Submitted:
01 August 2024
Posted:
06 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
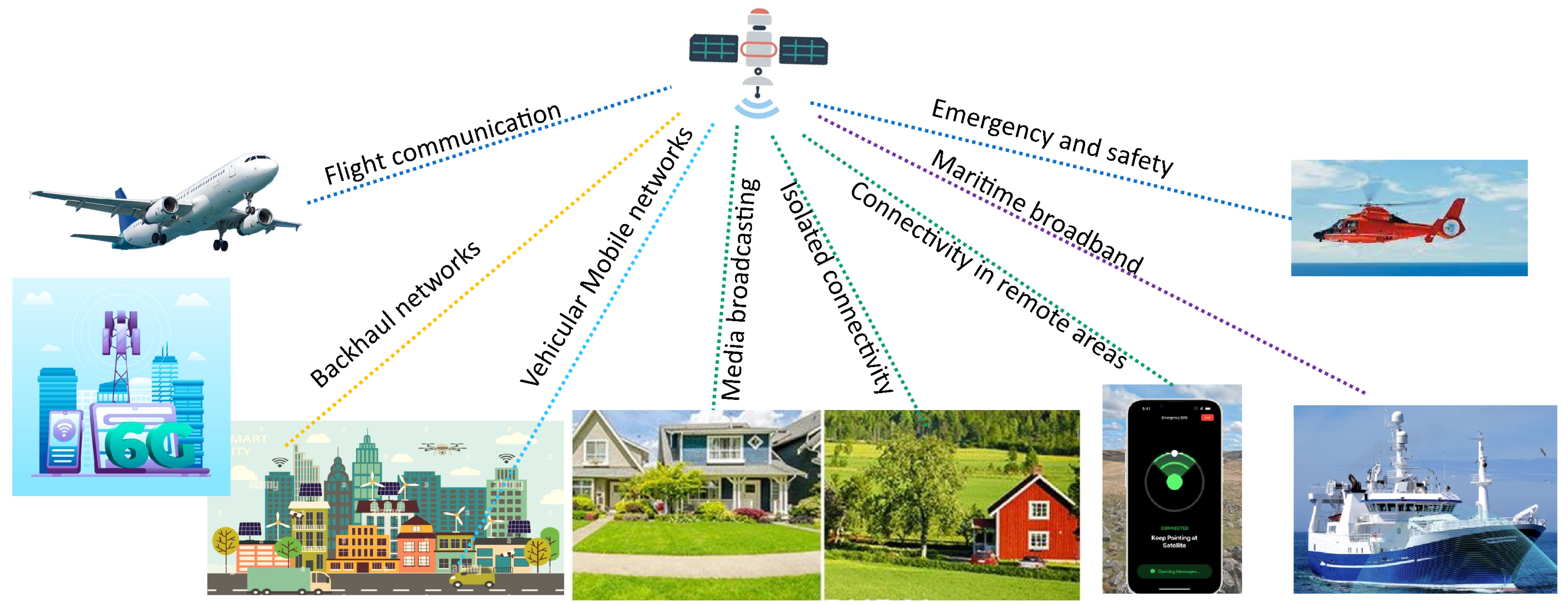
1. Introduction
- The review encapsulates passive beam steering techniques focusing on full-duplex systems incorporating passive metasurfaces.
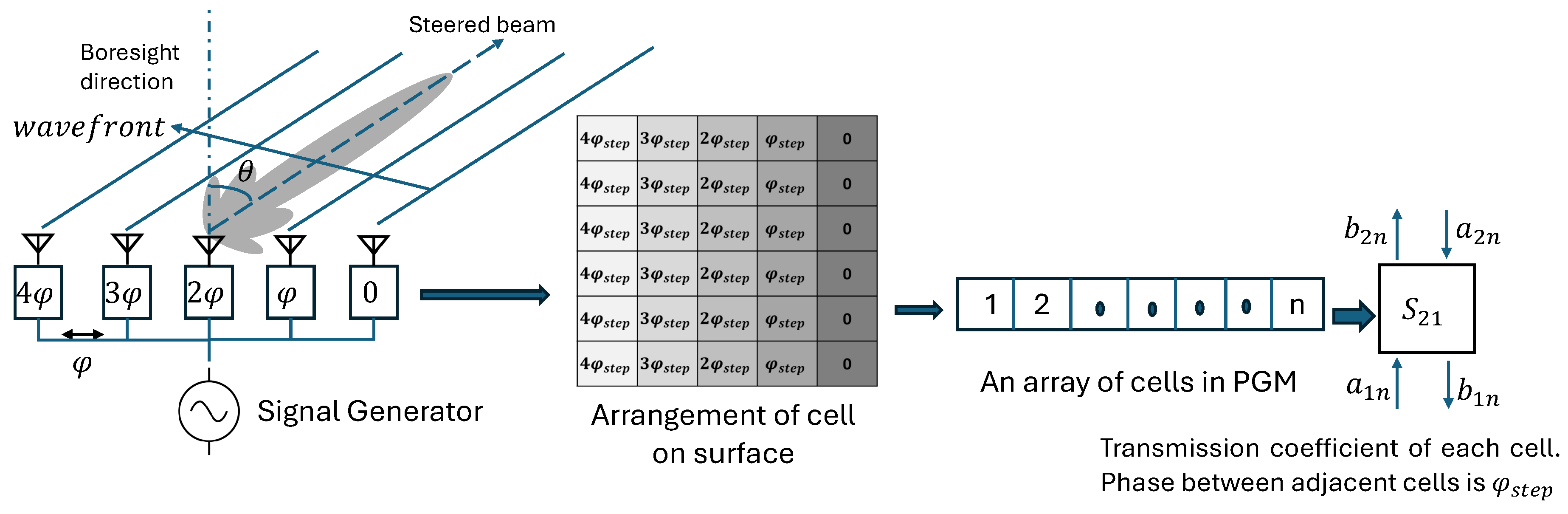
- Since the first step in designing a passive metasurface is finalizing the phase shifting cell, a subwavelength element that repeats periodically/aperiodically over the entire surface, careful design and selection are crucial and require deliberation. Therefore, the focus of this article is the design and analysis of different dual-band phase transformation cell topologies available in the literature, with the pros and cons of each on the system-level parameters. This analysis aims to provide a valuable resource for designers beginning the development of dual-band PGMs used in various applications such as dual-band beam-steering, dual-band phase correction, and dual-band lenses.
