Submitted:
15 July 2024
Posted:
16 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Clinical Data and Methods
1.1. General Information
1.2. Methods
1.3. Statistics
2. Results
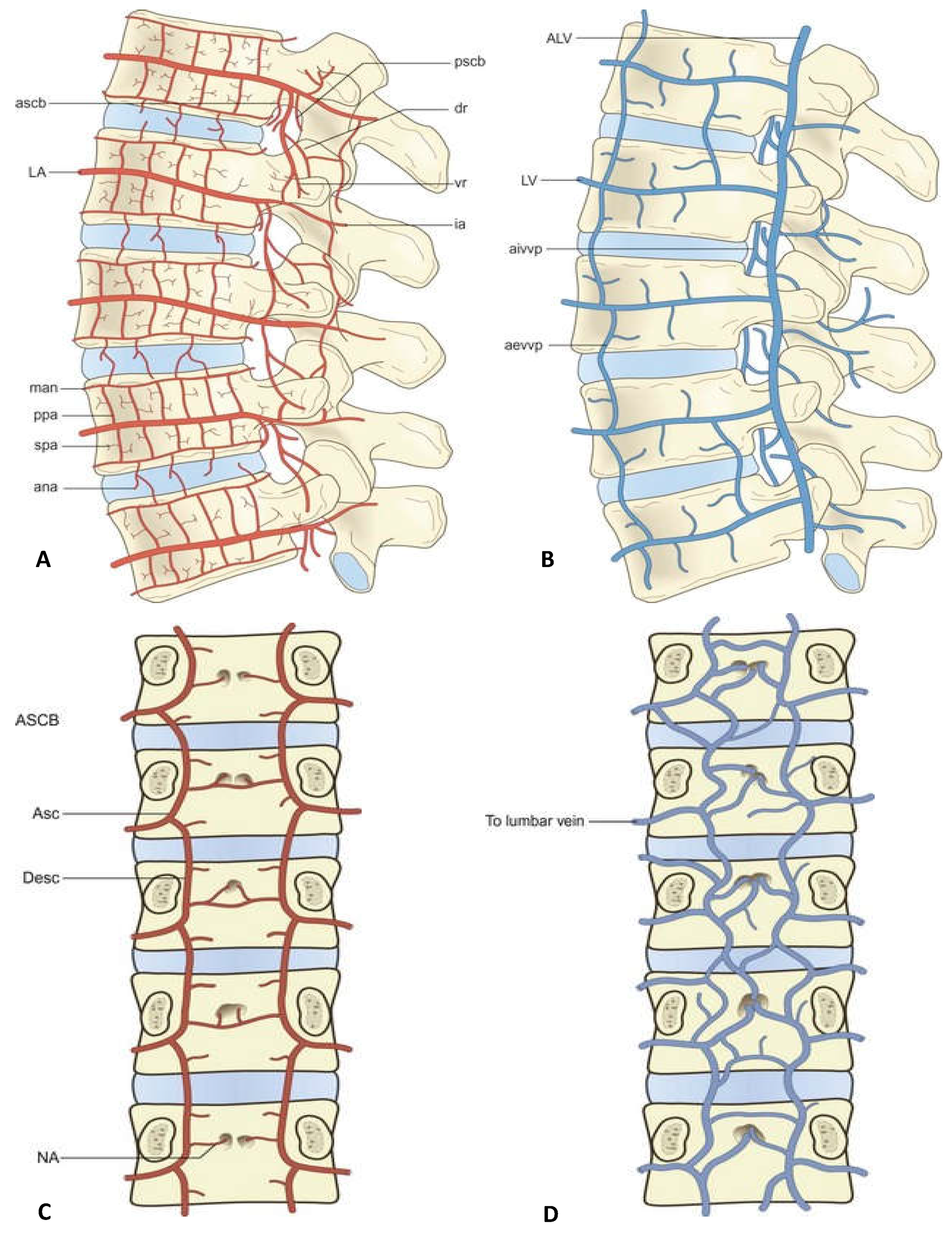
2.1. Ligaments Attached to the SAP
2.2. IVD and AF Under Endoscopy
2.3. Vascular System on the Dura and Nerve Root
3. Discussions
4. Conclusion
References
- Kohoutova, D.; Banks, M.; Bures, J. Advances in the Aetiology & Endoscopic Detection and Management of Early Gastric Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 6242–6250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Namba, K. Vascular Anatomy of the Cauda Equina and Its Implication on the Vascular Lesions in the Caudal Spinal Structure. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2016, 56, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martirosyan, Nikolay; Feuerstein, Jeanne; Theodore; et al. Blood supply and vascular reactivity of the spinal cord under normal and pathological conditions A review. Journal of neurosurgery. Spine 2011, 4, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.S.; Robertson, J.T.; Frederickson, R.C.; et al. Association between peridural scar and recurrent radicular pain after lumbar discectomy: magnetic resonance evaluation. ADCON-L European Study Group. Neurosurgery 1996, 38, 855–863. [Google Scholar]
- Umeh, Randle; et al. Transforaminal Ligaments of the Lumbar Spine: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2016, 8, e811–e819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhong, E.; Shi, B.; et al. The morphology and clinical significance of the intraforaminal ligaments at the L5-S1 levels. Spine J. 2016, 16, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marić, D.L.; Krstonošić, B.; Erić, M.; et al. An anatomical study of the lumbar external foraminal ligaments: appearance at MR imaging. Surg Radiol Anat. 2015, 37, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amonoo-Kuofi, H.S.; el-Badawi, M.G.; Fatani, J.A. Ligaments associated with lumbar intervertebral foramina. 1. L1 to L4. J Anat. 1988, 5, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.G.; Wen, Y.L.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.K. Ligament, nerve, and blood vessel anatomy of the lateral zone of the lumbar intervertebral foramina. Int Orthop. 2015, 5, 2135–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Structural names | Origins | Insertions | Innervative nerve | Route | Functions | Probability of existence | Variation rate | |
| Muscles attached to SAP | Multifidus muscle (MM) | Transverse process | Spinus process, lamina | Posterior rami | fan-shaped from the down -outside to the up-inside | Dorsal extension, lateral flexion, rotating vertebral body | 100% | |
| intertransversarii mediales lumborum | Accessory process, lateral side of transverse | Accessory process of upper level, transverse process of upper level | The dorsal ramus of spinal nerve | From inferior to superior | Lateral bending, keeping spine in balance | 100% | ||
