Submitted:
30 July 2024
Posted:
02 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
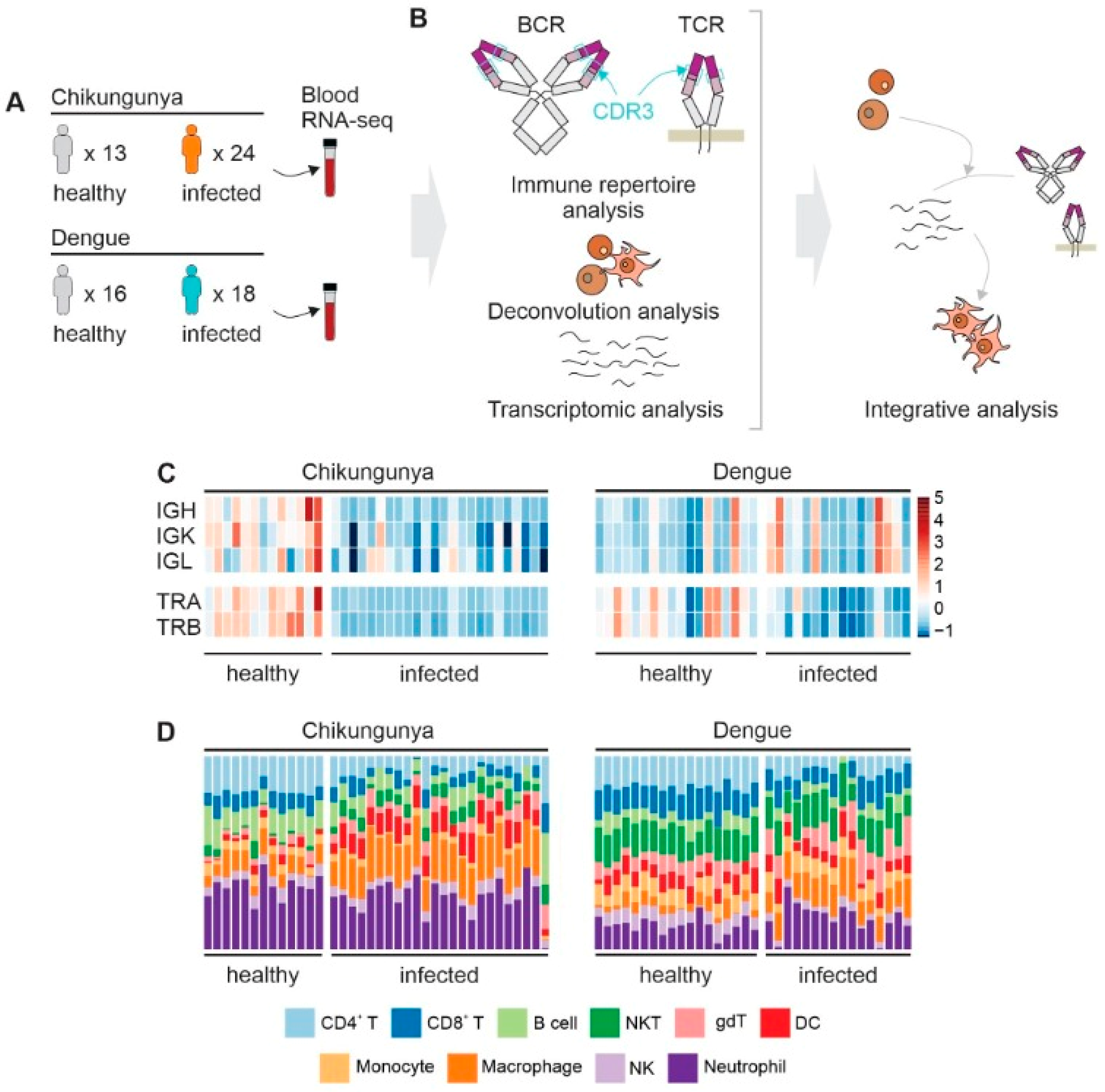
2.1. RNA-Seq Data
2.2. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
2.3. Cell Abundance, CDR3 Diversity and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CDR3 Diversity and Cell Abundance
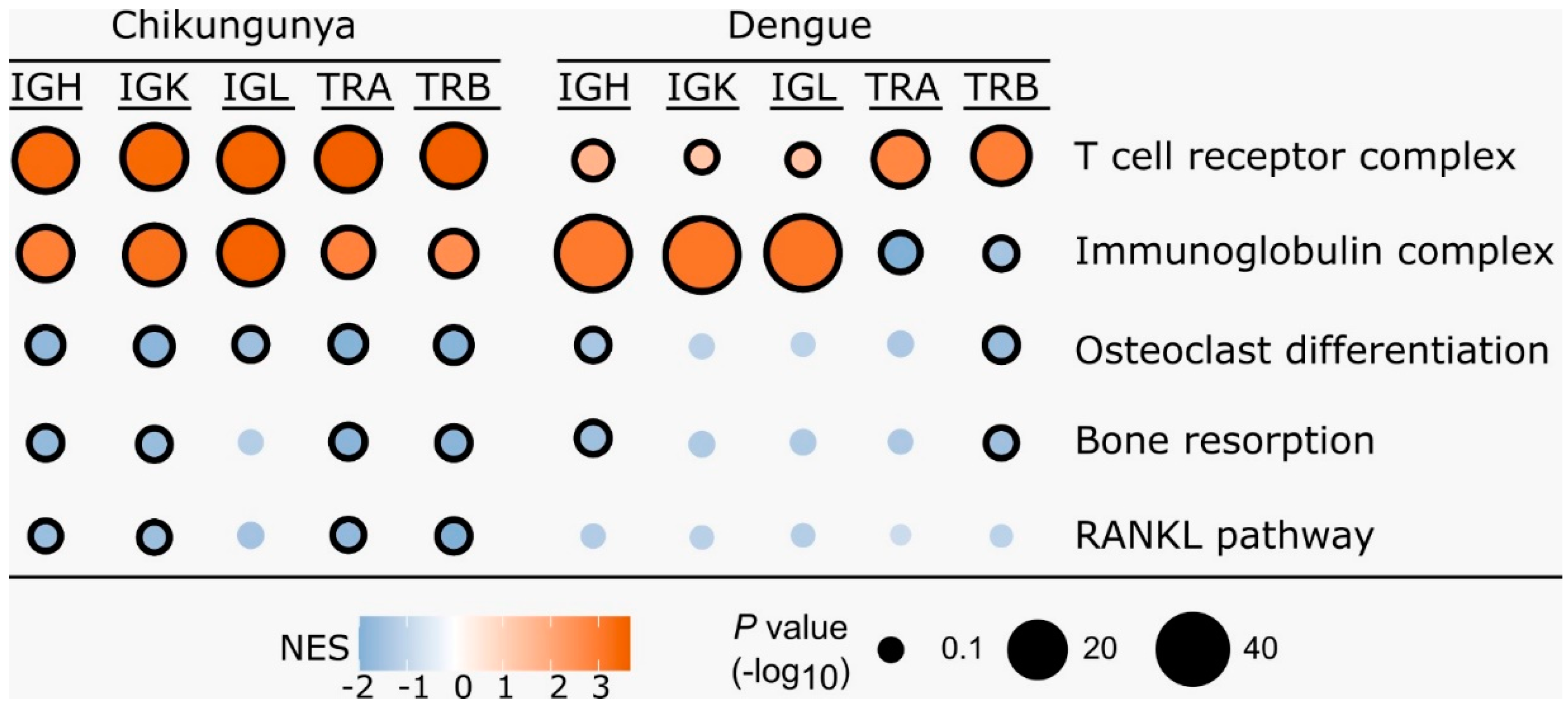
3.2. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
3.3. Transcriptomic Changes in Peripheral Blood during CHIKV Infection
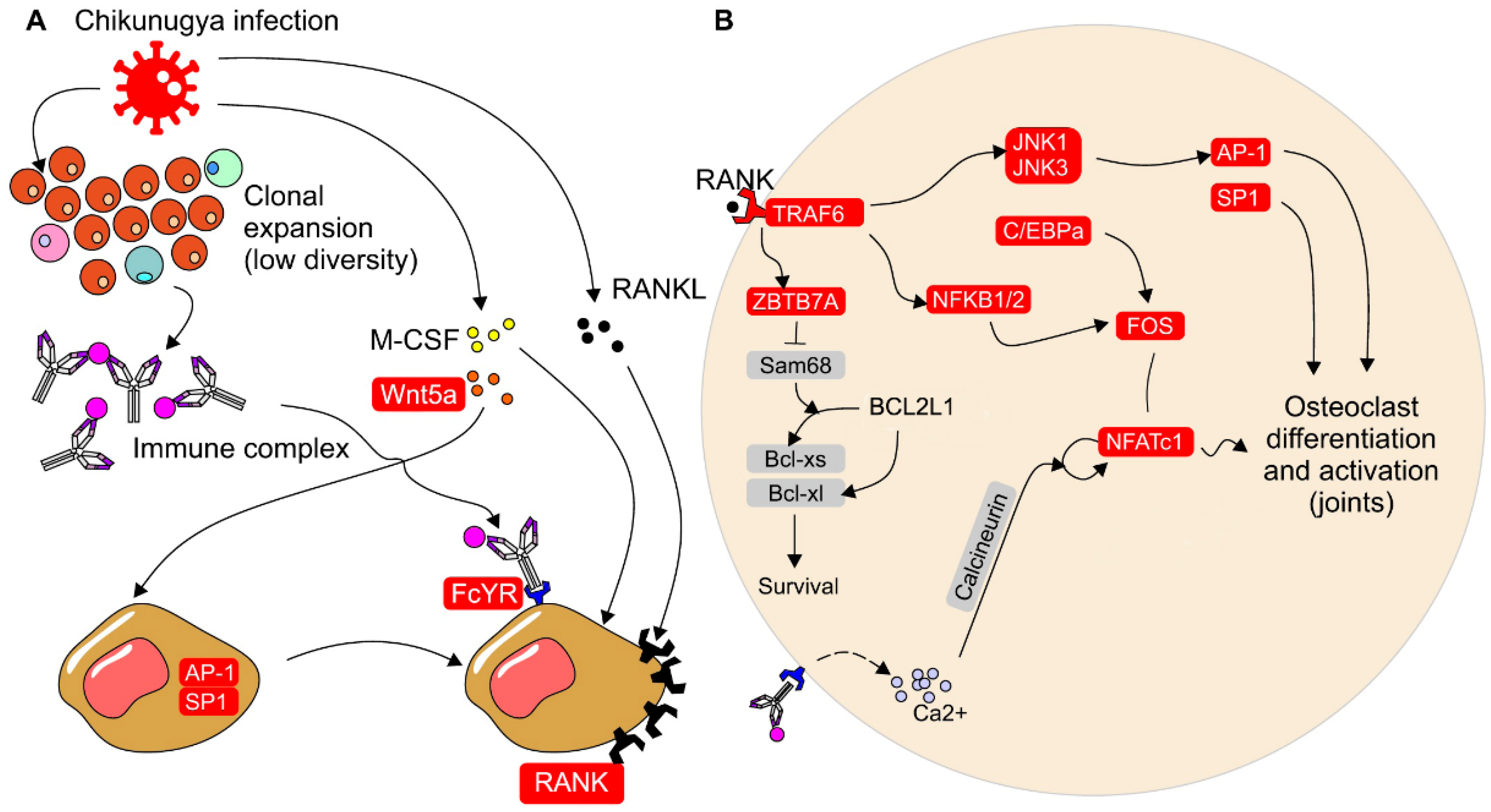
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manzoor, K.N.; Javed, F.; Ejaz, M.; Ali, M.; Mujaddadi, N.; Khan, A.A.; Khattak, A.A.; Zaib, A.; Ahmad, I.; Saeed, W.K.; et al. The global emergence of Chikungunya infection: An integrated view. Rev. Med Virol. 2021, 32, e2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoarau, J.-J.; Bandjee, M.-C.J.; Trotot, P.K.; Das, T.; Li-Pat-Yuen, G.; Dassa, B.; Denizot, M.; Guichard, E.; Ribera, A.; Henni, T.; et al. Persistent Chronic Inflammation and Infection by Chikungunya Arthritogenic Alphavirus in Spite of a Robust Host Immune Response. