissy, F.; Jacques, J.F.; et al. Combined Mass Spectrometry Imaging and Top-down Microproteomics Reveals Evidence of a Hidden Proteome in Ovarian Cancer. EBioMedicine 2017, 21, 55-64. [CrossRef]
- Doerr, A. Single-cell proteomics. Nat Methods 2019, 16, 20. [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, K.P.; Doolan, D.L. Immunomics: a 21st century approach to vaccine development for complex pathogens. Parasitology 2016, 143, 236-244. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, I.R.; Efroni, S. The Immune System Computes the State of the Body: Crowd Wisdom, Machine Learning, and Immune Cell Reference Repertoires Help Manage Inflammation. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 10. [CrossRef]
- Koelzer, V.H.; Sirinukunwattana, K.; Rittscher, J.; Mertz, K.D. Precision immunoprofiling by image analysis and artificial intelligence. Virchows Arch 2019, 474, 511-522. [CrossRef]
- Feldhahn, M.; Thiel, P.; Schuler, M.M.; Hillen, N.; Stevanovic, S.; Rammensee, H.G.; Kohlbacher, O. EpiToolKit--a web server for computational immunomics. Nucleic Acids Res 2008, 36, W519-522. [CrossRef]
- Lyons, Y.A.; Wu, S.Y.; Overwijk, W.W.; Baggerly, K.A.; Sood, A.K. Immune cell profiling in cancer: molecular approaches to cell-specific identification. NPJ Precis Oncol 2017, 1, 26. [CrossRef]
- Landhuis, E. Single-cell approaches to immune profiling. Nature 2018, 557, 595-597. [CrossRef]
- Finotello, F.; Eduati, F. Multi-Omics Profiling of the Tumor Microenvironment: Paving the Way to Precision Immuno-Oncology. Front Oncol 2018, 8, 430. [CrossRef]
- Lieber, S.; Reinartz, S.; Raifer, H.; Finkernagel, F.; Dreyer, T.; Bronger, H.; Jansen, J.M.; Wagner, U.; Worzfeld, T.; Müller, R.; et al. Prognosis of ovarian cancer is associated with effector memory CD8(+) T cell accumulation in ascites, CXCL9 levels and activation-triggered signal transduction in T cells. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1424672. [CrossRef]
- Khodadadian, A.; Darzi, S.; Haghi-Daredeh, S.; Sadat Eshaghi, F.; Babakhanzadeh, E.; Mirabutalebi, S.H.; Nazari, M. Genomics and Transcriptomics: The Powerful Technologies in Precision Medicine. Int J Gen Med 2020, 13, 627-640. [CrossRef]
- Olsen, E.A.; Hordinsky, M.; Whiting, D.; Stough, D.; Hobbs, S.; Ellis, M.L.; Wilson, T.; Rittmaster, R.S. The importance of dual 5alpha-reductase inhibition in the treatment of male pattern hair loss: results of a randomized placebo-controlled study of dutasteride versus finasteride. J Am Acad Dermatol 2006, 55, 1014-1023. [CrossRef]
- Whiting, D.A. Diagnostic and predictive value of horizontal sections of scalp biopsy specimens in male pattern androgenetic alopecia. J Am Acad Dermatol 1993, 28, 755-763. [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Cantisani, C.; Melis, L.; Iorio, A.; Scali, E.; Calvieri, S. Minoxidil use in dermatology, side effects and recent patents. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 2012, 6, 130-136. [CrossRef]
- Almohanna, H.M.; Ahmed, A.A.; Tsatalis, J.P.; Tosti, A. The Role of Vitamins and Minerals in Hair Loss: A Review. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2019, 9, 51-70. [CrossRef]
- Midorikawa, T.; Chikazawa, T.; Yoshino, T.; Takada, K.; Arase, S. Different gene expression profile observed in dermal papilla cells related to androgenic alopecia by DNA macroarray analysis. J Dermatol Sci 2004, 36, 25-32. [CrossRef]
- Botchkarev, V.A.; Botchkareva, N.V.; Nakamura, M.; Huber, O.; Funa, K.; Lauster, R.; Paus, R.; Gilchrest, B.A. Noggin is required for induction of the hair follicle growth phase in postnatal skin. Faseb j 2001, 15, 2205-2214. [CrossRef]
- Jamora, C.; DasGupta, R.; Kocieniewski, P.; Fuchs, E. Links between signal transduction, transcription and adhesion in epithelial bud development. Nature 2003, 422, 317-322. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Shin, J.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Joo, J.H.; Kwack, M.H.; Sung, Y.K.; Kang, N.G. Hair Thickness Growth Effect of Adenosine Complex in Male-/Female-Patterned Hair Loss via Inhibition of Androgen Receptor Signaling. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [CrossRef]
