Submitted:
25 May 2024
Posted:
27 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Water Quality Monitoring Based With IoT Application with Different Wireless Network
2.2. LoRa Overview
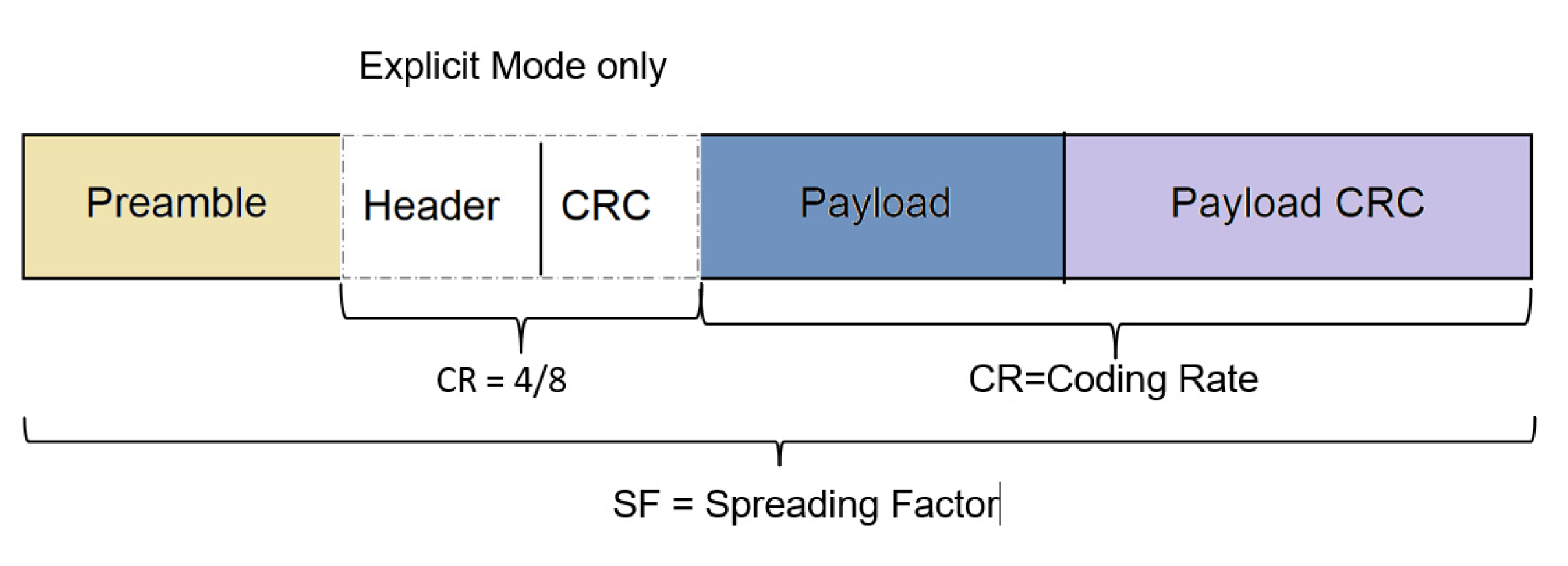
2.2.1. LoRa and Radio Modulation
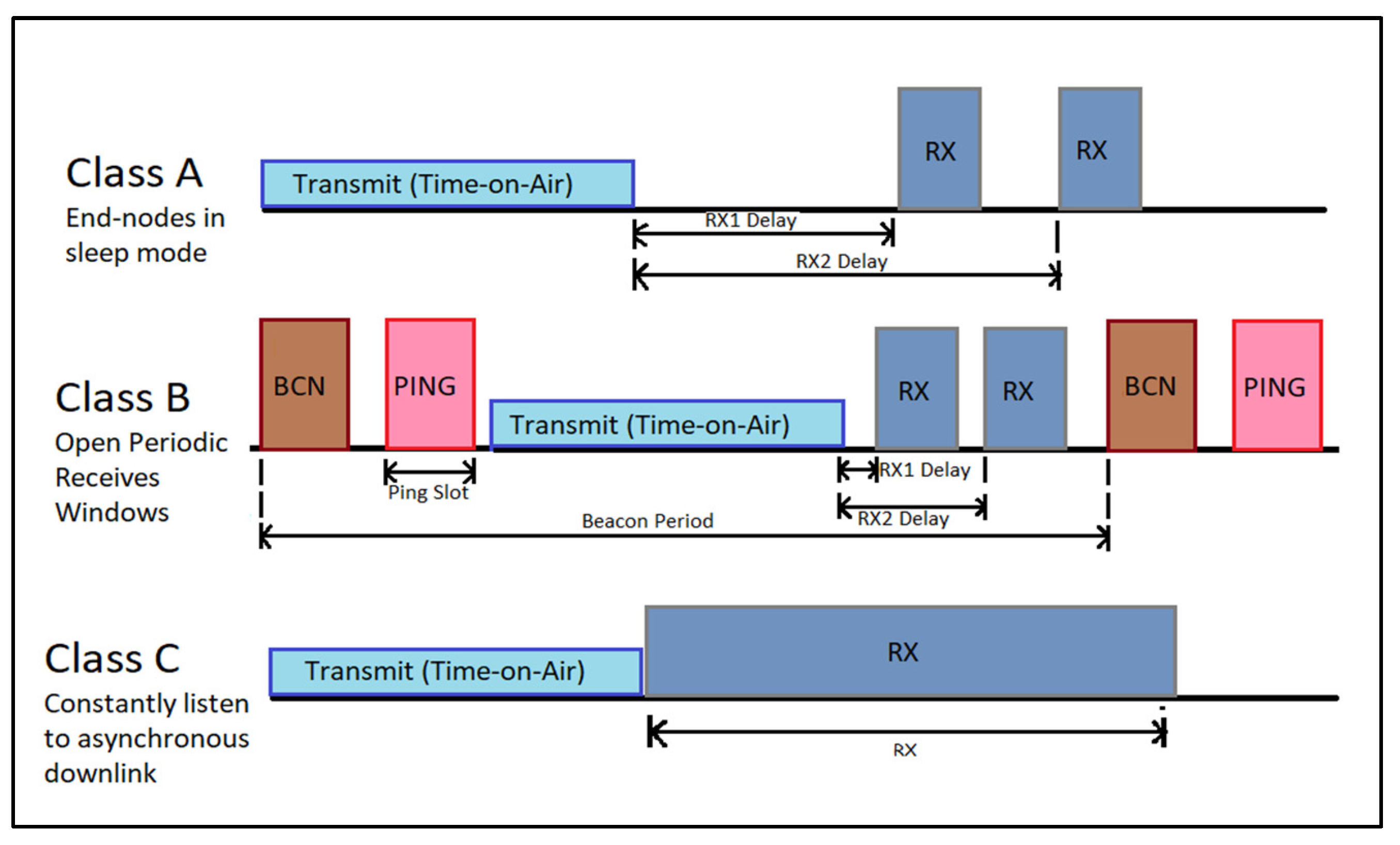
2.2.2. LoRaWAN
2.2.3. Implementation of LoRa in Application from the Previous Study
2. Methodology
3.1. Water Quality Monitoring System Built
3.2. LoRa Gateway Configuration
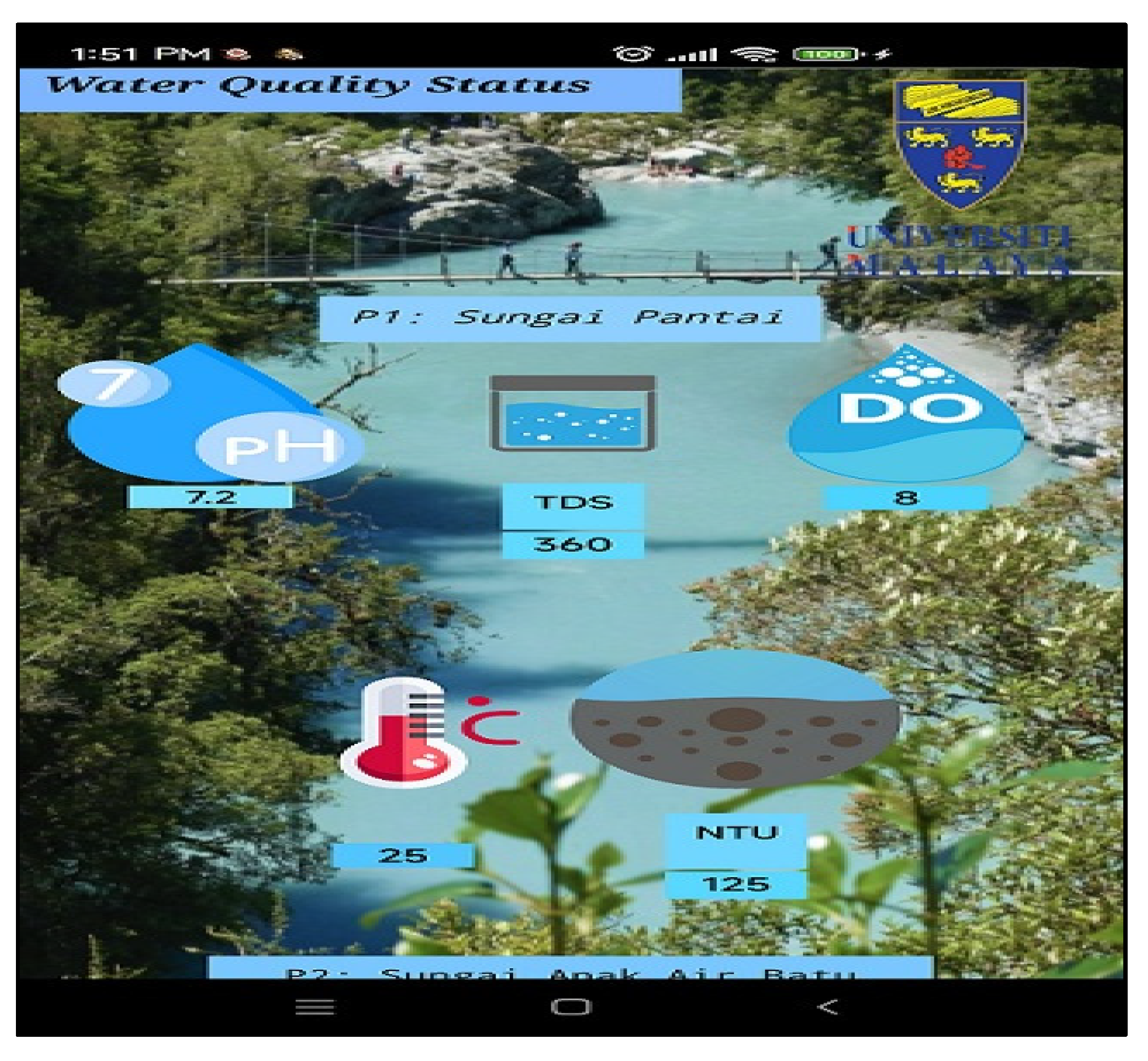
3.3. Water Quality Monitoring Dashboard
3.4. Evaluation of LoRa Performance
4. Result and Discussion
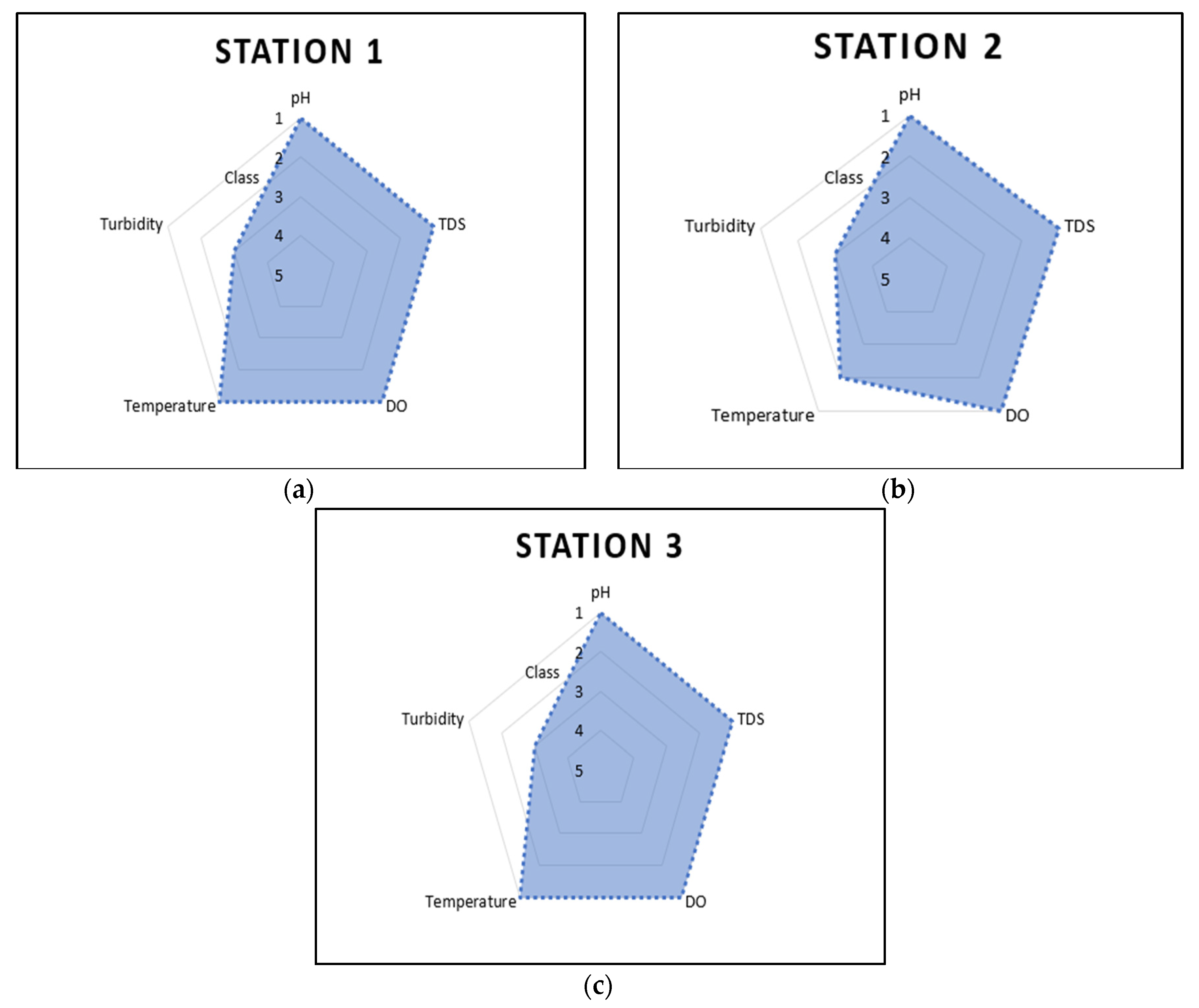
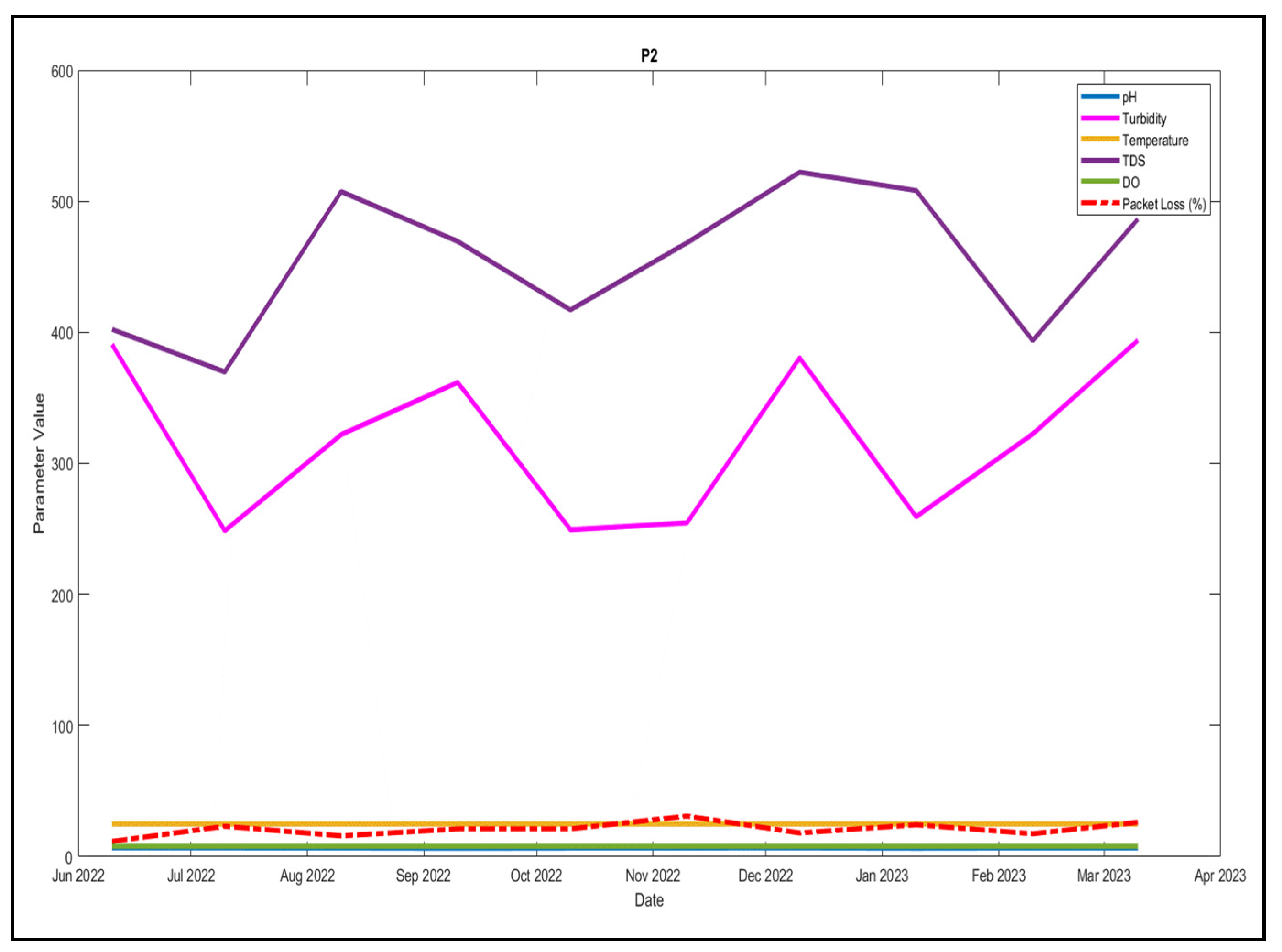
4.1. Water Quality Data
4.2. LoRa Network Performance
4.2.1. RSSI and SNR
4.2.2. Packet Loss
4.2.3. Path Loss
4.2.4. Received Power
