Submitted:
21 July 2024
Posted:
22 July 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Details
2.2. History
2.3. Assessment
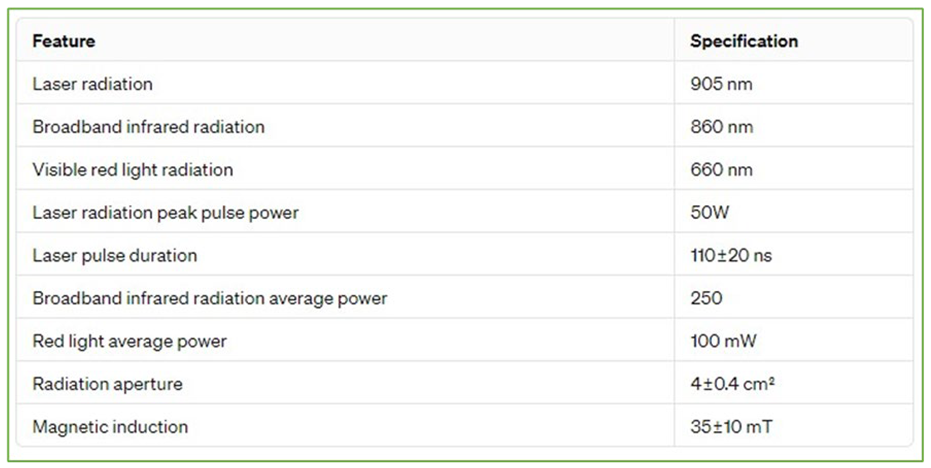
2.4. Methods
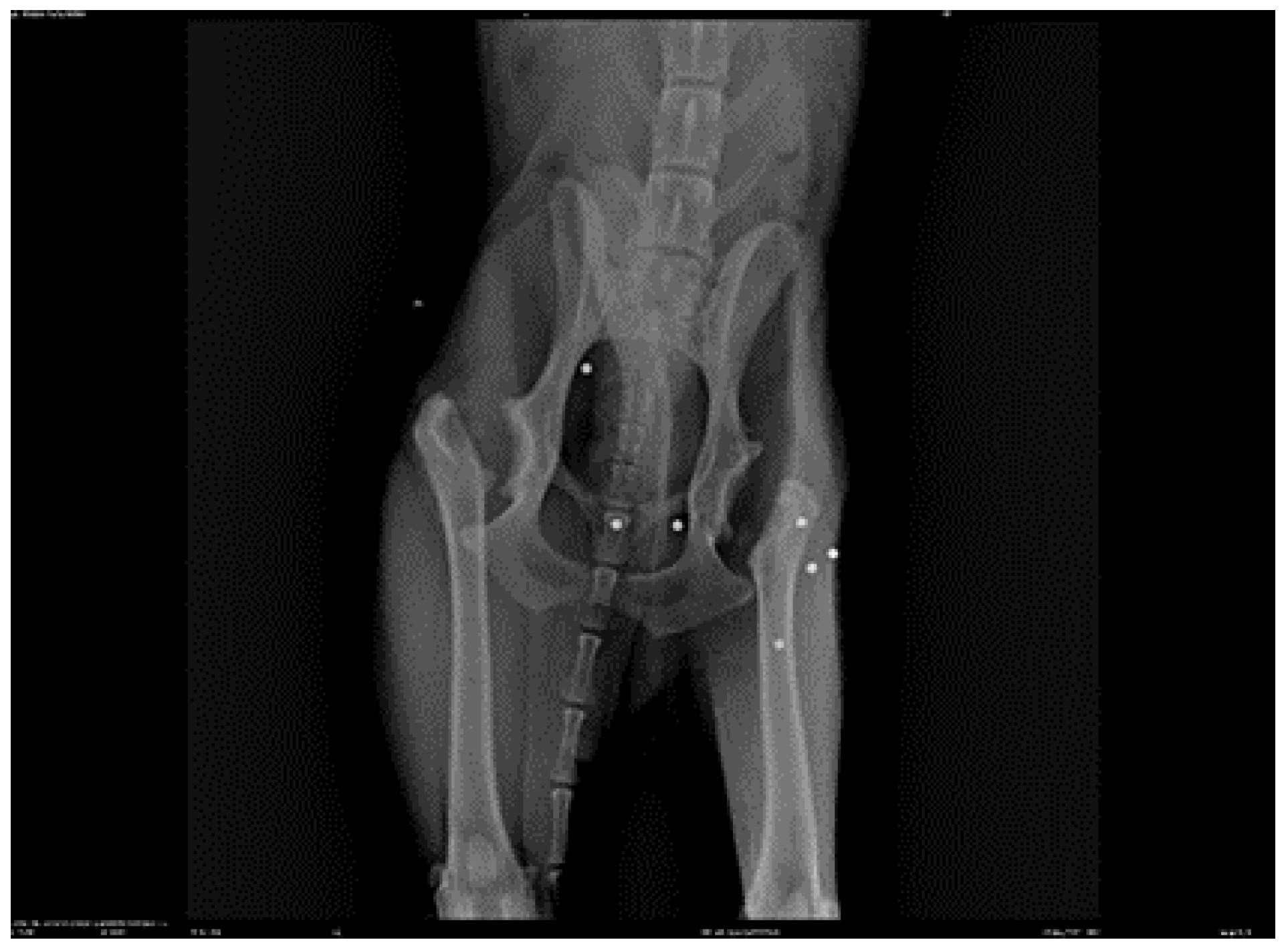
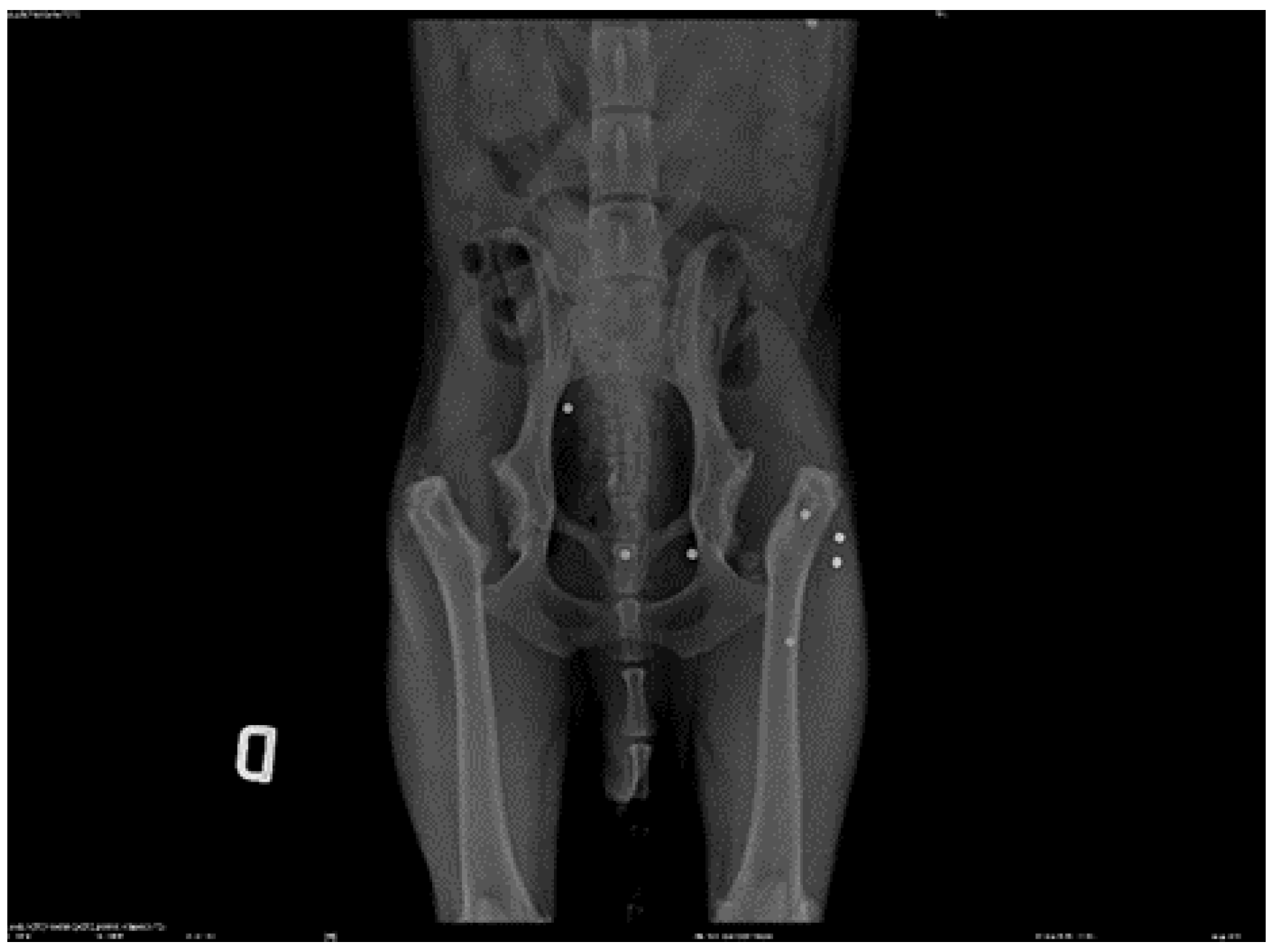
3. Results
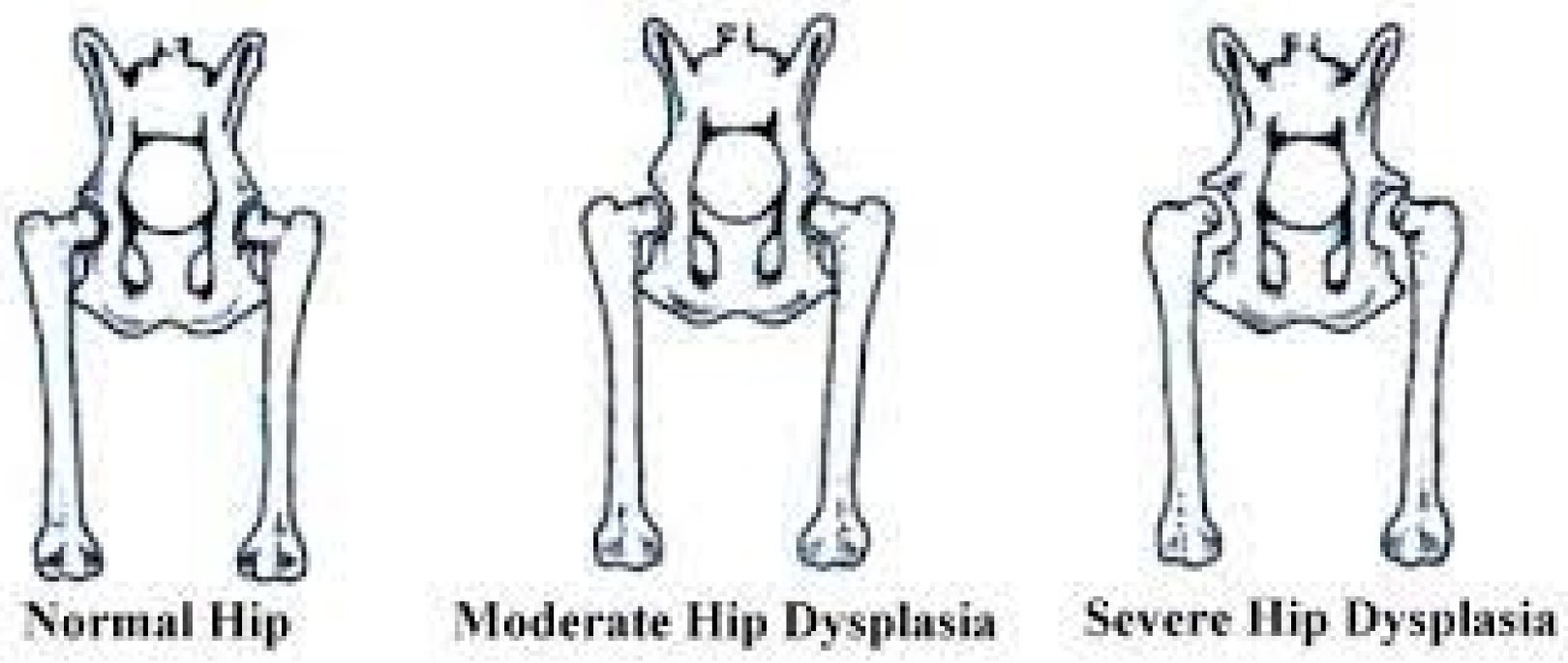
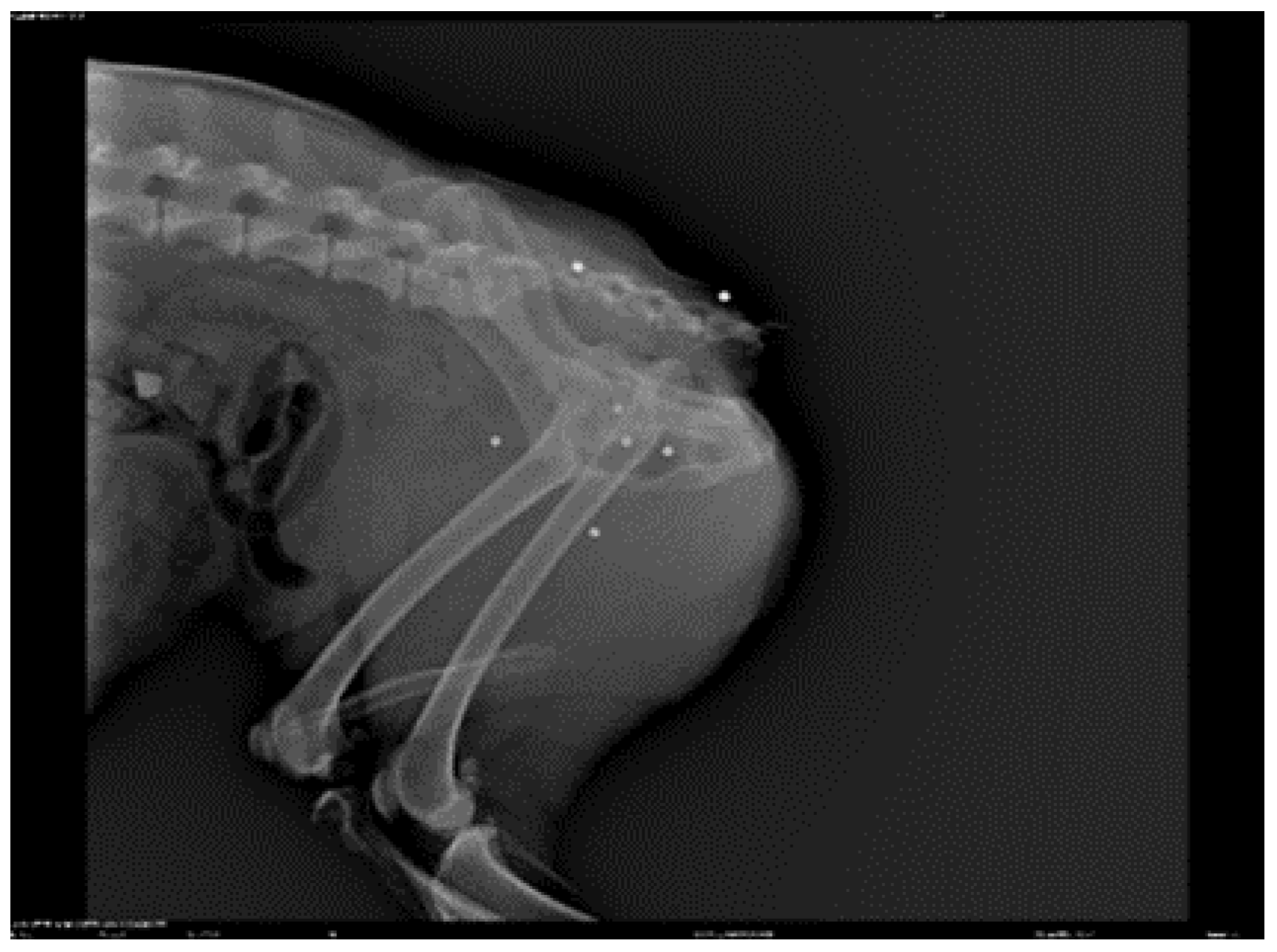
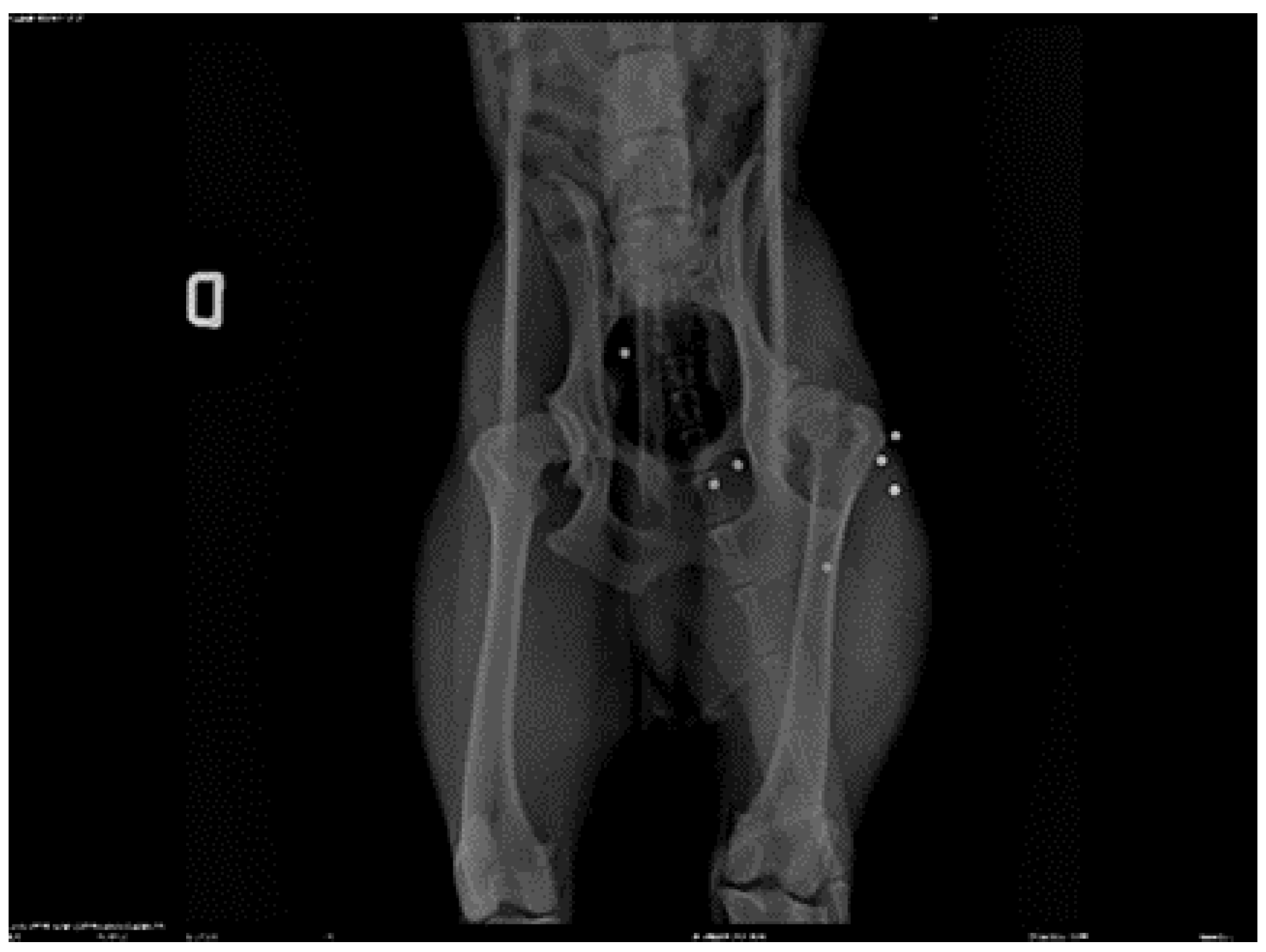
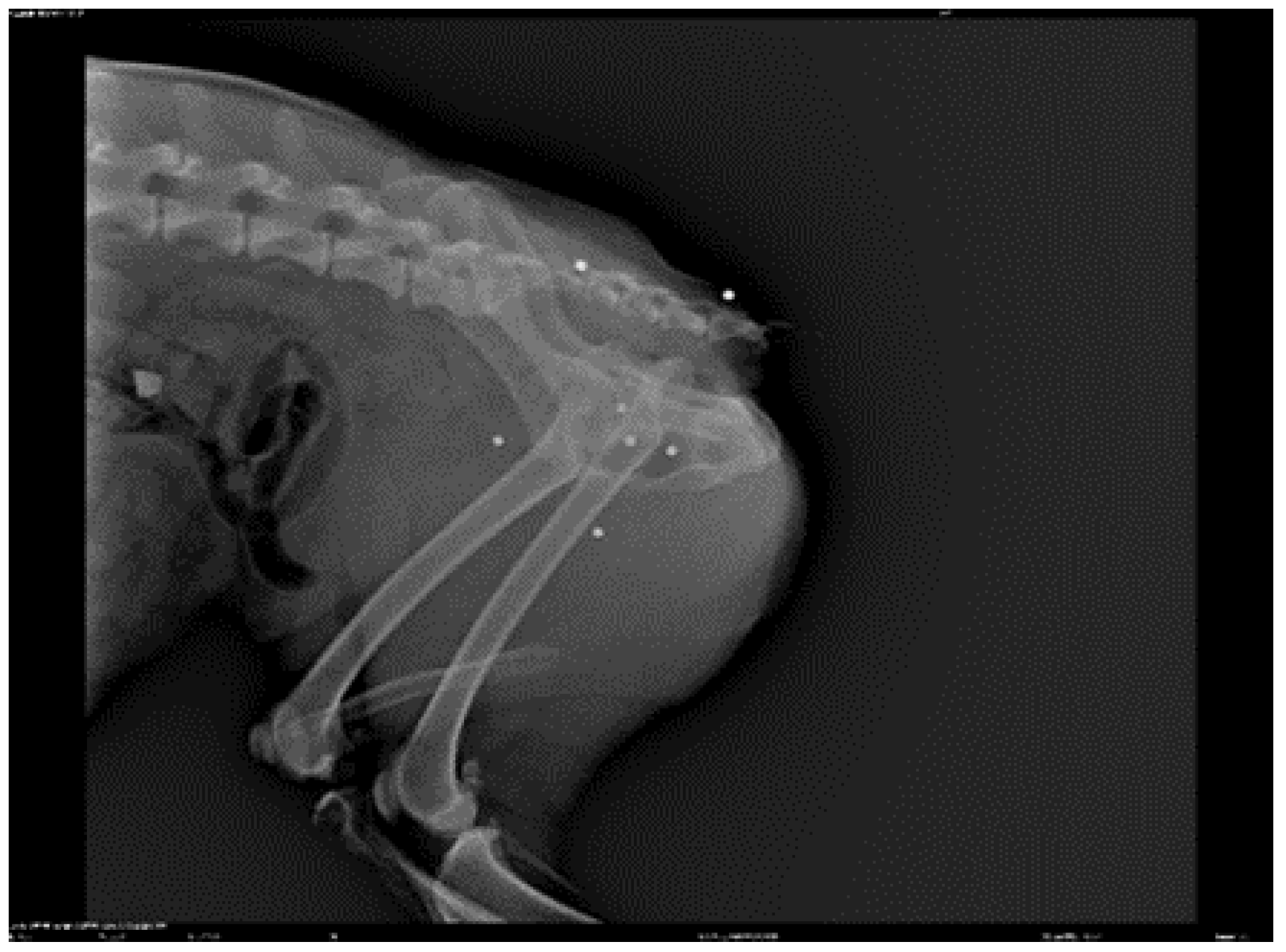

 |
 |
 |
 |
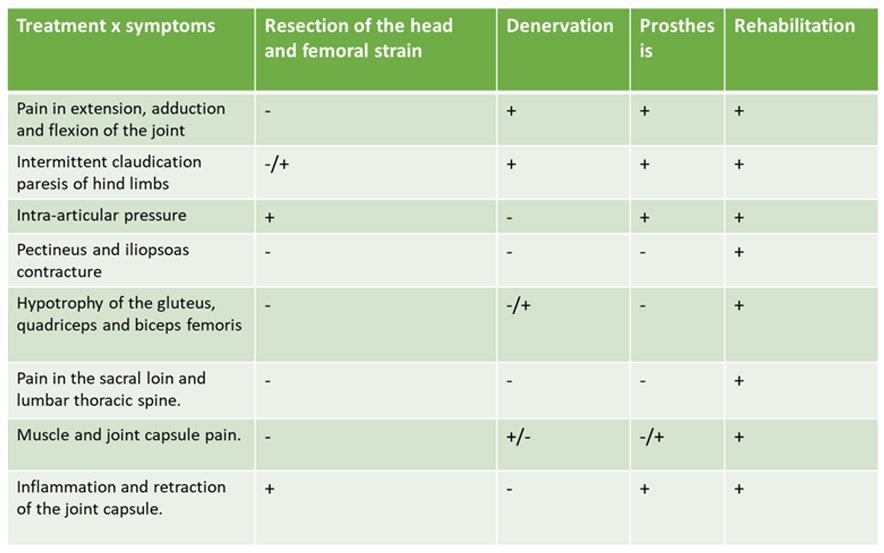
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
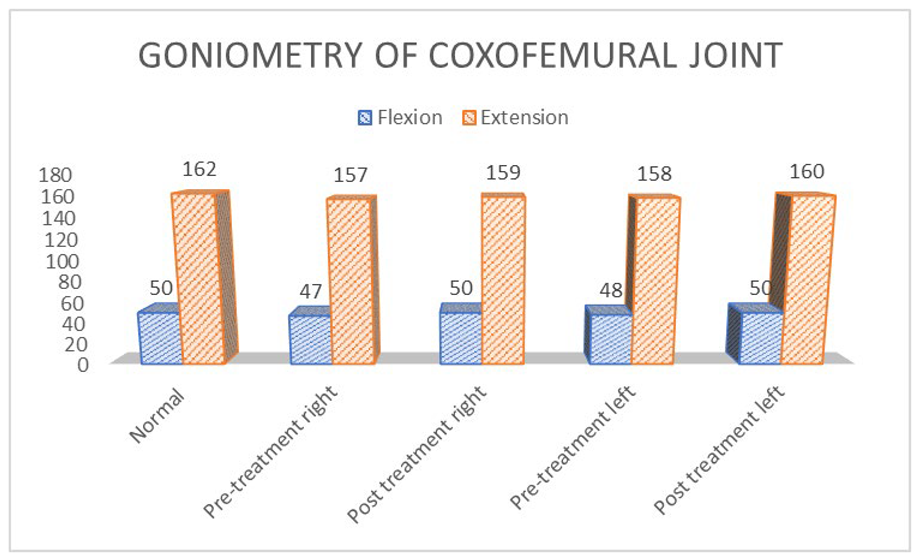
- Goniometry of the left coxofemoral joint pre-treatment: flexion 48° extension 158° (normal flexion 50° extension 162°) Post treatment flexion 50° extension 160°
- Goniometry of the right coxofemoral joint pre-treatment: flexion 47° extension 157° (normal flexion 50° extension 162°) Post treatment flexion 50° extension 159°
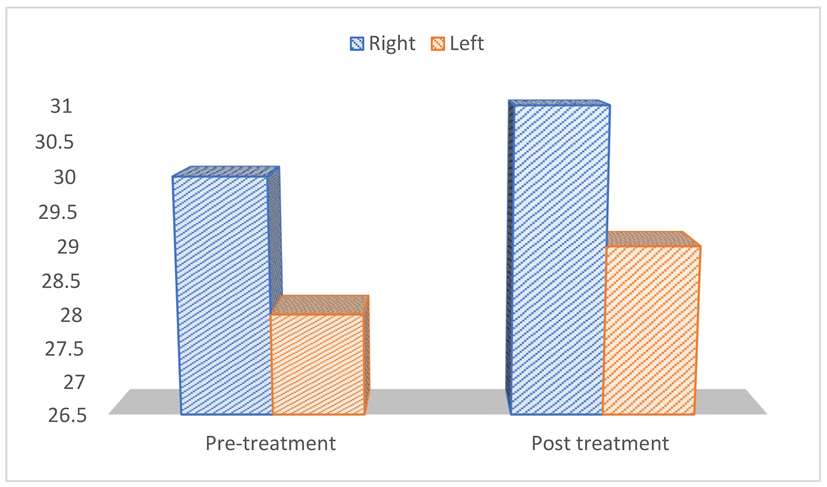
- Pre-treatment perimeter left thigh 28 cm left thigh 29 cm
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bettini, C.M.; et al. Incidence of coxofemoral dysplasia in Border Collie dogs. Unipar Veterinary and Zoological Sciences Archive 2007, 10, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin Junior, R.; Tomlinson, J. Radiographic diagnosis of canine hip dysplasia. Veterinary Medicine 1996, 91, 36–47. [Google Scholar]
- Minto, B.W.; et al. Clinical evaluation of acetabular denervation in dogs with coxofemoral dysplasia treated at the FMVZ Veterinary Hospital-Botucatu-SP. Veterinary and Animal Sciences 2012, 19, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, M.; et al. Effects of radial shock wave therapy on