1. Introduction
The urgent need to decarbonize industrial sectors has intensified the exploration of the role of hydrogen produced with renewable energies, particularly within hard-to-abate sectors such as steel, petrochemical, glass, cement, and paper and cardboard. Transitioning hydrogen into a practical energy vector demands a dual focus: a shift towards renewable energy sources and a meticulous examination of all conversion phases, [
1].
Direct electrification will play a growing role in industry, with important contributions in multiple applications. Some of these solutions are already mature or close to technological maturity and include the use of electric furnaces to replace natural gas boilers or the use of heat pumps for all low and medium temperature heating operations. However, the use of boilers is not always practical. For this reason, it is very useful to think of a combination of renewable energy and hydrogen.
The role of hydrogen in these industries is multifaceted, serving as a versatile resource not only in terms of alternative fuel for burners or system for the energy storage, but as raw materials foundational chemical components and as a catalyst for process innovation. Hydrogen emerges as a relevant element, not only for mitigating environmental impact by curbing emissions but also playing a central role in the definition of innovative processes [
2,
3]. But the multifaceted role of hydrogen, dissecting its involvement in all the sectors traditionally resistant to clean energy transition need to be investigated in detail, because in any case what must be determined is an overall energy saving and this is not always easy to achieve. From electrolysis to hydrogen storage and end-use applications, each phase of the “hydrogen process” demands meticulous evaluation of energy aspects. Achieving viable margins requires a nuanced understanding of the energy efficiency levels throughout the entire process, [
4].
This work sheds light on the critical dimensions necessary for successful coupling, emphasizing the need for a minimum scale to facilitate seamless integration of hydrogen in the hard to abate industrial sector. Currently, individual phases of the process are quite far to reach optimal efficiency levels, posing a challenge to the realization of a fully functional and sustainable hydrogen economy, [
5].
Considering that hydrogen from renewable energies will become a complementary technology in addition to electricity as part of an overall optimization of the energy system, the focus of this paper is to identify and delineate the minimum objectives that must be achieved for a harmonized and efficient hydrogen integration with specific focus in the “hard to abate” industrial sector. While the hydrogen supply chain encompasses various elements, current research focuses specifically on advancements in electrolysis, [
6,
7] storage techniques, [
8,
9] and on the practice of blended combustion, where hydrogen is combined with natural gas, offering a strategic approach to sectoral decarbonization, [
10,
11,
12]. Regarding hydrogen storage, the ongoing research emphasizes advancements aimed at enhancing the efficiency of compression technologies, including the development of advanced compressor designs and materials. This focus is particularly pertinent to gaseous hydrogen, given its simpler development with respect to liquid and chemical form, with the overarching goal of establish a trade-off between energy consumption and augmenting storage capacity. In terms of blending hydrogen with natural gas within existing gas networks and leveraging ready combustion technologies to facilitate a gradual transition to a low-carbon energy system, the aim is to illustrate a viable strategy for increasing the hydrogen percentage. Another element of interest is the integration of hydrogen as chemical agent in the industrial process, topic well developed in some specific sectors, like steel industrial sector [
13,
14,
15]. The various elements concerning hydrogen must be considered in a general analysis. Considering the intricacies of the process and delineating key milestones, this paper aspires to contribute to the practical realization of an effective roadmap for the future of hydrogen integration in the main hard-to-abate sectors with specific reference to some specific sectors. The author's original contribution lies in the evaluation based on typical mass and energy balances available in the literature, but in any case, not always easily applicable to specific contexts, to quantify the possible contribution of hydrogen taking into consideration both the final uses of the energy, maintaining the processes currently available, and evaluating possible changes to the processes. Although some considerations can be considered of a general nature, to better quantify some aspects, a specific context is taken as reference, such as that of the steel industry.
After this introductive chapter, the article is structured into four main sections, followed by a concluding section. The first section provides an overview of industries facing challenges in reducing emissions and explores the potential role of green hydrogen, derived from renewable sources hydrogen as the only relevant solution for decarbonization efforts.
Section 3 analyze and discusses methods and technologies related to green hydrogen production and storage.
Section 4 examines the utilization of hydrogen as a fuel in burner systems.
Section 5 focuses on the application of hydrogen as a chemical agent in industrial processes, with a specific emphasis on its use in the steel sector. In particular, the author tries to highlight how hydrogen can also be interesting as an element to innovate the production process, while paying attention to the energy balances of the process.
2. Hard to Abate Industry and the Prospect of Decarbonization: The Possible Role of Electricity and Green Hydrogen
The current topic of energy transition is a challenge that affects all sectors, from transport to construction and from energy to industry. Global energy-related CO
2 in 2022, reached the level of 37 Gtons, [
16]. With reference to the industrial field, it can be noted from the IEA report that approximately 9 Gtons of CO2 were emitted by industry in general, mainly by energy-intensive industries, in particular the steel sector contributed to 7.4% of global CO
2 emissions. The production of the main large-volume materials, including metals, cement, glass, basic chemicals, timber, plastic, rubber, and paper can be divided in two groups of processes identified as upstream and downstream.
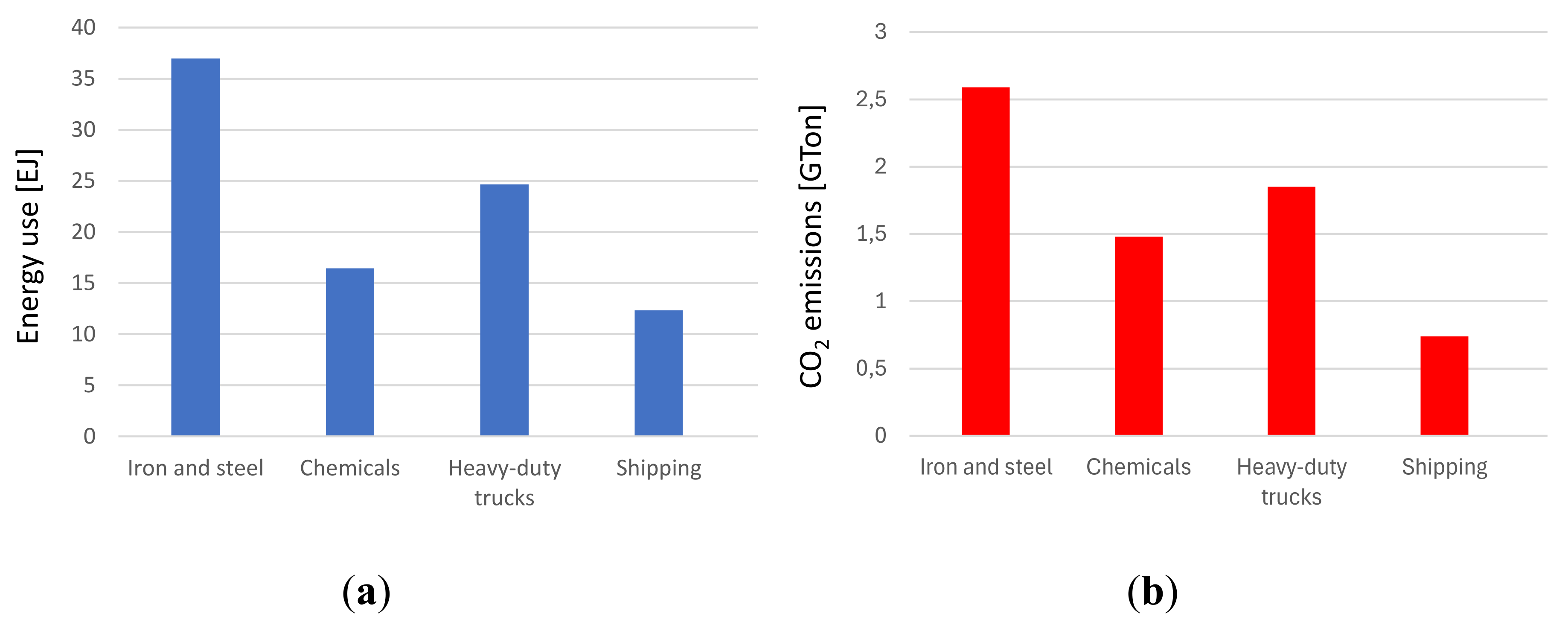
Downstream manufacturing sub-sectors, i.e. those closer to the final consumer, tend to account for larger shares of total value added than those upstream, which produce the main input materials for the downstream industries and use more relevant energy amounts. Among heavy industrial sectors worldwide, the steel industry ranks first in carbon dioxide (CO
2) emissions (
Figure 1).
