Of all the building materials used worldwide, concrete is the most widely employed because of its distinct benefits over other materials [
1]. An estimated 6 billion tonnes of ordinary concrete are manufactured annually worldwide [
2]. Unquestionably, cement plays a crucial role as the only binder in concrete, forming a solid substance that can support loads. It is vital to note that ordinary Portland cement has been a crucial component of concrete for over 200 years in the building industry [
3]. According to reports, the production of one tonne of Portland cement results in around one tonne of greenhouse gas emissions, and the cement manufacturing process accounts for 2% to 8% of the world's power usage [
4]. Cement is an essential part of a concrete mix, and its manufacture accounts for between 5% to 8% of the world's carbon dioxide emissions [
5]. Pozzolana from industrial and agricultural sources is seen to be the most practical option for cement binder sustainable development. Moreover, the most commonly used in agriculture are rice husk ash, coconut shell, and fuel ash from palm oil. Wood, plastic, and glass are a few of the materials that are frequently utilized in agriculture and industry. Researchers have long acknowledged pozzolanas for their abundant availability and supply of reactive silica. Due to the fact that waste materials typically resist natural deterioration, the environmental issue associated with the disposal problem is thought to be the primary driver that has spurred various researchers to investigate the potential use of all waste materials [
6]. The goal was waste reduction through the utilization of agricultural and industrial wastes generated during the manufacturing operations. Researchers and scientists are therefore working to create substitute binders. These environmentally friendly binders help to achieve waste management. Dumping or recycling garbage are the conventional methods for handling such wastes. Waste is often dumped by incineration or the use of landfills. These are expensive methods that harm the environment and human health [
7]. Due to its poor nutritional value, rice husk is a residue that should not be fed to animals. Because of its siliceous makeup, which is resistant to natural degradation, accumulation issues arise. In addition to being a very useful technique for reducing the volume of rice husk, burning the ashes is another way that rice-producing regions in Brazil generate electricity. Rice husk creates a significant amount of ashes when it is burned (RHA). Each tonne of rice typically yields 200 kilograms of rice husks, which when fully burned, create 40 kg of RHA. When burned, no other agricultural leftover produces as much ash as this one. Nearly 320,000 t/year of RHA might be generated in the area, according to a hard estimate, hence suitable alternative disposals need to be prepared to prevent negative environmental effects [
8]. According to World Rice Production" 2021/2022, about 36.4 million metric tons, third in the world. Again 513.68 million tons of rice are produced in worldwide [
9].
Table 1.
World Population by Country 2024 [
10].
| Country |
2021 Production |
2020 Production |
2019 Production |
| China |
212,843 |
211,860 |
209,614 |
| India |
195,425 |
186,500 |
174,717 |
| Bangladesh |
56,945 |
54,906 |
54,586 |
| Indonesia |
54,415 |
54,649 |
54,604 |
| Vietnam |
43,853 |
42,765 |
43,495 |
| Thailand |
33,582 |
30,231 |
28,618 |
| Myanmar |
24,910 |
25,983 |
26,270 |
| Philippines |
19,960 |
19,295 |
18,815 |
| Pakistan |
13,984 |
12,630 |
11,120 |
| Brazil |
11,661 |
11,091 |
10,369 |
| Cambodia |
11,410 |
11,248 |
10,886 |
| Japan |
10,525 |
10,469 |
10,527 |
About 20% of rice's weight is made up of rice husk. Furthermore, every year, about 150 million tonnes of rice husk are produced [
11]. There are not many nutrients in rice bran. Therefore, its primary uses are as fuel and for filling in land for livestock. It accumulates in large quantities and takes a long time to break down because solid waste is becoming a major environmental concern [
12]. Since rice husk ash includes silicious elements, it can be a significant source of silica. Thus, it can be utilized in place of some cement. It can improve the mechanical and durability properties of concrete mixes by up to 30% when used in place of cement [
12]. RHA is a highly reactive pozzolanic substance that is produced by burning nice at temperatures below 700°C in a regulated marine environment. Its content of amorphous silica is high [
13] Goat or sheep bones are materials that are considered waste for the industry and may be used in part place of fine or coarse aggregates in the construction sector. Nowadays, a variety of animals, such as goats, sheep, and cows, are utilised to manufacture meat-based delicacies. Large amounts of these waste bones are just dumped in trash cans and disposal sites, which pollutes the soil and water and degrades the ecosystem. Thus, it's crucial to investigate whether using animal bones to make concrete could be advantageous, but more significantly, it's important to think about how it could be used to provide high-quality buildings. Consequently, an attempt has been made to use these crushed bones in order to research the impact of animal bones on concrete. Numerous scientists have created concrete specimens from animal bones [
14]. According to department of livestock services of Bangladesh, total cattle production in Bangladesh is about 24.856 million and total ruminant production in Bangladesh is about 57.143 million [
15].
