Submitted:
15 May 2024
Posted:
16 May 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
I. Introduction
II. Behavioral Parameters
III. Higher moments
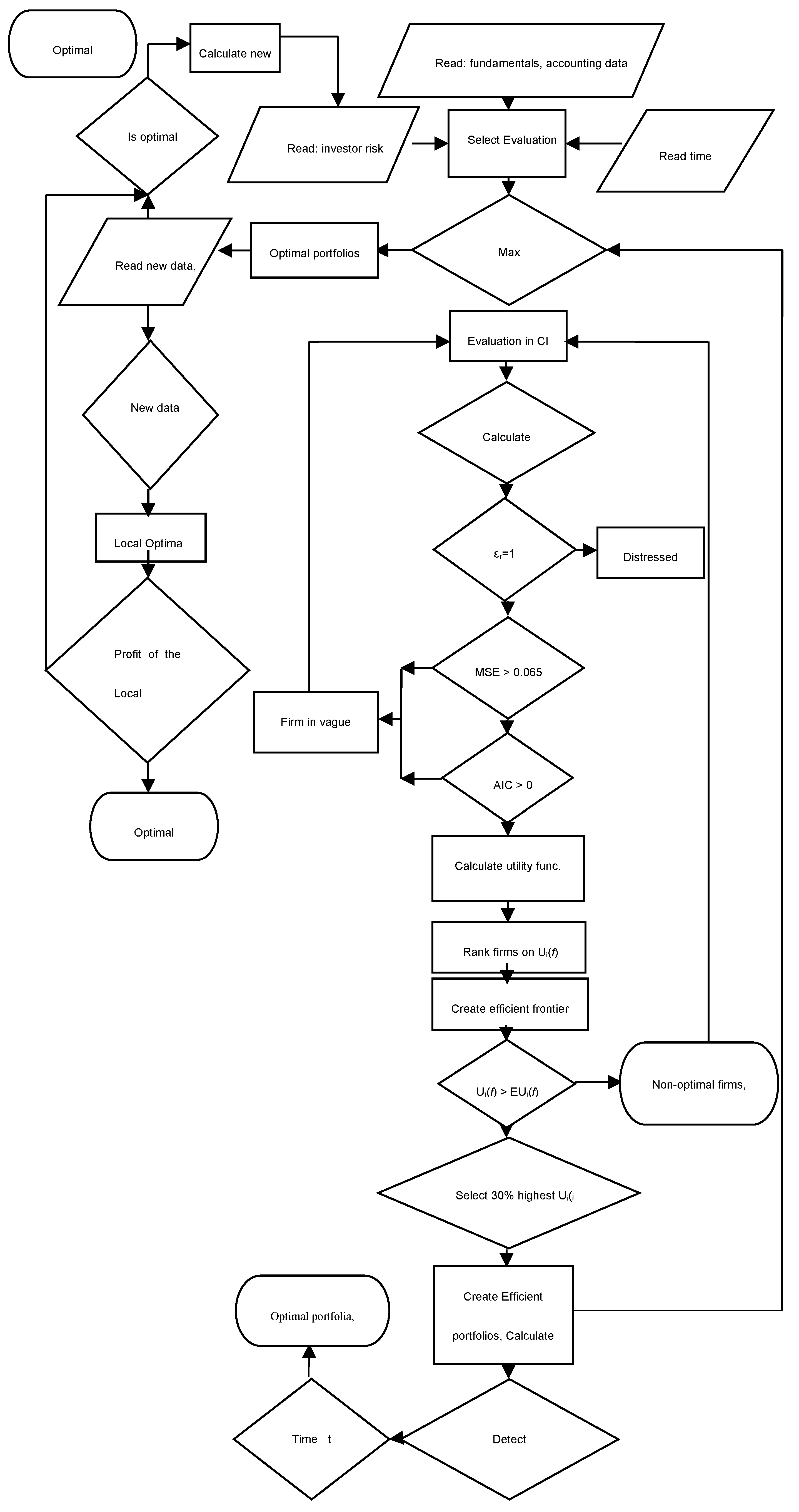
IV. Methodology
