Submitted:
18 June 2024
Posted:
20 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Rationale
1.2. Aim of the Study
1.3. Background
1.4. Literature Review
- ADT is based on a number of assumptions:
- The rotor is modelled as an actuator disk, which adds momentum and energy to the air;
- There is no inflow or outflow through the wake boundary;
- The flow is steady, incompressible and inviscid;
- The flow is one dimensional and uniform;
- The flow is uniform through the disk and wake;
- The disc does not impart any swirl to the flow.
1.5. Historical Perspective
1.6. The Optimum Propeller
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Propeller Theory—Geometry
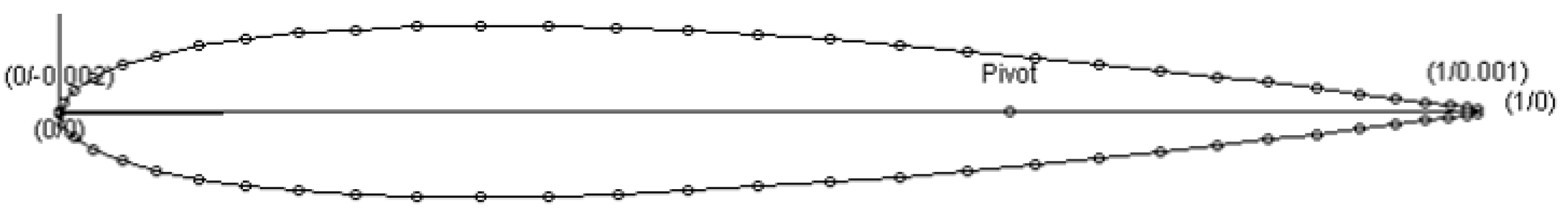
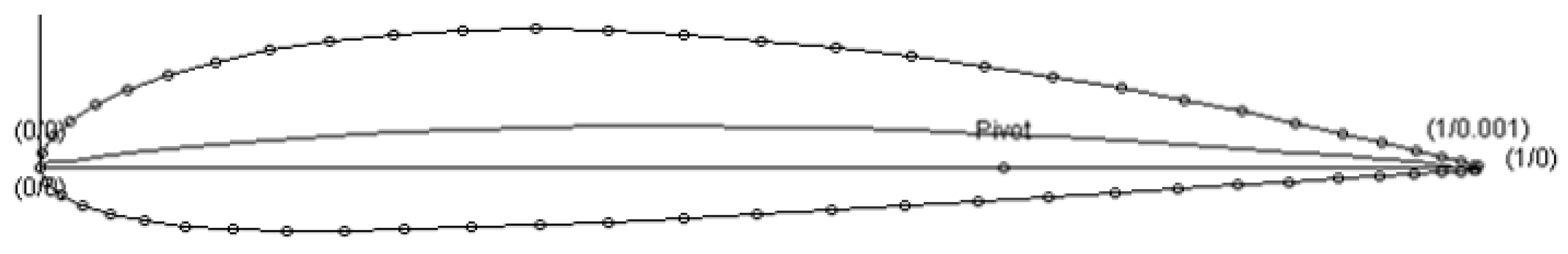
2.1.1. Airfoil Geometry
2.1.2. Propeller Geometry
2.2. Non-Dimensional Coefficients
2.3. Propeller/Rotor Efficiency
Propulsive Efficiency
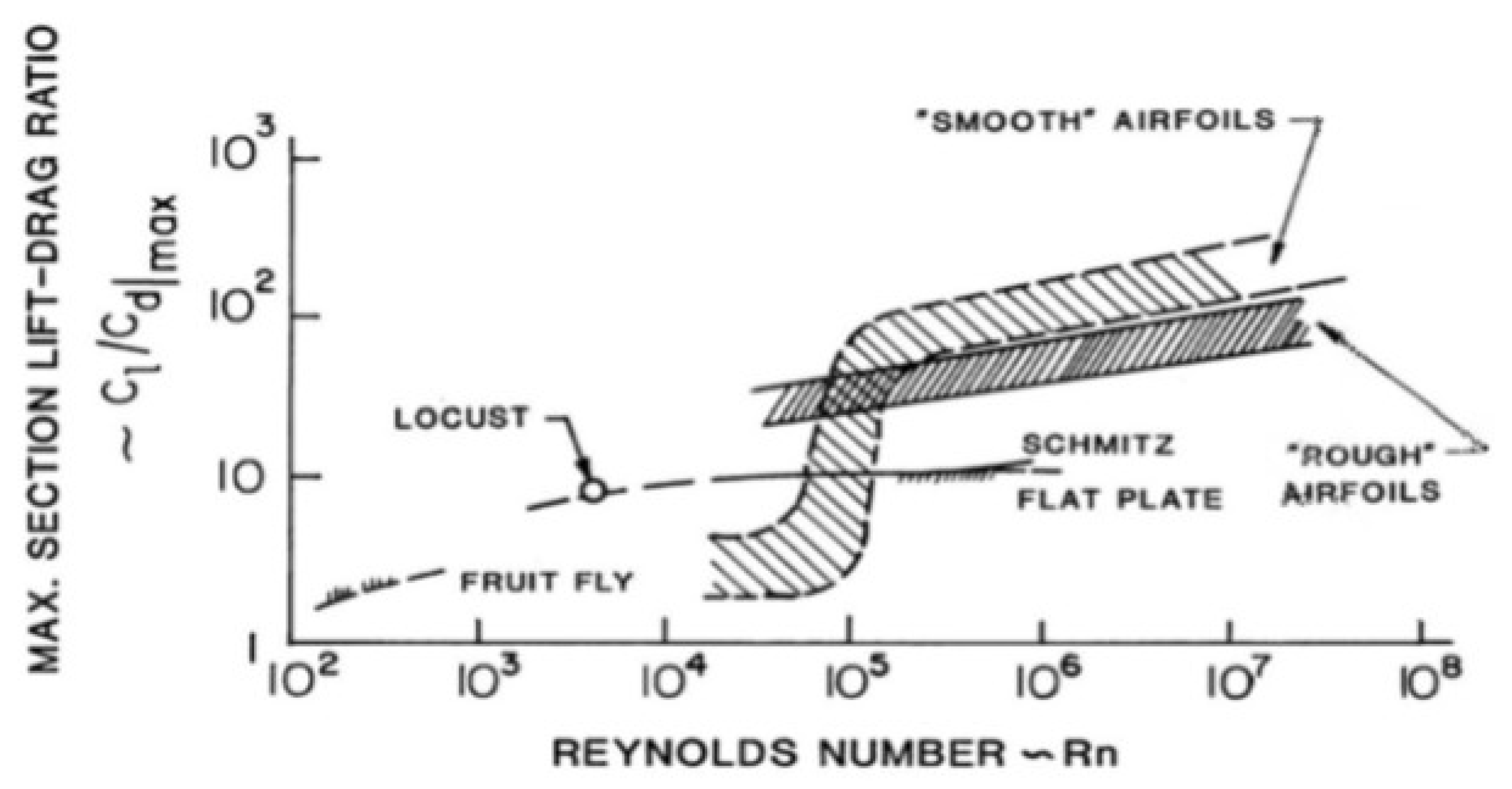
2.4. Reynolds Number
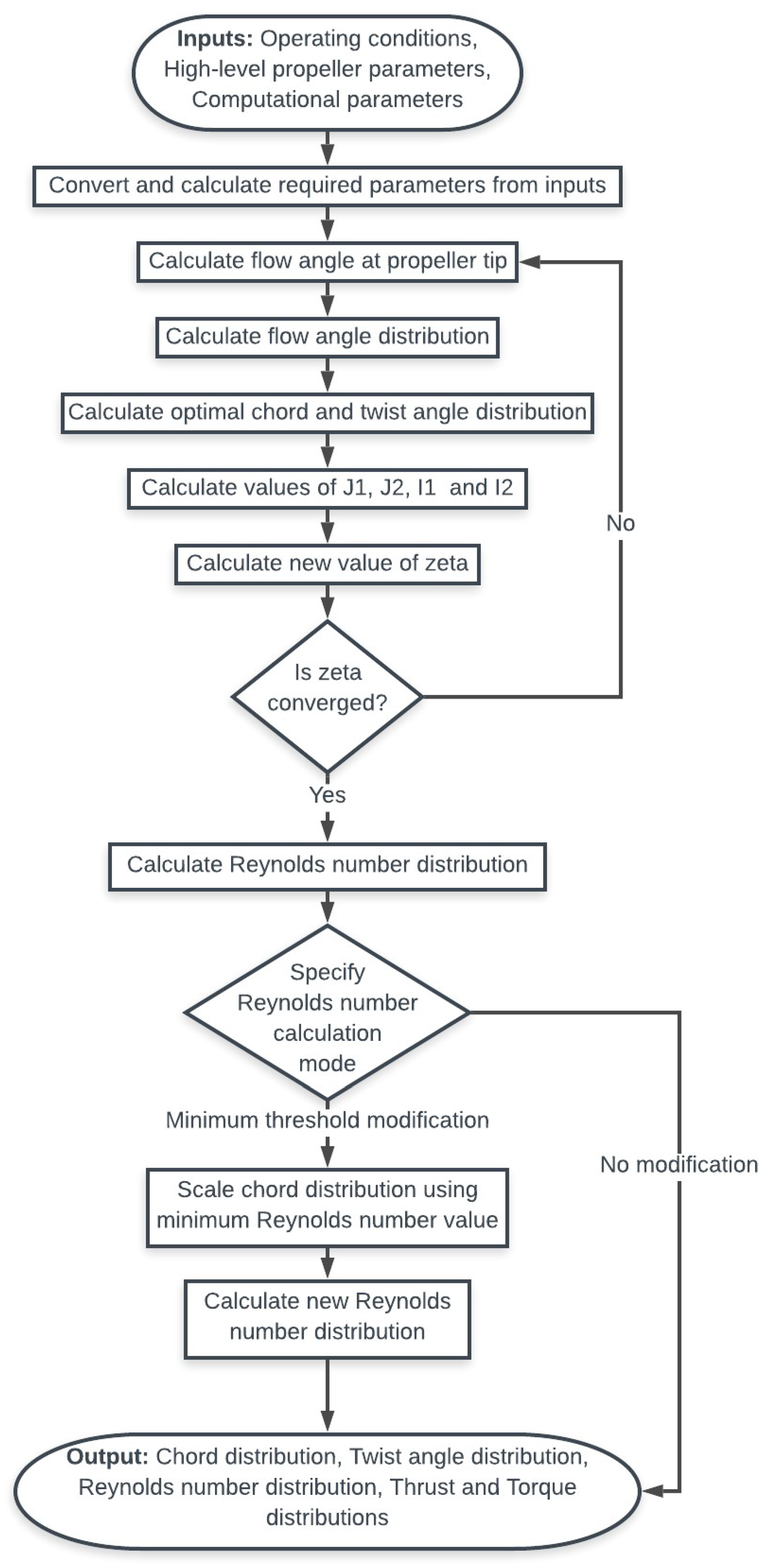
