Submitted:
03 July 2024
Posted:
04 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Morphological Analysis
2.2. Molecular Analysis
2.3. Abbreviations
3. Results
3.1. Systematics of Metachromadora Parobscura sp. Nov.
3.1.1. Type material
3.1.2. Type Locality and Habitat
3.1.3. Etymology
3.1.4. Measurements
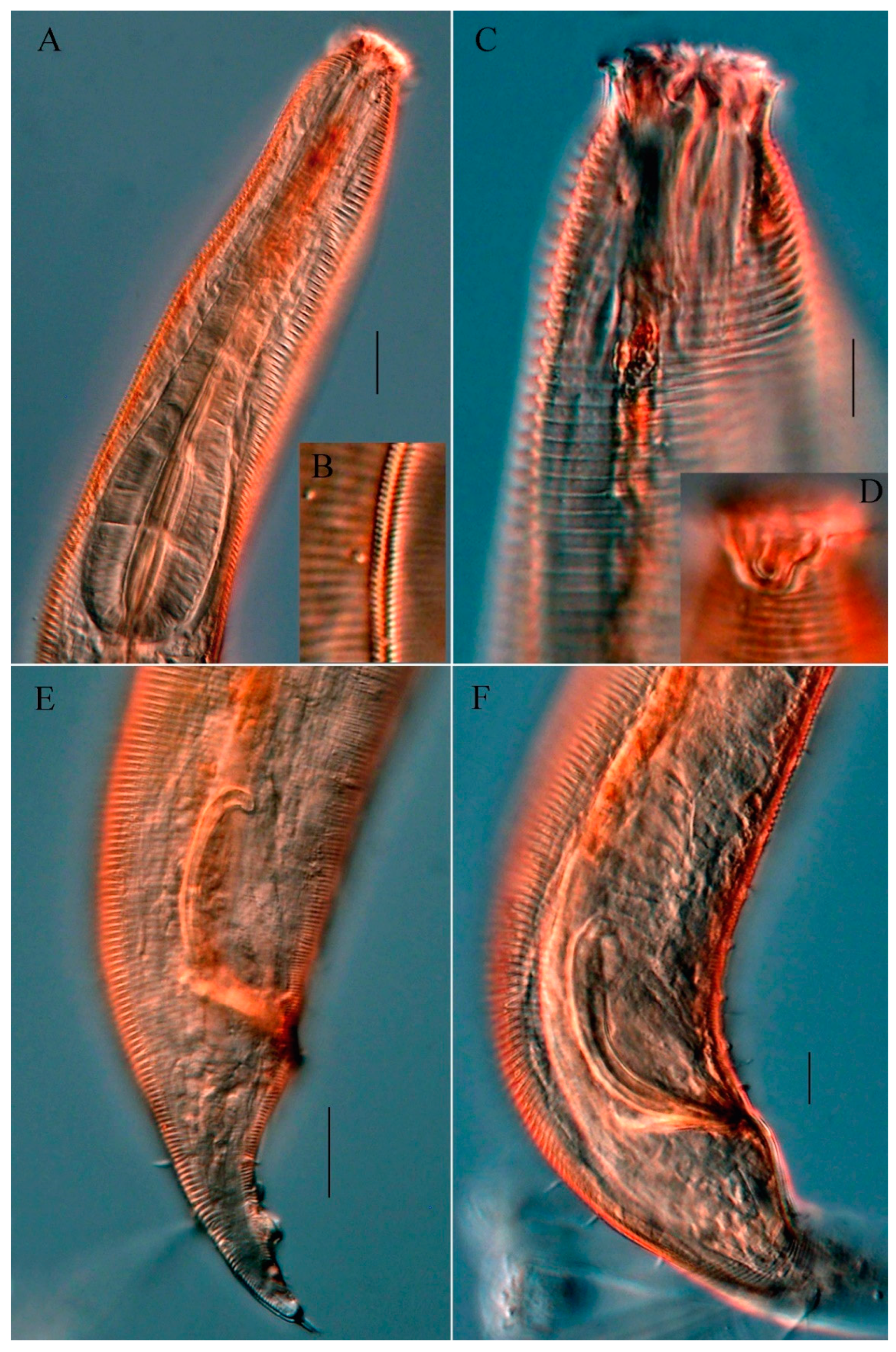
3.1.5. Description of Metachromadora Parobscura sp. nov. (Figure 1 and Figure 2 )
3.1.6. Diagnosis
3.1.7. Differential Diagnosis
