Submitted:
18 July 2024
Posted:
18 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1 Study Participants
2.2 Outcome Measures
2.2.1 Measurement of Anthropometric and Physical Function
2.2.2 Interview Survey
2.2.3 Blood Indicators
2.2.4 Cognitive Function
2.3 Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matyas, N.; Keser Aschenberger, F.; Wagner, G.; Teufer, B.; Auer, S.; Gisinger, C.; Kil, M.; Klerings, I.; Gartlehner, G. Continuing education for the prevention of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's-type dementia: a systematic review and overview of systematic reviews. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piolatto, M.; Bianchi, F.; Rota, M.; Marengoni, A.; Akbaritabar, A.; Squazzoni, F. The effect of social relationships on cognitive decline in older adults: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, M.N.; Szabo-Reed, A.N. Impact of Diet and Exercise Interventions on Cognition and Brain Health in Older Adults: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.C.; Alpass, F.M. Effectiveness of dairy products to protect against cognitive decline in later life: a narrative review. Front Nutr 2024, 11, 1366949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.H.; Ho, M.H.; Wang, C.S.; Chen, I.H. Effect of dietary patterns on cognitive functions of older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials: Dietary Patterns on Cognition of Older Adults. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2023, 110, 104967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaei, M.; Feng, L.; Yuan, J.M.; Pan, A.; Koh, W.P. Dairy, soy, and calcium consumption and risk of cognitive impairment: the Singapore Chinese Health Study. Eur J Nutr 2020, 59, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, M.; Ohara, T.; Ninomiya, T.; Hata, J.; Yoshida, D.; Mukai, N.; Nagata, M.; Uchida, K.; Shirota, T.; Kitazono, T. , et al. Milk and dairy consumption and risk of dementia in an elderly Japanese population: the Hisayama Study. J Am Geriatr Soc 2014, 62, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Fu, Z.; Chung, M.; Jang, D.J.; Lee, H.J. Role of milk and dairy intake in cognitive function in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr J 2018, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta-Triana, F.; Verdejo-Bravo, C.; Fernández-Pérez, C.; Martín-Sánchez, F.J. Effect of Milk and Other Dairy Products on the Risk of Frailty, Sarcopenia, and Cognitive Performance Decline in the Elderly: A Systematic Review. Adv Nutr 2019, 10, S105–s119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ano, Y.; Ozawa, M.; Kutsukake, T.; Sugiyama, S.; Uchida, K.; Yoshida, A.; Nakayama, H. Preventive effects of a fermented dairy product against Alzheimer's disease and identification of a novel oleamide with enhanced microglial phagocytosis and anti-inflammatory activity. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0118512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Kojima, N.; Osuka, Y.; Tokui, Y.; Takasugi, S.; Kawashima, A.; Yamaji, T.; Hosoi, E.; Won, C.W.; Kim, H. The Effects of Mold-Fermented Cheese on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Community-Dwelling Older Japanese Women With Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized, Controlled, Crossover Trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2019, 20, 1509–1514.e1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, H.; Makizako, H.; Doi, T.; Yoshida, D.; Tsutsumimoto, K.; Anan, Y.; Uemura, K.; Lee, S.; Park, H.; Suzuki, T. A large, cross-sectional observational study of serum BDNF, cognitive function, and mild cognitive impairment in the elderly. Front Aging Neurosci 2014, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunkyung Kim, Y.O. , Narumi Kojima, Hiroyuki Sasai, Kentaro Nakamura, Chisato Oba, Mayuki Sasaki and Takao Suzuki. Inverse Association between Cheese Consumption and Lower Cognitive Function in Japanese Community-Dwelling Older Adults Based on a Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Osuka, Y.; Kojima, N.; Wakaba, K.; Miyauchi, D.; Tanaka, K.; Kim, H. Effects of resistance training and/or beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate supplementation on muscle mass, muscle strength and physical performance in older women with reduced muscle mass: protocol for a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e025723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, M.; Motokawa, K.; Mikami, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Shirobe, M.; Edahiro, A.; Iwasaki, M.; Ohara, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Kawai, H. , et al. Low Dietary Variety and Diabetes Mellitus Are Associated with Frailty among Community-Dwelling Older Japanese Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versijpt, J.; Tant, M.; Beyer, I.; Bier, J.C.; Cras, P.; De Deyn, P.P.; De Wit, P.; Deryck, O.; Hanseeuw, B.; Lambert, M. , et al. Alzheimer's disease and driving: review of the literature and consensus guideline from Belgian dementia experts and the Belgian road safety institute endorsed by the Belgian Medical Association. Acta Neurol Belg 2017, 117, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Smailagic, N.; Roqué, I.F.M.; Ciapponi, A.; Sanchez-Perez, E.; Giannakou, A.; Pedraza, O.L.; Bonfill Cosp, X.; Cullum, S. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the detection of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015, 2015, Cd010783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crichton, G.E.; Murphy, K.J.; Bryan, J. Dairy intake and cognitive health in middle-aged South Australians. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2010, 19, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Sawyer Baker, P.; Allman, R.M.; Zamrini, E. Dietary factors and cognitive impairment in community-dwelling elderly. J Nutr Health Aging 2007, 11, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Klinedinst, B.S.; Le, S.T.; Larsen, B.; Pappas, C.; Hoth, N.J.; Pollpeter, A.