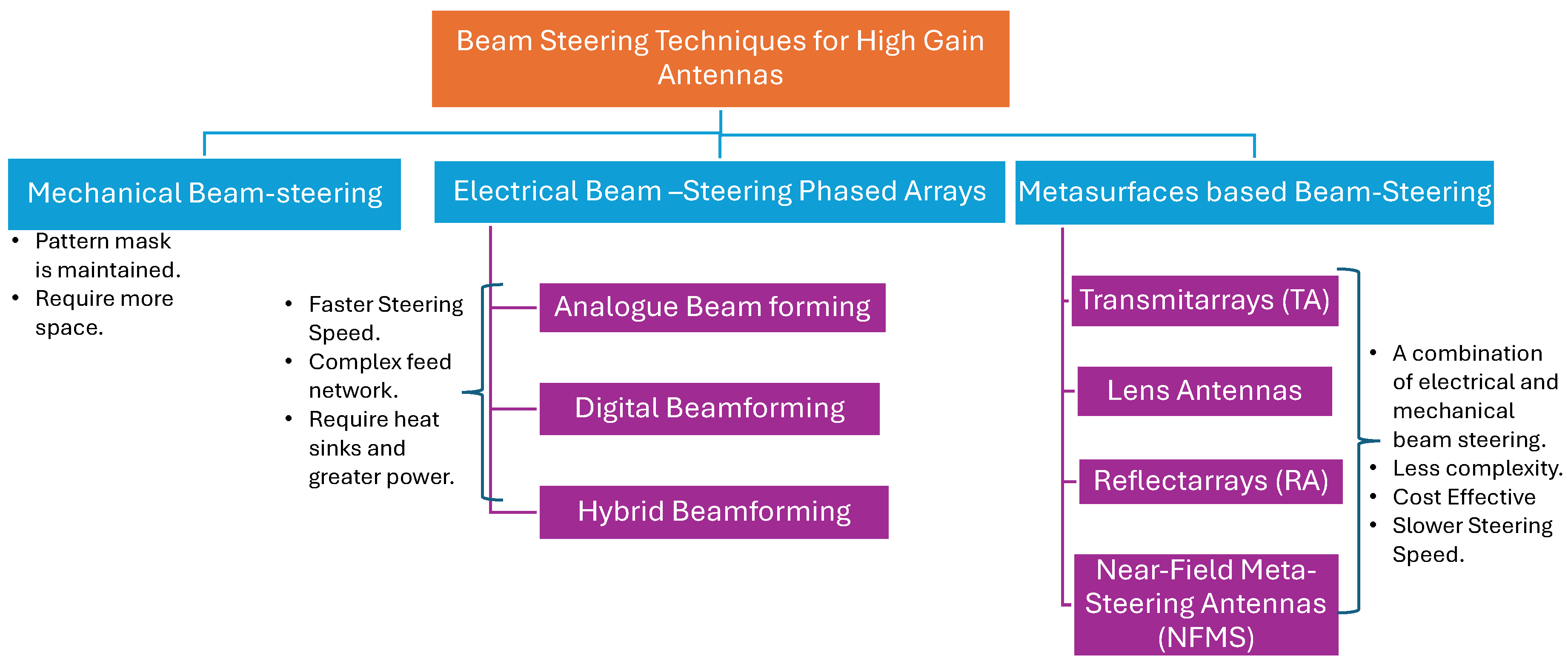
2. Dual-Band Metasurface Based Beam-Steering Techniques
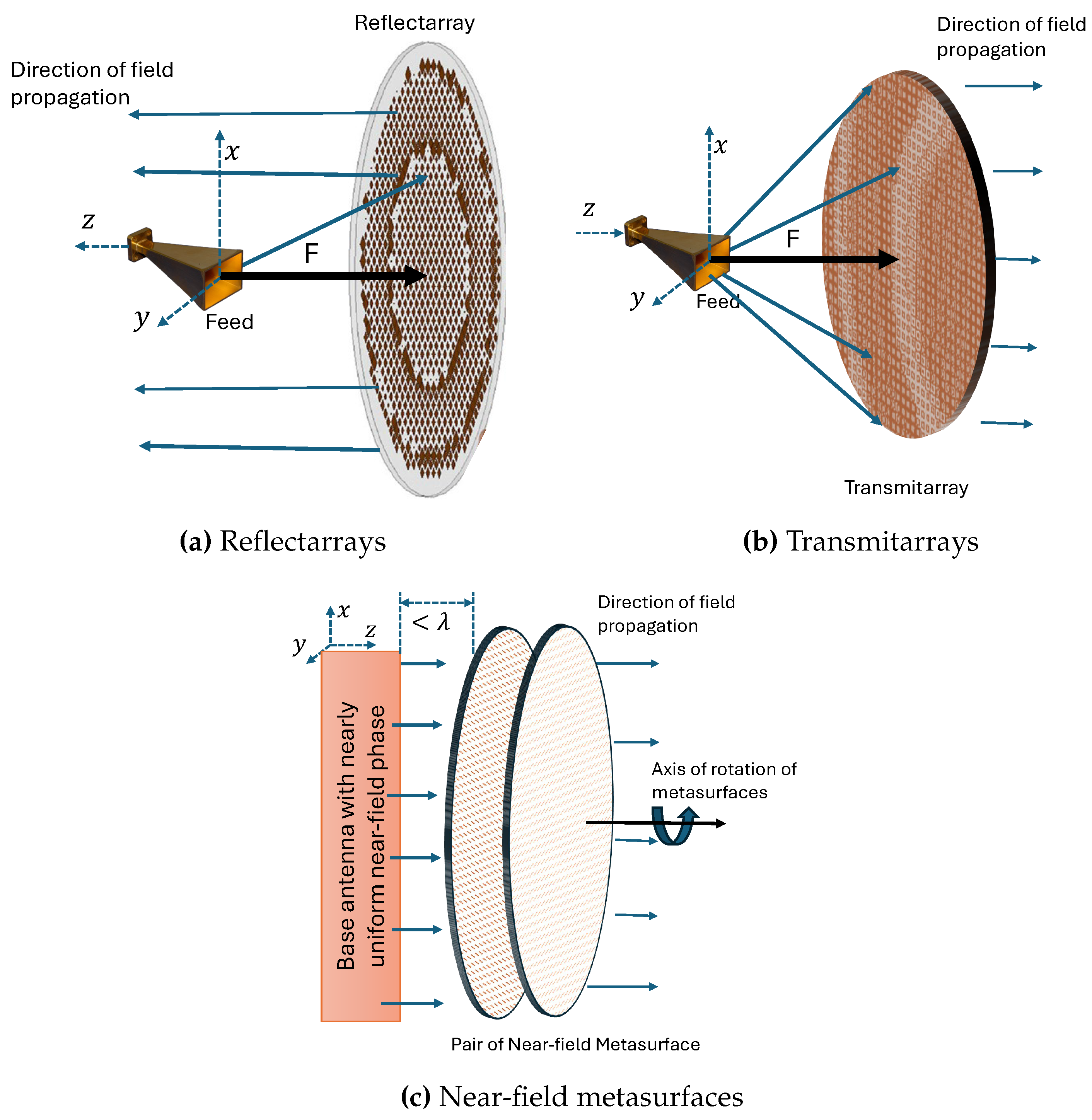
2.1. Reflectarray-Based Beam-Steering
2.2. Transmitarrays-Based Beam-Steering
2.3. Near-Field Meta-Steering Systems
2.4. A Comparative Analysis of Antenna Beam-Steering Based on RAs, TAs and NFMS
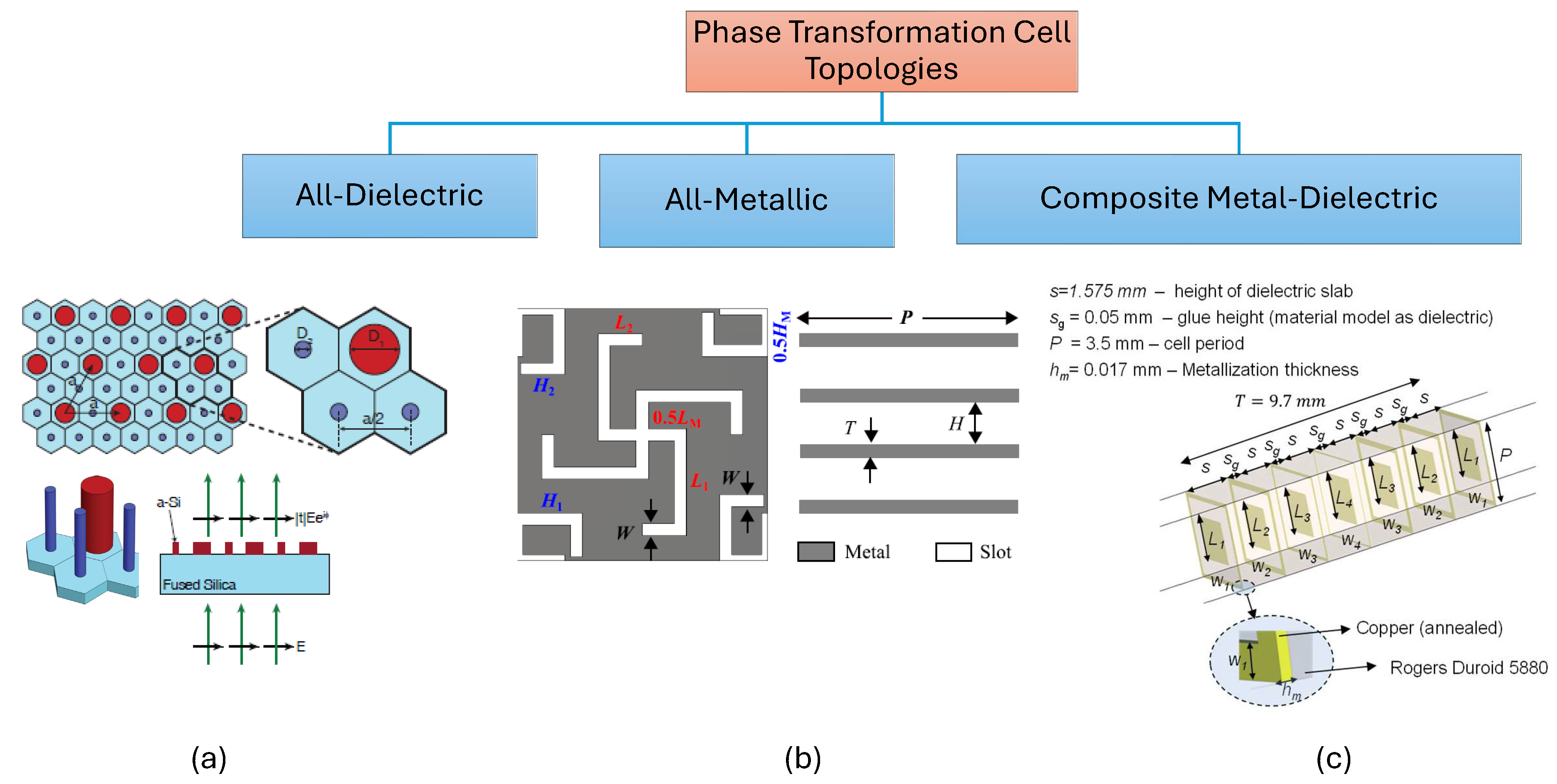
3. Passive Dual-Band Phase-Gradient Metasurfaces
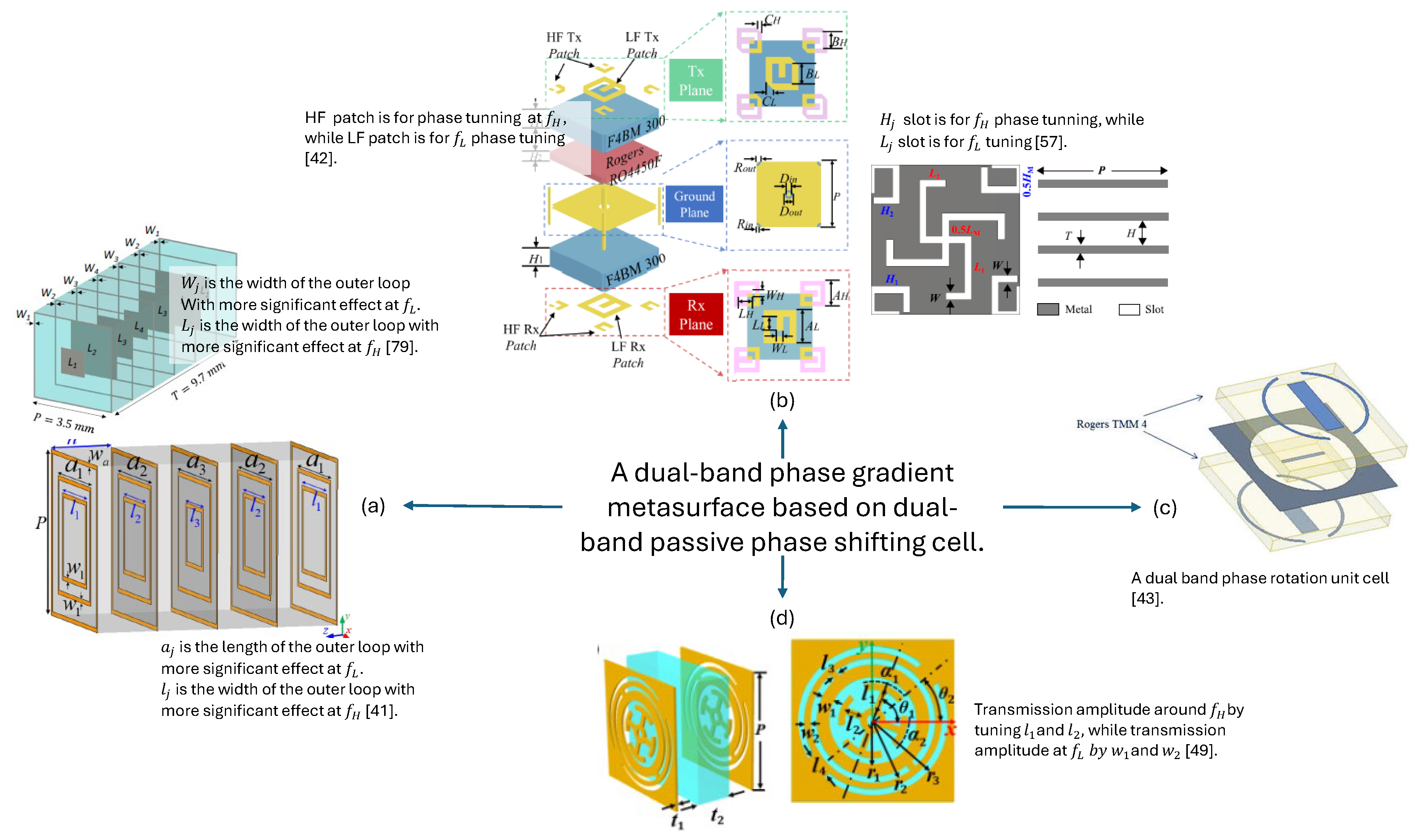
3.1. All-Dielectric Unit Cells
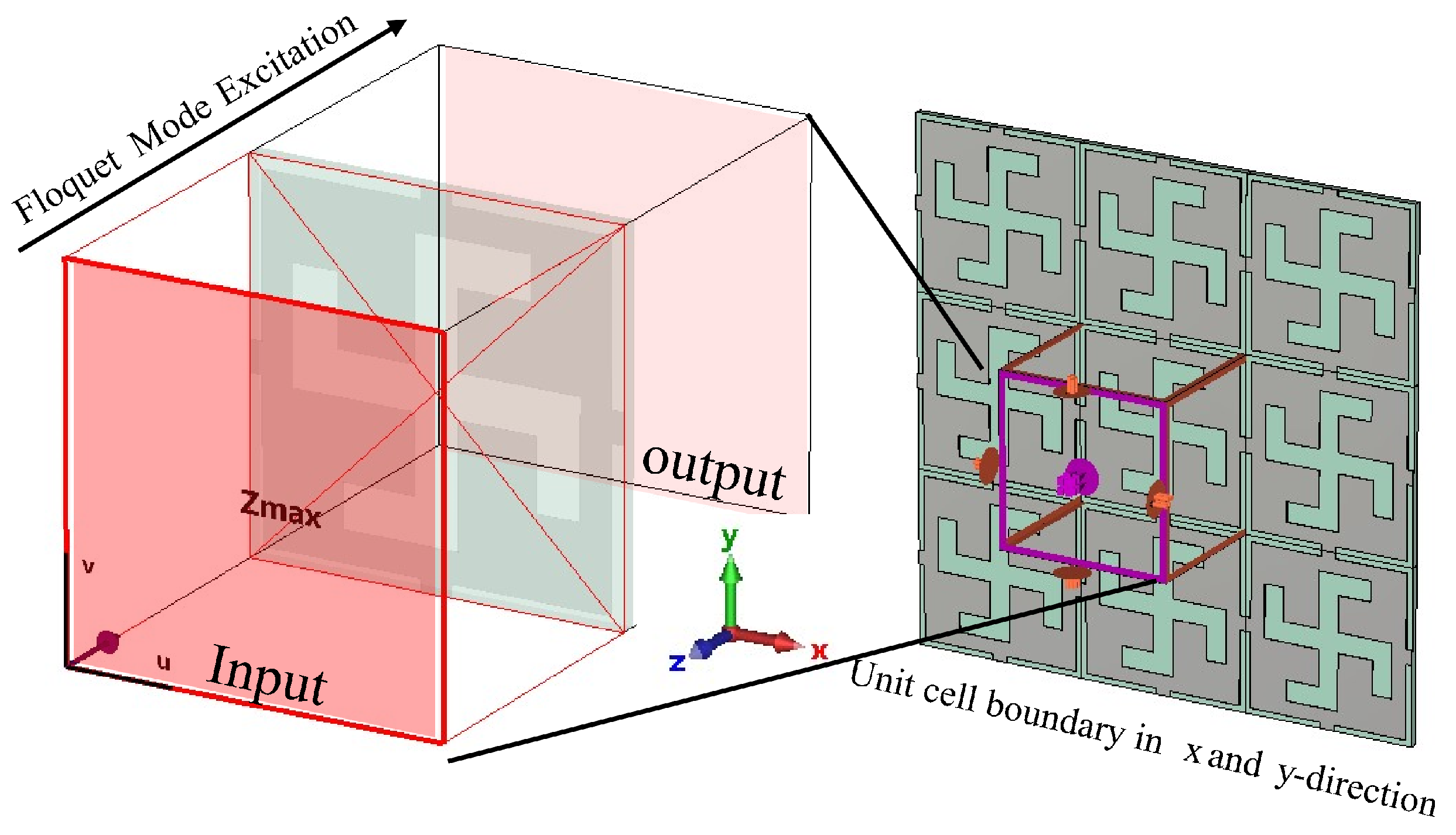
3.2. All-Metallic Unit cells
3.3. Composite Metal-Dielectric Unit Cells
4. A Comparison of Different Dual-Band Phase-Transformation Cells
5. Conclusions
- Interleaved Resonant Elements [42,45,46,47,48,50,51,52,57,67,84,85]: Enables independent tuning but may result in larger cell sizes that may lead to phase quantization error or grating lobes particularly at higher frequency band. The placement