| intertransversarii lateral lumborum | Accessory process, lateral side of tranverse | Accessory process of upper level, transverse process of upper level | The dorsal ramus of spinal nerve | From inferior- lateral to superior-medial | Lateral bending, keeping spine in balance | 100% | ||
| Ligaments attached to SAP | capsule ligaments | SAP | Inferior articular process (IAP) | The medial branch of dorsal ramus of spinal nerve (same level and upper level) | Wrapped up | Keep facet joint in place | 20% | |
| Superior corporotransverse ligaments | Posterior lateral side of vertebral body | Transverse process of same level | The medial branch of dorsal ramus of spinal nerve (same level and upper level) | From inferior- lateral to superius- medial obliquely | Protects the blood vessels and nerves in the foramen | 78% | 30% | |
| inferior corporotransverse ligaments |
Posterior lateral side of vertebral body | Transverse process of inferior level | The medial branch of dorsal ramus of spinal nerve (same level and upper level) | From superius-lateral to inferior -medial obliquely | Protect the blood vessels and nerves in the foramen | 69% | ||
| superior-transforaminal ligament |
Posterior lateral side of vertebral body | Inferior pedicle notched | The medial branch of dorsal ramus of spinal nerve (same level and upper level) | From anterior to lateral posterior foramen | Protect the blood vessels and nerves in the foramen | 84% | ||
| mid-transforaminal ligament |
Posterior lateral corner of annular fibrosis (AF) | Flavum ligament of posterior facet processes and facet capsule | The medial branch of dorsal ramus of spinal nerve (same level and upper level) | From anterior to lateral posterior foramen | Protect the blood vessels and nerves in the foramen | 71% | ||
| inferior-transforaminal ligament |
Posterior inferior side of vertebral body | Pedicle notched area of vertebral body | The medial branch of dorsal ramus of spinal nerve (same level and upper level) | From anterior to lateral posterior foramen | Protect the blood vessels and nerves in the foramen | 89% | ||
| Arteries in foramen (seen in the Figure 1) | anterior spinal canal branch (ascb.) | lumbar artery (la.) | running inferiorly into the foramen | Accompanying nerves of vascular sheath | From superius to inferior | Supplies the soft tissues in front of the foramen | 98% | |
| Lumbar ascending branch (ab.) | LA gives a new branch, ab. after the ascb. and lateral branch. | Foramen to posterior MM. | Modulated by accommodated nerves from the dr. | Running superiorly | Supplies the tissues in the foramen and the same level MM. | 100% | ||
| Lumbar descending branch (desc.) | Continuted ending branch of LA | Ends at the MM. and facet joints | Branch of dr. | Running inferiorly | Supplies the tissues in the facets, IVD and the inferior level MM. | 85% | ||
| posterior spinal canal branch (pscb) |
Originating from (lumbar artery, LA) | Ends at the intervertebral foramen | Modulated by accommodated nerves in vessel sheath | From superius to inferior | Supplies the tissues in the posterior foramen | 99% | ||
