1. Introduction
Vaccine preparedness for future virus outbreaks is an important element of public health protection highlighted by the pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). During the COVID-19 pandemic, the European Medicines Agency authorized 17 vaccines licensed against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and subsequently adapted two vaccines to match variants of concern better. These and nearly two hundred other vaccine candidates in clinical development have predominantly relied on the virus spike. This is because protection by licensed vaccines largely focused on measuring the anti-spike neutralizing antibodies, which were associated with curbing the SARS-CoV-2 infection pre-clinically [
1,
2,
3] and in human trials [
4,
5,
6,
7]. However, protection induced by the licensed SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and mediated by the spike-specific antibodies was typically narrow with limited coverage of other members of the same family, order or genus, and their clinical effectiveness waned over time with the emergence of escape SARS-CoV-2 variants [
8,
9]. Other immunological mechanisms have been implied for protection against severe COVID-19 [
10].
Multiple examples of protective CD8
+ T cells from animal models and growing correlative data from vaccine usage suggest a critical contribution of cellular responses to the COVID-19 vaccines’ clinical efficacy. Thus, murine CD8
+ T cells cross-protected against variants of concern [
11,
12]. In mice and monkeys challenged with SARS-CoV-2, CD8
+ T cells provided disease protection and their depletion led to increased virus replication [
2,
13]. In humans, the frequency of spike-specific CD8
+ T cells but not neutralizing antibody titres positively correlated with the viral clearance rate [
14]. CD4
+ and CD8
+ cytotoxic T cells displayed cross-reactivity against SARS-CoV-2 variants in convalescent donors [
15,
16], which were suggested to account for superior protection of mRNA-vaccinated individuals with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, having so-called hybrid immunity, compared with mRNA vaccine alone [
17]. A strong association between HLA-B*15:01 and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection was found, which was likely mediated by a pre-pandemic cross-reactive CD8
+ T-cell memory response to seasonal coronaviruses [
18]. In addition, old age was a strong predictor of the COVID-19 severity [
19] pointing to the well-demonstrated decline in naïve T cells in senesce [
20,
21].
For groups of viruses with a significant epidemic and pandemic risk of spill-over zoonosis and subsequent human transmission, it is prudent to develop a vaccine that is potentially effective not only against the currently prioritized outbreak species but that can protect against all members of the entire taxonomic group. Unlike neutralizing antibodies, the induction of T cells offers the possibility to develop a vaccine inducing broadly cross-reactive protection. The strategy is to focus vaccine-elicited T cells onto the shared, functionally conserved sub-protein regions of viral proteins [
22,
23,
24]. In natural infection, immunodominant CD8
+ T-cell responses are found against spike, matrix and nucleocapsid [
25]. However, these proteins are more variable [
26] and therefore responses against them are ultimately less protective. Dagotto et al. first described the design of a T-cell vaccine immunogen employing the most highly conserved region of the sarbecovirus replication transcription complex, which they called conserved region 1 [
11,
27]. When delivered by a vector derived from rhesus adenovirus serotype 52, the RhAd52.CoV.Consv region 1 vaccination lowered viral loads in the nasal turbinates following a mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 challenge [
11]. The present work builds on and endorses this approach using the CoV.Consv immunogen extended by an additional conserved region assembled into immunogen designated COVconsv12. We demonstrate the COVconsv12 preclinical immunogenicity in two strains of mice and assess its contribution to efficacy in Syrian hamsters when delivered by simian adenovirus-derived ChAdOx1, a vaccine vector with manufacturing capability sufficient to support the production of over three billion human doses during the COVID-19 pandemic.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatic Analysis
We assembled 205 sarbecoviruses representative of much of the known virus diversity in wild animal populations from GenBank and GISAID [
28,
29]. A sarbecovirus full proteome alignment was generated starting with a MAAFT alignment [
30], which was subsequently codon aligned, translated and optimized in regions of insertions using AliView [
31]. Only open reading frames were retained, only sequences that spanned the full proteome were included and only small sequence sets representative of the diversity among highly sampled SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1 sequences were utilized to avoid oversampling of these relatively highly conserved clades that entered and expanded within the human population. The maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree was generated using IQ tree [
32] (Fig. S1).
2.2. Cell Lines
Human embryonic kidney 293T-derived M9 cells [
33] were maintained in DMEM10 [DMEM medium supplemented with L-glutamine and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (GIBCO; #16250)]. HeLa cells were maintained in DMEM5 [DMEM medium supplemented with 5% FBS, L-glutamine and 1% penicillin/streptomycin]. All cell lines were grown in a humidified incubator at 37 °C with 5% CO
2 and obtained from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) (Manassas, VA, USA).
2.3. Vaccine Preparation
The COVconsv12 open reading frame based on the protein sequence found in the SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan reference strain (Accession NC_045512) was synthesized (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and inserted into the E1 region of the ChAdOx1 genome using the Bacterial Artificial Chromosome (BAC) [
23]. Linear ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 genomic DNA was excised using the Pme 1 restriction endonuclease and transfected into the adherent M9 cells [
33] using Lipofectamine
TM CD2000 Transfection Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific) following the vendor’s instructions [
23]. The ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 virus was harvested, plaque-purified and expanded for identity confirmation. Working virus stock was then grown in twelve T25 flasks, purified, titred, aliquoted and stored in -80 °C until use as described previously [
33].
The ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and ChAdOx1.GFP vaccine stocks were prepared similarly [
34].
2.4. Infection of HeLa Cells and Western Blot
HeLa cells were infected with ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 at indicated multiplicities of infection (MOI) and incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO
2 for 1 day. Cells were collected, washed, lysed in the LDS Sample Buffer with NuPAGE Sample Reducing Agent (Invitrogen), incubated at 95 °C for 5 minutes and placed on ice. The samples were then resolved with the NuPAGE electrophoresis system using the NuPAGE 4-12% Bis-Tris Gel (Invitrogen) and either stained with Coomassie brilliant blue or transferred onto Hamersham Hybond-LFP membranes (GE HealthCare Technologies Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) using the iBind Western Blot system (Invitrogen). The membranes were blocked with iBind solution with iBind addictive for 1 hour, washed with PBS plus 0.1% Tween-20 and incubated with mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) specific for the COVconsv12 C-terminal Pk-tag (generously provided by Dr. Richard E. Randall, St.Andrews University) for 1 hour [
35]. Bound primary antibodies were detected using alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-mouse mAb and visualized using the SigmaFast BCIP/NBT substrate (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate/nitro blue tetrazolium; SigmaAldrich Merck).
2.5. Immunofluorescence
HeLa cells were infected with ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 at MOI 10 and incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for 1 day. The cells were washed with PBS, fixed with 60% methanol/40% acetone, washed with PBS and incubated with 3% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in PBS for 30 minutes. Next, the cells were incubated with mouse anti-Pk tag mAb for 1 hour, washed 3x with PBS, incubated with goat anti-mouse FITC-conjugated mAb (Abcam) in PBS plus 3% BSA for 1 hour, washed 3x with PBS and the coverslips were mounted on microscope slides using Vectashield DAPI nuclear stain mounting medium (Vector laboratories). The slides were examined on a fluorescence microscope (Zeiss LSM 980 confocal microscope) and images were analyzed with the Zeiss Zen 3.0 image analysis software.
