Submitted:
29 May 2024
Posted:
30 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Quality Score Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
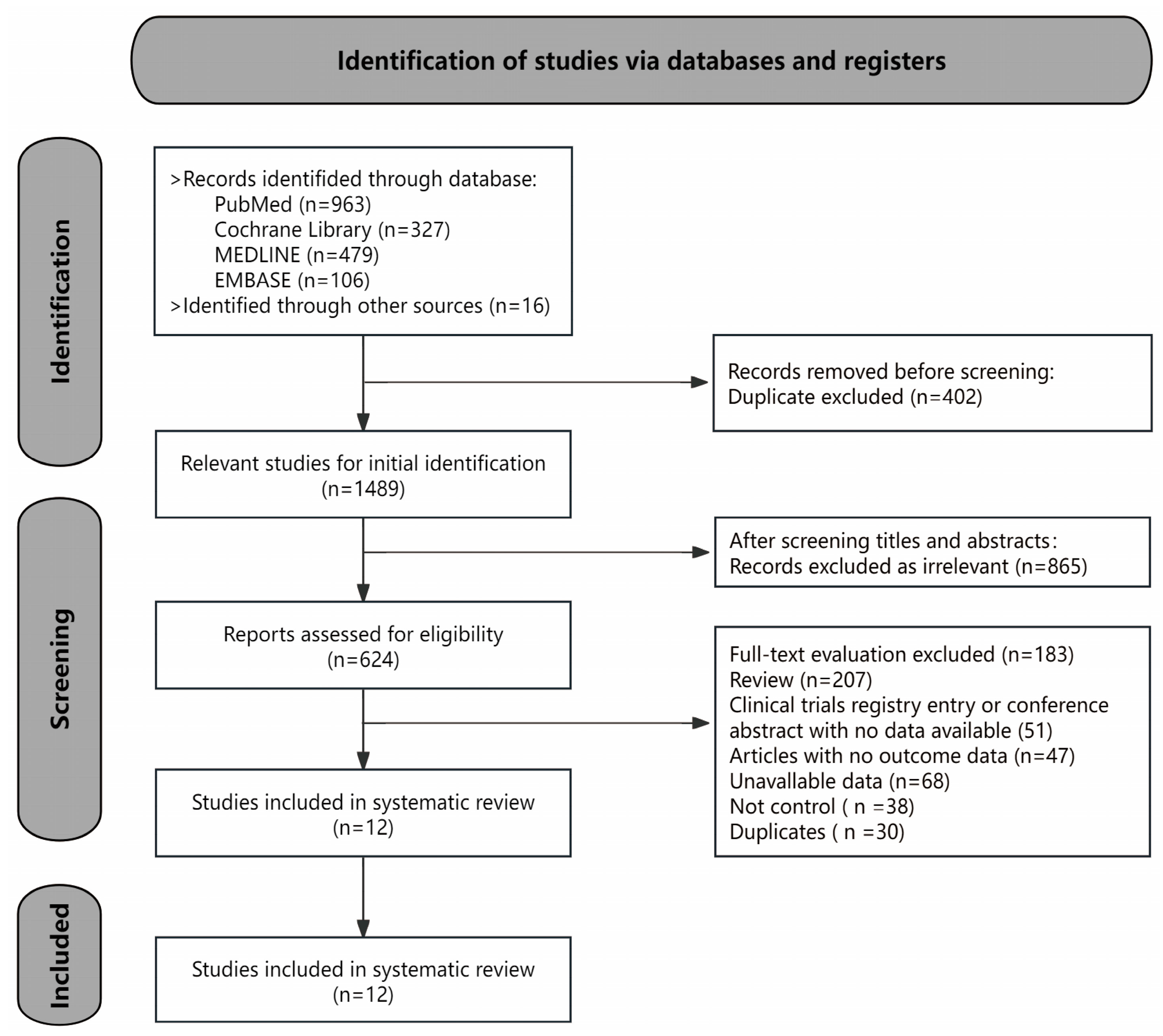
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Methodological Quality
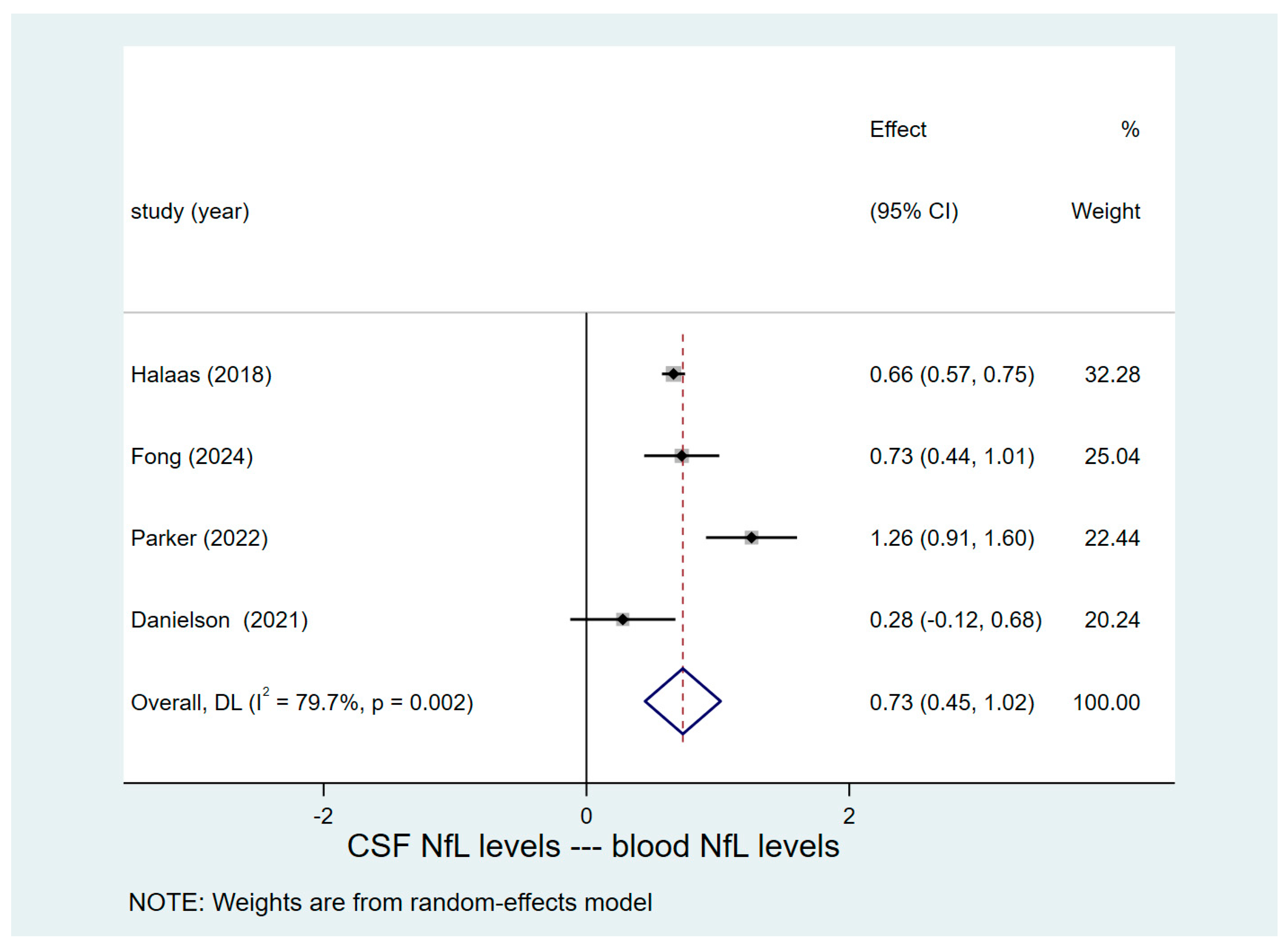
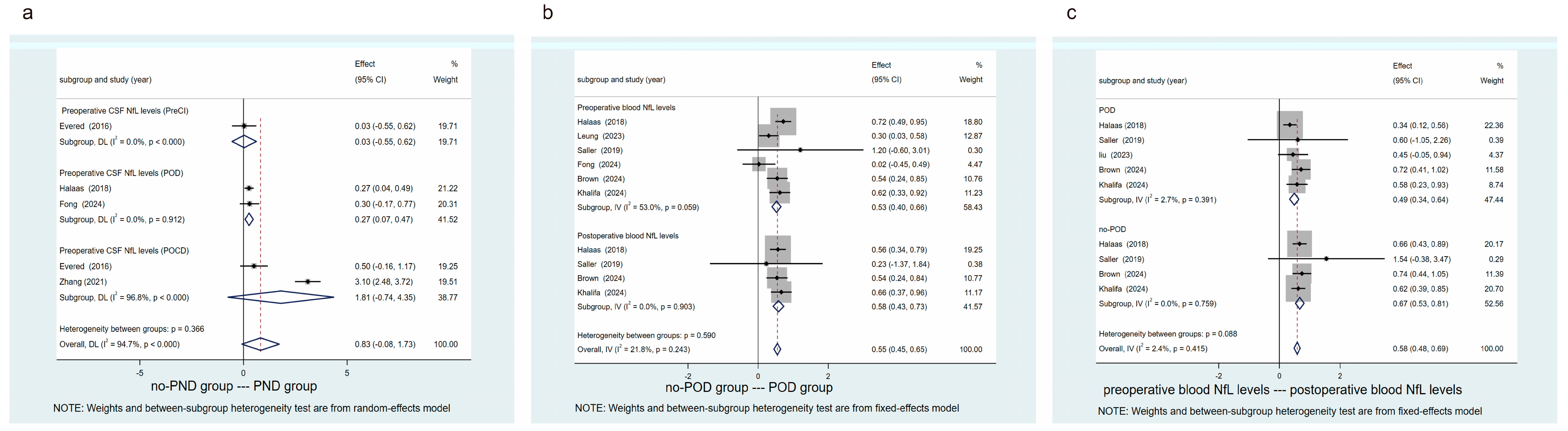
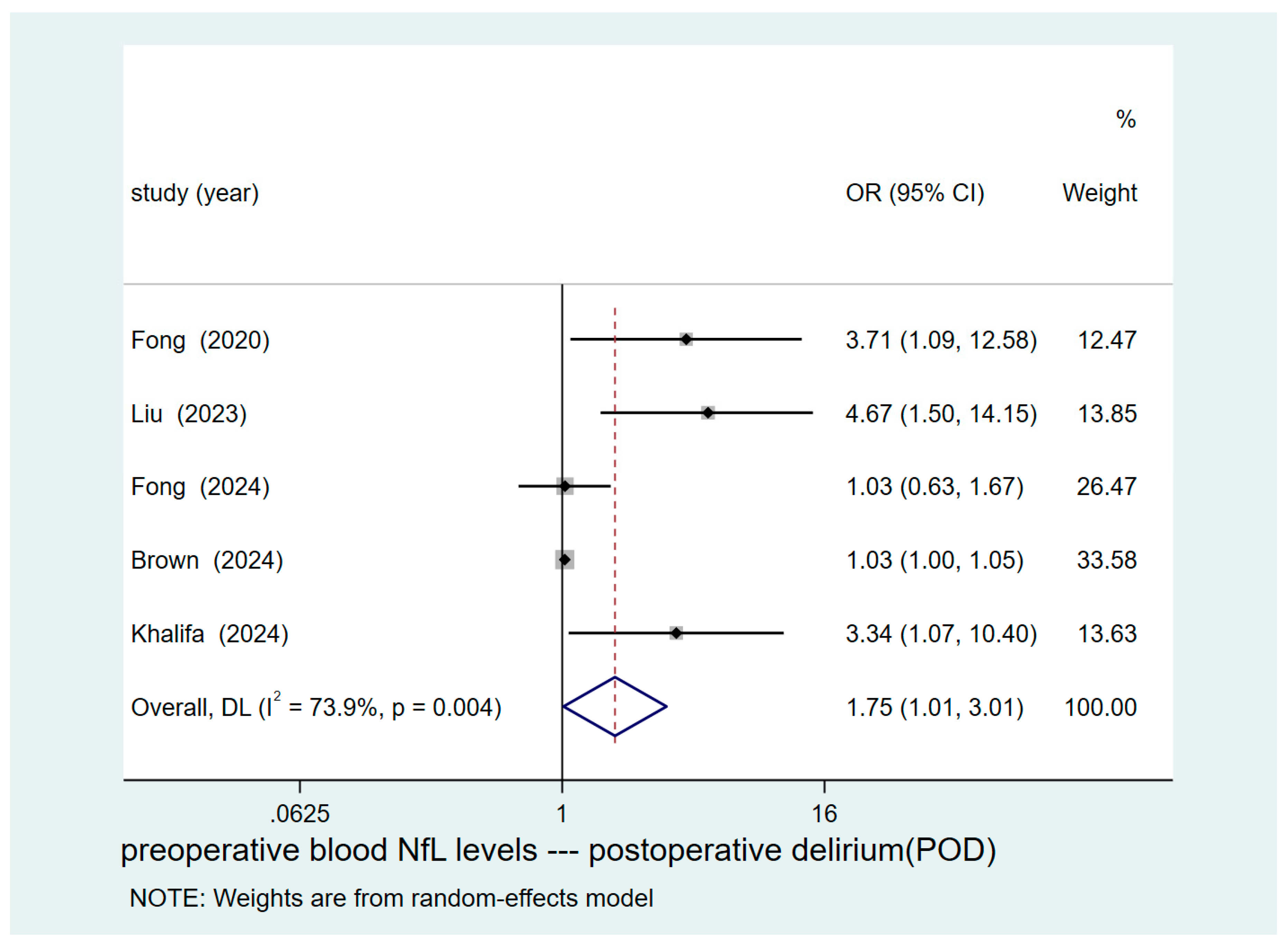
3.4. Results of Pooled Analysis
3.5. Reporting Biases
3.6. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moller, J.T.; Cluitmans, P.; Rasmussen, L.S.; Houx, P.; Rasmussen, H.; Canet, J.; Rabbitt, P.; Jolles, J.; Larsen, K.; Hanning, C.D. et al. Long-term postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly ISPOCD1 study. ISPOCD investigators. International Study of Post-Operative Cognitive Dysfunction. Lancet 1998, 351, 857-861. [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, J.; Christensen, K.B.; Lund, T.; Lohse, N.; Rasmussen, L.S. Long-term consequences of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 548-555. [CrossRef]
- Needham, M.J.; Webb, C.E.; Bryden, D.C. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction and dementia: what we need to know and do. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, i115-i125. [CrossRef]
- Evered, L.; Silbert, B.; Knopman, D.S.; Scott, D.A.; DeKosky, S.T.; Rasmussen, L.S.; Oh, E.S.; Crosby, G.; Berger, M.; Eckenhoff, R.G. Recommendations for the nomenclature of cognitive change associated with anaesthesia and surgery-2018. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 121, 1005-1012. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, K.; Zhu, B.; Zhou, B.; Ahmad, H.A.; Liu, L.; Wu, X. Neuropsychological Tests in Post-operative Cognitive Dysfunction: Methods and Applications. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 684307. [CrossRef]
- Borchers, F.; Spies, C.D.; Feinkohl, I.; Brockhaus, W.R.; Kraft, A.; Kozma, P.; Fislage, M.; Kühn, S.; Ionescu, C.; Speidel, S. et al. Methodology of measuring postoperative cognitive dysfunction: a systematic review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 126, 1119-1127. [CrossRef]
- Wiberg, S.; Holmgaard, F.; Zetterberg, H.; Nilsson, J.C.; Kjaergaard, J.; Wanscher, M.; Langkilde, A.R.; Hassager, C.; Rasmussen, L.S.; Blennow, K. et al. Biomarkers of Cerebral Injury for Prediction of Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2022, 36, 125-132. [CrossRef]
