Submitted:
23 May 2024
Posted:
24 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Membranes: Requirements, Types, Classification, and Separation Mechanisms
1.1. Requirements of Membranes
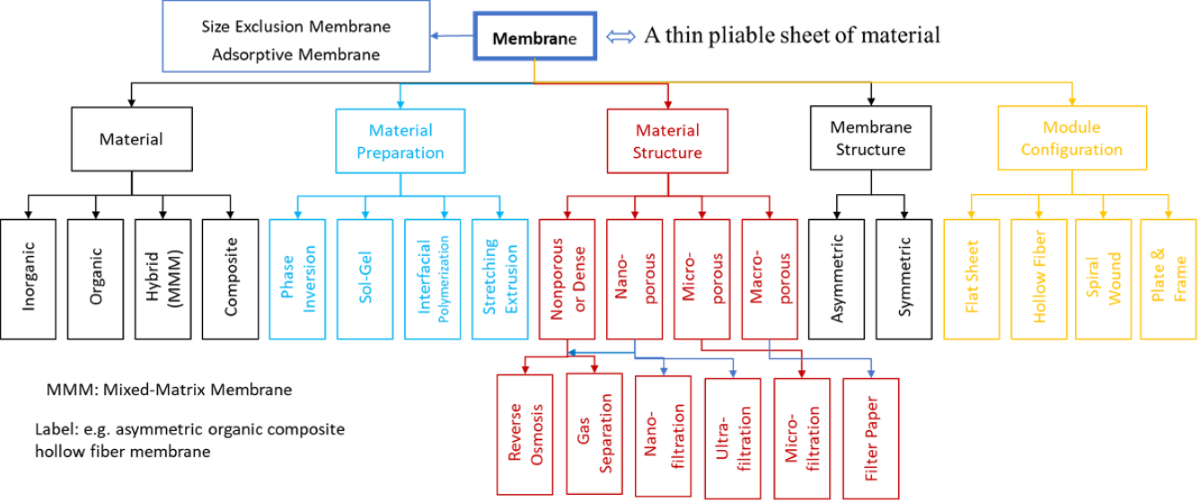
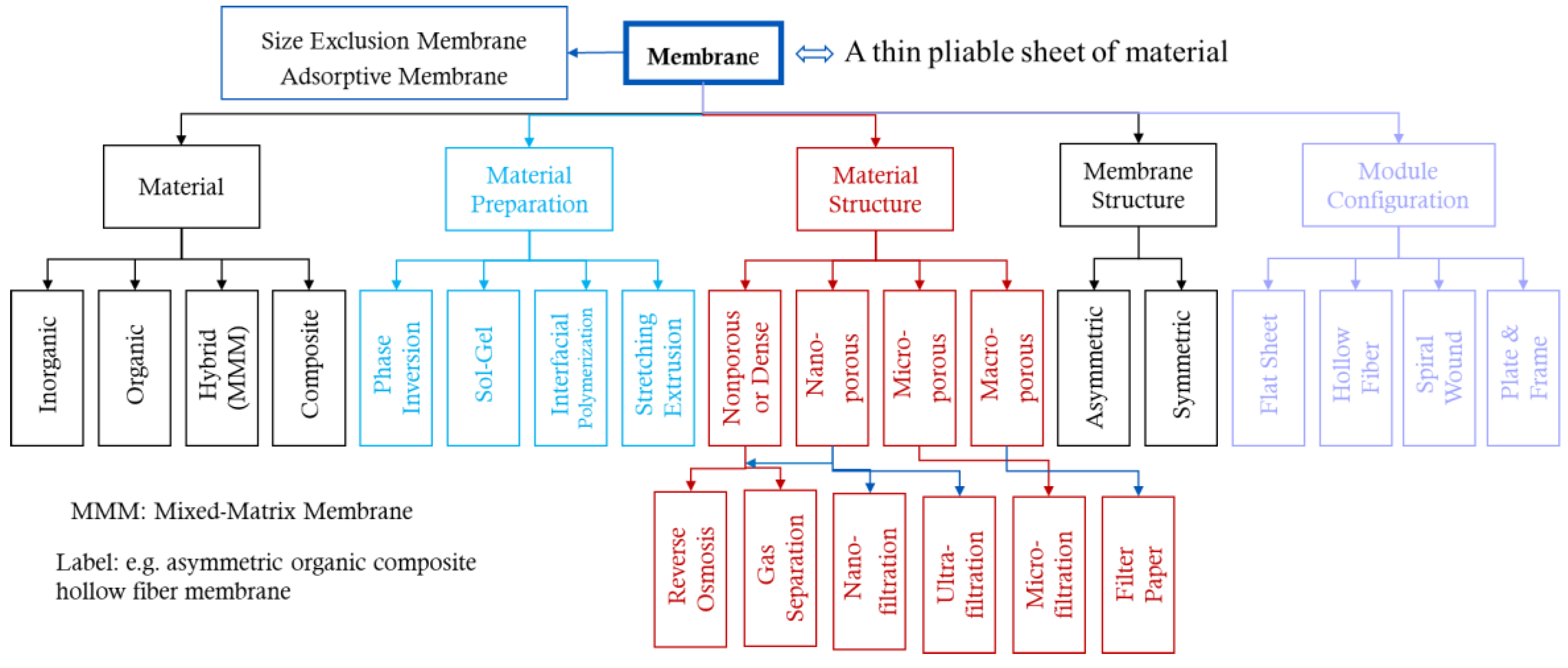
1.2. Types and Classification
| Size Range | Terminology |
|
Nanoscale 1-100 nm |
nanoparticles, nanomaterial, electrospun nanofibers, nanofibrils, nanocrystals, nanoporous, nanopores, nanofiltration (1-2 nm), ultrafiltration (2-100 nm) |
|
Microscale 100 nm - 10 µm |
microfibrils, microcrystals, microfibers, electrospun microfibers, fibrils, crystallites, microporous, micropores |
|
Macroscale >10 µm |
fibers, electrospun fibers, crystals, microporous, macropores |
1.3. Molecules and Particle Separation Mechanisms
1.4. Factors Affecting Permeation (Permeance and Selectivity)
| H₂O | H₂ | CO₂ | O₂ | H₂S | N₂ | CO | CH₄ | C₂H₆ | |
| Kinetic diameter (nm)* | 0.265 | 0.289 | 0.33 | 0.346 | 0.36 | 0.364 | 0.376 | 0.38 | 0.43 |
| Critical temperature (K)** | 647.1 | 33.2 | 304.2 | 154.6 | 373.5 | 126.2 | 133.2 | 190.6 | 305.3 |
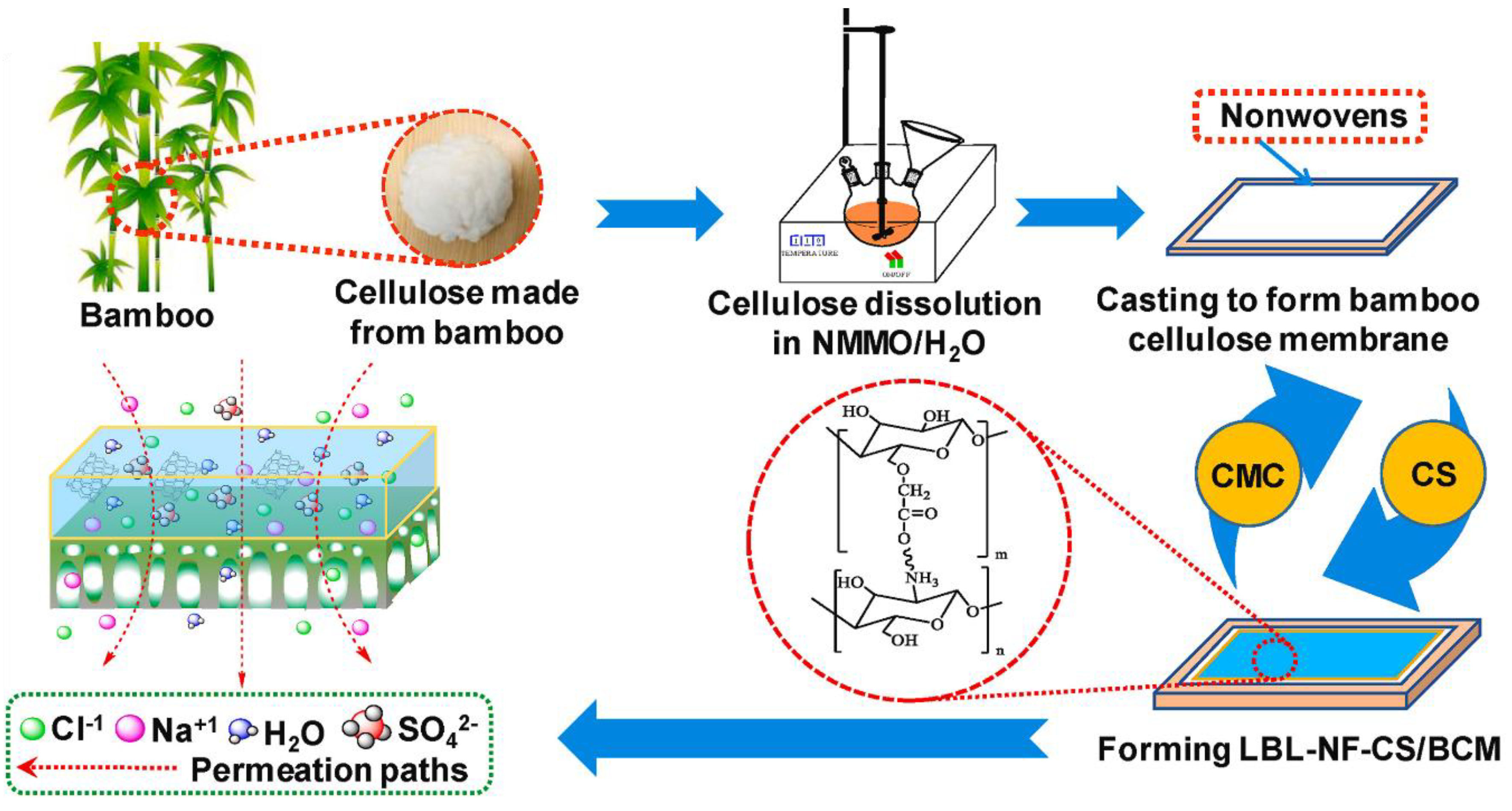
2. Cellulose Membranes
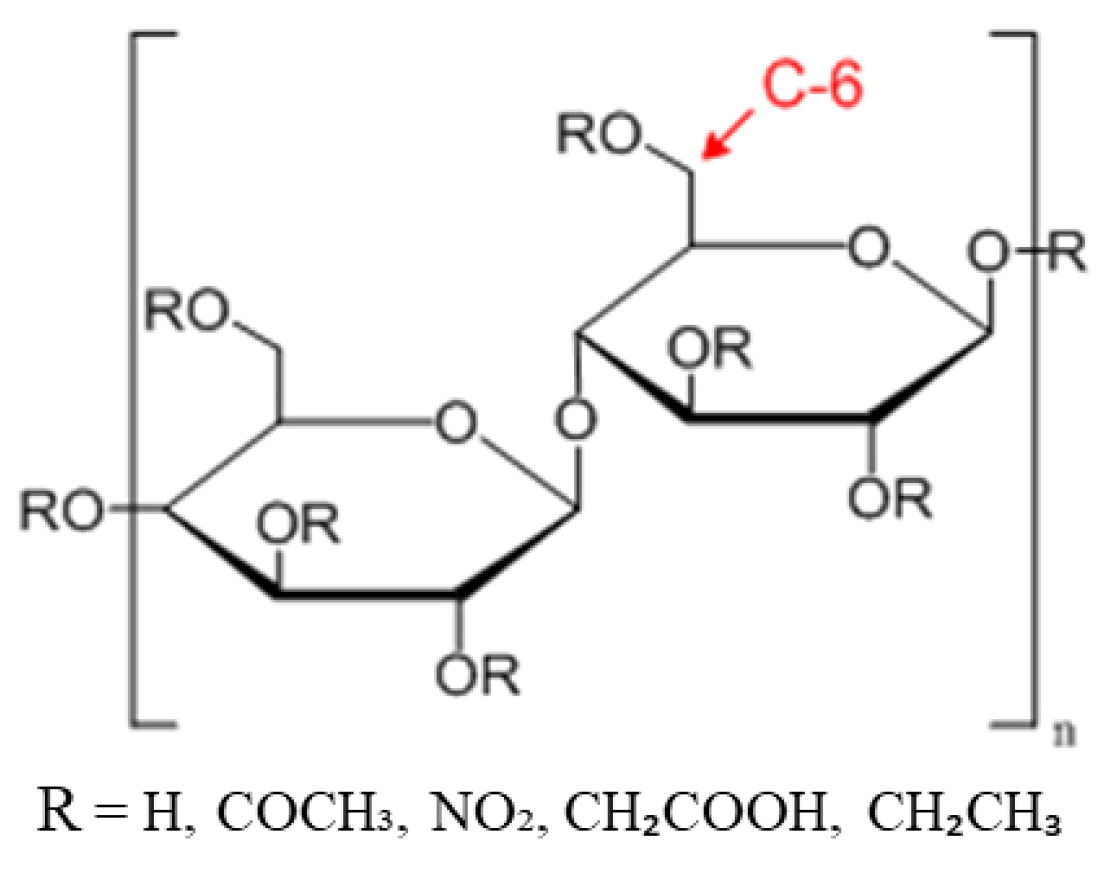
2.1. Cellulose Forms
2.2. Cellulosic Membrane Classification
- ❖
-
Cellulose membranes made from the solution of cellulose and cellulose derivatives
- ✓
- Regenerated cellulose membranes
- ✓
-
Cellulose derivative membranes
- ∘
- Cellulose acetate membranes
- ∘
- Cellulose nitrate membranes
- ∘
- Ethyl cellulose membranes
- ∘