The significant level of emissions is largely linked to the need to use significant quantities of fossil fuels, which can be used directly in the production process (think of the coal used to produce steel) and for the fueling of ovens that require often high temperatures. Looking at data obtainable from IEA, most of the process heat above 500°C (around 96%) is used in the three subsectors of steel, basic chemistry, and non-metallic materials (cement and pulp and paper); the steel industry alone contributes to 48%, [
17]. Proposals linked to possible future prospects with a view to decarbonisation have been made in all sectors. Among these, the increase in the share of electricity, possibly produced through renewable sources, and the systematic transition to electric ovens are certainly relevant. However, it is not always easy to replace ovens powered by fossil fuels with electric ovens, without distorting the production process to some extent.
Emissions for selected hard-to-abate sectors, 2022In this regard, the examples of the steel and glass sectors are relevant. An increasingly significant introduction of hydrogen could play an important role. This can be used either as a chemical agent to be introduced into industrial processes, modifying them appropriately or as a co-fuel or even as a pure fuel in ovens and burners or in energy storage. Not all “hard-to-abate” industries will see hydrogen playing the same role! While hydrogen can significantly contribute to decarbonizing some high-energy-intensive sectors like steel or ammonia production, its relevance may not be as pronounced in others. In other industrial sector, hydrogen might primarily serve as an alternative energy source or energy carrier to reduce carbon emissions associated with melting and production processes. However, its application might not be as direct as in other sectors. Therefore, it's essential to recognize that the role of hydrogen can vary significantly from one industry to another, and its effectiveness depends on its adaptation to the specific needs and operational conditions of each sector. For all the sectors, hydrogen as a carrier could therefore play a fundamental role in industrial processes, but its inclusion must be evaluated carefully, analysing the energy costs linked to its inclusion. The industrial sectors considered "hard to abate" are those in which reducing greenhouse gas emissions to very low levels or eliminating them altogether is particularly challenging due to the intrinsic characteristics of the involved industrial processes. These sectors represent a significant challenge in the transition to a low-CO2 economy. The main reasons why these sectors are considered "hard to abate" include:
- -
High levels of direct emissions: industrial sectors, such as steel, cement, and heavy chemicals production, emit large amounts of CO2 directly during production processes due to the direct use of carbon.
- -
Complex chemical processes: some sectors, like the chemical industry, involve complex chemical processes that require the use of specific chemicals or reactions that are challenging to substitute with low-carbon alternatives.
- -
High energy demand: sectors like heavy industry, ferrous materials production, and glass manufacturing require significant amounts of energy to heat furnaces or power production. This high energy demand result from the combustion of high-temperature fossil fuels and is difficult to be replaced with different (cleaner) energy sources.
- -
Long plant lifecycles: Industrial plants often have long lifecycles and require significant investments to be replaced or upgraded. Consequently, even if cleaner technologies exist, it may be costly and complex to replace existing plants with updated versions.
- -
Continuous demand for products: sectors, such as the automotive industry, are closely tied to the continuous demand for products which also makes it difficult to think about renewing production lines.
For "hard to abate" sectors, an integrated approach is needed involving the adoption of cleaner technologies, energy efficiency, fossil fuel replacement with renewable energy sources, and the development of innovative solutions for increasing the penetration of renewable energy sources. For this reason, it is appropriate to consider the possible implications of innovation processes, especially from a mass and energy balance point of view.
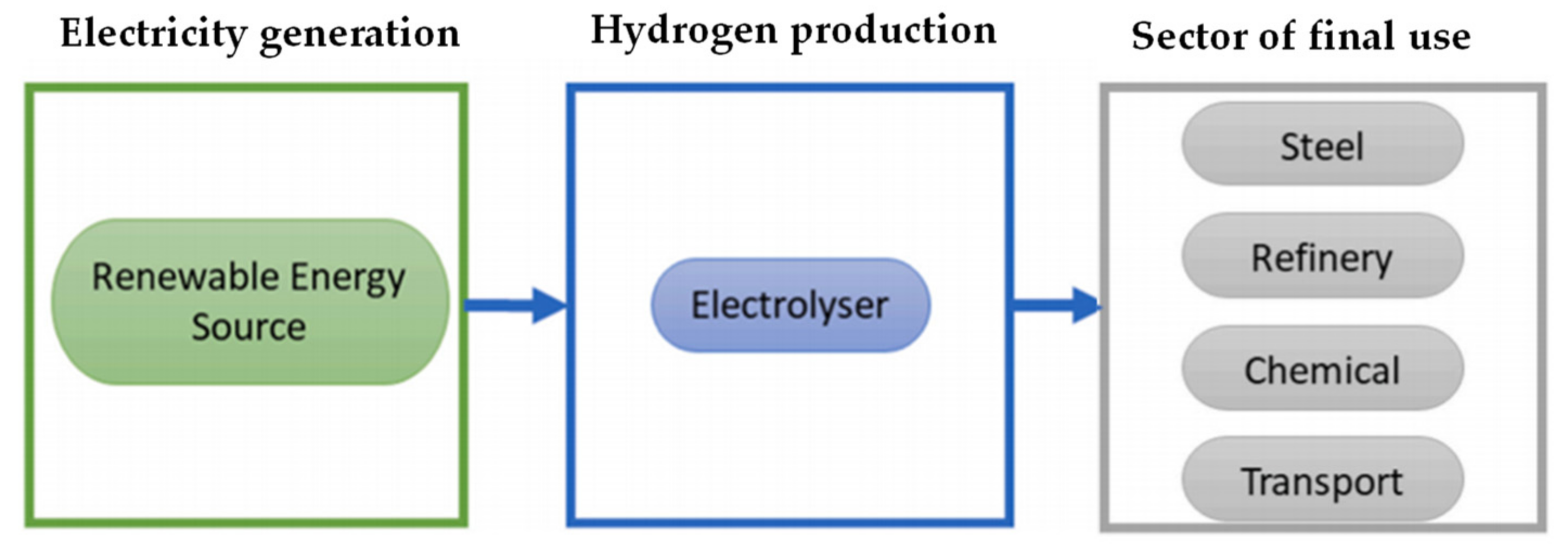
Figure 2.
Green hydrogen supply chain.
Figure 2.
Green hydrogen supply chain.
3. Hydrogen Production and Storage
Electrification is in general a way to implement the decarbonisation of many sectors. But not all sectors can be easily decarbonised in such a way; so-called hard-to-abate sectors can reach their sustainable goals by means of integration of hydrogen and renewable energy. In those sectors a real energy transition based on hydrogen will serve to allow the penetration of renewable sources. It must be considered that hydrogen is a secondary resource; so, it must be included within a supply chain from production to transport and storage up to final uses, therefore the energy costs of the entire production chain must be considered. To date, hydrogen is mainly produced using fossil resources; one of the most widespread methods is the steam reforming of methane, which covers over 60% of the demand, with a low production yield and high energy consumption.