Table 2.
Livestock population of Bangladesh (in lakh number) [
15]
| Name of Species |
2013-14 |
2014-15 |
2015-16 |
2016-17 |
2017-18 |
2018-19 |
2019-20 |
2020-21 |
2021-22 |
2022-23 |
| Cattle |
234.88 |
236.36 |
237.85 |
239.35 |
240.86 |
242.38 |
243.91 |
245.45 |
247.00 |
248.56 |
| Buffalo |
14.57 |
14.64 |
14.71 |
14.78 |
14.79 |
14.86 |
14.93 |
15.00 |
15.08 |
15.16 |
| Sheep |
32.06 |
32.70 |
33.35 |
34.01 |
34.68 |
35.37 |
36.07 |
36.79 |
37.52 |
38.27 |
| Goat |
254.39 |
256.02 |
257.66 |
259.31 |
261.00 |
262.67 |
264.35 |
266.04 |
267.74 |
269.45 |
| Total Ruminant |
535.90 |
539.72 |
543.57 |
547.45 |
551.33 |
555.28 |
559.26 |
563.28 |
567.34 |
571.43 |
In the year 2022, Bangladesh produced 209,016 thousand tonnes of meat from cattle and buffalo. From 1973 to 2022, Bangladesh's production of beef and buffalo meat increased at an average yearly rate of 1.04%, from 137,047 thousand tonnes to 209,016 thousand tonnes [