- Composite membranes
- ❖
-
Cellulose membranes made from cellulose particles
- ✓
- Cellulose fiber filters
- ✓
- Electrospun cellulose nanofiber membranes
- ✓
-
Nanocellulose membranes
- ∘
- Cellulose nanofibril membranes
- ∘
- Cellulose nanocrystal membranes
- ✓
-
Composite membranes
- ∘
- Cellulose particle-reinforced polymer membranes
- ∘
- Polymer fiber-reinforced cellulose membranes
2.3. Potential of Cellulose as a Material for Membranes
3. Preparation and Structure of Cellulosic Membranes through Dissolution
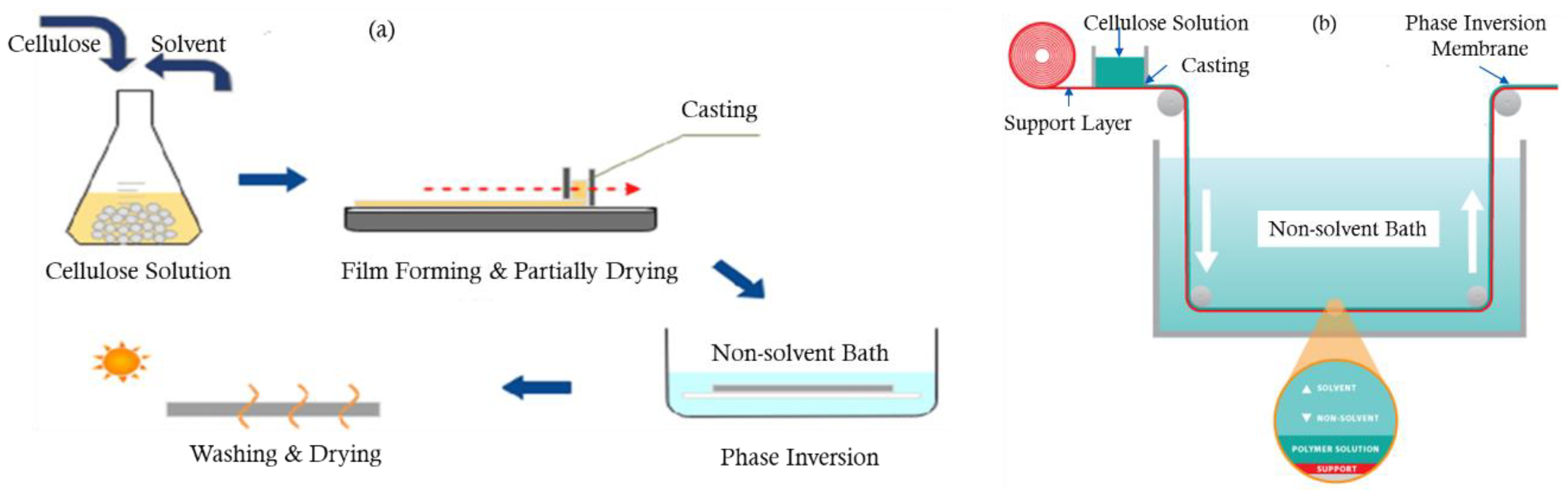
3.1. Phase Inversion
3.2. Structure of Phase Inversion Membranes
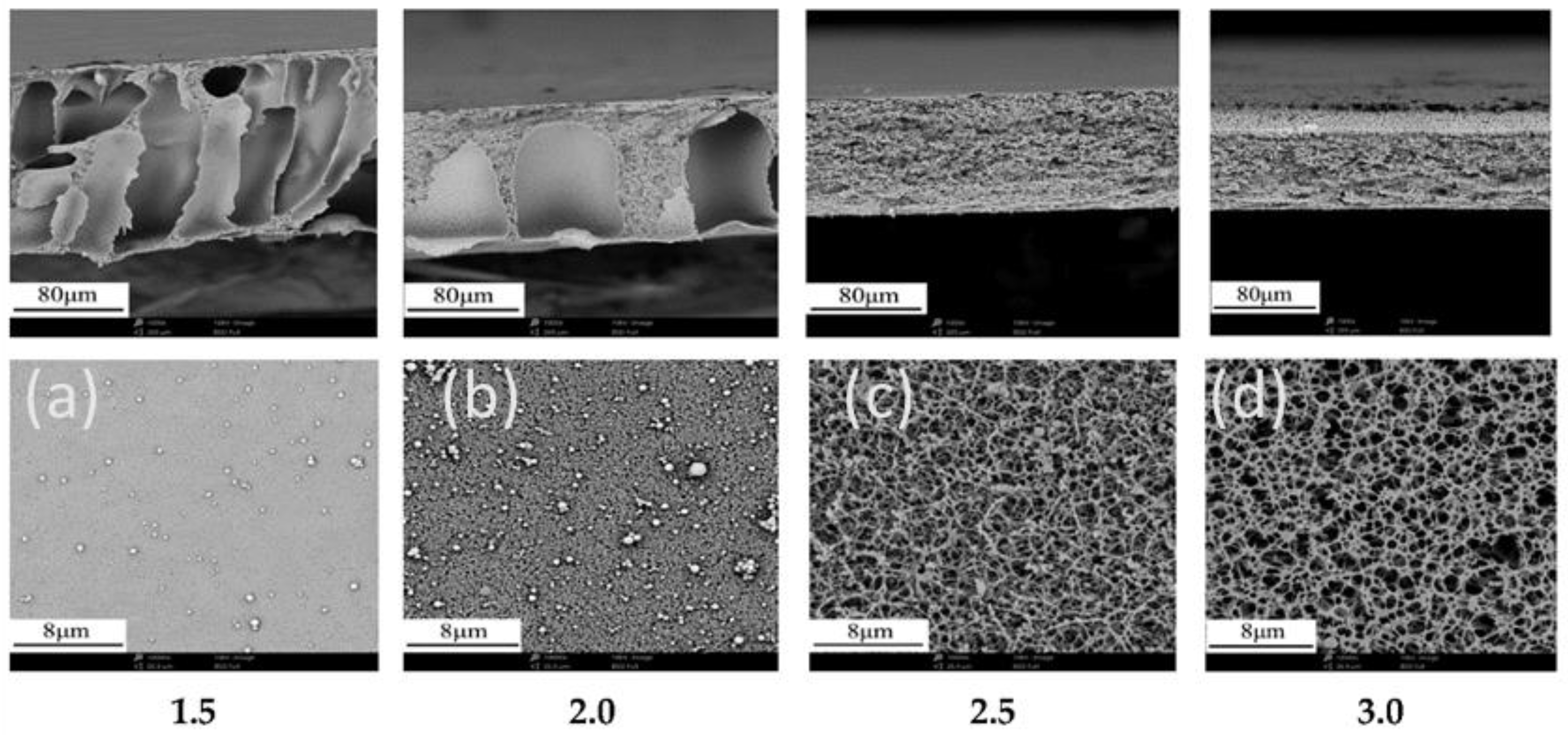
3.3. Factors Affecting Structure and Properties of Phase Inversion Membranes
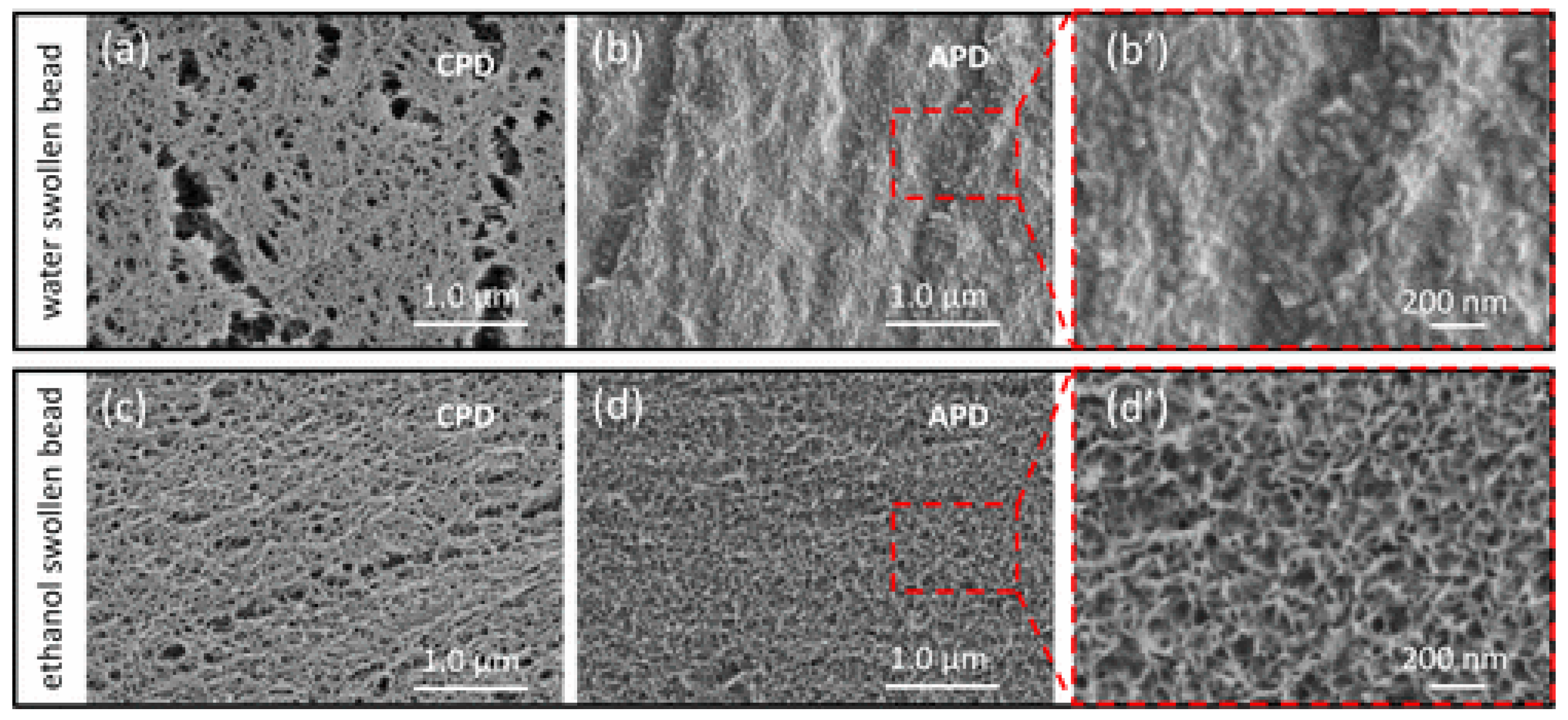
3.4. Regenerated Cellulose Membranes
3.5. Cellulose Acetate Membranes
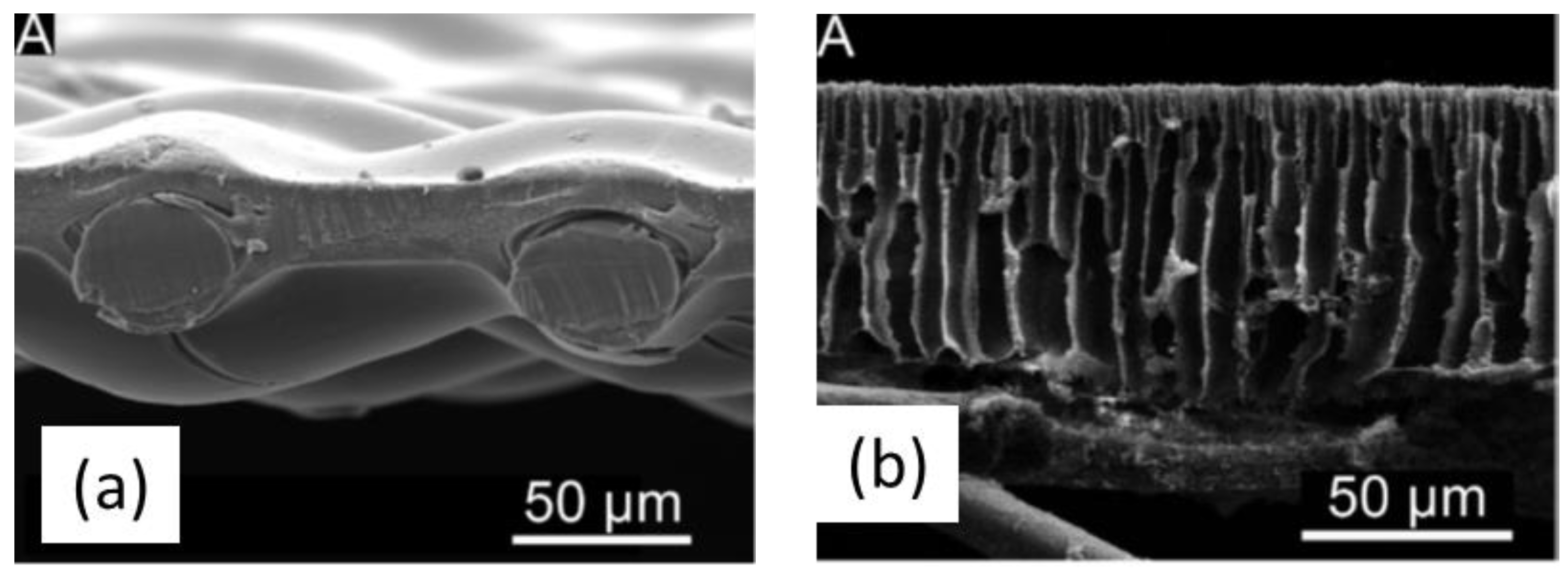
3.6. Other Cellulose Derivative Membranes
3.7. Composite Cellulosic Membranes
3.8. Water Vapor Separation Applications
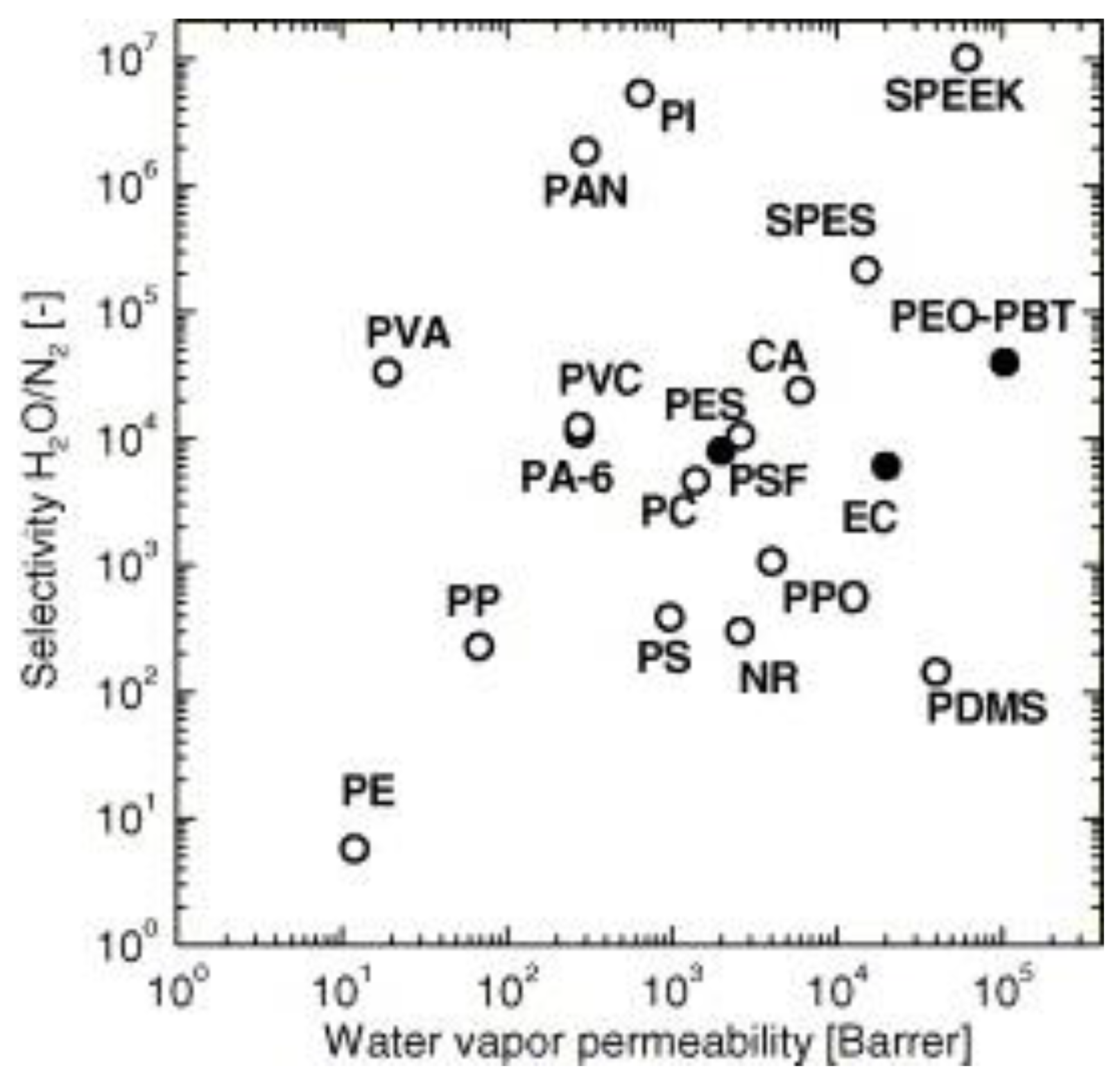
3.9. Carbon Dioxide Capture Applications
| Cellulosic material |
Permeability (Barrer) | Selectivity Coefficient | ||||||||
| H₂O | CO₂ | H₂ | O₂ | N₂ | H₂O/N₂ | CO₂/N₂ | H₂/N₂ | O₂/N₂ | ||
| Regenerated cellulose | 0%RH | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 0.7 | ||
| 43%RH | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 1.1 | |||
| 76%RH | 0.072 | 0.033 | 0.009 | 0.007 | 9.6 | 4.4 | 1.2 | |||
| 100%RH | 25,198 | 0.256 | 0.080 | 0.012 | 0.018 | 1,369,565 | 13.9 | 4.3 | 0.6 | |
