Submitted:
26 June 2024
Posted:
26 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Materials
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Image Acquisition
2.5. Behavioral Analysis
2.6. fMRI Analysis
2.6.1. Statistical Analysis
2.6.2. ROI Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Results
3.2. GLM Results
3.3. ROI Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Butterworth, B. Lexical Representation. In Language Production Vol. 2.; Butterworth, B., Ed.; Academic Press: London, 1983; pp. 257–294. [Google Scholar]
- Taft, M. Morphological Decomposition and the Reverse Base Frequency Effect. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. Sect. A: Hum. Exp. Psychol. 2004, 57, 745–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taft, M.; Forster, K.I. Lexical Storage and Retrieval of Prefixed Words. J Verbal Learn. Verbal Behav 1975, 14, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clahsen, H. Lexical Entries and Rules of Language: A Multidisciplinary Study of German Inflection. Behav. Brain Sci. 1999, 22, 991–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinker, S. Rules of Language. Science (1979) 1991, 253, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullman, M.T. Contributions of Memory Circuits to Language: The Declarative/Procedural Model. Cognition 2004, 92, 231–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joanisse, M.F.; Seidenberg, M.S. Imaging the Past: Neural Activation in Frontal and Temporal Regions during Regular and Irregular Past-Tense Processing. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 2005, 5, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marslen-Wilson, W.; Tyler, L.K. Rules, Representations, and the English Past Tense. Trends Cogn Sci 1998, 2, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClelland, J.L.; Patterson, K. Rules or Connections in Past-Tense Inflections: What Does the Evidence Rule Out? Trends Cogn Sci 2002, 6, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClelland, J.L.; Rumelhart, D.E. On Learning the Past Tenses of English Verbs. In Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition: Psychological and Biological Models; MIT Press: Cambridge, 1987; ISBN 9780262291262. [Google Scholar]
- Seidenberg, M.S.; McClelland, J.L. A Distributed, Developmental Model of Word Recognition and Naming. Psychol Rev 1989, 96, 523–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.H.; Meunier, F.; Marslen-Wilson, W.D. Neural Responses to Morphological, Syntactic, and Semantic Properties of Single Words: An FMRI Study. Brain Lang 2004, 89, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.T.; Jamison, H.L.; Matthews, P.M.; Gonnerman, L.M. Morphology and the Internal Structure of Words. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2004, 101, 14984–14988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, B.T.; Rastle, K. Neural Correlates of Morphological Decomposition during Visual Word Recognition. J Cogn Neurosci 2007, 19, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozic, M.; Tyler, L.K.; Li, S.; Wingfield, C.; Marslen-Wilson, W.D. Neurobiological Systems for Lexical Representation and Analysis in English. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Bozic, M.; Marslen-Wilson, W.D.; Stamatakis, E.A.; Davis, M.H.; Tyler, L.K. Differentiating Morphology, Form, and Meaning: Neural Correlates of Morphological Complexity. J Cogn Neurosci 2007, 19, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannest, J.; Newport, E.L.; Newman, A.J.; Bavelier, D. Interplay between Morphology and Frequency in Lexical Access: The Case of the Base Frequency Effect. Brain Res 2011, 1373, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozic, M.; Marslen-Wilson, W. Neurocognitive Contexts for Morphological Complexity: Dissociating Inflection and Derivation. Linguist. Lang. Compass 2010, 4, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, T. Neural Correlates of Morphological Processing: An Activation Likelihood Estimation Meta-Analysis. Cortex 2022, 151, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, L.K.; Bright, P.; Fletcher, P.; Stamatakis, E.A. Neural Processing of Nouns and Verbs: The Role of Inflectional Morphology. Neuropsychologia 2004, 42, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marslen-Wilson, W.D.; Tyler, L.K. Morphology, Language and the Brain: The Decompositional Substrate for Language Comprehension. