Submitted:
23 July 2024
Posted:
25 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacillus Licheniformis BCR 4-3 and Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) Culture
2.2. In Vitro Utilization of Ammonium, Nitrites and Nitrates by Bacilli and LAB
2.3. Experimental Design
2.3.1. Origin and Acclimatization of Experimental Shrimp
2.3.2. Bioassay: Effect of Bacilli and LAB on Water Quality, Growth, Survival, Immune System, and Intestinal Microbiota of Shrimp
2.3.3. Hemolymph Collection
2.3.4. Hemocyte Count
2.3.5. Superoxide Anion
2.3.6. Phenoloxidase Activity (PO) in Hemolymph
2.4. Water Sampling, TAN, Nitrites, and Nitrates Determination
2.5. Metagenomic Analysis
2.5.1. Extraction of Bacterial DNA, Library Preparation, and Sequencing in Illumina MiniSeq
2.5.2. Gut Bacterial Taxonomy, Abundance, and Diversity Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Utilization of Ammonium, Nitrites and Nitrates by Bacilli and LAB
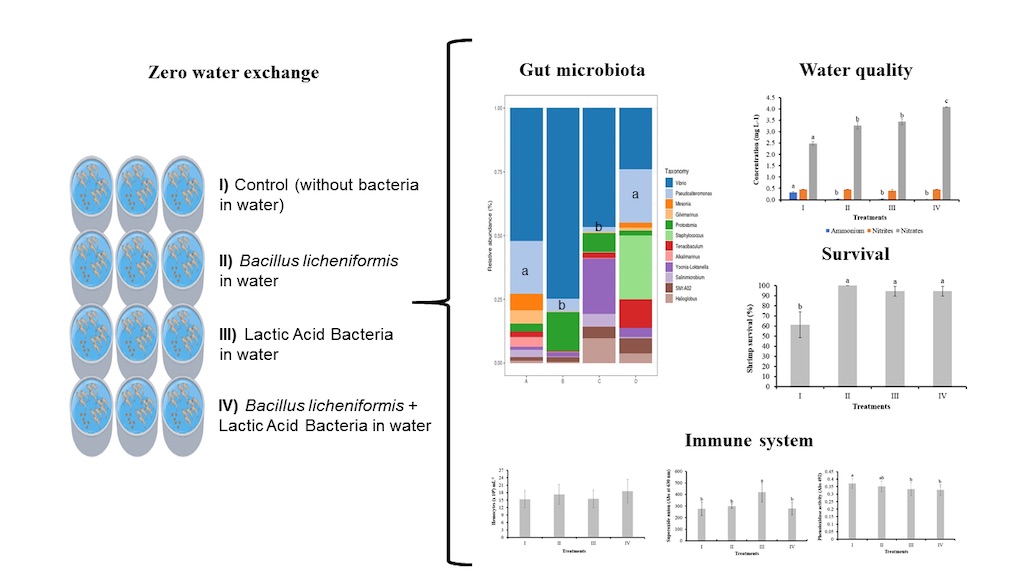
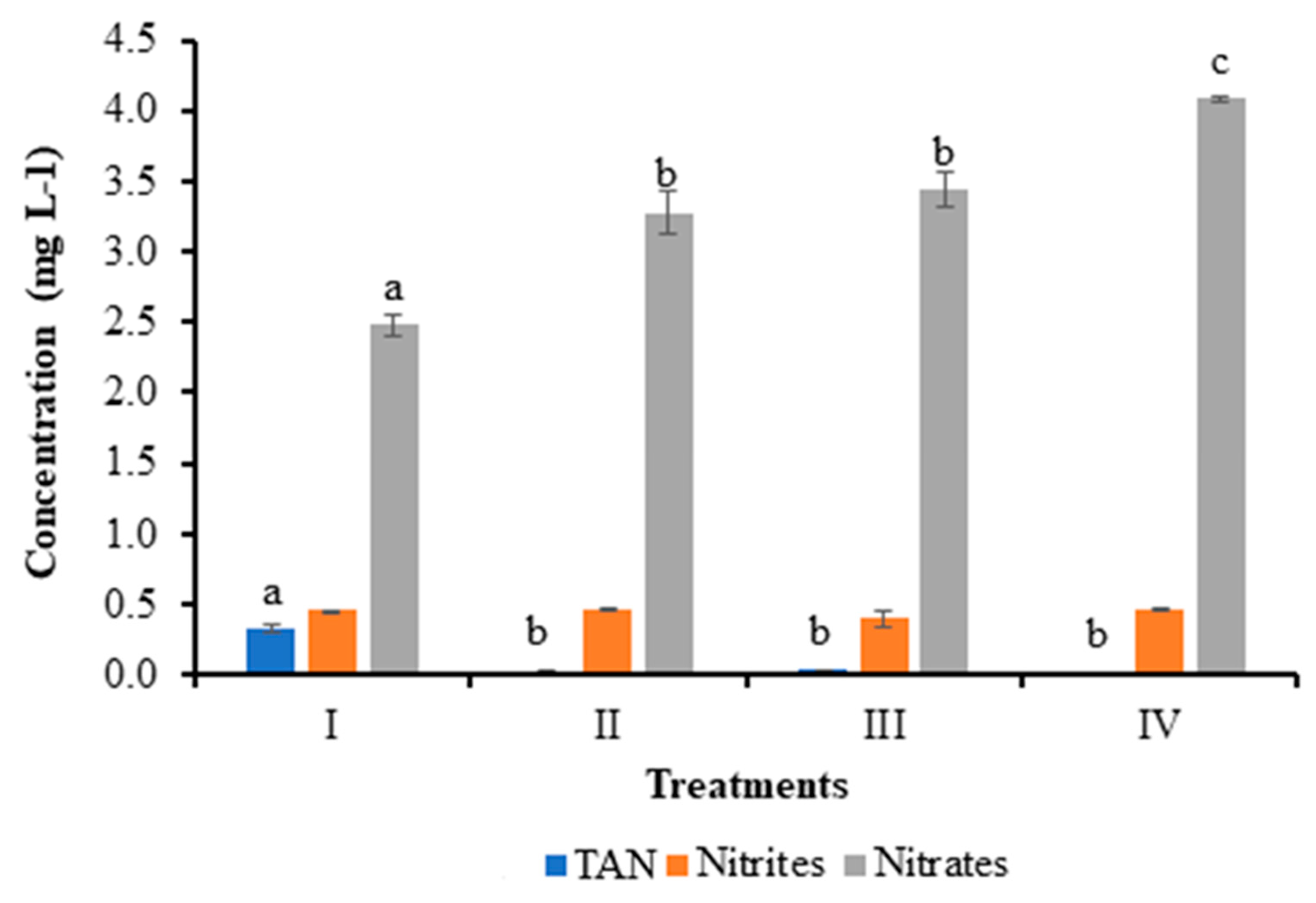
3.2. Effect of Bacilli and LAB on Culture Water Quality
3.2.1. Shrimp Growth
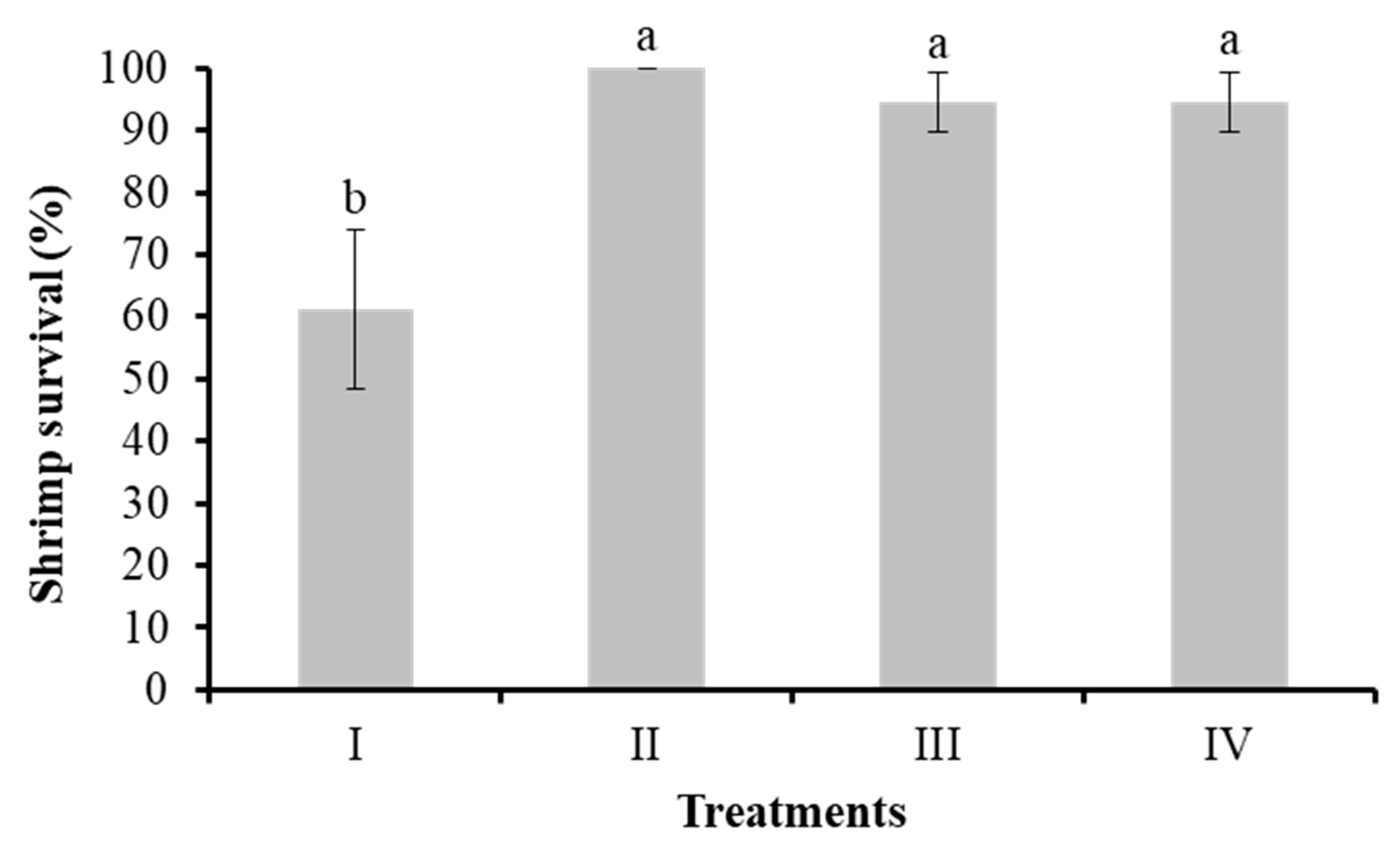
3.2.2. Shrimp Survival
3.3. Immune System
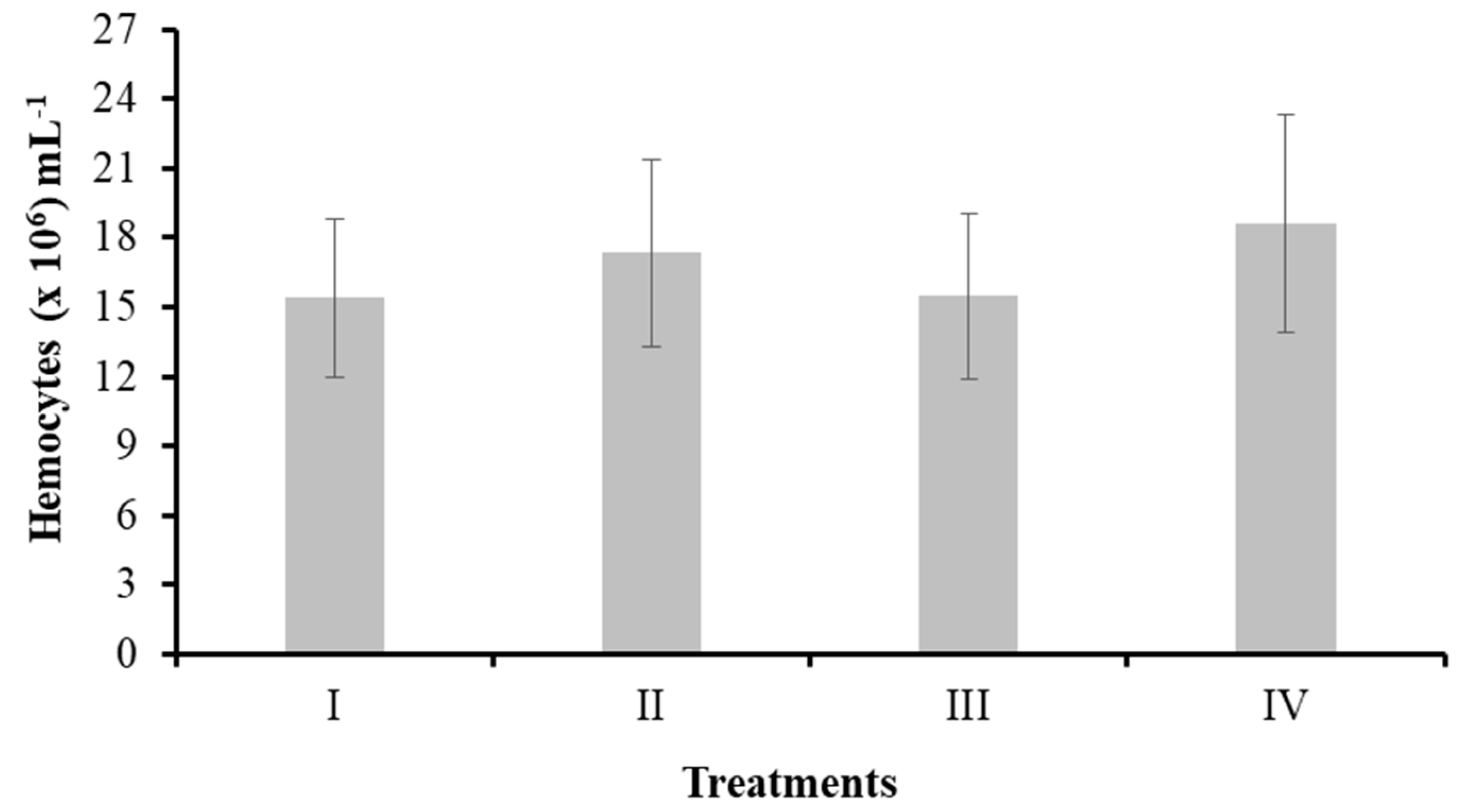
3.3.1. Total Hemocyte Count
3.3.2. Superoxide Anion
3.3.3. Phenoloxidase Activity in Shrimp Hemolymph
3.4. Gut Microbiota Analysis
3.4.1. Relative Bacterial Abundance in the Shrimp Gut
3.4.2. Alpha Diversity Indices
3.4.3. Beta Diversity Index
3.4.4. Bacterial Functional Profile Based on KEGG Pathway Analysis
3.5. Correlation between Functional Categories and Immune and Productive Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Estado Mundial de la Pesca y la Acuicultura 2020. Departamento de Pesca Acuicultura de la FAO. 2020.
