Submitted:
28 June 2024
Posted:
29 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
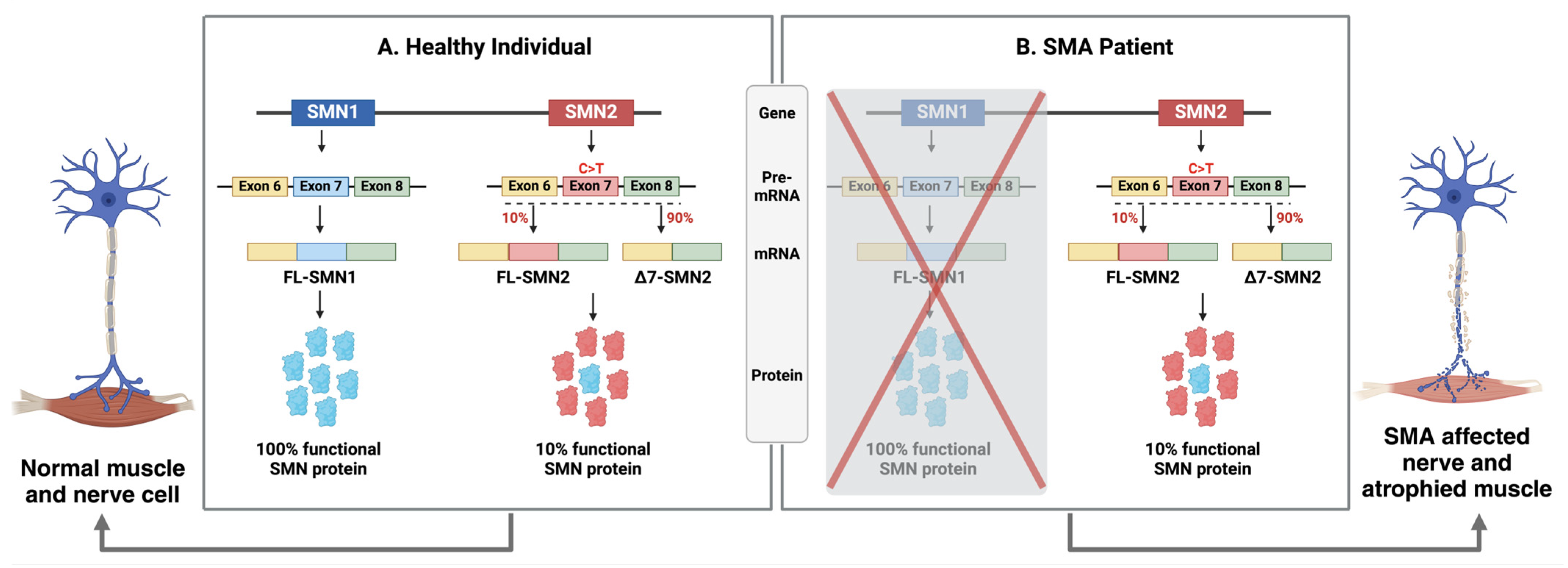
1.1. Genetic Background of SMA & Diverse Role of SMN
1.2. Clinical Manifestation of SMA
| SMA type | Age of Onset | Life Expectancy | SMN2 Copy Number | Clinical Manifestation | Alternative Name | Estimated SMA Portion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Prenatal | < 1month | 1 | Require assisted respiration at birth; Fetus dysplay reduced mobement | - | Unclear, maybe < 1% |
| 1 | 0-6 months | <2 years | 2 | Unable to sit independently, respiratory and feeding support required | Werdnig–Hoffman disease | ~60% |
| 2 | <18 months | >2 years | 3, 4 | Ability to independently sit, inability to walk, respiratory (often non-invasive) and feeding support required | Dubowitz disease | ~27% |
| 3a | 18 months – 3 years | Adult | 3, 4 | Full ambulation, but slowly progressive muscle atrophy and weakness. | Kugelberg–Welander disease | ~12% |
| 3b | >3 years | Adult | 4 | |||
| 4 | >21 years | Adult | ≥4 | Usually preserved walking ability | Adult- onset SMA | ~1% |
2. FDA Approved Gene-targeting SMN Replacement Therapies
2.1. Nusinersen
Outline
Discovery and Mechanism of action
Clinical trials
2.2. Onasemnogene Abeparvovec
Outline
Discovery and Mechanism of action
Clinical trials
2.3. Risdiplam
Outline
Discovery and Mechanism of action
Clinical trials
| Drug/company | Type | Mechanism of action | Status | Route of administration | Protocol | Targeted population | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nusinersen (Spinraza)/Biogen | Antisense oligonucleotide | splicing modifier of SMN2 (MOE chemistry targeting SMN2 ISS-N1 that promotes exon 7 inclusion) | FDA approval- December 2016; EMA approval- May 2017 | intrathecal | 3 loading doses at 14-day interval, 4th loading dose 30 days after the 3rd dose, and maintenance dose every 4 months thereafter | all ages and all types of SMA | up to $125,000 per dose; drug cost for the first year: $750,000 and then $375,000 annually |
| Onasemnogene abeparvovec-xioi (Zolgensma)/Novartis | Gene therapy | replacement of SMN1 gene (scAAV9-SMN under the control of a CBA promoter) | FDA approval- May 2019; EMA approval- conditional approval on May 2020 | intravenous | Single dose | FDA: SMA patient less than 2 years of age with bi-allelic mutations in the SMN1 gene. EMA: patients with 5q SMA with a bi-allelic mutation in the SMN1 gene and a clinical diagnosis of SMA type 1, or patients with 5q SMA with a bi-allelic mutation in the SMN1 gene and up to 3 copies of the SMN2 gene | $2,125,000 (single injection) |
| Risdiplam (Evrysdi)/Roche | Small molecule | splicing modifier of SMN2 | FDA approval- August 2020; EMA approval March 2021 | orally | Once daily | patients 2 months of age and older | up to $340,000 a year (cheaper in younger patient as dosing dependes on weight) |
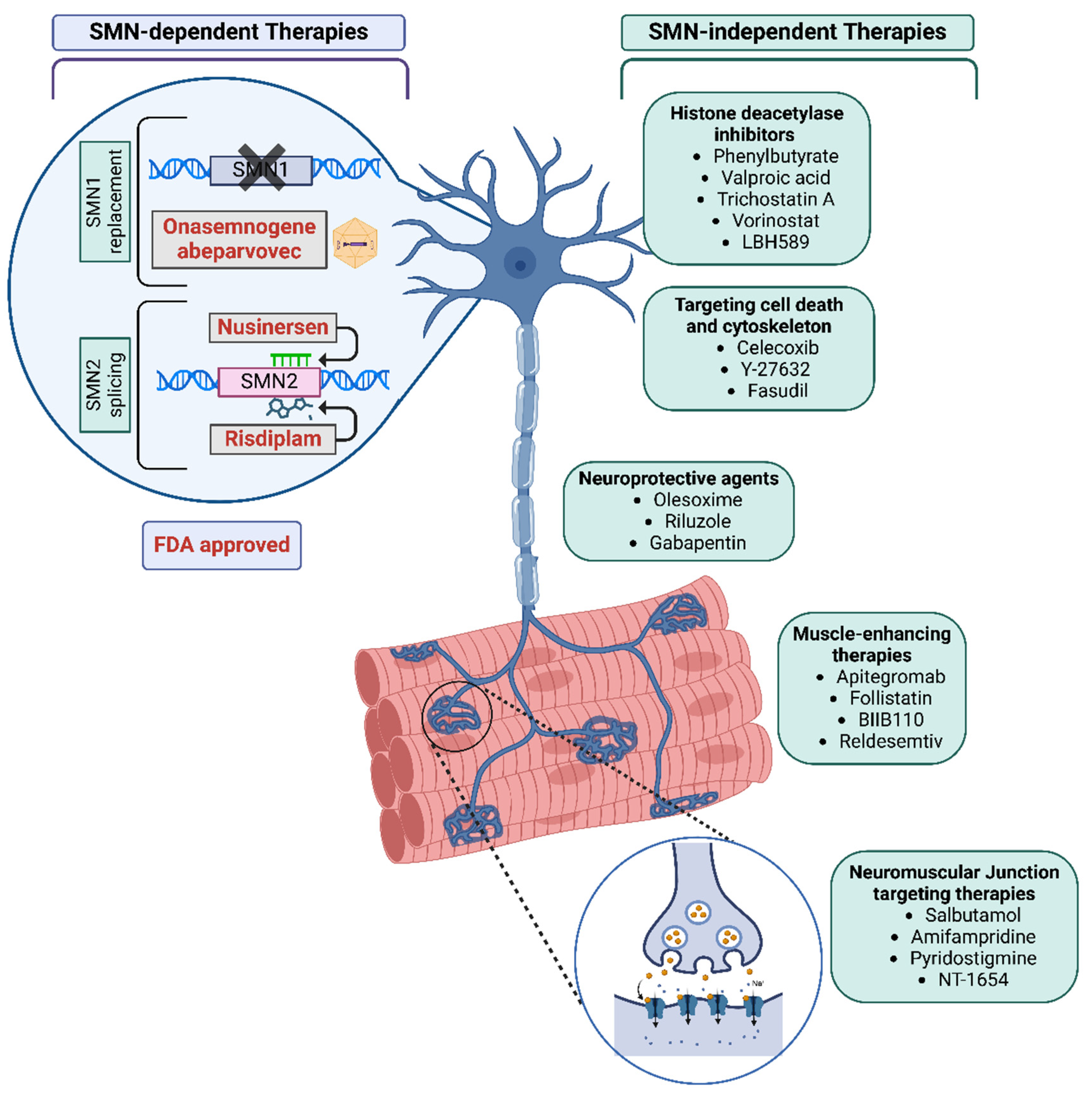
3. Broader Therapeutic Strategies: SMN-Dependent and Independent Approaches
4. Challenges in the treatment era: Are We There Yet in the Battle Against SMA?
5. Future directions: Advancing the battle against SMA
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Groen, E.J.N.; Talbot, K.; Gillingwater, T.H. Advances in Therapy for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Promises and Challenges. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, S.; Bürglen, L.; Reboullet, S.; Clermont, O.; Burlet, P.; Viollet, L.; Benichou, B.; Cruaud, C.; Millasseau, P.; Zeviani, M.; et al. Identification and Characterization of a Spinal Muscular Atrophy-Determining Gene. Cell 1995, 80, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrank, B.; Götz, R.; Gunnersen, J.M.; Ure, J.M.; Toyka, K.V.; Smith, A.G.; Sendtner, M. Inactivation of the Survival Motor Neuron Gene, a Candidate Gene for Human Spinal Muscular Atrophy, Leads to Massive Cell Death in Early Mouse Embryos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9920–9925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghes, A. H.; Beattie, C. E. Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Why Do Low Levels of Survival Motor Neuron Protein Make Motor Neurons Sick? Nat Rev Neurosci 2009, 10, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, G.; Gillingwater, T.H. Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Going Beyond the Motor Neuron. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, C.; Gilbert, N.; Simard, L. Smn Gene Duplication and the Emergence of the Smn2 Gene Occurred in Distinct Hominids: Smn2 Is Unique to Homo Sapiens. Hum. Genet. 2001, 108, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorson, C.L.; Androphy, E.J. An Exonic Enhancer Is Required for Inclusion of an Essential Exon in the Sma-Determining Gene Smn. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaytow, H.; Huang, Y.-T.; Gillingwater, T.H.; Faller, K.M.E. The Role of Survival Motor Neuron Protein (Smn) in Protein Homeostasis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3877–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Fischer, U.; Wang, F.; Dreyfuss, G. The Spinal Muscular Atrophy Disease Gene Product, Smn, and Its Associated Protein Sip1 Are in a Complex with Spliceosomal Snrnp Proteins. Cell 1997, 90, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, E.; Pera, M.C.; Scoto, M.; Finkel, R.; Muntoni, F. Spinal Muscular Atrophy - Insights and Challenges in the Treatment Era. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaytow, H.; Faller, K.M.; Huang, Y.-T.; Gillingwater, T.H. Spinal Muscular Atrophy: From Approved Therapies to Future Therapeutic Targets for Personalized Medicine. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, S.J.; Battle, D.J.; Dreyfuss, G. Molecular Functions of the Smn Complex. J. Child Neurol. 2007, 22, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keinath, M. C.; Prior, D. E.; Prior, T. W. Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Mutations, Testing, and Clinical Relevance. Appl Clin Genet 2021, 14, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorson, C.L.; Hahnen, E.; Androphy, E.J.; Wirth, B. A Single Nucleotide in the Smn Gene Regulates Splicing and Is Responsible for Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1999, 96, 6307–6311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monani, U.R.; Lorson, C.L.; Parsons, D.W.; Prior, T.W.; Androphy, E.J.; Burghes, A.H.M.; McPherson, J.D. A Single Nucleotide Difference That Alters Splicing Patterns Distinguishes the Sma Gene Smn1 from the Copy Gene Smn2. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, A.; DiDonato, C.J. Animal Models of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. J. Child Neurol. 2007, 22, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.-J.; Foster, D.G.; Zhang, N.-Y.; Kanisha, K.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Sclafani, R.A.; Hansen, K.C.; Peng, J.; Liu, C.-W. Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 9x Deubiquitinates and Stabilizes the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Protein-Survival Motor Neuron. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 43741–43752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, G.; Princivalle, A.; Forti, F.; Lizier, C.; Zeviani, M. Expression of the Smn Gene, the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Determining Gene, in the Mammalian Central Nervous System. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, S.; Sarret, C. Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Targets in Spinal Muscular Atrophy (Sma). Arch. De Pediatr. 2020, 27, 7S3–7S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coovert, D.D.; Le, T.T.; McAndrew, P.E.; Strasswimmer, J.; Crawford, T.O.; Mendell, J.R.; Coulson, S.E.; Androphy, E.J.; Prior, T.W.; Burghes, A.H.M. The Survival Motor Neuron Protein in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dreyfuss, G. A Novel Nuclear Structure Containing the Survival of Motor Neurons Protein. Embo J. 1996, 15, 3555–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T.; Almeida, F.; Calapez, A.; Lafarga, M.; Berciano, M. T.; Carmo-Fonseca, M. The Spinal Muscular Atrophy Disease Gene Product, Smn: A Link between Snrnp Biogenesis and the Cajal (Coiled) Body. J Cell Biol 1999, 147, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Gubitz, A.K.; Wan, L.; Battle, D.J.; Dostie, J.; Golembe, T.J.; Dreyfuss, G. Gemins Modulate the Expression and Activity of the Smn Complex. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, E.; Sumner, C. J.; Muntoni, F.; Darras, B. T.; Finkel, R. S. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2022, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.N.; Howell, M.D.; Ottesen, E.W.; Singh, N.N. Diverse Role of Survival Motor Neuron Protein. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Gene Regul. Mech. 2017, 1860, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, S.; Burlet, P.; Liu, Q.; Bertrandy, S.; Clermont, O.; Munnich, A.; Dreyfuss, G.; Melki, J. Correlation between Severity and Smn Protein Level in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Nat. Genet. 1997, 16, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, K.K.Y.; Lin, M.-Y.; Zingg, B.; Feng, Z.; Ko, C.-P. Synaptic Defects in the Spinal and Neuromuscular Circuitry in a Mouse Model of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. PLOS ONE 2010, 5, e15457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentis, G.Z.; Blivis, D.; Liu, W.; Drobac, E.; Crowder, M.E.; Kong, L.; Alvarez, F.J.; Sumner, C.J.; O'Donovan, M.J. Early Functional Impairment of Sensory-Motor Connectivity in a Mouse Model of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Neuron 2011, 69, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, E. V.; Simon, C.M.; Pagiazitis, J.G.; Chalif, J.I.; Vukojicic, A.; Drobac, E.; Wang, X.; Mentis, G.Z. Reduced Sensory Synaptic Excitation Impairs Motor Neuron Function Via Kv2.1 in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Nat Neurosci 2017, 20, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Valdivia, D.O.; Simon, C.M.; Hassinan, C.W.; Delestrée, N.; Ramos, D.M.; Park, J.H.; Pilato, C.M.; Xu, X.; Crowder, M.; et al. Impaired Prenatal Motor Axon Development Necessitates Early Therapeutic Intervention in Severe Sma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariya, S.; Park, G.