- Evered, L.; Atkins, K.; Silbert, B.; Scott, D.A. Acute peri-operative neurocognitive disorders: a narrative review. Anaesthesia 2022, 77 Suppl 1, 34-42. [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, X. The potential mechanism of postoperative cognitive dysfunction in older people. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 130, 110791. [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.; Browndyke, J.N.; Cooter, W.M.; Nobuhara, C.; Reese, M.; Acker, L.; Bullock, W.M.; Colin, B.J.; Devinney, M.J.; Moretti, E.W. et al. Postoperative changes in cognition and cerebrospinal fluid neurodegenerative disease biomarkers. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2022, 9, 155-170. [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.R.; Kobborg, T.; Shahim, P.; Blennow, K.; Rasmussen, L.S.; Zetterberg, H. Serum-neuroproteins, near-infrared spectroscopy, and cognitive outcome after beach-chair shoulder surgery: Observational cohort study analyses. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2021, 65, 26-33. [CrossRef]
- Osborn, K.E.; Khan, O.A.; Kresge, H.A.; Bown, C.W.; Liu, D.; Moore, E.E.; Gifford, K.A.; Acosta, L.; Bell, S.P.; Hohman, T.J. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma neurofilament light relate to abnormal cognition. Alzheimers Dement.-Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2019, 11, 700-709. [CrossRef]
- Lambertsen, K.L.; Soares, C.B.; Gaist, D.; Nielsen, H.H. Neurofilaments: The C-Reactive Protein of Neurology. Brain Sci. 2020, 10. [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, L.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P.; Di Filippo, M.; Parnetti, L.; Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in neurological disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2019, 90, 870-881. [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M.M.; Syrjanen, J.A.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Vemuri, P.; Skoog, I.; Machulda, M.M.; Kremers, W.K.; Knopman, D.S.; Jack, C.J. et al. Plasma and CSF neurofilament light: Relation to longitudinal neuroimaging and cognitive measures. Neurology 2019, 93, e252-e260. [CrossRef]
- Osborn, K.E.; Khan, O.A.; Kresge, H.A.; Bown, C.W.; Liu, D.; Moore, E.E.; Gifford, K.A.; Acosta, L.; Bell, S.P.; Hohman, T.J. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma neurofilament light relate to abnormal cognition. Alzheimers Dement.-Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2019, 11, 700-709. [CrossRef]