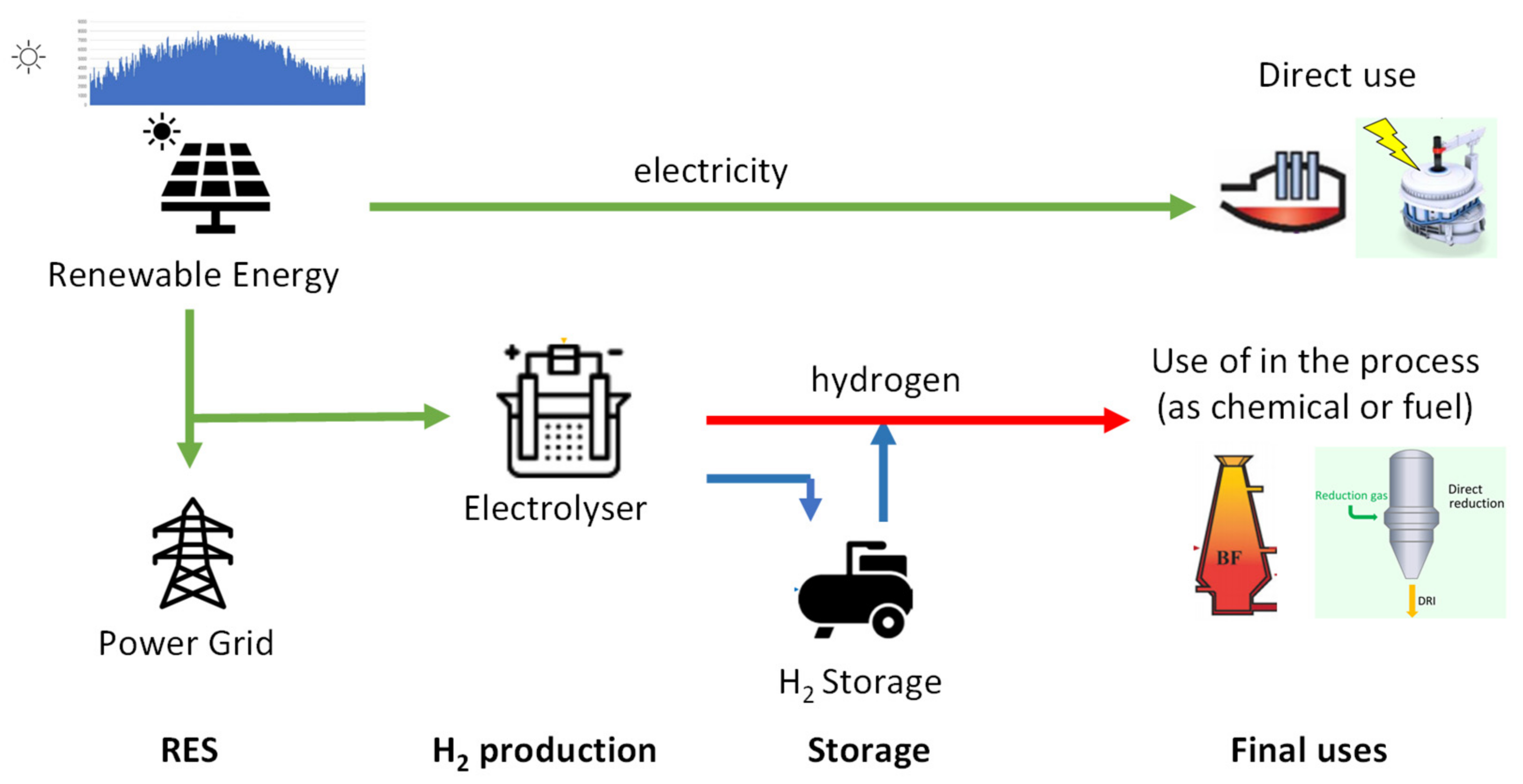
When thinking about using hydrogen to support the increase in the penetration of renewable energy, it is necessary to keep in mind the entire hydrogen supply chain, from production to end uses, also considering the need to accumulate hydrogen. While many routes are possible for the generation of green hydrogen (
Figure 3 provide one possible route), not all are convenient from a technical point of view.
Table 1 presents an example calculation of the energy consumption of the various production processes, from which the steam reforming of methane and the electrolysis of water can be seen as the two processes with the highest energy yield to focus on for a possible increase in hydrogen demand in view of its use in "hard to abate" industrial sectors. Considering the two processes, these allow the production of zero-emission hydrogen: the first with the addition of a carbon capture system, while the second through the electrolysis of water powered by renewable energy sources.
3.1. Hydrogen Production with Water Electrolysis
Focusing on the topic of water electrolysis, the most developed technologies are Alkaline (ALK), Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) and Solid Oxide (SOEC) which differ in operating conditions (T and P) and the electrolytes from which they take their name. The commercialized and most developed technologies are ALK and PEM, although it has the strong disadvantage of being made of high-quality materials which increase the cost and reduce the useful life, while solid SOEC could perhaps be relevant in the future industrial field thanks to lower electricity consumption favored using energy deriving from heat recovery, strongly present in "hard to abate" industrial sectors. This type of production is of interest for the energy transition, which is why research is very active in this specific sector. Research on electrolysis is still ongoing. It can be said that the topic of electrolysis is quite mature from a technological standpoint; however, when considering its integration into a production process, it's important to highlight that a significant percentage of energy is lost in the process (over 30 %). Summarizing the electrolytic process can be summarized, according to the actual state of the art, analyzed by the author of the present paper in [
6], that evidence a value of 0.6 for the efficiency of the electrolysis process, by the following synthetic equation, in which water and energy requirement to obtain 1 kg of hydrogen are outlined:
Considering the energy value of hydrogen, 120 MJ/kg (33,3 kWh) and the Lower Hearing Value (LHV) of 144 MJ/kg (40 kWh), at least 15 kWh are lost in the process. Furthermore, another significant issue is the durability of electrolysers, which is not high, along with the stability of their performance.
Table 2 summarizes the main relevant data that can be associated with the different technologies. With respect to Alkaline (ALK) electrolysis and Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) electrolysis, high temperature electrolysis technologies, Solid Oxide Electrolysis (SOEC) promise rather high efficiencies, but if we look closely, they shift the demand a lot on the thermal front and the high efficiency values therefore refer to cases in which waste heat can be available at high temperature. In any case, these technologies are not currently commercially available.
3.2. Hydrogen Storage and Its Role in “Load Levelling” between Renewable Power and Final Uses
One of the relevant roles of hydrogen is certainly that of being able to act as an accumulator of excess energy, possibly produced through renewable energy sources. The topic of hydrogen accumulation is one of the relevant topics, although obviously it is always best not to underestimate the energy aspect of the issue. This has been the subject of analysis, in recent times, also by the author of the present work in [
18]. Hydrogen storage presents a crucial solution for addressing the challenges of the energy transition in industries classified as 'hard to abate.' In those industries, hydrogen could serve as an alternative to electrochemical storage in terms of helping to align production levels with utilization levels, considering that significant amounts of energy could still be stored in these industries. In these industries, where substantial amounts of energy can be stored, hydrogen could be stored in gaseous or liquid form and used as a flexible energy resource. Hydrogen can be produced via water electrolysis using excess renewable energy during periods of overproduction, and then converted back into energy during peak demand periods. This approach could help mitigate the variability of renewable sources and support the transition to a more sustainable and resilient energy system.
4. Green Hydrogen as an Alternative Fuel in the Burners
After examining the possible systems to produce hydrogen, the role of hydrogen as a co-fuel mixed with methane is analysed. Compared to methane, hydrogen has different chemical-physical properties which, when mixed, bring about changes both to combustion and to the characteristics of the flame. We note large dimensions and high storage pressures, higher jet speed to maintain the same amount of heat released by the methane. High flame speed approximately 6 times that of methane which leads to short, compact, and turbulent flames, and problems with backfire, flashbacks, which is why premixed flames are not recommended. Since combustion with hydrogen causes a different adiabatic flame temperature, which changes the design temperature of the furnace, careful control of the mixing is therefore necessary to maintain product specifications. A wider flammability range with therefore combustion management problems but with a lower minimum ignition energy. Although CO
2 emissions decrease, high temperatures lead to high NO
X emissions, particularly thermal ones, therefore Dry Low NO
X or flameless configurations are recommended for future burner configurations. Finally, the small size of hydrogen leads to losses from possible welds and the chemical reactivity with steel alloys causes the material to become embrittled, more a problem of piping and storage than of the burner itself given the high operating speeds. A further consideration to make is the useful heat released.
Table 3 provides a comparison of the two fuels.