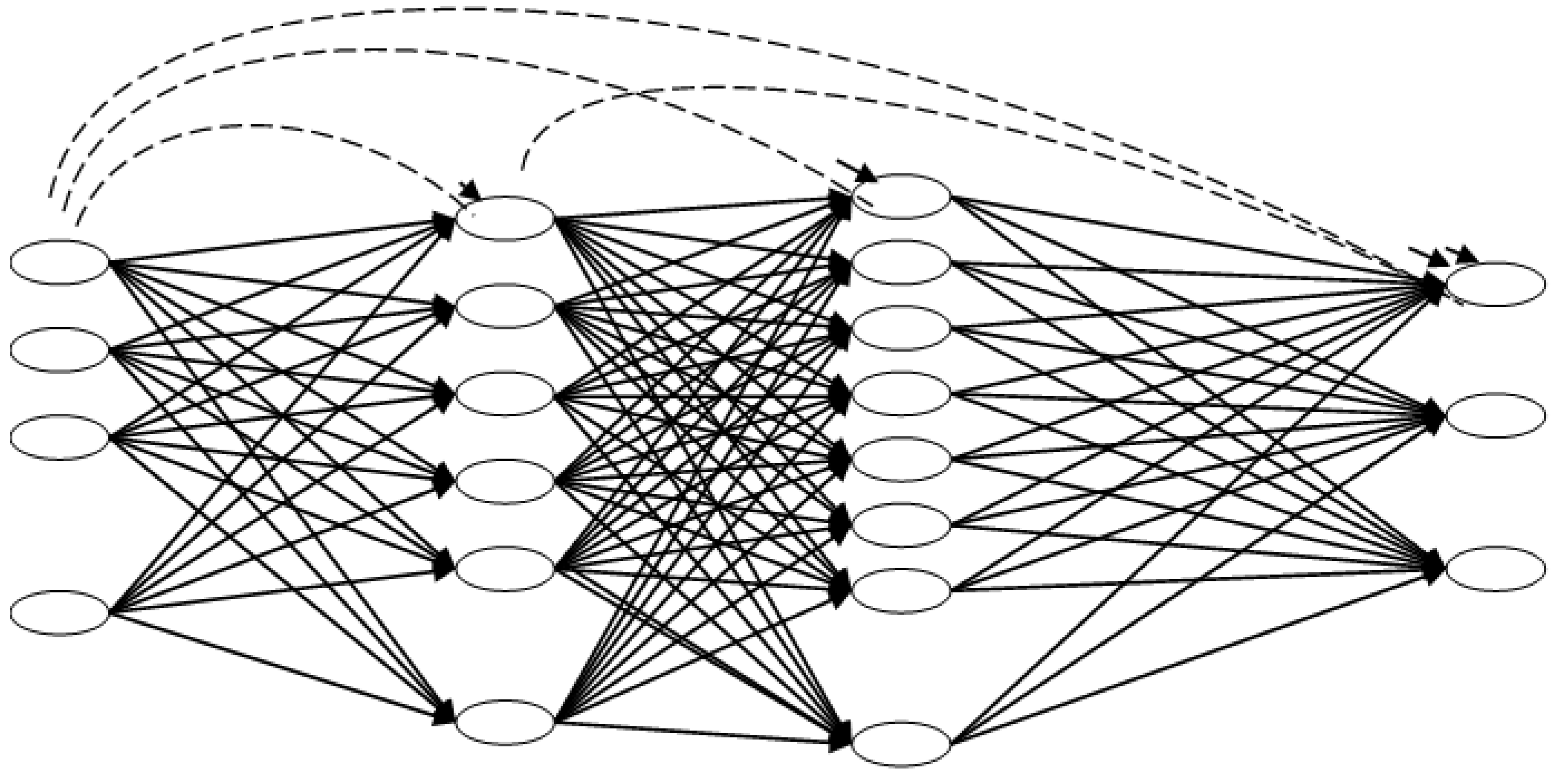
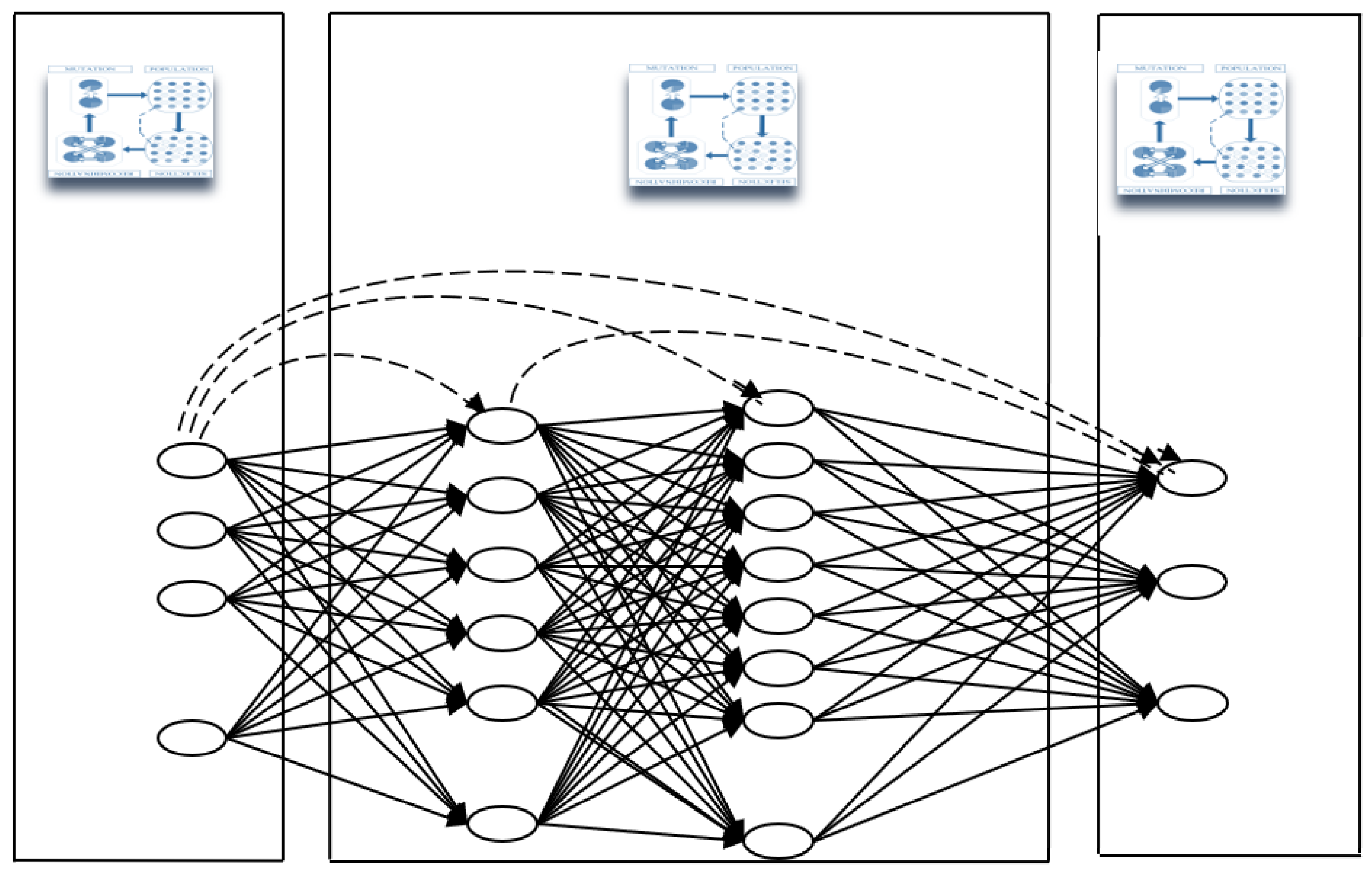
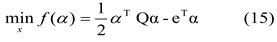
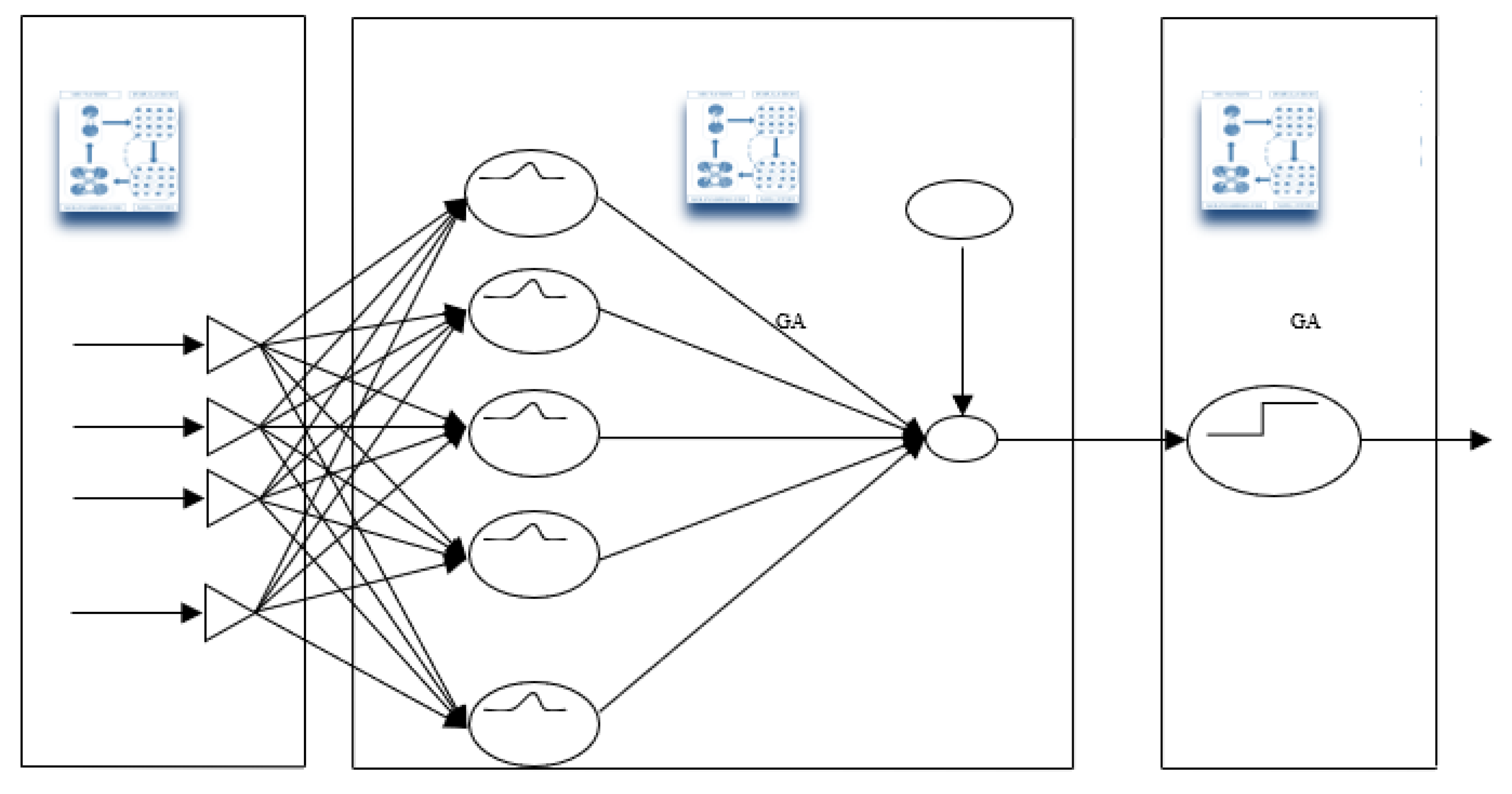
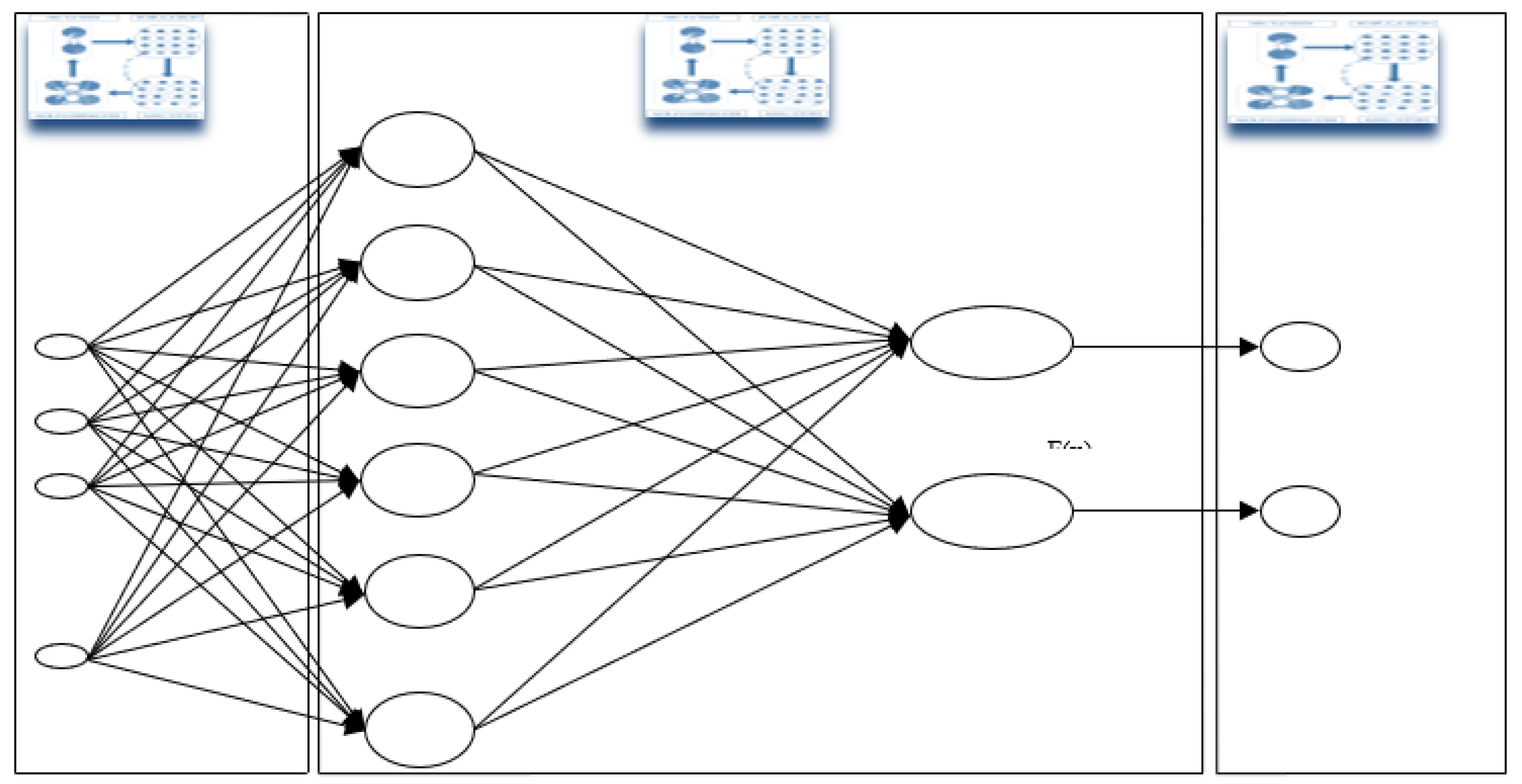
- I.
- on the inputs layer only,
- II.
- on the inputs and outputs layers only,
- III.
- in all the layers and cluster centers,
- IV.
- in all the layers and cluster centers with cross validation,
V. Data
- A.
- SVM of 500 or 1000
- B.
- SVM of 500 epochs and GA on inputs
- C.
- SVM of 1000 epochs and GA on inputs
- D.
- SVM of 500 epochs and GA on outputs
- E.
- SVM of 1000 epochs and GA on outputs
- F.
- SVM of 500 epochs and GA in all layers
- G.
- SVM of 1000 epochs and GA in all layers
- H.
- SVM of 500 epochs and GA on inputs, and Cross Validation
- I.
- SVM of 1000 epochs and GA on input, and Cross Validation
- J.