limb function of dogs with osteoarthritis of the hip. Veterinary Record 2007, 160, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, J.P.; Wind, A.; Davidson, A.P. Elbow dysplasia. In Hereditary Diseases of Bones and Joints in Dogs: Osteochondrosis, Hip Dysplasia, Elbow Dysplasia; Hanover: Schlütersche, 2000; pp. 41–94. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, A.A.; Berry, C.R.; Nahla, M.A. Quantitative evaluation of hip morphology to improve the identification of coxofemoral dysplasia in German Shepherd dogs. Am J Vet Res 2023, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piermattei, D. Arthroplasty for excision of the coxofemoral joint in dogs and cats. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol 2011, 24, 89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rocha, F.P.C.; et al. Coxofemoral dysplasia in dogs. Revista Cientí Eletrônica de Medicina Veterinária 2008, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Off, W.; Matis, U. Arthroplasty for excision of the coxofemoral joint in dogs and cats. Results of clinical, radiographic and gait analysis of the Department of Surgery, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Ludwig-Maximilians-University of Munich, Germany. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol 2010, 23, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virag, Y.; Gumpenberger, M.; Tichy, A.; Lutonsky, C.; Peham, C.; Bockstahler, B. Center of pressure and reaction forces of the soil in Labradors and Golden Retrievers with and without coxofemoral dysplasia at 4, 8 and 12 months of age. Front Vet Sci 2022, 9, 1087693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Reusing, M.S.O.; Villanova