2.6. Mice, Vaccinations and Preparation of Splenocytes and Lung Immune Cells
Six-week-old female BALB/c or C57BL/6 mice (Charles River, Harlow, UK) were immunized intramuscularly with 10
8 virus particles (vp) of either the ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 or ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine alone, or together at 10
8 vp each, and the T-cell responses were analyzed 9 days later. On the day of the killing, splenocytes were isolated as described previously [
36] and resuspended in R10 (RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% FCS, 1% penicillin/streptomycin and β-mercaptoethanol) for the ELISPOT assay. To obtain immune cells from the lungs, the dissected organs were cut into 1-mm
2 segments and digested with 1.4 mg/ml Collagenase (Sigma Aldrich, Gillingham, UK) and 60 µg/ml DNase Type IV (Sigma Aldrich) in R0 supplemented with β-mercaptoethanol in 1.8-ml volume for 60 minutes at 37 °C with shaking, after which 200 µl of FBS was added to quench the reaction. The cells were washed and resuspended in R10 for the ELIPOT assay.
2.7. Peptides
All peptides used in the ELISPOT assay were >90% pure by mass spectrometry (Synpeptide, Shanghai, China) and were dissolved in DMSO (Sigma-Aldrich, Pool, UK) to yield a stock of 10 mg/ml and stored at -80 °C until use.
2.8. Mouse IFN-γ ELISPOT Assay
The Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSPOT (ELISPOT) assay was performed using the Mouse IFN-γ ELISpot kit (Mabtech, Stockholm, Sweden) according to the manufacturer’s instructions as described [
37]. Immune splenocytes were collected and tested separately from individual mice. Peptides were used at 2 μg/ml each and splenocytes at 10
5 cells/well were added to 96-well plates (Millipore, UK) that had been pre-coated with 5 µg/ml anti-IFN-γ mAb AN18 (Mabtech). The cells were incubated at 37 °C in 5% CO
2 for 18 hours and washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) before the addition of 1 µg/ml biotinylated anti-IFN-γ Mab (Mabtech) at room temperature for 2 hours. The plates were then washed with PBS, incubated with 1 µg/ml streptavidin-conjugated alkaline phosphatase (Mabtech) at room temperature for 1 hour, washed with PBS, and individual spot-forming units (SFU) were detected as dark spots after a 10-minute reaction with 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-idolyl phosphate and nitro blue tetrazolium using an alkaline phosphatase-conjugate substrate (Bio-Rad, Richmond, CA, USA). SFUs were counted using the AID ELISpot Reader System (Autoimmun Diagnostika, Germany) and their frequencies were expressed per 10
6 splenocytes.
2.9. Hamster Vaccination and Challenge
Five groups of male and female Golden hamsters (5 animals per group) were administered intramuscularly 1x with the experimental vaccines as shown in
Table 1. Four weeks later, the hamsters were challenged intranasally with 30 µl (1.5 × 10
5 IU) Victoria-1 equally distributed between the two nostrils. Victoria-1 (BetaCoV/Australia/VIC1/2020, Genbank: MT007544) has no coding mutations relative to Wuhan-Hu-1 (NC_045512). The original virus (passage 3) was received from Dr Mike Catton, Victorian Infectious Diseases Reference Laboratory, Melbourne, from the first patient diagnosed with COVID-19 in Australia [
38]. The virus was supplied by the Centre for AIDS Reagents (CFAR #100980), NIBSC, as passage 4 grown in the VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cell line (CFAR #100978). Following the virus challenge, all animals were weighed daily up to the day of termination. Two hamsters from each group were euthanized at 6 days post-challenge, two further animals from each group at 7 days post-challenge and the final one from each group at 8 days post-challenge.
2.10. RT-qPCR
Oral swabs were taken from each animal at days -2, 1, 2, 3, 4, and at termination (days 6, 7 or 8) into Virus Transport Medium (VTM) (Hanks balanced salt solution with 2% heat-inactivated FBS, 1% penicillin/streptomycin, 0.5 µg/ml amphotericin B) for RT-qPCR analysis. Total nucleic acid was extracted from a 200-µl sample using the MagnaPure24 (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) External Lysis Pathogen 200 protocol with elution into 50 µl.
Tissues taken at termination (nasal turbinates, salivary gland, olfactory bulb, and trachea) were dissected and placed in RNALater (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Paisley, UK) and stored at -80 °C until use. Tissues were thawed and 20-50 mg homogenized in 300 µl of tissue culture medium and filtered. Total RNA was extracted by magnetic beads (MagnaPure 24, Roche), quantified by spectrophotometry, and normalized to 20 ng/µl.
For both swab and tissue extracts, RT-qPCR was performed in triplicate, with 5 µl per reaction, with primers and probe targeting the envelope protein as described previously [
39]. Viral shedding data were expressed in International Units per ml (IU/ml) calibrated against the WHO RNA standard for SARS-CoV-2 RNA (NIBSC: 20/146).
2.11. Hamster Pathology
Intact lungs were collected at post-mortem, the left lobe and right cranial lobe were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) at room temperature for 72 hours and embedded in paraffin wax following standard histological processes. 4-µm sections were mounted on poly-L-lysine coated slides for subsequent haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining or immunohistochemistry. For H&E staining, slides were de-waxed with xylene (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and re-hydrated via graded ethanol:water solutions (Thermo Fisher Scientific). H&E-stained sections were evaluated for pathological changes associated with disease and independently assigned a score from 0 to 4 (0 = absent, 1 = minimal, 2 = mild, 3 = moderate, 4 = marked) for each variable by two veterinary pathologists blinded to the treatment and groups.
2.12. Hamster Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemical staining was performed using the Leica Bond Polymer Refine staining system (Leica Microsystems DS9800, Wetzlar, Germany). Onboard de-waxing was performed following the standard Leica Bond protocol and staining was undertaken using IHC Protocol F with the following adaptations: additional non-specific block before primary antibody incubation [10% normal horse serum (Biorad, Hercules, CA, USA), Casein (Vector Labs) in PBS] and extended haematoxylin staining time for 10 minutes. Antibodies were diluted to their optimal staining concentration in Bond primary antibody diluent (Leica, AR9352) as follows: SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: 1:1000 (Leica, AR9961) 30 minutes, (Rabbit PAb 40150-T62-COV2-SIB, Sino Biologicals, Beijing, China), SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein: 1:2000 (Leica, AR9961) 30 minutes, (Mouse Mab 40143-MM05-SIB, Stratech Scientific/SinoBiologicals). For both antibodies antigen unmasking was undertaken using Heat-Induced Epitope Retrieval (HEIR) solution 1 (Leica AR9961) at 100 °C for 30 minutes.