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karen Bakker, Max Ritts, Smart Earth: A meta-review and implications for environmental governance, Global Environmental Change, Volume 52, 2018, Pages 201-211.
- Q. Zhou, K. Zheng, L. Hou, J. Xing and R. Xu, "Design and Implementation of Open LoRa for IoT," in IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 100649-100657, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Obaideen, K. et al. (2022) ‘The role of wastewater treatment in Achieving Sustainable Development Goals (sdgs) and sustainability guideline’, Energy Nexus, 7, p. 10 0112. [CrossRef]
- Academics, S.M. (2020) Roadmap for the national agenda on water sector transformation 2040, 2020 Annual Report Academy of Sciences Malaysia. (Chapter 1: pp 2).
- A. R. Haliza. (2021). A Review on Water Issues in Malaysia. International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science (2147-4478). 11. 860-875. 10.6007/IJARBSS/v11-i8/10783.
- N. Hassan Omer, ‘Water Quality Parameters’, Water Quality - Science, Assessments and Policy. IntechOpen, Jul. 29, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Gafri, Hasan & Mohamed Zuki, Fathiah & Mohamad, Zeeda & Nasaruddin, Affan & Sulaiman, Abdul & Norasiah, Siti. (2018). A study on water quality status of Varsity Lake and 1 Pantai River, Anak Air Batu River in UM Kuala Lumpur, 2 Malaysia and classify it based on (WQI) Malaysia. EQA. 29. 10.6092/issn.2281-4485/7967.
- Cham, H. et al. (2020) ‘Web-based system for visualisation of Water Quality index’, All Life, 13(1), pp. 426–432. [CrossRef]
- Keshipeddi, S.B. (2021) ‘IOT based Smart Water Quality Monitoring System’, SSRN Electronic Journal [Preprint]. [CrossRef]
- Karen Bakker, Max Ritts, Smart Earth: A meta-review and implications for environmental governance, Global Environmental Change, Volume 52, 2018, Pages 201-211,.
