Submitted:
17 July 2024
Posted:
18 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
Study Design
Study Population
Sample Size
Variables and Data Collection
Statistical Analysis
Ethical Consideration
Results
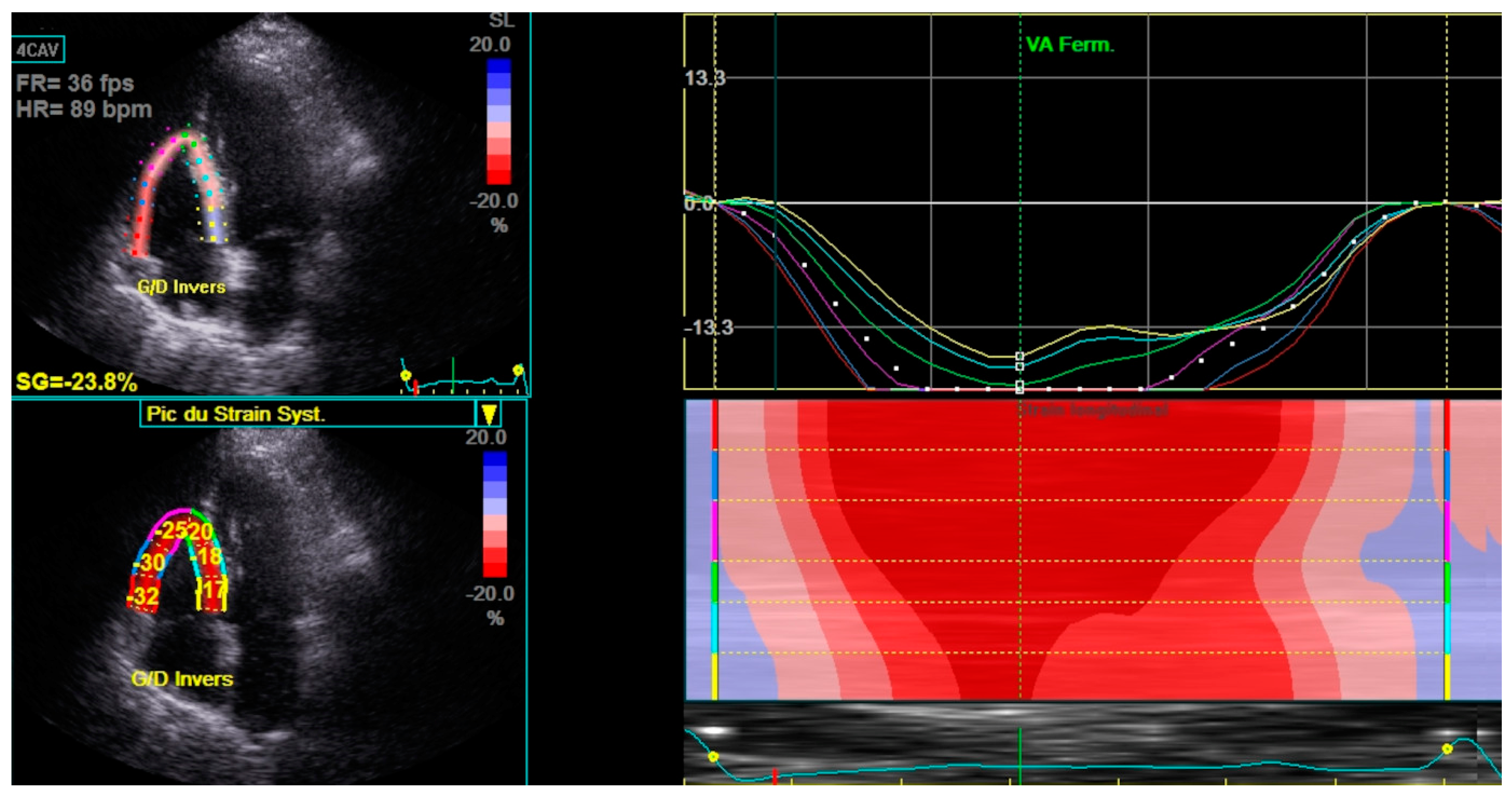
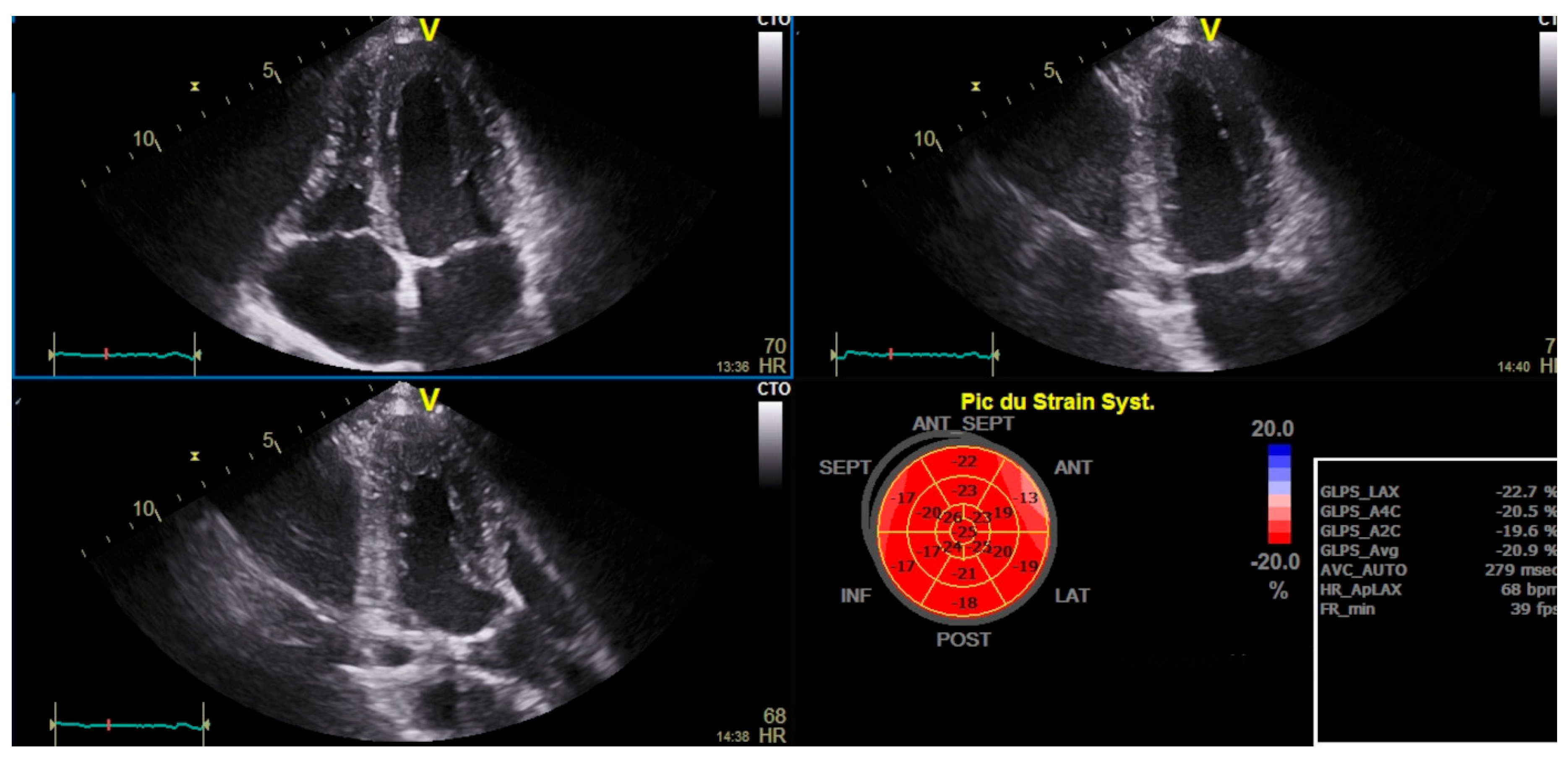
Haut du Formulaire
Discussion
Study Limitaions
Conclusions
Abbreviations
| IVS | inter ventricular septum |
| LVEDD | left ventricle end diastolic diameter |
| LVEF | Left ventricular ejection fraction |
| PW | posterior wall |
| RV | right ventricular |
| TAPSE | tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion |
| TTE | Conventional transthoracic echocardiography |
| CAT | COPD assessment test |
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| FAC | fractional area change |
| FEV1 | forced expiratory volume in the first second |
| GLS | global longitudinal strain |
| IVC | inferior vena cava |
| LA | Left atrium |
| LAA | left atrial area |
| m | meter |
| ml | milliliter |
| PH | Pulmonary hypertension |
| RA | Right atrium |
| S wave | right ventricular systolic myocardial velocity |
| RAA | right atrium area |
| RVBD | Right ventricle basal diameter |
| RV MCD | Right ventricle mid cavity diameter |
| RVLD | Right ventricle longitudinal diameter |
| sPAP | Systolic pulmonary artery pressure |
| TAD | tricuspid annulus diameter |
| TAPSE | tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion |
References
- Murray, C.J.; Lopez, A.D. Global mortality, disability, and the contribution of risk factors: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 1997, 349, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, K.F.; Hurd, S.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Buist, S.A.; Calverley, P. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: GOLD Executive Summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007, 176, 532–55. [Google Scholar]