- Shahim, P.; Politis, A.; van der Merwe, A.; Moore, B.; Chou, Y.Y.; Pham, D.L.; Butman, J.A.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Gill, J.M.; Brody, D.L. et al. Neurofilament light as a biomarker in traumatic brain injury. Neurology 2020, 95, e610-e622. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Eisenmenger, L.; Lindroth, H.; Booth, J.; Mohanty, R.; Nair, V.; Parker, M.; Kunkel, D.; Rivera, C.; Casey, C. et al. Perioperative ischaemic brain injury and plasma neurofilament light: a secondary analysis of two prospective cohort studies. Br. J. Anaesth. 2023, 130, e361-e369. [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, L.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P.; Di Filippo, M.; Parnetti, L.; Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in neurological disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2019, 90, 870-881. [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, J.L.; Marcantonio, E.R. Review articles: postoperative delirium: acute change with long-term implications. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 112, 1202-1211. [CrossRef]
- Casey, C.P.; Lindroth, H.; Mohanty, R.; Farahbakhsh, Z.; Ballweg, T.; Twadell, S.; Miller, S.; Krause, B.; Prabhakaran, V.; Blennow, K. et al. Postoperative delirium is associated with increased plasma neurofilament light. Brain. 2020, 143, 47-54. [CrossRef]
- Saller, T.; Petzold, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Kuhle, J.; Chappell, D.; von Dossow, V.; Klawitter, F.; Schurholz, T.; Hagl, C.; Reuter, D.A. et al. A case series on the value of tau and neurofilament protein levels to predict and detect delirium in cardiac surgery patients. Biomed. Pap-Olomouc 2019, 163, 241-246. [CrossRef]
- Alifier, M.; Olsson, B.; Andreasson, U.; Cullen, N.C.; Czyżewska, J.; Jakubów, P.; Sieśkiewicz, A.; Stasiak-Barmuta, A.; Hirnle, T.; Kornhuber, J. et al. Cardiac Surgery is Associated with Biomarker Evidence of Neuronal Damage. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 74, 1211-1220. [CrossRef]
- Fong, T.G.; Vasunilashorn, S.M.; Kivisäkk, P.; Metzger, E.D.; Schmitt, E.M.; Marcantonio, E.R.; Jones, R.N.; Shanes, H.T.; Arnold, S.E.; Inouye, S.K. et al. Biomarkers of neurodegeneration and neural injury as potential predictors for delirium. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2024, 39, e6044. [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E. et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021, 372, n71. [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [CrossRef]
- Fagundes, M.A.; Silva, A.; Fernandes, G.A.; Curado, M.P. Dietary Polyphenol Intake and Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Pripp, A.H. [Pearson’s or Spearman’s correlation coefficients]. Tidsskr. Nor. Laegeforen. 2018, 138. [CrossRef]