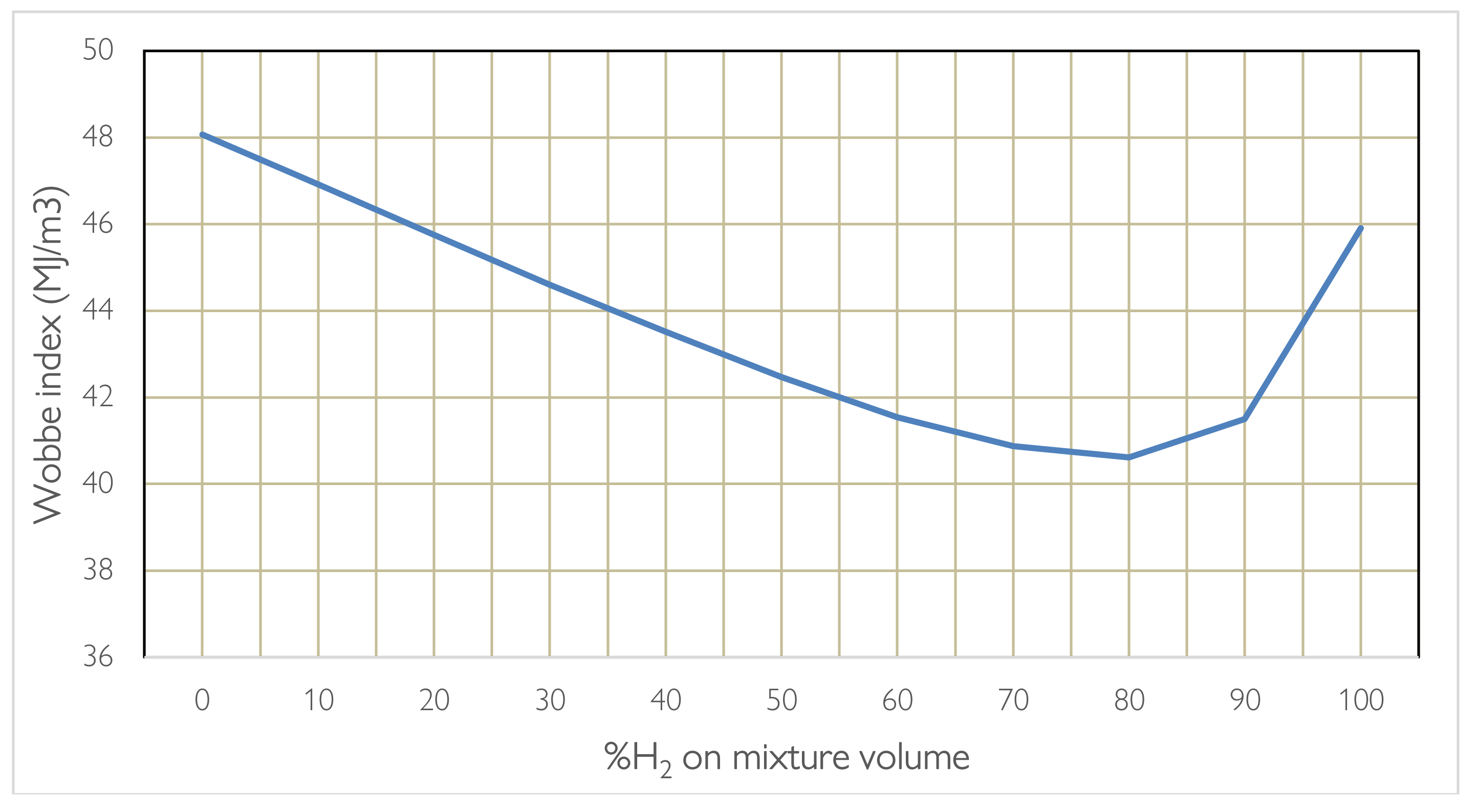
When blending or replacing one fuel with another, the power range and stability of combustion are influenced. Furthermore, we are talking about gas at different densities which influences the flow rate that passes through the same nozzle and the amount of heat exchanged. Here it is necessary to evaluate the rate of release of useful heat using the Wobbe Index. Carrying out the calculations according to the formula presented which depends on the calorific value and density of the hydro methane mixture in relation to the density of the air, it is noted that when the percentage varies the parameter does not have a linear trend but presents a valley around 80% of H2, therefore the most unfavourable percentage for combustion. Instead, it is noted that a 20% H2 mixture has the same heat exchanged as a 99% H2 mixture, which is why burner manufacturers recommend methane hydrogen blending on methane burners already operating up to 20% by volume for combustions in which the process requires T > 750 °C, for higher percentages a change in burner technology and in the design of the oven and the flue gas lines is necessary, even if on a thermal level it is not advantageous. As regards emissions, it is noted that as the hydrogen content increases, the %CO2 saved increases, although not linearly given the calculation in relation to the different volume and density. The chemical-physical properties of H2, when it is mixed with CH4, determine changes in the characteristics of the flame, compared to that of methane alone, which are more evident as the hydrogen content in the mixture increases. To take advantage of the blending technique in burners operating in the production lines production it is necessary to keep in mind that the heat exchange mode could be different, based on the %H2, to the point of having to foresee significant changes in the oven or in the fume recovery path. Hydrogen brings changes during combustion summarized in the list:
- -
Hydrogen contributes to combustion a quantity of heat 2.4 times greater than the 1 kg of CH4, but 3 times less than the m3 of CH4, due to the low density of the H2: this translates into large dimensions or high pressures of storage, a jet speed approximately 3 times higher and greater volumetric flow rates of the mixture;
- -
The flames have different shapes, increasingly shorter, compact but turbulent given the flame speed of H2 which is approximately 6 times greater than that of CH4;
- -
The high flame temperature of H2 can be harmful for some thermal specifications (for example in the polymerization oven in the painting line with the risk of burning the tape);
- -
The addition of hydrogen involves an expansion of the flammability field, increasing its reactivity, diffusivity, and reaction speed with problems in the management and safety of the flame, high risks of flashbacks, hence premixed combustion is not recommended. Burner manufacturers, [
19,
20] through experimental tests declare the feasibility of blending up to 20%H
2 by volume without making changes to the burner technology and the conditions of use for temperatures above 750 °C, given how the properties change of combustion. Going beyond these percentages does not even seem convenient in terms of the useful heat produced demonstrated by the trend of the Wobbe index, which for a specific gas is defined as:
where RD is the ratio between the density of natural gas and air. The Wobbe index has dimensionally the same unit of the calorific value. G is a Specific Gravity factor, which is assumed as the ratio between the density of the gas and the density of air, at the same temperature and pressure, [
21]. The Wobbe index helps ensure that different gas compositions can be safely and efficiently used in gas-fired appliances without causing operational issues such as flame instability or incomplete combustion. Gas appliances are typically designed to operate within a certain range of Wobbe index values to maintain consistent performance. The concept is that gas with similar Wobbe index but different compositions, can be replaced with each other as they release the same amount of energy in a furnace through the same nozzle with similar feed pressure. So, if the same concept is applied to a mixture of hydrogen and natural gas the Wobbe Index can be defined as:
In fact, by providing for a change of fuel, the power range and stability of combustion are different, the release rate of different fuels at the same flow rate can be very different. This is verified using the Wobbe index, a parameter used as an indicator of the interchangeability between gaseous fuels.
Figure 4 provides the different value of Wobbe index for a mixture of natural gas (approximated to methane) and hydrogen, with different volumetric percentages of hydrogen. The advantage of using a mixed mixture can be better appreciated by considering the aspect linked to CO
2 emissions. It can be seen how, by maintaining a percentage of hydrogen below 20% by volume there is an interesting decrease in CO
2 emissions resulting precisely from the presence of hydrogen in the chemical reaction of hydrogen combustion. The values in
Table 4 are referred to a blending of 20% in line with the values currently considered admissible based on the technology.
5. Hydrogen Produced with Green Electricity as a Chemical Agent in the Process: The Relevant Case of Steel Sector
As is known, hydrogen is used in many industrial sectors as a reducing agent. This pathway also enables a significant penetration of renewable energies in the aforementioned sectors. Green H₂, produced through renewable-powered water electrolysis can be used as a carbon-free feedstock and reductant to significantly reduce carbon emissions in several key industry sectors. It is well known that most of the H₂ production in the world comes from natural gas (via steam methane reforming or coal (via coal gasification).
In industries such as steelmaking, ammonia, and chemical manufacturing in general, hydrogen can serve as a raw material or as reducing agent for various processes. For example, hydrogen can replace coal in the direct reduction of iron ore (DRI) to produce steel, contributing to the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions significantly. But Hydrogen is also a critical raw material for ammonia production, as it serves as the key ingredient in the Haber-Bosch process, which is used to synthesize ammonia (NH3) from nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2). In the Haber-Bosch process, hydrogen acts as a reducing agent, providing the necessary electrons to convert nitrogen gas into ammonia. This process requires a large amount of hydrogen to ensure high conversion rates and ammonia yields.
Table 5.
Hydrogen Usage in Different Industries.
Table 5.