- Faber, M.J. et al. (2020) ‘A theoretical and experimental evaluation on the performance of Lora Technology’, IEEE Sensors Journal, 20(16), pp. 9480–9489. [CrossRef]
- Zourmand, A. et al. (2019) ‘Internet of things (IOT) using Lora Technology’, 2019 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Control and Intelligent Systems (I2CACIS) [Preprint]. [CrossRef]
- Bedi, G. et al. (2018) ‘Review of internet of things (IOT) in Electric Power and Energy Systems’, IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 5(2), pp. 847–870. [CrossRef]
- Moldobaeva, M. (2019) ‘Water quality monitoring by implementing zigbee network wireless sensors’, International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation, 23(4), pp. 1403–1413. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. , Chen, X. and Gu, D. (2018) ‘Design of water quality monitoring system for aquaculture based on Zigbee’, DEStech Transactions on Computer Science and Engineering [Preprint], (iceiti). [CrossRef]
- Dilshad, A., & Abishek, K. (2018). IoT based Smart River Monitoring System. International Of Advanced Research, Ideas and Innovation in Technology, 4(2), 60-64.
- Naj, N. and Sanzgiri, A. (2021) ‘An IOT based real-time monitoring of water quality system’, SSRN Electronic Journal [Preprint]. [CrossRef]
- Joseph Bryan G., I. , Meo Vincent C., C., Jen, A., Magno Christian Lemuel, S., Villaruel, K., Villeza, S., & Zaliman, S. (2018). Water Quality Monitoring System Using 3G Network. Journal Of Telecommunication, Electronic and Computer Engineering, 10(1-13), 15-18.
- BAFWAC-Ericsson. (2017). Using smart technology to monitor Stockholm’s water systems [Ebook] (pp. 3-5). Stockholm. Retrieved: https://ceowatermandate.org/wpcontent/uploads/2017/11/BAFWAC_-_Ericcson_11.2.pdf.
- Wu, Y., He, Y. and Shi, L. (2020) ‘Energy-saving measurement in Lorawan-based wireless sensor networks by using compressed sensing’, IEEE Access, 8, pp. 49477–49486. [CrossRef]
- RP002-1.0.0 LoRaWAN® Regional 49 Parameters. Fremont, California: LoRa Alliance, 2019, pp. 21-22, 83-86.
- Q. M. Qadir, "Analysis of the Reliability of LoRa," in IEEE Communications Letters, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 1037-1040, 21. 20 March. [CrossRef]
- Petajajarvi J, Mikhaylov K, Pettisalo M, et al. Performance of low-power wide-area network based on LoRa technology: Doppler robustness, scalability and coverage. Int J Distr Sensor Networks. 2017;13(13):155014771769941.
- Oliveira, R.; Guardalben, L.; Sargento, S. Long range communications in urban and rural environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC), Heraklion, Greece, 3–6 July 2017; pp. 810–817. [Google Scholar]
- "An In-depth Look at LoRaWAN® Class B Devices | DEVELOPER PORTAL", Lora-developers.semtech.com. [Online]. Available: https://lora-developers.semtech.com/library/tech-papers-and-guides/lorawan-class-b-devices/.
- M. Ertürk, M. Aydın, M. Büyükakkaşlar and H. Evirgen, "A Survey on LoRaWAN Architecture, Protocol and Technologies", Future Internet, vol. 11, no. 10, p. 216, 2019.
- Delobel, F.; Rachkidy, N.E.; Guitton, A. Analysis of the Delay of Confirmed Downlink Frames in Class Bof LoRaWAN. In Proceedings of the IEEE 85th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Sydney,Australia, 4–7 June 2017. pp. 1–6.
- Paredes, M., Bertoldo, S., Carosso, L., Lucianaz, C., Marchetta, E., Allegretti, M., & Savi, P. (2019). Propagation measurements for a LoRa network in an urban environment. Journal Of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 33(15), 2022-2036. [CrossRef]
- Rizzi M, Ferrari P, Flammini A, et al. Evaluation of the IoT LoRaWAN solution for Distributed measurement applications. IEEE Trans Instr. and Meas. 2017;66(12):3340–3349.
- E. Leon, C. Alberoni, M. Wister and J. Hernández-Nolasco, "Flood Early Warning System by Twitter Using LoRa", Proceedings, vol. 2, no. 19, p. 1213, 2018.
- G. Codeluppi, A. Cilfone, L. Davoli and G. Ferrari, "LoRaFarM: A LoRaWAN-Based Smart Farming Modular IoT Architecture", Sensors, vol. 20, no. 7, p. 2028, 2020.
- M. Abbasi, S. Khorasanian and M. Yaghmaee, "Low-Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) for Smart grid: An in-depth study on LoRaWAN", 2019 5th Conference on Knowledge Based Engineering and Innovation (KBEI), 2019.
- Prakosa, S.W. et al. (2021) ‘Design and implementation of Lora based IOT scheme for Indonesian Rural Area’, Electronics, 10(1), p. 77. [CrossRef]
- J. Lousado and S. Antunes, "Monitoring and Support for Elderly People Using LoRa Communication Technologies: IoT Concepts and Applications", Future Internet, vol. 12, no. 11, p. 206, 2020.