of cells to form the PGM needs careful investigation to avoid corner element shape discontinuities. Smaller unit cell topologies needs to be explored to design a PGM that can allow better resolution in phase correction/tunning and enhance the overall steering range of the antenna system.
- Concentric Cell [49]: The designed cell has a modified Jerusalem cross resonator and a modified complementary split ring resonator to tune transmission properties at two frequencies independently. The overall cell is concentric but at the cost of complex geometry for the overall cell.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SATCOM | Satellite Communications |
| COTM | Communication on the move |
| ITU | International Telecommunication Union |
| LEO | Lower Earth Orbit |
| MEO | Medium Earth Orbit |
| GEO | Geostationary Earth Orbit |
| PGM | Phase Gradient Metasurface |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| SOTM | SATCOM on the Move |
| NFMS | Near Field Meta-Steering |
| RA | Reflectarray |
| TA | Transmitarray |
| RHCP | Right Hand Circularly Polarized |
| LHCP | Left Hand Circularly Polarized |
| PSS | Phase Shifting Surfaces |
| MWS | Microwave Studio |
| PD | Phase Delay |
| PCB | Printed Circuit Board |
| PR | Phase Rotation |
References
- Skyquest. Satellite Data Services Market Insights. https://www.skyquestt.com/report/satellite-data-services-market.
- Fortune Business Insight. Fortune Business Insights: Satcom Market. https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/satellite-communication-satcom-market-102679.
- statista. Internet usage worldwide - Statistics & Facts. https://www.statista.com/topics/1145/internet-usage-worldwide/#topicOverview.
- straitsresearch. Satellite Communication Market. https://straitsresearch.com/report/satellite-communication-market#:~:text=Market%20Overview,period%20(2022%E2%80%932030).
- You, R.; Gao, W.; Wu, C.; Li, H. Technologies for spacecraft antenna engineering design; Springer, 2021.
- Viasat. Satellite communications in 2024: The ins and outs. https://news.viasat.com/blog/corporate/satellite-communications-in-2024-the-ins-and-outs.
- Huang, J.; Cao, J. Recent development of commercial satellite communications systems. Artificial intelligence in China: Proceedings of the international conference on artificial intelligence in China. Springer, 2020, pp. 531–536.
- imarc. Top Players in the Satellite Communication (SATCOM) Market. https://www.imarcgroup.com/satellite-communication-companies.
- RF Wireless World. Advantages and Disadvantages of LEO orbit. https://www.rfwireless-world.com/Terminology/Advantages-and-Disadvantages-of-LEO-orbit.html .
- Lockie, D.G.; Thomson, M. Spacecraft antennas and beam steering methods for satellite communciation system, 1997. US Patent 5,642,122.