Hydrogen Usage in Different Industries.
| Industry |
Hydrogen Use |
| Refinery |
Hydrogen is used for desulphurisation of products such as diesel and petrol. |
| Fertiliser |
Hydrogen is used for manufacturing ammonia, which in turn is used as a feedstock for ammonia-derived fertilisers such as urea and di-ammonium phosphate. |
| Methanol |
Hydrogen is used as a main feedstock to produce methanol, which is currently produced from natural gas |
| Hydrogen peroxide |
Hydrogen is used in the first step, i.e. hydrogenation of working solution of four-step hydrogen peroxide manufacturing process. |
| Steel |
Hydrogen is used as a reducing agent in steel manufacturing by direct reduced iron process |
| Float glass |
Hydrogen is used as a getter gas to prevent oxidation over the tin baths used in float glass manufacturing process, the glass formed on the baths is made without defects. |
| Optic fiber |
Hydrogen is used for refractive index increment; optical fiber is immersed in a hydrogen environment to absorb hydrogen up to several mol% in advance of UV irradiation to reduce defect formation in cables. |
| Pharma |
Hydrogen is used to produce hydrogen peroxide and active pharmaceutical ingredient, which is used in various medicine manufacturing. |
Very interesting is the case of steel sector, in which hydrogen can be used as reagent, contributing to reduce emissions. Steel is an indispensable material. It is widely used in infrastructure, buildings, transport vehicles, household appliances, medical equipment and many other industries, such as energy. It is in fact used in several renewable technologies, such as electric vehicles, wind turbines and solar photovoltaic (PV) structures [
22]. Steel's strength, durability, versatility, and recyclability make it suitable for a wide variety of applications. Demand for steel closely follows the development of an economy, particularly in the early stages of industrialization. Steel production has increased steadily over time. In absolute terms, steel production has risen from 190 million tons in 1950 to almost 1.85 billion tons in 2023 [
22,
23]. In 2023, total crude steel production was 1,878.5 Mt with China, India and Japan leading as producing countries, followed by the United States, Russia, South Korea, Germany, Turkey, Brazil and Iran, [
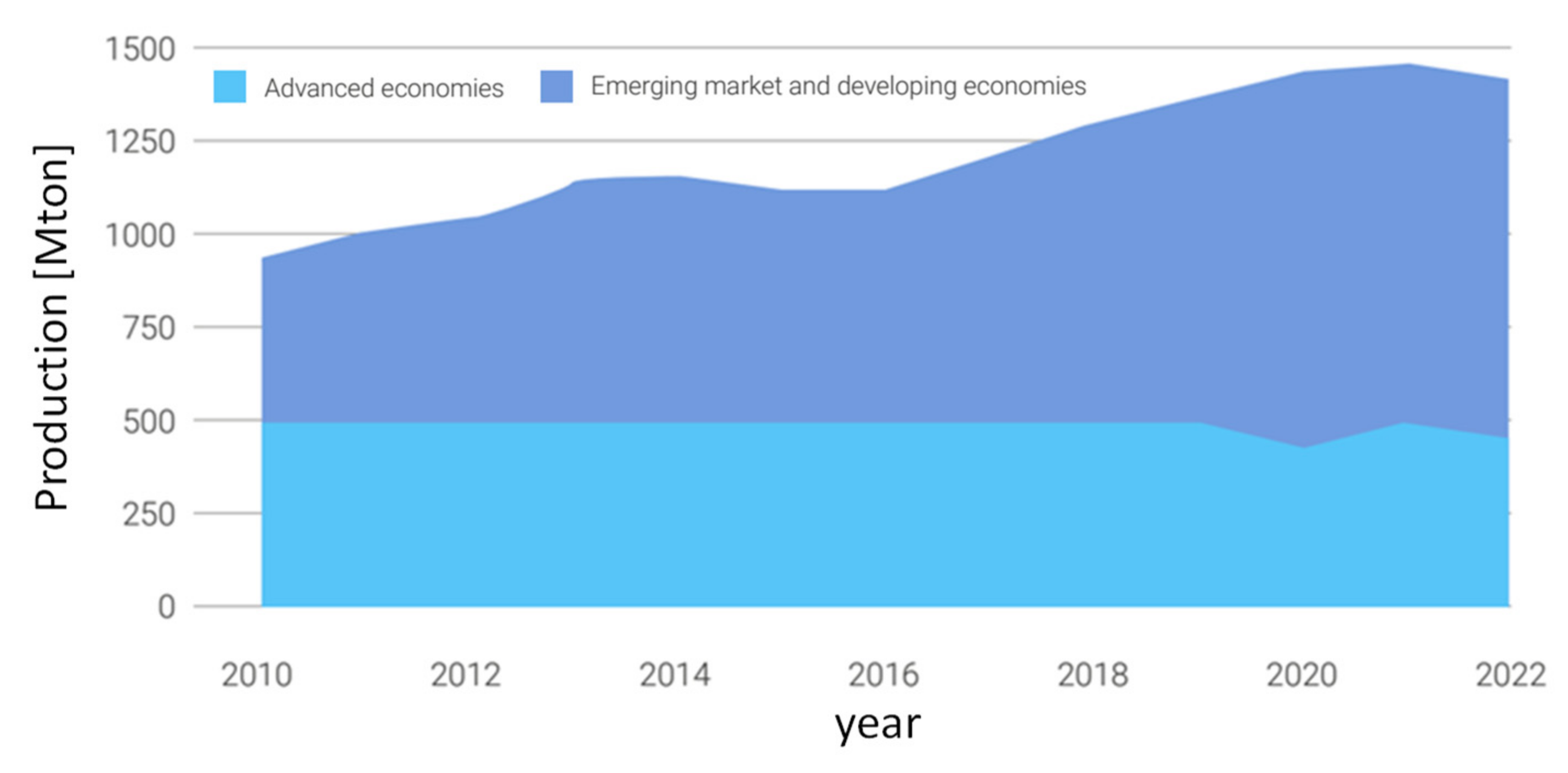
22]. Currently, about 75% of global steel is produced in emerging markets and developing economies, as represented in
Figure 5, [
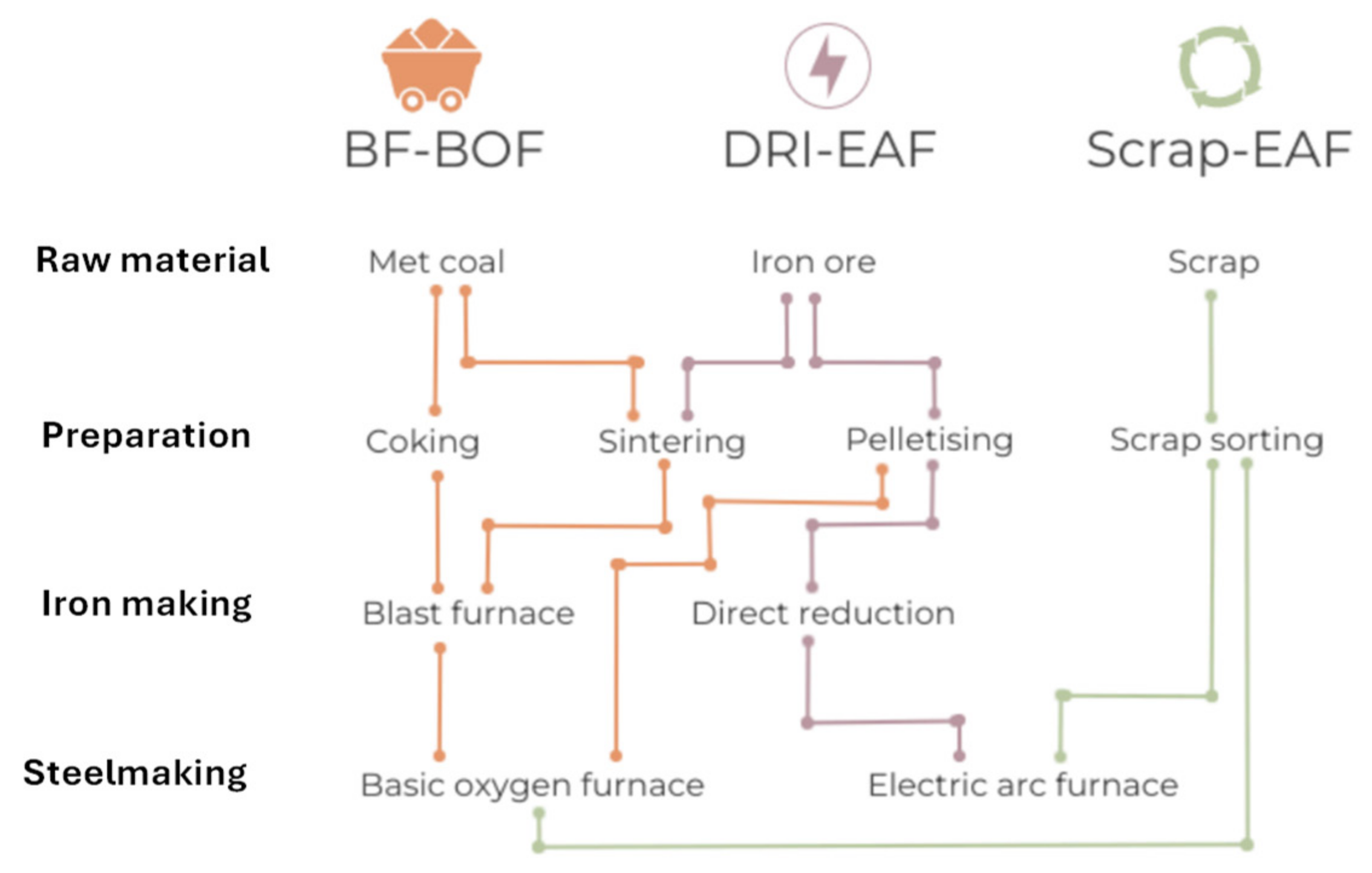
24]. The technology that has established itself over the last hundred years both for maximum productivity and efficiency and for excellent economics is the blast furnace (blast furnace) powered by carbon coke. The process in known with the acronym BF-BOF (Blast Furnace – Boiling Oxygen Furnace). It is characterized by high investment costs and production capacity in the order of millions of tons per year.