- Ober-Reynolds, B.; Wang, C.; Ko, J.M.; Rios, E.J.; Aasi, S.Z.; Davis, M.M.; Oro, A.E.; Greenleaf, W.J. Integrated single-cell chromatin and transcriptomic analyses of human scalp identify gene-regulatory programs and critical cell types for hair and skin diseases. Nat Genet 2023, 55, 1288-1300. [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, M.; Ghaffarpour, G.H.; Ghods, S. The effect of GGC and CAG repeat polymorphisms on the androgen receptor gene in response to finasteride therapy in men with androgenetic alopecia. J Res Med Sci 2019, 24, 104. [CrossRef]
- Mysore, V.; Shashikumar, B.M. Guidelines on the use of finasteride in androgenetic alopecia. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2016, 82, 128-134. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Fu, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Qu, Q.; Li, K.; Fan, Z.; Hu, Z.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals an Inhibitory Effect of Dihydrotestosterone-Treated 2D- and 3D-Cultured Dermal Papilla Cells on Hair Follicle Growth. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 724310. [CrossRef]
- Vogt, A.; Pfannes, E.K.B.; Fimmel, S.; Hadam, S.; Andruck, A.; Kottner, J.; Blume-Peytavi, U. Infundibular protein and RNA microarray analyses from affected and clinically non-affected scalp in male androgenetic alopecia patients. Exp Dermatol 2017, 26, 518-521. [CrossRef]
- Karnik, P.; Shah, S.; Dvorkin-Wininger, Y.; Oshtory, S.; Mirmirani, P. Microarray analysis of androgenetic and senescent alopecia: comparison of gene expression shows two distinct profiles. J Dermatol Sci 2013, 72, 183-186. [CrossRef]
- Philpott, M. Transcriptomic analysis identifies regulators of the Wnt signalling and hypoxia-inducible factor pathways as possible mediators of androgenetic alopecia. Br J Dermatol 2022, 187, 845. [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Jacobo, L.A.; Ancer-Arellano, C.I.; Villarreal-Villarreal, C.D.; Ortiz-Lopez, R.; Montufar-Martinez, M.; Trevino, V.; Santuario-Facio, S.K.; Sanchez-Cornejo, R.; Sanchez-Garcia, A.; Medina-De la Garza, C.E.; et al. Global expression profile and global genome methylation signatures in male patients with androgenetic alopecia. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2020, 34, e216-e218. [CrossRef]
- Michel, L.; Reygagne, P.; Benech, P.; Jean-Louis, F.; Scalvino, S.; Ly Ka So, S.; Hamidou, Z.; Bianovici, S.; Pouch, J.; Ducos, B.; et al. Study of gene expression alteration in male androgenetic alopecia: evidence of predominant molecular signalling pathways. Br J Dermatol 2017, 177, 1322-1336. [CrossRef]
- Premanand, A.; Rajkumari, B.R. In silico analysis of gene expression data from bald frontal and haired occipital scalp to identify candidate genes in male androgenetic alopecia. Arch Dermatol Res 2019, 311, 815-824. [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Morgan, B.A. Wnt signaling through the beta-catenin pathway is sufficient to maintain, but not restore, anagen-phase characteristics of dermal papilla cells. J Invest Dermatol 2004, 122, 239-245. [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, O.; Muñoz, A.; Esteller, M.; Fraga, M.F. Epigenetic alterations of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in human disease. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2007, 7, 13-21. [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Kwack, M.H.; Shin, S.H.; Oh, J.W.; Kang, B.M.; Kim, A.A.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, J.C.; Sung, Y.K. Identification of transcriptional targets of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in dermal papilla cells of human scalp hair follicles: EP2 is a novel transcriptional target of Wnt3a. J Dermatol Sci 2010, 58, 91-96. [CrossRef]
- Chew, E.G.; Ho, B.S.; Ramasamy, S.; Dawson, T.; Tennakoon, C.; Liu, X.; Leong, W.M.; Yang, S.Y.; Lim, S.Y.; Jaffar, H.; et al. Comparative transcriptome profiling provides new insights into mechanisms of androgenetic alopecia progression. Br J Dermatol 2017, 176, 265-269. [CrossRef]
- Trüeb, R.M. The impact of oxidative stress on hair. Int J Cosmet Sci 2015, 37 Suppl 2, 25-30. [CrossRef]
- Ku, H.C.; Cheng, C.F. Master Regulator Activating Transcription Factor 3 (ATF3) in Metabolic Homeostasis and Cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 556. [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Tan, S.J.; Wang, S.H.; Li, L.; Sun, X.F.; Shen, W.; Wang, X. Single-cell Transcriptome Profiling reveals Dermal and Epithelial cell fate decisions during Embryonic Hair Follicle Development. Theranostics 2020, 10, 7581-7598. [CrossRef]