2.13. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using Graph Pad Prism version 9.0 and SigmaPlot v12.5. For ELISPOT data, non-parametric tests were used and the median (IQR) are shown. To facilitate the analysis of log-transformed data, samples with undetectable SARS-CoV-2 by RT-qPCR were assigned an arbitrary value of 20 representing the limit of detection of the assay. Two-tailed p values were used and p values of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. The ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 Vaccine Design and Construction
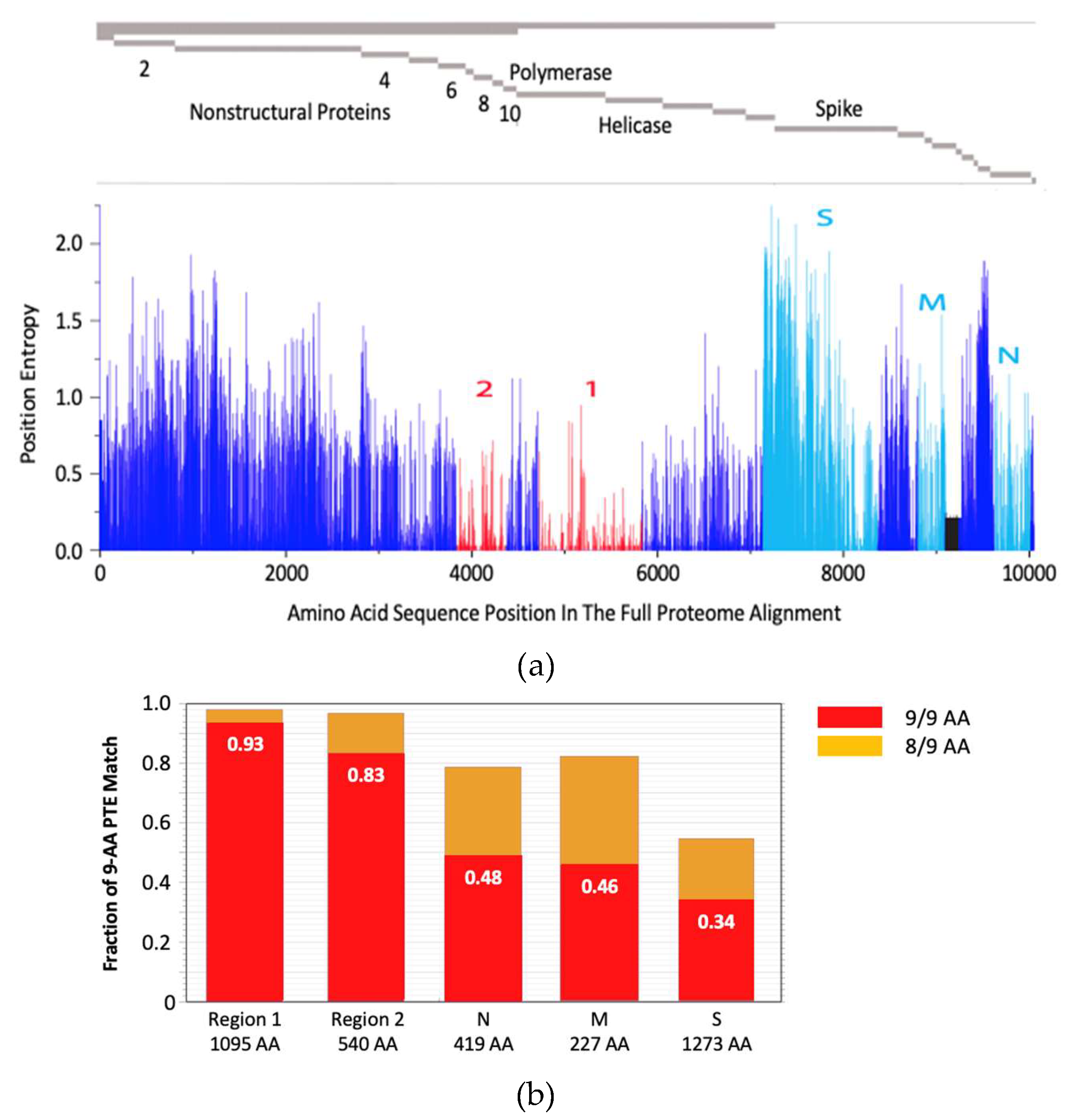
The rationale behind the pan-sarbecovirus T-cell immunogen design was described in detail by Dagotto et al. [
11]. Briefly, the central theorem of our strategy is to focus vaccine-elicited CD8
+ T cells on the most conserved (shared) regions of the sarbecovirus non-spike proteome so that the T-cell vaccines can be used together with the currently licensed spike vaccines and extend the spike vaccine-induced cross-reactive protection. Dalgotto et al. designated the conserved region used in their immunogen COV.Consv as region 1 [
11], which included the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) and helicase protein parts contiguously expressed as part of open reading frame (Orf) 1ab (amino acids 4692-5785 of Orf 1ab, or 300-932 of RdRp and 1-461 of helicase). Our immunogen is called COVconsv12 and extends region 1 with the polymerase enzymatic site inactivated by mutating two aspartic acids to two alanines [
40] by region 2, which is derived from conserved non-structural proteins 6-10 (amino acids 3848-4385 of Orf 1a) (
Figure 1a). A monoclonal mAb tag Pk was added to the C-terminus of the COVconsv12 protein to facilitate the gene product detection [
35]. The whole protein immunogen contains 1,642 amino acids. The COVconsv12 relevance for killer T-cell responses was determined by using the concept of potential T-cell epitopes (PTE), whereby a 9-amino acid-long window, the most frequent size of a CD8
+ T-cell epitope, is slid across proteins by 1 amino acid at a time to determine in each position the vaccine proportional match to the sequences of the input viruses. This PTE analysis confirmed that COVconsv12 regions 1 and 2 were each much more conserved across sarbecoviruses than any of the spike, nucleocapsid and matrix proteins (
Figure 1b).
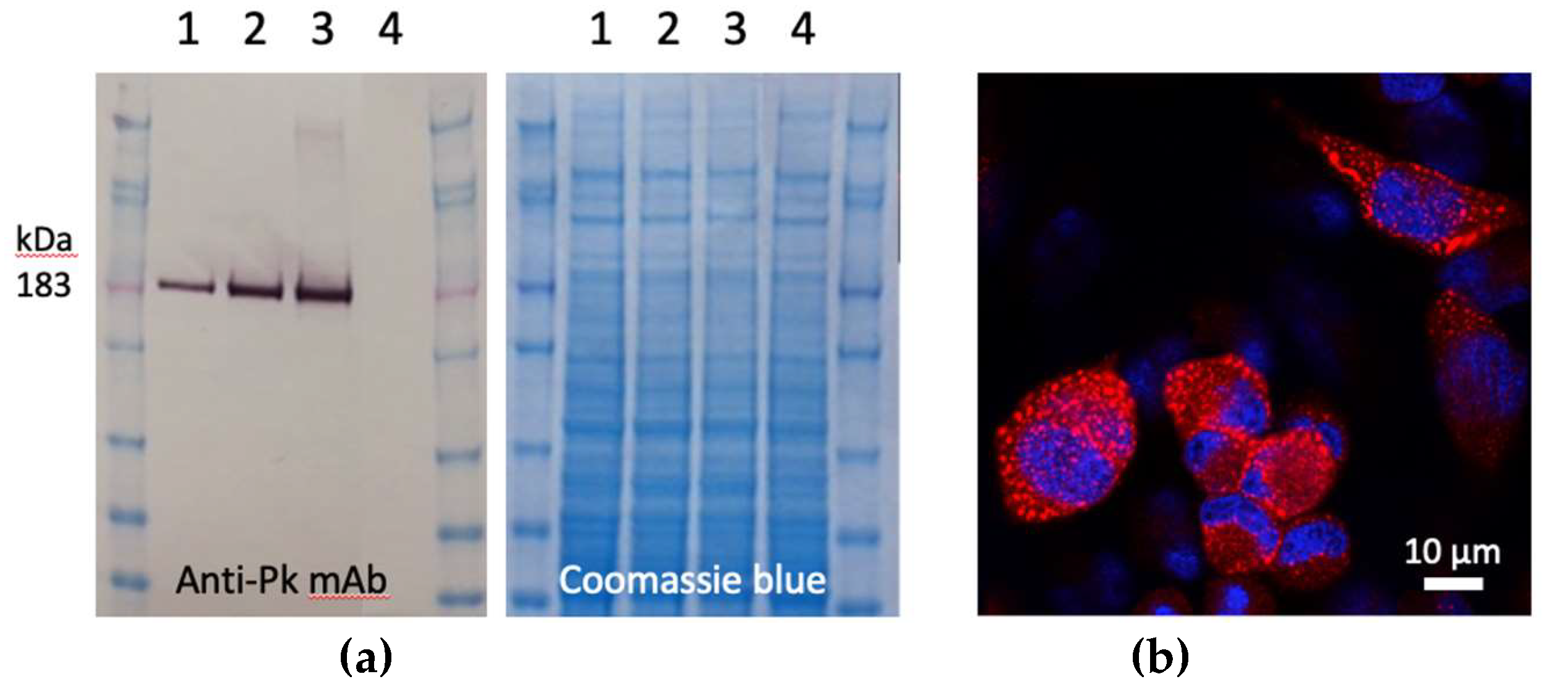
To construct the ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 vaccine, synthetic
COVconsv12 open-reading frame was inserted into the E1 locus of the ChAdOx1 vector genome, a working virus stock was prepared and the
COVconsv12 transgene product expression was detected in infected human cells (
Figure 2).