The steel industry is extremely carbon intensive. The main reason for this is the industry’s extensive use of metallurgical coal in blast furnaces to produce iron, the primary component of steel. Around 90% of the emissions from steel production arise from this process, [
25]. New steelmaking processes that do not rely on metallurgical coal, as DRI are emerging as viable alternatives. DRI is a form of iron produced through direct reduction, bypassing the carbon-intensive blast furnace process. DRI is produced at temperatures below iron's melting point. Basic oxygen furnace (BOFs) is replaced by Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) and this can be partially supported with renewable energy.
In secondary steel production, steel scrap is reclaimed and re-melted in an EAF, without the need for a new iron ore reduction process.
Figure 6 provides the main routes for steel production considering the primary process, that is followed by downstream processing, where finished steel products are obtained.
By making some evaluations on standard processes based on the methodology defined in [
26], it is possible to carry out mass and energy balances typical of the process, from which, based on the evaluations made using a simple one-dimensional model, the results that can be estimated can be are shown in the following
Table 6. Energy uses related to the production process can be estimated in the order of magnitude of 18-25 GJ/ton of steel produced. Most of this energy is thermal, i.e. natural gas.
As can be seen from the data in
Table 6, most of the energy demand is attributable to thermal energy and therefore, considering the technologies in use around the world, largely linked to natural gas. The possible role of hydrogen as a fuel in blend combustion with natural gas has already been analysed, in the previous section. But the role of hydrogen in this sector can also be another, that is, it can contribute to modifying the production process and progressively decarbonising the sector.
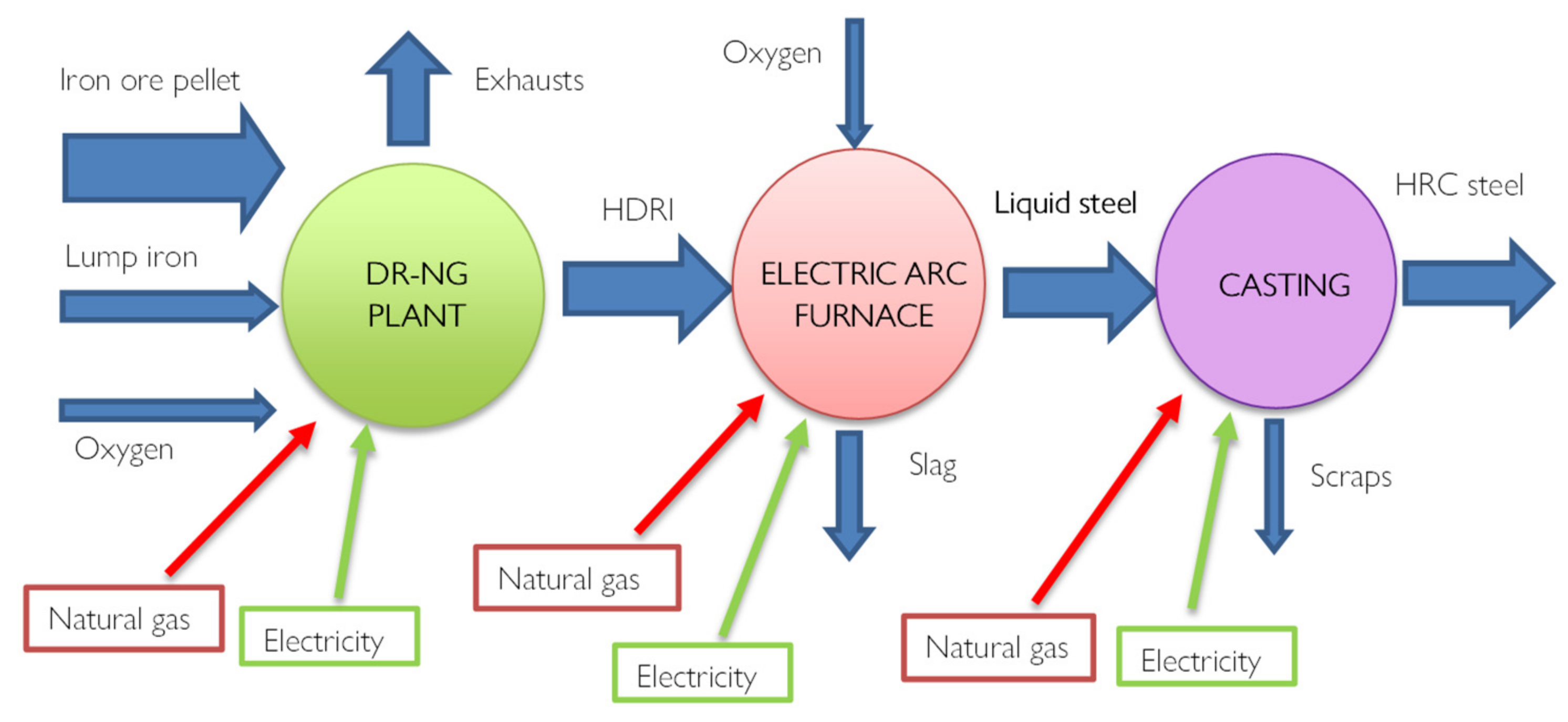
Using hydrogen to produce steel is not a new concept, in recent years the Direct reduction Iron technology (DRI) has been developed which today satisfies 7% of global steel production. Alternative reduction technologies include hydrogen-based direct reduction processes and electrolytic reduction methods. Most are not well developed and require huge amounts of green energy, but they hold the promise of carbon-neutral steelmaking, [
27]. Most of these plants consist of a furnace (Shaft Furnace) powered by methane rather than coal. Through reforming, which can be inside or outside the oven depending on the system, CO+H
2 syngas is generated which allows the direct reduction of iron. The novelty of this technology is therefore precisely the chemical process.
Furthermore, the final product is iron in the solid phase since the reductions take place at 800°C and therefore not at the melting temperatures, directly forming the DRI direct reduction iron.