| Dry* | 127.7 | 9.14 | 6.28 | 2.58 | 49.5 | 3.5 | 2.4 | |||
| Wet* | 1957.4 | 134.7 | 93.42 | 37.13 | 52.7 | 3.6 | 2.5 | |||
| Cellulose acetate** | 7,333 | 23.07 | 3.506 | 0.780 | 0.280 | 26,191 | 82.4 | 12.5 | 2.8 | |
| Cellulose nitrate | 6,293 | 2.120 | 2.000 | 1.947 | 0.116 | 54,253 | 18.3 | 17.2 | 16.8 | |
| Ethylcellulose | 8,933 | 113.1 | 87.06 | 14.67 | 4.426 | 2,018 | 25.5 | 19.7 | 3.3 | |
| Polydimethylsiloxane | 43,000 | 4651.6 | 939.9 | 926.6 | 470.6 | 91.4 | 9.9 | 2.0 | 2.0 | |
4. Nonwoven Membranes from Cellulose Particles
4.1. Types of Cellulose Particles
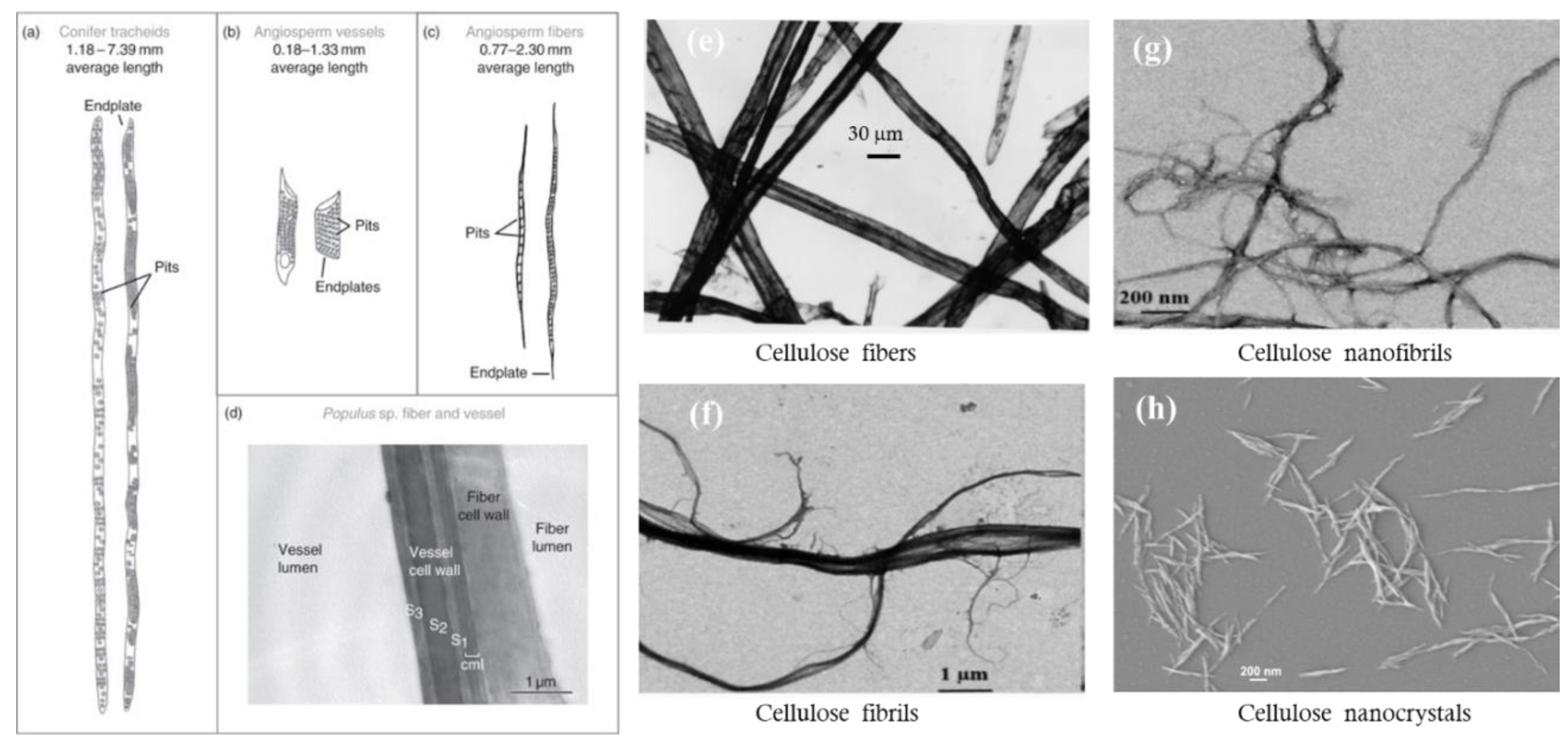
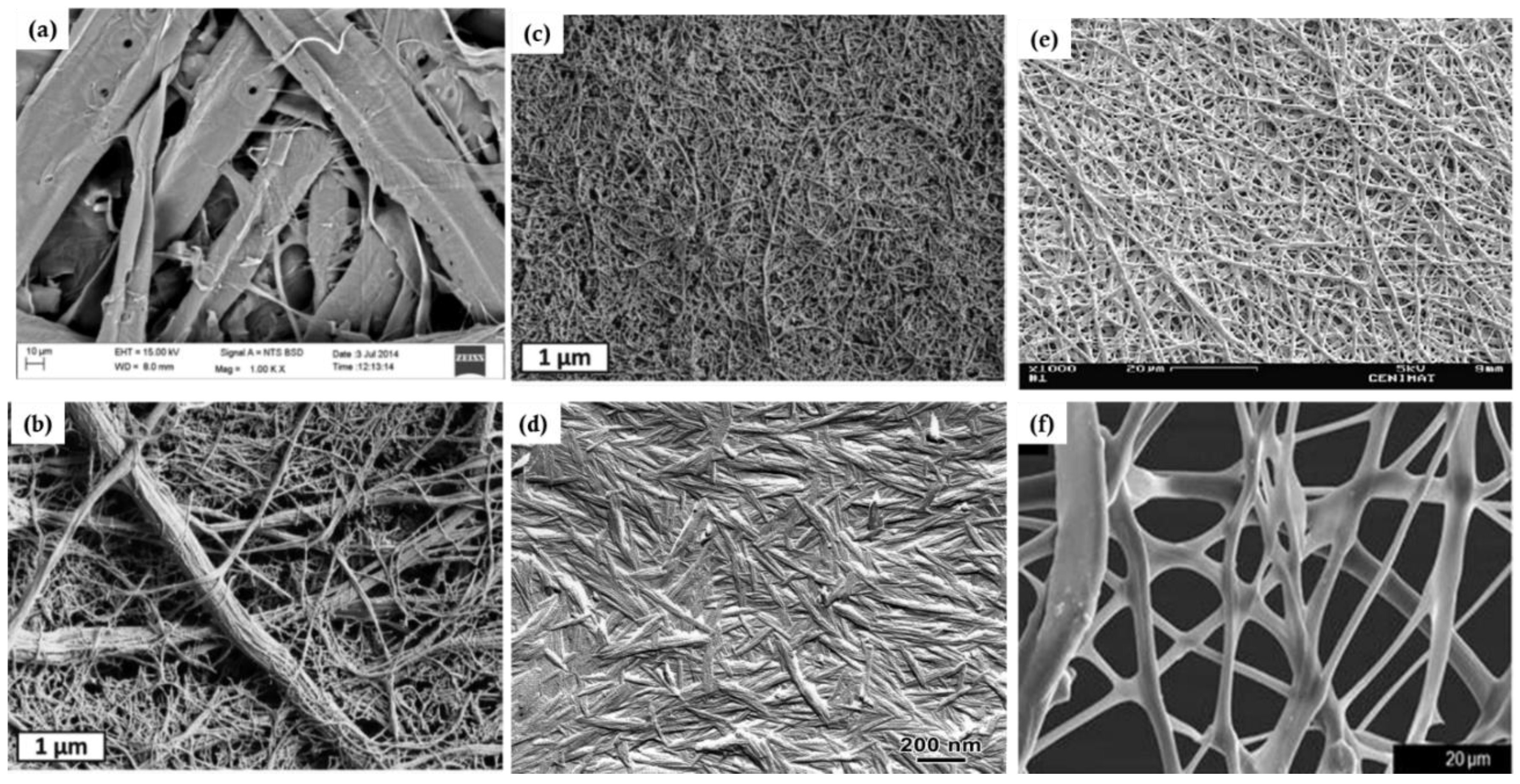
4.2. Impact of Particle Morphology on Pore Size and Porosity of Membrane Materials

4.3. Structure of Membrane Materials Made from Cellulose Particles
4.4. Processing-Structure Relationship of Cellulose Particle-Based Materials
4.5. Cellulose Particles-Based Membrane Structure Design
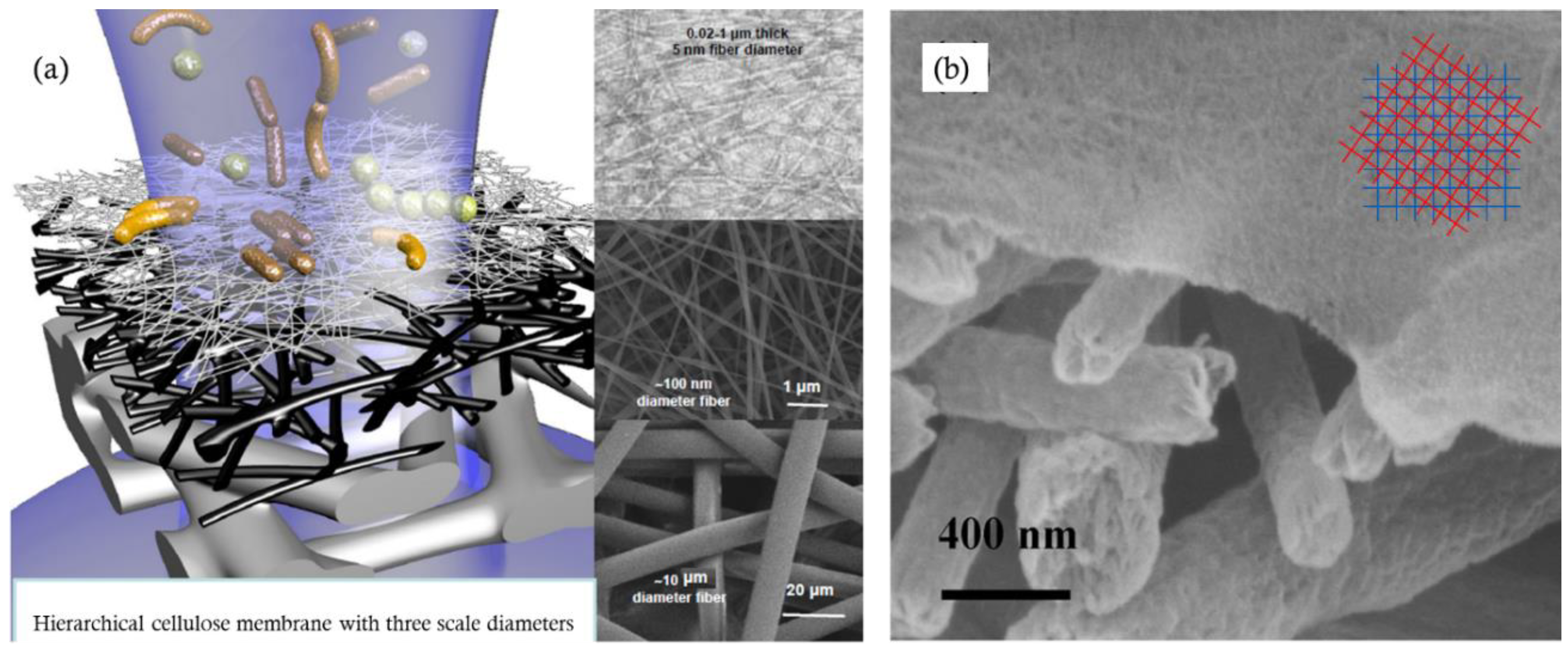
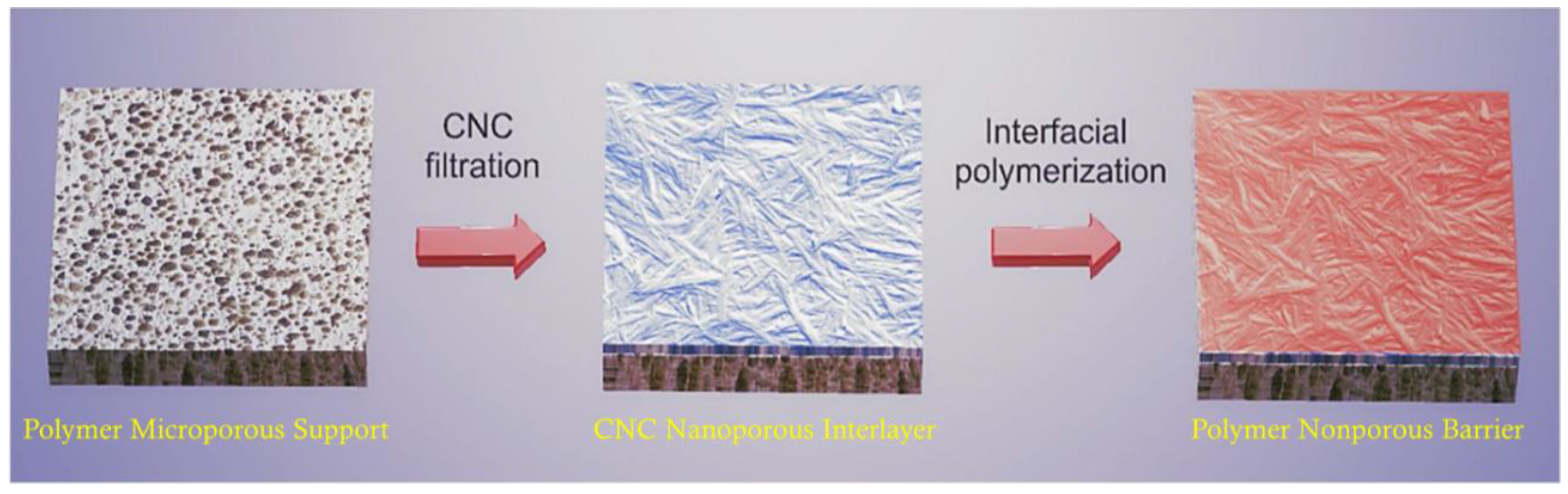
4.6. CNF Membranes
4.7. CNC Membranes
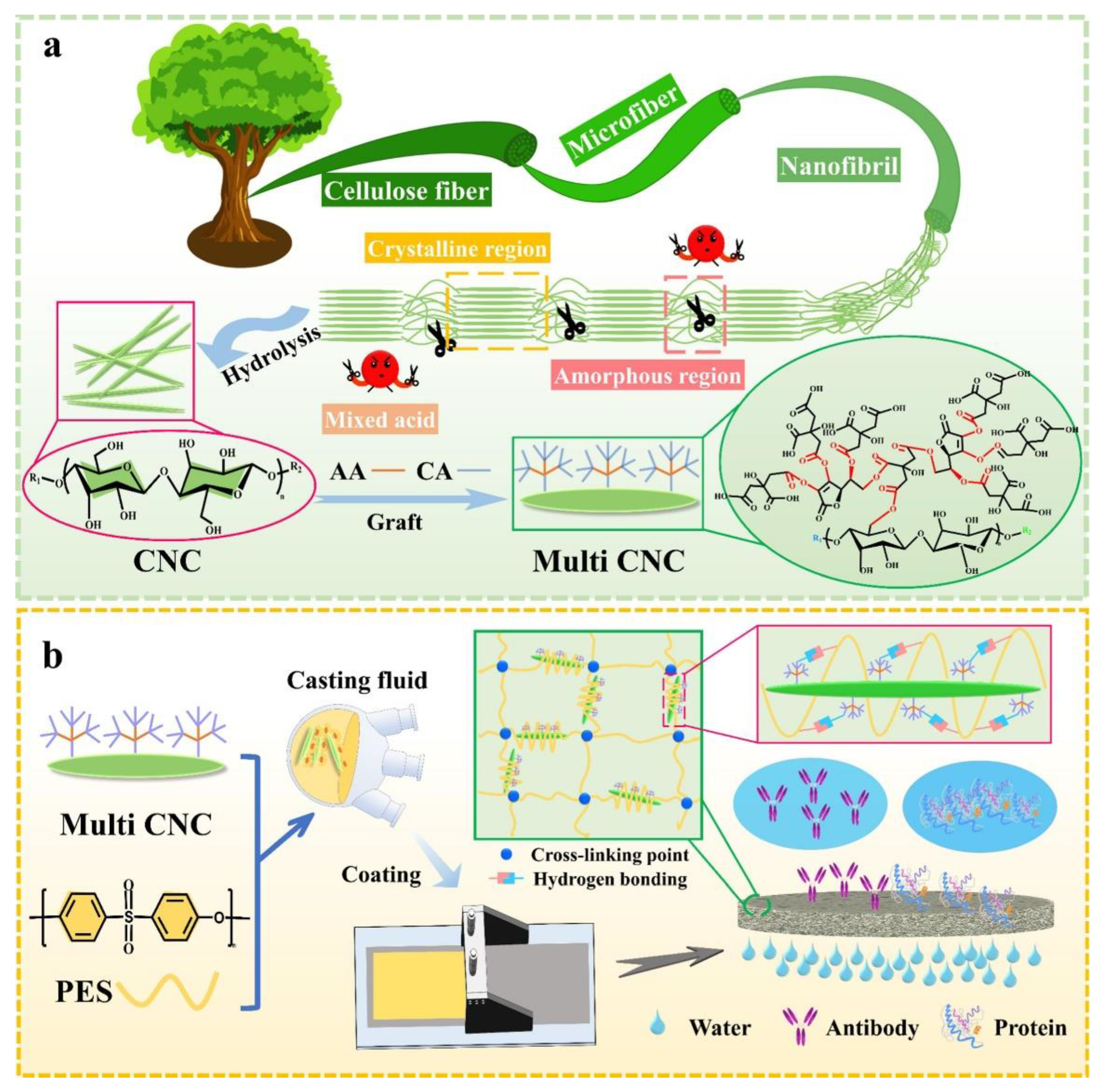
4.8. Bacterial Nanocellulose (BNC) Membranes
4.9. Anti-Fouling
4.10. Mechanical Strength
5. Summary
References
- Tanskyi, O. Zeolite Membrane Water Vapor Separation for Building Air-Conditioning and Ventilation Systems. 2015.