3.2. Systematics of Molgolaimus Longicaudatus sp. nov.
3.2.1. Type Material
3.2.2. Type Locality and Habitat
3.2.3. Etymology
3.2.4. Measurements
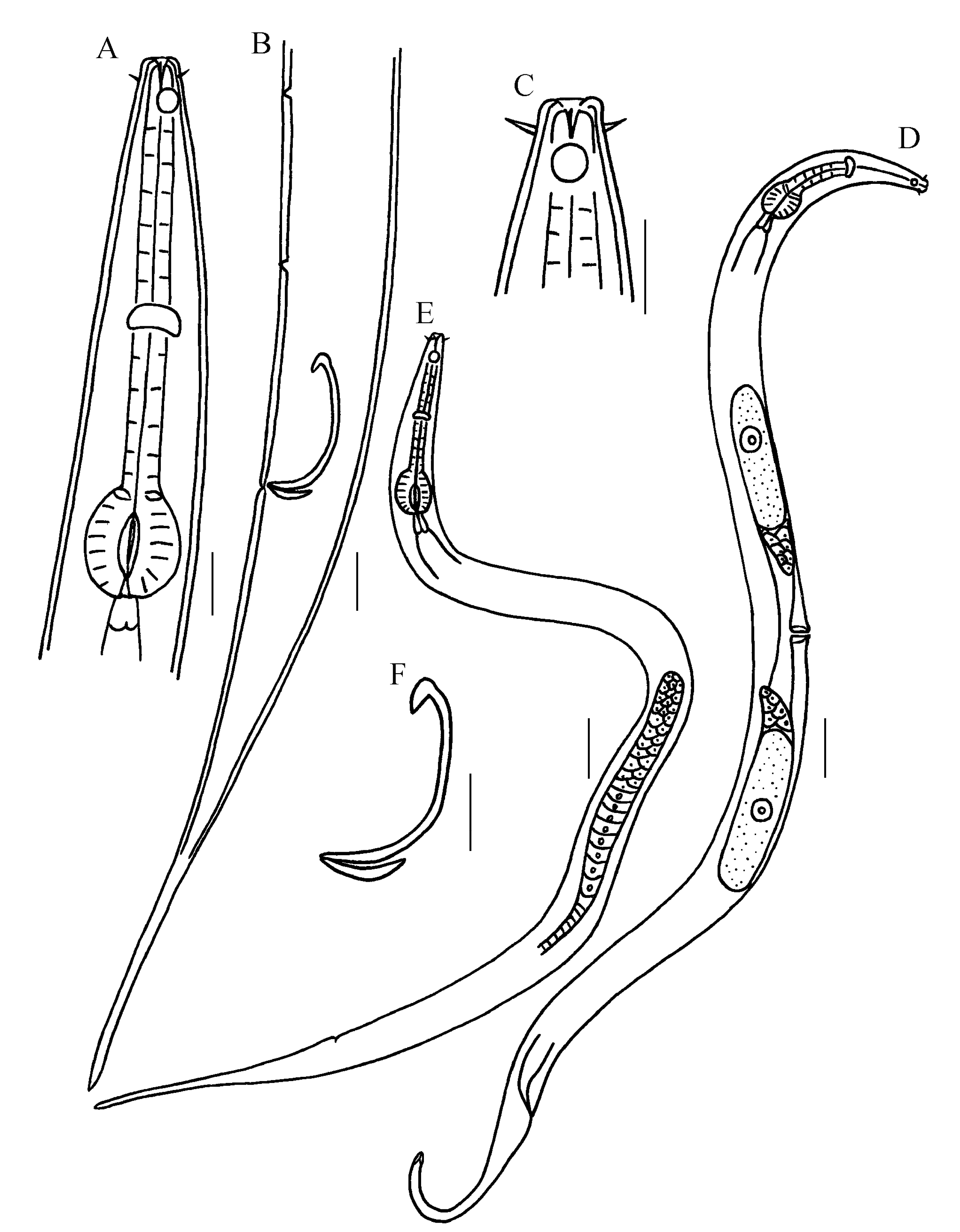
3.2.5. Description of Molgolaimus Longicaudatus sp. nov. (Figure 3 and Figure 4 )
3.2.6. Diagnosis
3.2.7. Differential Diagnosis
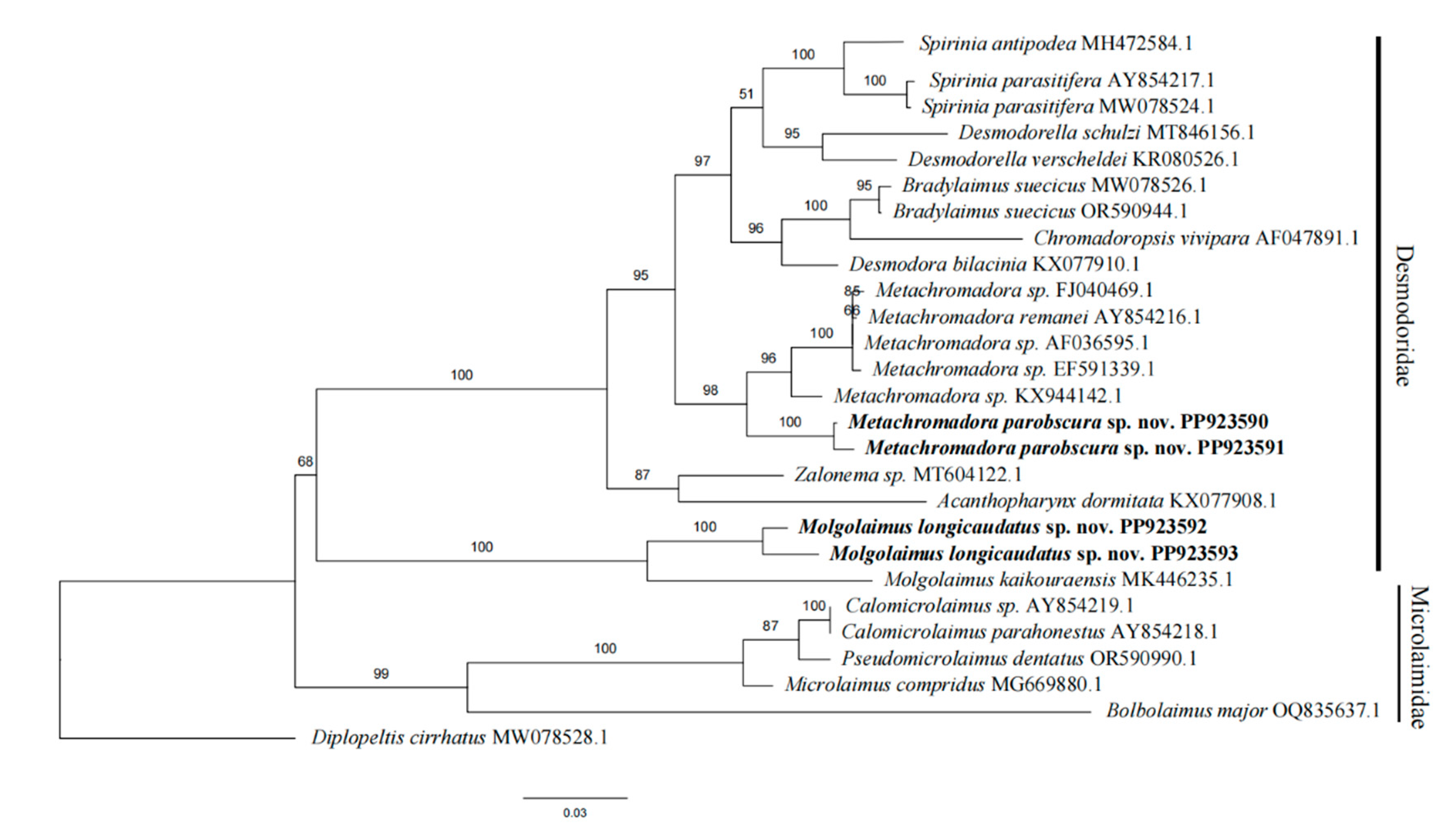
3.3. Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naidoo, G.; Naidoo, K.; Swart, A. Oil Pollution Effects on Nematodes in Mangrove Sediment: A Microcosm Study. 2021. Preprint (Version 1) at Research Square.doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-749759/v1. [CrossRef]
- Spedicato, A.; Zeppilli, D.; Thouzeau, G.; Michaud, E. Nematode diversity patterns in mangroves: a review of environmental drivers at different spatial scales. Biodivers Conserv. 2023, 32, 1451–1471.Author 1, A.; Author 2, B. Book Title, 3rd ed.; Publisher: Publisher Location, Country, 2008; pp. 154–196.