Figure 7 provides a scheme of the process with evidenced all the energy fluxes. Hydrogen, used as a reductant, has excellent kinematic properties, favoring the productivity and metallization of iron Fe > 90%, i.e. complete oxidation. From a thermal point of view, however, there are some disadvantages since the reduction reactions with H
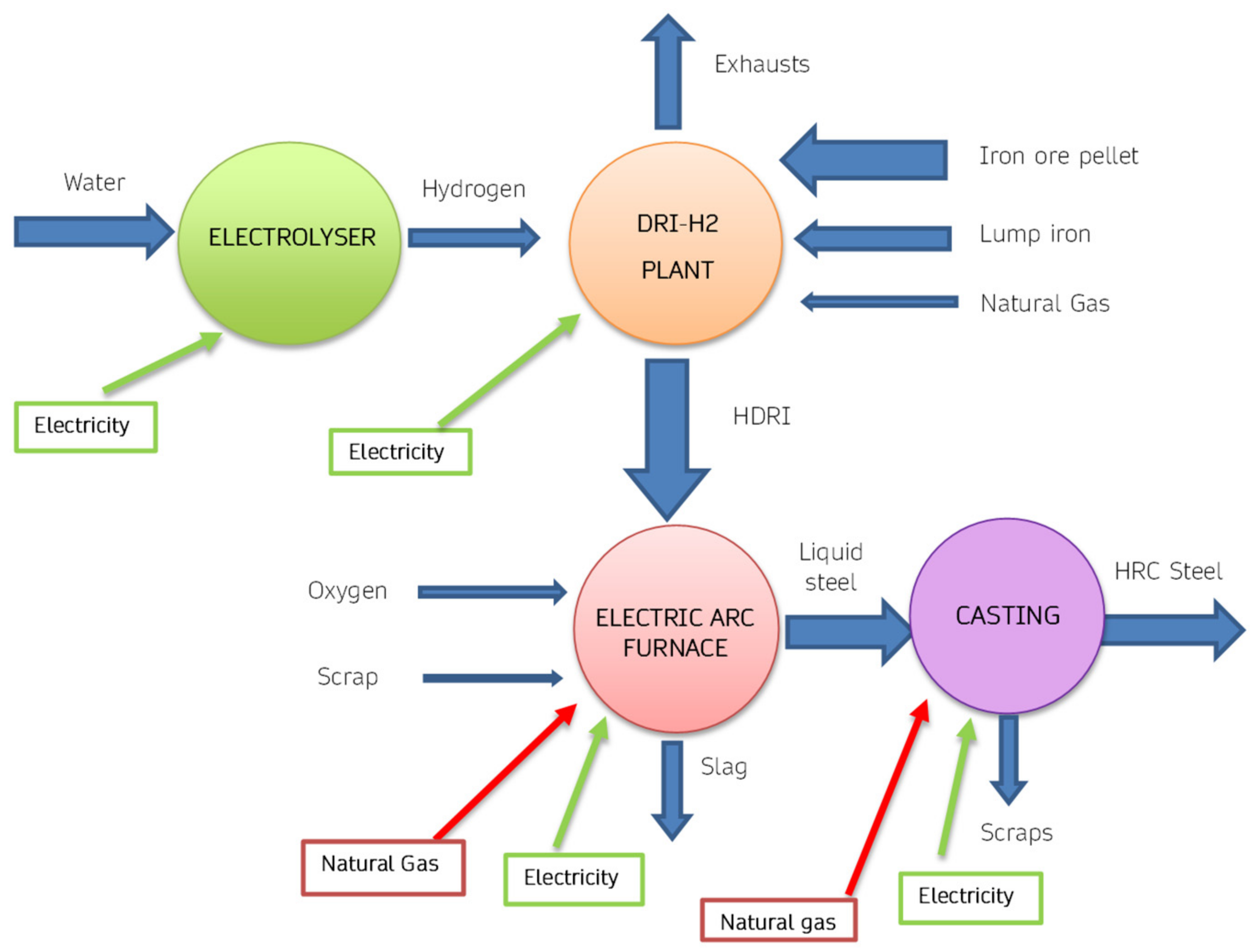
2 are endothermic. An innovative version of DRI technology is represented by the scheme of
Figure 8, in which hydrogen is obtained using an electrolyser. Therefore, in these plants the total energy requirement increases, due to the efficiency of the electrolytic process. Furthermore, the increase in energy expenditure also corresponds to a significant increase in the use of electricity, especially in the electrolysis process. Considering the production of 1 ton of H
2, approximately 70 kg of hydrogen are needed, therefore considering a need of approximately 55 kWh/kg, consequently approximately 3850 kWh are necessary for each ton of steel produced. From the point of view of CO
2 emissions produced, there is still an overall reduction, if green electricity is used.
Table 7 provides a comparative analysis between the two DRI processes, with specific attention to the mass flow rate involved in the processes while
Table 8 provides a comparison of energy consumption estimates per unit of finished product considering the traditional blast furnace process (BOF) and the two DRI processes, including the one based on hydrogen. The table also includes an estimate of the expected level of CO
2 emissions per ton of product, elaborated according to the model developed in [
28]. In
Table 8 the estimation of CO
2 emissions associated with the last process is omitted because in this case, it heavily depends on the type of energy resource used to generate the electricity introduced into the process (mainly in the electrolyser). As can be seen based on the evaluations made in this article, in fact the DRI process leads to a possible overall reduction in energy use in steel production processes, even if this is obviously conditioned, in the hydrogen production processes, by efficiency of electrolysers. Today, around 500 DRI plants are available globally, with a total capacity of 119 Mton, which represent approximately 7% of global steel production. DRI technology is used primarily in the Middle East/North Africa (44%), followed by Asia (25%) and Latin America (17%), [
29]. Considering the value of global production and the 500 plants, an average productivity per single DRI plant of approximately 250,000 tons of steel per year can be estimated.
As in the steel sector, achieving significant reductions in CO2 emissions through hydrogen may be quite challenging, this applies similarly to different “hard to abate” sectors, where identifying contributions from hydrogen other than those as a co-fuel may be even more difficult.
6. Integration of DRI-H2 Process with PV Systems
To reduce potential emissions, steel production processes should be combined with renewable energy use that allows the production of electricity and reduces emissions. Great relevance can be attributed, for example, to the possible integration of steel production processes with a photovoltaic (PV) system.
Considering the production capacity of a steel plant, which for a small to medium size could be of 1 million tonnes of steel annually, a large PV plant is required. The sizing of the system is quite simple, assuming that the productivity for each kW of peak power can be estimated by knowing the solar irradiation in the specific site and considering an appropriate balance of system efficiency for the PV plant (it usually assumes a value between 0.75 and 0.85) and considering the ideal specific energy produced by a PV plant,
, expressed in kWh/kW of peak power for the period considered (a day, a month, a year):
Considering some typical value for specific electricity consumption for a typical electrolyzer, as discussed in [
7],
(e.g. 55 kWh for 1 kg of hydrogen) and the typical mass of hydrogen required for producing a ton of steel in a typical benchmark DRI-H
2 process,
(e.g. 70 kg for each ton of steel produced) the size of the PV plant necessary to support the industrial process can be evaluated by means of the following equation:
Table 9 shows the typical sizes of photovoltaic plants that would be required to power existing steelmaking systems worldwide with green energy. As can be seen, these are very large-scale installations, which would therefore undoubtedly require substantial investments. Moreover, it is not feasible to construct plants directly tied to the production system. Nonetheless, these solutions can still be considered.
Hydrogen-based DRI production has been proven at precommercial scale and the first commercial scale plants are being built, or are at the advanced project stage: the conditions for energetic transition seems to be favourable but considering this and the economic situation, a large fraction of the projected growth in activity from hard-to-abate sectors is expected to come from developing economies, while action within the most developed countries appear to be critical, [
30]. The conditions for decarbonizing hard-to-abate energy sectors seem favourable because many plants in Europe have reached the end of their useful life and could be rebuilt on new foundations, explicitly implementing innovative technologies. Consider, for example, the cases of the steel plants in Piombino and Taranto in Italy, which could be reconstructed basing on DRI-H
2 technology and green electricity.
7. Conclusions
The decarbonisation of the hard-to-abate sectors will require a combination of approaches, given the characteristics of each sector. The transition in hard-to-abate sectors requires fundamental shifts, rather than gradual steps. Direct electrification will play an increasing role and hydrogen could play a relevant additional role.
This article illustrated the prospects of hydrogen, produced through renewable sources ("green hydrogen") as a method for the decarbonisation of sectors classified as "hard to abate". As is quite evident, the role of hydrogen is to be seen as an element capable of allowing partial or total powering of the various plants through renewable sources. The role of hydrogen in these sectors could be relevant both as a material for the process and as an alternative fuel. Even considering the technological limits linked to electrolysis (currently of the maximum order of around 60%) and the energy that is necessary for its accumulation (at least 10% of the accumulated energy) the insertion of hydrogen; however, it is a prospect to be carefully evaluated.