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, L. , et al. Genetic Factors of Alzheimer's Disease Modulate How Diet is Associated with Long-Term Cognitive Trajectories: A UK Biobank Study. J Alzheimers Dis 2020, 78, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.J.; Presse, N.; Rahme, E.; Ferland, G.; Bherer, L.; Chevalier, S. Milk, Yogurt, and Cheese Intake Is Positively Associated With Cognitive Executive Functions in Older Adults of the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2021, 76, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Dong, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Fang, A.; Giovannucci, E.L. Cheese consumption and multiple health outcomes: an umbrella review and updated meta-analysis of prospective studies. Adv Nutr 2023, 14, 1170–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippini, T.; Adani, G.; Malavolti, M.; Garuti, C.; Cilloni, S.; Vinceti, G.; Zamboni, G.; Tondelli, M.; Galli, C.; Costa, M. , et al. Dietary Habits and Risk of Early-Onset Dementia in an Italian Case-Control Study. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Goeij, L.C.; van de Rest, O.; Feskens, E.J.M.; de Groot, L.; Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M. Associations between the Intake of Different Types of Dairy and Cognitive Performance in Dutch Older Adults: The B-PROOF Study. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Nishi, S.K.; Babio, N.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Castañer, O.; Martínez, J.A.; Alonso-Gómez Á, M.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Vioque, J. , et al. Dairy Product Consumption and Changes in Cognitive Performance: Two-Year Analysis of the PREDIMED-Plus Cohort. Mol Nutr Food Res 2022, 66, e2101058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobreva, I.; Marston, L.; Mukadam, N. Which components of the Mediterranean diet are associated with dementia? A UK Biobank cohort study. Geroscience 2022, 44, 2541–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villoz, F.; Filippini, T.; Ortega, N.; Kopp-Heim, D.; Voortman, T.; Blum, M.R.; Del Giovane, C.; Vinceti, M.; Rodondi, N.; Chocano-Bedoya, P.O. Dairy Intake and Risk of Cognitive Decline and Dementia: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Adv Nutr 2024, 15, 100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghan, M.; Mente, A.; Rangarajan, S.; Sheridan, P.; Mohan, V.; Iqbal, R.; Gupta, R.; Lear, S.; Wentzel-Viljoen, E.; Avezum, A. , et al. Association of dairy intake with cardiovascular disease and mortality in 21 countries from five continents (PURE): a prospective cohort study. Lancet 2018, 392, 2288–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Sun, D. Meta-Analysis of Milk Consumption and the Risk of Cognitive Disorders. Nutrients 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camfield, D.A.; Owen, L.; Scholey, A.B.; Pipingas, A.; Stough, C. Dairy constituents and neurocognitive health in ageing. Br J Nutr 2011, 106, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Companys, J.; Pla-Pagà, L.; Calderón-Pérez, L.; Llauradó, E.; Solà, R.; Pedret, A.; Valls, R.M. Fermented Dairy Products, Probiotic Supplementation, and Cardiometabolic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Adv Nutr 2020, 11, 834–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijsbers, L.; Ding, E.L.; Malik, V.S.; de Goede, J.