- Halaas, N.B.; Blennow, K.; Idland, A.V.; Wyller, T.B.; Ræder, J.; Frihagen, F.; Staff, A.C.; Zetterberg, H.; Watne, L.O. Neurofilament Light in Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid of Hip Fracture Patients with Delirium. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2018, 46, 346-357. [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.M.; Rojas, J.C.; Tang, C.; Chan, B.; Lario-Lago, A.; Boxer, A.L.; Do, Q.; Kramer, J.H.; Du Z; Du P et al. Presence of Preoperative Neurodegeneration Biofluid Markers in Patients with Postoperative Delirium. Anesthesiology 2023, 139, 432-443. [CrossRef]
- Fong, T.G.; Vasunilashorn, S.M.; Ngo, L.; Libermann, T.A.; Dillon, S.T.; Schmitt, E.M.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Arnold, S.E.; Jones, R.N.; Marcantonio, E.R. et al. Association of Plasma Neurofilament Light with Postoperative Delirium. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 984-994. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Ye, C.; Ma, D.; Wang, E. Emergence delirium and postoperative delirium associated with high plasma NfL and GFAP: an observational study. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1107369. [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.H.; Kim, A.S.; Yanek, L.; Lewis, A.; Mandal, K.; Le L; Tian, J.; Neufeld, K.J.; Hogue, C.; Moghekar, A. Association of perioperative plasma concentration of neurofilament light with delirium after cardiac surgery: a nested observational study. Br. J. Anaesth. 2024, 132, 312-319. [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, C.; Robert, A.; Cappe, M.; Lemaire, G.; Tircoveanu, R.; Dehon, V.; Ivanoiu, A.; Piérard, S.; de Kerchove, L.; Jacobs, S.A. et al. Serum Neurofilament Light and Postoperative Delirium in Cardiac Surgery: A Preplanned Secondary Analysis of a Prospective Observational Study. Anesthesiology 2024, 140, 950-962. [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.; White, M.; Casey, C.; Kunkel, D.; Bo, A.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Pearce, R.A.; Lennertz, R.; Sanders, R.D. Cohort Analysis of the Association of Delirium Severity With Cerebrospinal Fluid Amyloid-Tau-Neurodegeneration Pathologies. J. Gerontol. Ser. A.-Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 494-501. [CrossRef]
- Evered, L.; Silbert, B.; Scott, D.A.; Ames, D.; Maruff, P.; Blennow, K. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarker for Alzheimer Disease Predicts Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction. Anesthesiology 2016, 124, 353-361. [CrossRef]