| branches accompanying dorsal ramus of spinal nerve (dr.) | originating from mscb of LA | ending in base of transverse process and facet | Modulated by accommodated nerves in vessel sheath | running along the dr. irregularly | Supplies the dr, facet jonts received supplies from both medially and laterally | 99% | ||
| posterior branch related to the pars interarticularis of the lamina (ia.) | Continuing of LA | crossing the joining area of pedicle and transverse, running to the posterior spinous process and facet process | Modulated by accommodated nerves in vessel sheath | Supplies the spinous process, and paraspinal muscles | 100% | |||
| veins in the foramen ( seen in the Figure 1) |
medial venous plexus of lumbar canal | joining lumbar ascending vein | descending branch of the medial branch of dorsal ramus of spinal nerve | From inferior to superior | Draining the veins in lumbar canal and foramen | 97% | ||
| Lumbar ascending vein | iliolumbar vein | left conjoining with left renal vein; right joining with inferior vena cava | From inferior to superior | Drain Vertebral body (VB) through central vein, lumbar segmental vein, and veins in foramen | 100% | |||
| Central vein | Central vein sinus | medial -anterior veinous plex of lumbar canal | from anterior to posterior | Drain VB | 100% | |||
| veins on the surface of IVD (seen in the Figure 1) | intervertebral vein (IVV) | Joining lumbar ascending vein | Underneath the pedicle, accompaied with exit nerve root, from inferior lateral to superius medial | Drain the region of foramen, lumbar canal and nerve root | 100% | |||
| lateral transverse branch | Communicated with IVV | Join the IVV | Lies in the lumbar canal anteriorly and posteriorly | Drain the lumbar canal | 91% | |||
| vein plex in the anterior of dura sac | drain the veins in the foramen and the veins lying in the anterior lumbar canal | joining segmental lumbar vein | sinuvertebral nerve (svn.) | longitudinal distribution in both ventral sides of dura sac from inferior to superior | Drain VB, foramen and annulus of IVD | 100% | ||
| arteries on the surface of IVD (seen in the Figure 1) | anastomosis over the surface of the intervertebral IVD (ana.) | metaphysial anastomosis (man.) | svn. | distributed on the surfaces of AF. | supplies the lumbar IVD | 95% | ||
| metaphysial anastomosis | communicated with ana. and primary periosteal artery (ppa.) | distributed on endplate epiphysis | supplies the endplate epiphysis and cartilage | 92% | ||||
| anterior spinal canal branch (ascb.) | Originated from segmental artery, communicated with adjacent segmental artery | distributed along the nerve root and foramen | supplies the nerve root and connective tissues in the foramen | 89% | ||||
| vessels on the dura and nerve root | generally, there are two main longitudinal veins and their communicated venous plex, while the vessels on the ventral side is hard to observe | joining the lateral transverse vein and lumbar ascending vein through aivvp. | drain connective tissues surrounding dura | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