- Villarreal, H.; Juárez, L. Super-intensive shrimp culture: Analysis and future challenges. J. World Aqua. Soc. 2012, 53, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, F.L.; Abreu, P.C.; Wasielesky, W. Importance of biofilm for water quality and nourishment in intensive shrimp. Aquaculture 2002, 203, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioses-Imán, D.S. Consorcios bacterianos nitrificantes inmovilizados en filtros de desechos agrícolas, como biorremediadores para cultivos de Litopenaeus vannamei, en agua dulce. Tesis. Universidad Nacional de Piura. Facultad de Ciencias. Escuela de Ciencias Biológicas Piura Perú, 2017, 50 pp.
- Hoang, P.H.; Nguyen, H.T.; Tran, T.T.; Do, L.P.; Le, T.N.C. Isolation and selection of nitrifying bacteria with high biofilm formation for treatment of ammonium polluted aquaculture water. J Vietn. Environ. 2016, 8, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyappan, S.; Mishra, S. Bioamelioration in aquaculture with a special reference to nitrifying bacteria. In: I.S.B. Singh, S.S. Pai, R. Philip and A. Mohandas (eds.) Aquaculture Medicine. CFDDM, CUSAT, India, 2003, pp 89-107.
- Ebeling, J.M.; Timmons, M.B.; Bisogni, J.J. Engineering analysis of the stoichiometry of photoautotrophic, autotrophic, and heterotrophic removal of ammonia-nitrogen in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture. 2006, 257, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claros-Bedoya, J.A. Graduate Thesis. Estudio del proceso de nitrificación y desnitrificación vía nitrito para el tratamiento biológico de corrientes de agua residual con alta carga de nitrógeno amoniacal. Universidad Politécnica de Valencia. 2012, 254 pp.
