Submitted:
14 June 2024
Posted:
17 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
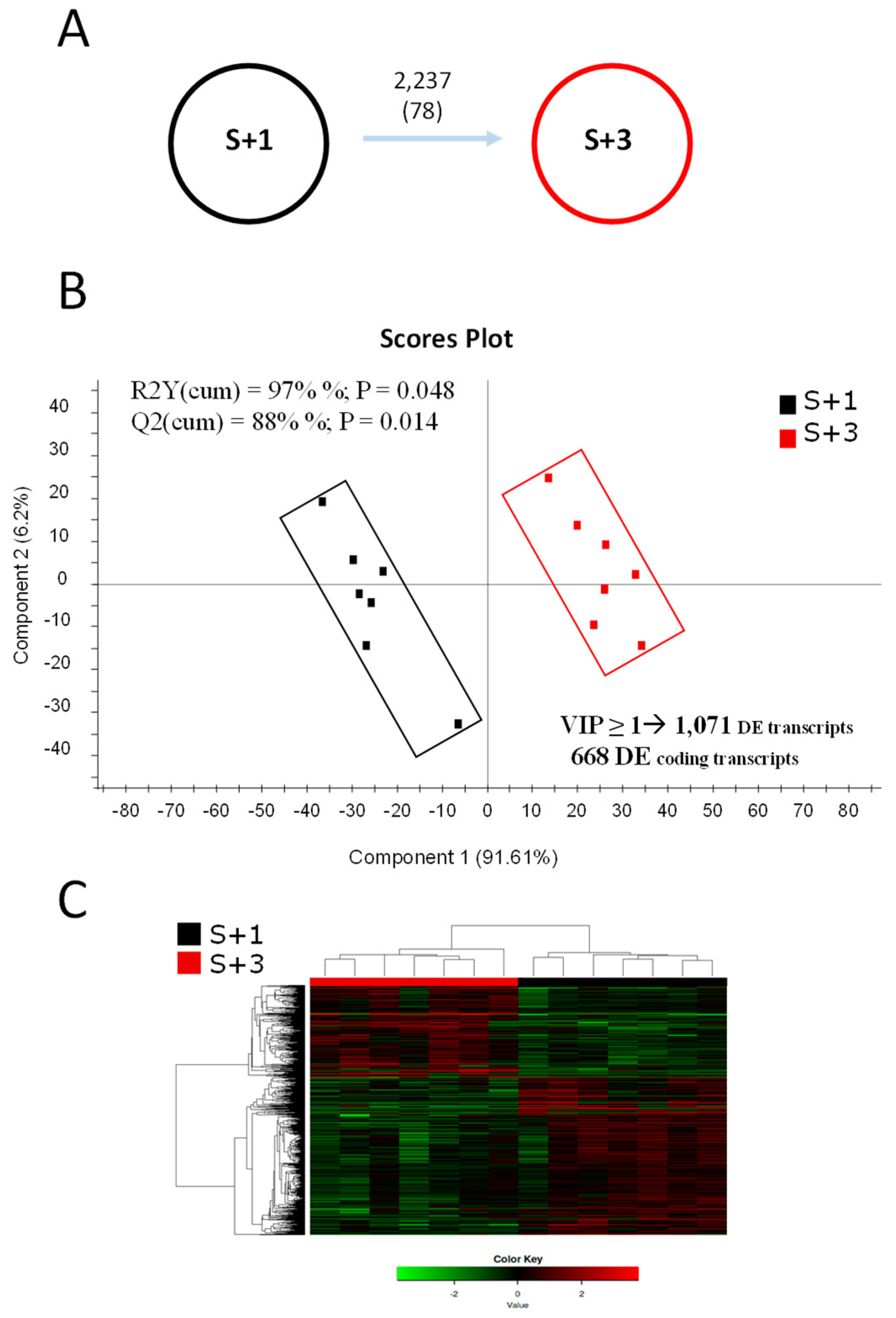
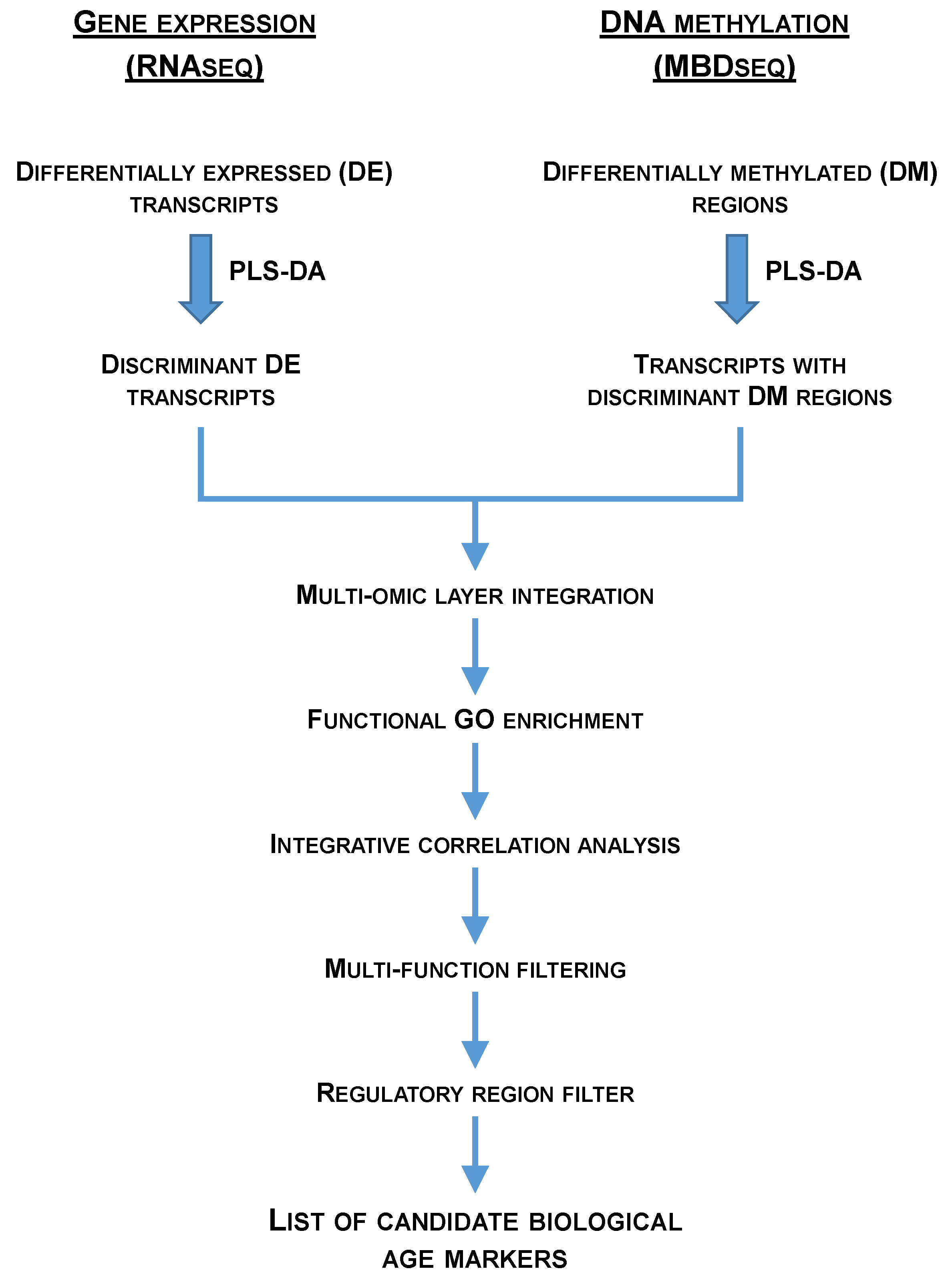
2.1. Age-Related Patterns of Gene Expression and Their Discriminant Analysis
2.2. Age-Related Patterns of Differentially Methylated DNA and Its Discriminant Analysis
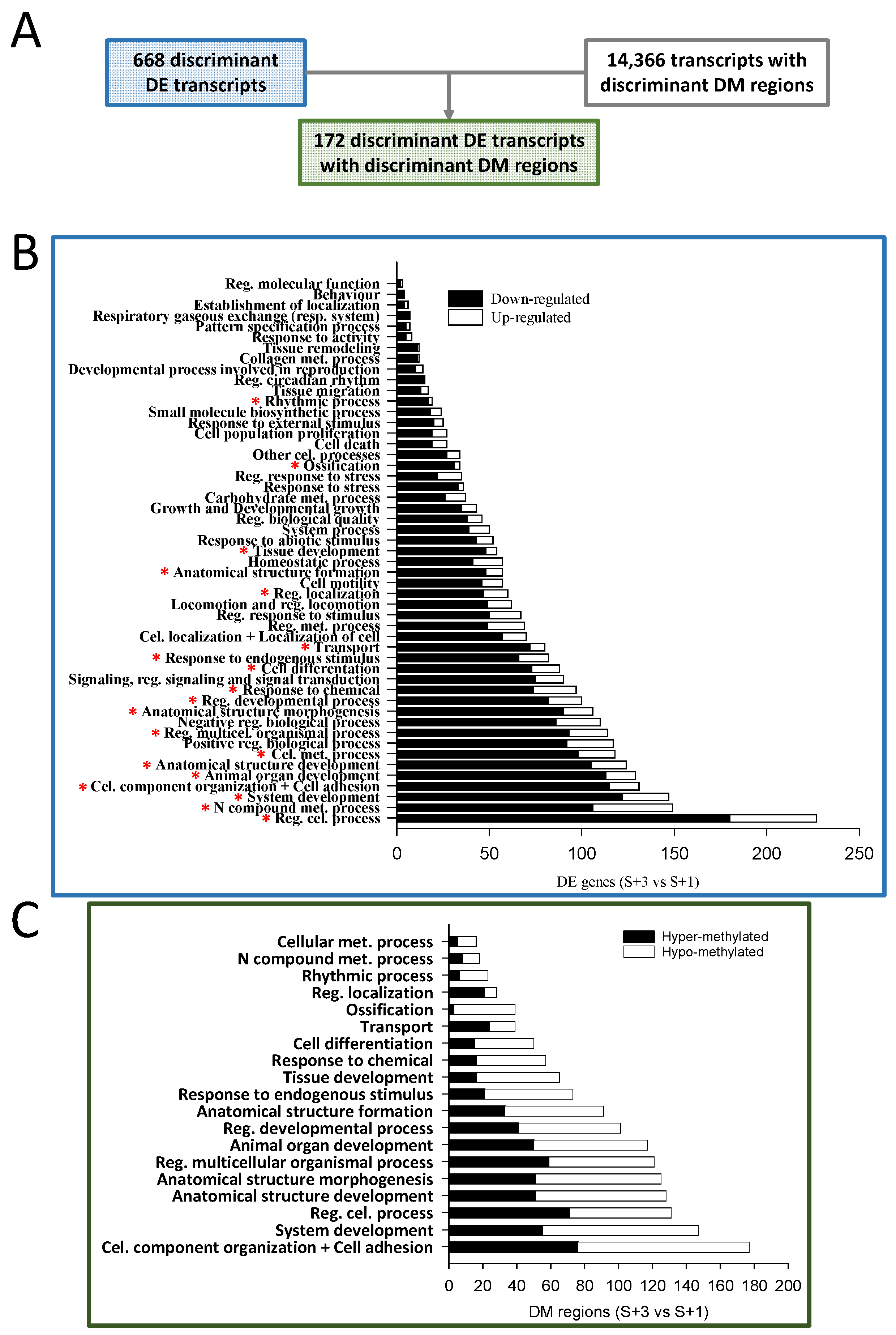
2.3. Functional Network Analysis of Differentially Expressed Transcripts and of Transcripts with Concomitant Differential Expression and Methylation
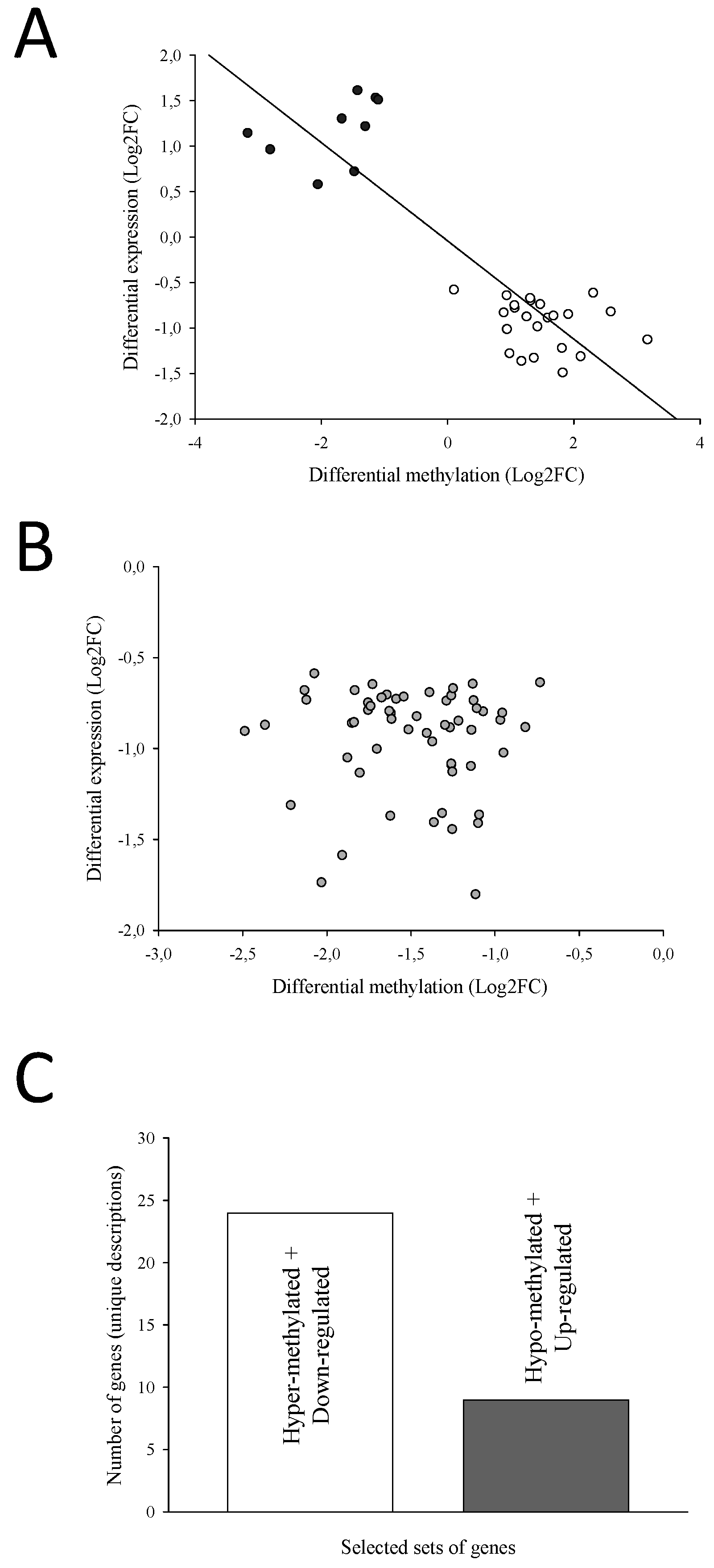
2.4. The Different Patterns of DNA Methylation and Expression
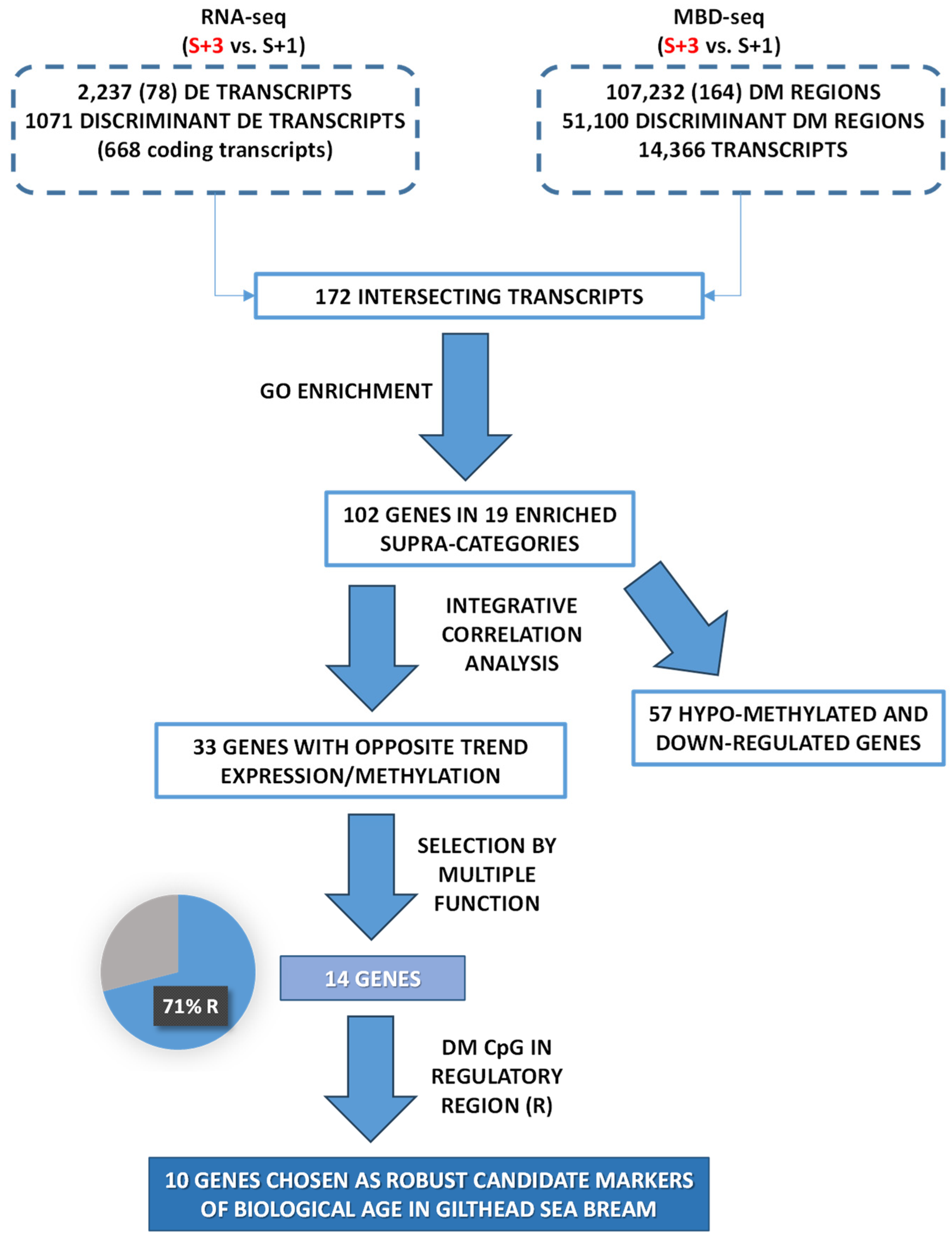
2.5. Candidate Markers of Biological Age
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ehics Statement
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. DNA/RNA Extraction
4.4. DNA/RNA Illumina Sequencing
4.5. Bioinformatic Analyses
4.6. Statistical Analysis and Data Filtering
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, A.; Sheikh Abdullah, S.R.; Hasan, H.A.; Othman, A.R.; Ismail, N. ‘Izzati Aquaculture Industry: Supply and Demand, Best Practices, Effluent and Its Current Issues and Treatment Technology. J Environ Manage 2021, 287, 112271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. A 