- S. N. S. Tahatahir et al., "IoT Architecture Based Water Resources Conservation Management Using LoRa," 2021 International Conference on Smart City and Green Energy (ICSCGE), Hangzhou, China, 2021, pp. 63-68. [CrossRef]
- Jáquez, A.D. et al. (2023) ‘Extension of Lora coverage and integration of an unsupervised anomaly detection algorithm in an IOT water quality monitoring system’, Water, 15(7), p. 1351. [CrossRef]
- Wei Chen, Xiao Hao, JianRong Lu, Kui Yan, Jin Liu, ChenYu He, Xin Xu, "Research and Design of Distributed IoT Water Environment Monitoring System Based on LoRa", Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, vol. 2021, Article ID 9403963, 13 pages, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A. , Adilah, N. and Salimi, I. (2019) ‘Performance of lora network for environmental monitoring system in Bidong Island Terengganu, Malaysia’, International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 10(11). [CrossRef]
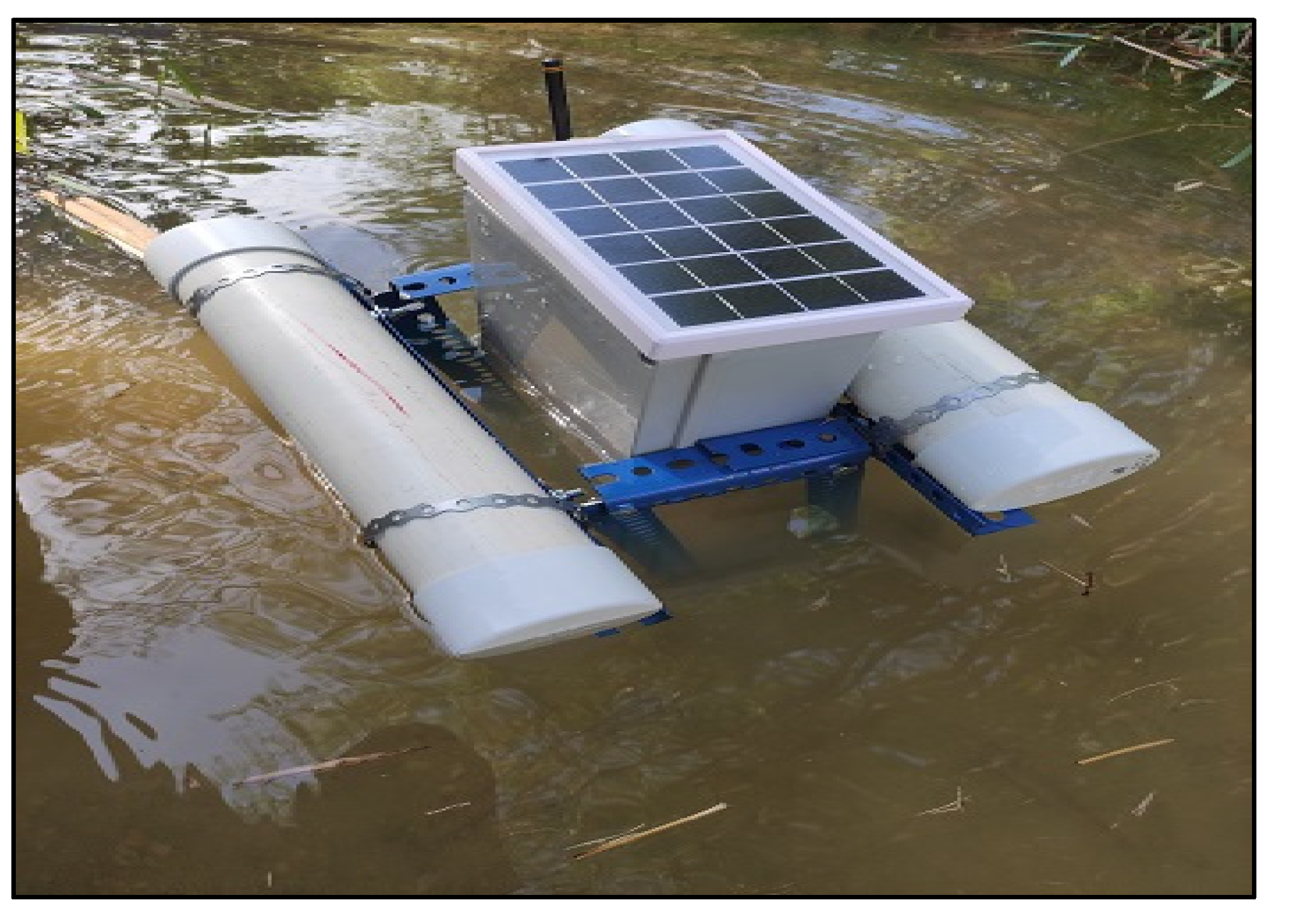
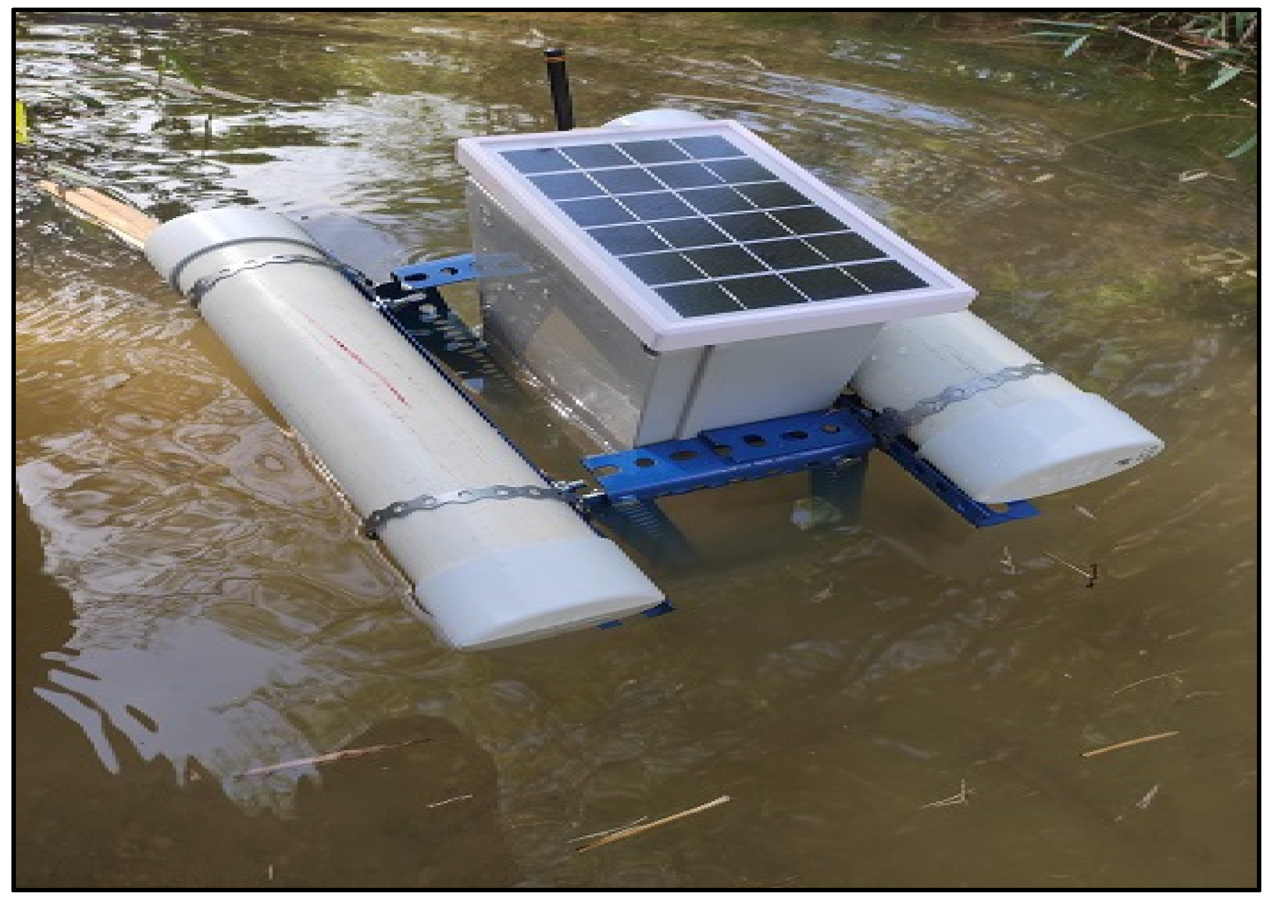








| Water Quality Sensor | Functions |
|---|---|
| Dissolved Oxygen | Examine the amount of oxygen volume for aquatic life |
| Temperature | Variables for other water properties |
| Turbidity | Water opacity |
| pH Meter | Acidification |