2.5. Propeller Geometry Optimization
2.6. Calculating Propeller Geometry
2.7. Optimising Propeller Geometry
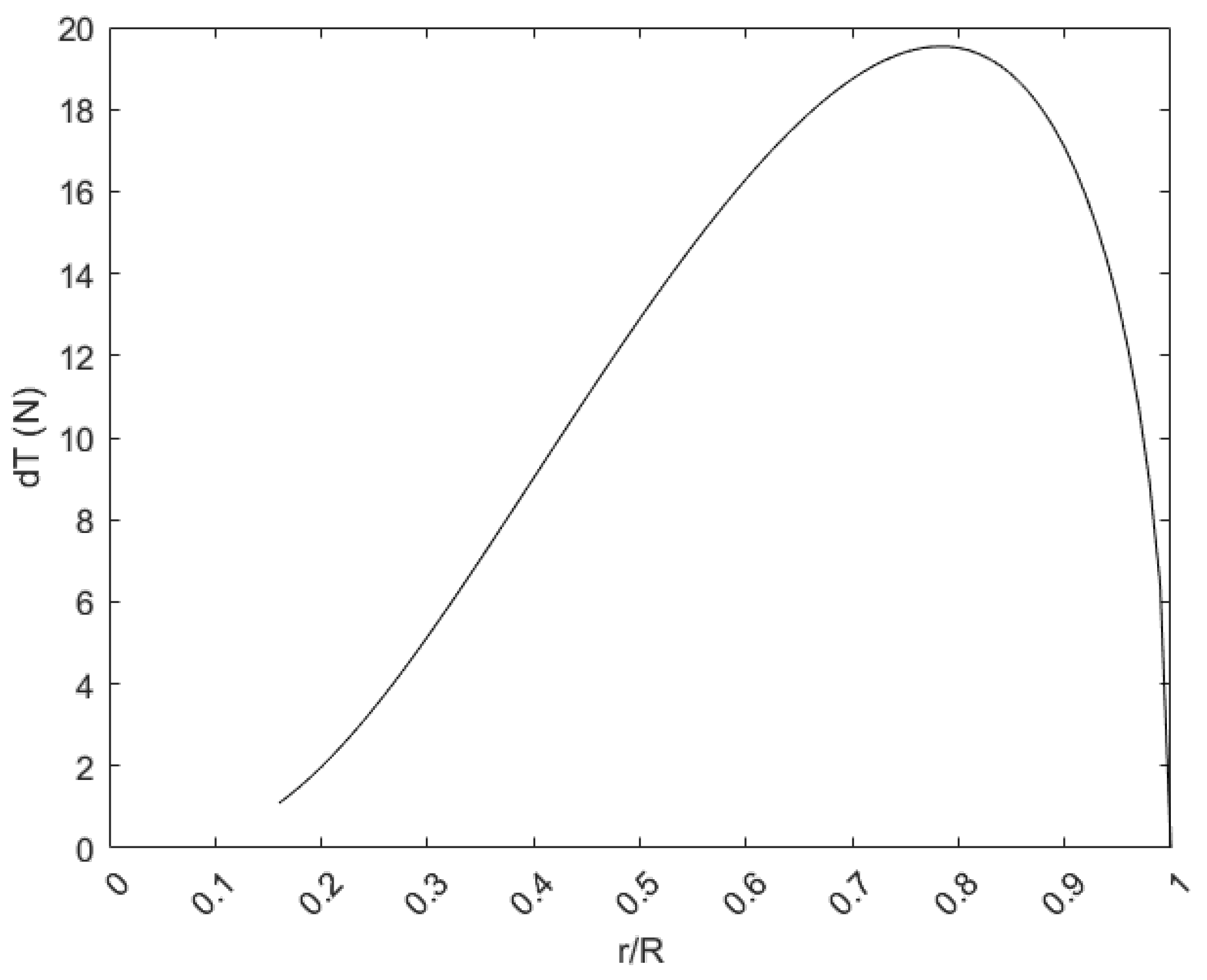
3. Results
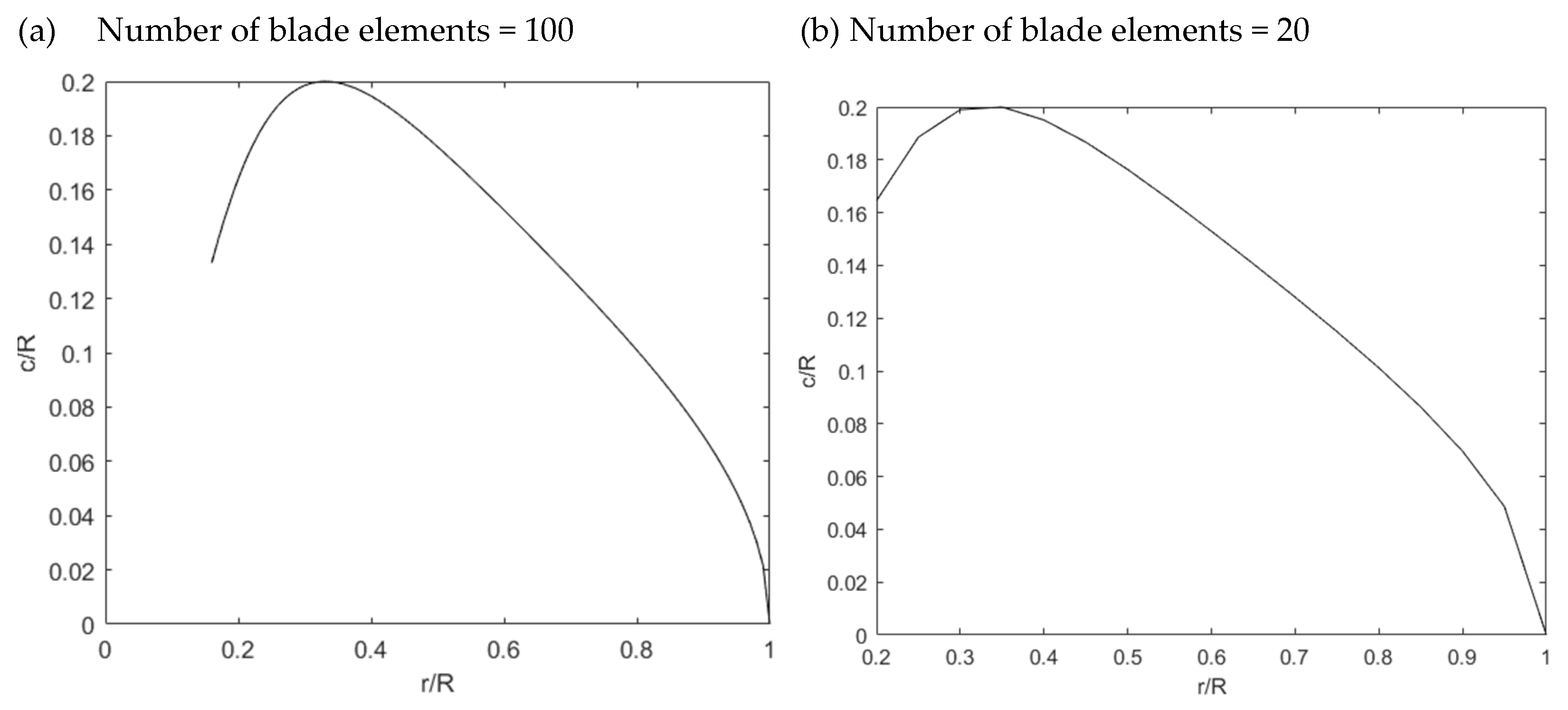
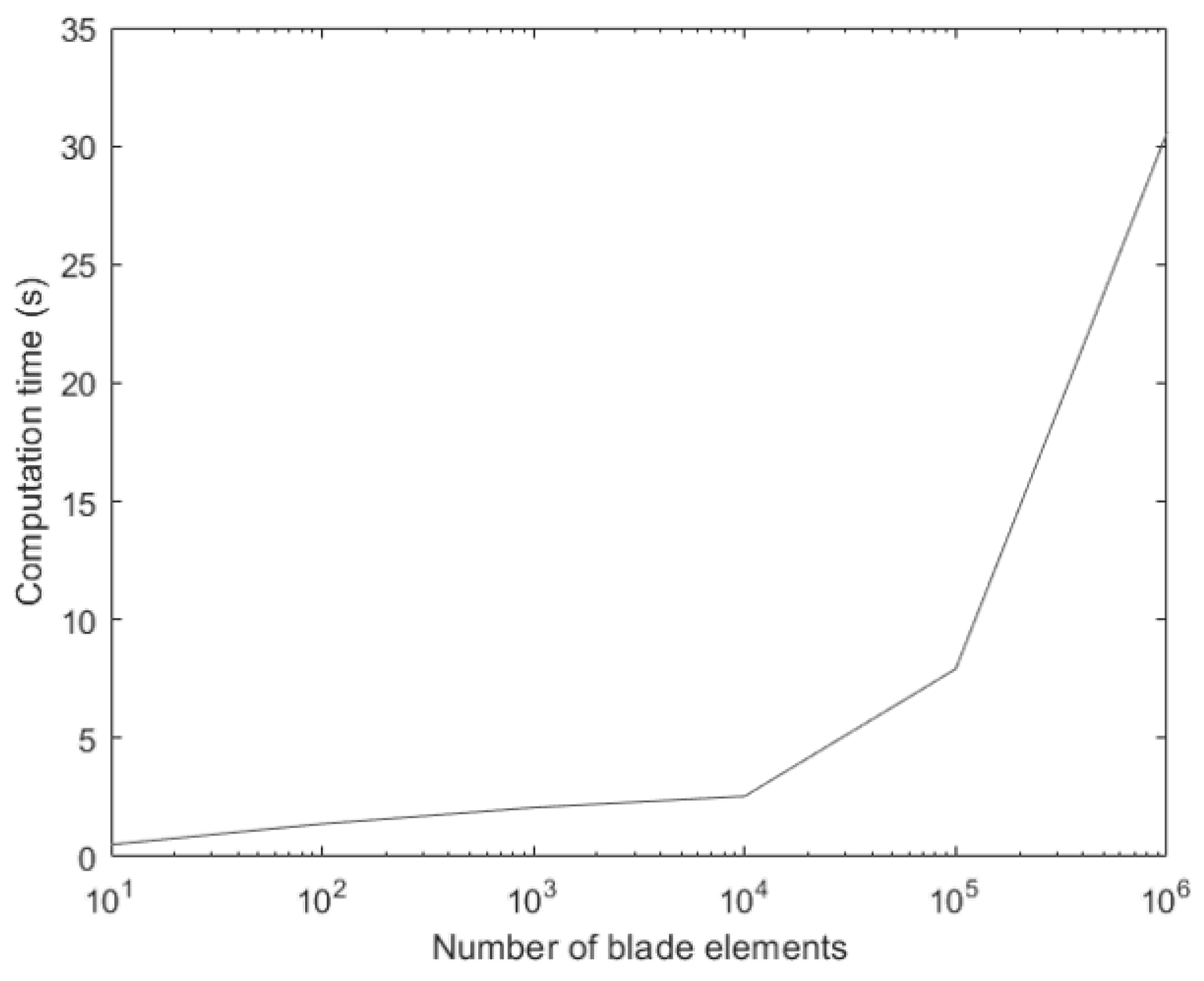
3.1. Implementing the Optimization Method Using MATLAB
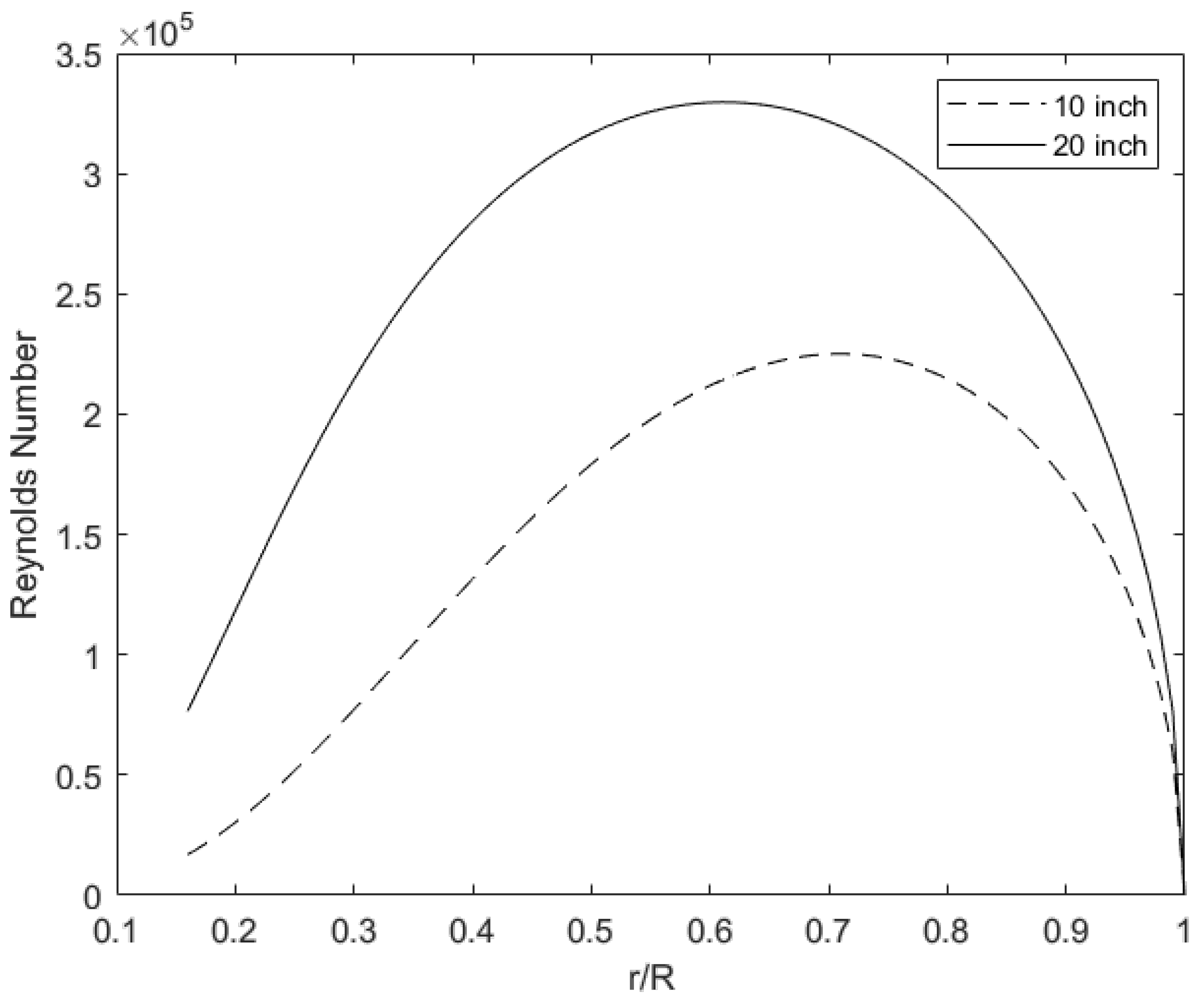