20-Year Retrospective Review of Global Aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North, B.P.; Turnbull, J.F.; Ellis, T.; Porter, M.J.; Migaud, H.; Bron, J.; Bromage, N.R. The Impact of Stocking Density on the Welfare of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss). Aquaculture 2006, 255, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Sun, G. Effects of Stocking Density on Growth Performance and Welfare-Related Physiological Parameters of Atlantic Salmon Salmo Salar L. in Recirculating Aquaculture System. Aquac Res 2017, 48, 2133–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wen, H.; Tian, J.; Jiang, M.; Liu, W.; Yang, C.; Yu, L.; Lu, X. Effect of Stocking Density on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Parameters, and Muscle Texture Properties of Genetically Improved Farm Tilapia, Oreochromis Niloticus. Aquaculture International 2018, 26, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, S.; Stentiford, G.D.; Leocadio, A.M.; Jeffery, K.R.; Metcalfe, J.D.; Katsiadaki, I.; Auchterlonie, N.A.; Mangi, S.C.; Pinnegar, J.K.; Ellis, T.; et al. Aquatic Food Security: Insights into Challenges and Solutions from an Analysis of Interactions between Fisheries, Aquaculture, Food Safety, Human Health, Fish and Human Welfare, Economy and Environment. Fish and Fisheries 2016, 17, 893–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo de Magalhães, C.S.F.; Cerqueira, M.A.C.; Schrama, D.; Moreira, M.J.V.; Boonanuntanasarn, S.; Rodrigues, P.M.L. A Proteomics and Other Omics Approach in the Context of Farmed Fish Welfare and Biomarker Discovery. Rev Aquac 2020, 12, 122–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stien, L.H.; Bracke, M.B.M.; Folkedal, O.; Nilsson, J.; Oppedal, F.; Torgersen, T.; Kittilsen, S.; Midtlyng, P.J.; Vindas, M.A.; Øverli, Ø.; et al. Salmon Welfare Index Model (SWIM 1.0): A Semantic Model for Overall Welfare Assessment of Caged Atlantic Salmon: Review of the Selected Welfare Indicators and Model Presentation. Rev Aquac 2013, 5, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, C.; Gismervik, K.; Iversen, M.H.; Kolarevic, J.; Nilsson, J.; Stien, L.H.; Turnbull, J.F. Welfare Indicators for Farmed Atlantic Salmon: Tools for Assessing Fish Welfare; Nofima: Tromso, Norway, 2018; 351p, ISBN 9788282965569. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, C.; Gismervik, K.; Iversen, M.H.; Kolarevic, J.; Nilsson, J.; Stien, L.H.; Turnbull, J.F. Welfare Indicators for Farmed Rainbow Trout: Tools for Assessing Fish Welfare, Nofima: Tromso, Norway, 2020, 310 pp; ISBN 9788282966207.