Júnior, J.A.; Weber, S.H. Efeitos terapêuticos do exercício em esteira aquática e da laserterapia de baixa intensidade em cães com displasia coxofemoral = Therapeutic effects of underwater treadmill exercise and low-level laser therapy in dogs with hip dysplasia. 2019. (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Ali, Q.; et al. Low Energy Laser Effects in Relieving Pain in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. International Journal of Medicine and Public Health 2018, 2, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Roush, J.K.; Unis, M.D.; Wodiske, T.; Baker, S.G. Comparison of four commercial devices to measure limb circumference in dogs. Veter Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2010, 23, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, A.R.S.; Denny, H.R.; Gibbs, C. Clinical hip dysplasia in growing dogs: the long-term results of conservative management. J. Small Anim. Pr. 1987, 28, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, T.; Nagy, G.; Barna, I.; Tefner, I.; Kadas, E.; Geher, P. The effect of physical therapy on beta-endorphin levels. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 100, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjordal, J.M.; Couppé, C.; Chow, R.T.; Tunér, J.; Ljunggren, E.A. A systematic review of low level laser therapy with location-specific doses for pain from chronic joint disorders. Aust. J. Physiother. 2003, 49, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockstahler, B.; Kräutler, C.; Holler, P.; Kotschwar, A.; Vobornik, A.; Peham, C. Pelvic Limb Kinematics and Surface Electromyography of the Vastus Lateralis, Biceps Femoris, and Gluteus Medius Muscle in Dogs with Hip Osteoarthritis. Veter Surg. 2011, 41, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockstahler, B.A.; Prickler, B.; Lewy, E.; Holler, P.J.; Vobornik, A.; Peham, C. Hind limb kinematics during therapeutic exercises in dogs with osteoarthritis of the hip joints. Am. J. Veter Res. 2012, 73, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.C.; Boston, R.C.; Coyne, J.C.; Farrar, J.T. Ability of the Canine Brief Pain Inventory to detect response to treatment in dogs with osteoarthritis. J. Am. Veter Med Assoc. 2008, 233, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartlidge, H. Hydrotherapy for the osteoarthritic dog: why might it help and is there any evidence? The Veterinary Nurse 2015, 6, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvet, A.; Laclair, J.; Elliott, D.A.; German, A.J. Incorporation of exercise, using an underwater treadmill, and active client education into a weight management program for obese dogs. Can. Vet. J. 2011, 52, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collard, F.; et al. Canine hip denervation: Comparison between clinical outcome and gait analysis. Revue de Medecine Veterinaire 2010, 161, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Crestani, M.V.; Telöken, M.A.; Gusmão, P.D.F. Impacto femoroacetabular: uma das condições precursoras da osteoartrose do quadril. Rev Bras Ortop 2006, 41, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Denning, W.E.; Bressel, E.; Dolny, D.G. Underwater Treadmill Exercise as a Potential Treatment for Adults With Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2010, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, R. Hidroterapia. In Fisiatria em Pequenos Animais; Lopes, R.S., Diniz, R., Eds.; Editora Inteligente: São Paulo, 2018; pp. 