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinker, S.; Ullman, M.T. The Past and Future of the Past Tense. Trends Cogn Sci 2002, 6, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, M.T. A Neurocognitive Perspective on Language: The Declarative/Procedural Model. Nat Rev Neurosci 2001, 2, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pliatsikas, C.; Johnstone, T.; Marinis, T. FMRI Evidence for the Involvement of the Procedural Memory System in Morphological Processing of a Second Language. PLoS One 2014, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannest, J.; Polk, T.A.; Lewis, R.L. Dual-Route Processing of Complex Words: New FMRI Evidence from Derivational Suffixation. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 2005, 5, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beretta, A.; Campbell, C.; Carr, T.H.; Huang, J.; Schmitt, L.M.; Christianson, K.; Cao, Y. An ER-FMRI Investigation of Morphological Inflection in German Reveals That the Brain Makes a Distinction between Regular and Irregular Forms. Brain Lang 2003, 85, 67–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, R.; Conant, L.L.; Waldron, E.; Binder, J.R. FMRI of Past Tense Processing: The Effects of Phonological Complexity and Task Difficulty. J Cogn Neurosci 2006, 18, 278–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtonen, M.; Vorobyev, V.A.; Hugdahl, K.; Tuokkola, T.; Laine, M. Neural Correlates of Morphological Decomposition in a Morphologically Rich Language: An FMRI Study. Brain Lang 2006, 98, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtonen, M.; Vorobyev, V.; Soveri, A.; Hugdahl, K.; Tuokkola, T.; Laine, M. Language-Specific Activations in the Brain: Evidence from Inflectional Processing in Bilinguals. J Neurolinguistics 2009, 22, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, S.; Miyamoto, T.; Riera, J.; Kim, J.; Akitsuki, Y.; Iwata, K.; Yoshimoto, K.; Horie, K.; Sato, S.; Kawashima, R. Cortical Mechanisms Involved in the Processing of Verbs: An FMRI Study. J Cogn Neurosci 2006, 18, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, H.; Park, C.; Lim, H.; Nam, K. Mental Representation and Processing Involved in Comprehending Korean Regular and Irregular Verb Eojeols: An FMRI and Reaction Time Study. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing: 13th International Conference, ICONIP 2006, Hong Kong, China, October 3-6, 2006. Proceedings, Part I 13; 2006; Vol. 4232, pp. 247–254.
- Russo, A.G.; Esposito, F.; Laudanna, A.; Mancuso, A.; Di Salle, F.; Elia, A.; De Martino, M. The Neural Substrate of Noun Morphological Inflection: A Rapid Event-Related FMRI Study in Italian. Neuropsychologia 2021, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grindrod, C.M.; Garnett, E.O.; Malyutina, S.; den Ouden, D.B. Effects of Representational Distance between Meanings on the Neural Correlates of Semantic Ambiguity. Brain Lang 2014, 139, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodd, J.M.; Davis, M.H.; Johnsrude, I.S. The Neural Mechanisms of Speech Comprehension: FMRI Studies of Semantic Ambiguity. Cereb. Cortex 2005, 15, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitello, S.; Rodd, J.M. Resolving Semantic Ambiguities in Sentences: Cognitive Processes and Brain Mechanisms. Lang Linguist Compass 2015, 9, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, J.R.; Desai, R.H. The Neurobiology of Semantic Memory. Trends Cogn Sci 2011, 15, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambon Ralph, M.A.; Jefferies, E.; Patterson, K.; Rogers, T.T. The Neural and Computational Bases of Semantic Cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 2017, 18, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, P.; Tamm, A. Barking up the Right Tree: Univariate and Multivariate FMRI Analyses of Homonym Comprehension. Neuroimage 2020, 219, 117050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, G.F.; Lambon Ralph, M.A. Mapping Domain-Selective and Counterpointed Domain-General Higher Cognitive Functions in the Lateral Parietal Cortex: Evidence from FMRI Comparisons of Difficulty-Varying Semantic Versus Visuo-Spatial Tasks, and Functional Connectivity Analyses. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 4199–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zempleni, M.Z.; Renken, R.; Hoeks, J.C.J.; Hoogduin, J.M.; Stowe, L.A. Semantic Ambiguity Processing in Sentence Context: Evidence from Event-Related FMRI. Neuroimage 2007, 34, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soveri, A.; Lehtonen, M.; Laine, M. Word Frequency and Morphological Processing in Finnish Revisited. Ment Lex 2007, 2, 359–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartiainen, J.; Aggujaro, S.; Lehtonen, M.; Hultén, A.; Laine, M.; Salmelin, R. Neural Dynamics of Reading Morphologically Complex Words. Neuroimage 2009, 47, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldfield, R.C. The Assessment and Analysis of Handedness: The Edinburgh Inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.; Kim, H. Frequency of Korean Language: Based on 15 Million Size Eojeol Sejong Syntactic and Semantic Corpus; Handkook munhwasa: Seoul, 2009; ISBN 9788957266366. [Google Scholar]
- Pae, H.K.; Bae, S.; Yi, K. Lexical Properties Influencing Visual Word Recognition in Hangul. Read Writ 2020, 33, 2391–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y. The Mechanism for Processing Regular and Irregular Inflections of Korean Verbs -A Priming Study-. Korean Lang. Lit. 2018, 183, 67–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Nam, K.; Koo, M. The Lexical Access of Regular and Irregular Korean Verbs in the Mental Lexicon. Korean J. Cogn. Sci. 2012, 23, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, T. Familiarity and Relatedness of Word Meanings: Ratings for 110 Homographs. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 1996, 28, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, H.; Garfield, L.; Millikan, J.A. Homographic Entries in the Internal Lexicon. J Verbal Learn. Verbal Behav 1970, 9, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, J.; Kim, J.; Nam, K. Temporal Dynamics of Form and Meaning in Morphologically Complex Word Processing: An ERP Study on Korean Inflected Verbs. J Neurolinguistics 2022, 64, 101098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, M.; Carreiras, M.; Jacobs, A.M. Contrasting Effects of Token and Type Syllable Frequency in Lexical Decision. Lang Cogn Process 2008, 23, 296–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, A.M. Optimal Experimental Design for Event-Related FMRI. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1999, 8, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing 2022.
- The MathWorks Inc. MATLAB Version: 23.2.0 (R2023b) 2023.
- Taylor, J.S.H.; Rastle, K.; Davis, M.H. Interpreting Response Time Effects in Functional Imaging Studies. Neuroimage 2014, 99, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneau, M.; Beaucousin, V.; Hervé, P.Y.; Duffau, H.; Crivello, F.; Houdé, O.; Mazoyer, B.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. Meta-Analyzing Left Hemisphere Language Areas: Phonology, Semantics, and Sentence Processing. Neuroimage 2006, 30, 1414–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolls, E.T.; Huang, C.C.; Lin, C.P.; Feng, J.; Joliot, M. Automated Anatomical Labelling Atlas 3. Neuroimage 2020, 206, 116189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, M.; Anton, J.-L.; Valabregue, R.; Poline, J.-B. Region of Interest Analysis Using the MarsBar Toolbox for SPM 99. Neuroimage 2002, 16, S497. [Google Scholar]
- Leminen, A.; Leminen, M.; Lehtonen, M.; Nevalainen, P.; Ylinen, S.; Kimppa, L.; Sannemann, C.; Mäkelä, J.P.; Kujala, T. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the Processing of Spoken Inflected and Derived Words: A Combined EEG and MEG Study. Front Hum Neurosci 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marslen-Wilson, W.; Tyler, L.K.; Waksler, R.; Older, L. Morphology and Meaning in the English Mental Lexicon; 1994; Vol. 101.