3.2. Reynolds Number Distribution
3.3. Program User Interface Design
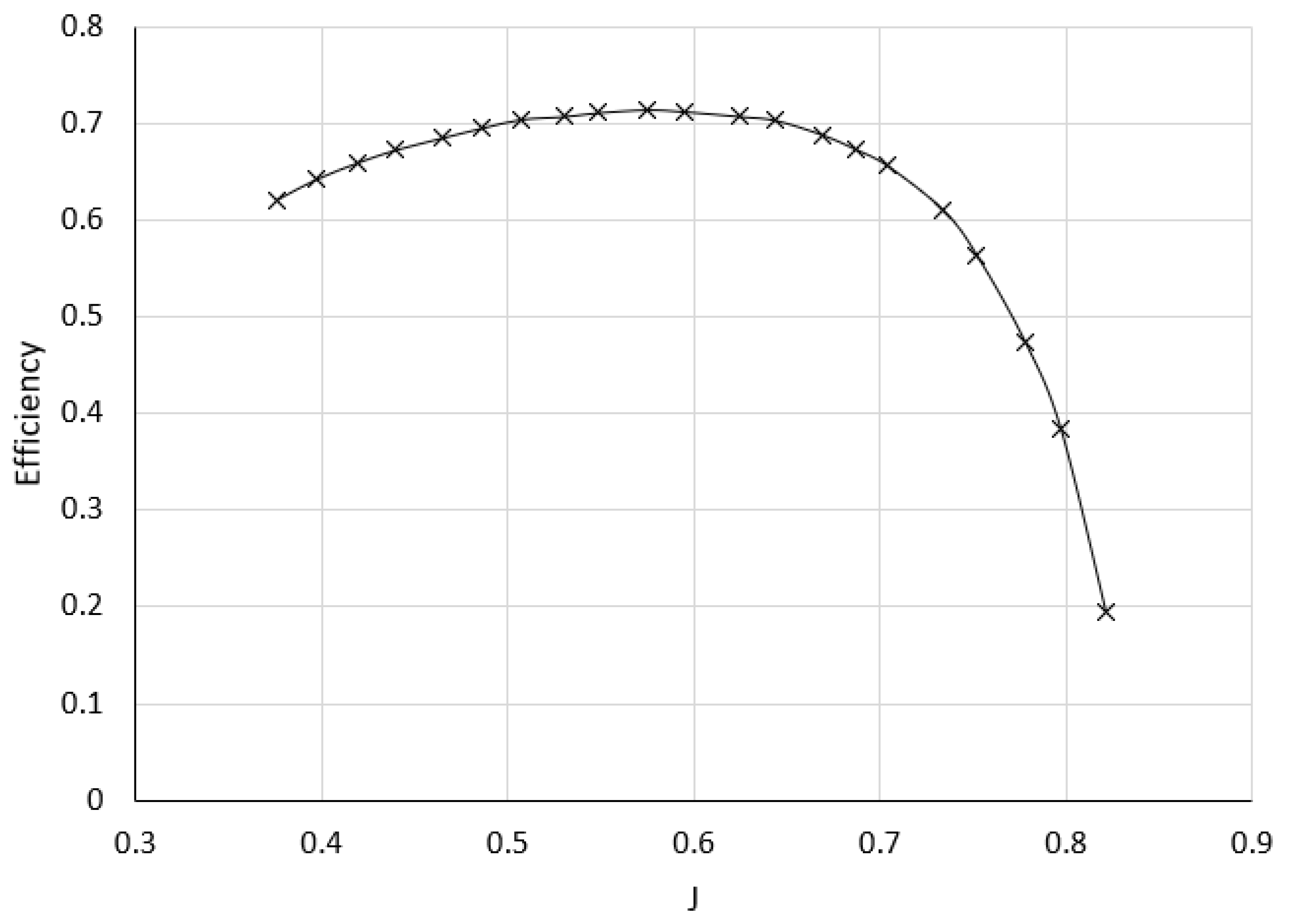
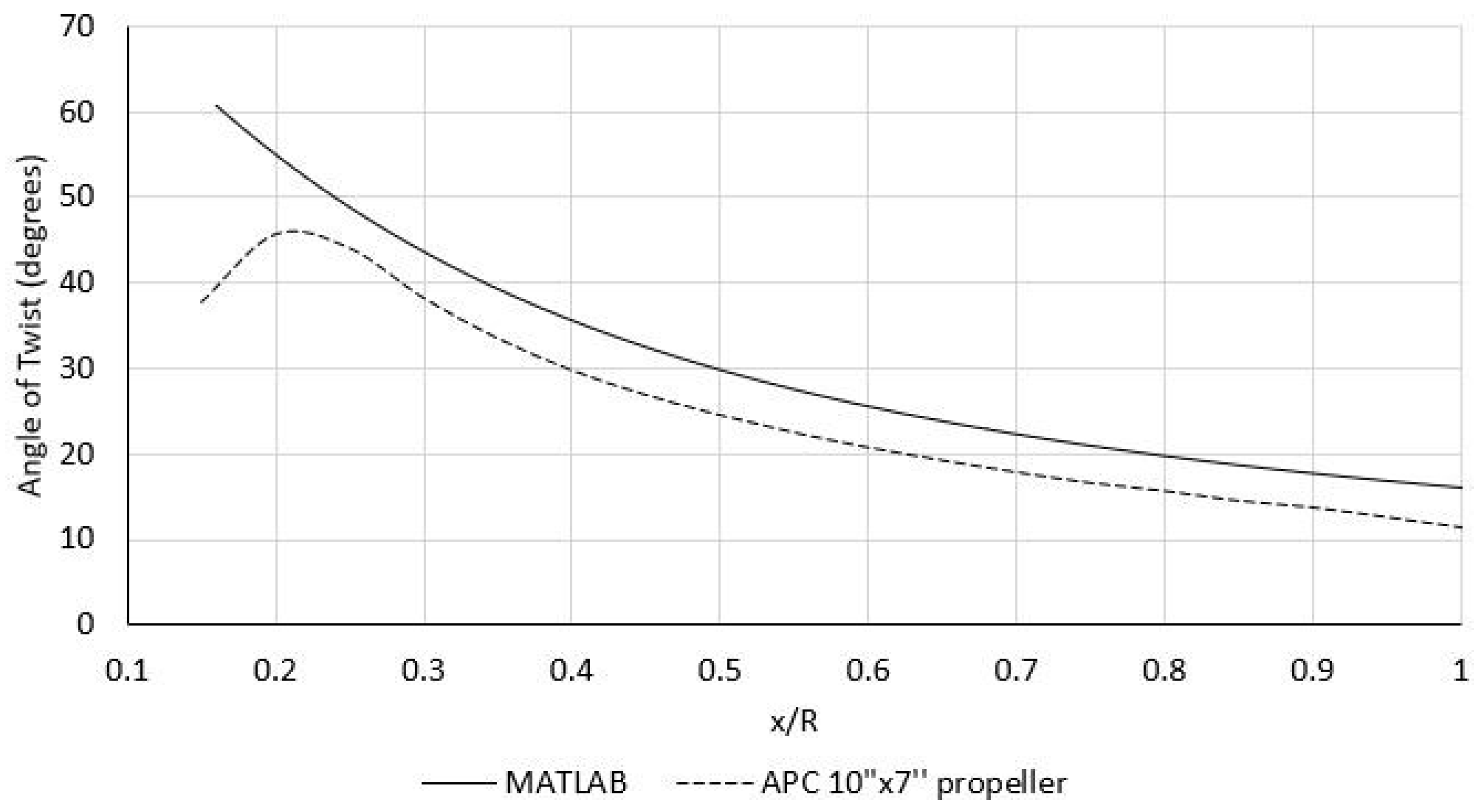
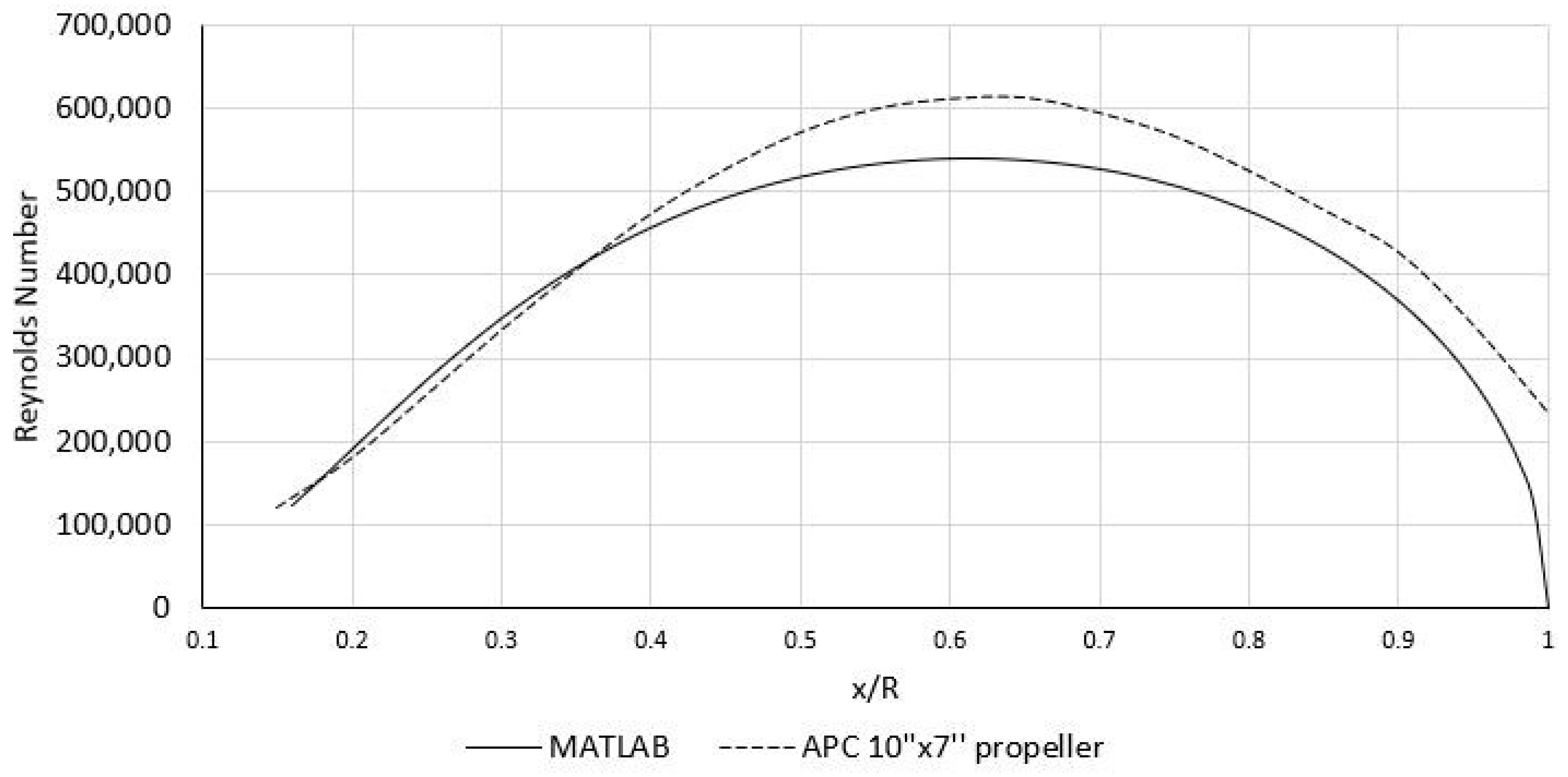
3.4. Validation of the MATLAB Program
4. Discussion
- A MATLAB tool has been developed, which takes inputs from the end user and calculates the optimal propeller geometry. The code is both fast, reliable and easy to use.
- Theoretically, the propeller design created will achieve higher efficiencies at a range of RPM values than commercially available propellers. From the MATLAB code, it was calculated that whilst operating at 6,500 RPM, an efficiency of 0.87 can be expected.