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Doust, S.; et al. Preliminary study of the hip dysplasia incidence based on clinical and radiographical examination in large breed dogs referred to veterinary teaching hospital of Ferdowsi University of Mashhad. Journal of Veterinary Research 2018, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Duff, R.; Campbell, J. Long term results of excision arthroplasty of the canine hip. Veter Rec. 1977, 101, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge-Hughes, L. Hip and Sacroiliac Disease: Selected Disorders and Their Management with Physical Therapy. Clin. Tech. Small Anim. Pr. 2007, 22, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginja, M.; Silvestre, A.; Gonzalo-Orden, J.; Ferreira, A. Diagnosis, genetic control and preventive management of canine hip dysplasia: A review. Veter J. 2009, 184, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greshake, R.J.; Ackerman, N. Ultrasound evaluation of the coxofemoral joints of the canine neonate. Veter Radiol. Ultrasound 1993, 34, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusi, N.; Tomas-Carus, P.; Häkkinen, A.; Häkkinen, K.; Ortega-Alonso, A. Exercise in waist-high warm water decreases pain and improves health-related quality of life and strength in the lower extremities in women with fibromyalgia. Arthritis Care Res. 2006, 55, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, T.A. Conservative Management of Hip Dysplasia. Veterinary Clinics: Small Animal Practice 2017, 47, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrigson, B.; Norberg, I.; Olssons, S. On