- Osoro, O.B.; Oughton, E.J. A techno-economic framework for satellite networks applied to low earth orbit constellations: Assessing Starlink, OneWeb and Kuiper. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 141611–141625. [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yang, F.; Han, G.; Li, Y. High-throughput SatCom-on-the-move antennas: technical overview and state-of-the-art. Digital Communications and Networks 2023. [CrossRef]
- Uchendu, I.; Kelly, J.R. Survey of beam steering techniques available for millimeter wave applications. Progress in electromagnetics research B 2016, 68, 35–54. [CrossRef]
- Zarb-Adami, K.; Faulkner, A.; De Vaate, J.B.; Kant, G.; Picard, P. Beamforming techniques for large-N aperture arrays. 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology. IEEE, 2010, pp. 883–890.
- Esselle, K.; Singh, K.; Thalakotuna, D.; Koli, M.N.Y.; Ahmed, F. Beam-steering antenna technologies for space-related applications. 2023 17th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP). IEEE, 2023, pp. 1–5.
- Ahmed, F.; Singh, K.; Esselle, K.P. State-of-the-art passive beam-steering antenna technologies: Challenges and capabilities. Ieee Access 2023. [CrossRef]
- Rudge, A.; Withers, M. New technique for beam steering with fixed parabolic reflectors. Proceedings of the Institution of Electrical Engineers. IET, 1971, Vol. 118, pp. 857–863.
- EM solutions. Em solutions. https://www.emsolutions.com.au/products-and-solutions/sotm/.
- Boriskin, A.; Sauleau, R. Aperture antennas for millimeter and sub-millimeter wave applications; Springer, 2018.
- Sazegar, M.; Nassar, I.; Eylander, C.; Momeni, A.; Eylander, B.; Stevenson, R. Ku-Band SATCOM User Terminal With Complete Beam Steering Using a Shared Aperture Metasurface for Full-Duplex Operation. 2023 17th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP). IEEE, 2023, pp. 1–3.
- Kymeta Corporation. Kymeta Terminal. https://www.kymetacorp.com/products/terminal/.
- ThinKom Solutions. ThinKom. https://www.thinkom.com/technology.
- Kymeta Corporation. Starlink for Homes. https://www.starlink.com/residential?utm_source=google&utm_medium=paid&utm_campaign=lf_au_res_egn_src_ggl_brd_stk-pe&utm_content=694470362766&utm_term=starlink&utm_id=&gad_source=1&gclid=EAIaIQobChMI18yNvuW5hQMVlhitBh2UggomEAAYASAAEgLbEPD_BwE.
- Gagnon, N. Phase shifting surface (PSS) and phase and amplitude shifting surface (PASS) for microwave applications; University of Ottawa (Canada), 2011.
- Afzal, M.U.; Esselle, K.P. Steering the beam of medium-to-high gain antennas using near-field phase transformation. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2017, 65, 1680–1690. [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Farahani, M.; Ghayekhloo, A.; Zarbakhsh, S.; Sebak, A.R.; Denidni, T.A. Beam tilting approaches based on phase gradient surface for mmWave antennas. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2020, 68, 4372–4385. [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Ahmed, F.; Esselle, K. Electromagnetic metasurfaces: Insight into evolution, design and applications. Crystals 2022, 12, 1769. [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Afzal, M.U.; Kovaleva, M.; Esselle, K.P. Controlling the most significant grating lobes in two-dimensional beam-steering systems with phase-gradient metasurfaces. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2019, 68, 1389–1401. [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Afzal, M.U.; Esselle, K.P. Designing efficient phase-gradient metasurfaces for near-field meta-steering systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 109080–109093. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yuan, C.; Liu, L.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, H. All-metal transmit-array for circular polarization design using rotated cross-slot elements for high-power microwave applications. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2017, 65, 3253–3256. [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.; Malech, R.; Kennedy, W. The reflectarray antenna. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 1963, 11, 645–651. [CrossRef]
- Mirmozafari, M.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, M.; Zhao, J.; Honari, M.M.; Booske, J.H.; Behdad, N. Mechanically reconfigurable, beam-scanning reflectarray and transmitarray antennas: A review. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 6890. [CrossRef]
- Budhu, J.; Grbic, A.; Michielssen, E. Dualband stacked metasurface reflectarray. 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and North American Radio Science Meeting. IEEE, 2020, pp. 821–822.
- Baladi, E.; Xu, M.Y.; Faria, N.; Nicholls, J.; Hum, S.V. Dual-band circularly polarized fully reconfigurable reflectarray antenna for satellite applications in the Ku-band. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2021, 69, 8387–8396. [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.; Yu, S.; Kou, N. A Dual-Band Beam Steering Array Antenna With Integration of Reflectarray and Phased Array. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters 2023. [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, J.H. Hybrid reflectarray antenna of passive and active unit cells for highly directive two-direction beam steering. IEEE Access 2022, 11, 6299–6304. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Gao, S.; Li, W.; Sobhy, M.; Bakaimi, I.; de Groot, C.K.; Hayden, B.; Reaney, I.; Yang, X. Multibeam dual-circularly polarized reflectarray for connected and autonomous vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2019, 68, 3574–3585. [CrossRef]
- Chi, P.L.; Cheng, Y.H.; Yang, T. Novel Dual-Frequency Independent Beam-Scanning Reflectarray. 2023 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (USNC-URSI). IEEE, 2023, pp. 1337–1338.
- Dussopt, L. Transmitarray antennas. Aperture Antennas for Millimeter and Sub-Millimeter Wave Applications 2018, pp. 191–220.
- Matos, S.A.; Lima, E.B.; Silva, J.S.; Costa, J.R.; Fernandes, C.A.; Fonseca, N.J.; Mosig, J.R. High gain dual-band beam-steering transmit array for satcom terminals at Ka-band. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2017, 65, 3528–3539. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Xue, Z.; Ren, W.; Li, W. Dual-band beam-scanning antenna using rotatable planar phase gradient transmitarrays. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2020, 68, 5021–5026. [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Liu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Yue, Z.; Wang, X. A low-profile dual-band dual-circularly polarized folded transmitarray antenna with independent beam control. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2021, 70, 3852–3857. [CrossRef]
- Naseri, P.; Mirzavand, R.; Mousavi, P. Dual-band circularly polarized transmit-array unit-cell at X and K bands. 2016 10th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP). IEEE, 2016, pp. 1–4.