-H.; Maeno-Hikichi, Y.; Leykekhman, O.; Lutz, C.; Arkovitz, M.S.; Landmesser, L.T.; Monani, U.R. Reduced Smn Protein Impairs Maturation of the Neuromuscular Junctions in Mouse Models of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 2552–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, L.M.; Comley, L.H.; Thomson, D.; Parkinson, N.; Talbot, K.; Gillingwater, T.H. Selective Vulnerability of Motor Neurons and Dissociation of Pre- and Post-Synaptic Pathology at the Neuromuscular Junction in Mouse Models of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 17, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Wang, X.; Choe, D.W.; Polley, M.; Burnett, B.G.; Bosch-Marcé, M.; Griffin, J.W.; Rich, M.M.; Sumner, C.J. Impaired Synaptic Vesicle Release and Immaturity of Neuromuscular Junctions in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Mice. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darras, B.T.; Crawford, T.O.; Finkel, R.S.; Mercuri, E.; De Vivo, D.C.; Oskoui, M.; Tizzano, E.F.; Ryan, M.M.; Muntoni, F.; Zhao, G.; et al. Neurofilament as a Potential Biomarker for Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, S. J.; Kissel, J. T. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Neurol Clin 2015, 33, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, B. Spinal Muscular Atrophy: In the Challenge Lies a Solution. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 306–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.T.; Coovert, D.D.; Monani, U.R.; Morris, G.E.; Burghes, A.H.M. The Survival Motor Neuron (Smn) Protein: Effect of Exon Loss and Mutation on Protein Localization. neurogenetics 2000, 3, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, P. J.; Man, N.T.; Lorson, C.L.; Le, T.T.; Androphy, E.J.; Burghes, A.H.; Morris, G.E. The Exon 2b Region of the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Protein, Smn, Is Involved in Self-Association and Sip1 Binding. Hum Mol Genet 2000, 9, 2869–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellizzoni, L.; Charroux, B.; Dreyfuss, G. Smn Mutants of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Patients Are Defective in Binding to Snrnp Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1999, 96, 11167–11172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frugier, T.; Tiziano, F.D.; Cifuentes-Diaz, C.; Miniou, P.; Roblot, N.; Dierich, A.; Le Meur, M.; Melki, J. Nuclear Targeting Defect of Smn Lacking the C-Terminus in a Mouse Model of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, B.G.; Muñoz, E.; Tandon, A.; Kwon, D.Y.; Sumner, C.J.; Fischbeck, K.H. Regulation of Smn Protein Stability. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.T.; Pham, L.T.; Butchbach, M.E.; Zhang, H.L.; Monani, U.R.; Coovert, D.D.; Gavrilina, T.O.; Xing, L.; Bassell, G.J.; Burghes, A.H. Smndelta7, the Major Product of the Centromeric Survival Motor Neuron (Smn2) Gene, Extends Survival in Mice with Spinal Muscular Atrophy and Associates with Full-Length Smn. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.L.; Pan, F.; Hong, D.; Shenoy, S.M.; Singer, R.H.; Bassell, G.J. Active Transport of the Survival Motor Neuron Protein and the Role of Exon-7 in Cytoplasmic Localization. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 6627–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahnen, E.; Schönling, J.; Rudnik-Schöneborn, S.; Raschke, H.; Zerres, K.; Wirth, B. Missense Mutations in Exon 6 of the Survival Motor Neuron Gene in Patients with Spinal Muscular Atrophy (Sma). Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça, R.d.H.; Matsui, C.; Polido, G.J.; Silva, A.M.S.; Kulikowski, L.; Dias, A.T.; Zanardo, E.A.; Solla, D.J.F.; Gurgel-Giannetti, J.; de Moura, A.C.M.L.; et al. Intragenic Variants in the Smn1 Gene Determine the Clinical Phenotype in 5q Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Neurol. Genet. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beattie, C.E.; Carrel, T.L.; McWhorter, M.L. Fishing for a Mechanism: Using Zebrafish to Understand Spinal Muscular Atrophy. J. Child Neurol. 2007, 22, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, S. J.; Kissel, J. T. Spinal Muscular Atrophy: A Timely Review. Arch Neurol 2011, 68, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubowitz, V. Ramblings in the History of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2009, 19, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, W.D.; Kassar, D.; Kissel, J.T. Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Diagnosis and Management in a New Therapeutic Era. Muscle Nerve 2014, 51, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, R.; Bertini, E.; Muntoni, F.; Mercuri, E.; Enmc Sma Workshop Study Group. 209th Enmc International Workshop: Outcome Measures and Clinical Trial Readiness in Spinal Muscular Atrophy 7-9 November 2014, Heemskerk, the Netherlands. Neuromuscul Disord 2015, 25, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awano, T.; Kim, J.-K.; Monani, U.R. Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Journeying from Bench to Bedside. Neurotherapeutics 2014, 11, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Amico, A.; Mercuri, E.; Tiziano, F.D.; Bertini, E. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2011, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T. H. New and Developing Therapies in Spinal Muscular Atrophy: From Genotype to Phenotype to Treatment and Where Do We Stand? Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aartsma-Rus, A. Fda Approval of Nusinersen for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Makes 2016 the Year of Splice Modulating Oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acid. Ther. 2017, 27, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Spinraza™ Safely and Effectively. Food and Drug Administration, 2016.