In particular, the possible uses of hydrogen in specific sectors were examined; among these the steel sector appears quite interesting. In steel and iron industrial sector, hydrogen is promising both as a reductant for the DRI process, which already currently concerns around 7% of global steel production, and as a co-fuel which could already be used in furnaces currently available, present in companies in mixtures of up to 20% with natural gas, already resulting in some reduction in CO2 emissions. It is quite difficult to quantify the contribution that hydrogen could make in terms of decarbonisation of these sectors, but hydrogen is certainly to be considered an interesting prospect.
The role of green electricity supported by hydrogen is crucial; however, it is important not to underestimate the fact that powering a typical production plant will require very significant power capacities. As discussed in
Section 6, even for a next-generation DRI plant with an annual production of about 1 million tons of steel, it would be necessary to deploy photovoltaic plants with a capacity of 3200 MW. Therefore, it is certainly not feasible to directly connect photovoltaic plants to production facilities. However, integrating renewable generation from a complex energy system with large industrial plants can indeed be a key element in enabling further penetration of renewable power. Of course, a systemic vision will be necessary to achieve this type of transition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.F.; methodology, A.F.; software, A.F, M.R.; validation, A.F., M.R.; formal analysis, A.F., M.R; investigation, A.F.; resources, A.F.; data curation, A.F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.F.; writing—review and editing, A.F., M.R.; visualization, A.F., M.R; supervision, A.F.; project administration, A.F.; funding acquisition, A.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Recovery and Resilience Plan (NRRP), Mission 4 Component 2 Investment 1.3—Call for tender No. 1561 of 11.10.2022 of Ministero dell’Università e della Ricerca (MUR); project funded by the European Union—NextGenerationEU. Award Number: Project code PE0000021, Concession Decree No. 1561 of 11.10.2022 adopted by Ministero dell’Università e della Ricerca (MUR), CUP I53C22001450006, according to attachment E of Decree No. 1561/2022, Project title “Network 4 Energy Sustainable Transition—NEST”.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The author gratefully acknowledges the support of Isabella Biasci, for the model and the elaboration of
Figure 7 and
Figure 8, rearranged from her Master Thesis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jayachandran, M., Gatla, R. K., Flah, A., Milyani, A. H., Milyani, H. M., Blazek, V., Prokop, L. & Kraiem, H. (2024). Challenges and Opportunities in Green Hydrogen Adoption for Decarbonizing Hard-to-Abate Industries: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Access.
- Azadnia, A. H., McDaid, C., Andwari, A. M., & Hosseini, S. E. (2023). Green hydrogen supply chain risk analysis: A european hard-to-abate sectors perspective. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 182, 113371.
- Zaiter, I., Ramadan, M., Bouabid, A., El-Fadel, M., & Mezher, T. (2023). Potential utilization of hydrogen in the UAE's industrial sector. Energy, 280, 128108.
- Qureshi, F., Yusuf, M., Khan, M. A., Ibrahim, H., Ekeoma, B. C., Kamyab, H., … & Chelliapan, S. (2023). A State-of-The-Art Review on the Latest trends in Hydrogen production, storage, and transportation techniques. Fuel, 340, 127574.
- Franco, A., & Giovannini, C. (2023). Routes for Hydrogen Introduction in the Industrial Hard-to-Abate Sectors for Promoting Energy Transition. Energies, 16(16), 6098.
- Vidas, L., & Castro, R. (2021). Recent developments on hydrogen production technologies: State-of-the-art review with a focus on green-electrolysis. Applied Sciences, 11(23), 11363.
- Franco, A., & Giovannini, C. (2023). Recent and Future Advances in Water Electrolysis for Green Hydrogen Generation: Critical Analysis and Perspectives. Sustainability, 15(24), 16917.
- Tang, D., Tan, G. L., Li, G. W., Liang, J. G., Ahmad, S. M., Bahadur, A., … & Bououdina, M. (2023). State-of-the-art hydrogen generation techniques and storage methods: A critical review. Journal of Energy Storage, 64, 107196.
- Usman, M. R. (2022). Hydrogen storage methods: Review and current status. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 167, 112743.
- Giacomazzi, E., Troiani, G., Di Nardo, A., Calchetti, G., Cecere, D., Messina, G., & Carpenella, S. (2023). Hydrogen Combustion: Features and Barriers to its Exploitation in the Energy Transition. Energies, 16(20), 7174.
- Mayrhofer, M., Koller, M., Seemann, P., Prieler, R., & Hochenauer, C. (2021). Assessment of natural gas/hydrogen blends as an alternative fuel for industrial heat treatment furnaces. International journal of hydrogen energy, 46(41), 21672-21686.
- Luzzo, I., Cirilli, F., Jochler, G., Gambato, A., Longhi, J., & Rampinini, G. (2021). Feasibility study for the utilization of natural gas and hydrogen blends on industrial furnaces. Matériaux & Techniques, 109(3-4), 306.
- Wang, R. R., Zhao, Y. Q., Babich, A., Senk, D., & Fan, X. Y. (2021). Hydrogen direct reduction (H-DR) in steel industry—An overview of challenges and opportunities. Journal of Cleaner Production, 329, 129797.
- Bhaskar, A., Assadi, M., & Nikpey Somehsaraei, H. (2020). Decarbonization of the iron and steel industry with direct reduction of iron ore with green hydrogen. Energies, 13(3), 758.
- Liu, W., Zuo, H., Wang, J., Xue, Q., Ren, B., & Yang, F. (2021). The production and application of hydrogen in steel industry. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 46(17), 10548-10569.
- International Energy Agency (IEA) CO2 Emissions in 2022. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/co2-emissions-in-2022 (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- International Energy Agency (IEA) Data and statistics. Available online: https://www.iea.org/energy-system/industry (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Franco, A., & Giovannini, C. (2024). Franco A, Giovannini C. Hydrogen Gas Compression for Efficient Storage: Balancing Energy and Increasing Density. Hydrogen. 2024; 5(2):293-311. [CrossRef]
- Cokain, K., Cochran, M. (2021). CO2 Reduction Options for High Temperature Industrial Combustion. Bloom Engineering. Available online: https://afrc.net/papers/2021/18%20-%20CO2%20Reduction%20Options%20for%20High%20Temperature%20Industrial%20Combustion.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- GF ELTI. Dalla sperimentazione all'uso quotidiano: H2 Burn technology, 2022 (in italian). Available online: https://www.gfelti.com/website/others/H2-Burn-IT.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Klimstra, J. (1986). Interchangeability of gaseous fuels—The importance of the Wobbe-index. SAE transactions, 962-972.
- IRENA (2023). Towards a circular steel industry, International Renewable Energy Agency, Abu Dhabi. Available online: www.irena.org/Publications/2023/Jul/Towards-a-Circular-Steel-Industry (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- World Steel Association (2024), December 2023 crude steel production and 2023 global crude steel production totals”, World Steel Association. Available online: https://worldsteel.org/wp-content/uploads/December-2023-crudesteel-production-and-2023-global-crude-steel-production-totals-1.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- McKinsey, (2022) Steel. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/sustainability/our-insights/spotting-green-business-opportunities-in-a-surging-net-zero-world/transition-to-net-zero/steel (accessed on 4 May 2024).
- Minerals Research Institute of Western Australia, 2023, Western Australia’s Grene Steel Opportunity, MRIWA Project. Available online: https://www.mriwa.wa.gov.au/minerals-research-advancing-western-australia/focus-areas/green-steel/green-steel-resources/ (accessed on 4 May 2024).
- Jin, P., Jiang, Z., Bao, C., Hao, S., & Zhang, X. (2017). The energy consumption and carbon emission of the integrated steel mill with oxygen blast furnace. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 117, 58-65.
- Ito, A., Langefeld, B., & Götz, N. (2020). The Future of Steelmaking-How the European steel industry can achieve carbon neutrality. Roland Berger, 16.
- Biasci I. (2023), Methodology for the reduction of CO2 emissions in steel production and transformation processes, Master Thesis in Energy Engineering at the University of Pisa (in Italian). Available online: https://etd.adm.unipi.it/t/etd-01242023-172910/.
- Baig, S., & Murray, B. (2016). Cost effectiveness analysis of HYL and Midrex DRI technologies for the iron and steel-making industry. Duke University. Available online: https://dukespace.lib.duke.edu/server/api/core/bitstreams/19daa588-bc17-4bc8-8acc-a3b3b2e6ff91/content (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- IRENA (2024), Decarbonising hard-to-abate sectors with renewables: Perspectives for the G7, International Renewable Energy Agency, Abu Dhabi. (Accessed on 26 of May 2024).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).