- Naseri, P.; Matos, S.A.; Costa, J.R.; Fernandes, C.A.; Fonseca, N.J. Dual-band dual-linear-to-circular polarization converter in transmission mode application to K/Ka--band satellite communications. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2018, 66, 7128–7137. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ren, W.; Zeng, Q.; Xue, Z.; Li, W. Dual-band beam-scanning antenna at ka-band by rotation of two transmitarrays. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters 2022, 21, 1792–1796. [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Xu, S.; Li, M. A dual-band orthogonally polarized contour beam transmitarray design. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2021, 69, 4538–4545. [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.O.; Hassani, H.R.; Rahmati, B. Dual-band, dual-polarised metallic slot transmitarray antenna. IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation 2017, 11, 402–409.
- Pham, K.T.; Sauleau, R.; Fourn, E.; Diaby, F.; Clemente, A.; Dussopt, L. Dual-band transmitarrays with dual-linear polarization at Ka-band. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2017, 65, 7009–7018. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhai, G.; Ding, J. Ultrathin Dual-Band Wide-Angle Beam Scanning Metalens Based on High-Efficiency Meta-Atom. Advanced Photonics Research 2022, 3, 2100186. [CrossRef]
- Hasani, H.; Silva, J.S.; Capdevila, S.; García-Vigueras, M.; Mosig, J.R. Dual-band circularly polarized transmitarray antenna for satellite communications at (20, 30) GHz. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2019, 67, 5325–5333. [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.K.; Guang, L.; González-Ovejero, D.; Sauleau, R. Dual-band transmitarray with low scan loss for satcom applications. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2020, 69, 1775–1780. [CrossRef]
- Hasani, H.; Silva, J.S.; Mosig, J.R.; Garcia-Vigueras, M. Dual-band 20/30 GHz circularly polarized transmitarray for SOTM applications. 2016 10th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP). IEEE, 2016, pp. 1–3.
- Singh, K.; Afzal, M.U.; Esselle, K.P. Efficient Near-Field Meta-Steering Systems for Connectivity-On-The-Move Applications using Hybrid Metasurfaces. 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (AP-S/URSI). IEEE, 2022, pp. 641–642.
- Koli, M.N.Y.; Afzal, M.U.; Esselle, K.P. Increasing the gain of beam-tilted circularly polarized radial line slot array antennas. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2022, 70, 4392–4403. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Afzal, M.U.; Hayat, T.; Esselle, K.P.; Thalakotuna, D.N. A near-field meta-steering antenna system with fully metallic metasurfaces. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2022, 70, 10062–10075. [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.A.; Hashmi, R.M.; Attygalle, M.; Esselle, K.P.; Borg, D. Ultrawideband beam steering at mm-wave frequency with planar dielectric phase transformers. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2021, 70, 1719–1728. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Afzal, M.U.; Esselle, K.P.; Thalakotuna, D.N. Novel Dual-Band Phase-Gradient Metascreen and Dual-Band Near-Field Meta-Steering Antenna. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2024. [CrossRef]
- Ettorre, M.; Pavone, S.; Casaletti, M.; Albani, M.; Mazzinghi, A.; Freni, A. Aperture Antennas for Millimeter and Sub-Millimeter Wave Applications. Cham: Springer 2018, pp. 243–288.
- Huang, J. Analysis of a microstrip reflectarray antenna for microspacecraft applications. The Telecommunications and Data Acquisition Report 1995.
- Gagnon, N.; Petosa, A.; McNamara, D.A. Printed hybrid lens antenna. IEEE transactions on antennas and propagation 2012, 60, 2514–2518. [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, N.; Petosa, A. Using rotatable planar phase shifting surfaces to steer a high-gain beam. IEEE transactions on antennas and propagation 2013, 61, 3086–3092. [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, N.; Petosa, A.; McNamara, D.A. Thin microwave quasi-transparent phase-shifting surface (PSS). IEEE transactions on antennas and propagation 2010, 58, 1193–1201. [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Pors, A.; Bozhevolnyi, S.I. Gradient metasurfaces: a review of fundamentals and applications. Reports on Progress in Physics 2017, 81, 026401. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, J.C. On the rotation of plane of polarisation of electric wave by a twisted structure. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London 1898, 63, 146–152.
- Ali, A.; Mitra, A.; Aïssa, B. Metamaterials and metasurfaces: A review from the perspectives of materials, mechanisms and advanced metadevices. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1027. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna theory: analysis and design; John wiley & sons, 2016.