4.1. Recommendations for Further Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | Propeller disc area (m2) |
| B | Number of propeller blades |
| c | Blade chord length (m) |
| D | Propeller diameter (inches) |
| F | Prandtl’s momentum loss factor |
| G | Circulation function |
| I1 | Thrust loading integral |
| I2 | Thrust loading integral |
| J | Propeller advance ratio, V/n D |
| J1 | Power Loading integral |
| J2 | Power Loading integral |
| n | Number of complete revolutions per second |
| p | Propeller pitch (inches) |
| P | Shaft power consumed by propeller (W) |
| Q | Propeller shaft torque (Nm) |
| r | Distance along the propeller radius (m) |
| R | Propeller blade radius (m) |
| T | Thrust produced by the propeller (N) |
| V | Freestream velocity (m/s) |
| V1 | Displacement velocity (m/s) |
| W | Total local velocity (m/s) |
| cD | Airfoil section coefficient of drag |
| cL | Airfoil section coefficient of lift |
| CT | Thrust Coefficient |
| CP | Power Coefficient |
| CQ | Torque Coefficient |
| mblade | Mass of a propeller blade (kg) |
| Pc | Design Power Coefficient |
| Tc | Design Thrust Coefficient |
| v, | Displacement velocity (m/s) |
| waxial | Induced axial velocity component (m/s) |
| wswirl | Induced swirl velocity component (m/s) |
| xblade | Extension of a propeller blade (m) |
| xCoG | Distance from centre of rotation to propeller blade centre of gravity (m) |
| Re | Reynolds number |
| Greek Symbols | |
| α | Propeller blade angle of attack (degree) |
| β | Propeller blade angle of twist (degree) |
| ζ | Displacement velocity ratio, v1/V |
| ηp | Propeller efficiency, Tc/Pc ≡ J CT/CP |
| µ | Viscosity of air (kgm−1 s−1) |
| ξ | Non-dimensional radius, r/R |
| Γ | Circulation (m2/sec) |
| ρ | Air density (kgm−3) |
| σ | Rotor solidity |
| Ω | Propeller angular speed (rad/s) |
| φ | Flow angle (degree) |
| φs | Wake helix angle (degree) |
| φt | Flow angle at propeller blade tip (degree) |
Appendix A—MATLAB Program Code
References
- Archer, R.D.; Saarlas, M. An Introduction to Aerospace Propulsion, 1st Ed. Prentice Hall, US, 1996. pp. 68–121. ISBN: 978-0131204966.
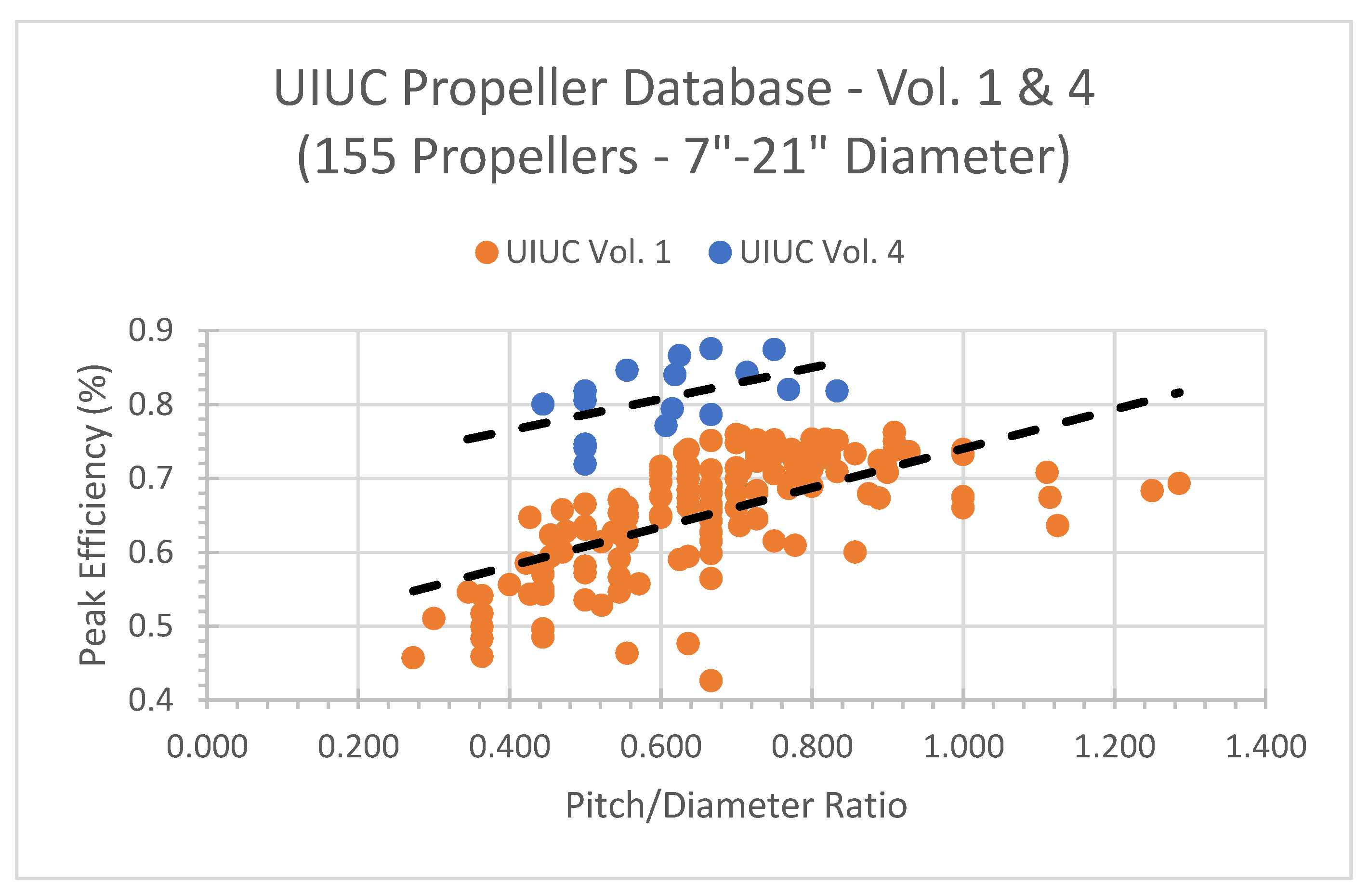
- Brandt, J.; Deters, R.; Ananda, G.; Selig, M. UIUC Propeller Database. Available online: https://m-selig.ae.illinois.edu/props/propDB.html, Oct. 2019. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. (Accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Bhagwat, M. J. (2015). Optimum Loading and Induced Swirl Effects in Hover. Journal of the American Helicopter Society, 60(1), 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Sampath, R. An Investigation into UAV Scale Propellers. Master’s Thesis, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mejzlik Propellers. Available online: https://www.mejzlik.eu/technical-data/propeller_data, (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Weishaeupl, A. Evaluating the Performance of Scale Propellers Using the Heliciel Software and RCBenchmark Thrust Stands, Master’s Thesis, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, E.; Barnaby, S,; Wingfield, C,; Cowper, W.J.E.,; Rigg, A.,; Stromeyer, C.E,; Thornycroft, J.T,; Froude, R.E,; and Greenhill, A.G. The Screw Propeller, In: Minutes of the Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers, pp. 390–392, 1890.