- Sahraean, N.; Van Campenhout, J.; Rigaux, A.; Mosallanejad, H.; Leliaert, F.; Moens, T. Lack of population genetic structure in the marine nematodes Ptycholaimellus pandispiculatus and Terschellingia longicaudata in beaches of the Persian Gulf, Iran. Mar. Ecol. 2017, 38, e12426.https://doi.org/10.1111/maec.12426. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.P.; Guo, Y.Q. Three new free-living marine nematode species of Subsphaerolaimus Lorenzen, 1978, Halichoanolaimus de Man, 1886 and Belbolla Andrássy, 1973 from mangrove wetlands in Taiwan. Zootaxa. 2023, 5361(3), 301–322.
- Wang, Y.; Pang, X. P.; GUO Guo, Y.Q. Study on marine nematodes community in Jinhai bay mangrove wetland, Beihai, Guangxi. Oceanologia Et Limnologia Sinica. 2020, 51(3), 583–590.
- Zhou, X.P.; Zeng, J.L.; Cai, L.Z.; Fu, S.J.; Tan, W.J. Two New Species of Free-Living Marine Nematodes of the Desmodoridae from Mangrove Wetlands of Xiamen Bay, China. J. Ocean Univ. China. 2020, 19, 143–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-020-4080-6. [CrossRef]
- Armenteros, M.; Ruiz-Abierno, A.; Decraemer, W. Revision of Desmodorinae and Spiriniinae (Nematoda: Desmodoridae) with redescription of eight known species. European Journal of Taxonomy. 2014, 96, 1–32. http://doi.org/10.5852/ejt.2014.96. [CrossRef]
- Maria, T.F.; Smol, N.; Esteves, AM. Two new species of Metachromadora (Nematoda: Desmodoridae) from Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and a revised dichotomous key to the genus. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 2014, 94(1),105–114. doi:10.1017/S0025315413001161. [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, G.; Vanreusel, A.; Decraemer, W. Taxonomy and biogeography of Molgolaimus Ditlevsen, 1921 (Nematoda: Chromadoria) with reference to the origins of deep sea nematodes. Antarctic Science. 2006, 18(1), 23–50. doi:10.1017/S0954102006000034. [CrossRef]
- Portnova, D. Free-living nematodes from the deep-sea Håkon Mosby Mud Volcano, including the description of two new and three known species. Zootaxa. 2019, 2096, 197–213.
- Leduc, D.; Fu, S.; Zhao, Z.Q. New nematode species from the continental slope of New Zealand (Chromadorea, Microlaimida, and Chromadorida), and unexpected placement of the genus Molgolaimus Ditlevsen, 1921. Mar. Biodiv. 2019, 49, 2267–2280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-019-00961-z. [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Xu, K. Spirobolbolaimus undulatus sp. nov. in intertidal sediment from the East China Sea, with transfer of two Microlaimus species to Molgolaimus (Nematoda, Desmodorida). Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 2017, 97 (6), 1335–1342.
- Macheriotou, L.G.K.B.; Nguyen, D.T.; Phuong Nguyen, T.X.; Noppe, F.; Armenteros, M.; Boufahja, F.; Rigaux, A.; Vanreusel, A.; Derycke, S. Metabarcoding free-living marine nematodes using curated 18S and CO1 reference sequence databases for species-level taxonomic assignments. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 1211–1226.
- Avó, A.P.; Daniell, T.J.; Roy, N.; Solange, O.; Jordana, B.; Helena, A. DNA barcoding and morphological identification of benthic nematodes assemblages of estuarine intertidal sediments: Advances in molecular tools for biodiversity assessment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 66.
- van Megen, H.; van den Elsen, S.; Holterman, M.; Karssen, G.; Mooyman, P.; Bongers, T.; Holovachov, O.; Bakker, J.; Helder, J. A phylogenetic tree of nematodes based on about 1200 full-length small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Nematology. 2009, 11, 927–950.