- Zumft, W.G. Cell biology and molecular basis of denitrification. Microbiol. Molec. Biol. Rev. 1997, 61, 533–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.P.; Wang, S.M.; Zhang, D.W.; Zhou, L.X. Isolation and nitrogen removal characteristics of an aerobic heterotrophic nitrifying–denitrifying bacterium, Bacillus subtilis A1. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noorak, S.; Rakkhiaw, S.; Limjirakhajornt, K.; Uppabullung, A.; Keawtawee, T.; Sangnoi, Y. Nitrite oxidizing bacteria for water treatment in coastal aquaculture system. IOP Conference Series: Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 137, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doñate, C.; Balasch, J.C.; Callol, A.; Bobe, J.; Tort, L.; MacKenzie, S. The effects of immunostimulation through dietary manipulation in the rainbow trout; evaluation of mucosal immunity. Mar. Biotechnol. 2010, 12, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-González, A.; Moreno-Herrera, J.T.; Campa-Córdova, Á.I.; González-Ocampo, H.A.; Fierro-Coronado, J.A.; Álvarez-Ruíz, P.; Bueno-Ibarra, M.A. Respuesta inmune y expresión de genes en el camarón blanco (Litopenaeus vannamei) inducida por inmunoestimulantes microbianos. Latin. Am. J. Aquatic. Res. 2013, 41, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Xu, J.; Zhao, J. Classification and phagocytosis of circulating haemocytes in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) and the effect of extrinsic stimulation on circulating haemocytes in vivo. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 39, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Shao, M.K.; Kang, H. Classification of haematopoietic cells and haemocytes in Chinese prawn Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 21, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagutao, F.F.; Maningas, M.B.; Kondo, H.; Aoki, T.; Hirono, I. Transglutaminase regulates immune-related genes in shrimp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.W.; Wang, J.X. Pattern recognition receptors acting in innate immune system of shrimp against pathogen infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponprateep, S.; Vatanavicharn, T.; Lo, C.F. Alpha-2-macroglobulin is a modulator of prophenoloxidase system in pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 62, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Estrada, A.M.; Gollas-Galvan, T.; Martinez-Cordova, L.R.; Martinez-Porchas, M. Predictive functional profiles using metagenomic 16S rRNA data: a novel approach to understanding the microbial ecology of aquaculture systems. Rev. Aquacul. 2019, 11, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, B.; Jiang, K.; Qi, C.; Wang, L. Bacterial population in intestines of Litopenaeus vannamei fed different probiotics or probiotic supernatant. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 1736–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremaroli, V.; Backhed, F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 2012, 489, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escamilla-Montes, R.; Luna-González, A.; Flores-Miranda, M.C.; Álvarez- Ruiz, P.; Fierro-Coronado, J.A. Isolation and characterization of potential probiotic bacteria suitable for mollusk larvae cultures. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2015, 45, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Madrigal, K.Y.; Luna-González, A.; Escobedo-Bonilla, C.M.; Fierro-Coronado, J.A.; Maldonado-Mendoza, I.E. Screening for potential probiotic bacteria to reduce prevalence of WSSV and IHHNV in whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) under experimental conditions. Aquaculture 2011, 322-323, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.M.; He, Y.; Bhandari, B. “Encapsulation of nanoparticles of dlimonene by spray drying: role of emulsifiers and emulsifying techniques, ” Dry. Technol. 2007, 25, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Lara-Espinoza, C.; Espinosa-Plasencia, A.; Rivera-Domínguez, M.; Astorga-Cienfuegos, K.; Acedo-Félix, E.; Bermúdez-Almada, M. Desarrollo de camarón Litopenaeus vannamei en un sistema de cultivo intensivo con biofloc y nulo recambio de agua. AquaTIC 2015, 43, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ricker, W.E. Growth rates and models. In: W. S. Hoar, D. J. Randall & J. R. Brett (Eds.). Fish physiology, Volume VIII, Bioenergetics and growth. Academic Press. New York, United States. 1979, pp. 599–675.
- Vargas-Albores, F.; Guzmán, M.A.; Ochoa, J.L. An anticoagulant solution for haemolymph collection and prophenoloxidase studies of penaeid shrimp (Penaeus californiensis). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A: Physiol. 1993, 106, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.L.; Hsieh, Y.T. Immunostimulation of tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) hemocytes for generation of microbicidalsubstances: Analysis of reactive oxygen species. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1994, 18, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, J.D.H.; Parsons, T.R. A Parctical Handbook of Seawater Analysis. Bulletin 167. Second edition. 1972, .323 pp.
- Azmat, M.A.; Khan, I.A.; Cheema, H.M.; Rajwana, I.A.; Khan, A.S.; Khan, A.A. Extraction of DNA suitable for PCR applications from mature leaves of Mangifera indica L. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 2012, 13, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huse, S.M.; Dethlefsen, L.; Huber, J.A.; Welch, D.M.; Relman, D.A.; Sogin, M.L. Exploring Microbial Diversity and Taxonomy Using SSU rRNA Hypervariable Tag Sequencing. PLOS Gen. 2008, 4, e1000255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Maruyama, F.; Kato, H.; Toyoda, A.; Dozono, A.; Ohtsubo, Y. Design and experimental application of a novel non-degenerate universal primer set that amplifies prokaryotic 16S rRNA genes with a low possibility to amplify eukaryotic rRNA genes. DNA Res. 2014, 21, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volant, S.; Lechat, P.; Woringer, P.; Motref, L.; Campagne, P. SHAMAN: a user-friendly website for metataxonomic analysis from raw reads to statistical analysis. BMC Bioinforma. 2020, 21, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhariwal, A.; Chong, J.; Habib, S.; King, L.I.; Agellon, L.B.; Xia, J. MicrobiomeAnalyst: a web-based tool for comprehensive statistical, visual and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Liu, P.; Zhou, G.; Xia, J. Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for comprehensive statistical, functional, and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nature Protocols 2020, 15, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardou, F.; Ariel, F.; Simpson, C.G.; Romero, N.; Laporte, P.; Balzergue, S. Long noncoding RNA modulates alternative splicing regulators in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell. 2014, 30, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, S.; Haque, M.M.; Mande, S.S. Vikodak - A Modular Framework for Inferring Functional Potential of Microbial Communities from 16S Metagenomic Datasets. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0148347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, P. Introducción a la Estadistica. 1997. MacGraw-Hill, Interamericana 428 p.
- Zokaeifar, H.; Babaei, N.; Saad, C.R.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Sijam, K.; Balcazar, J.L. Administration of Bacillus subtilis strains in the rearing water enhances the water quality, growth performance, immune response, and resistance against Vibrio harveyi infection in juvenile white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 36, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieke, T.; Meinelt, T.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Pan, B.; Straus, D.L.; Steinberg, C.E. Sustainable aquaculture requires environmental-friendly treatment strategies for fish diseases. Rev. Aquacu. 2019, 12, 943–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, J.C. Acute toxicity of ammonia on Litopenaeus vannamei Boone juveniles at different salinity levels. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2001, 259, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, J.C. Acute toxicity of nitrite on Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) juveniles at different salinity levels. Aquaculture. 2003, 224, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Zeng, C. Toxic Effects of Ammonia, Nitrite, and Nitrate to Decapod Crustaceans: A Review on Factors Influencing their Toxicity, Physiological Consequences, and Coping Mechanisms. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2013, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, E.; Bondioli, A.C.V.; Melo, C.; Henriques, M.B. Nitrite toxicity to Litopenaeus schmitti (Burkenroad, 1936, Crustacea) at different salinity levels. Aquac. Res. 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Y.; Erchao, L.; Tongyu, L.; Yongyi, J.; Jian, G.; Qin, Z.G.; Liqiao, C. Response of gut health and microbiota to sulfide exposure in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 63, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, K.; Safitri, R.; Fajriani, N.; Gifari, Z.A.; Wariata, I.W.; Rosyidi, A. In vitro screening of ammonia and nitrite-degrading bacteria isolated from broiler chicken (Gallus gallus domesticus) intestines and pond sediment of nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): a preliminary study. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 913, 012072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalloo, R.; Ramchuran, S.; Ramduth, D.; Görgens, J.; Gardiner, N. Isolation and selection of Bacillus spp. as potential biological agents for enhancement of water quality in cultura of ornamental fish. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar]
- Daims, H.; Lücker, L.; Wagner, M.A. New Perspective on Microbes Formerly Known as Nitrite-Oxidizing Bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zokaeifar, H.; Balcázar, J.L.; Saad, C.R.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Sijam, K.; Arshad, A.; Njat, N. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on the growth performance, digestive enzymes, immune gene expression and disease resistance of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lezama, C.; Paniagua, J.; Zamora, J. Bioremediation of effluents ones of the culture of Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) using microbial mats in a recirculating system. Latin Am. J. Aquatic Res. 2010, 38, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, C. G.; Fu, Y.-W.; Guo, S.-Q.; Luo, J.-J.; Zhang, Q.-Z. Isolation and Characterization of an Aerobic Denitrifier Bacillus sp. SC16 from an Intensive Aquaculture Pond. Water. 2020, 12, 3559. [Google Scholar]
- Giatsis, C.; Sipkema, D.; Smidt, H.; Verreth, J.; Verdegem, M. The Colonization Dynamics of the Gut Microbiota in Tilapia Larvae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuellar-Gempeler, C.; Leibold, M.A. Multiple colonist pools shape fiddler crab-associated bacterial communities. The ISME J. 2018, 12, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Yayu, Q.; Jian, G.; Qin, L.C.; Fenglu, H.; Erchao, L. Deep insight into bacterial community characterization and relationship in the pond water, sediment and the gut of shrimp (Penaeus japonicus). Aquaculture 2021, 539, 736658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, J.L.; Bäckhed, F. Diet–microbiota interactions as moderators of human metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 535, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimrat, S.; Suksawat, S.; Boonthai, T.; Vuthiphandchai, V. Potential Bacillus probiotics enhance bacterial numbers, water quality and growth during early development of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 159, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, N.S.H.; Adorian, T.; Ghafari, H.; Farsani, J.; Hoseinifar, S.H. The effects of dietary probiotic Bacilli (Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis) on growth performance, feed efficiency, body composition and immune parameters of whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) postlarvae. ” Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 1926–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinifar, S.H.; Dadar, M.; Ringø, E. Modulation of nutrient digestibility and digestive enzyme activities in aquatic animals: the functional feed additives scenario. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 3987–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessione, E. Lactic acid bacteria contribution to gut microbiota complexity: lights and shadows. Fron. Cell. Infec. Microbiol. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, M.; Plínio, S.A.; Valenzuela, J.; Rodriguez-Fuentes, G.; Campos, B. R.; Wasielesky Jr, W.; Gaxiola, G.G. Chronic effect of nitrite on the rearing of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in two salinities. Mar. Freshwater Behav. Physiol. 2016, 49, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Jia, X.; Qiuran, Y.; Chang, X.; Li, Z.; Jian, G.Q. Toxic effect of chronic nitrite exposure on growth and health in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture. 2020, 529, 735664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.R.; de Furtado, P.S.; D'Incao, F.; Wasielesky, W.; Poersch, L.H. Compostos nitrogenados sobre o consumo alimentar de camarão-rosa Farfantepenaeus brasiliensis. Ciên Rural 2013, 43, 2202–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L. Effects of ammonia and nitrite accumulation on the survival and growth performance of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Inv. Surv. J. 2017, 14, 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.O.C.; Wickins, J.F. Crustacean farming: ranching and culture. First Edition. Blackwell Sci Publ Oxford U.K., 1992, 392 p.