16]. One of the waste materials taken out of butchered animals (cows and oxen) is bone, which has a high calcium concentration. Conversely, calcium oxide makes up 60% to 67% of portland cement. This suggests that there is a chance to replace some of the cement with bone waste. The disposal location releases toxic gases when it burns, contributing to environmental contamination even with its high calcium oxide level. One source of expense for trash transportation and management in major municipalities is waste disposal. The main detrimental effects on the environment and human well-being are disease linked to respiratory causes due to foul odors, loss of beauty in city landscapes, and natural landscape changes brought on by trash disposal. A sustainable ecosystem and inexpensive cementing material are two benefits of properly using this bone debris [
17]. If deemed appropriate, using cow bones in place of fine aggregate will aid in environmental cleanup and the transformation of waste into wealth. When working with concrete, one might assume that the ratio of cement to water is inversely proportional to the concrete's strength, provided that full compaction is maintained at a specific age and standard temperature [
18]. A study on rice husk ash (RHA) as a Portland cement substitute found that
10-15% RHA optimizes mortar strength. Lower temperatures yield amorphous RHA, enhancing strength through calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel formation. Higher RHA levels above 10% reduce strength due to limited calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)
2) and increased porosity. White RHA, burnt below 800°C, showed the best performance, especially in seawater, due to more C-S-H gel but is constrained by Ca(OH)
2 availability for the reaction. The ideal RHA content for cement mortar is around
15% for balanced strength and binder properties [
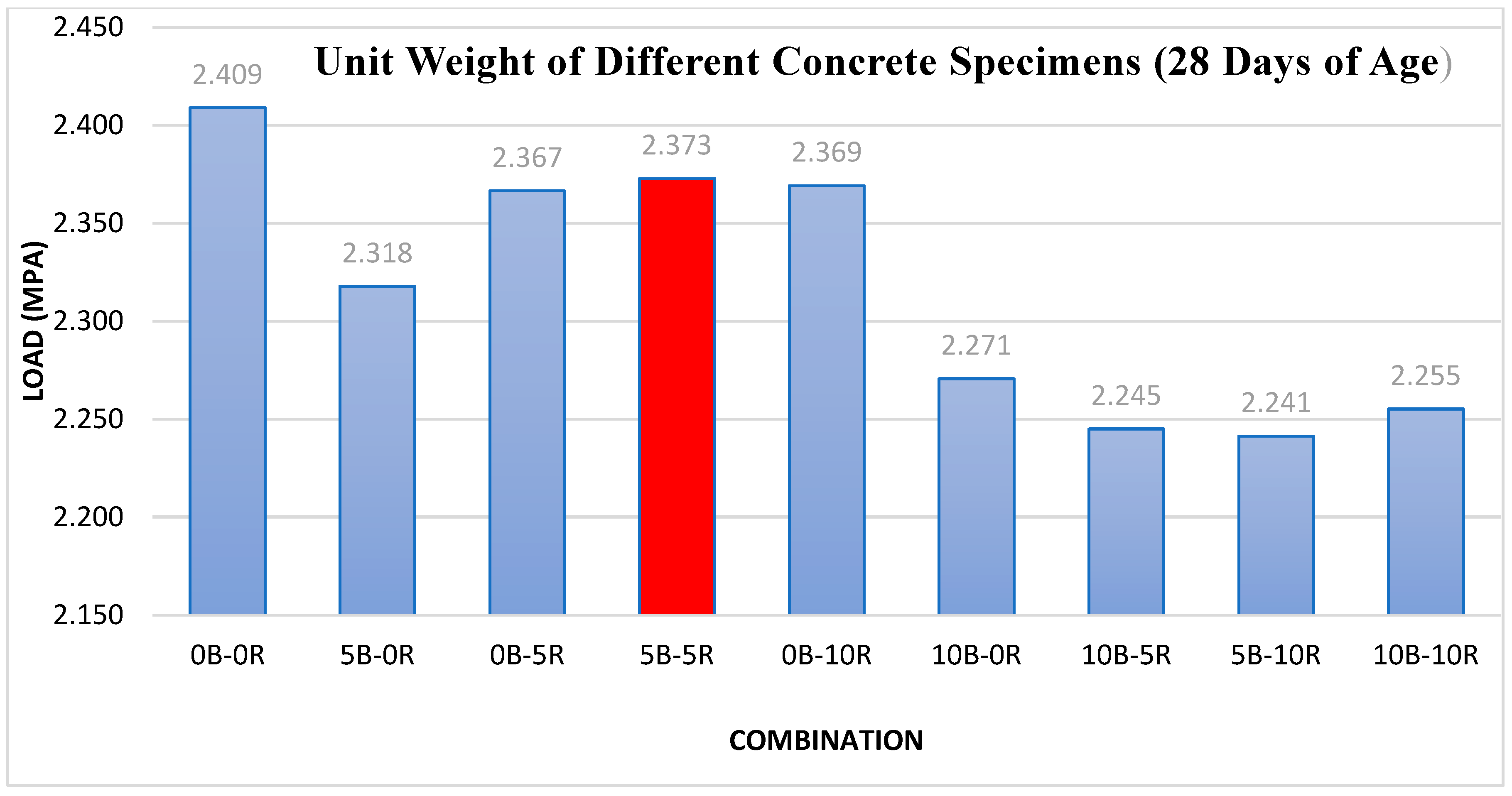
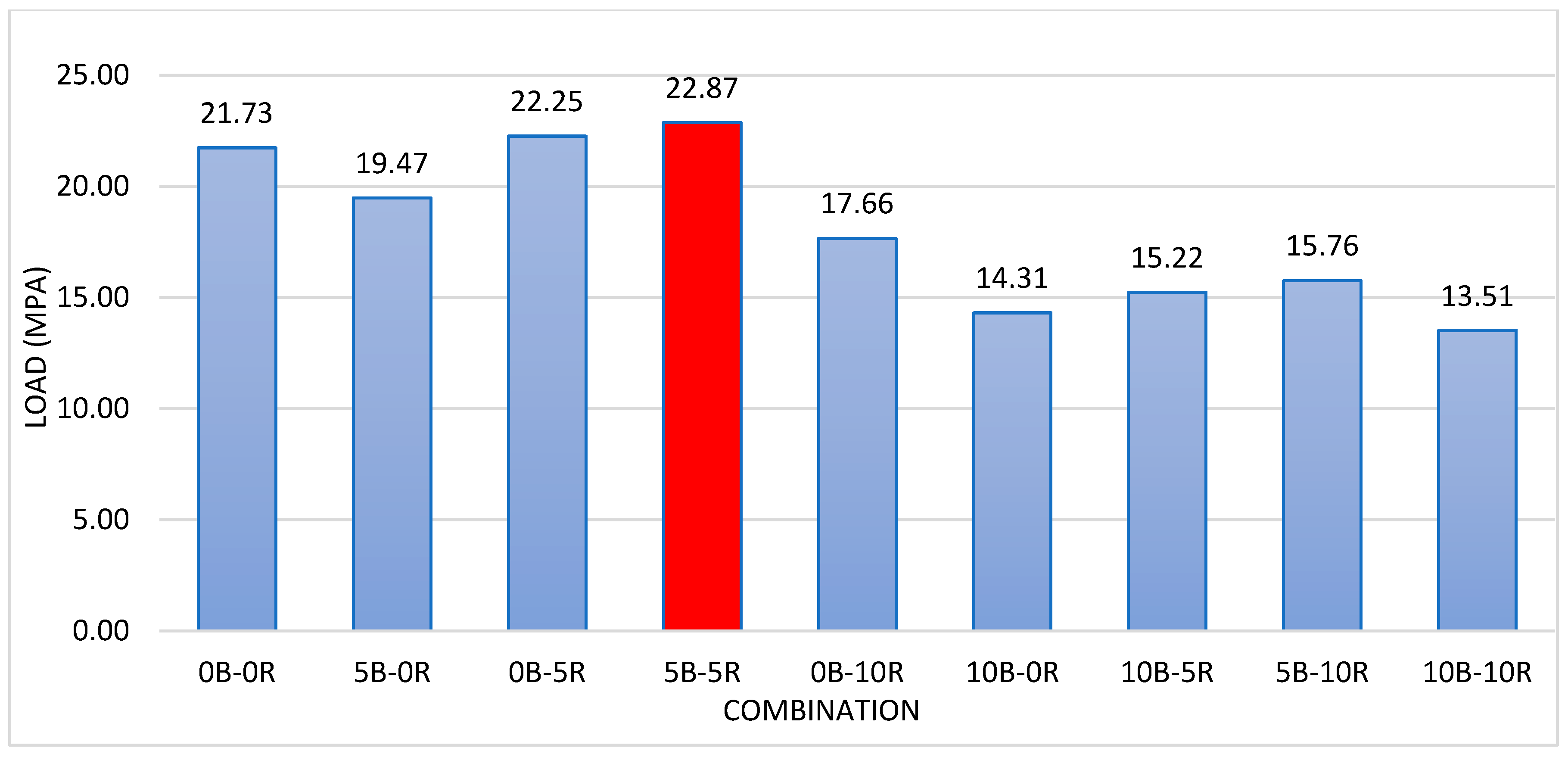
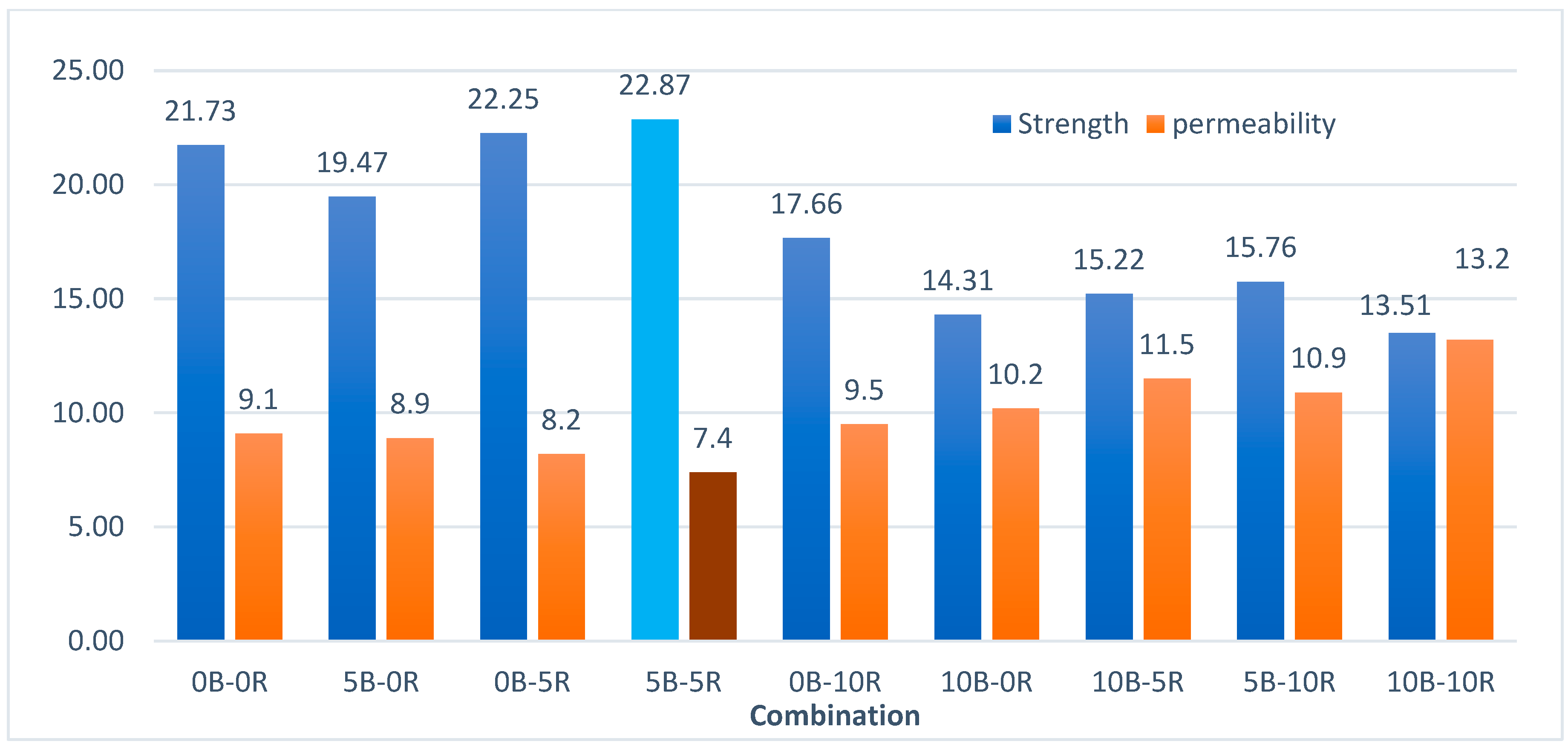
19]. The study used river sand and 20mm crushed rock as aggregates, borehole water, and Portland composite cement for testing. Animal bone ash, processed through drying and controlled burning, was mixed in proportions of 1:2:4 with a 0.6 water-to-cement ratio. Cast specimens measured 150mm cubed. Over 28 days, compressive strength peaked at