- Sadoul, B.; Geffroy, B. Measuring Cortisol, the Major Stress Hormone in Fishes. J Fish Biol 2019, 94, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winberg, S.; Höglund, E.; Øverli, Ø. Variation in the Neuroendocrine Stress Response. In Fish Physiology; Elsevier Inc., 2016; Vol. 35, pp. 35–74.
- Madaro, A.; Nilsson, J.; Whatmore, P.; Roh, H.J.; Grove, S.; Stien, L.H.; Olsen, R.E. Acute Stress Response on Atlantic Salmon: A Time-Course Study of the Effects on Plasma Metabolites, Mucus Cortisol Levels, and Head Kidney Transcriptome Profile. Fish Physiol Biochem 2023, 49, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matley, J.K.; Johansen, L.K.; Klinard, N.V.; Eanes, S.T.; Jobsis, P.D. Habitat Selection and 3D Space Use Partitioning of Resident Juvenile Hawksbill Sea Turtles in a Small Caribbean Bay. Mar Biol 2021, 168, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulou, D.G.; Vouidaskis, C.; Papandroulakis, N. Swimming Behavior as a Potential Metric to Detect Satiation Levels of European Seabass in Marine Cages. Front Mar Sci 2024, 11, 1350385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calduch-Giner, J.; Holhorea, P.G.; Ferrer, M.A.; Naya-Català, F.; Rosell-Moll, E.; Vega García, C.; Prunet, P.; Espmark, A.M.; Leguen, I.; Kolarevic, J.; et al. Revising the Impact and Prospects of Activity and Ventilation Rate Bio-Loggers for Tracking Welfare and Fish-Environment Interactions in Salmonids and Mediterranean Farmed Fish. Front Mar Sci 2022, 9, 854888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzi, D.; Rasmussen, J.A.; Carøe, C.; Sveier, H.; Nordøy, K.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Limborg, M.T. Salmon Gut Microbiota Correlates with Disease Infection Status: Potential for Monitoring Health in Farmed Animals. Anim Microbiome 2021, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo-Bretón, R.; Cools, S.; Belenguer, A.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Croes, E.; Holhorea, P.G.; Naya-Català, F.; Boon, H.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Gilthead Sea Bream Microbiota Shifts Associated with Thermal Stress and Dietary Intervention during a Record Heat Summer. In Proceedings of the Aquaculture Europe 2023, Viena, Austria, 2023 (19-21 September 2023). [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, K.; Laroche, O.; Walker, S.P.; Symonds, J.E. Effects of Water Temperature on the Gut Microbiome and Physiology of Chinook Salmon (Oncorhynchus Tshawytscha) Reared in a Freshwater Recirculating System. Aquaculture 2022, 560, 738529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, D.; Rimoldi, S.; Torrecillas, S.; Rapp, J.; Moroni, F.; Herrera, A.; Gómez, M.; Fernández-Montero, Á.; Terova, G. Impact of Polypropylene Microplastics and Chemical Pollutants on European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus Labrax) Gut Microbiota and Health. Science of the Total Environment 2022, 805, 150402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, R.; Cheng, Z.; Peng, L.; Mehmood, T.; Gao, L.; Zhuo, S.; Wang, L.; Su, Y. Effects of Biodegradable and Conventional Microplastics on the Intestine, Intestinal Community Composition, and Metabolic Levels in Tilapia (Oreochromis Mossambicus). Aquatic Toxicology 2023, 265, 106745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toxqui-Rodríguez, S.; Naya-Català, F.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Piazzon, M.C.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Fish Microbiomics: Strengths and Limitations of MinION Sequencing of Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus Aurata) Intestinal Microbiota. Aquaculture 2023, 569, 739388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Older, C.E.; Yamamoto, F.Y.; Griffin, M.J.; Ware, C.; Heckman, T.I.; Soto, E.; Bosworth, B.G.; Waldbieser, G.C. Comparison of High-Throughput Sequencing Methods for Bacterial Microbiota Profiling in Catfish Aquaculture. N Am J Aquac 2024, 86, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Tu, K.; Zheng, Z. Insights into the Intestinal Microbiota of Several Aquatic Organisms and Association with the Surrounding Environment. Aquaculture 2019, 507, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naya-Català, F.; Piazzon, M.C.; Torrecillas, S.; Toxqui-Rodríguez, S.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Fontanillas, R.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Montero, D.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Genetics and Nutrition Drive the Gut Microbiota Succession and Host-Transcriptome Interactions through the Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus Aurata) Production Cycle. Biology (Basel) 2022, 11, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, S. DNA Methylation Age of Human Tissues and Cell Types. Genome Biol 2013, 14, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paoli-Iseppi, R.; Deagle, B.E.; Polanowski, A.M.; McMahon, C.R.; Dickinson, J.L.; Hindell, M.A.; Jarman, S.N. Age Estimation in a Long-Lived Seabird (Ardenna Tenuirostris) Using DNA Methylation-Based Biomarkers. Mol Ecol Resour 2019, 19, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piferrer, F.; Anastasiadi, D. Age Estimation in Fishes Using Epigenetic Clocks: Applications to Fisheries Management and Conservation Biology. Front Mar Sci 2023, 10, 1062151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, R.E.; Noble, D.W.A.; Johnson, S.L.; Hesselson, D.; Nakagawa, S. The Role of Non-Genetic Inheritance in Evolutionary Rescue: Epigenetic Buffering, Heritable Bet Hedging and Epigenetic Traps. Environ Epigenet 2016, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrott, B.B.; Bertucci, E.M. Epigenetic Aging Clocks in Ecology and Evolution. Trends Ecol Evol 2019, 34, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, E.M.; Wason, M.W.; Rhodes, O.E.; Parrott, B.B. Exposure to ionizing radiation disrupts normal epigenetic aging in Japanese medaka. Aging 2021, 13, 22752–22771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, C.G.; Lowe, R.; Adams, P.D.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Beck, S.; Bell, J.T.; Christensen, B.C.; Gladyshev, V.N.; Heijmans, B.T.; Horvath, S.; et al. DNA Methylation Aging Clocks: Challenges and Recommendations. Genome Biol 2019, 20, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gensous, N.; Sala, C.; Pirazzini, C.; Ravaioli, F.; Milazzo, M.; Kwiatkowska, K.M.; Marasco, E.; De Fanti, S.; Giuliani, C.; Pellegrini, C.; et al. A Targeted Epigenetic Clock for the Prediction of Biological Age. Cells 2022, 11, 4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutledge, J.; Oh, H.; Wyss-Coray, T. Measuring Biological Age Using Omics Data. Nat Rev Genet 2022, 23, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, R.; Fu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q. Epigenetic Clock: A Promising Biomarker and Practical Tool in Aging. Ageing Res Rev 2022, 81, 101743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangili, M.; Slettenhaar, A.J.; Sudyka, J.; Dugdale, H.L.; Pen, I.; Palsbøll, P.J.; Verhulst, S. DNA Methylation Markers of Age(Ing) in Non-Model Animals. Mol Ecol 2023, 32, 4725–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateson, M.; Poirier, C. Can Biomarkers of Biological Age Be Used to Assess Cumulative Lifetime Experience? Animal Welfare 2019, 28, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, L.J.; Winckler, C.; Hintze, S.; Forkman, B. Towards a Positive Welfare Protocol for Cattle: A Critical Review of Indicators and Suggestion of How We Might Proceed. Front Anim Sci 2021, 2, 753080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.N.; Araujo, M.S.; Pértille, F.; Zanella, A.J. How Epigenetics Can Enhance Pig Welfare? Animals 2022, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colditz, I.G.; Smith, E.G.; Ingham, A.B.; Dominik, S. Indicators of Functional Integrity in Production Animals. Anim Prod Sci 2023, 63, 825–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.J.; Chandra, T. Epigenetic Age Prediction. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Arcos Hodar, J.; del Sol, A. Measuring Biological Age Using a Functionally Interpretable Multi-Tissue RNA Clock. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naya-Català, F.; Belenguer, A.; Montero, D.; Torrecillas, S.; Soriano, B.; Calduch-Giner, J.; Llorens, C.; Fontanillas, R.; Sarih, S.; Zamorano, M.J.; et al. Broodstock Nutritional Programming Differentially Affects the Hepatic Transcriptome and Genome-Wide DNA Methylome of Farmed Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus Aurata) Depending on Genetic Background. BMC Genomics 2023, 24, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdivieso, A.; Anastasiadi, D.; Ribas, L.; Piferrer, F. Development of Epigenetic Biomarkers for the Identification of Sex and Thermal Stress in Fish Using DNA Methylation Analysis and Machine Learning Procedures. Mol Ecol Resour 2023, 23, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beemelmanns, A.; Ribas, L.; Anastasiadi, D.; Moraleda-Prados, J.; Zanuzzo, F.S.; Rise, M.L.; Gamperl, A.K. DNA Methylation Dynamics in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar) Challenged With High Temperature and Moderate Hypoxia. Front Mar Sci 2021, 7, 604878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simó-Mirabet, P.; Perera, E.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Local DNA Methylation Helps to Regulate Muscle Sirtuin 1 Gene Expression across Seasons and Advancing Age in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus Aurata). Front Zool 2020, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, B.; Wang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wang, J. Transcriptome Analysis Provides Insights into Hepatic Responses to Moderate Heat Stress in the Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss). Gene 2017, 619, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beemelmanns, A.; Zanuzzo, F.S.; Xue, X.; Sandrelli, R.M.; Rise, M.L.; Gamperl, A.K. The Transcriptomic Responses of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar) to High Temperature Stress Alone, and in Combination with Moderate Hypoxia. BMC Genomics 2021, 22, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgerhout, E.; Mommens, M.; Johnsen, H.; Aunsmo, A.; Santi, N.; Andersen, O. Genetic Background and Embryonic Temperature Affect DNA Methylation and Expression of Myogenin and Muscle Development in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar). PLoS One 2017, 12, e0179918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veron, V.; Marandel, L.; Liu, J.; Vélez, E.J.; Lepais, O.; Panserat, S.; Skiba, S.; Seiliez, I. DNA Methylation of the Promoter Region of Bnip3 and Bnip3l Genes Induced by Metabolic Programming 06 Biological Sciences 0604 Genetics. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.L.; Guo, S.N.; Yuan, S.S.; Xia, H.; Zhu, Q.L.; Lv, Z.M. Preheating Mitigates Cadmium Toxicity in Zebrafish Livers: Evidence from Promoter Demethylation, Gene Transcription to Biochemical Levels. Aquatic Toxicology 2017, 190, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stien, L.H.; Bracke, M.; Noble, C.; Kristiansen, T.S. Assessing Fish Welfare in Aquaculture. In The welfare of the fish; Kristiansen, T.S., Ferno, A., Pavlidis, M.A., van de Vis, H., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 303–322. [Google Scholar]
- van de Vis, H.; Kolarevic, J.; Stien, L.H.; Kristiansen, T.S.; Gerritzen, M.; van de Braak, K.; Abbink, W.; Sæther, B.-S.; Noble, C. Welfare of Farmed Fish in Different Production Systems and Operations. In The welfare of the fish; Kristiansen, T.S., Ferno, A., Pavlidis, M.A., van de Vis, H., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 323–362. [Google Scholar]
- Piferrer, F.; Blázquez, M.; Navarro, L.; González, A. Genetic, Endocrine, and Environmental Components of Sex Determination and Differentiation in the European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus Labrax L.). Gen Comp Endocrinol 2005, 142, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Martín, L.; Blázquez, M.; Viñas, J.; Joly, S.; Piferrer, F. Balancing the Effects of Rearing at Low Temperature during Early Development on Sex Ratios, Growth and Maturation in the European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus Labrax). Limitations and Opportunities for the Production of Highly Female-Biased Stocks. Aquaculture 2009, 296, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simó-Mirabet, P.; Felip, A.; Estensoro, I.; Martos-Sitcha, J.A.; de las Heras, V.; Calduch-Giner, J.; Puyalto, M.; Karalazos, V.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Impact of Low Fish Meal and Fish Oil Diets on the Performance, Sex Steroid Profile and Male-Female Sex Reversal of Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus Aurata) over a Three-Year Production Cycle. Aquaculture 2018, 490, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holhorea, P.G.; Felip, A.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Afonso, J.M.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Use of Male-to-Female Sex Reversal as a Welfare Scoring System in the Protandrous Farmed Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus Aurata). Front Vet Sci 2023, 9, 1083255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenk, S.; Houseley, J. Gene Expression Hallmarks of Cellular Ageing. Biogerontology 2018, 19, 547–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. Hallmarks of Aging: An Expanding Universe. Cell 2023, 186, 243–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegeman, R.; Weake, V.M. Transcriptional Signatures of Aging. J Mol Biol 2017, 429, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shavlakadze, T.; Morris, M.; Fang, J.; Wang, S.X.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, W.; Tse, H.W.; Mondragon-Gonzalez, R.; Roma, G.; Glass, D.J. Age-Related Gene Expression Signature in Rats Demonstrate Early, Late, and Linear Transcriptional Changes from Multiple Tissues. Cell Rep 2019, 28, 3263–3273.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando-Herraez, I.; Evano, B.; Stubbs, T.; Commere, P.H.; Jan Bonder, M.; Clark, S.; Andrews, S.; Tajbakhsh, S.; Reik, W. Ageing Affects DNA Methylation Drift and Transcriptional Cell-to-Cell Variability in Mouse Muscle Stem Cells. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijima, Y.; Wantong, W.; Igarashi, Y.; Yoshitake, K.; Asakawa, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Watabe, S.; Kinoshita, S. Age-Associated Different Transcriptome Profiling in Zebrafish and Rats: An Insight into the Diversity of Vertebrate Aging. Mar Biotechnol 2022, 24, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Teefy, B.B.; Lu, R.J.; Nozownik, S.; Tyers, A.M.; Valenzano, D.R.; Benayoun, B.A. Transcriptomes of Aging Brain, Heart, Muscle, and Spleen from Female and Male African Turquoise Killifish. Sci Data 2023, 10, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The Hallmarks of Aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Gil, L.; Pascual-Ahuir, A.; Proft, M. Genomic Instability and Epigenetic Changes during Aging. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 14279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.; Pfeifer, G.P. Aging and DNA Methylation. BMC Biol 2015, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupkovitz, G.; Kabiljo, J.; Kothmayer, M.; Schlick, K.; Schöfer, C.; Lagger, S.; Pusch, O. Analysis of Methylation Dynamics Reveals a Tissue-Specific, Age-Dependent Decline in 5-Methylcytosine Within the Genome of the Vertebrate Aging Model Nothobranchius Furzeri. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 8, 627143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyn, H.; Li, N.; Ferreira, H.J.; Moran, S.; Pisano, D.G.; Gomez, A.; Diez, J.; Sanchez-Mut, J.V.; Setien, F.; Carmona, F.J.; et al. Distinct DNA Methylomes of Newborns and Centenarians. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109, 10522–10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.A.; Akman, K.; Calimport, S.R.G.; Wuttke, D.; Stolzing, A.; De Magalhães, J.P. The Role of DNA Methylation in Aging, Rejuvenation, and Age-Related Disease. Rejuvenation Res 2012, 15, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoda, N.; Izawa, T.; Yoshizawa, A.; Yokoi, H.; Kikuchi, Y.; Hashimoto, N. Decrease in Cytosine Methylation at CpG Island Shores and Increase in DNA Fragmentation during Zebrafish Aging. Age (Omaha) 2014, 36, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadi, D.; Piferrer, F. A Clockwork Fish: Age Prediction Using DNA Methylation-Based Biomarkers in the European Seabass. Mol Ecol Resour 2020, 20, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newell-Price, J.; Adrian, J.L.C.; King, P. DNA Methylation and Silencing of Gene Expression. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2000, 11, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biermann, K.; Steger, K. Epigenetics in Male Germ Cells. J Androl 2007, 28, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.A. Functions of DNA Methylation: Islands, Start Sites, Gene Bodies and Beyond. Nat Rev Genet 2012, 13, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, L.D.; Le, T.; Fan, G. DNA Methylation and Its Basic Function. Neuropsychopharmacol 2013, 38, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenet, F.; Moh, M.; Funk, P.; Feierstein, E.; Viale, A.J.; Socci, N.D.; Scandura, J.M. DNA Methylation of the First Exon Is Tightly Linked to Transcriptional Silencing. PLoS One 2011, 6, e14524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasiadi, D.; Esteve-Codina, A.; Piferrer, F. Consistent Inverse Correlation between DNA Methylation of the First Intron and Gene Expression across Tissues and Species. Epigenet Chromatin 2018, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, G.C.; Hawkins, R.D.; Caballero, O.L.; Lo, C.; Lister, R.; Pelizzola, M.; Valsesia, A.; Ye, Z.; Kuan, S.; Edsall, L.E.; et al. Global DNA Hypomethylation Coupled to Repressive Chromatin Domain Formation and Gene Silencing in Breast Cancer. Genome Res 2012, 22, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Han, H.; DeCarvalho, D.D.; Lay, F.D.; Jones, P.A.; Liang, G. Gene Body Methylation Can Alter Gene Expression and Is a Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchuk, I. Role of DNA Methylation in Genome Stability. In Genome Stability: From Virus to Human Application; Kovalchuk, I., Kovalchuk, O., Eds.; Academic Press, London, United Kingdom, 2021; pp. 435–452 ISBN 9780323856799.
- Vikeså, V.; Nankervis, L.; Hevrøy, E.M. Appetite, Metabolism and Growth Regulation in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar L.) Exposed to Hypoxia at Elevated Seawater Temperature. Aquac Res 2017, 48, 4086–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naya-Català, F.; Martos-Sitcha, J.A.; de las Heras, V.; Simó-Mirabet, P.; Calduch-Giner, J.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Targeting the Mild-Hypoxia Driving Force for Metabolic and Muscle Transcriptional Reprogramming of Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus Aurata) Juveniles. Biology (Basel) 2021, 10, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.T.; Fei, Z.; Haghani, A.; Robeck, T.R.; Zoller, J.A.; Li, C.Z.; Lowe, R.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Vu, H.; et al. Universal DNA Methylation Age across Mammalian Tissues. Nat Aging 2023, 3, 1144–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toiber, D.; Sebastian, C.; Mostoslavsky, R. Characterization of Nuclear Sirtuins: Molecular Mechanisms and Physiological Relevance. In Histone deacetylases: the biology and clinical implication; Yao, T.-P., Seto, E., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 189–224. [Google Scholar]
- Bellet, M.M.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Mammalian Circadian Clock and Metabolism - The Epigenetic Link. J Cell Sci 2010, 123, 3837–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch-Presegué, L.; Vaquero, A. Sirtuin-Dependent Epigenetic Regulation in the Maintenance of Genome Integrity. FEBS Journal 2015, 282, 1745–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.H.; Kong, Q.P.; Perry, B.; He, Y.H. Progress on the Role of DNA Methylation in Aging and Longevity. Brief Funct Genomics 2016, 15, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Cao, J.; Hu, K.; He, X.; Yun, D.; Tong, T.; Han, L. Sirtuins and Their Biological Relevance in Aging and Age-Related Diseases. Aging Dis 2020, 11, 927–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitajima, Y.; Yoshioka, K.; Suzuki, N. The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Regulation of the Skeletal Muscle Homeostasis and Atrophy: From Basic Science to Disorders. J Physiol Sci 2020, 70, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, B.Y.; Medhurst, A.D.; Jackson, M.; Rose, S.; Jenner, P. Proteasomal Activity in Brain Differs between Species and Brain Regions and Changes with Age. Mech Ageing Dev 2005, 126, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasuri, K.; Nguyen, A.; Zhang, L.; Fernandez-Kim, O.S.; Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Blalock, B.A.; De Cabo, R.; Keller, J.N. Comparison of Rat Liver and Brain Proteasomes for Oxidative Stress-Induced Inactivation: Influence of Ageing and Dietary Restriction. Free Radic Res 2009, 43, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrington, D.A.; Husom, A.D.; Thompson, L.V. Altered Proteasome Structure, Function, and Oxidation in Aged Muscle. The FASEB Journal 2005, 19, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogan, N.J.; Lam, M.H.Y.; Fillingham, J.; Keogh, M.C.; Gebbia, M.; Li, J.; Datta, N.; Cagney, G.; Buratowski, S.; Emili, A.; et al. Proteasome Involvement in the Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks. Mol Cell 2004, 16, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salah Fararjeh, A.F.; Al-Khader, A.; Al-Saleem, M.; Abu Qauod, R. The Prognostic Significance of Proteasome 26S Subunit, Non-ATPase (PSMD) Genes for Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Patients. Cancer Inform 2021, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, D.W.; Godson, C.; Brazil, D.P.; Martin, F. Extracellular BMP-Antagonist Regulation in Development and Disease: Tied up in Knots. Trends Cell Biol 2010, 20, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, R.; Schirwis, E.; Blaauw, B.; Bortolanza, S.; Zhao, J.; Enzo, E.; Stantzou, A.; Mouisel, E.; Toniolo, L.; Ferry, A.; et al. BMP Signaling Controls Muscle Mass. Nat Genet 2013, 45, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilwik, R.; Snijders, T.; Leenders, M.; Groen, B.B.L.; van Kranenburg, J.; Verdijk, L.B.; Van Loon, L.J.C. The Decline in Skeletal Muscle Mass with Aging Is Mainly Attributed to a Reduction in Type II Muscle Fiber Size. Exp Gerontol 2013, 48, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruparelia, A.A.; Salavaty, A.; Barlow, C.K.; Lu, Y.; Sonntag, C.; Hersey, L.; Eramo, M.J.; Krug, J.; Reuter, H.; Schittenhelm, R.B.; et al. The African Killifish: A Short-Lived Vertebrate Model to Study the Biology of Sarcopenia and Longevity. Aging Cell 2024, 23, e13862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges-Savola, C.A.; Fernandez, H.L. A Role for Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide in the Regulation of Rat Skeletal Muscle G 4 Acetylcholinesterase. Neurosci Lett 1995, 190, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, H.L.; Chen, M.; Nadelhaft, I.; Durr, J.A. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptides: Their Binding Sites and Receptor Accessory Proteins in Adult Mammalian Skeletal Muscles. Neuroscience 2003, 119, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Fu, W.-m.; Greengard, P.; Poo, M.-m. Calcitonin gene-related peptide potentiates synaptic responses at developing neuromuscular junction. Letters to Nature 1993, 363, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arden, W.A.; Fiscus, R.R.; Beihn, L.D.; Derbin, M.; Oremus, R.; Gross, D.R. Skeletal Muscle Microcirculatory Response to Rat α-Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide. Neuropeptides 1994, 27, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Fujimori, A.; Goto, K. Local Neurogenic Regulation of Rat Hindlimb Circulation: Role of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide in Vasodilatation after Skeletal Muscle Contraction. Br J Pharmacol 1997, 122, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Yamanaka, A.; Fujimori, A.; Goto, K. Local Neurogenic Regulation of Rat Hindlimb Circulation: CO 2-Induced Release of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide from Sensory Nerves. Br J Pharmacol 1997, 122, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Dickerson, I.M.; Russo, A.F. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptor Activation by Receptor Activity-Modifying Protein-1 Gene Transfer to Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloise, F.F.; Cordeiro, A.; Ortiga-Carvalho, T.M. Role of Thyroid Hormone in Skeletal Muscle Physiology. J Endocrinol 2018, 236, R57–R68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Kerbl-Knapp, J.; Zhang, F.; Korbelius, M.; Kuentzel, K.B.; Vujić, N.; Akhmetshina, A.; Hörl, G.; Paar, M.; Steyrer, E.; et al. Metabolomic Profiles of Mouse Tissues Reveal an Interplay between Aging and Energy Metabolism. Metabolites 2022, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.J.; Lin, I.H.; Lee, C.W.; Chen, Y.F. Aged Skeletal Muscle Retains the Ability to Remodel Extracellular Matrix for Degradation of Collagen Deposition after Muscle Injury. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonami, A.; Kato, R.; Taniguchi, K.; Yoshiga, D.; Taketomi, T.; Fukuyama, S.; Harada, M.; Sasaki, A.; Yoshimura, A. Spred-1 Negatively Regulates Interleukin-3-Mediated ERK/Mitogen-Activated Protein (MAP) Kinase Activation in Hematopoietic Cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2004, 279, 52543–52551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, K.; Okubo, K.; Yoda, M.; Otsu, K.; Ishii, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Itoh, Y.; Horiuchi, K. Targeted Ablation of P38α MAPK Suppresses Denervation-Induced Muscle Atrophy. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 9037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingrel, J.B.; Kuntzweiler, T. Na+,K+-ATPase. J Biol Chem 1994, 269, 19659–19662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, G.; Mercer, R.W. Isozymes of the Na-K-ATPase: Heterogeneity in Structure, Diversity in Function. Am J Physiol 1998, 275, (Renal Physiol 44) F633-F650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfield, V.A.; Loppin, B.; Thisse, B.; Thisse, C.; Postlethwait, J.H.; Mohideen, M.-A.P.K.; Johannes, S.; Rajarao, R.; Levenson, R. Na,K-ATPase a and b Subunit Genes Exhibit Unique Expression Patterns during Zebrafish Embryogenesis. Mech Develop 2002, 116, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, J.G.; Semple, J.W.; Bystriansky, J.S.; Schulte, P.M. Na+/K+-ATPase α-Isoform Switching in Gills of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) during Salinity Transfer. Journal of Experimental Biology 2003, 206, 4475–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doǧanli, C.; Kjaer-Sorensen, K.; Knoeckel, C.; Beck, H.C.; Nyengaard, J.R.; Honoré, B.; Nissen, P.; Ribera, A.; Oxvig, C.; Lykke-Hartmann, K. The A2Na+/K+-ATPase Is Critical for Skeletal and Heart Muscle Function in Zebrafish. J Cell Sci 2012, 125, 6166–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.K.; Madsen, S.S.; Kristiansen, R. Osmoregulation and Salinity Effects on the Expression and Activity of Na+,K+-ATPase in the Gills of European Sea Bass, Dicentrarchus Labrax (L.). Journal of Experimental Zoology 1998, 282, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, W.S.; Bryson, S.E. Transport Mechanisms of Seawater Teleost Chloride Cells: An Inclusive Model of a Multifunctional Cell. Comp Biochem Physiol 1998, 119, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.H.; Tsai, R.S.; Lee, T.H. Expression and Distribution of Na, K-ATPase in Gill and Kidney of the Spotted Green Pufferfish, Tetraodon Nigroviridis, in Response to Salinity Challenge. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 2004, 138, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laiz-Carrión, R.; Guerreiro, P.M.; Fuentes, J.; Canario, A.V.M.; Martín Del Río, M.P.; Mancera, J.M. Branchial Osmoregulatory Response to Salinity in the Gilthead Sea Bream, Sparus Auratus. J Exp Zool A Comp Exp Biol 2005, 303, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prochniewicz, E.; Thompson, L.V.; Thomas, D.D. Age-Related Decline in Actomyosin Structure and Function. Exp Gerontol 2007, 42, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jylhävä, J.; Pedersen, N.L.; Hägg, S. Biological Age Predictors. EBioMedicine 2017, 21, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holly, A.C.; Melzer, D.; Pilling, L.C.; Henley, W.; Hernandez, D.G.; Singleton, A.B.; Bandinelli, S.; Guralnik, J.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Harries, L.W. Towards a Gene Expression Biomarker Set for Human Biological Age. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bafei, S.E.C.; Shen, C. Biomarkers Selection and Mathematical Modeling in Biological Age Estimation. npj Aging 2023, 9, 13, doi.org/10.1038/s41514–023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, R.; Edwards, R. Quality Control and Preprocessing of Metagenomic Datasets. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Naya-Català, F.; Soriano, B.; Piazzon, M.C.; Hafez, A.; Gabaldón, T.; Llorens, C.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Calduch-Giner, J.A. Genome Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis Reveal Recent Species-Specific Gene Duplications in the Plastic Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus Aurata). Front Mar Sci 2019, 6, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential Gene and Transcript Expression Analysis of RNA-Seq Experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 2012, 7, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, L.; Trapnell, C.; Kelley, D. CummeRbund: Analysis, Exploration, Manipulation, and Visualization of Cufflinks High-Throughput Sequencing Data R Package. Version 2. 2013.