the Etiology and Pathogenesis of Hip Dysplasia: a Comparative Review. J. Small Anim. Pr. 1966, 7, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honmura, A.; Yanase, M.; Obata, J.; Haruki, E. Therapeutic effect of Ga-Al-As diode laser irradiation on experimentally induced inflammation in rats. Lasers Surg. Med. 1992, 12, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaegger, G.; Marcellin-Little, D.J.; Levine, D. Reliability of goniometry in Labrador Retrievers. Am. J. Veter Res. 2002, 63, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinet, G.H.; Kass, P.H.; Wallace, L.J.; Guffy, M.M. Association between pelvic muscle mass and canine hip dysplasia. J. Am. Veter Med Assoc. 1997, 210, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazis, A. Canine hip dysplasia. Part I: Aetiopathogenesis & diagnostic approach. Hellenic Journal of Companion Animal Medicine 2016, 5, 37. [Google Scholar]
- König, H.E.; Liebich, H.-G. Anatomia dos Animais Domésticos: Texto e Atlas Colorido. Artmed Editora 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, G.; Holt, S. The Effects of Low-level Laser Therapy on the Gait of the Osteoarthritic Canine Hindlimb. BVNA Congress 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Matera, J.M.; Tatarunas, A.C.; Oliveira, S.M. Uso do laser arseneto de gálio (904nm) após excisão artroplástica da cabeça do fêmur em cães. Acta Cirúrgica Brasileira 2003, 18, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, G.; O’donovan, J.; Jones, B.; McAllister, H.; Seed, M.; Mooney, C. Randomised double-blind, positive-controlled trial to assess the efficacy of glucosamine/chondroitin sulfate for the treatment of