Submitted:
30 July 2024
Posted:
01 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. AP and Chitosan Purification : Making Stock Solutions
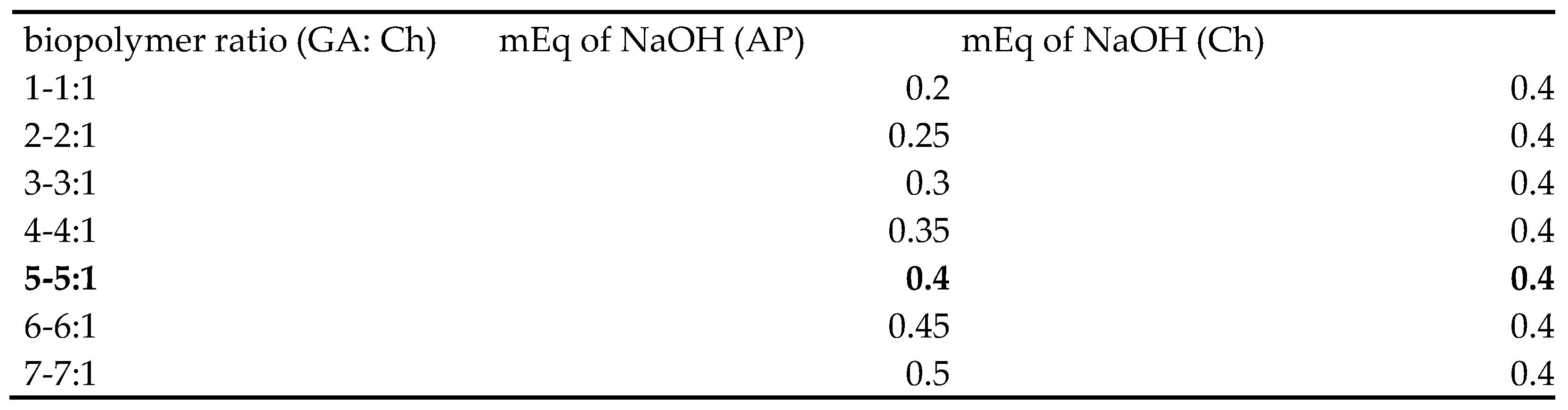
2.3. pH’s Impact on Coacervate Yield during Potentiometric Titration and Coacervate Preparation
2.4. Rheological Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
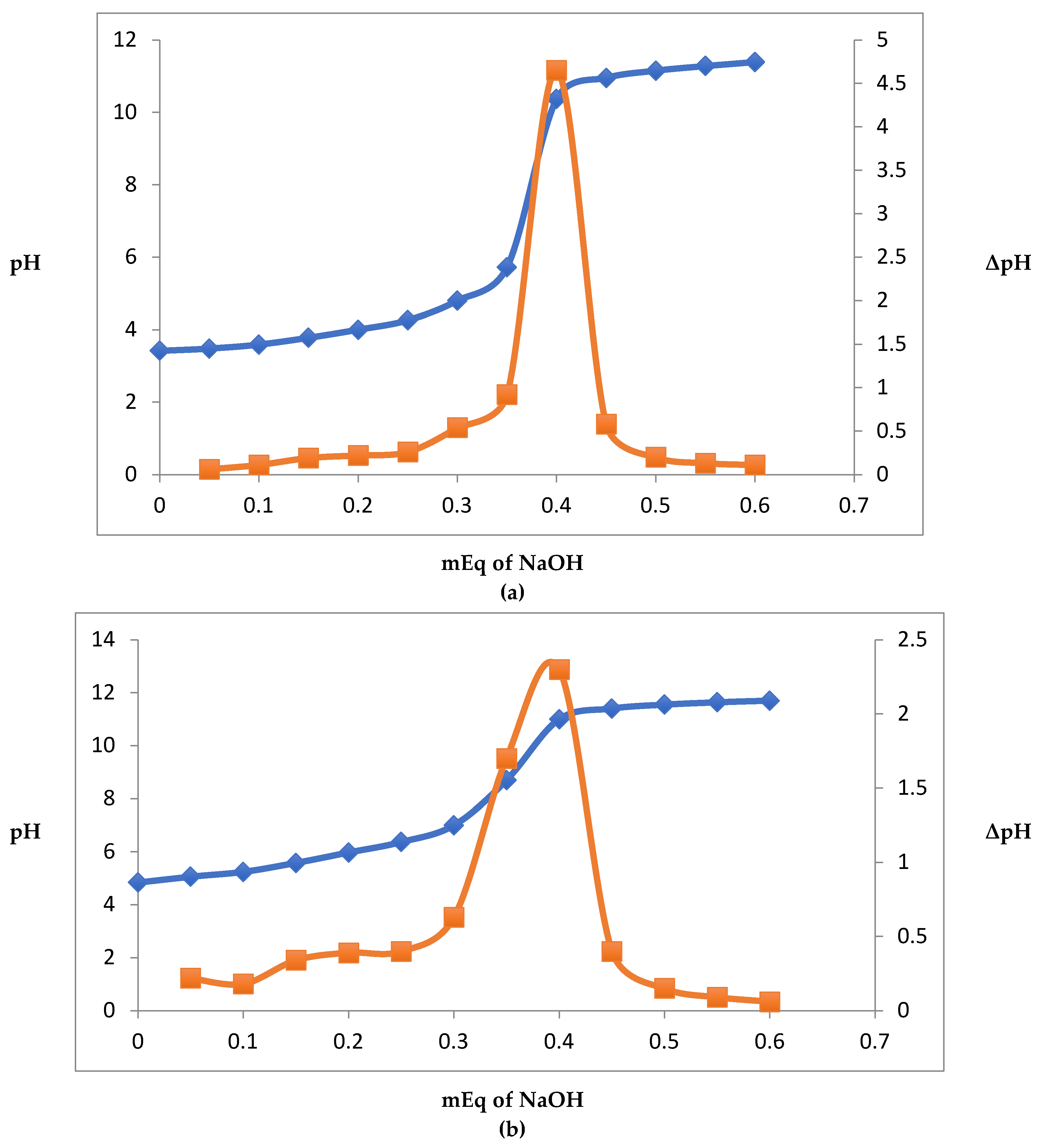
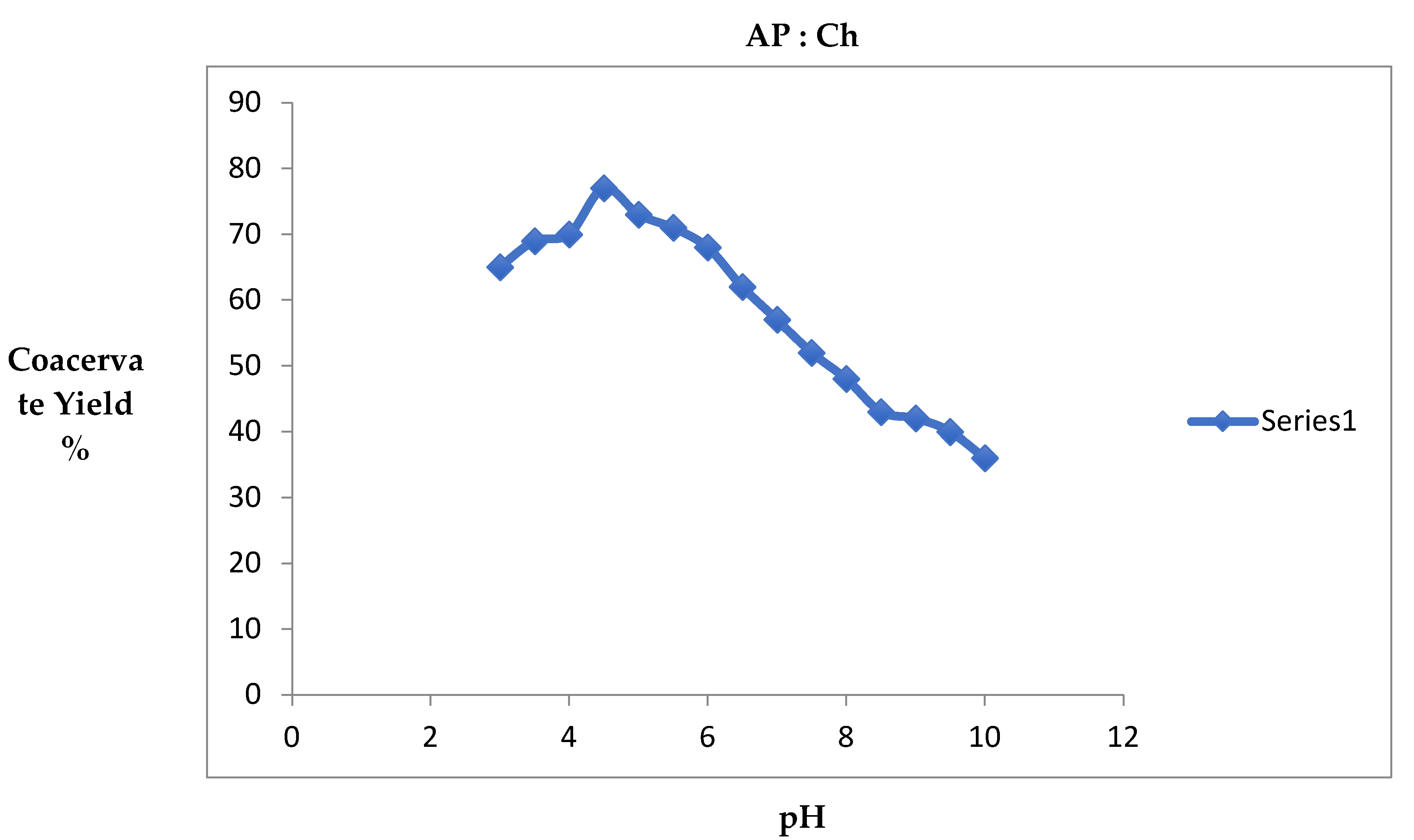
3.1. Equivalence Point and Effect of pH on Coacervate Yield
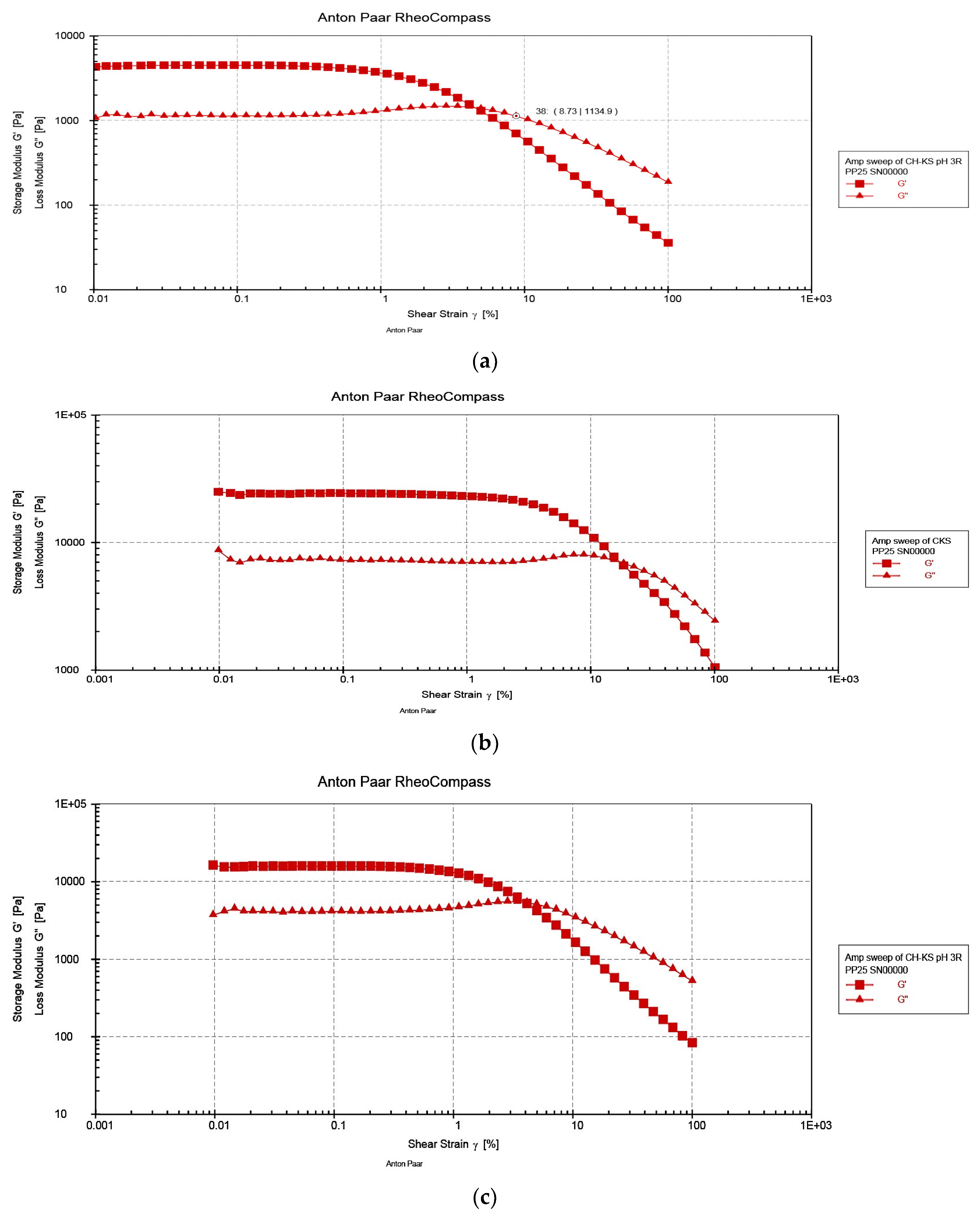
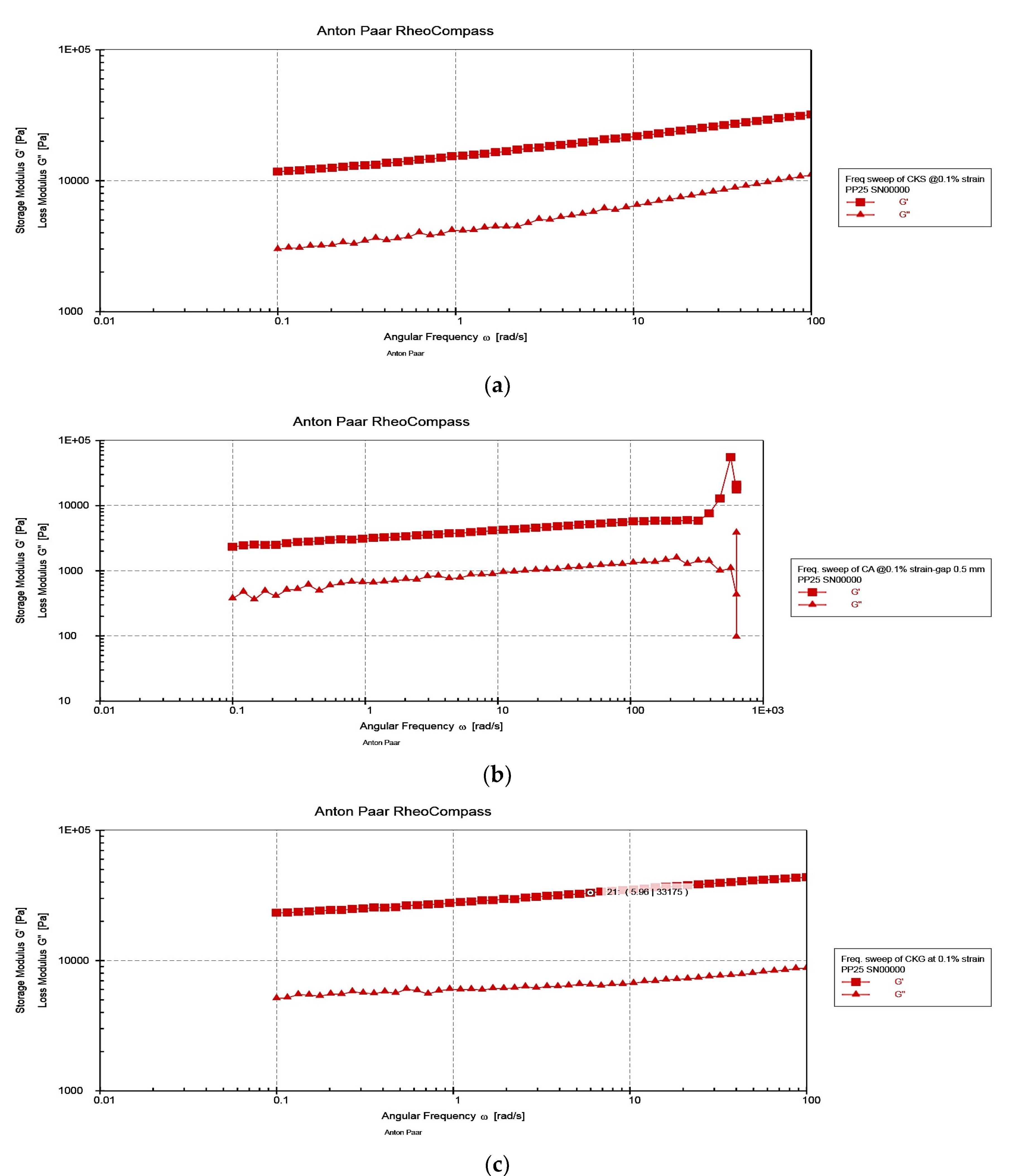