| TDS | Salinity and Total Dissolved Solids for Conductivity |
| Parameter | Setup | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Spread Factor | 7 | 9 | 12 |
| Bandwidth (kHz) | 125 | ||
| Frequency Plan | 868/915 MHz | ||
| Transmitted Power (dBm) | 14 | ||
| Antenna Gain (dBi) Data Transfer Rate (kbps) |
2.1 | ||
| 5.47 | 1.758 | 0.25 | |
| Parameter | Setup | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Spread Factor | 7 | 9 | 12 |
| Bandwidth (kHz) | 125 | ||
| Frequency Plan | 868/915 MHz | ||
| Transmitted Power (dBm) | 14 | ||
| Antenna Gain (dBi) | 3 | ||
| Data Transfer Rate (kbps) | 5.47 | 1.758 | 0.25 |
| Water Station | pH | Turbidity (NTU) |
Temperature (°C) |
Total Dissolved Solid (mg/l) |
Dissolved Oxygen (mg/l) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
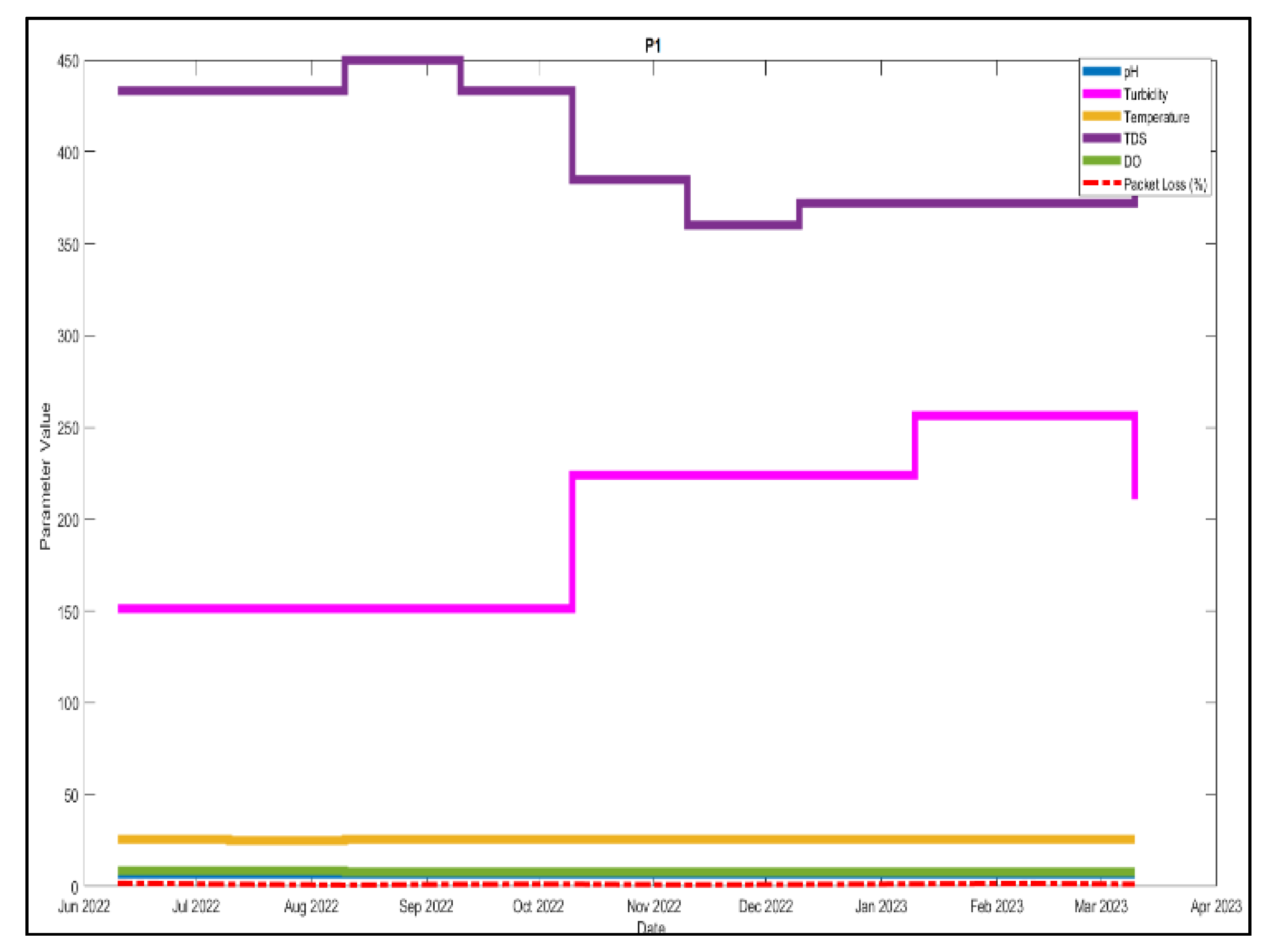
| P1 | 6.9777 | 213.2889 | 25.4 | 434.1407 | 8.1036 |
| P2 | 6.6643 | 285.4009 | 27.57 | 440.4035 | 7.0559 |
| P3 | 6.9985 | 183.0859 | 25.1 | 346.0336 | 7.9974 |
| Antenna Gain (dBi) |
Water Station | Distance (m) |
SF | Maximum (dBm) |
Minimum (dBm) |
Mean (dBm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | P1 | 117 | 7 | -98 | -111 | -99.22 |
| 9 | -92 | -102 | -97.04 | |||
| 12 | -87 | -93 | -90.14 | |||
| P2 | 1560 | 7 | -115 | -118 | -116.73 | |
| 9 | -112 | -118 | -113.88 | |||