dogs with osteoarthritis. Veter J. 2007, 174, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, S.; Coutinho, I.; Rebelo, P. Hidroterapia canina. Revista Portuguesa de Ciências Veterinárias 2015, 110, 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Millis, D.L.; Levine, D. The Role of Exercise and Physical Modalities in The Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Veter Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pr. 1997, 27, 913–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.A.; Ruiz-Gómez, M.J.; Gil-Carmona, L.; Souvirón, A.; Martínez-Morillo, M. He-Ne laser has no effect on cell cycle phases of human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Rev. Esp. Fisiol. 1995, 51, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Pluhar, G.E.; Nielsen, C. Diagnosis and treatment of hind limb muscle strain injuries in 22 dogs. Veter Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2005, 18, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.C.; Parisi, J.R.; Maglioni, C.B.; Machado, G.B.; Barragán-Iglesias, P.; Silva, J.R.T.; Silva, M.L. Antinociceptive effects of low-level laser therapy at 3 and 8 j/cm2 in a rat model of postoperative pain: possible role of endogenous Opioids. Lasers Surg. Med. 2017, 49, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prankel, S. Hydrotherapy in practice. Practice 2008, 30, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuvir, H.; et al. Treatment of canine hip dysplasia: A review. J Anim Sci Adv 2013, 3, 589–597. [Google Scholar]