- Almagro, P.; Barreiro, B.; de Echagüen, A.O.; Quintana, S.; Carballeira, M.R.; Heredia, J.L.; Garau, J. Risk Factors for Hospital Readmission in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Respiration 2006, 73, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNee, W. Pathophysiology of cor pulmonale in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Part One. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994, 150, 833–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hesse, K.; Bourke, S.; Steer, J. Heart failure in patients with COPD exacerbations: Looking below the tip of the iceberg. Respir. Med. 2022, 196, 106800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Chhabra, S.K. Coexistent Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease-Heart Failure: Mechanisms, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Dilemmas. Indian J. Chest Dis. Allied Sci. 2022, 52, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elçioğlu, B.C.; Kamat, S.; Yurdakul, S.; Şahin, .T.; Sarper, A.; Yıldız, P.; Aytekin, S. Assessment of subclinical left ventricular systolic dysfunction and structural changes in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Intern. Med. J. 2021, 52, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoos, M.M.; Dalsgaard, M.; Kjærgaard, J.; Moesby, D.; Jensen, S.G.; Steffensen, I.; Iversen, K.K. Echocardiographic predictors of exercise capacity and mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2013, 13, 84–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolarek, D.; Gruchała, M.; Sobiczewski, W. Echocardiographic evaluation of right ventricular systolic function: The traditional and innovative approach. Cardiol. J. 2017, 24, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh SJ, Puhan MA, Andrianopoulos V, Hernandes NA, Mitchell KE, Hill CJ, et al. An official systematic review of the European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society: measurement properties of field walking tests in chronic respiratory disease. Eur Respir J. déc 2014;44(6):1447-78.