- Danielson, M.; Wiklund, A.; Granath, F.; Blennow, K.; Mkrtchian, S.; Nellgård, B.; Oras, J.; Fagerlund, M.J.; Granström, A.; Schening, A. et al. Association between cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of neuronal injury or amyloidosis and cognitive decline after major surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 126, 467-476. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fu, Q. [Correlation of cerebrospinal fluid amyloid β-protein 42 and neurofilament light protein levels with postoperative neurocognitive dysfunction in elderly patients]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2021, 41, 574-578. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, A.; Rao, M.V.; Veeranna; Nixon, R.A. Neurofilaments and Neurofilament Proteins in Health and Disease. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9. [CrossRef]
- Luigetti, M.; Primiano, G.; Basile, V.; Vitali, F.; Pignalosa, S.; Romano, A.; Sabino, A.; Marino, M.; Di Santo, R.; Ciasca, G. et al. Serum Neurofilament and Free Light Chain Levels in Patients Undergoing Treatment for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.G.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Thompson, J.L.; Chandrasekhar, R.; Ware, L.B.; Ely, E.W.; Girard, T.D. Endothelial Activation and Blood-Brain Barrier Injury as Risk Factors for Delirium in Critically Ill Patients. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, e809-e817. [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Zhou, M. Neurofilament Light Chain as a Potential Biomarker in Plasma for Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 85. [CrossRef]
- Leuzy, A.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Palmqvist, S.; Janelidze, S.; Dage, J.L.; Hansson, O. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e14408. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Pedrini, S.; Ashton, N.J.; Tegg, M.; Goozee, K.; Singh, A.K.; Karikari, T.K.; Simrén, J.; Vanmechelen, E.; Armstrong, N.J. et al. Diagnostic and prognostic plasma biomarkers for preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers. Dement. 2022, 18, 1141-1154. [CrossRef]
- Krogseth, M.; Watne, L.O.; Juliebø, V.; Skovlund, E.; Engedal, K.; Frihagen, F.; Wyller, T.B. Delirium is a risk factor for further cognitive decline in cognitively impaired hip fracture patients. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2016, 64, 38-44. [CrossRef]
- Evered, L.; Silbert, B.; Scott, D.A.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K. Association of Changes in Plasma Neurofilament Light and Tau Levels With Anesthesia and Surgery: Results From the CAPACITY and ARCADIAN Studies. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 542-547. [CrossRef]