3.2. Rheological Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bungenberg de Jong, H.G.; Kruyt, H.R. Coacervation (partial miscibility in colloid systems). Proc. Koninkl. Med. Akad. Wetenschap 1929, 32, 849–856. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, C.; Mekhloufi, G.; Schmitt, C.; Renard, D.; Robert, P.; Lehr, C.M.; Lamprecht, A.; Hardy, J. Self-assembly of β-lactoglobulin and acacia gum in aqueous solvent: structure and phase-ordering kinetics. Langmuir 2002, 18, 10323–10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaught, A.D.; Wilkinson, A. Compendio de Terminologiá Quıḿica; Sintesis: Madrid, Spain, 2003; p. 117. [Google Scholar]
- Weinbreck, F.; de Vries, R.; Schrooyen, P.; de Kruif, C.G. Complex coacervation of whey proteins and gum arabic. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaibara, K.; Okazaki, T.; Bohidar, H.B.; Dubin, P.L. pH-induced coacervation in complexes of bovine serum albumin and cationic polyelectrolytes. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veis, A.; Aranyi, C. Phase separation in polyelectrolyte systems. I. Complex coacervates of gelatin. J. Phys. Chem. 1960, 64, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, A.S.; Miekka, R.G. Polycation-polyanion complexes: preparation and properties of poly(vinyl benzyl trimethyl ammonium) and poly(styrene sulfonate). J. Phys. Chem. 1961, 65, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Reist, M.; Mayer, J.M.; Felt, O.; Gurn, R. Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilay, E.; Basak-Kayitmazer, A.; Dubin, P.L. Complexation and coacervation of polyelectrolytes with oppositely charged colloids. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 167, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizilay, E.; Maccarrone, S.; Foun, E.; Dinsmore, A.D.; Dubin, P.L. Clustering in polyelectrolyte-micelle complex coacervation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 7256–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollakup, R.; Smitthipong, W.; Eisenbach, C.D.; Tirrell, M. Phase behavior and coacervation of aqueous poly(acrylic acid)- poly(allylamine) solutions. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayitmazer, A.B.; Strand, S.P.; Tribet, C.; Jaeger, W.; Dubin, P.L. Effect of polyelectrolyte structure on protein-polyelectrolyte coacervates: coacervates of bovine serum albumin with poly- (diallyldimethylammonium chloride) vs. chitosan. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3568–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bungenberg de Jong, H.G. In Colloid Science; Kruyt, H.R., Ed.; Elsevier Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1949; Vol. II, Chapter X, pp 339−432.