- Serhier Z, Bendahhou K, Ben Abdelaziz A, Bennani MO. Methodological sheet n°1: How to calculate the size of a sample for an observational study? Tunis Med. janv 2020;98(1):1-7.
- Agustí A, Celli BR, Criner GJ, Halpin D, Anzueto A, Barnes P, et al. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2023 Report: GOLD Executive Summary. Eur Respir J. avr 2023;61(4):2300239.
- Houben-Wilke, S.; Janssen, D.J.A.; Franssen, F.M.E.; Vanfleteren, L.E.G.W.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Spruit, M.A. Contribution of individual COPD assessment test (CAT) items to CAT total score and effects of pulmonary rehabilitation on CAT scores. Heal. Qual. Life Outcomes 2018, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, B.L.; Steenbruggen, I.; Miller, M.R.; Barjaktarevic, I.Z.; Cooper, B.G.; Hall, G.L.; Hallstrand, T.S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; McCarthy, K.; McCormack, M.C.; et al. Standardization of Spirometry 2019 Update. An Official American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society Technical Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, e70–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firnhaber, J.M. Performance and Interpretation of Office Spirometry. Prim. Care: Clin. Off. Pr. 2021, 48, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh SJ, Puhan MA, Andrianopoulos V, Hernandes NA, Mitchell KE, Hill CJ, et al. An official systematic review of the European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society: measurement properties of field walking tests in chronic respiratory disease. Eur Respir J. déc 2014;44(6):1447-78.
- Krittanawong C, Maitra NS, Hassan Virk HU, Farrell A, Hamzeh I, Arya B, et al. Normal Ranges of Right Atrial Strain. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. mars 2023;16(3):282-94.