- Arbabi, E.; Arbabi, A.; Kamali, S.M.; Horie, Y.; Faraon, A. Multiwavelength polarization-insensitive lenses based on dielectric metasurfaces with meta-molecules. Optica 2016, 3, 628–633. [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.A.; Hashmi, R.M.; Esselle, K.P.; Weily, A.R. Compact high-gain antenna with simple all-dielectric partially reflecting surface. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2018, 66, 4343–4348. [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.U.; Esselle, K.P.; Lalbakhsh, A. A methodology to design a low-profile composite-dielectric phase-correcting structure. IEEE antennas and wireless propagation letters 2018, 17, 1223–1227. [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.U.; Esselle, K.P.; Zeb, B.A. Dielectric phase-correcting structures for electromagnetic band gap resonator antennas. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2015, 63, 3390–3399. [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Abdel-Mageed, M.; Mittra, R. Flat-lens design using field transformation and its comparison with those based on transformation optics and ray optics. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters 2013, 12, 777–780. [CrossRef]
- Emara, M.K.; Tomura, T.; Hirokawa, J.; Gupta, S. Fabry–Pérot-Based Compound All-Dielectric Huygens’ Structure for Circularly Polarized Millimeter-Wave Beamforming. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters 2020, 19, 1784–1788. [CrossRef]
- Al-Nuaimi, M.K.T.; Hong, W.; Zhang, Y. Design of high-directivity compact-size conical horn lens antenna. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters 2014, 13, 467–470. [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, H.; Albadalejo-Lijarcio, J.L.; Zetterstrom, O.; Tyc, T.; Quevedo-Teruel, O. H-plane horn antenna with enhanced directivity using conformal transformation optics. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 14322. [CrossRef]
- Holzman. A highly compact 60-GHz lens-corrected conical horn antenna. IEEE antennas and wireless propagation letters 2004, 3, 280–282. [CrossRef]
- Munk, B.A. Frequency selective surfaces: theory and design; John Wiley & Sons, 2005.
- Abdelrahman, A.H.; Yang, F.; Elsherbeni, A.Z.; Nayeri, P.; Balanis, C.A. Analysis and design of transmitarray antennas 2017.
- Ryan, C.G.; Chaharmir, M.R.; Shaker, J.; Bray, J.R.; Antar, Y.M.; Ittipiboon, A. A wideband transmitarray using dual-resonant double square rings. IEEE Transactions on antennas and propagation 2010, 58, 1486–1493. [CrossRef]
- Matos, S.A.; Lima, E.B.; Costa, J.R.; Fernandes, C.A.; Fonseca, N.J. Generic formulation for transmit-array dual-band unit-cell design. 2017 11th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP). IEEE, 2017, pp. 2791–2794.
- Lima, E.B.; Matos, S.A.; Costa, J.R.; Fernandes, C.A.; Fonseca, N.J. Circular polarization wide-angle beam steering at Ka-band by in-plane translation of a plate lens antenna. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2015, 63, 5443–5455. [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Withayachumnankul, W.; Al-Sarawi, S.; Abbott, D. Design of dual-band frequency selective surface with miniaturized elements. 2014 International Workshop on Antenna Technology: Small Antennas, Novel EM Structures and Materials, and Applications (iWAT). IEEE, 2014, pp. 201–204.
- Li, M.; Behdad, N. Wideband true-time-delay microwave lenses based on metallo-dielectric and all-dielectric lowpass frequency selective surfaces 2013. 61, 4109–4119.
- Naseri, P.; Matos, S.A.; Costa, J.R.; Fernandes, C.A. Phase-Delay Versus Phase-Rotation Cells for Circular Polarization Transmit Arrays—Application to Satellite Ka-Band Beam Steering. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2018, 66, 1236–1247. [CrossRef]
- Nabeel, M.I.; Afzal, M.U.; Singh, K.; Thalakotuna, D.N.; Esselle, K.P. Dual-Band Printed Near-Field Metasurface with Independent Phase Transformation for Enhanced Antenna Gain. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters 2024. [CrossRef]
- Mutluer, E.; Döken, B.; Kartal, M. A dual-band frequency selective surface design for satellite applications. 2018 18th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS). IEEE, 2018, pp. 43–46.
- Chaharmir, M.R.; Shaker, J. Design of a multilayer X-/Ka-band frequency-selective surface-backed reflectarray for satellite applications. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2015, 63, 1255–1262. [CrossRef]

| Ref | Resonant Element | Topology | Number of Layers | Cell Size | Frequency Capability | Polarization | Phase Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [78] | Double Square Loop | Composite separated by air gap | 4 | Wideband (29-32 GHz) | CP | NA | |
| [85] | 4-arm structure for one band, 4-leg structure for other-band | Composite | One metal and one dielectric layer | Dual-band Ku/Ka (14.1-16 GHz and 29.2-36.8 GHz) | Dual | Separate tuning of elements by length variation | |
| [86] | Cross dipole for higher frequency, backed by square loops for lower frequency | Composite interleaved structure | Five dielectric and seven metal layers | and | Dual Band (20,30 GHz) | CP | NA |
| [52] | Split ring center elements for lower frequency, quarter split circle at corners for higher frequency | Composite | Five metal and four dielectric layers | 0.53 and 0.8 | Dual Band (20,30 GHz) | CP | Independent phase tuning by rotation of split rings |
| [79] | Square Patch Middle and square loop mentions shape against design frequ | Composite | seven metal and six dielectric layers | Dual Band (20,30 GHz) | CP | Optimal Phase Pair Selection | |
| [42] | High frequency and low frequency patches | Composite | Three metal & two dielectric layers, bonded together | 0.49 and 0.6 | Dual band (12,15 GHz) | Dual CP | NA |
| [50] | Swastika cross slot for lower frequency, half cross slot on cell corners for higher frequency | Composite, Thin substrate separated by air gap | Three metal and three dielectric layers | Dual band (20,30 GHz) | CP | Independent Frequency tuning by length variation | |
| [41] | Three concentric square loops | Composite structure, bonded layers | Five metal & four dielectric layers | Dual band (8,14 GHz) | CP | Optimum Phase pair by length variation | |
| [51] | Vertical and Horizontal Dipoles | Composite Bonded Layers | Three metal and three dielectric layers | Dual-band (20,30 GHz) | LP | Independent frequency tuning as the resonating elements are cross-polarized | |
| [47] | Cross slot and magnetic dipole slot | All metal | Three metal layers | Dual-band (11, 12.5 GHz) | CP | Independent frequency tuning as the resonating elements are cross-polarized | |
| [57] | Modified swastika slot in the middle for LF, and half swastika slot in corners for HF | All metal, separated by air gap | Four metal layers | Dual-band (Ku) | CP | Optimum phase pair with partially independent phase response |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