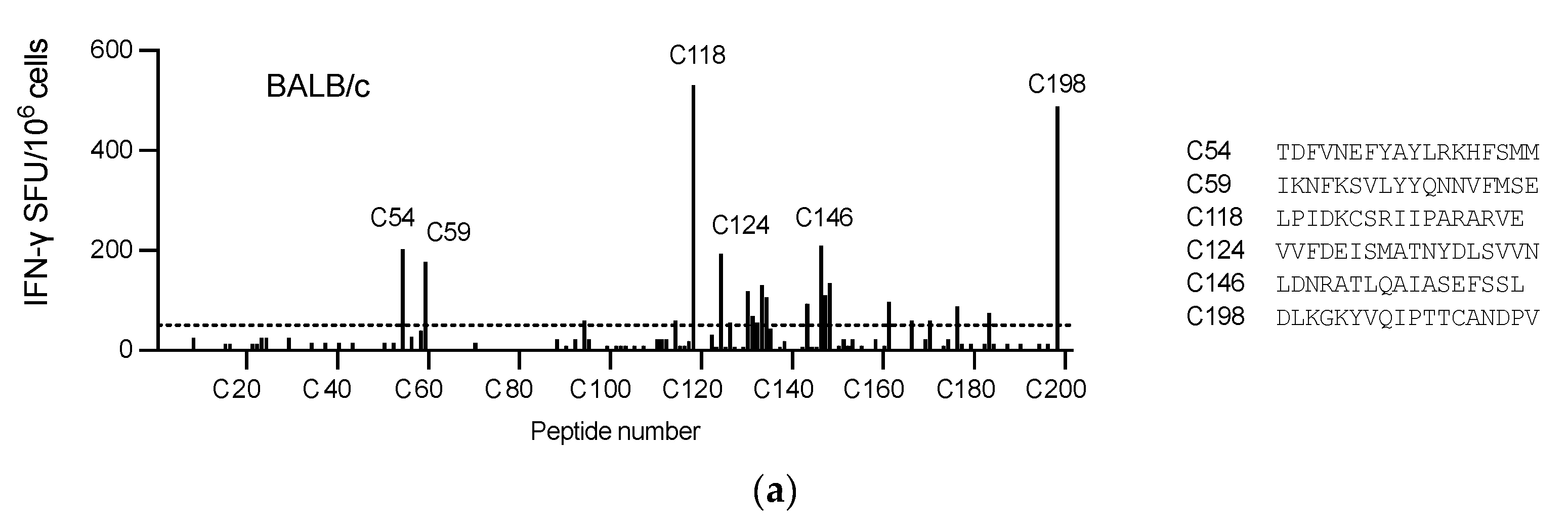
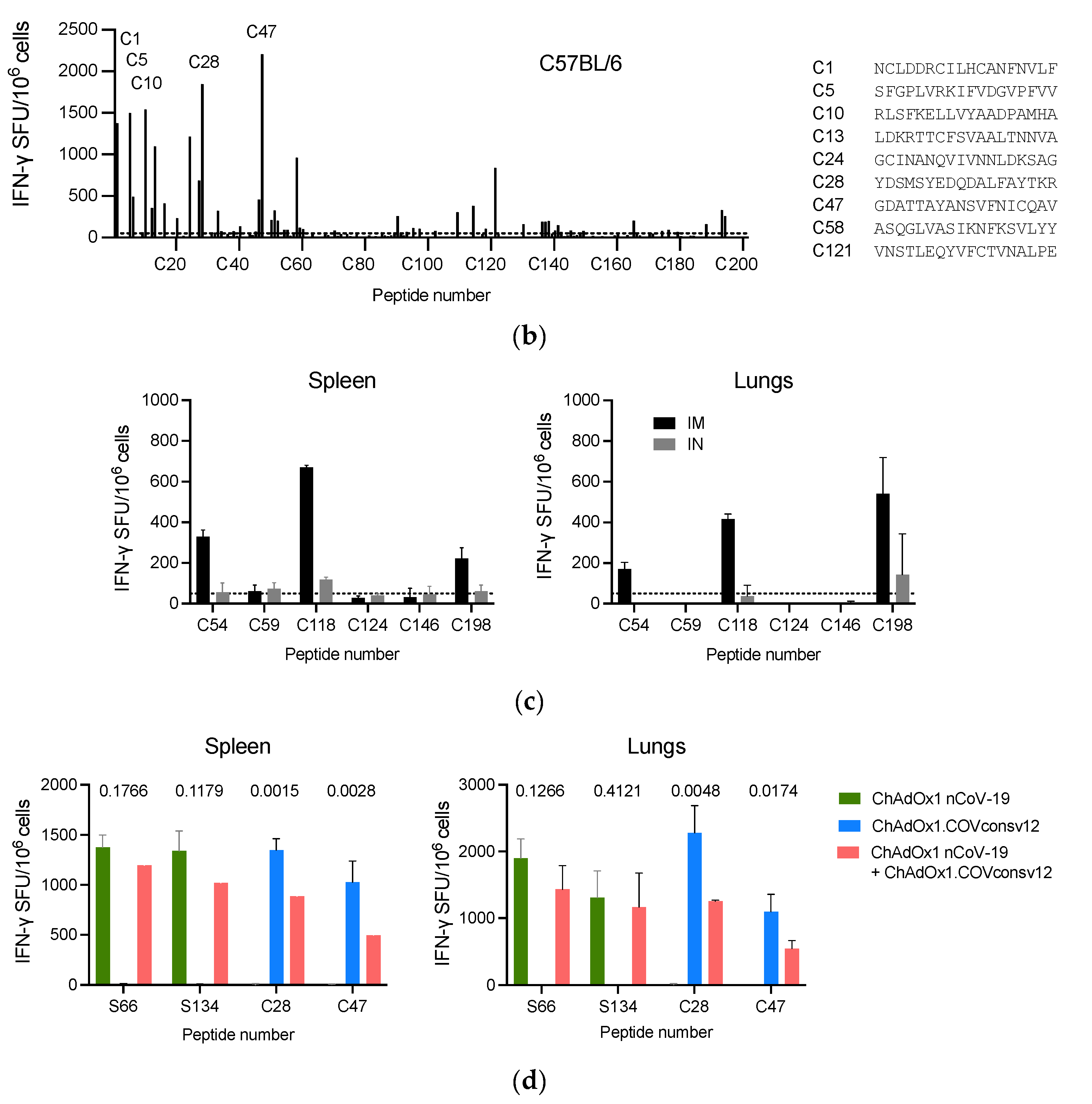
3.2. Induction of Broad T-cell Responses in Mice
A well-defined mouse model was first used to confirm the ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 vaccine immunogenicity. BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice received a single vaccine dose intramuscularly (IM) and their vaccine-elicited T-cells were enumerated 9 days later. Stimulation with overlapping peptides across the entire immunogen in an IFN-
γ ELISPOT assay revealed broadly specific T-cell responses in both murine strains (
Figure 3a and b). The ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 vaccine was then delivered by the IM and intranasal (IN) routes to demonstrate induction of COVconsv12 T cells in the spleens and lungs (
Figure 3c). Finally, the ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 vaccine was co-administered with the spike vaccine ChAdOx1 nCoV-19. This elicited parallel responses to COVconsv12 and the spike, although the mixed immunization resulted in lower specific T-cell frequencies compared to the individual vaccines alone. The difference reached statistical significance for the COVconsv12-derived peptides (
Figure 3d). Overall, the murine experiments demonstrated induction of broad coronavirus-specific T-cell responses.