| 12 | -102 | -115 | -109.4 | |||
| P3 | 566 | 7 | -110 | -113 | -111.74 | |
| 9 | -105 | -113 | -107.92 | |||
| 12 | -97 | -109 | -102.87 | |||
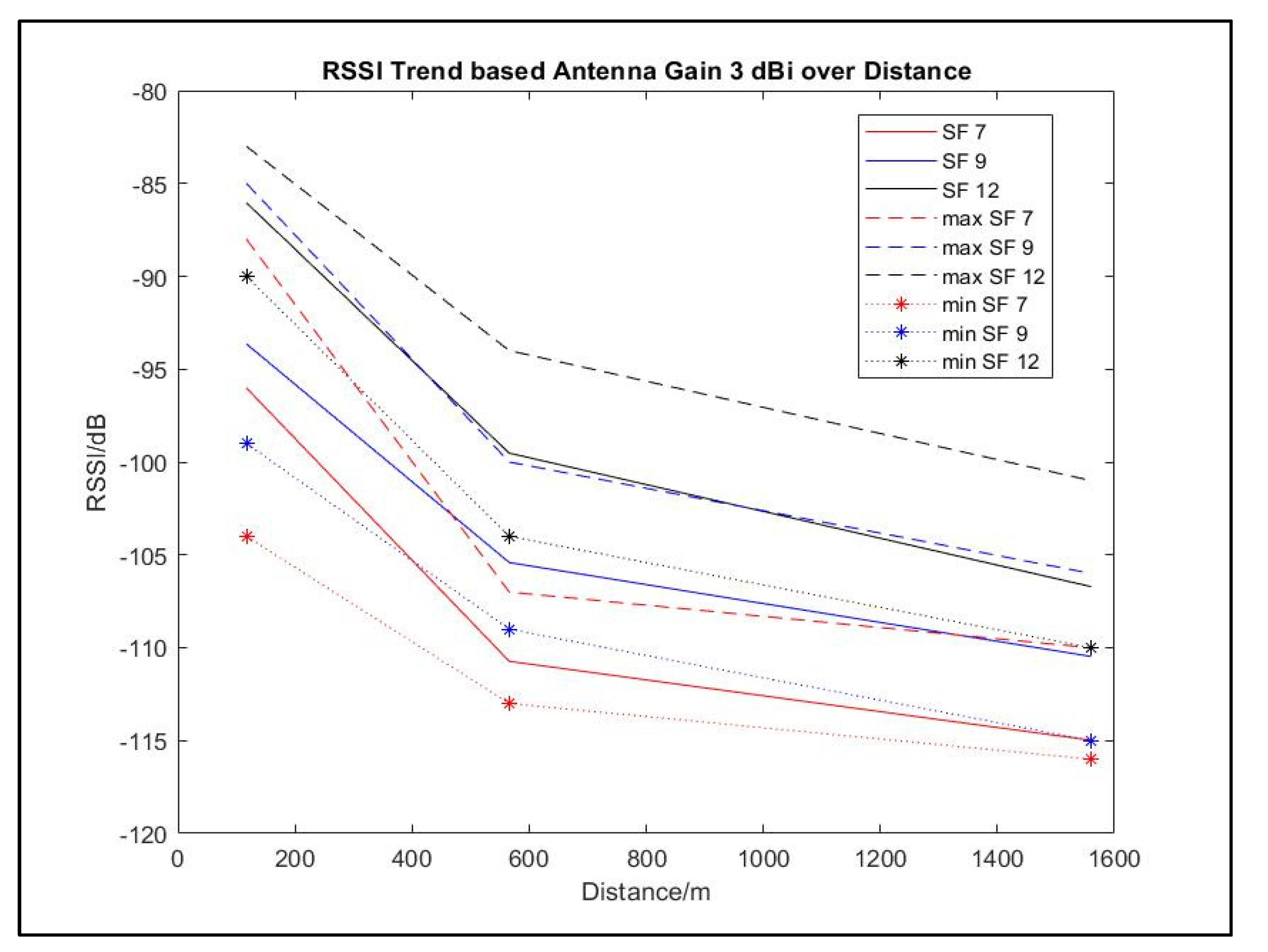
| 3 | P1 | 117 | 7 | -88 | -104 | -96.01 |
| 9 | -85 | -99 | -93.64 | |||
| 12 | -83 | -90 | -86.04 | |||
| P2 | 1560 | 7 | -110 | -116 | -114.98 | |
| 9 | -106 | -115 | -110.47 | |||
| 12 | -101 | -110 | -106.71 | |||
| P3 | 566 | 7 | -107 | -113 | -110.73 | |
| 9 | -100 | -109 | -105.41 | |||
| 12 | -94 | -104 | -99.52 |
| Antenna Gain (dBi) |
Water Station | Distance (m) |
SF | Maximum (dBm) |
Minimum (dBm) |
Mean (dBm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
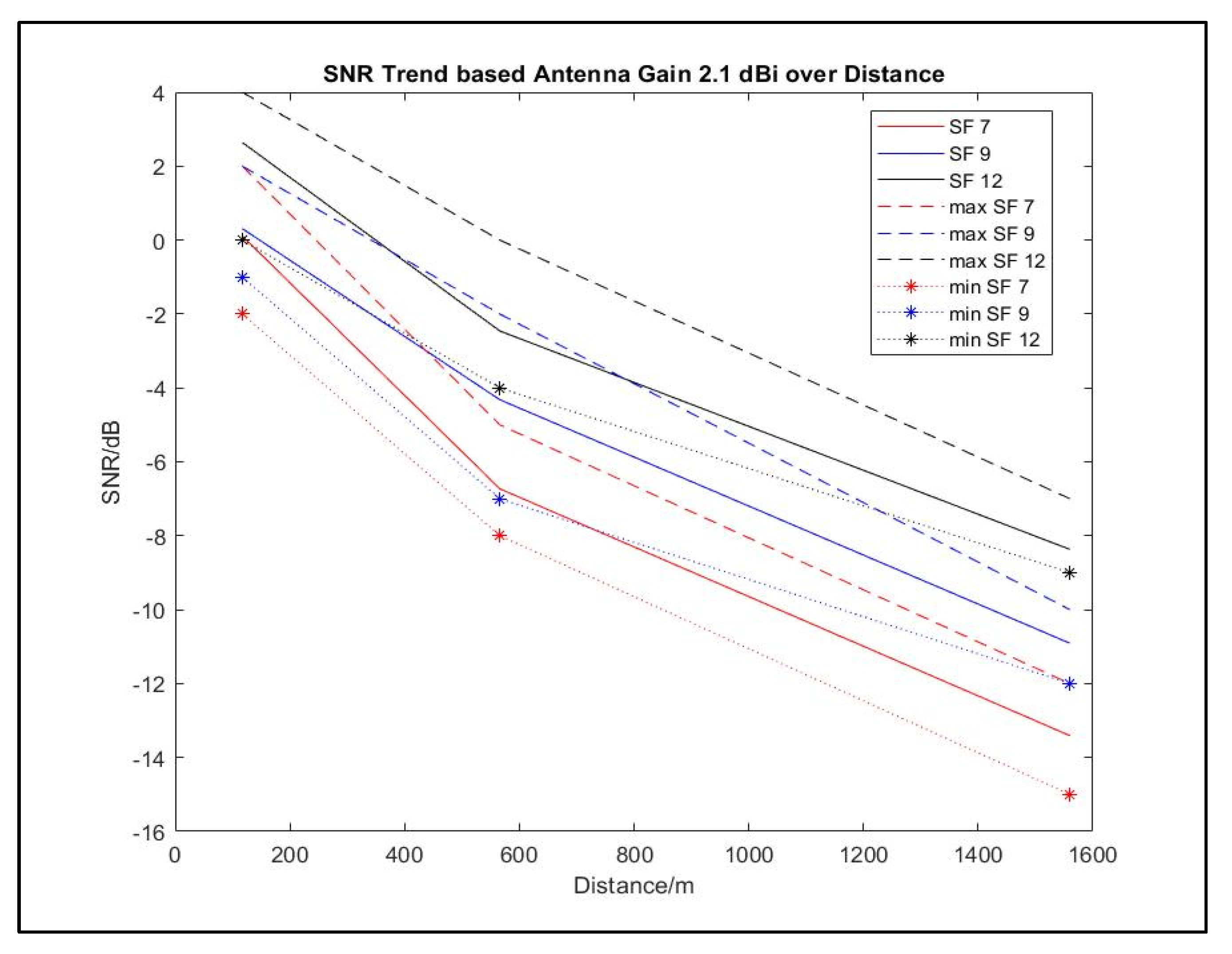
| 2.1 | P1 | 117 | 7 | 2 | -2 | 0.11 |
| 9 | 2 | -1 | 0.31 | |||
| 12 | 4 | 0 | 2.64 | |||
| P2 | 1560 | 7 | -12 | -15 | -13.41 | |
| 9 | -10 | -12 | -10.91 | |||
| 12 | -7 | -9 | -8.37 | |||
| P3 | 566 | 7 | -5 | -8 | -6.73 | |
| 9 | -2 | -7 | -4.32 | |||
| 12 | 0 | -4 | -2.46 | |||
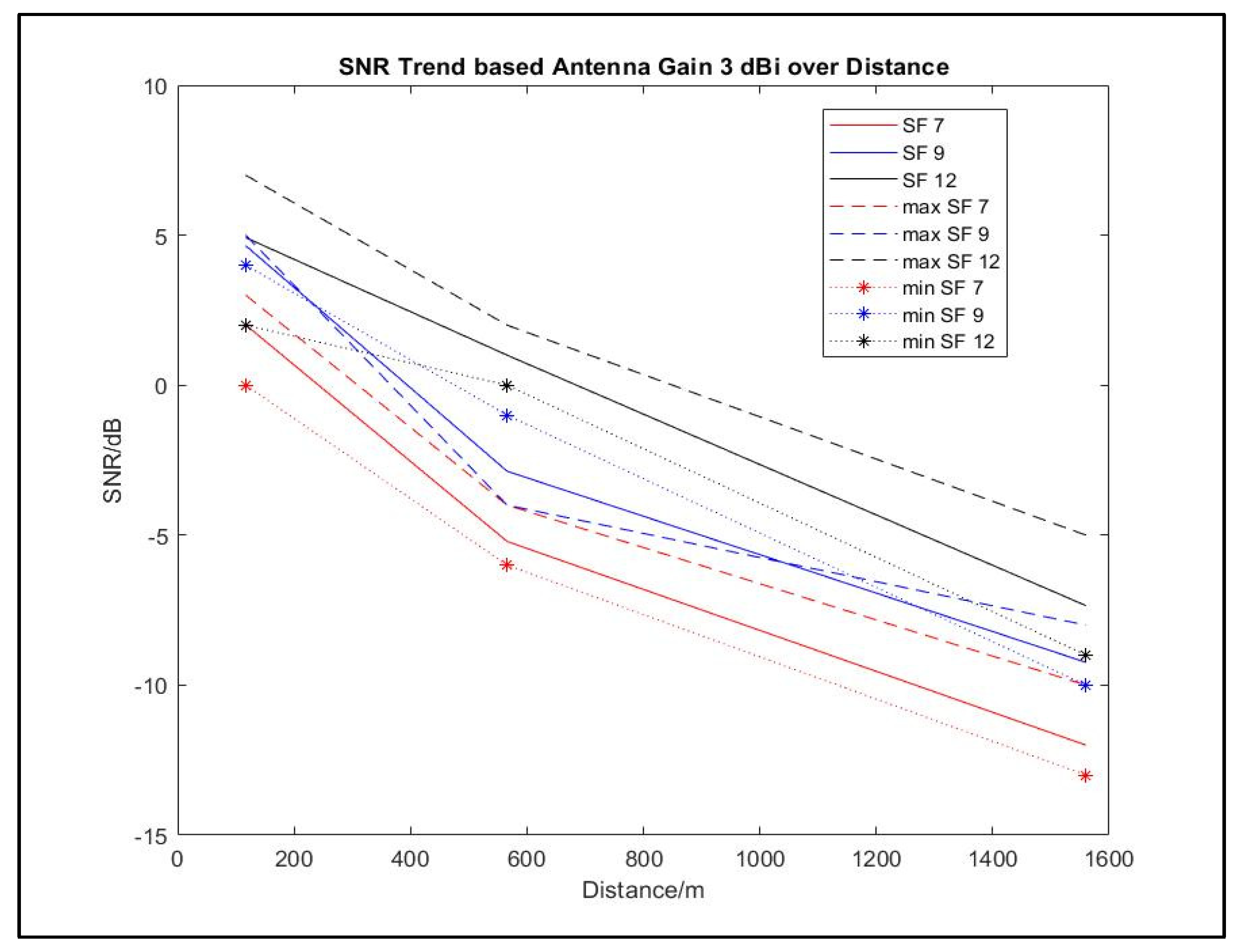
| 3 | P1 | 117 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 2.01 |
| 9 | 5 | 4 | 4.65 | |||
| 12 | 7 | 2 | 4.92 | |||
| P2 | 1560 | 7 | -10 | -13 | -12 | |
| 9 | -8 | -10 | -9.24 | |||
| 12 | -5 | -9 | -7.35 | |||
| P3 | 566 | 7 | -4 | -6 | -5.21 | |