- Devlin, J.T.; Jamison, H.L.; Gonnerman, L.M.; Matthews, P.M. The Role of the Posterior Fusiform Gyrus in Reading. J Cogn Neurosci 2006, 18, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, L.; Dehaene, S.; Naccache, L.; Lehéricy, S.; Dehaene-Lambertz, G.; Hénaff, M.-A.; Michel, F. The Visual Word Form Area. Brain 2000, 123, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, L.; Lehéricy, S.; Chochon, F.; Lemer, C.; Rivaud, S.; Dehaene, S. Language-specific Tuning of Visual Cortex? Functional Properties of the Visual Word Form Area. Brain 2002, 125, 1054–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehaene, S.; Naccache, L.; Cohen, L.; Bihan, D.L.; Mangin, J.-F.; Poline, J.-B.; Rivière, D. Cerebral Mechanisms of Word Masking and Unconscious Repetition Priming. Nat Neurosci 2001, 4, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastle, K.; Davis, M.H.; New, B. The Broth in My Brother’s Brothel: Morpho-Orthographic Segmentation in Visual Word Recognition. Psychon Bull Rev 2004, 11, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronbichler, M.; Hutzler, F.; Wimmer, H.; Mair, A.; Staffen, W.; Ladurner, G. The Visual Word Form Area and the Frequency with Which Words Are Encountered: Evidence from a Parametric FMRI Study. Neuroimage 2004, 21, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhnke, P.; Chapman, C.A.; Cheung, V.K.M.; Turker, S.; Graessner, A.; Martin, S.; Williams, K.A.; Hartwigsen, G. The Role of the Angular Gyrus in Semantic Cognition: A Synthesis of Five Functional Neuroimaging Studies. Brain Struct Funct 2023, 228, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedny, M.; McGill, M.; Thompson-Schill, S.L. Semantic Adaptation and Competition during Word Comprehension. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 2574–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, L.K.; Cheung, T.P.L.; Devereux, B.J.; Clarke, A. Syntactic Computations in the Language Network: Characterizing Dynamic Network Properties Using Representational