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Soedamah-Muthu, S.S. Consumption of dairy foods and diabetes incidence: a dose-response meta-analysis of observational studies. Am J Clin Nutr 2016, 103, 1111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engberink, M.F.; Geleijnse, J.M.; de Jong, N.; Smit, H.A.; Kok, F.J.; Verschuren, W.M. Dairy intake, blood pressure, and incident hypertension in a general Dutch population. J Nutr 2009, 139, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Lopez, L.; Aguilar-Toala, J.E.; Hernandez-Mendoza, A.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; Liceaga, A.M.; Gonzalez-Cordova, A.F. Invited review: Bioactive compounds produced during cheese ripening and health effects associated with aged cheese consumption. J Dairy Sci 2018, 101, 3742–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ano, Y.; Kutsukake, T.; Hoshi, A.; Yoshida, A.; Nakayama, H. Identification of a novel dehydroergosterol enhancing microglial anti-inflammatory activity in a dairy product fermented with Penicillium candidum. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0116598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Oba, C.; Nakamura, K.; Takeo, H.; Toya, H.; Furuichi, K. Milk-based culture of Penicillium camemberti and its component oleamide affect cognitive function in healthy elderly Japanese individuals: a multi-arm randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Front Nutr 2024, 11, 1357920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Domain | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Daily | 271 | 26.2 |
| Once every 2 days | 242 | 23.4 | |
| Once or twice a week | 323 | 31.3 | |
| No intake | 197 | 19.1 | |
| Total | 1033 | 100.0 | |
| Type 1 | Processed cheese | 767 | 78.5 |
| Fresh cheese | 69 | 7.1 | |
| Camembert cheese | 119 | 12.2 | |
| Blue mold cheese | 16 | 1.6 | |
| Other | 6 | 0.6 | |
| Total | 977 | 100.0 |
| Variables | Cheese Intake | n | Mean ± SD | t-value | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | No | 197 | 71.4 ± 4.2 | 1.418 | 0.079 |
| Yes | 836 | 71.9 ± 4.5 | |||
| Calf circumference, cm | No | 197 | 34.2 ± 3.0 | 1.050 | 0.147 |
| Yes | 836 | 34.5 ± 2.9 | |||
| Grip strength, kg | No | 196 | 21.1 ± 3.9 | 1.502 | 0.067 |
| Yes | 829 | 21.6 ± 3.9 | |||
| Usual walking speed, m/s | No | 195 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 0.094 | 0.462 |
| Yes | 835 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | |||
| RSST, times/30 s | No | 197 | 3.8 ± 1.8 | 0.092 | 0.463 |
| Yes | 828 | 3.8 ± 1.7 | |||
| DVS, points | No | 196 | 4.0±1.9 | 5.069 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 833 | 4.8±2.0 | |||
| Creatinine, mg/dL | No | 196 | 0.67±0.13 | 2.670 | 0.004 |
| Yes | 836 | 0.71±0.30 | |||
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | No | 196 | 222.6±36.4 | 1.777 | 0.038 |
| Yes | 836 | 227.7±35.2 | |||
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dL | No | 196 | 68.8 ± 18.1 | 1.073 | 0.142 |
| Yes | 836 | 70.3 ± 18.4 | |||
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | No | 196 | 148.7 ± 82.2 | 1.180 | 0.120 |