- Luzzi, L.A.; Gerraughty, R.J. Effects of selected variables on the extractability of oils from coacervate capsules. J. Pharm. Sci. 1964, 53, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Mynar, J.L.; Yoshida, M.; Lee, E.; Lee, M.; Okuro, K.; Kinbara, K.; Aida, T. High-water-content mouldable hydrogels by mixing clay and a dendritic molecular binder. Nature 2010, 463, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiitu, M.; Hiekkataipale, P.; Hartikainen, J.; Makela, T.; Ikkala, O. Viscoelastic and electrical transitions in gelation of electrically conducting polyaniline. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 5212–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- te Nijenhuis, K. Thermoreversible networks: viscoelastic properties and structure of gels. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1997, 130, 1–267. [Google Scholar]
- Burchard, W.; Ross-Murphy, S.B. Physical Networks: Polymers and Gels; Elsevier Applied Science: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Flory, P.J. Molecular size distribution in three dimensional polymers. I. Gelation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1941, 63, 3083–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmayer, W.H. Theory of molecular size distribution and gel formation in branched-chain polymers. J. Chem. Phys. 1943, 11, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In Chemical and Physical Networks: Formation and Control of Properties; te Nijenhuis, K., Mijs, W.S., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1998; Vol. 1.
- Lee, S.B.; Lee, Y.M.; Song, K.W.; Park, M.H. Preparation and properties of polyelectrolyte complex sponges composed of hyaluronic acid and chitosan and their biological behaviors. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankalia, M.G.; Mashru, R.C.; Sankalia, J.M.; Sutariya, V.B. Reversed chitosan-alginate polyelectrolyte complex for stability improvement of α-amylase: optimization and physicochemical characterization. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 65, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werle, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Bernkop-Schnurch, A. Modified chitosans for oral drug delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 1643–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowska, A. Current research on the blends of natural and synthetic polymers as new biomaterials: review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1254–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, V.G.M.; Madhusudhana, K.; Sashidhar, R.B.; Ramakrishna, S.; Khar, R.K.; Ahmed, F.J.; Diwan, P.V. Polyelectrolyte complexes of gum kondagogu and chitosan, as diclofenac carriers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehdi, I. Characteristics, chemical composition and utilisation of Albizia julibrissin seed oil. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico Arce, M.L.; Gale, S.L.; Maxted, N. A taxonomic study of Albizia (Leguminosae: Mimosoideae: Ingeae) in Mexico and Central America. An. Jard. Bot. Madr. 2008, 65, 255–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparajita, S.; Rout, G.R. Molecular analysis of Albizia species using AFLP markers for conservation strategies. J. Genet. 2010, 89, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachuau, L.; Mazumder, B. Albizia procera gum as an excipient for oral controlled release matrix tablet. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussinovitch, A. Plant Gum Exudates of the World: Sources, Distribution, Properties and Applications, CRC Press, Florida, 2010.