- Singh, N. K.; Singh, N.N.; Androphy, E.J.; Singh, R.N. Splicing of a Critical Exon of Human Survival Motor Neuron Is Regulated by a Unique Silencer Element Located in the Last Intron. Mol Cell Biol 2006, 26, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottesen, E.W. Iss-N1 Makes the First Fda-Approved Drug for Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Transl. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Vickers, T.A.; Okunola, H.L.; Bennett, C.F.; Krainer, A.R. Antisense Masking of an Hnrnp A1/A2 Intronic Splicing Silencer Corrects Smn2 Splicing in Transgenic Mice. Am J Hum Genet 2008, 82, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.N.; Howell, M.D.; Androphy, E.J.; Singh, R.N. How the Discovery of Iss-N1 Led to the First Medical Therapy for Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Sahashi, K.; Hung, G.; Rigo, F.; Passini, M.A.; Bennett, C.F.; Krainer, A.R. Antisense Correction of Smn2 Splicing in the Cns Rescues Necrosis in a Type Iii Sma Mouse Model. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.H.; Schray, R.C.; Patterson, C.A.; Ayitey, S.O.; Tallent, M.K.; Lutz, G.J. Oligonucleotide-Mediated Survival of Motor Neuron Protein Expression in Cns Improves Phenotype in a Mouse Model of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 7633–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passini, M.A.; Bu, J.; Richards, A.M.; Kinnecom, C.; Sardi, S.P.; Stanek, L.M.; Hua, Y.; Rigo, F.; Matson, J.; Hung, G.; et al. Antisense Oligonucleotides Delivered to the Mouse Cns Ameliorate Symptoms of Severe Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 72ra18–72ra18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigo, F.; Chun, S.J.; Norris, D.A.; Hung, G.; Lee, S.; Matson, J.; Fey, R.A.; Gaus, H.; Hua, Y.; Grundy, J.S.; et al. Pharmacology of a Central Nervous System Delivered 2'-O-Methoxyethyl-Modified Survival of Motor Neuron Splicing Oligonucleotide in Mice and Nonhuman Primates. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 350, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Sahashi, K.; Rigo, F.; Hung, G.; Horev, G.; Bennett, C.F.; Krainer, A.R. Peripheral Smn Restoration Is Essential for Long-Term Rescue of a Severe Spinal Muscular Atrophy Mouse Model. Nature 2011, 478, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, E.Y.; Miller, M.R.; Robbins, K.L.; Lombardi, A.M.; Atkinson, A.K.; Brehm, A.J.; Lorson, C.L. Morpholino Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting Intronic Repressor Element1 Improve Phenotype in Sma Mouse Models. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 4832–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, R.S.; Mercuri, E.; Darras, B.T.; Connolly, A.M.; Kuntz, N.L.; Kirschner, J.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Saito, K.; Servais, L.; Tizzano, E.; et al. Nusinersen Versus Sham Control in Infantile-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, E.; Darras, B.T.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Day, J.W.; Campbell, C.; Connolly, A.M.; Iannaccone, S.T.; Kirschner, J.; Kuntz, N.L.; Saito, K.; et al. Nusinersen Versus Sham Control in Later-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vivo, D.C.; Bertini, E.; Swoboda, K.J.; Hwu, W.-L.; Crawford, T.O.; Finkel, R.S.; Kirschner, J.; Kuntz, N.L.; Parsons, J.A.; Ryan, M.M.; et al. Nusinersen Initiated in Infants During the Presymptomatic Stage of Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Interim Efficacy and Safety Results from the Phase 2 Nurture Study. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2019, 29, 842–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, T.A. Therapeutic Advances in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Paediatr. Child Heal. 2023, 33, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, V.A.; Pirola, A.; Albamonte, E.; Pane, M.; Lizio, A.; D'Amico, A.; Catteruccia, M.; Cutrera, R.; Bruno, C.; Pedemonte, M.; et al. Respiratory Needs in Patients with Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy Treated with Nusinersen. J. Pediatr. 2020, 219, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamadani, F.; Zhang, K.; Parikh, R.; Wu, H.; Rasmussen, T.P.; Bahal, R.; Zhong, X.-B.; Manautou, J.E. Adverse Drug Reactions and Toxicity of the Food and Drug Administration-Approved Antisense Oligonucleotide Drugs. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2022, 50, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakevska, Z.; Yokota, T. Challenges and Future Perspective of Antisense Therapy for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: A Review. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2023, 102, 151326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foust, K.D.; Nurre, E.; Montgomery, C.L.; Hernandez, A.; Chan, C.M.; Kaspar, B.K. Intravascular Aav9 Preferentially Targets Neonatal Neurons and Adult Astrocytes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 27, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, J.; Nobre, R.J.; de Almeida, L.P. Gene Therapy for the Cns Using Aavs: The Impact of Systemic Delivery by Aav9. J. Control. Release 2016, 241, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valori, C.F.; Ning, K.; Wyles, M.; Mead, R.J.; Grierson, A.J.; Shaw, P.J.; Azzouz, M. Systemic Delivery of Scaav9 Expressing Smn Prolongs Survival in a Model of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 35ra42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.; Ferraiuolo, L.; Schmelzer, L.; Braun, L.; McGovern, V.; Likhite, S.; Michels, O.; Govoni, A.; Fitzgerald, J.; Morales, P.; et al. Improving Single Injection Csf Delivery of Aav9-Mediated Gene Therapy for Sma: A Dose-Response Study in Mice and Nonhuman Primates. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendell, J.R.; Al-Zaidy, S.; Shell, R.; Arnold, W.D.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R.; Prior, T.W.; Lowes, L.; Alfano, L.; Berry, K.; Church, K.; et al. Single-Dose Gene-Replacement Therapy for Spinal Muscular Atrophy. New Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zaidy, S.; Pickard, A.S.; Kotha, K.; Alfano, L.N.; Lowes, L.; Paul, G.; Church, K.; Lehman, K.; Sproule, D.M.; Dabbous, O.; et al. Health Outcomes in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 1 Following Avxs-101 Gene Replacement Therapy. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 54, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowes, L. P.; Alfano, L.N.; Arnold, W.D.; Shell, R.; Prior, T.W.; McColly, M.; Lehman, K.J.; Church, K.; Sproule, D.M.; Nagendran, S.; Menier, M.; Feltner, D.E.; Wells, C.; Kissel, J.T.; Al-Zaidy, S.; Mendell, J. Impact of Age and Motor Function in a Phase 1/2a Study of Infants with Sma Type 1 Receiving Single-Dose Gene Replacement Therapy. Pediatr Neurol 2019, 98, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Onasemnogene Abeparvovec: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, A.; Calderon, H. Onasemnogene Abeparvovec (AVXS-101) for the Treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 26, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, K.A.; Farrar, M.A.; Muntoni, F.; Saito, K.; Mendell, J.R.; Servais, L.; McMillan, H.J.; Finkel, R.S.; Swoboda, K.J.; Kwon, J.M.; et al. Onasemnogene Abeparvovec for Presymptomatic Infants with Two Copies of Smn2 at Risk for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 1: The Phase Iii Spr1nt Trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Zolgensma Safely and Effectively. Food and Drug Administration, 2019.
- Dhillon, S. Risdiplam: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naryshkin, N.A.; Weetall, M.; Dakka, A.; Narasimhan, J.; Zhao, X.; Feng, Z.; Ling, K.K.Y.; Karp, G.M.; Qi, H.; Woll, M.G.; et al. Motor Neuron Disease. Smn2 Splicing Modifiers Improve Motor Function and Longevity in Mice with Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Science 2014, 345, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratni, H.; Karp, G.M.; Weetall, M.; Naryshkin, N.A.; Paushkin, S.V.; Chen, K.S.; McCarthy, K.D.; Qi, H.; Turpoff, A.; Woll, M.G.; et al. Specific Correction of Alternative Survival Motor Neuron 2 Splicing by Small Molecules: Discovery of a Potential Novel Medicine to Treat Spinal Muscular Atrophy. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 6086–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratni, H.; Ebeling, M.; Baird, J.; Bendels, S.; Bylund, J.; Chen, K.S.; Denk, N.; Feng, Z.; Green, L.; Guerard, M.; et al. Discovery of Risdiplam, a Selective Survival of Motor Neuron-2 ( Smn2) Gene Splicing Modifier for the Treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (Sma). J Med Chem, 2018; 61, 6501–6517. [Google Scholar]
- Poirier, A.; Weetall, M.; Heinig, K.; Bucheli, F.; Schoenlein, K.; Alsenz, J.; Bassett, S.; Ullah, M.; Senn, C.; Ratni, H.; et al. Risdiplam Distributes and Increases Smn Protein in Both the Central Nervous System and Peripheral Organs. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2018, 6, e00447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaramakrishnan, M.; McCarthy, K.D.; Campagne, S.; Huber, S.; Meier, S.; Augustin, A.; Heckel, T.; Meistermann, H.; Hug, M.N.; Birrer, P.; et al. Binding to Smn2 Pre-Mrna-Protein Complex Elicits Specificity for Small Molecule Splicing Modifiers. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Bai, R.; Shi, Y. Molecular Choreography of Pre-Mrna Splicing by the Spliceosome. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2019, 59, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratni, H.; Scalco, R.S.; Stephan, A.H. Risdiplam, the First Approved Small Molecule Splicing Modifier Drug as a Blueprint for Future Transformative Medicines. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 874–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranello, G.; Darras, B.T.; Day, J.W.; Deconinck, N.; Klein, A.; Masson, R.; Mercuri, E.; Rose, K.; El-Khairi, M.; Gerber, M.; et al. Risdiplam in Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy. New Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranello, G.; Servais, L.; Day, J.W.; Deconinck, N.; Mercuri, E.; Klein, A.; Darras, B.; Masson, R.; Kletzl, H.; Cleary, Y.; et al. Firefish Part 1: 1-Year Results on Motor Function in Babies with Type 1 Sma (S25.003). Neurology 2019, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servais, L.; Baranello, G.; Day, J.W.; Deconinck, N.; Mercuri, E.; Klein, A.; Darras, B.; Masson, R.; Kletzl, H.; Cleary, Y.; et al. Firefish Part 1: Survival, Ventilation and Swallowing Ability in Infants with Type 1 Sma Receiving Risdiplam (Rg7916) (S25.008). Neurology 2019, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servais, L.; Baranello, G.; Masson, R.; Mazurkiewicz-Bełdzińska, M.; Rose, K.; Vlodavets, D.; Xiong, H.; Zanoteli, E.; El-Khairi, M.; Fuerst-Recktenwald, S.; et al. Firefish Part 2: Efficacy and Safety of Risdiplam (Rg7916) in Infants with Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy (Sma) (1302). Neurology 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, R.S.; McDermott, M.P.; Kaufmann, P.; Darras, B.T.; Chung, W.K.; Sproule, D.M.; Kang, P.B.; Foley, A.R.; Yang, M.L.; Martens, W.B.; et al. Observational Study of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type I and Implications for Clinical Trials. Neurology 2014, 83, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analyst R, Webcast A. Roche Ir - Aan 2020 Highlights.