3.3. Hints of Improved Recovery after Virus Challenge through Combination of Spike and T-cell Vaccines in Hamsters
Infection of Syrian hamsters with SARS-CoV-2 results in the development of a robust upper and lower respiratory tract disease [
41], which was successfully used for the preclinical efficacy testing of several COVID-19 vaccines including Oxford-AstraZeneca
ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 [
1,
3,
42]. Here, we first vaccinated two male and two female Syrian hamsters with 2.5 × 10
8 vp of ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 and assayed the splenocytes, lung cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells for vaccine-induced coronavirus-specific T cells 13 days later. IFN-γ-producing spot-forming units were detected upon peptide pool and individual peptide restimulations reaching at best approximately 500 SFU/10
6 cells, although likely background responses were observed and the more positive peptide specificities were not entirely consistent between tissues. Discrepancies were also detected between the pool and single peptide responses (Fig. S2).
Next, five groups of five mixed male/female Syrian hamsters were immunized with the ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 vaccine alone, ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 together with 1/50th of the protective spike vaccine ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 [ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (1/50)], ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (1/50), full hamster-protective dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 alone and a ChAdOx1 vector with irrelevant immunogen green fluorescent protein (GFP) as a negative control (
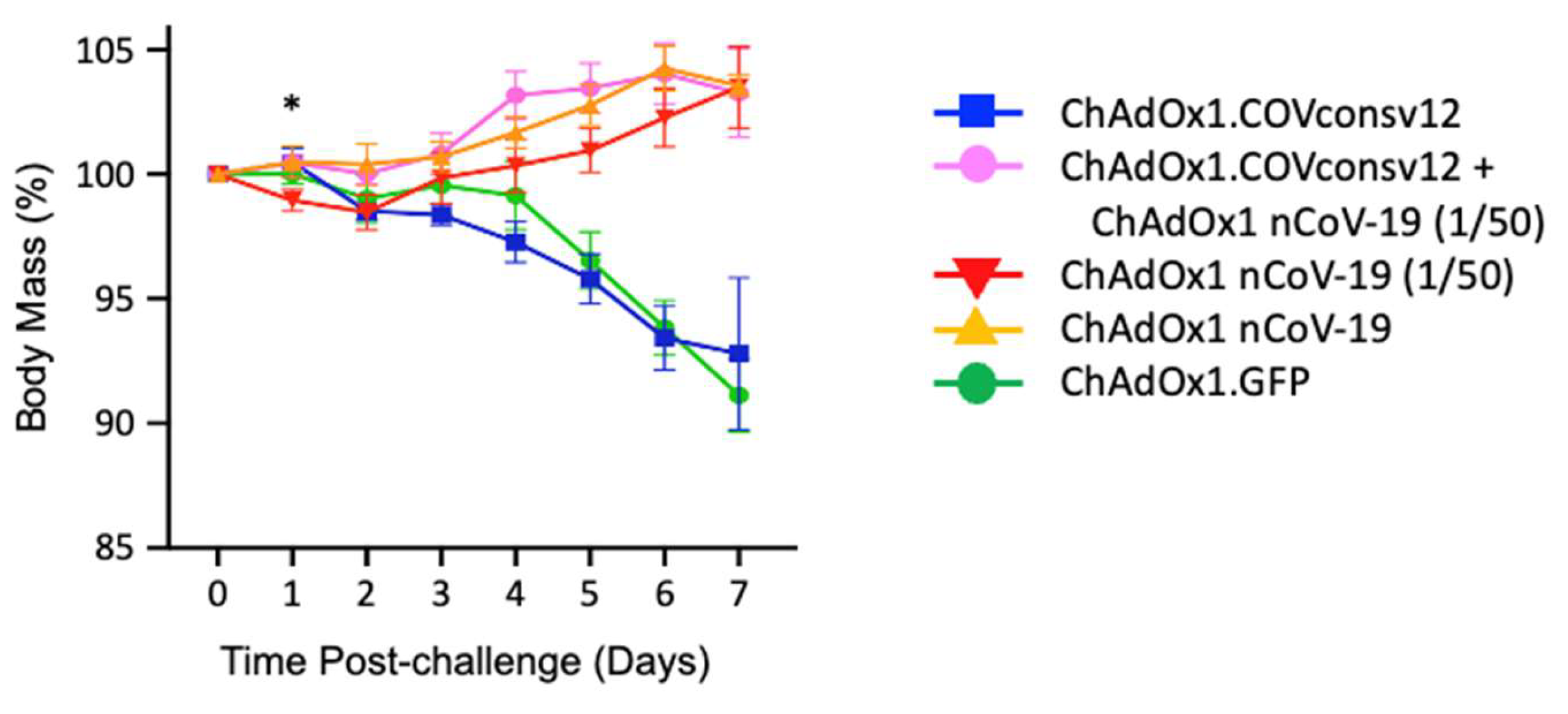
Table 1). The animals were challenged with SARS-CoV-2, Victoria-1 2 weeks later (see Fig. S3 for the alignment of COVconsv12 and the challenge virus), and their body mass was recorded daily thereafter. The ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 protective dose, ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (1/50) and the combined regimen allowed animals to gain body mass steadily after 2 days post-challenge. There was a statistically significant difference in the body mass between animals receiving the ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (1/50) together (Group 2) and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (1/50) only (Group 3) on day 1 after challenge (two-tailed p = 0.023; Student’s t-test). While this trend was maintained till day 6, the dif- ference was no longer significant. The ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 vaccine alone (Group 1) offered no benefit over the first 7 days after the coronavirus challenge and the hamsters reacted similarly to the negative control-treated animals (Group 5) leading to a loss of about 7% of their body mass (
Figure 4).