23.43 N/mm² with
5% bone ash, but dropped to
16.49 N/mm² at
20%. The findings suggest that up to
5% animal bone ash is viable for lightweight structures, as higher percentages weaken the material [
20]. The study indicates that replacing cement with animal bone powder (ABP) in concrete reduces compressive, split tensile, and flexural strengths as ABP content increases. For control samples (0% ABP), compressive strength increased with age, peaking at 33.63 MPa at 28 days. However, with 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20% ABP, compressive strength significantly declined. Similarly, split tensile and flexural strengths also decreased with higher ABP percentages. The study found that 5% ABP replacement yielded comparable strength to the control, and 10% ABP replacement achieved required strength standards, making up to 10% ABP viable without compromising concrete strength [
21]. The study shows that replacing cement with animal bone powder (ABP) reduces concrete strength and workability as ABP dosage increases. An optimal 10% ABP replacement maintains acceptable strength and workability, making it the best balance for concrete mixes while ensuring desired performance characteristics [
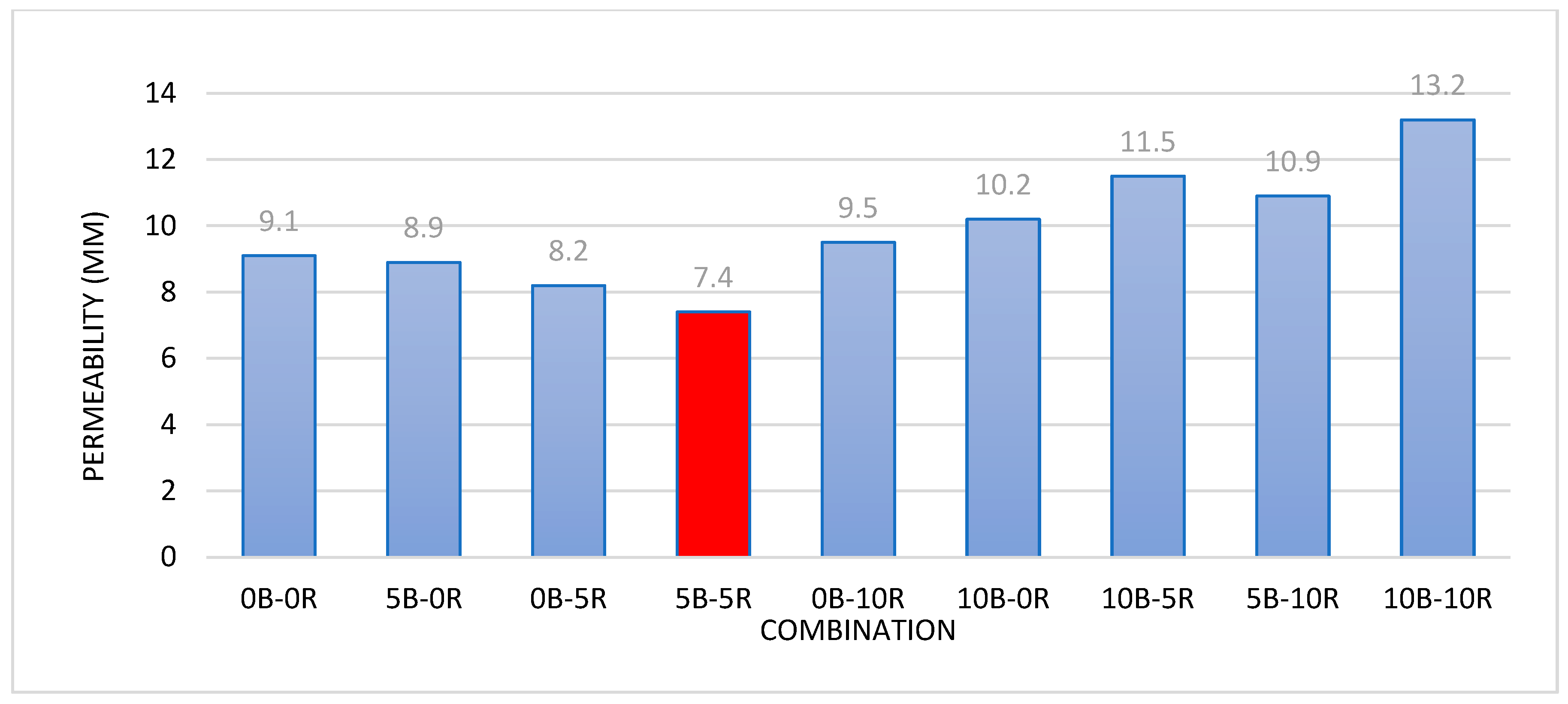
22]. In this study, four concrete mix ratios were created, with one control mix (0% RHA) and three mixes containing 10%, 15%, and 20% rice husk ash (RHA) as partial cement substitutes. The water volume (225.5 kg/m³), coarse aggregates (590 kg/m³), fine aggregates (910 kg/m³), superplasticizer concentration (1%), and water-to-binder ratio (0.41) remained constant. Each mix produced nine cubes (150x150x150 mm) and nine cylinders (300x150 mm) for compressive and tensile strength tests at 7, 28, and 56 days. Rapid chloride permeability tests at 28 days showed reduced ion penetration with higher RHA content, except at 20% RHA. The 10% RHA mix demonstrated exceptional chloride ion resistance [
23].