- Werber, J.R.; Osuji, C.O.; Elimelech, M. Materials for Next-Generation Desalination and Water Purification Membranes. Nature Reviews Materials 2016, 1, 16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.L.; Nunes, S.P. Materials and Membrane Technologies for Water and Energy Sustainability. Sustainable Materials and Technologies 2016, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Elam, J.W.; Darling, S.B. Membrane Materials for Water Purification: Design, Development, and Application. Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology 2016, 2, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.-F.; Ooi, B.S.; Leo, C.P. Future Perspectives of Nanocellulose-Based Membrane for Water Treatment. Journal of Water Process Engineering 2020, 37, 101502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, W.R.; Cassey, B.; Jones, P.; Oatley, D.L. Modelling the Performance of Membrane Nanofiltration—Application to an Industrially Relevant Separation. Journal of Membrane Science 2004, 242, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiano, F.; Briceño, K.; Marino, T.; Molino, A.; Christensen, K.V.; Figoli, A. Advances in Biopolymer-Based Membrane Preparation and Applications. Journal of Membrane Science 2018, 564, 562–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, S.; Davarnejad, R.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F. Membranes Based on Non-Synthetic (Natural) Polymers for Wastewater Treatment. Polymer Testing 2020, 84, 106381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, W.; Wensley, C.; Chen, M.; Venugopal, K.; Miller, B.; Stuart, J. Recent Advances in Cellulosic Membranes for Gas Separation and Pervaporation. Gas Separation & Purification 1989, 3, 162–169. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, D.C.; Nguyen, N.C. Membrane Processes and Their Potential Applications for Fresh Water Provision in Vietnam. Vietnam Journal of Chemistry 2017, 55, 533–533. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Z.; Rui, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z. A Review on Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Membranes for Water Purification. Polymers 2019, 11, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Craig, V.S.; Lai, Z. Selective Separation of Oil and Water with Mesh Membranes by Capillarity. Advances in colloid and interface science 2016, 235, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Kantzas, A. Capillary Number Correlations for Gas-Liquid Systems. Journal of Canadian Petroleum Technology 2007, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.A.Q.; Salvemini, F.; Ramandi, H.L.; Fitzgerald, P.; Roshan, H. Configurational Diffusion Transport of Water and Oil in Dual Continuum Shales. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Drioli, E.; Golemme, G. Membrane Gas Separation: A Review/State of the Art. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 4638–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, J.; Chung, T.S. Gas Permeability, Diffusivity, and Solubility of Poly (4-vinylpyridine) Film. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics 1999, 37, 2851–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia Kinetic Diameter Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kinetic_diameter.