- Drzewiecki, S. Méthode pour la détermination des éléments mécaniques des propulseurs hélicoïdaux. imprimerie Gauthier-Villars et Fils, 1892. (in French).
- Weick, F. Simplified Propeller Design for Low-Powered Airplanes, NASA Technical Note 212, 1925.
- Glauert, H. Airplane Propellers, In: Aerodynamic Theory, Durand, W.F., Ed. pp. 169–360, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Germany. 1935. [CrossRef]
- Stickle, G.; and Crigler, J. Propeller Analysis from Experimental Data, National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics - Report Number 712, 1940.
- Theodorsen, T. Theory of Propellers. McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1st ed., 1948.
- McMasters, J. and Henderson, M. Low-Speed Single Element Airfoil Synthesis. Boeing Commercial Airplane Co., 1979.
- Gamble, D.E. Automated Dynamic Propeller Testing at Low Reynolds Numbers. Master’s Thesis, Oklahoma State University, Oklahoma, US, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, L.D. Design and Performance Calculations of a Propeller for very High-Altitude Flight, Master’s Thesis, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, US, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Merchant, M.P. Propeller Performance Measurement for Low Reynolds Number Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Applications. Master’s Thesis, Wichita State University, Kansas, US, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, I.M. Low Reynolds Propellers for Increased Quadcopters Endurance, Master’s Thesis, Universidade da Beira Interior, Covilhã, Portugal, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestre, M.A.R.; Morgardo, J,; Alves, P,; Santos, P,; Gamboa, P,; and Pa’scoa, J.C. Propeller Performance Measurements at Low Reynolds Numbers, International Journal of Mechanics, vol. 9, 2015, ISSN: 1998-4448.
- Kuantama, E.; Craciun, D.; Tarca, I. and Tarca, R. Quadcopter Propeller Design and Performance Analysis, In: New Advances in Mechanisms, Mechanical Transmissions and Robotics, pp. 269–277, Springer International Publishing, Oct 2016. [CrossRef]
- Prior, S.D. Optimizing Small Multi-Rotor Unmanned Aircraft, Ch. 5, pp. 33–64. Taylor & Francis, London, UK. 2018. ISBN: 978-1138369887.
- Ning, Z. and Hu, H. An Experimental Study on the Aerodynamic and Aeroacoustic Performances of a Bio-inspired UAV Propeller, In: 35th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, June 2017. [CrossRef]
- Larrabee, E.E. Design of Propellers for Motorsoarers, NASA Publication: The Science and Technology of Low Speed and Motorless Flight, 1 January 1979.
- Adkins, C. and Liebeck, R. Design of Optimum Propellers, Journal of Propulsion and Power, vol. 10, no. 5, 1994. [CrossRef]
- Betz, A. and Prandtl, L. Screw Propellers with Minimum Energy Loss, Gottingen Reports, pp. 193– 213, 1919.
- Goldstein, S. On the Vortex Theory of Screw Propellers, In: Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A, vol. 123, pp. 440–465, 1929.
- Klesa, J. Increasing of Aircraft Propeller Efficiency by using Variable Twist Propeller Blades, 2008. Available online: https://stc.fs.cvut.cz/history/2008/sbornik/Papers/D2/Klesa_Jan_12122.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- JavaFoil. Available online: https://www.mh-aerotools.de/airfoils/javafoil.htm (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Drela, M. QProp. Available online: https://web.mit.edu/drela/Public/web/qprop/ (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Leishman, G.J. Principles of Helicopter Aerodynamics. 2nd Ed. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 2016. ISBN: 978-1107013353.
- Korkan, K.; Camba, J.; and Morris, P. Aerodynamic Databanks for Clark-Y, NACA 4-digit and NACA 16-series Airfoil Families, Technical Report, Aerospace Engineering Department, Texas A&M University, Texas, US. 1986.
- Airfoil Tools, Airfoil Database (1,638 Airfoils). Available online: http://airfoiltools.com/search/index (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Advanced Precision Composites, “APC Propeller Performance Data.”. Available online: https://www.apcprop.com/technical-information/performance-data/, (accessed on 28 May 2024).



| Propeller | Rotor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CTp | Propeller Thrust Coefficient | CT | Rotor Thrust Coefficient |
| CPp | Propeller Power Coefficient | CP | Rotor Power Coefficient |
| CQp | Propeller Torque Coefficient | CQ | Rotor Torque Coefficient |
| Input | Unit |
|---|---|
| Diameter (D) | Inch |
| Velocity (V) | m/s |
| Shaft Power (P) | W |
| Propeller Speed | RPM |
| Air Density (ρ) | kgm−3 |
| Number of Blades (B) | - |
| Airfoil CL | - |
| Airfoil CD | - |
| Non-Dimensional Hub Radius | - |
| Angle of Attack (α) | Degree |
| Displacement velocity ratio convergence level | - |
| Number of blade elements | - |
| Input | Input Value |
|---|---|
| Diameter (D) | 10 inch |
| Velocity (V) | 15.87 m/s |
| Shaft Power (P) | 68.77 W |
| Propeller Speed (n x 60) | 6,519 RPM |
| Air Density (ρ) | 1.225 kgm−3 |
| Number of Blades (B) | 2 |
| Airfoil CL | 0.4 |
| Airfoil CD | 0.02 |
| Non-Dimensional Hub Radius Angle of Attack (α) |
0.15 0◦ |
| Displacement velocity ratio convergence level | 0.1 |
| Number of blade elements | 100 |
| MATLAB program | UIUC Experimental Results (2) | APC Theoretical Results (32) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ηp | 0.870 | 0.714 | 0.727 |
| CT | 0.0626 | 0.0514 | 0.0477 |
|
CP J |
0.0414 0.5751 |
0.0414 0.5751 |
0.0405 0.6166 |
| Pitch at 0.75R | 8.6” | 7” | 7” |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