- Mercuri, E.; Barisic, N.; Boespflug-Tanguy, O.; Deconinck, N.; Kostera-Pruszczyk, A.; Masson, R.; Mazzone, E.; Nascimento, A.; Saito, K.; Vlodavets, D.; et al. Sunfish Part 2: Efficacy and Safety of Risdiplam (Rg7916) in Patients with Type 2 or Non-Ambulant Type 3 Spinal Muscular Atrophy (Sma) (1260). Neurology 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriboga, C.; Bruno, C.; Day, J.W.; Duong, T.; Fischer, D.; Kirschner, J.; Muntoni, F.; Fuerst-Recktenwald, S.; Gerber, M.; Gorni, K.; et al. Jewelfish: Safety and Pharmacodynamic Data in Non-Naïve Patients with Spinal Muscular Atrophy (Sma) Receiving Treatment with Risdiplam (Rg7916) (772). Neurology 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriboga, C.A.; Mercuri, E.; Fischer, D.; Kraus, D.; Yeung, W.Y.; Kletzl, H.; Gerber, M.; Cleary, Y.; Gorni, K.; Khwaja, O. Jewelfish: Risdiplam (Rg7916) Increases Smn Protein in Non-Naïve Patients with Sma. In 23rd International Annual Congress of the World Muscle Society; Mendoza, Argentina: Roche, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bertini, E.; Day, J.; Muhaizea, M.; Xiong, H.; Servais, L.; Prufer, A.; Tichy, M.; Yeung, W.; Gorni, K. P.362rainbowfish: A Study of Risdiplam (Rg7916) in Newborns with Pre-Symptomatic Spinal Muscular Atrophy (Sma). Neuromuscul. Disord. 2019, 29, S187–S187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakazu, J.; Walker, N.L.; Babin, K.C.; Trettin, K.A.; Lee, C.; Sutker, P.B.; Kaye, A.M.; Kaye, A.D. Risdiplam for the Use of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Orthop. Rev. 2021, 13, 25579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Amico, A.; Mercuri, E.; Tiziano, F.D.; Bertini, E. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2011, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-H. New and Developing Therapies in Spinal Muscular Atrophy: From Genotype to Phenotype to Treatment and Where Do We Stand? International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, A.N.; Androphy, E.J.; Hodgetts, K.J. Small Molecules in Development for the Treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 10067–10083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brichta, L.; Hofmann, Y.; Hahnen, E.; Siebzehnrubl, F.A.; Raschke, H.; Blumcke, I.; Eyupoglu, I.Y.; Wirth, B. Valproic Acid Increases the Smn2 Protein Level: A Well-Known Drug as a Potential Therapy for Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Hum Mol Genet 2003, 12, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, C.J.; Huynh, T.N.; Markowitz, J.A.; Perhac, J.S.; Hill, B.; Coovert, D.D.; Schussler, K.; Chen, X.; Jarecki, J.; Burghes, A.H.M.; et al. Valproic Acid Increases Smn Levels in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Patient Cells. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 54, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassi, C.; Angelozzi, C.; Tiziano, F.D.; Vitali, T.; De Vincenzi, E.; Boninsegna, A.; Villanova, M.; Bertini, E.; Pini, A.; Neri, G.; et al. Phenylbutyrate Increases Smn Expression in Vitro: Relevance for Treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 12, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadman, R. I.; van der Pol, W.L.; Bosboom, W.M.; Asselman, F.L.; van den Berg, L.H.; Iannaccone, S.T.; Vrancken, A.F. Drug Treatment for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Types Ii and Iii. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2020, 1, CD006282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, L.-K.; Tsai, M.-S.; Ting, C.-H.; Li, H. Multiple Therapeutic Effects of Valproic Acid in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Model Mice. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 86, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafay, A.; Hieu, T.H.; Doheim, M.F.; Kassem, M.A.M.; Eldoadoa, M.F.; Holloway, S.K.; Abo-Elghar, H.; Hirayama, K.; Huy, N.T. Efficacy and Safety of Valproic Acid for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahe, C.; Vitali, T.; Tiziano, F.D.; Angelozzi, C.; Pinto, A.M.; Borgo, F.; Moscato, U.; Bertini, E.; Mercuri, E.; Neri, G. Phenylbutyrate Increases Smn Gene Expression in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Patients. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 13, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauke, J.; Riessland, M.; Lunke, S.; Eyüpoglu, I.Y.; Blümcke, I.; El-Osta, A.; Wirth, B.; Hahnen, E. Survival Motor Neuron Gene 2 Silencing by DNA Methylation Correlates with Spinal Muscular Atrophy Disease Severity and Can Be Bypassed by Histone Deacetylase Inhibition. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 18, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narver, H.L.; Kong, L.; Burnett, B.G.; Choe, D.W.; Bosch-Marcé, M.; Taye, A.A.; Eckhaus, M.A.; Sumner, C.J. Sustained Improvement of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Mice Treated with Trichostatin a Plus Nutrition. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayangaç-Erden, D.; Bora, G.; Ayhan, P.; Kocaefe, C.; Dalkara, S.; Yelekçi, K.; Demir, A.S.; Erdem-Yurter, H. Histone Deacetylase Inhibition Activity and Molecular Docking of (E )-Resveratrol: Its Therapeutic Potential in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2009, 73, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliarini, V.; Guerra, M.; Di Rosa, V.; Compagnucci, C.; Sette, C. Combined Treatment with the Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Lbh589 and a Splice-Switch Antisense Oligonucleotide Enhances Smn2 Splicing and Smn Expression in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Cells. J. Neurochem. 2019, 153, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiziano, F.D.; Lomastro, R.; Pinto, A.M.; Messina, S.; D'Amico, A.; Fiori, S.; Angelozzi, C.; Pane, M.; Mercuri, E.; Bertini, E.; et al. Salbutamol Increases Survival Motor Neuron (Smn) Transcript Levels in Leucocytes of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (Sma) Patients: Relevance for Clinical Trial Design. J. Med Genet. 2010, 47, 856–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, L.; Cossins, J.; Beeson, D. Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptor Agonists Enhance Achr Clustering in C2c12 Myotubes: Implications for Therapy of Myasthenic Disorders. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2018, 5, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, S.; Giossi, R.; Zanin, R.; Porcelli, V.; Iannacone, C.; Baranello, G.; Ingenito, G.; Iyadurai, S.; Stevic, Z.; Peric, S.; Maggi, L. Amifampridine Safety and Efficacy in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Ambulatory Patients: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Phase 2 Trial. J Neurol 2022, 269, 5858–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, M.; A Wijngaarde, C.; Bartels, B.; Asselman, F.-L.; Otto, L.A.M.; E Habets, L.; A van Eijk, R.P.; Middelkoop, B.M.; Goedee, H.S.; de Groot, J.F.; et al. Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial with Pyridostigmine in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Types 2-4. Brain Commun. 