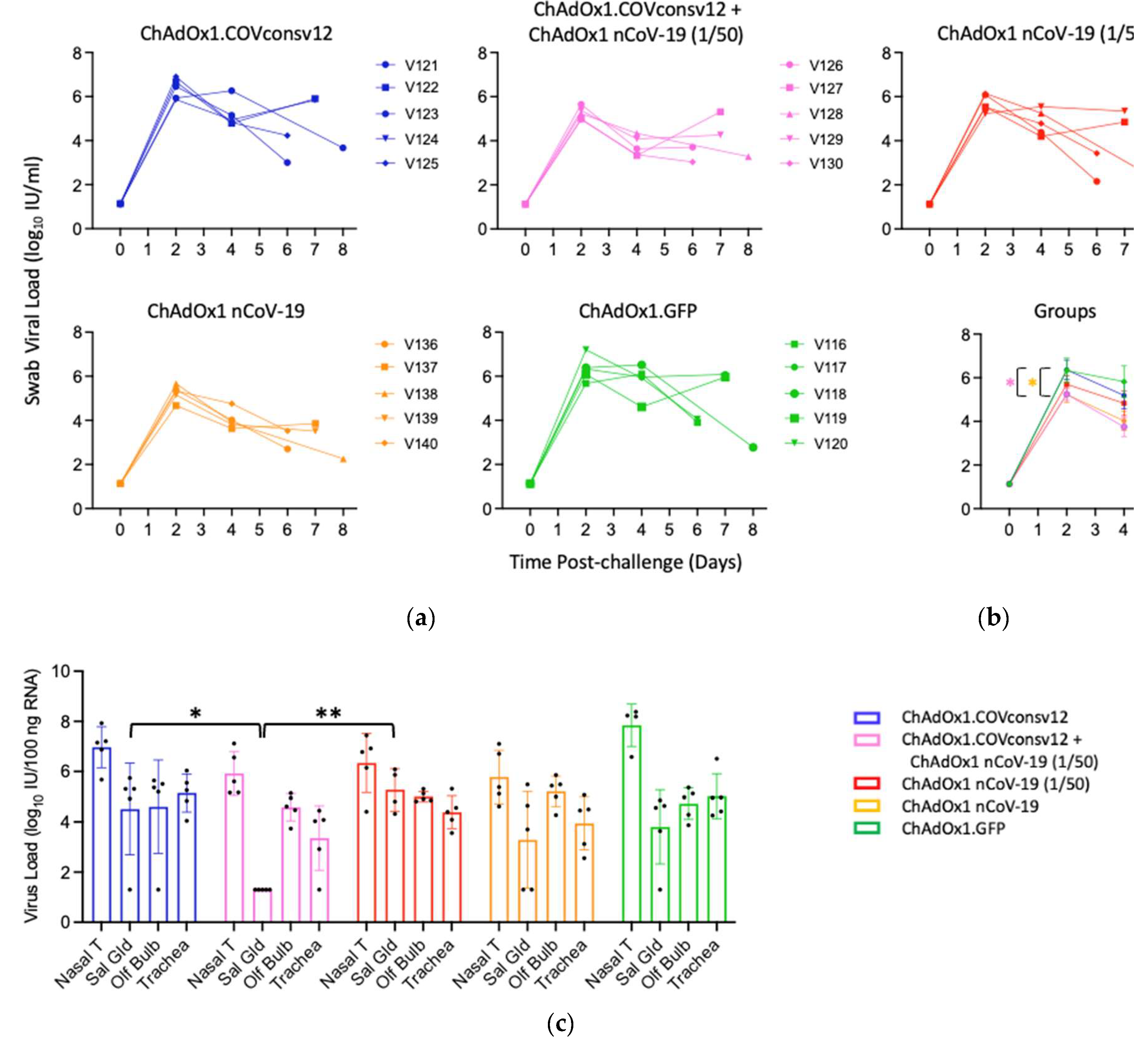
Viral load in the upper respiratory tract was measured by RT-qPCR of SARS-CoV-2 in oral swabs. The combined ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 + ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (1/50) regimen and the spike vaccine alone were significantly more efficient in reducing the virus load compared to the other three vaccinations including the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (1/50) alone on day 4 (p = 0.010; two-tailed Student’s t-test Groups 2 vs. 3) (
Figure 5a and b). The overall pattern of the relative virus distribution and the number of detected genome copies across the tested tissues broadly concurred with the swab virus loads showing a trend of the lowest viremia achieved by the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and the combined ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (1/50) vaccination (
Figure 5c).
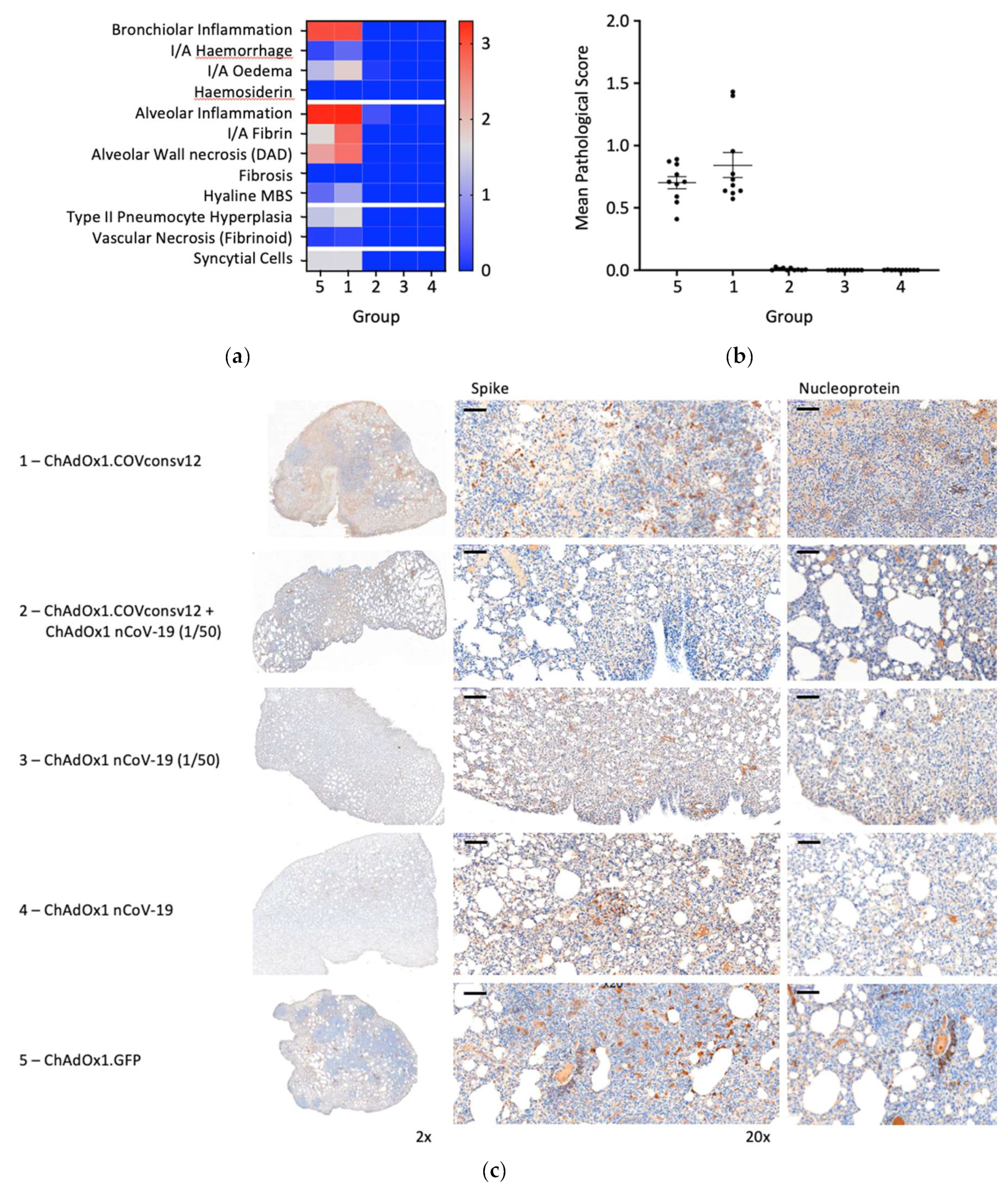
Randomly selected animals in all groups were examined post-mortem for overt signs of pathology. The negative control animals, which received ChAdOx1.GFP, showed pathology expected in the hamster model following the SARS-CoV-2 challenge and a very similar pathology was observed in the ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 group. In contrast, vaccination with the spike vaccine ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 ameliorated such pathological changes (
Figure 6a and b). This was further supported by the immunohistochemical staining of the lung sections for the challenge virus spike and nucleoprotein, noticeable bronchiolar and alveolar eosinophil inflammation, vacuolization and more clumps of positively stained syncytial cells in the absence of the spike vaccine (
Figure 6c). Thus, in the Syrian hamster model, only marginal signs of improved recovery were detected following the addition of the T-cell vaccine. No significant differences between males and females were detected.