- Hasin, Y.; Seldin, M.; Lusis, A. Multi-omics approaches to disease. Genome Biol 2017, 18, 83. [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Snyder, M.P. Integrative omics for health and disease. Nat Rev Genet 2018, 19, 299-310. [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.K.; Liu, R.H.; Jin, H.Z.; Liu, X.R.; Ye, J.; Shan, L.; Zhang, W.D. “Omics” in pharmaceutical research: overview, applications, challenges, and future perspectives. Chin J Nat Med 2015, 13, 3-21. [CrossRef]
- Collins, F.S.; Varmus, H. A new initiative on precision medicine. N Engl J Med 2015, 372, 793-795. [CrossRef]
- Adir, O.; Poley, M.; Chen, G.; Froim, S.; Krinsky, N.; Shklover, J.; Shainsky-Roitman, J.; Lammers, T.; Schroeder, A. Integrating Artificial Intelligence and Nanotechnology for Precision Cancer Medicine. Adv Mater 2020, 32, e1901989. [CrossRef]
- Bhuvaneshwar, K.; Belouali, A.; Singh, V.; Johnson, R.M.; Song, L.; Alaoui, A.; Harris, M.A.; Clarke, R.; Weiner, L.M.; Gusev, Y.; et al. G-DOC Plus - an integrative bioinformatics platform for precision medicine. BMC Bioinformatics 2016, 17, 193. [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, S.J. Precision medicine in oncology drug development: a pharma perspective. Drug Discov Today 2015, 20, 1455-1463. [CrossRef]
- Biankin, A.V.; Piantadosi, S.; Hollingsworth, S.J. Patient-centric trials for therapeutic development in precision oncology. Nature 2015, 526, 361-370. [CrossRef]
- Zanfardino, M.; Franzese, M.; Pane, K.; Cavaliere, C.; Monti, S.; Esposito, G.; Salvatore, M.; Aiello, M. Bringing radiomics into a multi-omics framework for a comprehensive genotype-phenotype characterization of oncological diseases. J Transl Med 2019, 17, 337. [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Chuong, C.-M. Aging, alopecia, and stem cells. Science 2016, 351, 559-560, doi:doi:10.1126/science.aaf1635.
- Moyse, E.; Krantic, S.; Djellouli, N.; Roger, S.; Angoulvant, D.; Debacq, C.; Leroy, V.; Fougere, B.; Aidoud, A. Neuroinflammation: A Possible Link Between Chronic Vascular Disorders and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Muddapu, V.R.; Dharshini, S.A.P.; Chakravarthy, V.S.; Gromiha, M.M. Neurodegenerative Diseases – Is Metabolic Deficiency the Root Cause? Frontiers in Neuroscience 2020, 14. [CrossRef]
- Blackhurst, B.M.; Funk, K.E. Viral pathogens increase risk of neurodegenerative disease. Nature Reviews Neurology 2023, 19, 259-260. [CrossRef]
- Khalid, K.A.; Nawi, A.F.M.; Zulkifli, N.; Barkat, M.A.; Hadi, H. Aging and Wound Healing of the Skin: A Review of Clinical and Pathophysiological Hallmarks. Life 2022, 12, 2142.
- Bonomini, F.; Rodella, L.F.; Rezzani, R. Metabolic syndrome, aging and involvement of oxidative stress. Aging Dis 2015, 6, 109-120. [CrossRef]
- Jensterle, M.; Rizzo, M.; Haluzík, M.; Janež, A. Efficacy of GLP-1 RA Approved for Weight Management in Patients With or Without Diabetes: A Narrative Review. Advances in Therapy 2022, 39, 2452-2467. [CrossRef]
- Seon, M.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Son, Y.; Song, J.; Kim, O.Y. Circulating GLP-1 Levels as a Potential Indicator of Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Adult Women. Nutrients 2021, 13, 865.
- Obermeyer, Z.; Emanuel, E.J. Predicting the Future - Big Data, Machine Learning, and Clinical Medicine. N Engl J Med 2016, 375, 1216-1219. [CrossRef]
- van Deursen, J.M. Senolytic therapies for healthy longevity. Science 2019, 364, 636-637, doi:doi:10.1126/science.aaw1299.
- Strauss, M.T.; Bludau, I.; Zeng, W.F.; Voytik, E.; Ammar, C.; Schessner, J.P.; Ilango, R.; Gill, M.; Meier, F.; Willems, S.; et al. AlphaPept: a modern and open framework for MS-based proteomics. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 2168. [CrossRef]
- Ferrell, J.E., Jr.; Tsai, T.Y.; Yang, Q. Modeling the cell cycle: why do certain circuits oscillate? Cell 2011, 144, 874-885. [CrossRef]
- Lotfollahi, M.; Wolf, F.A.; Theis, F.J. scGen predicts single-cell perturbation responses. Nat Methods 2019, 16, 715-721. [CrossRef]
- Goecks, J.; Jalili, V.; Heiser, L.M.; Gray, J.W. How Machine Learning Will Transform Biomedicine. Cell 2020, 181, 92-101. [CrossRef]
- Topol, E.J. High-performance medicine: the convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat Med 2019, 25, 44-56. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