- Barro, C.; Chitnis, T.; Weiner, H.L. Blood neurofilament light: a critical review of its application to neurologic disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 2508-2523. [CrossRef]
- Andersson, E.; Janelidze, S.; Lampinen, B.; Nilsson, M.; Leuzy, A.; Stomrud, E.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Hansson, O. Blood and cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light differentially detect neurodegeneration in early Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 95, 143-153. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, S.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lei, Q.; Li, Z. NREM sleep loss increases neurofilament light chain levels in APP/PS1 and C57BL/6 J mice. Sleep Breath. 2023, 27, 1495-1504. [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Shanker, A.; Khera, T.; Subramaniam, B. Neurofilament light: a narrative review on biomarker utility. Fac Rev 2021, 10, 46. [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.L.; Cardoso, B.; Ramos, I.; Oliveira, B.; Dos, S.M.; de Miranda, A.S.; de Almeida, T.; Vieira, M.; Machado, F.S.; Ferreira, A.J. et al. Physical training improves exercise tolerance, cardiac function and promotes changes in neurotrophins levels in chagasic mice. Life Sci. 2019, 232, 116629. [CrossRef]
- Cata, J.P.; Abdelmalak, B.; Farag, E. Neurological biomarkers in the perioperative period. Br. J. Anaesth. 2011, 107, 844-858. [CrossRef]
- McKay, T.B.; Rhee, J.; Colon, K.; Adelsberger, K.; Turco, I.; Mueller, A.; Qu, J.; Akeju, O. Preliminary Study of Serum Biomarkers Associated With Delirium After Major Cardiac Surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2022, 36, 118-124. [CrossRef]
- Deiner, S.; Baxter, M.G.; Mincer, J.S.; Sano, M.; Hall, J.; Mohammed, I.; O’Bryant, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Eckenhoff, R. Human plasma biomarker responses to inhalational general anaesthesia without surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2020, 125, 282-290. [CrossRef]
- Vutskits, L.; Xie, Z. Lasting impact of general anaesthesia on the brain: mechanisms and relevance. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 705-717. [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.; Yan, J.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, B.; Li, S. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the aged: the collision of neuroinflammaging with perioperative neuroinflammation. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 27-37. [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, X. The potential mechanism of postoperative cognitive dysfunction in older people. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 130, 110791. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.Y.; Xiong, B.R.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, W.C.; Yang, H.; Gao, F.; Xiang, H.B.; Manyande, A.; Tian, X.B.; Tian, Y.K. PGE2-EP3 signaling exacerbates hippocampus-dependent cognitive impairment after laparotomy by reducing expression levels of hippocampal synaptic plasticity-related proteins in aged mice. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2018, 24, 917-929. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Sun, J.; Qian, Y. Cerebral mast cells contribute to postoperative cognitive dysfunction by promoting blood brain barrier disruption. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 298, 158-166. [CrossRef]
- Teipel, S.J.; Stahl, R.; Dietrich, O.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Perneczky, R.; Bokde, A.L.; Reiser, M.F.; Möller, H.J.; Hampel, H. Multivariate network analysis of fiber tract integrity in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 2007, 34, 985-995. [CrossRef]
- Becher, R.D.; Vander, W.B.; Leo-Summers, L.; Desai, M.M.; Gill, T.M. The Incidence and Cumulative Risk of Major Surgery in Older Persons in the United States. Ann. Surg. 2023, 277, 87-92. [CrossRef]
- Strøm, C.; Rasmussen, L.S.; Sieber, F.E. Should general anaesthesia be avoided in the elderly? Anaesthesia 2014, 69 Suppl 1, 35-44. [CrossRef]
| Study | Contry | Surgery | Anesthesia | Sample Size (Male/Female) |
Age Range | Study Design | Diagnostic Criteria or Method |
No. of PNDs/no-PNDs |
Biomarker Measured |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Halaas 2018 [29] |
China |
Hip fracture |
SA |
77/237 | 85 (79–79) | Case-control | CAM | POD/no-POD (162/152) |
CSF-NfL(Pre-Op) sNfL(Pre-Op/Post-Op1) |
| Leung 2023 [30] |
USA |
Noncardiac surgery |
GA |
73/131 | 72.91±5.82 | Case-control | CAM | POD/no-POD (102/102) |
pNfL(Pre-Op/Post-Op1) |
| Fong 2020 [31] |
USA |
Elective surgery |
GA |
52/56 | 77±5 | Prospective cohort | CAM | POD/no-POD (54/54) |
pNfL(Pre-Op/Post-Op2) |
| Saller 2019 [22] |
Germany |
Cardiac surgery |
GA |
6(Male) | 76±5 | Case-control | CAM-ICU | POD/no-POD (3/3) |
pNfL(Pre-Op) |
| Liu 2023 [32] |
China |
Elective surgery |
GA |
36/28 | POD (69.22±5.00) no-POD (70.31±3.82) |
Case-control | CAM | POD/no-POD (32/32) |
pNfL(Pre-Op/Post-Op1) |
| Fong 2024 [24] |
USA |
Elective surgery |
GA |
14/56 | 74.7±6.9 | Case-control | CAM | POD/no-POD (35/35) |
CSF-NfL(Pre-Op) pNfL(Pre-Op) |