4. Discussion
In the present work, we describe the design of a new candidate pan-sarbecovirus T-cell immunogen delivered by a purposed-designed vaccine vector assembled into vaccine ChAdOx1.COVconsv12. The
COVconsv12 synthetic transgene was inserted into a genome of in-human proven simian adenovirus vector ChAdOx1 and the expression of its product was readily detected in infected human cells. Intramuscular administration of the ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 vaccine to three rodent models resulted in no adverse events. Vaccination of the BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice induced broad T-cell responses. In outbred Syrian hamsters, coronavirus-specific T cells were detected using a commercially available kit, albeit their specificity was somewhat less consistent likely due to less well-established reagents in this model (Fig. S2). Vaccination of hamsters with the T-cell vaccine alone provided no detectable protective immunity against the experimental challenge with the Victoria-1 strain of SARS-CoV-2. A moderate additional beneficial contribution of the ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 vaccine-elicited T-cells to the protection against the challenge virus was detected when 1/50th of the protective dose of the Oxford-AstraZeneca ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine was used for vaccination. Overall, these results concur with the protective efficacy of the RhAd52.CoV.Consv vaccine in mice [
11] and together demonstrate the proof of concept that vaccines including only the most highly conserved regions of the sarbecovirus proteome can elicit CD8
+ T-cell responses contributing to protection.
The COVconsv12 immunogen has the potential to be developed further towards human testing because it only matters what happens in people. The PTE coverage and thus the relevance for T-cell induction of these conserved regions to other more distant coronavirus lineages could be broadened by the inclusion of a polyvalent cocktail of Epigraphs [
27,
44]. We and others have used the Epigraph computer algorithm to design such immunogen cocktails to extend the breadth of immune responses for a pan-filovirus vaccine [
45] and broad T-cell and B-cell responses against the influenza virus [
46,
47,
48], that conferred protection in animal models against highly diverse viral challenges. Furthermore, unlike the single vaccine-dose protection against SARS-CoV-2 achieved by several vaccines important for rapid antibody-based protection of the public at the start of a new outbreak, induction of more protective T cells requires a heterologous vaccine boost, such as that delivered by the poxvirus MVA vector [
49,
50], to achieve higher frequencies of relevant CD8
+ T cells and more beneficial protective effect. In essence, pre-outbreak vaccine-elicited broadly specific killer T-cells can slow new outbreak viruses, lessen disease severity and buy time for the more tailored spike vaccines or other interventions to be manufactured and deployed. Effective T cells show greater durability than the spike-specific antibodies [
16,
51,
52,
53] and may further fortify antibody protection. Through their association with better clinical outcomes, CD8
+ T cells may help to prevent long COVID-19 [
54,
55].
In conclusion, the rapid development and deployment of the COVID-19 vaccines was a great success in biomedical research, which saved many millions of lives. The mechanisms contributing to the containment of the SARS-CoV-2 infection and amelioration of the COVID-19 disease were multifactorial. Their deeper understanding will guide the optimization of the next-generation vaccines against ever-emerging new coronavirus variants.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1: Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on an alignment of the full proteome. Figure S2: Pilot immunogenicity study of ChAdOx1.COVconsv12 in Syrian hamsters. Figure S3: Amino acid alignment of the challenge virus and the vaccine.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.H., B.K. and N.A.; methodology, E.G.-T.W., S.K., D.F., S.M., C.H., J.H. and S.C.G.; software, B.K.; validation, T.H., E.G.-T.W., S.K., D.F. J.H. and N.A.; formal analysis, T.H., E.G.-T.W., S.K., D.F., C.H., B.K., and N.A; investigation, E.G.-T.W., S.K., D.F. and N.A.; resources, T.H.; data curation, T.H., E.G.-T.W., S.K., D.F. and N.A.; writing—original draft preparation, T.H., S.K. and D.F.; writing—review and editing, all authors.; visualization, T.H.; supervision, T.H. and N.A.; project administration, E.G.-T.W. and A.C.; funding acquisition, T.H.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The mouse study protocol was approved by the local Clinical Medicine Ethical Review Committee, University of Oxford and conformed strictly to the UK Home Office Guidelines under the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986. Experiments were conducted under project license PP1892852 held by T.H. Hamster study protocols were approved by the MHRA local animal welfare and ethical review body (AWERB) and conducted under Project License PP2209804 held by N.A.