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5914–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuklia, W.; Kasisith, J.; Modhiran, N.; Rodpai, E.; Thannagith, M.; Thongsakulprasert, T.; Smith, D.R.; Ubol, S. Osteoclastogenesis induced by CHIKV-infected fibroblast-like synoviocytes: A possible interplay between synoviocytes and monocytes/macrophages in CHIKV-induced arthralgia/arthritis. Virus Res. 2013, 177, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, M.; Boire, G.; Komarova, S.; Dixon, S.; Sims, S.; Harrison, R.; Nabavi, N.; Maria, O.; Manolson, M.; Mizianty, M.; et al. The increased in vitro osteoclastogenesis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis is due to increased percentage of precursors and decreased apoptosis — The In Vitro Osteoclast Differentiation in Arthritis (IODA) study. Bone 2011, 48, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noret, M.; Herrero, L.; Rulli, N.; Rolph, M.; Smith, P.N.; Li, R.W.; Roques, P.; Gras, G.; Mahalingam, S. Interleukin 6, RANKL, and Osteoprotegerin Expression by Chikungunya Virus-Infected Human Osteoblasts. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares-Schanoski, A.; Cruz, N.B.; de Castro-Jorge, L.A.; de Carvalho, R.V.H.; da Rós, N.; Oliveira. ; Costa, D.D.; dos Santos, C.L.S.; Cunha, M.d.P.; Oliveira, M.L.S.; et al. Systems analysis of subjects acutely infected with the Chikungunya virus. PLOS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsalik, E.L.; Fiorino, C.; Aqeel, A.; Liu, Y.; Henao, R.; Ko, E.R.; Burke, T.W.; Reller, M.E.; Bodinayake, C.K.; Nagahawatte, A.; et al. The Host Response to Viral Infections Reveals Common and Virus-Specific Signatures in the Peripheral Blood. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 741837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 2014; 15(12),550.
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. The R package Rsubread is easier, faster, cheaper and better for alignment and quantification of RNA sequencing reads. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.R.; Zhang, Q.; Lei, Q.; Luo, M.; Xie, G.Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, A.Y. ImmuCellAI: A Unique Method for Comprehensive T-Cell Subsets Abundance Prediction and its Application in Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Bolotin, D.; Poslavsky, S.; Davydov, A.N.; E Frenkel, F.; Fanchi, L.; I Zolotareva, O.; Hemmers, S.; Putintseva, E.V.; Obraztsova, A.S.; Shugay, M.; et al. Antigen receptor repertoire profiling from RNA-seq data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 908–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazarov, V.; Tsvetkov, V.; Fiadziushchanka, S.; et al. immunarch: Bioinformatics Analysis of T-Cell and B-Cell Immune Repertoires. https://immunarch.com/. https://github.com/immunomind/immunarch. 2023.
- Harrell, F.E., Jr.; HMISC: Harrell Miscellaneous. R Package Version 4.1-1. 2018. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=Hmisc (accessed on 21 March 2022).
- Korotkevich, G.; Sukhov, V.; Budin, N.; Shpak, B.; Artyomov, M.N. Fast gene set enrichment analysis. bioRxiv. 2016. Available from: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10. 1101. [Google Scholar]
- Liberzon, A.; Subramanian, A.; Pinchback, R.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1739–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolich-Žugich, J.; Slifka, M.K.; Messaoudi, I. The many important facets of T-cell repertoire diversity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiberville, S.-D.; Boisson, V.; Gaudart, J.; Simon, F.; Flahault, A.; de Lamballerie, X. Chikungunya Fever: A Clinical and Virological Investigation of Outpatients on Reunion Island, South-West Indian Ocean. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J.S.; Botero, S.; Simon, S.M. Sequencing the peripheral blood B and T cell repertoire – Quantifying robustness and limitations. J. Immunol. Methods 2018, 463, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi N, Kobayashi Y, Udagawa N. Osteoclasts. Principles of Bone Biology [Internet]. Elsevier; 2020. p. 111–131. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier. 9780.