Similarity Analysis. Front Psychol 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, E.; Colé, P.; Badier, J.M.; Zielinski, C.; Chanoine, V.; Ziegler, J.C. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Morphological Processing in Visual Word Recognition. J Cogn Neurosci 2016, 28, 1228–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friederici, A.D. The Cortical Language Circuit: From Auditory Perception to Sentence Comprehension. Trends Cogn Sci 2012, 16, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagoort, P. On Broca, Brain, and Binding: A New Framework. Trends Cogn Sci 2005, 9, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

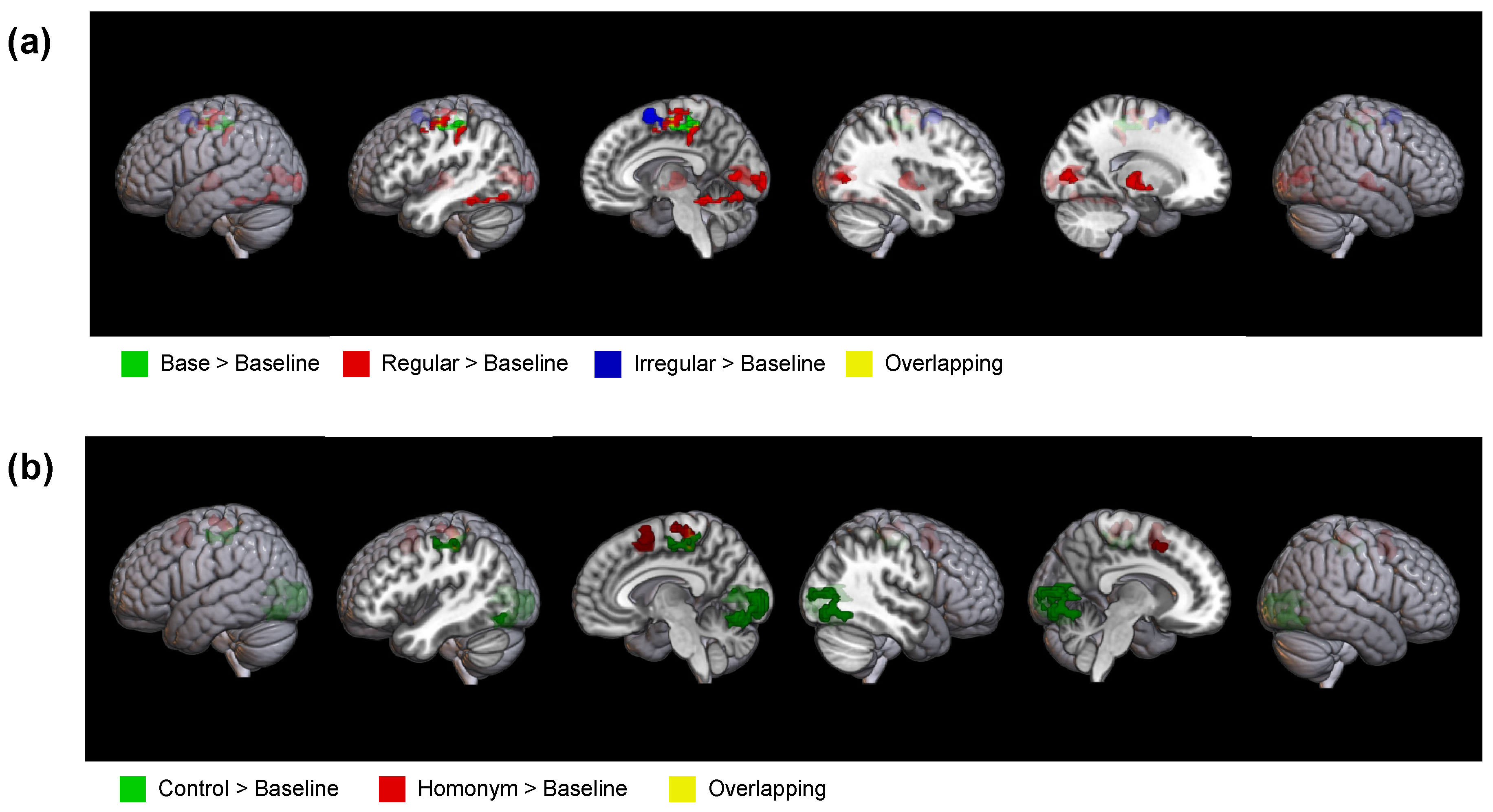
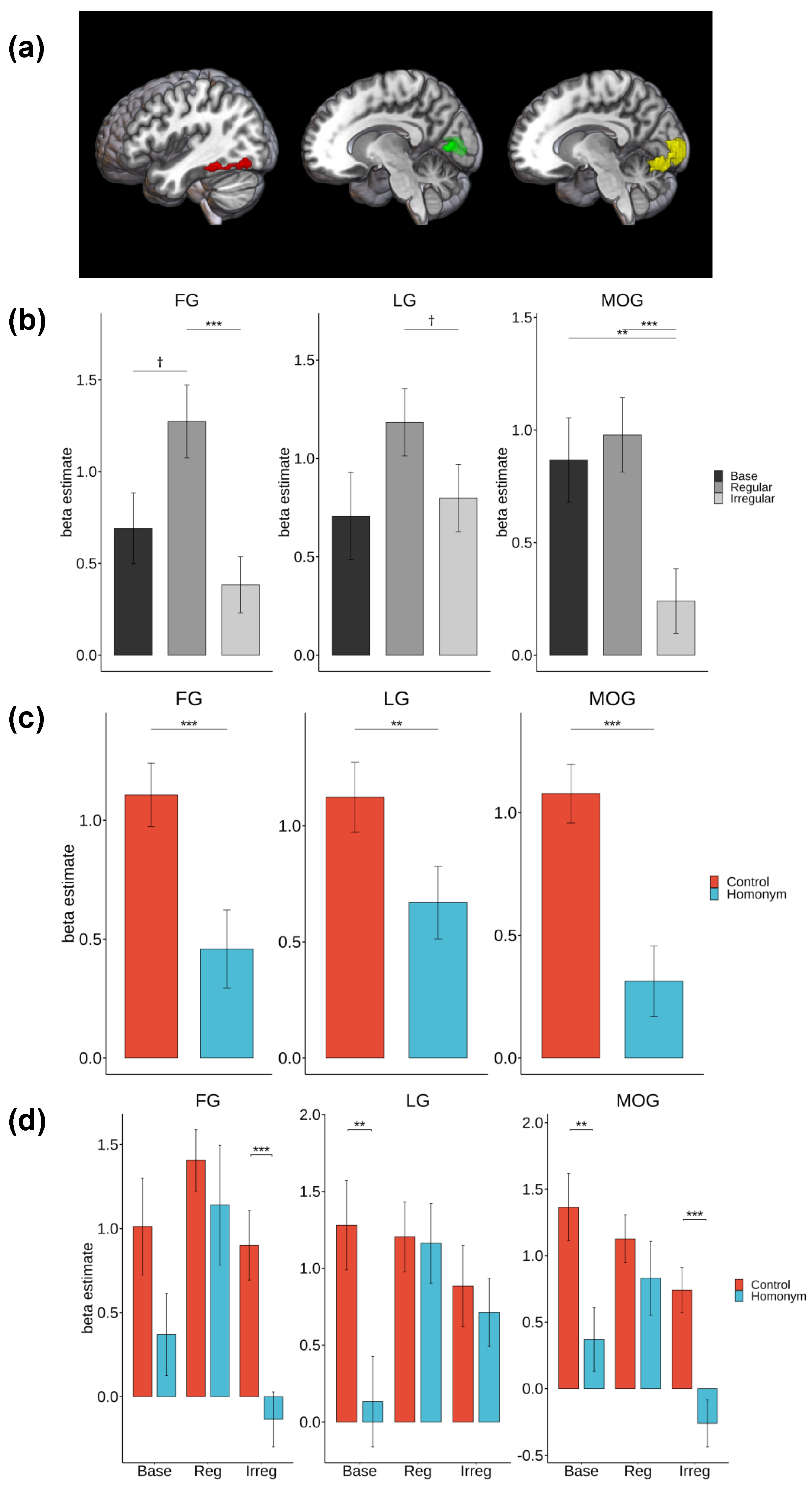
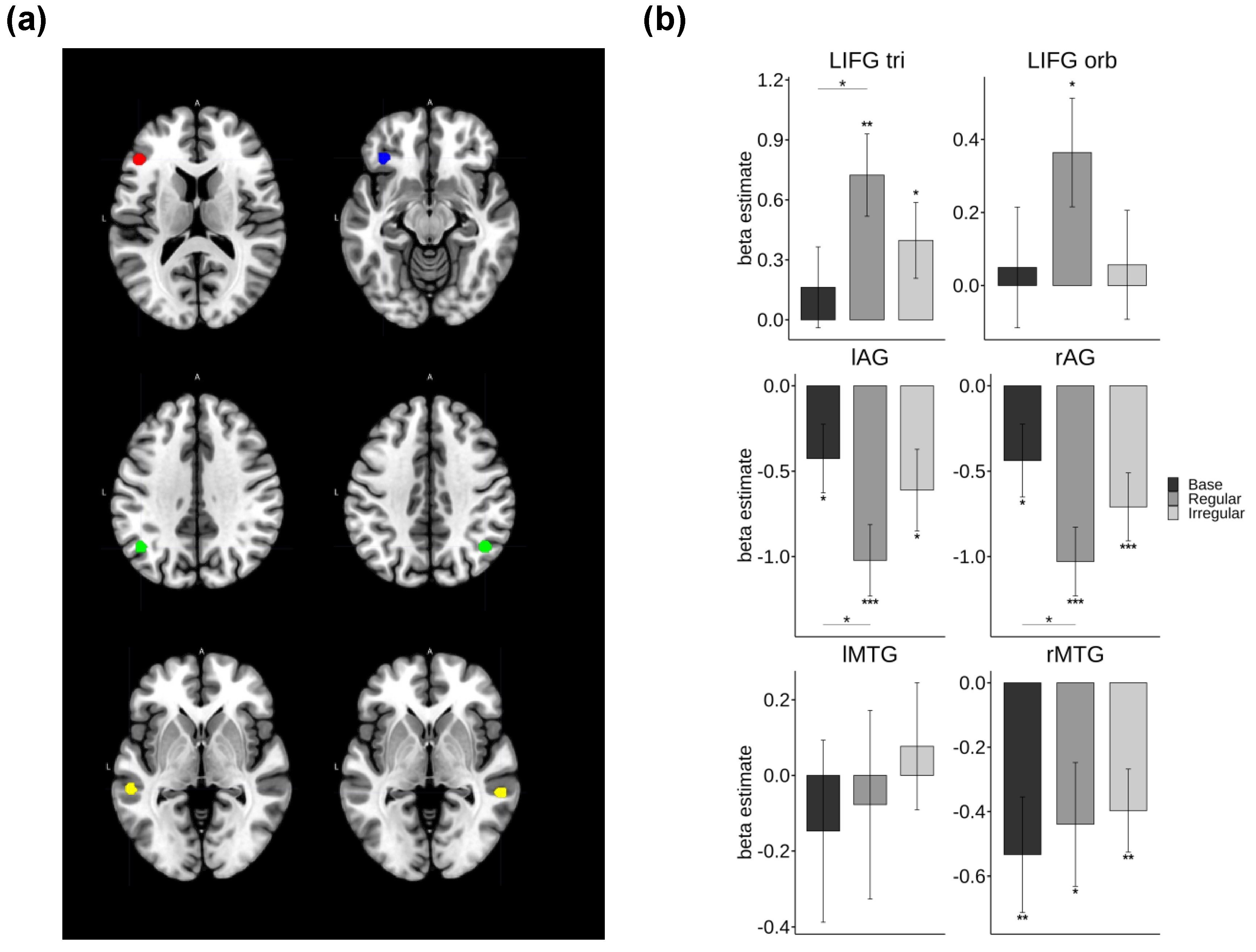
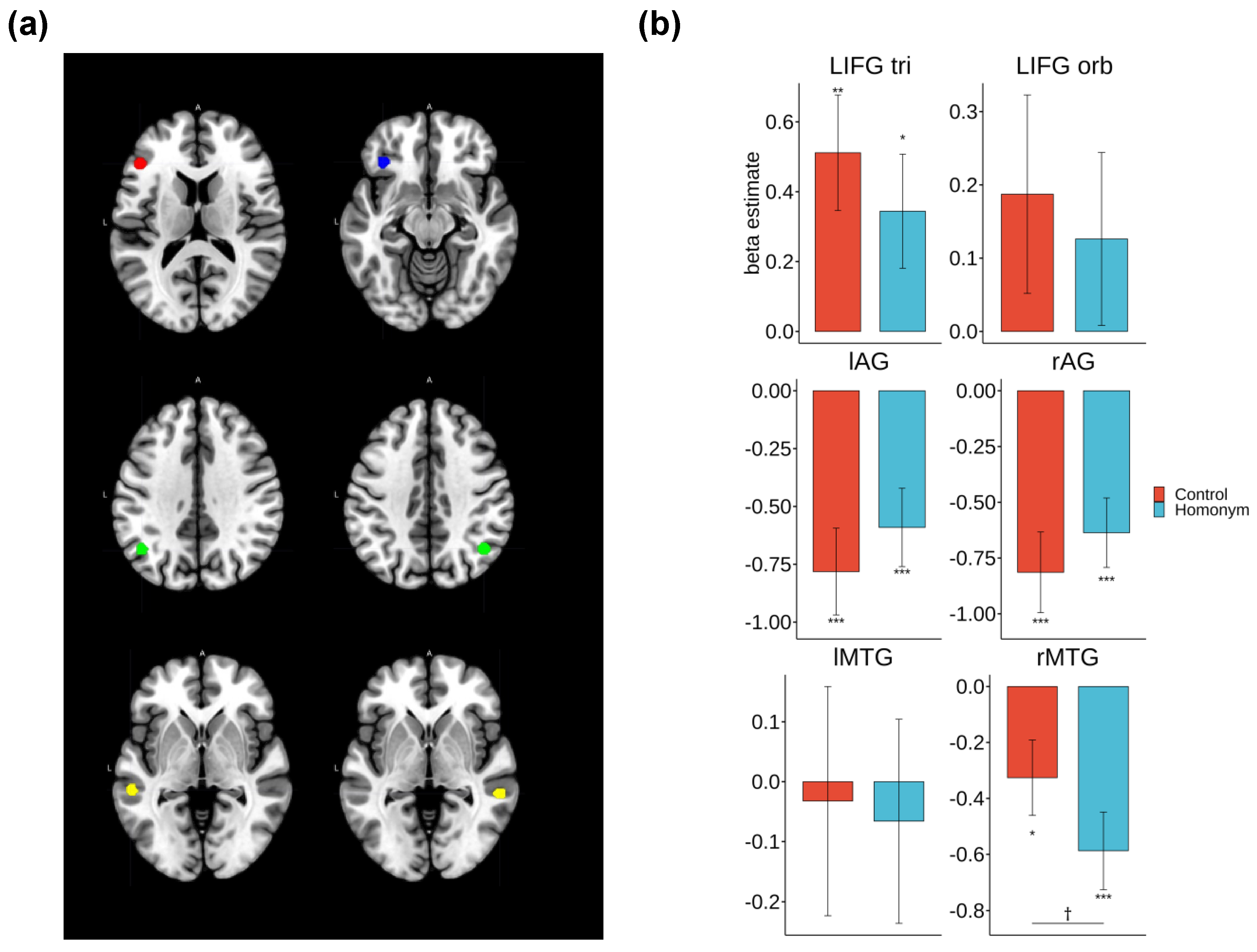
| Inflection type |
Semantic ambiguity | |||
| Control | Homonym | |||
| RT (ms) | ACC (%) | RT (ms) | ACC (%) | |
| Base | 568.66 (113.13) |
93.38 (24.89) |
554.9 (105.14) |