Data Availability Statement
All data are provided within the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr Simon Priestnall and Alejandro Suarez-Bonnet, Royal Veterinary College, Hawkshead Campus, for performing an independent blinded evaluation of histological materials generated during this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fischer, R.J. , et al. , ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) protects Syrian hamsters against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.351 and B.1.1.7. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 5868. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McMahan, K. , et al. , Correlates of protection against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques. Nature 2021, 590, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tostanoski, L.H. , et al. , Ad26 vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 severe clinical disease in hamsters. Nat Med 2020, 26, 1694–1700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baden, L.R. , et al. , Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N Engl J Med 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, S. , et al. , Correlates of protection against symptomatic and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Med 2021, 27, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, P.B. , et al. , Immune correlates analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial. Science 2022, 375, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walsh, K.A. , et al. , SARS-CoV-2 detection, viral load and infectivity over the course of an infection. J Infect 2020, 81, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tregoning, J.S. , et al. , Progress of the COVID-19 vaccine effort: viruses, vaccines and variants versus efficacy, effectiveness and escape. Nat Rev Immunol 2021, 21, 626–636. [Google Scholar]
- Willett, B.J. , et al. , SARS-CoV-2 Omicron is an immune escape variant with an altered cell entry pathway. Nat Microbiol 2022, 7, 1161–1179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahrokhian, S.H. , et al. , COVID-19 vaccines: Immune correlates and clinical outcomes. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2024, 20, 2324549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dagotto, G. , et al. , Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a rhesus adenoviral vaccine targeting conserved COVID-19 replication transcription complex. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Tarke, A. , et al., SARS-CoV-2 vaccination induces immunological T cell memory able to cross-recognize variants from Alpha to Omicron. Cell 2022, 185, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingstad-Bakke, B. , et al. , Vaccine-induced systemic and mucosal T cell immunity to SARS-CoV-2 viral variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022, 119, e2118312119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koutsakos, M., et al., SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infection induces rapid memory and de novo T cell responses. Immunity, 2023.
- Guo, L. , et al. , Durability and cross-reactive immune memory to SARS-CoV-2 in individuals 2 years after recovery from COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Microbe 2024, 5, e24–e33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keeton, R. , et al. , Impact of SARS-CoV-2 exposure history on the T cell and IgG response. Cell Rep Med 2023, 4, 100898. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, J.M. , et al. , Cytotoxic T Cells Targeting Spike Glycoprotein Are Associated with Hybrid Immunity to SARS-CoV-2. J Immunol 2023, 210, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Augusto, D.G. , et al. , A common allele of HLA is associated with asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nature 2023, 620, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, C. , et al. , Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern Med 2020, 180, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Briceno, O. , et al. , Reduced naive CD8(+) T-cell priming efficacy in elderly adults. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qi, Q. , et al. , Diversity and clonal selection in the human T-cell repertoire. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, 13139–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letourneau, S. , et al. , Design and pre-clinical evaluation of a universal HIV-1 vaccine. PLoS One 2007, 2, e984. [Google Scholar]
- Ondondo, B. , et al. , Novel Conserved-region T-cell Mosaic Vaccine With High Global HIV-1 Coverage Is Recognized by Protective Responses in Untreated Infection. Mol Ther 2016, 24, 832–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rolland, M., D.C. Nickle, and J.I. Mullins, HIV-1 group M conserved elements vaccine. PLoS Pathog 2007, 3, e157.
- Grifoni, A. , et al. , SARS-CoV-2 human T cell epitopes: Adaptive immune response against COVID-19. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 1788. [Google Scholar]
- Nesamari, R., et al., Post-pandemic memory T cell response to SARS-CoV-2 is durable, broadly targeted, and cross-reactive to the hypermutated BA.2.86 variant. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 162–169 e3.
- Theiler, J. and B. Korber, Graph-based optimization of epitope coverage for vaccine antigen design. Stat Med 2018, 37, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, R.E. , et al. , COVIDSeq as Laboratory Developed Test (LDT) for Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern (VOC). Arch Clin Biomed Res 2022, 6, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khare, S. , et al. , GISAID’s Role in Pandemic Response. China CDC Wkly 2021, 3, 1049–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, K. Rozewicki, and K.D. Yamada, MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief Bioinform 2019, 20, 1160–1166.
- Liu, B. , et al. , A comprehensive dataset of animal-associated sarbecoviruses. Sci Data 2023, 10, 681. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trifinopoulos, J. , et al. , W-IQ-TREE: a fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hannoun, Z. , et al. , Adenovirus DNA Polymerase Loses Fidelity on a Stretch of Eleven Homocytidines during Pre-GMP Vaccine Preparation. Vaccines (Basel) 2022, 10, 960. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Folegatti, P.M. , et al. , Safety and immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: a preliminary report of a phase 1/2, single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanke, T., Szawlowski, and R.E. Randall, Construction of solid matrix-antibody-antigen complexes containing simian immunodeficiency virus p27 using tag-specific monoclonal antibody and tag-linked antigen. J Gen Virol 1992, 73, 653–60.
- Beavis, A.C. , et al. , Combined intranasal and intramuscular parainfluenza 5-, simian adenovirus ChAdOx1- and poxvirus MVA-vectored vaccines induce synergistically HIV-1-specific T cells in the mucosa. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1186478. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wee, E.G. , et al. , Effect of Epitope Variant Co-delivery on the Depth of CD8 T-cell responses Induced by HIV-1 Conserved Mosaic Vaccines. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 2021, 21, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caly, L. , et al. , Isolation and rapid sharing of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) from the first patient diagnosed with COVID-19 in Australia. Med J Aust 2020, 212, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M. , et al. , Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y. , et al. , Structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19 virus. Science 2020, 368, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Fontela, C. , et al. , Animal models for COVID-19. Nature 2020, 586, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M. , et al. , Attenuated activation of pulmonary immune cells in mRNA-1273-vaccinated hamsters after SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Clin Inest 2021, 131, e148036. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y. and Y. Hochberg, Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Royal Stat Soc Series B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Theiler, J. , et al. , Epigraph: A Vaccine Design Tool Applied to an HIV Therapeutic Vaccine and a Pan-Filovirus Vaccine. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 33987. [Google Scholar]
- Rahim, M.N. , et al. , Complete protection of the BALB/c and C57BL/6J mice against Ebola and Marburg virus lethal challenges by pan-filovirus T-cell epigraph vaccine. PLoS Pathog 2019, 15, e1007564. [Google Scholar]
- Bullard, B.L. , et al. , An epitope-optimized human H3N2 influenza vaccine induces broadly protective immunity in mice and ferrets. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petro-Turnquist, E. , et al. , Multivalent Epigraph Hemagglutinin Vaccine Protects against Influenza B Virus in Mice. Pathogens 2024, 13, 97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petro-Turnquist, E. , et al. , Adenoviral-vectored epigraph vaccine elicits robust, durable, and protective immunity against H3 influenza A virus in swine. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1143451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borthwick, N., et al., Safety and immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1-MVA-vectored conserved mosaic HIVconsvX candidate T-cell vaccines in HIV-CORE 005.2: an open-label, dose-escalation, first-in-man phase 1 trial in adults living without HIV-1 in the UK. Lancet Microbe, In press.
- Chanda, C., et al., Safety and broad immunogenicity of HIVconsvX conserved mosaic candidate T-cell vaccines vectored by ChAdOx1 and MVA in HIV-CORE 006: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 1 trial in healthy adults living without HIV-1 in Eastern and Southern Africa. Priprints with the Lancet, Submitted. https://ssrn.com/abstract=4771407.
- Alter, G., et al., Immunogenicity of Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 variants in humans. Nature 2021, 596, 268–272.
- Goel, R.R. , et al. , mRNA vaccines induce durable immune memory to SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern. Science 2021, 374, abm0829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J. , et al. , Vaccines elicit highly conserved cellular immunity to SARS-CoV-2 Omicron. Nature 2022, 603, 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, J.M. , et al. , Immunological memory to SARS-CoV-2 assessed for up to 8 months after infection. Science 2021, 371, eabf4063. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robbiani, D.F. , et al. , Convergent antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in convalescent individuals. Nature 2020, 584, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).