- Maeda, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Udagawa, N.; Uehara, S.; Ishihara, A.; Mizoguchi, T.; Kikuchi, Y.; Takada, I.; Kato, S.; Kani, S.; et al. Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling between osteoblast-lineage cells and osteoclast precursors enhances osteoclastogenesis. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayanagi, H.; Kim, S.; Koga, T.; Nishina, H.; Isshiki, M.; Yoshida, H.; Saiura, A.; Isobe, M.; Yokochi, T.; Inoue, J.-I.; et al. Induction and Activation of the Transcription Factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) Integrate RANKL Signaling in Terminal Differentiation of Osteoclasts. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Junior, E.S.; Taira, T.M.; Fukada, S.Y. Bone—From macrophage to osteoclast and osteolytic diseases. In Macrophages in the Human Body. Camara, N.O.S., Braga, T.T. Eds.; Academic Press, 2022; p. 161–180.
- Chen, W.; Zhu, G.; Hao, L.; Wu, M.; Ci, H.; Li, Y.-P. C/EBPα regulates osteoclast lineage commitment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2013, 110, 7294–7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard-Chamard, H.; Carrier, N.; Dufort, P.; Durand, M.; de Brum-Fernandes, A.; Boire, G.; Komarova, S.; Dixon, S.; Harrison, R.; Manolson, M.; et al. Osteoclasts and their circulating precursors in rheumatoid arthritis: Relationships with disease activity and bone erosions. Bone Rep. 2020, 12, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, M.; Komarova, S.V.; Bhargava, A.; Trebec-Reynolds, D.P.; Li, K.; Fiorino, C.; Maria, O.; Nabavi, N.; Manolson, M.F.; Harrison, R.E.; et al. Monocytes from patients with osteoarthritis display increased osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption: The In Vitro Osteoclast Differentiation in Arthritis study. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 65, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.-Y.; Tee, S.Z.-Y.; Wong, M.M.-T.; Chow, S.-K.; Peh, S.-C.; Teow, S.-Y. Pathogenic Role of Immune Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Implications in Clinical Treatment and Biomarker Development. Cells 2018, 7, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Shobuike, T.; Shiraki, M.; Kamohara, A.; Hirata, H.; Murayama, M.; Mawatari, D.; Ueno, M.; Morimoto, T.; Kukita, T.; et al. Leukemia/lymphoma-related factor (LRF) or osteoclast zinc finger protein (OCZF) overexpression promotes osteoclast survival by increasing Bcl-xl mRNA: A novel regulatory mechanism mediated by the RNA binding protein SAM68. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 102, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhrbier, A. Rheumatic manifestations of chikungunya: emerging concepts and interventions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.; Creecy, A.; Awosanya, O.D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 and its Multifaceted Impact on Bone Health: Mechanisms and Clinical Evidence. Current Osteoporosis Reports 2024, 22: 135-145.
- Caetano, C.C.S.; Azamor, T.; Meyer, N.M.; Onwubueke, C.; Calabrese, C.M.; Calabrese, L.H.; Visperas, A.; Piuzzi, N.S.; Husni, M.E.; Foo, S.-S.; et al. Mechanistic insights into bone remodelling dysregulation by human viral pathogens. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drissi, H.; Sanjay, A. The Multifaceted Osteoclast; Far and Beyond Bone Resorption. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 1753–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negishi-Koga, T.; Gober, H.-J.; Sumiya, E.; Komatsu, N.; Okamoto, K.; Sawa, S.; Suematsu, A.; Suda, T.; Sato, K.; Takai, T.; et al. Immune complexes regulate bone metabolism through FcRγ signalling. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6637–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harre, U.; Lang, S.C.; Pfeifle, R.; Rombouts, Y.; Frühbeißer, S.; Amara, K.; Bang, H.; Lux, A.; Koeleman, C.A.; Baum, W.; et al. Glycosylation of immunoglobulin G determines osteoclast differentiation and bone loss. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartholomeeusen, K.; Daniel, M.; LaBeaud, D.A.; et al. Chikungunya fever. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2023, 9(1), 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, D.L.; Boyle, W.J.; Simonet, W.S.; Kostenuik, P.J.; Dougall, W.C.; Sullivan, J.K.; Martin, J.S.; Dansey, R. Bench to bedside: elucidation of the OPG–RANK–RANKL pathway and the development of denosumab. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Zhang, Q.; He, P.; Zhou, B.; He, K.; Sun, X.; Lei, G.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z. Targeted apoptosis of macrophages and osteoclasts in arthritic joints is effective against advanced inflammatory arthritis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