- Boyd, C.E. Consideraciones sobre la calidad del agua y del suelo en cultivos de camarón. In: Haws, M. C., Boyd, C.E. (eds.). Métodos para Mejorar la Camaronicultura en Centroamérica. Editorial-Imprenta UCA, Managua, Nicaragua, 2002, pp 24-25.
- Boardman, G.D.; Starbuck, S.M.; Hudgins, D.B.; Li, X.Y.; Kuhn, D.D. Toxicity of ammonia to three marine fish and three marine invertebrates. Environ. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 34–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Shigui, J. Effects of Dietary Clostridium butyricum on the Growth, Digestive Enzyme Activity, Antioxidant Capacity, and Resistance to Nitrite Stress of Penaeus monodon. Prob. Antim. Prot. 2019, 11, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Gai, C.; Ye, G. Aeromonas hydrophila, an emerging causative agent of freshwaterfarmed whiteleg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, J.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Yeh, S.T.; Huang, C.L. White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei That Have Received Gracilaria tenuistipitata Extract Show Early Recovery of Immune Parameters after Ammonia Stressing. Mar. Drugs. 2015, 13, 3606–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, A.; Xian, J.; Chen, X.; Gou, N. Effect of nitrite on immunity of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei at low temperature and low salinity. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.C.; Yeh, S.P.; Hu, S.Y.; Lin, H.L; Liu, C.H. Intestinal microbiota of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, fed diets containing Bacillus subtilis E20-fermented soybean meal (FSBM) or an antimicrobial peptide derived from B. subtilis E20- FSBM. Aquac. Res. 2019, 51, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Xiong, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, H.; Guo, A.; Wu, J.; Dai, H. Bacterioplankton assemblages as biological indicators of shrimp health status. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 38, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo-Granados, F.; Gallardo-Becerra, L.; Leonardo-Reza, M.; Ochoa-Romo, J.P.; Ochoa-Leyva, A. A meta-analysis reveals the environmental and host factors shaping the structure and function of the shrimp microbiota. Peer J. 2018, 6, e5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, E.C.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.D.; Wang, S.F.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, M.L.; Qin, J.G.; Chen, L.Q. Gut microbiota and its modulation for healthy farming of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Rev. Fish Sci. Aquacult. 