| Yes | 836 | 156.6 ± 91.4 | |||
| Albumin, g/dL | No | 196 | 4.4 ± 0.3 | 0.385 | 0.350 |
| Yes | 836 | 4.4 ± 0.3 | |||
| HbA1c, % | No | 196 | 5.5 ± 0.6 | 0.138 | 0.445 |
| Yes | 836 | 5.6 ± 0.6 | |||
| GDS score, points | No | 197 | 2.8±2.8 | 3.336 | 0.000 |
| Yes | 835 | 2.2±2.3 | |||
| MMSE score, points | No | 194 | 27.8±2.3 | 1.962 | 0.025 |
| Yes | 827 | 28.3±1.9 | |||
| Temporal orientation | No | 194 | 4.8±0.5 | 2.516 | 0.006 |
| Yes | 830 | 4.9±0.4 | |||
| Spatial orientation | No | 195 | 4.9 ± 0.4 | 0.908 | 0.182 |
| Yes | 830 | 4.9 ± 0.3 | |||
| Registration | No | 195 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 1.228 | 0.110 |
| Yes | 830 | 3.0 ± 0.2 | |||
| Attention and calculation | No | 195 | 4.0 ± 1.3 | 2.633 | 0.004 |
| Yes | 829 | 4.3 ± 1.0 | |||
| Remote memory | No | 195 | 2.4 ± 0.8 | 2.414 | 0.008 |
| Yes | 830 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | |||
| Other functions | No | 195 | 8.7 ± 0.5 | 0.361 | 0.359 |
| Yes | 828 | 8.7 ± 0.6 | |||
| Number of chronic disease, n | No | 197 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 1.661 | 0.049 |
| Yes | 831 | 2.3±1.7 | |||
| Diabetes, yes (%) | No | 15/197 | 7.6 | 0.649 | 0.42 |
| Yes | 79/836 | 9.4 | |||
| Hyperlipidemia, yes (%) | No | 66/197 | 33.5 | 0.004 | 0.947 |
| Yes | 278/836 | 33.3 | |||
| Falls, yes (%) | No | 29/197 | 14.7 | 0.237 | 0.626 |
| Yes | 112/836 | 13.4 | |||
| Urinary incontinence, yes (%) | No | 79/197 | 40.1 | 0.233 | 0.629 |
| Yes | 351/836 | 42.0 | |||
| Milk intake, yes (%) | No | 86/197 | 56.3 | 26.792 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 210/836 | 74.9 |
| Variables | Category | n | Mean ± SD | t-value | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | Other | 759 | 71.8 ± 4.5 | 0.487 | 0.313 |
| Camembert | 119 | 72.0 ± 4.8 | |||
| Calf circumference, cm | Other | 759 | 34.5±2.8 | 1.680 | 0.047 |
| Camembert | 119 | 34.1±3.2 | |||
| Grip strength, kg | Other | 753 | 21.5 ± 3.8 | 1.131 | 0.129 |
| Camembert | 118 | 22.0 ± 4.2 | |||
| Usual walking speed, m/s | Other | 757 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 0.892 | 0.186 |
| Camembert | 119 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | |||
| RSST, times/30 s | Other | 752 | 3.8 ± 1.7 | 0.770 | 0.221 |
| Camembert | 118 | 3.9 ± 1.8 | |||
| DVS, points | Other | 757 | 4.8 ± 1.9 | 0.148 | 0.441 |
| Camembert | 118 | 4.8 ± 2.0 | |||
| Creatinine, mg/dL | Other | 759 | 0.7 ± 0.3 | 0.645 | 0.260 |
| Camembert | 119 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | |||
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | Other | 759 | 227.4 ± 35.4 | 0.150 | 0.440 |
| Camembert | 119 | 227.9 ± 35.4 | |||
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dL | Other | 759 | 70.0 ± 18.5 | 1.148 | 0.126 |
| Camembert | 119 | 72.1 ± 18.1 | |||
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | Other | 759 | 156.3 ± 91.8 | 0.556 | 0.289 |
| Camembert | 119 | 151.3 ± 85.0 | |||
| Albumin, g/dL | Other | 759 | 4.4 ± 0.3 | 1.312 | 0.095 |
| Camembert | 119 | 4.4 ± 0.3 | |||
| HbA1c, % | Other | 759 | 5.6 ± 0.6 | 0.507 | 0.306 |
| Camembert | 119 | 5.5 ± 0.5 | |||