- Remedios, A.M.; Fries, C.L. Treatment of canine hip dysplasia: a review. Can. Vet. J. 1995, 36, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Syrcle, J. Hip Dysplasia: Clinical Signs and Physical Examination Findings. Veterinary Clinics: Small Animal Practice 2017, 47, 769–775. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, G.; Tai, M.; Zhao, M. Electrically stimulated cell migration and its contribution to wound healing. Burn. Trauma 2018, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upariputti, R.; Vijarnsorn, M.; Niyom, S.; Boonyong, S. Effect of interferential current therapy on ground reaction force in dogs with hip osteoarthritis: A randomized placebo controlled cross-over clinical trial. Thai J. Veter Med. 2018, 48, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vince, K.J. Canine hip dysplasia: surgical treatment for the military working dog. Army Med. Dep. J. 2007, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, L.J. Pectineus Tendon Surgery for the Management of Canine Hip Dysplasia. Veter Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pr. 1992, 22, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, J.P.; Cartee, R.E.; Marich, K.W. Preliminary study on the use of ultrasonic transmission imaging to evaluate the hip joint in the immature dog. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1983, 9, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, E. Swim to Recovery: Canine Hydrotherapy Healing. Veloce Publishing Ltd., 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zink, C.; Carr, B.J. What is a canine athlete? Canine sports medicine and rehabilitation 2018, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zink, C.; Van Dyke, J.B. Canine sports medicine and rehabilitation. John Wiley & Sons, 2018. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