- Wikipedia Critical Point (Thermodynamics) Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Critical_point_(thermodynamics).
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Chu, H.; Qi, G.; Ding, H.; Gao, X.; Meng, J. Molecular Simulation on Permeation Behavior of CH4/CO2/H2S Mixture Gas in PVDF at Service Conditions. Polymers 2022, 14, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houde, A.; Stern, S. Solubility and Diffusivity of Light Gases in Ethyl Cellulose at Elevated Pressures Effects of Ethoxy Content. Journal of membrane science 1997, 127, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, B.Y.; Pekgenc, E.; Vatanpour, V.; Koyuncu, I. A Review of Cellulose-Based Derivatives Polymers in Fabrication of Gas Separation Membranes: Recent Developments and Challenges. Carbohydrate Polymers 2023, 121296. [Google Scholar]
- Visanko, M.; Liimatainen, H.; Sirviö, J.A.; Hormi, O. A Cross-Linked 2,3-Dicarboxylic Acid Cellulose Nanofibril Network: A Nanoporous Thin-Film Layer with Tailored Pore Size for Composite Membranes. Separation and Purification Technology 2015, 154, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norizan, M.N.; Shazleen, S.S.; Alias, A.H.; Sabaruddin, F.A.; Asyraf, M.R.M.; Zainudin, E.S.; Abdullah, N.; Samsudin, M.S.; Kamarudin, S.H.; Norrrahim, M.N.F. Nanocellulose-Based Nanocomposites for Sustainable Applications: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Mathew, A.P. Cellulose-Based Materials for Water Remediation: Adsorption, Catalysis, and Antifouling. Frontiers in Chemical Engineering 2021, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gao, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhang, L.; Qu, P.; Bai, L. Preparation and Characteristics of Polysulfone Dialysis Composite Membranes Modified with Nanocrystalline Cellulose. BioResources 2011, 6, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, D.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, H.; Cao, S.; Chen, L.; Ni, Y.; Huang, L. Ultra-Low Pressure Cellulose-Based Nanofiltration Membrane Fabricated on Layer-by-Layer Assembly for Efficient Sodium Chloride Removal. Carbohydrate polymers 2021, 255, 117352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaari, N.Z.K.; Abd Rahman, N.; Sulaiman, N.A.; Tajuddin, R.M. Thin Film Composite Membranes: Mechanical and Antifouling Properties.; EDP Sciences, 2017; Vol. 103, p. 06005.
- Synder Filtration Definition Of Phase Inversion Membrane Available online: https://synderfiltration.com/learning-center/articles/introduction-to-membranes/phase-inversion-membranes-immersion-precipitation/.
- Wang, J.; Song, H.; Ren, L.; Talukder, M.E.; Chen, S.; Shao, J. Study on the Preparation of Cellulose Acetate Separation Membrane and New Adjusting Method of Pore Size. Membranes 2021, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Kruteva, M.; Mystek, K.; Dulle, M.; Ji, W.; Pettersson, T.; Wågberg, L. Macro-and Microstructural Evolution during Drying of Regenerated Cellulose Beads. ACS nano 2020, 14, 6774–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekin, F.S.; Çulfaz-Emecen, P.Z. Controlling Cellulose Membrane Performance via Solvent Choice during Precursor Membrane Formation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 2185–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsvik, I.L.; Hägg, M.-B. Pressure Retarded Osmosis and Forward Osmosis Membranes: Materials and Methods. Polymers 2013, 5, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lu, A.; Zhang, L. Recent Advances in Regenerated Cellulose Materials. Progress in Polymer Science 2016, 53, 169–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Chen, R.; Luo, S.; Yu, W.; Yuan, J.; Lin, F.; Wang, M.; Cao, X.; Liao, Y.; Huang, B. Regenerated Cellulose Membranes for Efficient Separation of Organic Mixtures. Separation and Purification Technology 2024, 328, 125118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lin, X.; White, K.L.; Lin, S.; Wu, H.; Cao, S.; Huang, L.; Chen, L. Effect of the Degree of Substitution on the Hydrophobicity of Acetylated Cellulose for Production of Liquid Marbles. Cellulose 2016, 23, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, D.; Castro, M.C.R.; Figueiredo, A.; Vilarinho, M.; Machado, A. Green Synthesis of Cellulose Acetate from Corncob: Physicochemical Properties and Assessment of Environmental Impacts. Journal of Cleaner Production 2020, 260, 120865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Yao, Z.; Wang, X.; Crombeen, M.; Sweeney, D.G.; Tam, K.C. Cellulose-Based Materials in Wastewater Treatment of Petroleum Industry. Green Energy & Environment 2020, 5, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenvi, S.S.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A.F. A Review on RO Membrane Technology: Developments and Challenges. Desalination 2015, 368, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Hu, L.; Jin, J. Interfacial Design of Mixed Matrix Membranes for Improved Gas Separation Performance. Advanced Materials 2016, 28, 3399–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Fei, P.; Cheng, B.; Meng, J.; Liao, L. Synthesis, Characterization and Excellent Antibacterial Property of Cellulose Acetate Reverse Osmosis Membrane via a Two-Step Reaction. Carbohydrate Polymers 2019, 216, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Yao, F.; Liu, L.; Cai, M. Recyclable Heterogeneous Palladium-Catalyzed Carbon–Carbon Coupling Polycondensations toward Highly Purified Conjugated Polymers. Journal of Polymer Research 2019, 27, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Guzman, M.R.; Andra, C.K.A.; Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Dizon, G.V.C.; Caparanga, A.R.; Huang, S.-H.; Lee, K.-R. Increased Performance and Antifouling of Mixed-Matrix Membranes of Cellulose Acetate with Hydrophilic Nanoparticles of Polydopamine-Sulfobetaine Methacrylate for Oil-Water Separation. Journal of Membrane Science 2021, 620, 118881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraj, P.; Nagendran, A.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T. Separation of Macromolecular Proteins and Removal of Humic Acid by Cellulose Acetate Modified UF Membranes. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2016, 89, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Isloor, A.M.; Todeti, S.R.; Ibrahim, G.P.S.; Inamuddin; Ismail, A.F.; Asiri, A.M. Improved Separation of Dyes and Proteins Using Membranes Made of Polyphenylsulfone/Cellulose Acetate or Acetate Phthalate. Environmental Chemistry Letters 2020, 18, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; RaoT, S.; Isloor, A.M.; Ibrahim, G.P.S.; Inamuddin; Ismail, N.; Ismail, A.F.; Asiri, A.M. Use of Cellulose Acetate/Polyphenylsulfone Derivatives to Fabricate Ultrafiltration Hollow Fiber Membranes for the Removal of Arsenic from Drinking Water. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2019, 129, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Duan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, K.; Dai, L.; Shen, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Ni, Y. Cellulose-Based Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane with Core-Sheath Structure and Robust Photocatalytic Activity for Simultaneous and Efficient Oil Emulsions Separation, Dye Degradation and Cr(VI) Reduction. Carbohydrate Polymers 2021, 258, 117676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herron, J. Asymmetric Forward Osmosis Membranes. 2008.
- Yip, N.Y.; Tiraferri, A.; Phillip, W.A.; Schiffman, J.D.; Elimelech, M. High Performance Thin-Film Composite Forward Osmosis Membrane. Environmental science & technology 2010, 44, 3812–3818. [Google Scholar]
- Alsvik, I.L.; Hägg, M.-B. Preparation of Thin Film Composite Membranes with Polyamide Film on Hydrophilic Supports. Journal of membrane science 2013, 428, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.D.; Uddin, F.J.; Rashid, T.U.; Shahruzzaman, M. Cellulose Acetate-Based Membrane for Wastewater Treatment—A State-of-the-Art Review. Materials Advances 2023, 4, 4054–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, K.D.; Burris Jr., F.O.; Riley, R.L. Kinetic Study of the Hydrolysis of Cellulose Acetate in the pH Range of 2–10. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 1966, 10, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.A.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, F. Preparation and Application of Functionalized Cellulose Acetate/Silica Composite Nanofibrous Membrane via Electrospinning for Cr(VI) Ion Removal from Aqueous Solution. Journal of Environmental Management 2012, 112, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emam, H.E.; El-Shahat, M.; Abdelhameed, R.M. Observable Removal of Pharmaceutical Residues by Highly Porous Photoactive Cellulose acetate@MIL-MOF Film. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2021, 414, 125509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Liu, S.; Ge, B.; Xing, L.; Chen, H. Cellulose Nitrate Membrane Formation via Phase Separation Induced by Penetration of Nonsolvent from Vapor Phase. Journal of membrane science 2007, 295, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-G.; Kresse, I.; Xu, Z.-K.; Springer, J. Effect of Temperature and Pressure on Gas Transport in Ethyl Cellulose Membrane. Polymer 2001, 42, 6801–6810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Baig, M.I.; de Vos, W.M.; Lindhoud, S. Preparation of Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose–Chitosan Complex Membranes through Sustainable Aqueous Phase Separation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Pasaoglu, M.E.; Barzegar, H.; Teber, O.O.; Kaya, R.; Bastug, M.; Khataee, A.; Koyuncu, I. Cellulose Acetate in Fabrication of Polymeric Membranes: A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.Q.; Kanehashi, S.; Doherty, C.M.; Hill, A.J.; Kentish, S.E. Water Vapor Permeation through Cellulose Acetate Membranes and Its Impact upon Membrane Separation Performance for Natural Gas Purification. Journal of Membrane Science 2015, 487, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gardner, D.J.; Stark, N.M.; Bousfield, D.W.; Tajvidi, M.; Cai, Z. Moisture and Oxygen Barrier Properties of Cellulose Nanomaterial-Based Films. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2017, 6, 49–70. [Google Scholar]
- Alikhani, N.; Bousfield, D.W.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Tajvidi, M. Numerical Simulation of the Water Vapor Separation of a Moisture-Selective Hollow-Fiber Membrane for the Application in Wood Drying Processes. Membranes 2021, 11, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhani, N.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Dewar, D.; Tajvidi, M. Exploration of Membrane-Based Dehumidification System to Improve the Energy Efficiency of Kiln Drying Processes: Part I Factors That Affect Moisture Removal Efficiency. Wood and Fiber Science 2020, 52, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, S.J.; Van de Ven, W.; Potreck, J.; Mulder, M.; Wessling, M. Transport of Water Vapor and Inert Gas Mixtures through Highly Selective and Highly Permeable Polymer Membranes. Journal of Membrane Science 2005, 251, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yuan, Q. Gas Permeability of a Novel Cellulose Membrane. Journal of membrane science 2002, 204, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, S. Permeability and Diffusion Data. In The Wiley Database of Polymer Properties; Wiley Online Library, 2003; pp. 543–568.