2022, 5, fcac324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boido, M.; De Amicis, E.; Valsecchi, V.; Trevisan, M.; Ala, U.; Ruegg, M.A.; Hettwer, S.; Vercelli, A. Increasing Agrin Function Antagonizes Muscle Atrophy and Motor Impairment in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-K.; Caine, C.; Awano, T.; Herbst, R.; Monani, U.R. Motor Neuronal Repletion of the Nmj Organizer, Agrin, Modulates the Severity of the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Disease Phenotype in Model Mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaifer, K. A.; Villalon, E.; Smith, C.E.; Simon, M.E.; Marquez, J.; Hopkins, A.E.; Morcos, T.I.; Lorson, C.L. Aav9-Dok7 Gene Therapy Reduces Disease Severity in Smn(2b/-) Sma Model Mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020, 530, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Meng, J.; Malerba, A.; Catapano, F.; Sintusek, P.; Jarmin, S.; Feng, L.; Lu-Nguyen, N.; Sun, L.; Mariot, V.; et al. Myostatin Inhibition in Combination with Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy Improves Outcomes in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. J. Cachex- Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 768–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.K.; O’shea, K.M.; Khairallah, R.J.; Howell, K.; Paushkin, S.; Chen, K.S.; Cote, S.M.; Webster, M.T.; Stains, J.P.; Treece, E.; et al. Specific Inhibition of Myostatin Activation Is Beneficial in Mouse Models of Sma Therapy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 28, 1076–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, T. O.; Darras, B.T.; Day, J.W.; Young, S.D.; Duong, T.; Nelson, L.L.; Barrett, D.; Song, G.; Bilic, S.; Cote, S.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Apitegromab in Patients with Spinal Muscular Atrophy Types 2 and 3: The Phase 2 Topaz Study. Neurology 2024, 102, e209151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Ling, K.K.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, C.; Karp, G.; Welch, E.M.; Naryshkin, N.; Ratni, H.; Chen, K.S.; Metzger, F.; et al. Pharmacologically Induced Mouse Model of Adult Spinal Muscular Atrophy to Evaluate Effectiveness of Therapeutics after Disease Onset. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.J.; Hwee, D.T.; Kim, L.H.; Durham, N.; Yang, H.T.; Hinken, A.C.; Kennedy, A.R.; Terjung, R.L.; Jasper, J.R.; Malik, F.I.; et al. Fast Skeletal Muscle Troponin Activator Ck-2066260 Increases Fatigue Resistance by Reducing the Energetic Cost of Muscle Contraction. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 4615–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marisa Wexler, MS. Reldesemtiv (Formerly Ck-2127107) for Sma. Nov. 15, 2022 2022.
- Boyd, P.J.; Tu, W.-Y.; Shorrock, H.K.; Groen, E.J.N.; Carter, R.N.; Powis, R.A.; Thomson, S.R.; Thomson, D.; Graham, L.C.; Motyl, A.A.L.; et al. Bioenergetic Status Modulates Motor Neuron Vulnerability and Pathogenesis in a Zebrafish Model of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. PLOS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordet, T.; Buisson, B.; Michaud, M.; Drouot, C.; Galea, P.; Delaage, P.; Akentieva, N.P.; Evers, A.S.; Covey, D.F.; Ostuni, M.A.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Cholest-4-En-3-One, Oxime (Tro19622), a Novel Drug Candidate for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2007, 322, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, B.; Karakaya, M.; Kye, M.J.; Mendoza-Ferreira, N. Twenty-Five Years of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Research: From Phenotype to Genotype to Therapy, and What Comes Next. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 2020, 21, 231–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russman, B.S.; Iannaccone, S.T.; Samaha, F.J. A Phase 1 Trial of Riluzole in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 1601–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darras, B. T. Spinal Muscular Atrophies. Pediatr Clin North Am 2015, 62, 743–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlini, L.; Solari, A.; Vita, G.; Bertini, E.; Minetti, C.; Mongini, T.; Mazzoni, E.; Angelini, C.; Morandi, L. Role of Gabapentin in Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Results of a Multicenter, Randomized Italian Study. J Child Neurol 2003, 18, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.; Moore, D.; Dronsky, V.; Bradley, W.; Barohn, R.; Bryan, W.; Prior, T.; Gelinas, D.; Iannaccone, S.; Kissel, J.; et al. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Gabapentin in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2001, 191, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custer, S.K.; Androphy, E.J. Autophagy Dysregulation in Cell Culture and Animals Models of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 61, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, A.; Schiaffino, L.; Boido, M.; Valsecchi, V.; Guglielmotto, M.; De Amicis, E.; Puyal, J.; Garcera, A.; Tamagno, E.; Soler, R.M.; et al. Inhibition of Autophagy Delays Motoneuron Degeneration and Extends Lifespan in a Mouse Model of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, 3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, F.; Abadía-Molina, F.; MacKenzie, D.; Hadwen, J.; Shamim, F.; O'Reilly, S.; Holcik, M.; MacKenzie, A. Celecoxib Increases Smn and Survival in a Severe Spinal Muscular Atrophy Mouse Model Via P38 Pathway Activation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3415–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nölle, A.; Zeug, A.; van Bergeijk, J.; Tönges, L.; Gerhard, R.; Brinkmann, H.; Al Rayes, S.; Hensel, N.; Schill, Y.; Apkhazava, D.; et al. The Spinal Muscular Atrophy Disease Protein Smn Is Linked to the Rho-Kinase Pathway Via Profilin. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 4865–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowerman, M.; Beauvais, A.; Anderson, C.L.; Kothary, R. Rho-Kinase Inactivation Prolongs Survival of an Intermediate Sma Mouse Model. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 1468–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowerman, M.; Murray, L.M.; Boyer, J.G.; Anderson, C.L.; Kothary, R. Fasudil Improves Survival and Promotes Skeletal Muscle Development in a Mouse Model of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 24–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowery, S.; Oliver, A. Incidence of Postdural Puncture Headache and Backache Following Diagnostic/Therapeutic Lumbar Puncture Using a 22g Cutting Spinal Needle, and after Introduction of a 25g Pencil Point Spinal Needle. Paediatr Anaesth 2008, 18, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hache, M.; Swoboda, K.J.; Sethna, N.; Farrow-Gillespie, A.; Khandji, A.; Xia, S.; Bishop, K.M. Intrathecal Injections in Children with Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Nusinersen Clinical Trial Experience. J Child Neurol 2016, 31, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, A.; Chehade, L.; Kothary, R. Curing Sma: Are We There Yet? Gene Ther 2023, 30, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitschmidt, L.; Pichlmaier, L.; Eckerland, M.; Steindor, M.; Olivier, M.; Fuge, I.; Kölbel, H.; Hirtz, R.; Stehling, F. Nusinersen Does Not Improve Lung Function in a Cohort of Children with Spinal Muscular Atrophy - a Single-Center Retrospective Study. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2021, 31, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-K.; Jha, N.N.; Feng, Z.; Faleiro, M.R.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Wei-Lapierre, L.; Dirksen, R.T.; Ko, C.-P.; Monani, U.R. Muscle-Specific Smn Reduction Reveals Motor Neuron-Independent Disease in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Models. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1271–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Hernández, R.; Soler-Botija, C.; Also, E.; Alias, L.; Caselles, L.; Gich, I.; Bernal, S.; Tizzano, E.F. The Developmental Pattern of Myotubes in Spinal Muscular Atrophy Indicates Prenatal Delay of Muscle Maturation. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnik-Schöneborn, S.; Vogelgesang, S.; Armbrust, S.; Graul-Neumann, L.; Fusch, C.; Zerres, K. Digital Necroses and Vascular Thrombosis in Severe Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Muscle Nerve 2010, 42, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, D.M.; D’ydewalle, C.; Gabbeta, V.; Dakka, A.; Klein, S.K.; Norris, D.A.; Matson, J.; Taylor, S.J.; Zaworski, P.G.; Prior, T.W.; et al. Age-Dependent Smn Expression in Disease-Relevant Tissue and Implications for Sma Treatment. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4817–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguise, M.; Baranello, G.; Mastella, C.; Beauvais, A.; Michaud, J.; Leone, A.; De Amicis, R.; Battezzati, A.; Dunham, C.; Selby, K.; et al. Abnormal Fatty Acid Metabolism Is a Core Component of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 1519–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, T.O.; Sladky, J.T.; Hurko, O.; Besner-Johnston, A.; Kelley, R.I. Abnormal Fatty Acid Metabolism in Childhood Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 45, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinderer, C.; Bell, P.; Katz, N.; Vite, C.H.; Louboutin, J.-P.; Bote, E.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Casal, M.L.; Bagel, J.; et al. Evaluation of Intrathecal Routes of Administration for Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors in Large Animals. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018, 29, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinderer, C.; Katz, N.; Dyer, C.; Goode, T.; Johansson, J.; Bell, P.; Richman, L.; Buza, E.; Wilson, J.M. Translational Feasibility of Lumbar Puncture for Intrathecal Aav Administration. Mol. Ther. - Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 17, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Alstyne, M.; Tattoli, I.; Delestrée, N.; Recinos, Y.; Workman, E.; Shihabuddin, L.S.; Zhang, C.; Mentis, G.Z.; Pellizzoni, L. Gain of Toxic Function by Long-Term Aav9-Mediated Smn Overexpression in the Sensorimotor Circuit. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, D.; Mohr, F.; McMillan, H.; Tukov, F.F.; Montgomery, K.; Kleyn, A.; Sun, R.; Tauscher-Wisniewski, S.; Kaufmann, P.; Kullak-Ublick, G. Hepatotoxicity Following Administration of Onasemnogene Abeparvovec (Avxs-101) for the Treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 74, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Evrysdi Safely and Effectively. Food and Drug Administration, 2020.
- Dangouloff, T.; Servais, L. Clinical Evidence Supporting Early Treatment of Patients with Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Current Perspectives. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2019, ume 15, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Collins, E.; Lewis, L.; Guntrum, D.; Eichinger, K.; Voter, K.; Abdel-Hamid, H.Z.; Ciafaloni, E. Combination Therapy with Nusinersen and Avxs-101 in Sma Type 1. Neurology 2019, 93, 640–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, Y.; Rao, V.K.; Arya, K.; Kuntz, N.L.; DiDonato, C.J.; Napchan-Pomerantz, G.; Agarwal, A.; Stefans, V.; Katsuno, M.; Veerapandiyan, A. Combination Molecular Therapies for Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Muscle Nerve 2020, 62, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercuri, E.; Finkel, R.S.; Muntoni, F.; Wirth, B.; Montes, J.; Main, M.; Mazzone, E.S.; Vitale, M.; Snyder, B.; Quijano-Roy, S.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Part 1: Recommendations for Diagnosis, Rehabilitation, Orthopedic and Nutritional Care. Neuromuscul Disord 2018, 28, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boemer, F.; Caberg, J.-H.; Beckers, P.; Dideberg, V.; di Fiore, S.; Bours, V.; Marie, S.; Dewulf, J.; Marcelis, L.; Deconinck, N.; et al. Three Years Pilot of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Newborn Screening Turned into Official Program in Southern Belgium. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent Servais, Manu Vatish "First Uk Pilot Study of Newborn Screening for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Launched in Oxford." University of Oxford, 2022.
- Summerton, J.; Weller, D. Morpholino Antisense Oligomers: Design, Preparation, and Properties. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev 1997, 7, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, U. S.; Yokota, T. Enhancing Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Therapeutic Delivery with Dg9, a Versatile Cell-Penetrating Peptide. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porensky, P.N.; Mitrpant, C.; McGovern, V.; Bevan, A.K.; Foust, K.D.; Kaspar, B.K.; Wilton, S.; Burghes, A.H. A Single Administration of Morpholino Antisense Oligomer Rescues Spinal Muscular Atrophy in Mouse. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Janghra, N.; Mitrpant, C.; Dickinson, R.L.; Anthony, K.; Price, L.; Eperon, I.C.; Wilton, S.D.; Morgan, J.; Muntoni, F. A Novel Morpholino Oligomer Targeting Iss-N1 Improves Rescue of Severe Spinal Muscular Atrophy Transgenic Mice. Hum. Gene Ther. 2013, 24, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizzardo, M.; Simone, C.; Salani, S.; Ruepp, M.D.; Rizzo, F.; Ruggieri, M.; Zanetta, C.; Brajkovic, S.; Moulton, H.M.; Muehlemann, O.; et al. Effect of Combined Systemic and Local Morpholino Treatment on the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Delta7 Mouse Model Phenotype. Clin Ther 2014, 36, 340–356.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, S.M.; Hazell, G.; Shabanpoor, F.; Saleh, A.F.; Bowerman, M.; Sleigh, J.N.; Meijboom, K.E.; Zhou, H.; Muntoni, F.; Talbot, K.; et al. Systemic Peptide-Mediated Oligonucleotide Therapy Improves Long-Term Survival in Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2016, 113, 10962–10967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bersani, M.; Rizzuti, M.; Pagliari, E.; Garbellini, M.; Saccomanno, D.; Moulton, H.M.; Bresolin, N.; Comi, G.P.; Corti, S.; Nizzardo, M. Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Conjugated Morpholino Rescues Sma in a Symptomatic Preclinical Model. Mol. Ther. 2021, 30, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslesh, T.; Erkut, E.; Ren, J.; Lim, K.R.Q.; Woo, S.; Hatlevig, S.; Moulton, H.M.; Gosgnach, S.; Greer, J.; Maruyama, R.; et al. Dg9-Conjugated Morpholino Rescues Phenotype in Sma Mice by Reaching the Cns Via a Subcutaneous Administration. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