- Morris, D.A.; Krisper, M.; Nakatani, S.; Köhncke, C.; Otsuji, Y.; Belyavskiy, E.; Radha Krishnan, A.K.; Kropf, M.; Osmanoglou, E.; Boldt, L.-H.; et al. Normal range and usefulness of right ventricular systolic strain to detect subtle right ventricular systolic abnormalities in patients with heart failure: A multicentre study. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 18, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pio, S.M.; Medvedofsky, D.; Stassen, J.; Delgado, V.; Namazi, F.; Weissman, N.J.; Grayburn, P.; Kar, S.; Lim, D.S.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Changes in Left Ventricular Global Longitudinal Strain in Patients With Heart Failure and Secondary Mitral Regurgitation: The COAPT Trial. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2023, 12, e029956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elçioğlu, B.C.; Kamat, S.; Yurdakul, S.; Şahin, .T.; Sarper, A.; Yıldız, P.; Aytekin, S. Assessment of subclinical left ventricular systolic dysfunction and structural changes in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Intern. Med. J. 2021, 52, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonisen, N.R.; Connett, J.E.; Enright, P.L.; Manfreda, J. Hospitalizations and Mortality in the Lung Health Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunninghake, D.B. Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2005, 2, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaouat, A.; Bugnet, A.-S.; Kadaoui, N.; Schott, R.; Enache, I.; Ducoloné, A.; Ehrhart, M.; Kessler, R.; Weitzenblum, E. Severe Pulmonary Hypertension and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.; Avian, A.; Bachmaier, G.; Troester, N.; Tornyos, A.; Douschan, P.; Foris, V.; Sassmann, T.; Zeder, K.; Lindenmann, J.; et al. Severe Pulmonary Hypertension in COPD. Chest 2022, 162, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst JR, Skolnik N, Hansen GJ, Anzueto A, Donaldson GC, Dransfield MT, et al. Understanding the impact of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations on patient health and quality of life. Eur J Intern Med. mars 2020;73:1-6.
- Freixa, X.; Portillo, K.; Paré, C.; Garcia-Aymerich, J.; Gomez, F.P.; Benet, M.; Roca, J.; Farrero, E.; Ferrer, J.; Fernandez-Palomeque, C.; et al. Echocardiographic abnormalities in patients with COPD at their first hospital admission. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 41, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.H.; Rashid, M.H.; A Miah, N.; Israt, S.; Atiqullah, S.; Akbar, M.S. Correlation Study between COPD and Heart Failure in Elderly Patient. . 2022, 31, 498–505. [Google Scholar]
- Jörgensen, K.; Müller, M.F.; Nel, J.; Upton, R.N.; Houltz, E.; Ricksten, S.-E. Reduced Intrathoracic Blood Volume and Left and Right Ventricular Dimensions in Patients With Severe Emphysema. Chest 2007, 131, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, C.; van Essen, F.; Linnhoff, F.; Schueler, R.; Hammerstingl, C.; Nickenig, G.; Skowasch, D.; Weber, M. Speckle tracking echocardiography in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and overlapping obstructive sleep apnea. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2016, ume 11, 1823–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, S.; Muñoz, X.; Rios, J.; Morell, F.; Ferrer, J. Body weight and comorbidity predict mortality in COPD patients treated with oxygen therapy. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Pislaru, S.V.; Soo, W.M.; Huang, R.; Greason, K.L.; Mathew, V.; Sandhu, G.S.; Eleid, M.F.; Suri, R.M.; Oh, J.K.; et al. Impact of right ventricular size and function on survival following transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 221, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilde JM, Skjørten I, Grøtta OJ, Hansteen V, Melsom MN, Hisdal J, et al. Right Ventricular Dysfunction and Remodeling in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Without Pulmonary Hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. sept 2013;62(12):1103-11.