- Kaushik, M.; Fraschini, C.; Chauve, G.; Putaux, J.-L.; Moores, A. Transmission Electron Microscopy for the Characterization of Cellulose Nanocrystals. The transmission electron microscope-theory and applications 2015, 130–163. [Google Scholar]
- Patten, A.M.; Vassão, D.G.; Wolcott, M.P.; Davin, L.B.; Lewis, N.G. 3.27 - Trees: A Remarkable Biochemical Bounty. In Comprehensive Natural Products II; Liu, H.-W. (Ben), Mander, L., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, 2010; pp. 1173–1296. ISBN 978-0-08-045382-8. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, G.D. A Photographic Study of the Effects of Beating on Fiber Structure. 1956.
- Tayeb, A.H.; Tajvidi, M.; Bousfield, D. Paper Based Oil Barrier Packaging Using Lignin-Containing Cellulose Nanofibrils. Molecules 2020, 25, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anžlovar, A.; Krajnc, A.; Žagar, E. Silane Modified Cellulose Nanocrystals and Nanocomposites with LLDPE Prepared by Melt Processing. Cellulose 2020, 27, 5785–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, I.P.; Berry, G.; Cho, H.; Riveros, G. Alternative High-Performance Fibers for Nonwoven HEPA Filter Media. Aerosol Science and Engineering 2023, 7, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, M.; Berglund, L.A.; Isaksson, P.; Lindstrom, T.; Nishino, T. Cellulose Nanopaper Structures of High Toughness. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matilainen, K.; Hämäläinen, T.; Savolainen, A.; Sipiläinen-Malm, T.; Peltonen, J.; Erho, T.; Smolander, M. Performance and Penetration of Laccase and ABTS Inks on Various Printing Substrates. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslannejad, H.; Hassanizadeh, S.; Raoof, A.; de Winter, D.; Tomozeiu, N.; Van Genuchten, M.T. Characterizing the Hydraulic Properties of Paper Coating Layer Using FIB-SEM Tomography and 3D Pore-Scale Modeling. Chemical Engineering Science 2017, 160, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioux, R.W. The Rate of Fluid Absorption in Porous Media. 2003.
- Motamedian, H.R.; Halilovic, A.E.; Kulachenko, A. Mechanisms of Strength and Stiffness Improvement of Paper after PFI Refining with a Focus on the Effect of Fines. Cellulose 2019, 26, 4099–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, M.S.; Onelli, O.D.; Jacucci, G.; Lovikka, V.; Rojas, O.J.; Ikkala, O.; Vignolini, S. Anomalous-Diffusion-Assisted Brightness in White Cellulose Nanofibril Membranes. Advanced Materials 2018, 30, 1704050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosu, C.; Maximean, D.M.; Kundu, S.; Almeida, P.L.; Danila, O. Perspectives on the Electrically Induced Properties of Electrospun Cellulose/Liquid Crystal Devices. Journal of Electrostatics 2011, 69, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, S.-L.; Kang, S.-G.; Chin, I.-J. Characterization of Cellulose Fibers Electrospun Using Ionic Liquid. Cellulose 2010, 17, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Burger, C.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Ultrafine Polysaccharide Nanofibrous Membranes for Water Purification. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Deng, C.; Soyekwo, F.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhu, A.M. Sub-10 Nm Wide Cellulose Nanofibers for Ultrathin Nanoporous Membranes with High Organic Permeation. Advanced Functional Materials 2016, 26, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mautner, A.; Lee, K.-Y.; Tammelin, T.; Mathew, A.P.; Nedoma, A.J.; Li, K.; Bismarck, A. Cellulose Nanopapers as Tight Aqueous Ultra-Filtration Membranes. Reactive and Functional Polymers 2015, 86, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuruddin, M.; Chowdhury, R.A.; Lopez-Perez, N.; Montes, F.J.; Youngblood, J.P.; Howarter, J.A. Influence of Free Volume Determined by Positron Annihilation Lifetime Spectroscopy (PALS) on Gas Permeability of Cellulose Nanocrystal Films. ACS applied materials & interfaces 2020, 12, 24380–24389. [Google Scholar]
- Wohlert, M.; Benselfelt, T.; Wågberg, L.; Furó, I.; Berglund, L.A.; Wohlert, J. Cellulose and the Role of Hydrogen Bonds: Not in Charge of Everything. Cellulose 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Sharma, S.K.; Lindström, T.; Hsiao, B.S. Nanocellulose-enabled Membranes for Water Purification: Perspectives. Advanced Sustainable Systems 2020, 4, 1900114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehaqui, H.; Michen, B.; Marty, E.; Schaufelberger, L.; Zimmermann, T. Functional Cellulose Nanofiber Filters with Enhanced Flux for the Removal of Humic Acid by Adsorption. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2016, 4, 4582–4590. [Google Scholar]
- Lalia, B.S.; Guillen, E.; Arafat, H.A.; Hashaikeh, R. Nanocrystalline Cellulose Reinforced PVDF-HFP Membranes for Membrane Distillation Application. Desalination 2014, 332, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Burger, C.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Ultra-Fine Cellulose Nanofibers: New Nano-Scale Materials for Water Purification. Journal of Materials Chemistry 2011, 21, 7507–7510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyekwo, F.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, R.; Qu, Y.; Lin, C.; Huang, X.; Zhu, A.; Liu, Q. Cellulose Nanofiber Intermediary to Fabricate Highly-Permeable Ultrathin Nanofiltration Membranes for Fast Water Purification. Journal of Membrane Science 2017, 524, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhu, C.; Mathew, A.P. Mechanically Robust High Flux Graphene Oxide-Nanocellulose Membranes for Dye Removal from Water. Journal of hazardous materials 2019, 371, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Burger, C.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Nanofibrous Microfiltration Membrane Based on Cellulose Nanowhiskers. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Burger, C.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Highly Permeable Polymer Membranes Containing Directed Channels for Water Purification. 2012.
- Karim, Z.; Mathew, A.P.; Grahn, M.; Mouzon, J.; Oksman, K. Nanoporous Membranes with Cellulose Nanocrystals as Functional Entity in Chitosan: Removal of Dyes from Water. Carbohydrate Polymers 2014, 112, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, B.-J.; Kim, D.H.; Yasin, A.S.; Mnoyan, A.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, Y.J.; Ra, H.; Lee, K. Solar-Driven Desalination Using Salt-Rejecting Plasmonic Cellulose Nanofiber Membrane. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2023, 634, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Zhou, D.; Xue, M.; Ou, J.; Xie, Y.; Lei, S.; et al. A Superhydrophobic Pulp/Cellulose Nanofiber (CNF) Membrane via Coating ZnO Suspensions for Multifunctional Applications. Industrial Crops and Products 2022, 187, 115526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yoon, K.; Rong, L.; Mao, Y.; Mo, Z.; Fang, D.; Hollander, Z.; Gaiteri, J.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. High-Flux Thin-Film Nanofibrous Composite Ultrafiltration Membranes Containing Cellulose Barrier Layer. Journal of Materials Chemistry 2010, 20, 4692–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettotti, P.; Scarpa, M. Nanocellulose and Its Interface: On the Road to the Design of Emerging Materials. Advanced Materials Interfaces 2022, 9, 2101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uetani, K.; Izakura, S.; Kasuga, T.; Koga, H.; Nogi, M. Self-Alignment Sequence of Colloidal Cellulose Nanofibers Induced by Evaporation from Aqueous Suspensions. Colloids and Interfaces 2018, 2, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Burger, C.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Fabrication and Characterization of Cellulose Nanofiber Based Thin-Film Nanofibrous Composite Membranes. Journal of Membrane Science 2014, 454, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Low, Z.-X.; Xie, Z.; Wang, H. TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Nanofibers: A Renewable Nanomaterial for Environmental and Energy Applications. Advanced Materials Technologies 2021, 6, 2001180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrrahim, M.N.F.; Mohd Kasim, N.A.; Knight, V.F.; Ong, K.K.; Mohd Noor, S.A.; Abdul Halim, N.; Ahmad Shah, N.A.; Jamal, S.H.; Janudin, N.; Misenan, M.S.M.; et al. Emerging Developments Regarding Nanocellulose-Based Membrane Filtration Material against Microbes. Polymers 2021, 13, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.R.; Sharma, S.K.; Hsiao, B.S. Chapter 5 - Nanocellulose in Membrane Technology for Water Purification. In Separation Science and Technology; Ahuja, S., Ed.; Academic Press, 2022; Vol. 15, pp. 69–85 ISBN 1877-1718.