- Mhinzi, G.S. Properties of gum exudates from selected Albizia species from Tanzania. Food Chem. 2002, 77, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeku, O.A. Assessment of Albizia zygia gum as a binding agent in tablet formulations. Acta Pharm. 2005, 55, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Femi-Oyewo, M.N.; Adedokun, M.O.; Olusoga, T.O. Evaluation of the suspending properties of Albizia zygia gum on sulphadimidine suspension. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2004, 3, 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Pachuau, L.; Lalhlenmawia, H.; Mazumder, B. Characteristics and composition of Albizia procera (Roxb.) Benth gum. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2012, 40, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, R.C.M.; Santana, S.A.; Rodrigues, J.F. Composition and rheological properties of Albizia lebbeck gum exudates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 44, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhinzi, G.S. Properties of gum exudates from selected Albizia species from Tanzania. Food Chem. 2002, 77, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pinto, G.L.; Martinez, M.; Beltran, O.; Rincon, F.; Clamens, C.; Igartuburu, J.M.; Guerrero, R.; Vera, A. Characterization of polysaccharides isolated from gums of two Venezuelan specimens of Albizia niopoides var. colombiana. Ciencia 2002, 19, 382–387. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, Y.; Nose, M.; Miyatake, K.; Sekine, J.; Oura, R.; Shigemasa, Y. Physical changes of chitin and chitosan in canine gastrointestinal tract. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 44, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weecharangsan, W.; Opanasopit, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Apirakaramwong, A.; Rojanarata, T.; Ruktanonchai, U.; Lee, R.J. Evaluation of chitosan salts as non-viral gene vectors in CHO-K1 cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 348, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recillas, M.; Silva, L.L.; Peniche, C.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Rinaudo, M.; Argüelles-Monal, W.M. Thermoresponsive behavior of chitosan-g-N-isopropylacrylamide copolymer solutions. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.L.G.C.; Pais, A.A.C.C.; Redinha, J.S. Maximum likelihood estimation with nonlinear regression in polarographic and potentiometric studies. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 433, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, S.; Kumagai, H.; Sakiyama, T.; Chu, C.; Nakamura, K. Method for analyzing pH-sensitive swelling of amphoteric hydrogels- application to a polyelectrolyte complex gel prepared from xanthan and chitosan. Biosci., Biotechnol. Biochem. 1995, 59, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhloufi, G.; Sanchez, C.; Renard, D.; Guillemin, S.; Hardy, J. pH-induced structural transitions during complexation and coacerva- tion of β-lactoglobulin and acacia gum. Langmuir 2005, 21, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinbreck, F.; Nieuwenhuijse, H.; Robijn, G.W.; de Kruif, C.G. Complexation of whey proteins with carrageenan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3550–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstoguzov, V.B. Some thermodynamic considerations in food formulation. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, P.M.; Ninhami, B.W. pH-dependent interactions between adsorbed chitosan layers. Langmuir 1992, 8, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Dasgupta, P.C.; Sircar, A.K. Studies in polyelectrolytes. II. Gum arabate. J. Colloid Sci. 1951, 6, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, C.; Dammer, C.; Guenet, J.M. On the definition of thermoreversible gels: the case of syndiotactic polystyrene. Polymer 1994, 35, 4243–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molecular Gels: Materials with Self-Assembled Fibrillar Networks; Weiss, R.G., Terech, P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006.