96.78 (17.67) |
| Regular | 583.21 (114.33) |
87.98 (32.56) |
601.97 (121.54) |
85.19 (35.58) |
| Irregular | 587.87 (121.57) |
90.85 (28.87) |
593.92 (121.29) |
90.12 (29.87) |
| Contrast | Cluster size |
Brain regions | Hemisphere | MNI coordinates | Z | ||
| x | y | z | |||||
| Base > Mask | 89 | Precentral gyrus | L | –36 | –28 | 56 | 5.75 |
| Reg > Mask | 71 | Calcarine | L | –12 | –100 | –4 | 5.10 |
| 32 | Middle occipital gyrus | R | 36 | –76 | 2 | 3.40 | |
| 116 | Calcarine | R | 9 | –82 | 8 | 4.60 | |
| Lingual gyrus | L | 0 | –73 | 5 | 3.97 | ||
| Calcarine | R | 6 | –88 | 2 | 3.94 | ||
| 55 | Postcentral gyrus | L | –48 | –16 | 56 | 4.54 | |
| Precentral gyrus | L | –33 | –10 | 65 | 4.00 | ||
| –51 | –4 | 50 | 3.81 | ||||
| 98 | Thalamus | R | 21 | –22 | 2 | 4.23 | |
| Putamen | R | 30 | –4 | –7 | 3.87 | ||
| 65 | Fusiform gyrus | L | –42 | –40 | –19 | 4.16 | |
| –39 | –76 | –13 | 3.91 | ||||
| –42 | –55 | –19 | 3.55 | ||||
| 39 | Inferior parietal gyrus | L | –39 | –28 | 38 | 3.98 | |