- De Ley, I.T.; De Ley, P.; Vierstraete, A.; Karssen, G.; Moens, M.; Vanfleteren, J. Phylogenetic analysis of Meloidogyne small subunit rDNA. Journal of Nematology. 2002, 34, 319–327.
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML Version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014, 30, 1312–1313.
- Platt, H.M.; Warwick, R.M. Free-living Marine Nematodes, Part I, British Enoplids. In Synopses of the British Fauna (New Series). The Linnean Society of London: London, UK. 1998, p. 248.
- Timm, R.W. The marine nematodes of the Bay of Bengal. Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences. 1961, 1, 1–88.
- Wieser, W.; Hopper, B. Marine nematodes of the east coast of North America. I Florida. Bulletin Museum of Comparative Zoology. 1967, 135 (5), 239–344.
- Gerlach, S. A. Nematoden aus der familie der chromadoridae von den deutschen Küsten. Kieler Meeresforschungen. 1951, 8, 106–132.
- Pastor, C. T.; Ward, D. New species of Hopperia (Nematoda, Comesomatidae) and Metachromadora (Nematoda, Desmodoridae) from Patagonia, Chubut. Zootaxa. 2004, 542, 1–15.
- Gagarin, V. G.; Nguyen V. T. Three new species of free-living marine nematodes of the order Desmodorida (Nematoda) from Vietnam. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal. 2010, 89(4), 398–406.
- Gagarin, V. G.; Tu, N. D. Two new species of free living nematodes (Nematoda and Chromadorea) from mangrove thicket in Vietnam. Inland Water Biology. 2014, 7 (4), 338–347.
- Nguyen, D. Tu.; Gagarin V.G.; Phan K. Long.; Nguyen T. X. P.; Nguyen V. T. Two new species of free-living marine nematodes (Nematoda) from an area near the mouth of the Yen River of Vietnam. Biologiya Morya. 2016, 42(6), 439–448.
- Zhou, X.; Zeng, J.; Cai, L.; Fu, S.; Tan, W. Two New Species of Free-Living Marine Nematodes of the Desmodoridae from Mangrove Wetlands of Xiamen Bay, China. Journal of Ocean University of China. 2020, 19(1), 143–150.
- Murphy, D. G. An initial report on a collection of Chilean marine nematodes. Mitt. hamb. zool. Mus. Inst. 1966, 63, 29–50.
- Warwick, R. M. Fourteen new species of free-living marine nematodes from the Exe estuary. Bull. Br. Mus. nat. Hist. (Zool.). 1970, 19 (4), 137–177.
- Muthumbi, A. W.; Vincx, M. Nematodes from the Indian Ocean: description of six new species of the genus Molgolaimus Ditlevsen, 1921 (Nematoda: Desmodoridae). Bulletin de l’institut Royal dae Sciences Naturelles de Belgique. Biologie. 1996, 66, 17–28.
- Vincx, M. Free-living marine nematodes from the Southern Bight of the North Sea. Ph. D. thesis, State University of Ghent. 678 pp.
- De Ward, C. T. P. New species of Hopperia (Nematoda, Comesomatidae) and Metachromadora (Nematoda, Desmodoridae) from Patagonia, Chubut, Argentina. Zootaxa. 2004, 542, 1–15.
- Furstenberg, J.P.; Vincx, M. Three new species of Chromadoropsis species (Nematoda, Desmodoridae) from Southern Africa and the North Sea. South African Journal of Zoology. 1988, 23, 215–223. [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, A.; Riemann, F. The Bremerhaven checklist of aquatic nematodes. A catalogue of Nematoda Adenophorea excluding the Dorylaimida. Part 1. Veröff Inst Meer Bremerhaven. 1973, 4, 1–736.
- Jensen, P. Revision of Microlaimidae, erection of Molgolaimidae fam. N., and remarks on the systematic position of Paramicrolaimus (Nematoda, Desmodorida). Zool Scr . 1978, 7, 159–173. [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, S. The phylogenetic systematics of freeliving nematodes. London: The Ray Society, 1994, 383 pp.