| GDS score, points | Other | 758 | 2.2 ± 2.3 | 1.240 | 0.108 |
| Camembert | 119 | 1.9 ± 2.2 | |||
| MMSE score, points | Other | 750 | 28.3±2.0 | 2.527 | 0.006 |
| Camembert | 119 | 28.7±1.4 | |||
| Temporal orientation | Other | 753 | 4.9±0.4 | 2.430 | 0.008 |
| Camembert | 119 | 4.9±0.2 | |||
| Spatial orientation | Other | 753 | 4.9 ± 0.3 | 0.675 | 0.250 |
| Camembert | 119 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | |||
| Registration | Other | 753 | 3.0 ± 0.2 | 0.826 | 0.205 |
| Camembert | 119 | 3.0 ± 0.2 | |||
| Attention and calculation | Other | 752 | 4.2±1.1 | 1.827 | 0.035 |
| Camembert | 119 | 4.4±0.8 | |||
| Remote memory | Other | 753 | 2.5 ± 0.7 | 0.530 | 0.298 |
| Camembert | 119 | 2.6 ± 0.6 | |||
| Otherfunctions | Other | 751 | 8.7±0.6 | 2.255 | 0.013 |
| Camembert | 119 | 8.8±0.4 | |||
| Number of chronic disease, N | Other | 755 | 2.3 ± 1.7 | 0.611 | 0.271 |
| Camembert | 118 | 2.4 ± 1.9 | |||
| Diabetes, yes (%) | Other | 69/759 | 9.1 | 0.059 | 0.807 |
| Camembert | 10/119 | 8.4 | |||
| Hyperlipidemia, yes (%) | Other | 249/759 | 32.8 | 1.159 | 0.282 |
| Camembert | 45/119 | 37.8 | |||
| Falls, yes (%) | Other | 100/759 | 13.2 | 0.029 | 0.864 |
| Camembert | 15/119 | 12.6 | |||
| Urinary incontinence, yes (%) | Other | 311/759 | 41.0 | 0.538 | 0.463 |
| Camembert | 53/119 | 44.5 | |||
| Milk intake, yes (%) | Other | 558/759 | 73.5 | 0.237 | 0.626 |
| Camembert | 90/119 | 75.6 |
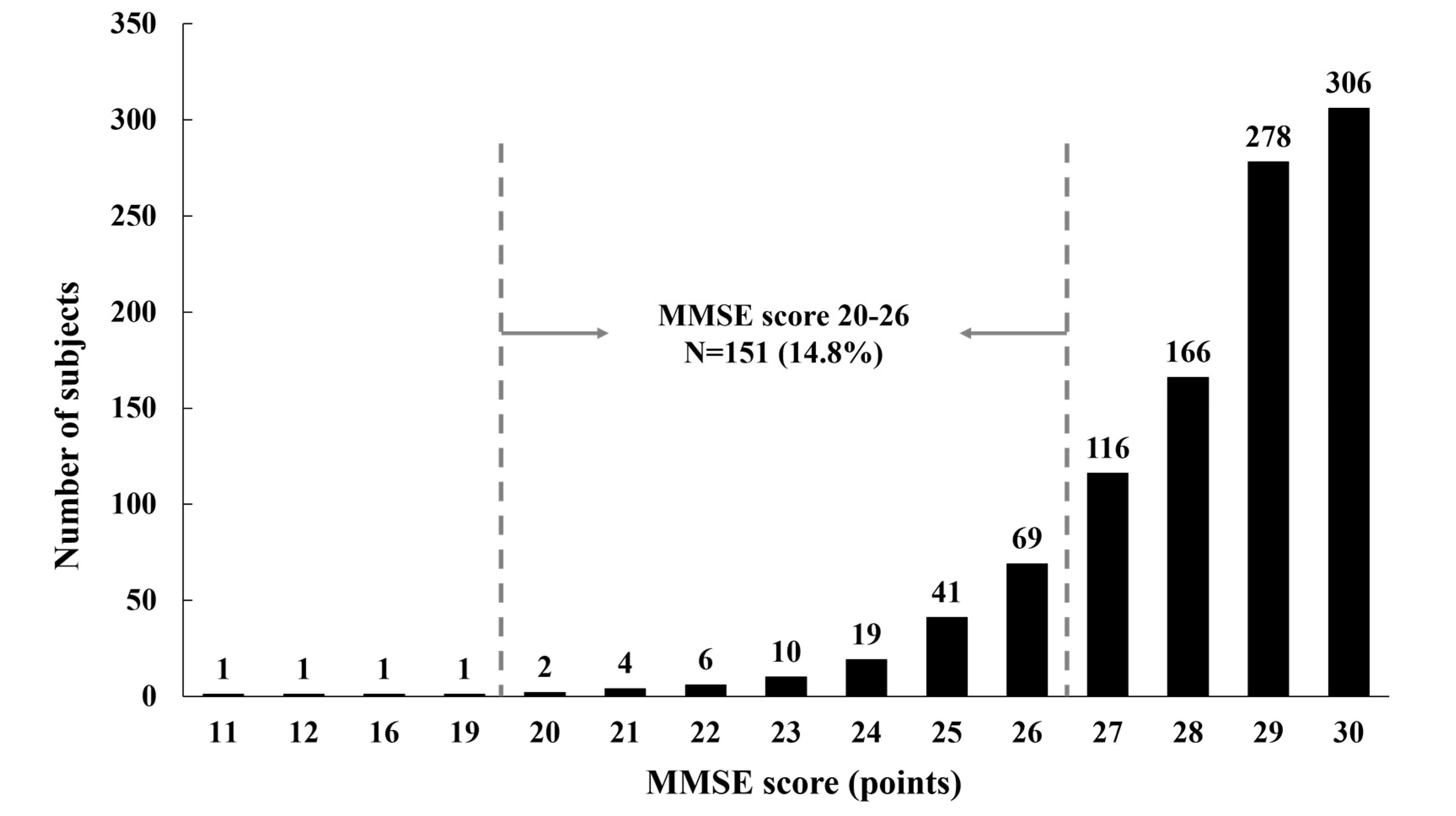
| Variables | Category | N | Mean ± SD | t-value | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | MMSE score ≥27 | 866 | 71.4 ±4.4 | 6.403 | <0.001 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 151 | 73.9 ±4.3 | |||
| Calf circumference, cm | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 866 | 34.5 ±2.9 | 2.185 | 0.015 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 151 | 33.9 ±2.6 | |||
| Grip strength, kg | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 860 | 21.7 ±3.9 | 3.800 | <0.001 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 150 | 20.4 ±0.8 | |||
| Usualwalkingspeed, m/s | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 863 | 1.4 ±0.2 | 5.042 | <0.001 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 151 | 1.2 ±0.3 | |||
| RSST, times/30sec | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 863 | 3.9 ±1.8 | 2.941 | 0.002 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 151 | 3.4 ±1.4 | |||
| DVS, points | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 864 | 4.6 ± 1.9 | 1.087 | 0.139 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 149 | 4.8 ± 2.0 | |||
| Creatinine, mg/dL | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 866 | 0.7 ± 0.3 | 0.645 | 0.260 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 151 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | |||
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 866 | 227.0 ± 35.8 | 0.987 | 0.162 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 151 | 223.9 ± 32.5 | |||
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dL | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 866 | 70.3 ± 18.6 | 1.116 | 0.132 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 151 | 68.4 ± 17.2 | |||