- Hilde, J.M.; Skjørten, I.; Grøtta, O.J.; Hansteen, V.; Melsom, M.N.; Hisdal, J.; Humerfelt, S.; Steine, K. Right Ventricular Dysfunction and Remodeling in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Without Pulmonary Hypertension. Circ. 2013, 62, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonauro, A.; Santoro, C.; Galderisi, M.; Canora, A.; Sorrentino, R.; Esposito, R.; Lembo, M.; Canonico, M.E.; Ilardi, F.; Fazio, V.; et al. Impaired Right and Left Ventricular Longitudinal Function in Patients with Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Han, W.; Li, J. Readmission rate for acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Med. 2022, 206, 107090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total (N=80 ) N(%) or Mean ±SD |
|---|---|
| Age (Years) | 65.6±8.9 |
| Gender (n, %) | |
| Male | 67(83.8) |
| Female | 13(16.3) |
| Living Habits (n, %) | |
| Current smoker | 29(36 .2) |
| Former smoker | 42(52.5) |
| Never smoked | 9(11.3) |
| FEV1 (ml) | 1954 ±639 |
| 6MWD (meter) | 396±121 |
| CAT score (n, %) | |
| <10 | 24(30.0) |
| 10-20 | 30(37.5) |
| 21-30 | 17(21.3) |
| >30 | 9(11.3) |
| Cardiac echography | Total(n=80) Mean±SD |
|---|---|
| LVEF (%) | 60.7±5.1 |
| FAC (%) | 45.4±7.7 |
| TAD ( mm) | 27.7±2.7 |
| RVBD (mm) | 32.3±3.6 |
| RV MCD (mm) | 24.4±2.5 |
| RVLD (mm) | 62.5±5.7 |
| RAA (cm2) | 12.6±2.1 |
| S RV (cm/s) | 12.8±2.1 |
| TAPSE (mm) | 20.8±3.28 |
| sPAP (mmHg) | 32.8±6.4 |
| RV wall thickness (mm) | 6.6±0.8 |
| IVC (mm) | 14.9±1.3 |
|
E/A ratio E/e’ ratio |
0.98±0.29 6.2±3.3 |
| LAA (cm2) | 14.5±2.4 |
| IVS thickness (mm) | 9.0±0.8 |
| LVEDD (mm) | 45.8±3.4 |
| PW thickness (mm) | 8.7±0.9 |
| RV Strain (%) | -19.9±3.7 |
| RA Strain (%) | 24.5±6.6 |
| LV GLS (%) | -21.1±2.4 |
| Characteristics | Normal RV Strain (N=32) N (%) Or Mean±SD | Impaired RV Strain (N=48) N (%) Or Mean±SD |