- Garai, A.; Nandi, A.K. Rheology of polyaniline-dinonylnaphthalene disulfonic acid (DNNDSA) montmorillonite clay nano- composites in the sol state: shear thinning versus pseudo-solid behavior. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laneuville, S.I.; Turgeon, S.L.; Sanchez, C.; Paquin, P. Gelation of native β-lactoglobulin induced by electrostatic attractive interaction with xanthan gum. Langmuir 2006, 22, 7351–7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohidar, H.; Dubin, P.L.; Majhi, P.R.; Tribet, C.; Jaeger, W. Effects of protein−polyelectrolyte affinity and polyelectrolyte molec- ular weight on dynamic properties of bovine serum albumin- poly(diallylmethylammonium chloride) coacervates. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lee, J.; Wang, Y.-W.; Huang, Q. Composition and rheological properties of β-lactoglobulin/pectin coacervates: effects of salt concentration and initial protein/polysaccharide ratio. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marudova, M.; McDougall, A.J.; Ring, S.G. Physicochemical studies of pectin/poly-L-lysine gelation. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
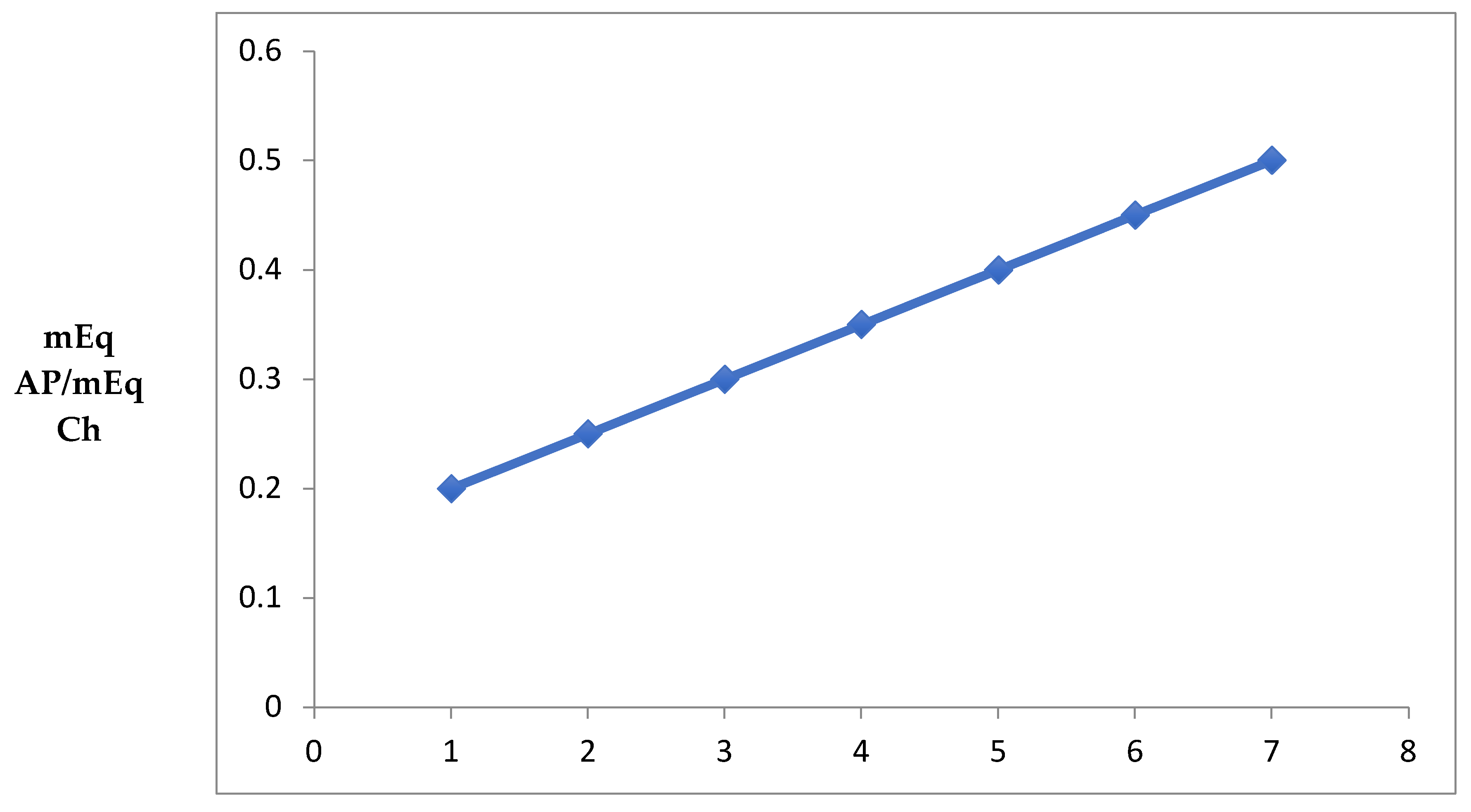
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