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 866 | 155.4 ± 91.0 | 0.095 | 0.462 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 151 | 154.6 ± 83.9 | |||
| Albumin, g/dL | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 866 | 4.4 ±0.3 | 2.304 | 0.011 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 151 | 4.3 ±0.3 | |||
| HbA1c, % | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 866 | 5.5 ± 0.6 | 1.152 | 0.125 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 151 | 5.6 ± 0.8 | |||
| GDS score, points | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 865 | 2.2 ±2.3 | 1.890 | 0.030 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 151 | 2.6 ±2.7 | |||
| Number of chronic diseases, N | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 861 | 2.3 ± 1.7 | 0.080 | 0.468 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 151 | 2.3 ± 1.8 | |||
| Diabetes, yes (%) | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 75/866 | 8.7 | 1.645 | 0.200 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 18/151 | 11.9 | |||
| Hyperlipidemia, yes (%) | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 299/866 | 34.5 | 2.599 | 0.107 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 42/151 | 27.8 | |||
| Falls, yes (%) | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 113/866 | 13.0 | 0.529 | 0.467 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 23/151 | 15.2 | |||
| Urinary incontinence, yes (%) | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 363/866 | 41.9 | 0.039 | 0.844 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 62/151 | 41.1 | |||
| Milk intake, yes (%) | MMSE score ≥ 27 | 624/866 | 72.1 | 0.64 | 0.424 |
| MMSE score 20–26 | 104/151 | 68.9 |
| Independent Variable | Model I | Model II | Model III | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-value | OR | 95% CI | p-value | OR | 95% CI | p-value | |
| Type of cheese, camembert cheese | 0.484 | 0.238–0.984 | 0.045 | 0.465 | 0.224–0.966 | 0.040 | 0.448 | 0.214–0.936 | 0.033 |
| Cheese intake, yes | 0.816 | 0.354–1.881 | 0.634 | 0.640 | 0.269–1.521 | 0.312 | 0.605 | 0.252–1.455 | 0.262 |
| Age, 1 year | 1.114 | 1.061–1.170 | <0.001 | 1.114 | 1.059–1.171 | <0.001 | |||
| Calf circumference, 1 unit | 0.972 | 0.899–1.051 | 0.476 | 0.963 | 0.890–1.042 | 0.353 | |||
| Grip strength, 1 unit | 0.981 | 0.923–1.043 | 0.540 | 0.989 | 0.929–1.052 | 0.722 | |||
| Usual walking speed, 1 unit | 0.259 | 0.113–0.591 | 0.001 | 0.260 | 0.109–0.621 | 0.002 | |||
| Diabetes, yes | 1.724 | 0.899–3.304 | 0.101 | ||||||
| Creatinine, 1 unit | 0.964 | 0.548–1.695 | 0.898 | ||||||
| Total cholesterol, 1 unit | 1.001 | 0.995–1.007 | 0.738 | ||||||
| Albumin, 1 unit | 1.105 | 0.488–2.500 | 0.811 | ||||||
| RSST, 1 unit | 0.865 | 0.750–0.995 | 0.046 | ||||||
| Urinary incontinence, yes | 1.093 | 0.644–1.854 | 0.742 | ||||||
| GDS score, 1 unit | 0.964 | 0.879–1.057 | 0.436 | ||||||
| Milk intake, yes | 0.954 | 0.601–1.513 | 0.841 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