2018, 26, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, K.; Wu, J.; Qiuqian, L.; Yang, K.; Qian, Y.; Demin, Z. Changes in intestinal bacterial communities are closely associated with shrimp disease severity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6911–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rungrassamee, W.; Klanchui, A.; Maibun, S.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. Bacterial dynamics in intestines of the black tiger shrimp and the Pacific white shrimp during Vibrio harveyi exposure. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 133, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Wen, M.; Xiang, L.; Shen, H.; Jiang, G.; Cheng, J.; Hu, Y.; Qian, J. Segmental variations in intestinal microbiota composition and functional capacity along the digestive tract of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 34, 101922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, H.; Gholami, A.M.; Berry, D.; Desmarchelier, C.; Hahne, H.; Loh, G.; Mondot, S.; Lepage, P.; Rothballer, M.; Walker, A.; et al. High-fat diet alters gut microbiota physiology in mice. ISME J. 2014, 8, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.; Saier, M.H. Gut Bacteroides species in health and disease. Gut Microbes. 2021, 13, 1848158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsbrink, J.; Zhu, Y.; Kharade, S.S.; Kwiatkowski, K.J.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Koropatkin, N. M.; McBride, M.J.; Pope, P.B. A polysaccharide utilization locus from Flavobacterium johnsoniae enables conversion of recalcitrant chitin. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otta, S.; Karunasagar, I.K.I. Bacterial fora associated with shrimp culture ponds growing Penaeus monodon. J. Aquac. Trop. 1999, 14, 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Intriago, J.; Quimi, J.; Risco, J.; López, J.; Yalta, J.; Bermudez, M.; Mialhe, E. Metagenómica de la microbiota de juveniles de Litopenaeus vannamei inoculados con bacterias probióticas y patógenas. AquaTIC 2018, 51, 16–29. [Google Scholar]
- Vega-Carranza, A.S. Efecto de plantas medicinales, probióticos, prebióticos, paraprobióticos y postbióticos en la microbiota intestinal, crecimiento, supervivencia y respuesta inmune del camarón blanco (Penaeus vannamei) retado con Vibrio parahaemolyticus. MS Dissertion. 2020. CIIDIR-IPN. 100 p.
- Zheng, Y.; Yu, M.; Liu, Y.; Su, Y.; Xu, T.; Yu, M.; Zhang, X.H. Comparison of cultivable bacterial communities associated with Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) larvae at different health statuses and growth stages. Aquaculture. 