- Zhu, C.; Liu, P.; Mathew, A.P. Self-Assembled TEMPO Cellulose Nanofibers: Graphene Oxide-Based Biohybrids for Water Purification. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2017, 9, 21048–21058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, N.; Sharma, R.; Foorginezhad, S.; Jouyandeh, M.; Asadnia, M.; Rabiee, M.; Akhavan, O.; Lima, E.C.; Formela, K.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; et al. Green and Sustainable Membranes: A Review. Environmental Research 2023, 231, 116133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visanko, M.; Liimatainen, H.; Sirviö, J.A.; Haapala, A.; Sliz, R.; Niinimäki, J.; Hormi, O. Porous Thin Film Barrier Layers from 2,3-Dicarboxylic Acid Cellulose Nanofibrils for Membrane Structures. Carbohydrate Polymers 2014, 102, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Thin-Film Nanofibrous Composite Membranes Containing Cellulose or Chitin Barrier Layers Fabricated by Ionic Liquids. Polymer 2011, 52, 2594–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Li, M.; Chen, X.; Xue, M.; Ou, J.; Lei, S.; et al. Functional and Versatile Colorful Superhydrophobic Nanocellulose-Based Membrane with High Durability, High-Efficiency Oil/Water Separation and Oil Spill Cleanup. Surface and Coatings Technology 2022, 445, 128714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L. Preparation and Characterization of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Composite Membranes Blended with Nano-Crystalline Cellulose. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International 2012, 22, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norfarhana, A.S.; Ilyas, R.A.; Ngadi, N. A Review of Nanocellulose Adsorptive Membrane as Multifunctional Wastewater Treatment. Carbohydrate Polymers 2022, 291, 119563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Liu, Y.; Bossa, N.; Ding, A.; Ren, N.; Li, G.; Liang, H.; Wiesner, M.R. Incorporation of Cellulose Nanocrystals (CNCs) into the Polyamide Layer of Thin-Film Composite (TFC) Nanofiltration Membranes for Enhanced Separation Performance and Antifouling Properties. Environmental Science & Technology 2018, 52, 11178–11187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaeiarani, J.; Bajwa, D.S.; Chanda, S. Cellulose Nanocrystal Based Composites: A Review. Composites Part C: Open Access 2021, 5, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Ding, A.; Li, G.; Liang, H. Application of Cellulose Nanocrystals in Water Treatment Membranes: A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Wu, H.; Ding, J.; Ding, A.; Zhang, X.; Ren, N.; Li, G.; Liang, H. Cellulose Nanocrystal-Blended Polyethersulfone Membranes for Enhanced Removal of Natural Organic Matter and Alleviation of Membrane Fouling. Chemical Engineering Journal 2020, 382, 122919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solhi, L.; Guccini, V.; Heise, K.; Solala, I.; Niinivaara, E.; Xu, W.; Mihhels, K.; Kröger, M.; Meng, Z.; Wohlert, J.; et al. Understanding Nanocellulose–Water Interactions: Turning a Detriment into an Asset. Chemical Reviews 2023, 123, 1925–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Ji, X.; He, Q.; Gu, H.; Zhang, W.; Deng, Z. Nanocelluloses Fine-Tuned Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Membrane for Enhanced Separation and Antifouling. Carbohydrate Polymers 2024, 323, 121383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, Z.; Mathew, A.P.; Kokol, V.; Wei, J.; Grahn, M. High-Flux Affinity Membranes Based on Cellulose Nanocomposites for Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Industrial Effluents. RSC Advances 2016, 6, 20644–20653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, F. Improvement of Antifouling Performances for Modified PVDF Ultrafiltration Membrane with Hydrophilic Cellulose Nanocrystal. Applied Surface Science 2018, 440, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Yang, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Robust and Highly Hydrophilic Ultrafiltration Membrane with Multi-Branched Cellulose Nanocrystals for Permeability-Selectivity Anti-Trade-off Property. Applied Surface Science 2023, 614, 156157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asempour, F.; Emadzadeh, D.; Matsuura, T.; Kruczek, B. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Cellulose Nanocrystals-Based Thin Film Nanocomposite Membranes for Reverse Osmosis Applications. Desalination 2018, 439, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Mhatre, S.; Chen, J.; Shi, X.; Yang, H.; Cheng, W.; Yue, Y.; Han, G.; Rojas, O.J. Composites Based on Electrospun Fibers Modified with Cellulose Nanocrystals and SiO2 for Selective Oil/Water Separation. Carbohydrate Polymers 2023, 299, 120119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Li, J.; Bao, Z.; Hu, M.; Nian, R.; Feng, D.; An, D.; Li, X.; Xian, M.; Zhang, H. A Natural in Situ Fabrication Method of Functional Bacterial Cellulose Using a Microorganism. Nature Communications 2019, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud, A.; Saleem, H.; Zaidi, S.J. Progress and Prospects of Nanocellulose-Based Membranes for Desalination and Water Treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, H.; Wahid, F.; Santos, H.A.; Khan, T. Advances in Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications of Functional Bacterial Cellulose-Based Nanocomposites. Carbohydrate Polymers 2016, 150, 330–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeyaratne, W.D.N. Potential Differences of Plant Nanocellulose and Bacterial Nanocellulose in Water Purification. In Nanocellulose and Its Composites for Water Treatment Applications; CRC Press, 2021; pp. 91–105.
- Tahir, D.; Karim, M.R.A.; Hu, H.; Naseem, S.; Rehan, M.; Ahmad, M.; Zhang, M. Sources, Chemical Functionalization, and Commercial Applications of Nanocellulose and Nanocellulose-Based Composites: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Jiang, Q.; Ghim, D.; Liu, K.-K.; Sun, H.; Derami, H.G.; Wang, Z.; Tadepalli, S.; Jun, Y.-S.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Catalytically Active Bacterial Nanocellulose-Based Ultrafiltration Membrane. Small 2018, 14, 1704006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Chen, C.; Hu, Y.; Wei, F.; Cui, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Sun, D. Three-Dimensional Bacterial Cellulose/Polydopamine/TiO2 Nanocomposite Membrane with Enhanced Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation for Dyes under Ultraviolet-Visible Irradiation. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2020, 562, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Neto, E.P.; Ullah, S.; da Silva, T.C.A.; Domeneguetti, R.R.; Perissinotto, A.P.; de Vicente, F.S.; Rodrigues-Filho, U.P.; Ribeiro, S.J.L. Bacterial Nanocellulose/MoS2 Hybrid Aerogels as Bifunctional Adsorbent/Photocatalyst Membranes for in-Flow Water Decontamination. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2020, 12, 41627–41643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami Derami, H.; Jiang, Q.; Ghim, D.; Cao, S.; Chandar, Y.J.; Morrissey, J.J.; Jun, Y.-S.; Singamaneni, S. A Robust and Scalable Polydopamine/Bacterial Nanocellulose Hybrid Membrane for Efficient Wastewater Treatment. ACS Applied Nano Materials 2019, 2, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Ghim, D.; Cao, S.; Tadepalli, S.; Liu, K.-K.; Kwon, H.; Luan, J.; Min, Y.; Jun, Y.-S.; Singamaneni, S. Photothermally Active Reduced Graphene Oxide/Bacterial Nanocellulose Composites as Biofouling-Resistant Ultrafiltration Membranes. Environmental Science & Technology 2019, 53, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Lindström, T.; Sharma, P.R.; Chi, K.; Hsiao, B.S. Nanocellulose for Sustainable Water Purification. Chemical Reviews 2022, 122, 8936–9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Ma, H.; Taha, A.A.; Hsiao, B.S. High-Flux Anti-Fouling Nanofibrous Composite Ultrafiltration Membranes Containing Negatively Charged Water Channels. Journal of Membrane Science 2020, 612, 118382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, P.; Yang, M.; Ma, H.; Huang, X.; Walker, H.; Hsiao, B.S. Biofouling-Resistant Nanocellulose Layer in Hierarchical Polymeric Membranes: Synthesis, Characterization and Performance. Journal of Membrane Science 2019, 579, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Sanchez, A.; Jalvo, B.; Mautner, A.; Rissanen, V.; Kontturi, K.S.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Tammelin, T.; Mathew, A.P. Charged Ultrafiltration Membranes Based on TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Nanofibrils/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Antifouling Coating. RSC Advances 2021, 11, 6859–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, A.J.; Walther, A. Cellulose Nanofibril Nanopapers and Bioinspired Nanocomposites: A Review to Understand the Mechanical Property Space. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2017, 5, 16003–16024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindström, T. Aspects on Nanofibrillated Cellulose (NFC) Processing, Rheology and NFC-Film Properties. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science 2017, 29, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.R.; Sharma, S.K.; Lindström, T.; Hsiao, B.S. Water Purification: Nanocellulose-Enabled Membranes for Water Purification: Perspectives (Adv. Sustainable Syst. 5/2020). Advanced Sustainable Systems 2020, 4, 2070009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Bian, H.; Jiao, L.; Wu, W.; Deng, Y.; Dai, H. High Wet-Strength, Thermally Stable and Transparent TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Nanofibril Film via Cross-Linking with Poly-Amide Epichlorohydrin Resin. RSC advances 2017, 7, 31567–31573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mautner, A.; Lucenius, J.; Österberg, M.; Bismarck, A. Multi-Layer Nanopaper Based Composites. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1759–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, M.S.; Kurki-Suonio, S.; Schacher, F.H.; Hietala, S.; Rojas, O.J.; Ikkala, O. Water-Resistant, Transparent Hybrid Nanopaper by Physical Cross-Linking with Chitosan. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, L.; Feng, X. Use of Chitosan to Reinforce Transparent Conductive Cellulose Nanopaper. Journal of Materials Chemistry C 2018, 6, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahimanolis, N.; Salminen, A.; Penttilä, P.A.; Korhonen, J.T.; Johansson, L.-S.; Ruokolainen, J.; Serimaa, R.; Seppälä, J. Nanofibrillated Cellulose/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composite with Improved Wet Strength. Cellulose 2013, 20, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visanko, M.; Liimatainen, H.; Sirvio, J.A.; Heiskanen, J.P.; Niinimäki, J.; Hormi, O. Amphiphilic Cellulose Nanocrystals from Acid-Free Oxidative Treatment: Physicochemical Characteristics and Use as an Oil–Water Stabilizer. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 2769–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes Diniz, J.; Gil, M.; Castro, J. Hornification—Its Origin and Interpretation in Wood Pulps. Wood Science and Technology 2004, 37, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idström, A.; Brelid, H.; Nydén, M.; Nordstierna, L. CP/MAS 13C NMR Study of Pulp Hornification Using Nanocrystalline Cellulose as a Model System. Carbohydrate polymers 2013, 92, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Österberg, M.; Vartiainen, J.; Lucenius, J.; Hippi, U.; Seppälä, J.; Serimaa, R.; Laine, J. A Fast Method to Produce Strong NFC Films as a Platform for Barrier and Functional Materials. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2013, 5, 4640–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, M.; Fournier, C.; Driemeier, C.; Picart, C.; Foster, E.J.; Bras, J. Tunable Structural and Mechanical Properties of Cellulose Nanofiber Substrates in Aqueous Conditions for Stem Cell Culture. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2034–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).