| 9 | -4 | -1 | -2.87 | |||
| 12 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| Antenna Gain (dBi) |
Water Station | Distance (m) |
SF | Packet Loss % |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | P1 | 117 | 7 | 1.7 | |
| 9 | 1.2 | ||||
| 12 | 0.4 | ||||
| P2 | 1560 | 7 | 22 | ||
| 9 | 13 | ||||
| 12 | 15 | ||||
| P3 | 566 | 7 | 6 | ||
| 9 | 3.2 | ||||
| 12 | 2 | ||||
| 3 | P1 | 117 | 7 | 1.2 | |
| 9 | 0.3 | ||||
| 12 | < 0 | ||||
| P2 | 1560 | 7 | 10 | ||
| 9 | 5.4 | ||||
| 12 | 2.8 | ||||
| P3 | 566 | 7 | 3 | ||
| 9 | 2.2 | ||||
| 12 | 5 | ||||
| Antenna Gain (dBi) |
Water Station | Distances (m) | Path Loss FSDP (dB) |
Path Loss Oku-Hata (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | P1 | 117 | 65.31 | 88.21 |
| P2 | 1560 | 83.61 | 127.34 | |
| P3 | 566 | 74.81 | 112.03 | |
| 3 | P1 | 117 | 64.41 | 88.21 |
| P2 | 1560 | 82.71 | 127.34 | |
| P3 | 566 | 73.91 | 112.03 |
| Antenna Gain (dBi) |
Station | Distances (m) | Received Sensitivity (dBm) |
Received Power (dBm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | P1 | 117 | -116.72 | -109.65 |
| P2 | 1560 | -127.9 | -120.75 | |
| P3 | 566 | -121.35 | -113.86 | |
| 3 | P1 | 117 | -118.58 | -108.34 |
| P2 | 1560 | -129.1 | -118.02 | |
| P3 | 566 | -122.98 | -112.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