2016, 451, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Pan, L.; Huang, F.; Song, M.; Tian, C.; Zhang, M. Metagenomic insights into the structure and function of intestinal microbiota of the farmed Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture. 2019, 499, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.; Domínguez-Borbor, C.; Salazar, L.; Debut, A.; Vizuete, K.; Sonnenholzner, S.; Alexis, F.; Rodríguez, J. The probiotics Vibrio diabolicus (Ili), Vibrio hepatarius (P62), and Bacillus cereus sensu stricto (P64) colonize internal and external surfaces of Penaeus vannamei shrimp larvae and protect it against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criminger, J.D.; Hazen, T.H.; Sobecky, P.A.; Lovell, C.R. Nitrogen Fixation by Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Its Implications for a New Ecological Niche. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W. Characterization and classification of novel marine nitrogen-fixing bacterial isolates from the lagoon sediment of Dongsha Island. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widanarni, W.; Tepu, I.; Sekenda, S.; Setiawati, M. Seleksi bakteri probiotik untuk biokontrol vibriosis pada larva udang windu (Penaues monodon) menggunakan cara kultur bersama. J. Riset Akuakultur 2009, 4, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorieul, N.; Wabete, D.; Ansquer, J.R.; Mailliez, M.; Pallud, C.; Zhang, M.; Lindivat, V.; Buolo, D. Pham. Survival improvement conferred by the Pseudoalteromonas sp. NC201 probiotic in Litopenaeus stylirostris exposed to Vibrio nigripulchritudo infection and salinity stress. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Xu, S.Y.; Ren, Z.G.; Tao, L.; Jiang, J.W.; Zheng, S.S. Application of metagenomics in the human gut microbiome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamsah, H.; Widanarni, W.; Alimuddin, A.; Yuhana, M.; Junior, M.Z.; Hidayatullah, D. Immune response and resistance of Pacific white shrimp larvae administered probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotic through the bio-encapsulation of Artemia sp. Aquac. Intern. 2019, 27, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhani, D.E.; Widanarni, W.; Sukenda, S. Microencapsulation of probiotics and its applications with prebiotic in Pacific white shrimp larvae through Artemia sp. Jurnal Akuakultur Indonesia 2019, 18, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Chatelier, E. T.; Nielsen, J.; Qin, E.; Prifti, F.; Hildebrand, G. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature. 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Bäckhed, F.; Fulton, L.; Gordon, J.I. Diet-Induced Obesity Is Linked to Marked but Reversible Alterations in the Mouse Distal Gut Microbiome. Cell Host Microb. 2008, 3, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, T.P.; Bellwood, D.R.; Folke, C.; Steneck, R.; Wilson, J. New paradigms for supporting the resilience of marine ecosystems. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Robin, L.; Chazdon, R.; Colwell, K.; Tsung-Jen, S. Abundance-based similarity indices and their estimation when there are unseen species in samples. Biometrics. 2016, 62, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Non-parametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scandinavian J. Statistics. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R. M.; Hartmann, E.; Hollister, B. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Handelsman, J. Introducing SONS, a tool for operational taxonomic unit-based comparisons of microbial community memberships and structures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6773–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomisto, H. A diversity of beta diversities: straightening up a concept gone awry. Part 1. Defining beta diversity as a function of alpha and gamma diversity. Ecography 2010, 33, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsman, A.; St-Pierre, B.; Rosales-Leija, M.; Brown, M.; Gibbons, W. Investigation of the potential effects of host genetics and probiotic treatment on the gut bacterial community composition of aquaculture- raised Pacific whiteleg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Microorganisms. 2019, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Carranza, A.S.; Escamilla-Montes, R.; Luna-González, A.; Fierro-Coronado, J.A.; Diarte-Plata, G.; García-Gutiérrez, C. Survival, immune response, and gut microbiota in Litopenaeus vannamei fed with synbiotics and postbiotics and challenged with Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquac. Intern. 2024, 32, 361–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ge, C.; Li, W.; Yao, H. The intestinal bacterial community and functional potential of Litopenaeus vannamei in the coastal areas of China. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dopson, M.; Ossandon, F.J.; Lövgren, L.; Holmes, D.S. Metal resistance or tolerance? Acidophiles confront high metal loads via both abiotic and biotic mechanisms. Frontiers in Microbiology 2014, 5, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Yun, W.; Xian, D.; Dalin, X.; Jiasong, Z. Response of intestine microbiota, digestion, and immunity in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei to dietary succinate. Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Xu, S.Y.; Ren, Z.G.; Tao, L.; Jiang, J.W.; Zheng, S.S. Application of metagenomics in the human gut microbiome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.A.; Marnett, L.J. Introduction to lipid biochemistry, metabolism, and signaling. Chemical Reviews 2011, 111, 5817–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radzikowska, U.; Rinaldi, A.; Çelebi, O.; Sözener, Z.; Karaguzel, D.; Wojcik, M. The Influence of Dietary Fatty Acids on Immune Responses. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatanaka, E.; Levada-Pires, A.C.; Pithon-Curi, T.C.; Curi, R. Systematic study on ROS production induced by oleic, linoleic, and gamma-linolenic acids in human and rat neutrophils. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Zhanhu, H.; Jianbo, Y.; Yuan, L.; Yanmei, Q.; Bin, L. Taxonomic and functional metagenomic profiling of gastrointestinal tract microbiome of the farmed adult turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 86, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Luqing, P.; Fei, H.; Shuo, G.; Chen, S.; Mingzhu, Z.; Ziyan, H. Metagenomic analysis of composition, function and cycling processes of microbial community in water, sediment and effluent of Litopenaeus vannamei farming environments under different culture modes. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
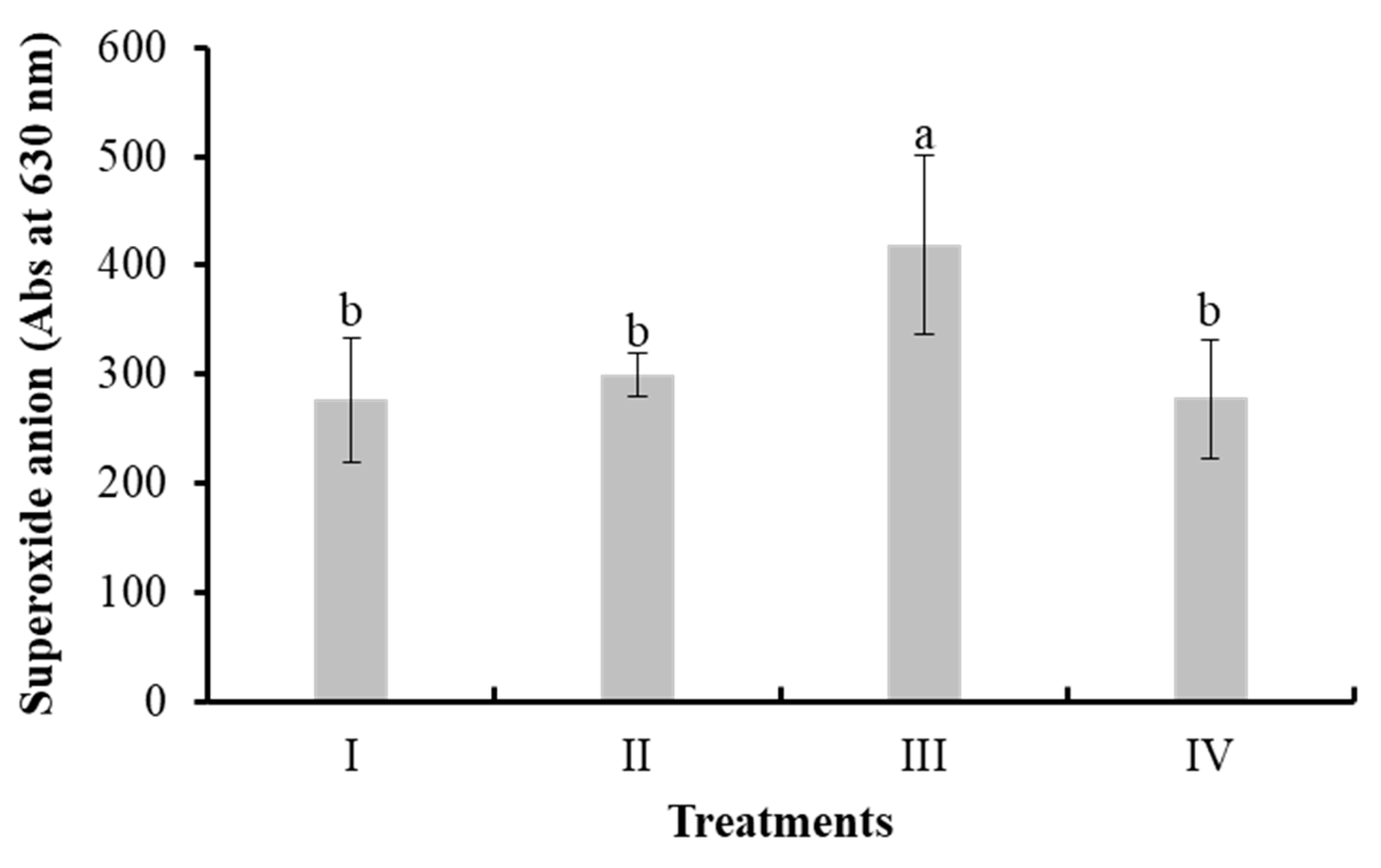
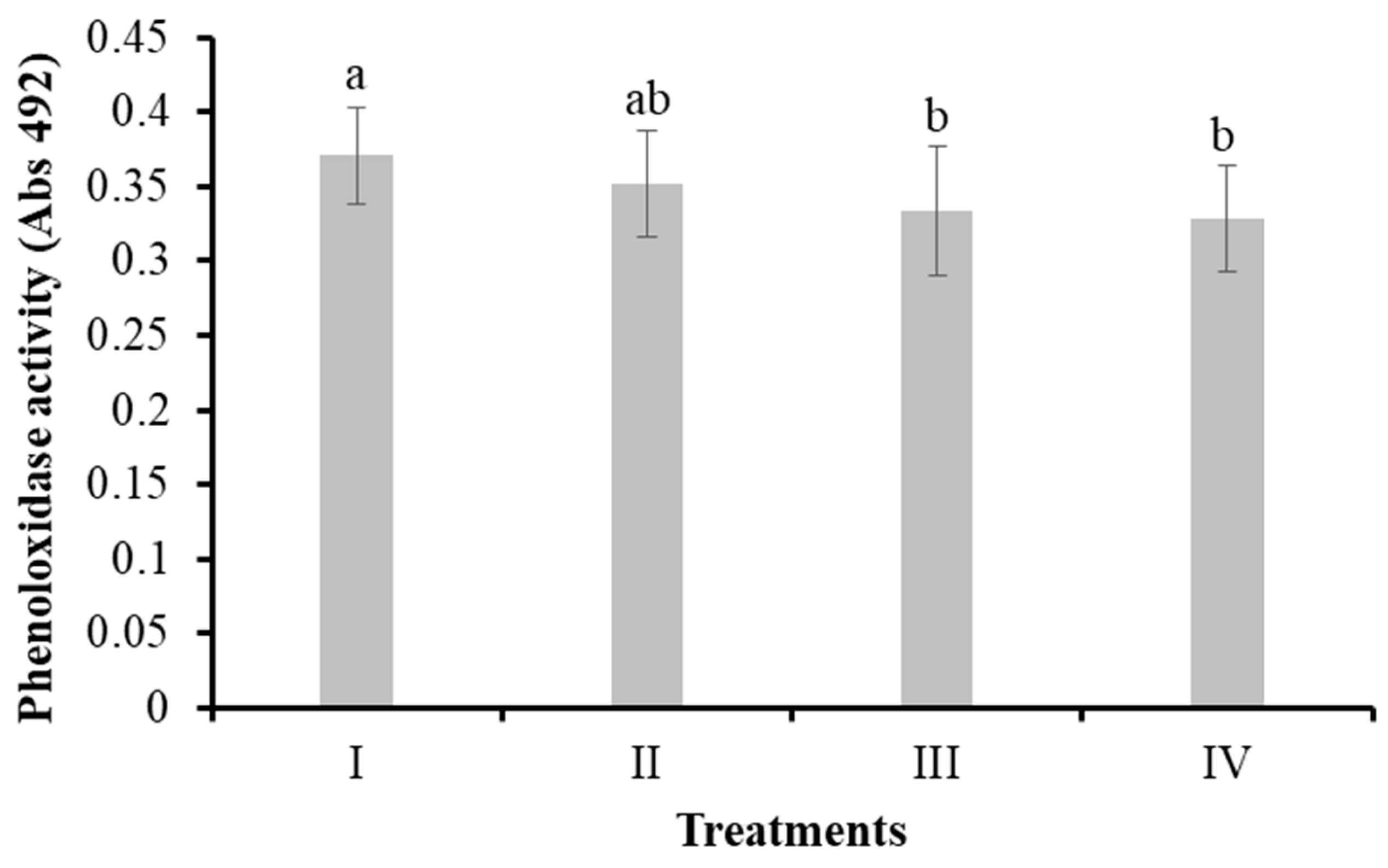
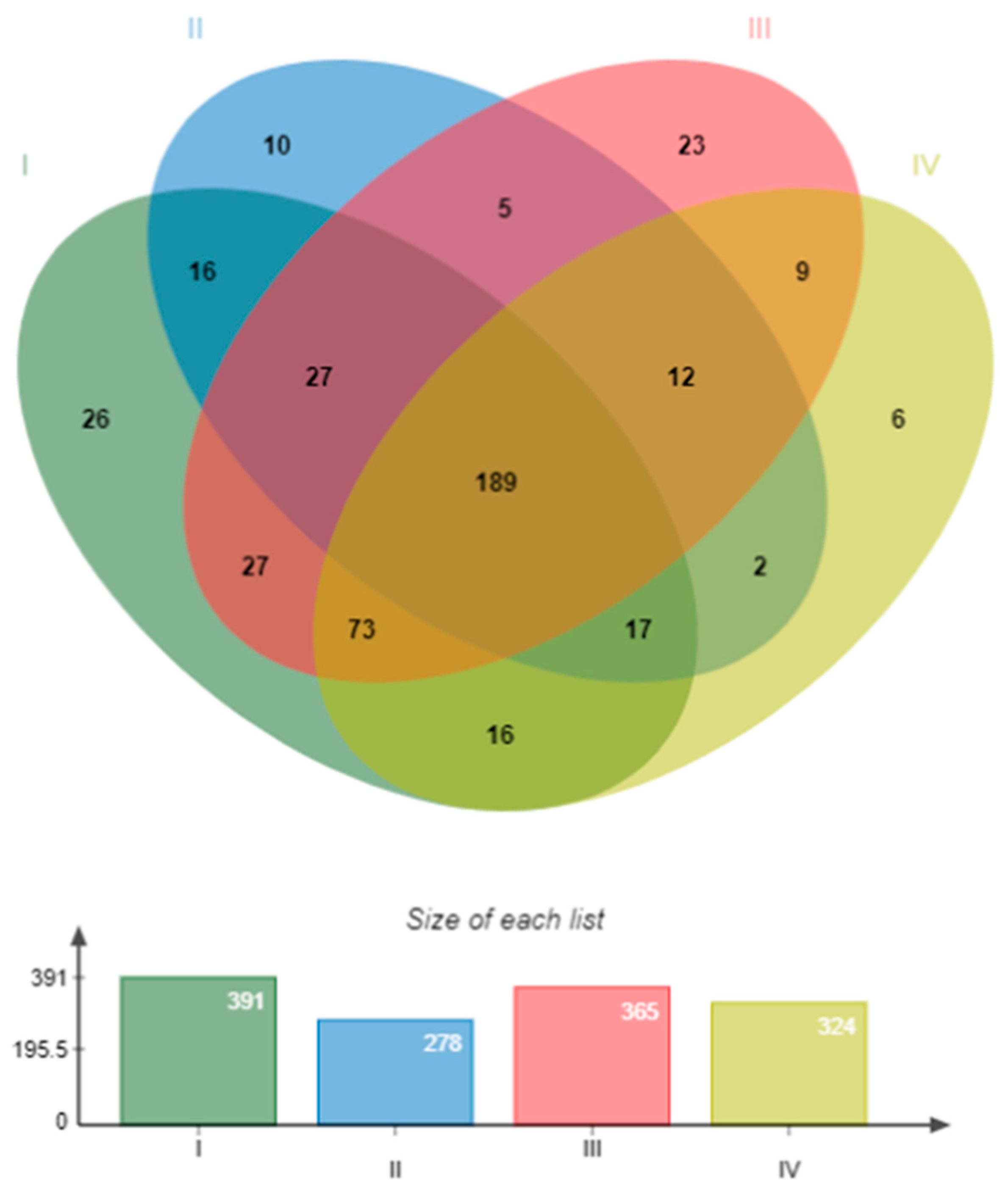
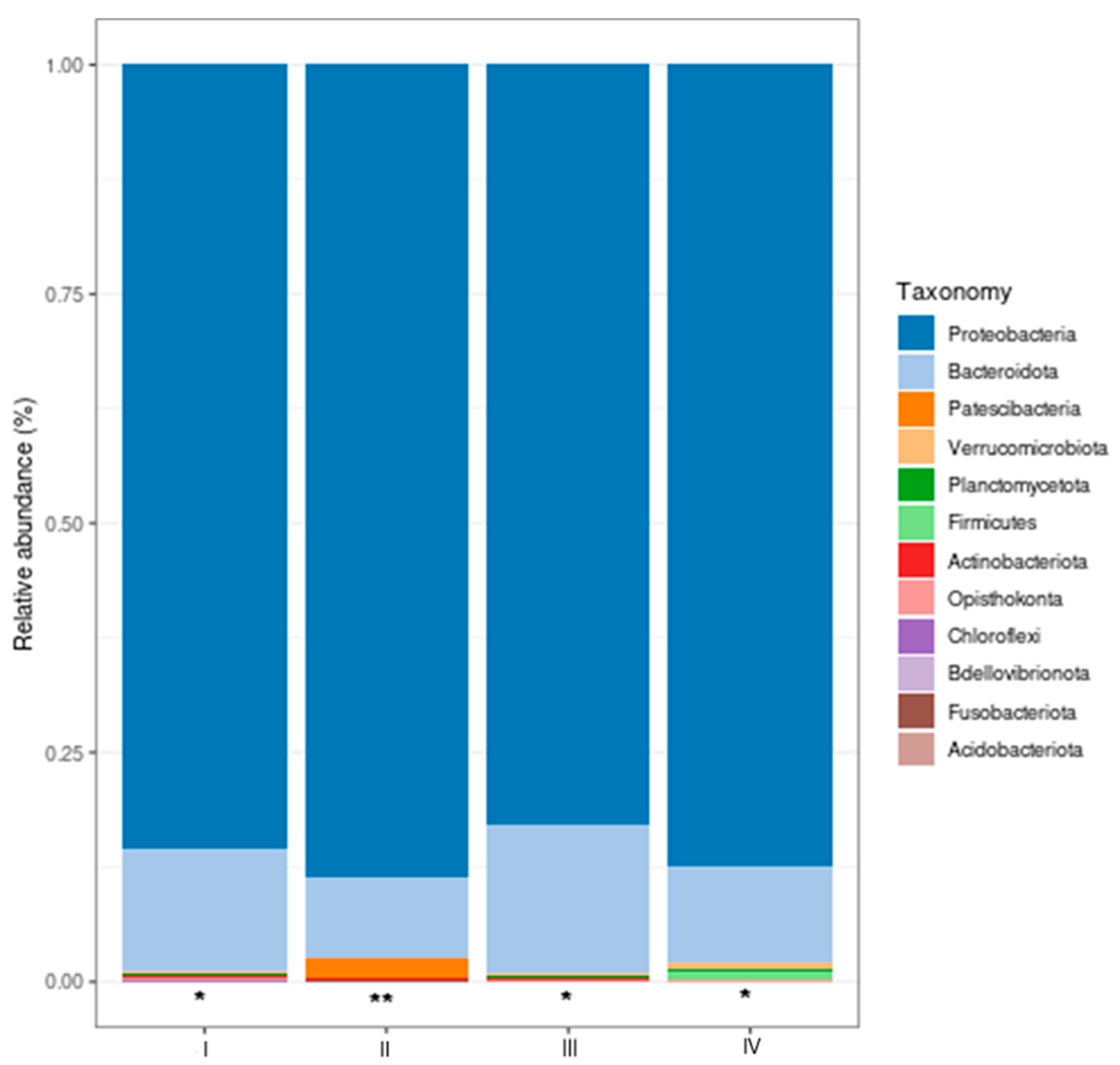
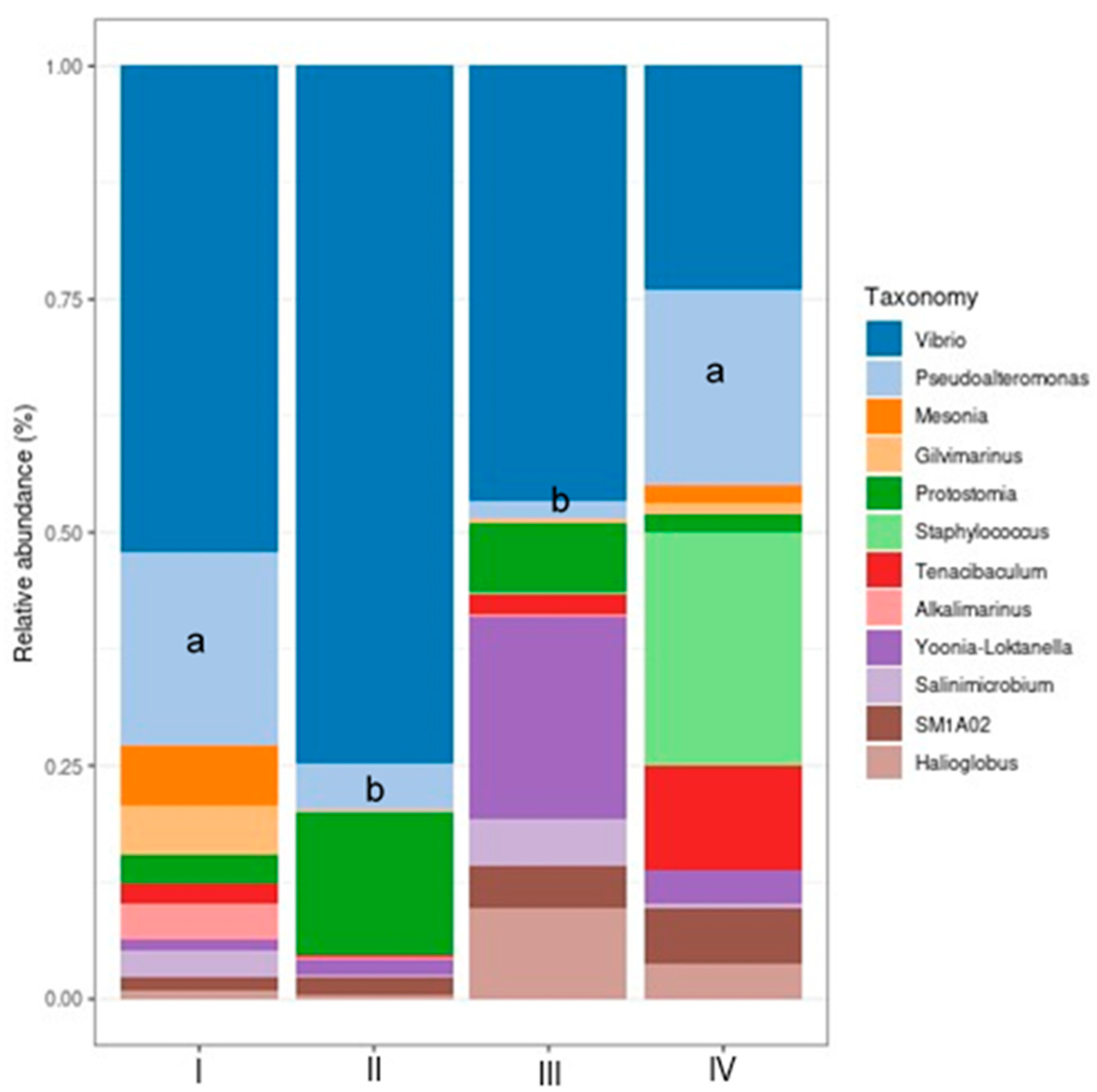
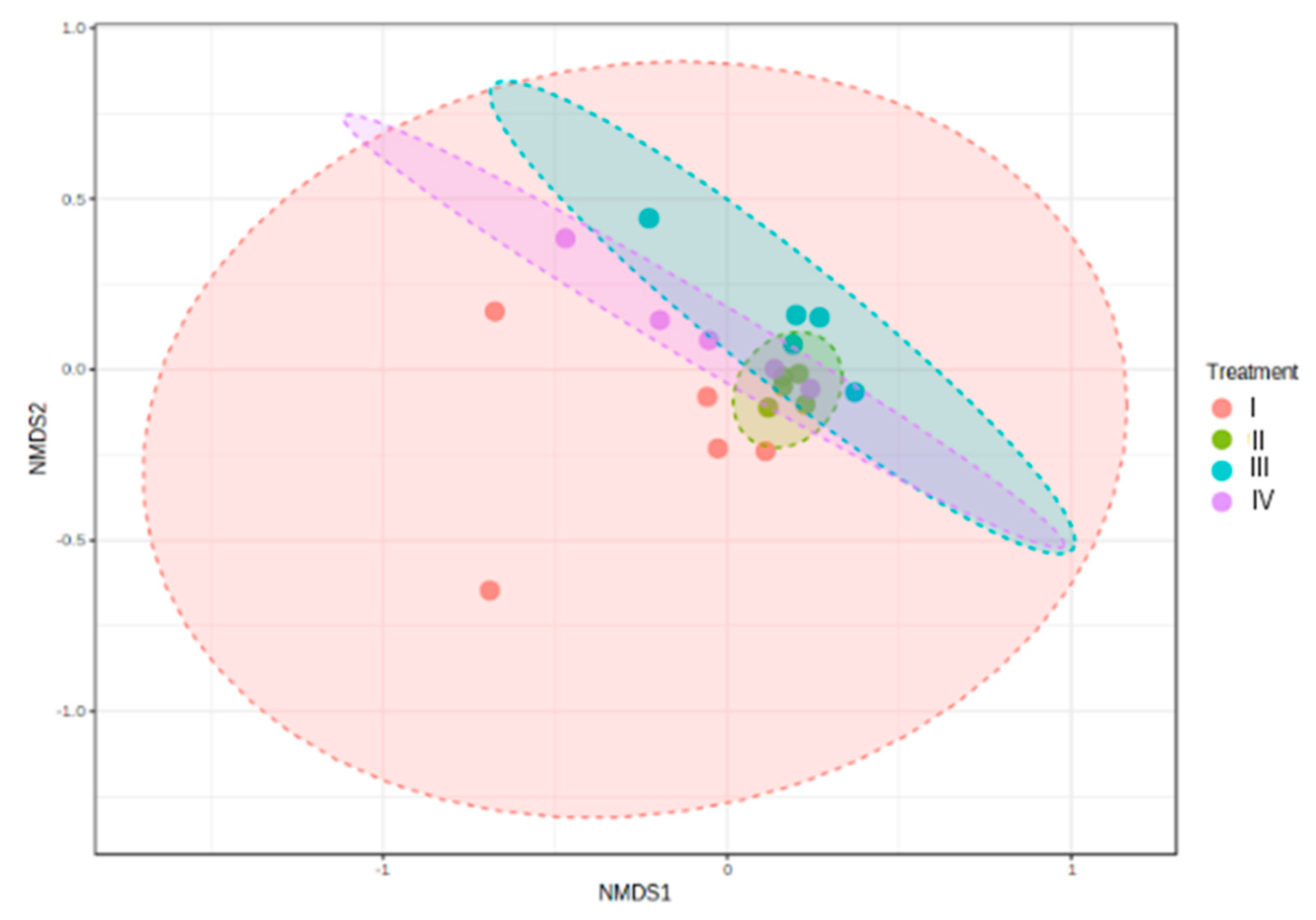
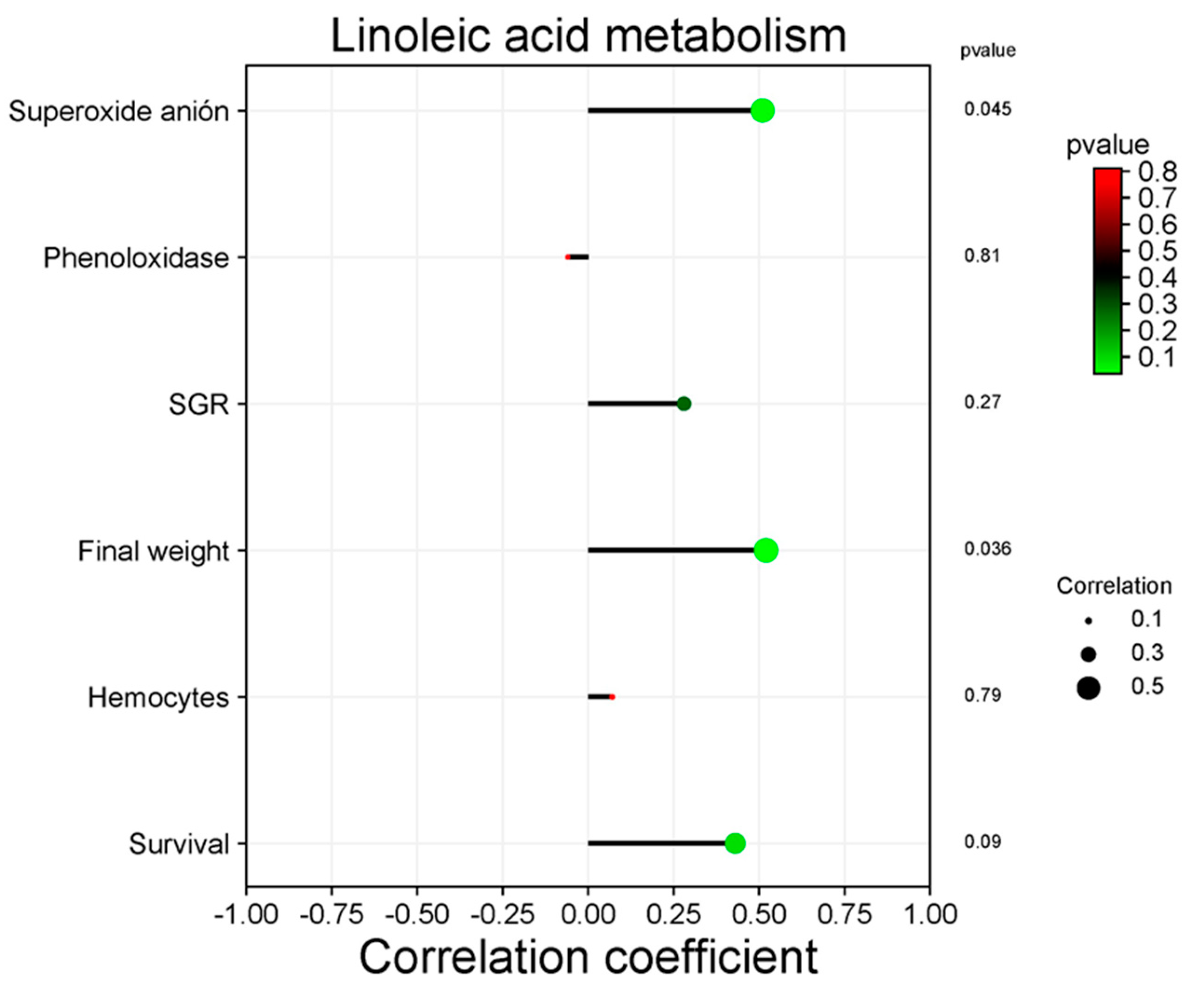
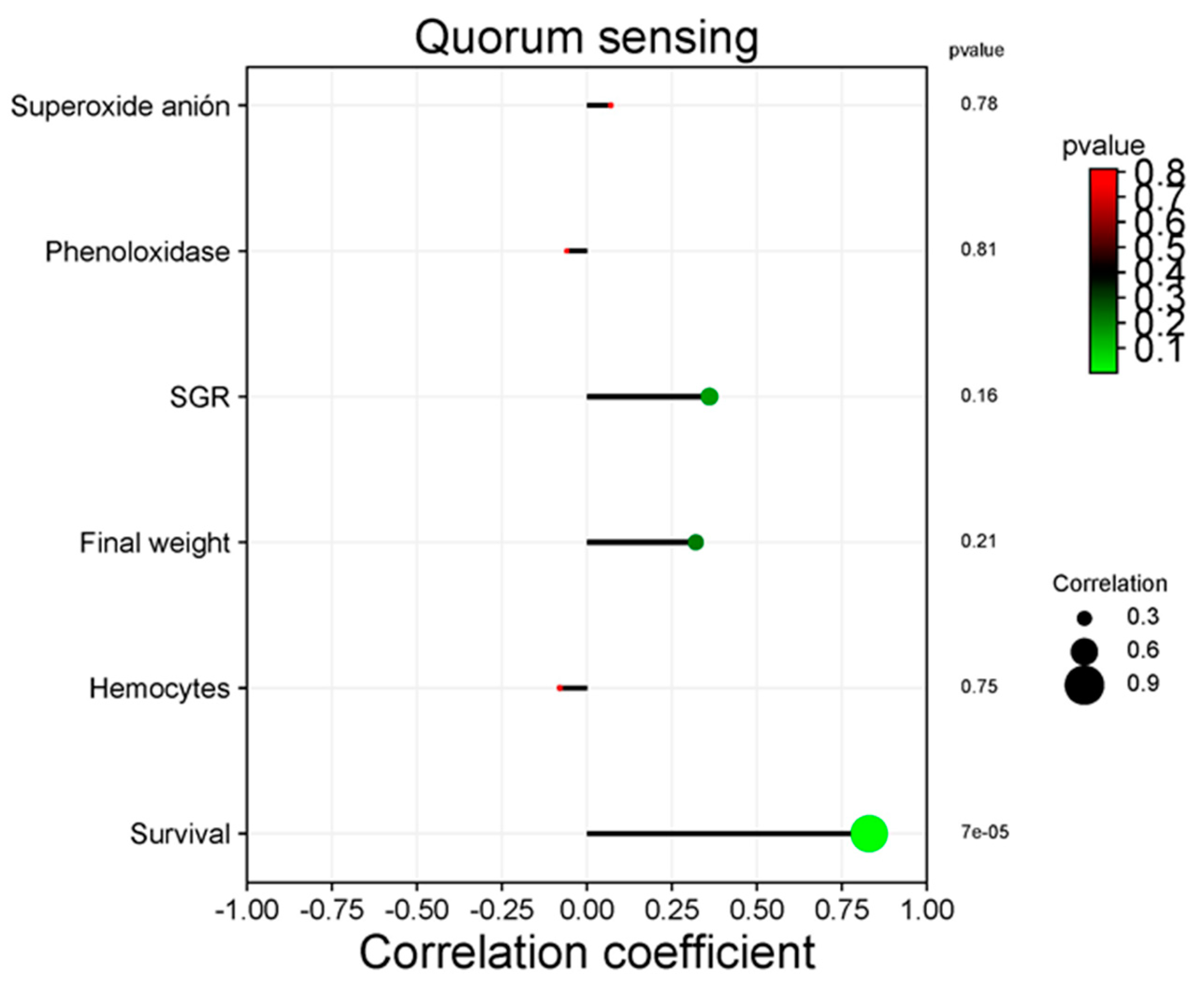
| Treatment | DO (mg mL-1) | pH | T (°C) | S (PSU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control (I) | 5.2±0.05 | 8.2±0.05 | 29.8±0.3 | 30±0.03 |
| II | 5.2±0.01 | 8.2±0.02 | 30.0±0.4 | 30±0.02 |
| III | 5.2±0.04 | 8.2±0.04 | 29.8±0.5 | 30±0.04 |
| IV | 5.3±0.08 | 8.2±0.06 | 30.0±0.3 | 30±0.03 |
| Optimal range | 4 to 10 | 8.1 to 9 | 23 to 30 | 15 to 35 |
| Shrimp growth | I | II | III | IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial weigth (g) | 0.7±0.05 | 0.79±0.06 | 0.73±0.05 | 0.77 0.07 |
| Final weigth (g) | 3.09±0.27b | 4.18±0.53a | 3.87±0.23ab | 4.10±0.09a |
| SGR (%d-1) | 4.16±0.32 0.3271b | 4.75±0.25 25.2522 | 4.76±0.33 | 4.78±0.35 |
| Indices | I | II | III | IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon | 1.71±0.62 | 1.22±0.18 | 1.19±0.53 | 1.47±0.35 |
| Simpson | 0.60±0.16 | 0.53±0.13 | 0.40±0.21 | 0.47±0.13 |
| Chao1 | 149.74±27.71a | 93.95±25.25b 25.2522 | 137.03±10.27a | 137.10±14.54a |
| ACE | 146.34±27.87a 27.87.64 | 88.95±28.97b 2282828.9728.9705 | 132.22±15.70ab | 115.50±45.48ab |
| Treatment | Metabolism (%) | GIP (%) | HD (%) | EIP (%) | CP (%) | OS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 61.05±1.22 | 11.01±0.15 | 11.43±0.63 | 1.39±0.23 | 6.90±0.58 | 8.19±0.11 |
| Bacilli in water | 60.03±0.14 | 10.92±0.05 | 11.94±0.04 | 1.59±0.01 | 7.38±0.04 | 8.10±0.01 |
| LAB in water | 60.19±0.44 | 10.88±0.13 | 11.87±0.17 | 1.55±0.10 | 7.22±0.35 | 8.27±0.32 |
| Bacilli and LAB in water | 60.16±0.39 | 11.00±0.05 | 11.85±0.17 | 1.49±0.14 | 7.21±0.22 | 8.27±0.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