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and Memory-Efficient Alignment of Short DNA Sequences to the Human Genome. Genome Biol 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet 2000, .16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lienhard, M.; Grimm, C.; Morkel, M.; Herwig, R.; Chavez, L. MEDIPS: Genome-Wide Differential Coverage Analysis of Sequencing Data Derived from DNA Enrichment Experiments. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thévenot, E.A.; Roux, A.; Xu, Y.; Ezan, E.; Junot, C. Analysis of the Human Adult Urinary Metabolome Variations with Age, Body Mass Index, and Gender by Implementing a Comprehensive Workflow for Univariate and OPLS Statistical Analyses. J Proteome Res 2015, 14, 3322–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Van Treuren, W.; Lozupone, C.; Faust, K.; Friedman, J.; Deng, Y.; Xia, L.C.; Xu, Z.Z.; Ursell, L.; Alm, E.J.; et al. Correlation Detection Strategies in Microbial Data Sets Vary Widely in Sensitivity and Precision. ISME Journal 2016, 10, 1669–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A Graphical Gene-Set Enrichment Tool for Animals and Plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopfenstein, D.V.; Zhang, L.; Pedersen, B.S.; Ramírez, F.; Vesztrocy, A.W.; Naldi, A.; Mungall, C.J.; Yunes, J.M.; Botvinnik, O.; Weigel, M.; et al. GOATOOLS: A Python Library for Gene Ontology Analyses. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 10872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Xie, Y.; Ma, J.; Luo, X.; Nie, P.; Zuo, Z.; Lahrmann, U.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. IBS: An Illustrator for the Presentation and Visualization of Biological Sequences. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3359–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Functional process | n | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| System development | 17 | abi3bp, arhgap24, bmp1, calcrl, col5a1, kcp, mical2, myo18b, nrp2, spred2, thrb, wfikkn2, parp3, psmd2, ramp1, sirt1, smad1 |
| Anatomical structure development | 12 | arhgap24, calcrl, col5a1, kidins220, mical2, myo18b, nrp2, thrb, phf6, ramp1, sirt1, smad1 |
| Anatomical structure morphogenesis | 12 | arhgap24, bmp1, calcrl, col5a1, mical2, myo18b, nrp2, thrb, psmd2, ramp1, sirt1, smad1 |
| Reg. multicel. organismal process | 11 | abi3bp, atp1a2, bmp1, calcrl, sema6d, spred2, zbtb20, parp3, scn3b, sirt1, smad1 |
| Cel. component organization | 10 | abi3bp, bmp1, col5a1, col6a3, colgalt1, kirrel1, mical2, nrp2, olfml2a, myoz2 |
| Response to endogenous stimulus | 10 | atp1a2, kcp, kidins220, nrp2, spred2, thrb, wfikkn2, ramp1, sirt1, smad1 |
| Animal organ development | 9 | abi3bp, bmp1, calcrl, col5a1, mical2, nrp2, spred2, thrb, smad1 |
| Reg. cel. process | 9 | abi3bp, calcrl, col5a1, colgalt, ksr1, nrp2, ramp1, sirt1, smad1 |
| Anatomical structure formation | 8 | arhgap24, calcrl, col5a1, nrp2, myoz2, ramp1, sirt1, smad1 |
| Reg. developmental process | 8 | abi3bp, bmp1, col5a1, sema6d, spred2, psmd2, sirt1, smad1 |
| Reg. localization | 4 | atp1a2, fgf14, hecw2, scn3b |
| Tissue development | 4 | bmp1, col5a1, sirt1, smad1 |
| Transport | 4 | atp1a2, fgf14, hecw2, scn3b |
| Response to chemical | 3 | calcrl, zbtb20, sirt1 |
| N compound met. process | 2 | psmd2, srm |
| Ossification | 2 | bmp1, smad1 |
| Rhythmic process | 2 | tef, sirt1 |
| Cell differentiation | 1 | col5a1 |
| Genes | n | Functional processes |
|---|---|---|
| sirt1 | 11 | Anatomical structure development, Anatomical structure formation, Anatomical structure morphogenesis, Reg. cel. process, Reg. developmental process, Reg. multicel. organismal process, Response to chemical, Response to endogenous stimulus, Rhythmic process, System development, Tissue development |
| smad1 | 11 | Anatomical structure development, Anatomical structure formation, Anatomical structure morphogenesis, Animal organ development, Ossification, Reg. cel. process, Reg. developmental process, Reg. multicel. organismal process, Response to endogenous stimulus, System development, Tissue development |
| col5a1 | 10 | Anatomical structure development, Anatomical structure formation, Anatomical structure morphogenesis, Animal organ development, Cell differentiation, Cel. component organization, Reg. cel. process, Reg. developmental process, System development, Tissue development |
| calcrl | 8 | Anatomical structure development, Anatomical structure formation, Anatomical structure morphogenesis, Animal organ development, Reg. cel. process, Reg. multicel. organismal process, Response to chemical, System development |
| nrp2 | 8 | Anatomical structure development, Anatomical structure formation, Anatomical structure morphogenesis, Animal organ development, Cel. component organization, Reg. cel. process, Response to endogenous stimulus, System development |
| bmp1 | 8 | Anatomical structure morphogenesis, Animal organ development, Cel. Component organization, Ossification, Reg. developmental process, Reg. multicel. Organismal process, System development, Tissue development |
| ramp1 | 6 | Anatomical structure development, Anatomical structure formation, Anatomical structure morphogenesis, Reg. cel. process, Response to endogenous stimulus, System development |
| abi3bp | 6 | Animal organ development, Cel. component organization, Reg. cel. process, Reg. developmental process, Reg. multicel. organismal process, System development |
| mical2 | 5 | Anatomical structure development, Anatomical structure morphogenesis, Animal organ development, Cel. component organization, System development |
| Thrb | 5 | Anatomical structure development, Anatomical structure morphogenesis, Animal organ development, Response to endogenous stimulus, System development |
| spred2 | 5 | Animal organ development, Reg. developmental process, Reg. multicel. organismal process, Response to endogenous stimulus, System development |
| arhgap24 | 4 | Anatomical structure development, Anatomical structure formation, Anatomical structure morphogenesis, System development |
| psmd2 | 4 | Anatomical structure morphogenesis, N compound met. process, Reg. developmental process, System development |
| atp1a2 | 4 | Reg. localization, Reg. multicel. organismal process, Response to endogenous stimulus, Transport |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