- Leduc, D.; Verdon, V.; Zhao, Z.Q. Phylogenetic position of the Paramicrolaimidae, description of a new Paramicrolaimus species and erection of a new order to accommodate the Microlaimoidea (Nematoda: Chromadorea). Zool J Linnaean Soc. 2018, 183, 52–69. [CrossRef]


| Morphological Characters | Holotype | Paratype | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ♂1 | ♂2 | ♂3 | ♂4 | ♀1 | ♀2 | |
| a | 14.0 | 14.0 | 17.3 | 15.3 | 11.7 | 12.2 |
| b | 4.1 | 4.2 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.3 | 4.2 |
| c | 11.5 | 13.2 | 14.8 | 12.5 | 15.6 | 17.7 |
| c’ | 2.0 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 2.0 | 2.2 |
| Total body length | 896 | 977 | 1020 | 915 | 935 | 976 |
| Maximum body diameter | 64 | 70 | 59 | 60 | 80 | 80 |
| Head diameter | 22 | 24 | 24 | 23 | 26 | 28 |
| Amphideal fovea width | 15 | 13 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 16 |
| Amphideal fovea c.b.d. | 25 | 24 | 26 | 24 | 27 | 24 |
| Amphideal fovea as % of c.b.d. | 60 | 54 | 50 | 63 | 63 | 67 |
| Pharynx length | 216 | 233 | 234 | 210 | 220 | 232 |
| Pharynx c.b.d. | 59 | 67 | 57 | 60 | 71 | 75 |
| Length of double bulb | 77 | 84 | 91 | 90 | 95 | 92 |
| Bulb as % of pharynx length | 35.6 | 36.1 | 38.9 | 42.9 | 43.0 | 40.0 |
| Spicule length as arch | 68 | 63 | 68 | 64 | ||
| Gubernacular length | 31 | 30 | 31 | 31 | ||
| Cloacal /Anal body diameter | 39 | 39 | 39 | 43 | 30 | 25 |
| Distance from first precloacal supplement to anus | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Distance from last precloacal supplement to anus | 85 | 101 | 114 | 106 | ||
| Precloacal supplement number | 6 | 8 | 6 | 8 | ||
| Distance from the first protuberance to cloaca | 38 | 43 | 44 | 38 | ||
| Distance from the second protuberance to cloaca | 50 | 52 | 52 | 48 | ||
| Tail length | 78 | 74 | 69 | 73 | 60 | 55 |
| Vulva from anterior end | 520 | 575 | ||||
| Vulva c.b.d. | 77 | 80 | ||||
| V% | 55.6 | 58.9 | ||||
| species | Body Length (µm) |
Spicule Length (µm) |
numbers of supplements | internal division of pharyngeal bulb | protuberances on the tail | a | b | c | c’ | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M.(M.) complexa | 758-940 | 74 | 17 | tripartite | 2 | 8.4-11.3 | 3.4-4.4 | 7.3-12.1 | 1.3 | [19] |
| M.(M.) pulvinata | 1720 | 55 | 23 | tripartite | 2 | 18.1 | 5.4 | 15.6 | 2.0 | [20] |
| (M.) remanei | 1100-1300 | 49-55 | 5 | bipartite | * | 14 | 4.9 | 14 | 1.9-2.2 | [21] |
| M.(M.) vulgaris | 1100-1200 | 72 | 0 | tripartite | 0 | 14.1-20.0 | 4.4-4.9 | 12.1-14.5 | 1.8-2.8 | [19] |
| M.(M.) zaixsi | 890-1160 | 40-52 | 0 | tripartite | 0 | 10.5-19.3 | 4.7-7.2 | 6.8-10.1 | 1.7-2.8 | [22] |
| M.(M.) minor | 594-641 | 35-36 | 12-16 | tripartite | * | 12-15 | 4.2-4.7 | 13.5-14.9 | 1.4-1.5 | [23] |
| M.(M.) orientalis | 859-1133 | 59-63 | 0 | bipartite | ** | 13-15 | 4.8-5.3 | 15.3-19.2 | 1.0-1.3 | [24] |
| M.(M.) obscura | 786-1008 | 75-78 | 13-14 | bipartite | 2 | 11-15 | 4.2-4.5 | 10.7-12.1 | 1.4-1.6 | [25] |
| M.(M.) xiamenensis | 741-888 | 46-56 | 18 | bipartite | 3 | 11.0-14.3 | 4.4-5.2 | 10.1-12.2 | 1.5-1.7 | [26] |