| Postcentral gyrus | L | –42 | –34 | 50 | 3.85 | ||
| Irreg > Mask | 55 | Supplementary motor area | L | –3 | 8 | 65 | 3.64 |
| Middle cingulate cortex | L | –3 | –4 | 50 | 3.44 | ||
| Contrast | Cluster size |
Brain regions | Hemisphere | MNI coordinates | Z | ||
| x | y | z | |||||
| Con > Mask | 285 | Calcarine | L | –12 | –100 | –4 | 5.18 |
| Fusiform gyrus | L | –36 | –79 | –16 | 4.67 | ||
| Middle occipital gyrus | L | –27 | –88 | 2 | 4.65 | ||
| 105 | Postcentral gyrus | L | –36 | –34 | 56 | 4.68 | |
| L | –42 | –16 | 50 | 3.53 | |||
| Precentral gyrus | L | –33 | –16 | 50 | 4.27 | ||
| 316 | Calcarine | R | 9 | –82 | 8 | 4.26 | |
| Lingual gyrus | R | 15 | –94 | –7 | 4.23 | ||
| Hom > Mask | 119 | Supplementary motor area | R | 9 | 14 | 47 | 4.55 |
| L | –6 | 5 | 56 | 4.42 | |||
| 57 | Postcentral gyrus | L | –36 | –34 | 56 | 4.10 | |
| Precentral gyrus | L | –24 | –19 | 68 | 3.46 | ||
| –33 | –22 | 65 | 3.46 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