P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Years) | 65.4±.8 | 65.7±9.5 | 0.87 |
| Gender | 0.083 | ||
| Male | 24(35.8) | 43(64.2) | |
| Female | 8(61.5) | 5(38.5) | |
| Living Habits | 0.005 | ||
| Current smoker | 17(9.3) | 12(40.7) | |
| Former smoker | 9(21.4) | 33(78.6) | |
| Never smoked | 6(66.7) | 3(33.3) | |
| FEV1(ml) | 2182±407 | 1626±727 | 0.012 |
| 6MWD(m) | 470±104 | 310±113 | 0.001 |
| CAT | 13±6 | 21±10 | 0.012 |
| <10 | 16(66.6) | 8(33.3) | |
| 10-20 | 16(53.3) | 14(46.6) | |
| 21-30 | 0(0.0) | 17(100) | |
| >30 | 0(0.0) | 9(100) |
| Characteristics | Normal RV strain (N=32) Mean±SD | Reduced RV Strain (N=48) Mean±SD | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| LV Ejection fraction (%) | 60.75±4.819 | 60.77±9.599 | 0.986 |
| FAC (%) | 50.343±5.839 | 42.166±7.143 | 0.000 |
| TAD (mm) | 27.593±2.949 | 27.854±2.576 | 0.677 |
| RVBD (mm) | 32.593±3.653 | 32.208±3.649 | 0.645 |
| RVMD (mm) | 23.875±2.485 | 24.750±2.621 | 0.140 |
| RVLD (mm) | 60.875±6.282 | 63.583±5.089 | 0.037 |
| RAA (cm2) | 12.531±2.361 | 12.693±2.041 | 0.744 |
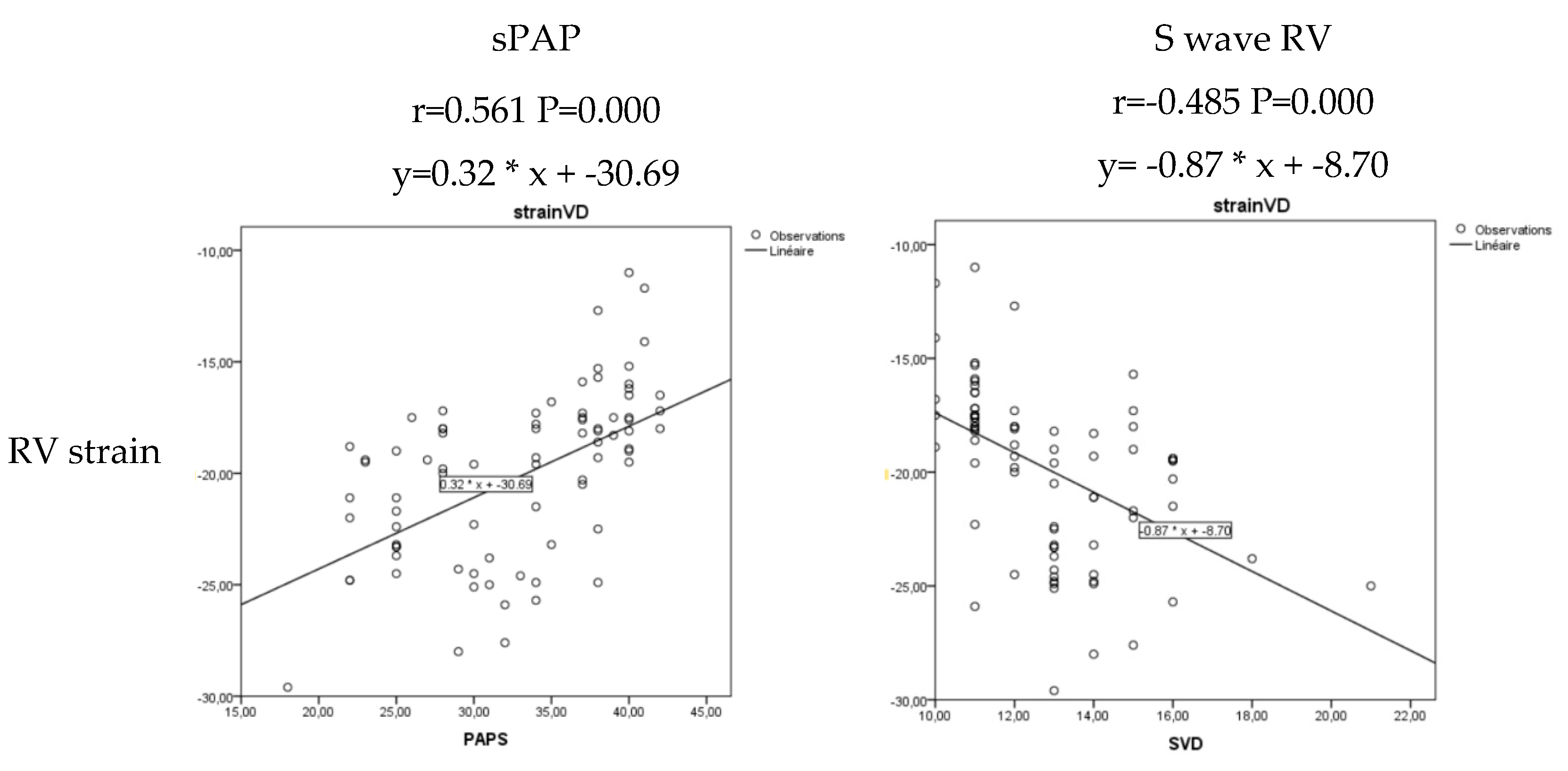
| S wave RV (cm/s) | 13.906±1.956 | 12.062±1.803 | 0.000 |
| TAPSE (mm) | 22.937±3.426 | 19.500±2.352 | 0.000 |
| sPAP (mmHg) | 29.000±5.364 | 35.375±5.796 | 0.000 |
| RV wall thickness (mm) | 6.343±1.035 | 6.708±0.682 | 0.061 |
| IVC (mm) | 14.66±1.537 | 15.17±1.226 | 0.104 |
| E/A | 1.060±0.290 | 0.938±0.282 | 0.065 |
| LAA (cm2) | 14.931±2.597 | 14.333±2.364 | 0.290 |
| IVS thickness (mm) | 8.906±0.928 | 9.208±0.742 | 0.111 |
| LV EDD (mm) | 45.312±3.335 | 46.229±3.520 | 0.248 |
| LV PW (mm) | 8.625±0.975 | 8.791±0988 | 0.460 |
| aOR | 95%CI | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6MWD | 0.985 | 0.978 | 0.993 | 0.001 |
| sPAP | 1.214 | 1.079 | 1.366 | 0.000 |
| S wave RV | 0.526 | 0.338 | 0.818 | 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