| M. (M.) parobscura sp. nov. | 896-1020 | 63-68 | 6-8 | bipartite |
2 | 14.0-17.3 | 4.1-4.4 | 11.5-14.8 | 1.7-2.0 | this study |
| Morphological Characters | Holotype | Paratype | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ♂1 | ♂2 | ♂3 | ♂4 | ♀1 | ♀2 | ♀3 | |
| a | 31.0 | 30.9 | 28.3 | 30.1 | 28.2 | 24.8 | 28.3 |
| b | 8.0 | 7.4 | 7.7 | 8.2 | 7.9 | 7.9 | 8.2 |
| c | 5.7 | 5.4 | 5.7 | 5.6 | 6.7 | 6.9 | 6.1 |
| c’ | 7.6 | 7.7 | 7.2 | 7.4 | 6.9 | 6.4 | 7.2 |
| Total body length | 775 | 742 | 735 | 752 | 789 | 793 | 791 |
| Maximum body diameter | 25 | 24 | 26 | 25 | 28 | 32 | 28 |
| Head diameter | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 5 |
| Cephalic setae length | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Amphideal fovea width | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| Amphideal fovea c.b.d. | 9 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 |
| Amphidial fovea from anterior end | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 6 |
| Amphideal fovea as % of c.b.d. | 33.3 | 37.5 | 44.4 | 44.4 | 44.4 | 37.5 | 37.5 |
| Nerve ring width | 14 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 15 |
| Nerve ring c.b.d. | 20 | 20 | 21 | 20 | 20 | 21 | 20 |
| Pharynx length | 97 | 100 | 96 | 92 | 100 | 101 | 97 |
| Pharynx c.b.d. | 22 | 23 | 22 | 23 | 23 | 25 | 22 |
| Diameter of esophageal bulb | 17 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 19 | 17 |
| Spicule length as arch | 33 | 35 | 33 | 32 | |||
| Gubernacular length | 11 | 11 | 11 | 12 | |||
| Cloacal or anal body diameter | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 17 | 18 | 18 |
| Cloacal /Anal body diameter | 1.8 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.8 | |||
| Distance from first precloacal supplement to anus | 34 | 31 | 41 | 25 | |||
| Distance from second precloacal supplement to anus | 62 | 68 | 72 | 43 | |||
| Tail length | 136 | 138 | 130 | 134 | 117 | 115 | 129 |
| Vulva from anterior end | 348 | 339 | 343 | ||||
| Vulva c.b.d. | 28 | 30 | 26 | ||||
| V% | 44.1 | 42.7 | 43.3 | ||||
| species | Body Length (µm) |
Spicule Length (µm) |
numbers of supplements | a | b | c | c’ | spic/abd | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. pecticauda | 750-850 | - | absent | 23.6-30.6 | 6.6-7.2 | 7.7-10.2 | - | - | [27] |
| M. sapiens | 435-620 | 35 | absent | 19.5-24.5 | 5.4-6.8 | 8.8-10.5 | 2.6-3.5 | 1.9 | [9] |
| M. spirifer | 880-1060 | 22-25 | absent | 36.6-38.0 | 6.2-7.3 | 8.5-11.2 | 5.4-5.7 | 1.2-1.5 | [28] |
| M. drakus | 495-575 | 19-20 | 1 | 35.5-42.7 | 6.1-7.0 | 7.0-7.9 | 5.3-6.2 | 1.4-1.6 | [9] |
| M. exceptionregulum | 585-600 | 28-31 | 1 | 28.4-31.5 | 5.7-6.1 | 7.5-8.9 | 3.6-4.6 | 1.6-1.8 | [9] |
| M. mareprofundus | 610-630 | 29-32 | 1 | 24.1-30.7 | 5.8-6.7 | 7.2-7.6 | 4.6-5.1 |
1.6-1.9 | [9] |
| M. gazii | 382-430 | 29 | 2 | 27.5 | 5.6 | 6.0-6.1 | - | 2.2-2.9 | [29] |
| longicaudatus sp. nov. | 735-775 | 32-35 | 2 | 28.3-31.0 | 7.4-8.2 | 5.4-5.7 | 7.2-7.7 | 1.8-1.9 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