| Brown 2024 [33] |
USA |
Cardiac surgery |
GA |
131/44 | 70.5(7.6) | Prospective cohort | CAM/CAM-ICU | POD/no-POD (78/97) |
pNfL(Pre-Op/Post-Op1) |
| Khalifa 2024 [34] |
Belgium |
Cardiac surgery |
GA |
180/40 | POD (74 [64, 79]) no-POD (67 [59, 74]) |
Prospective cohort | CAM/CAM-ICU | POD/no-POD (65/155) |
pNfL(Pre-Op/Post-Op1) |
| Parker 2022 [35] |
USA |
Thoracic vascular surgery |
GA |
18/13 | POD (68.5 [61.5-73]) no-POD (72 [67-77]) |
Prospective cohort | CAM-ICU | POD/no-POD (22/9) |
CSF-NfL(Pre-Op) sNfL(Pre-Op) |
| Evered 2016 [36] |
Australia |
Total hip replacement | Combined SA and GA |
19/40 | 70.4±7 | Prospective cohort | ISPOCD test battery | POCD/no-POCD (15/44) |
CSF-NfL(Pre-Op) |
| Danielson 2021 [37] |
Sweden |
Knee or hip replacement |
SA |
9/18 | POCD (71 [65-76]) no-POCD (68 [65-71]) |
Prospective cohort | ISPOCD test battery | POCD/no-POCD (6/21) |
CSF-NfL(Pre-Op) sNfL(Pre-Op) |
| Zhang 2021 [38] |
China |
Knee or hip replacement |
SA |
50/40 | POCD (68.2±4.3) no-POCD (68.9±4.0) |
Prospective cohort | ISPOCD test battery | POCD/no-POCD (38/52) |
CSF-NfL(Pre-Op) |
|
Study |
Study design |
Selection | Comparability | Exposure/Outcome | Scores | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | ||||||
| Halaas 2018 [29] | Case-control | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 0 | ☆ | 7 | |||
| Leung 2023 [30] | Case-control | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 9 | |||
| Fong 2020 [31] | Prospective cohort | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 0 | ☆ | 7 | |||
| Saller 2019 [22] | Case-control | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 0 | ☆ | 0 | 6 | |||
| Liu 2023 [32] | Case-control | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 0 | ☆ | 7 | |||
| Fong 2024 [24] | Case-control | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 8 | |||
| Brown 2024 [33] | Prospective cohort | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆☆ | ☆ | 0 | 0 | 7 | |||
| Khalifa 2024 [34] | Prospective cohort | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 0 | 7 | |||
| Parker 2022 [35] | Prospective cohort | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 0 | 0 | ☆ | 6 | |||
| Evered 2016 [36] | Prospective cohort | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 0 | ☆ | 0 | 6 | |||
| Danielson 2021 [37] | Prospective cohort | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 0 | ☆ | 7 | |||
| Zhang 2021 [38] | Prospective cohort | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | ☆ | 0 | 0 | 6 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