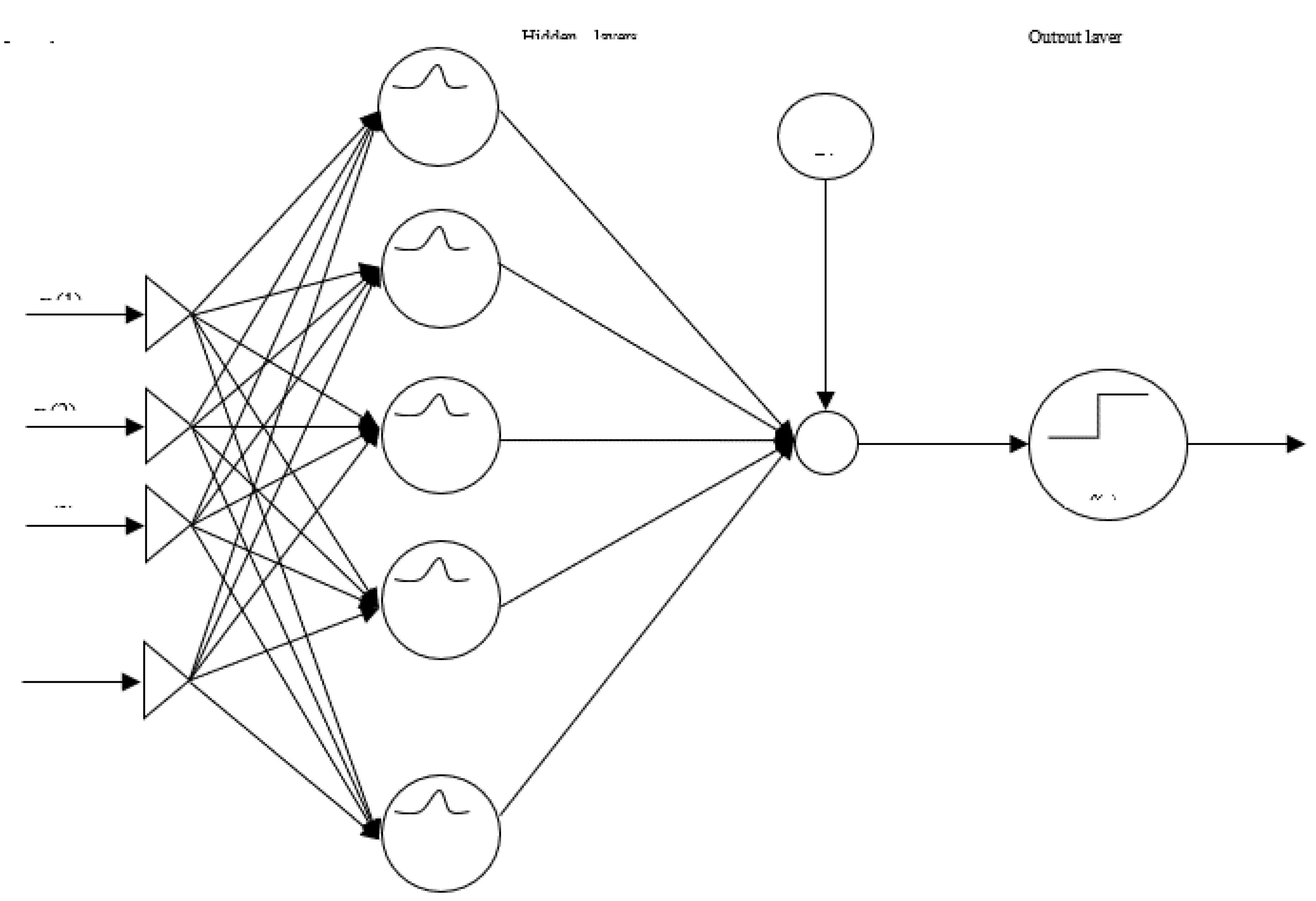
- RBF Neural Nets,
- K.
- RBF hybrids in inputs GA,
- L.
- RBF hybrids in inputs and outputs GA,
- M.
- RBF hybrids of GA in all layers,
- N.
- RBF hybrids of GA in all layers and Cross Validation,
| Models | Active Confusion Matrix | Performance | Time | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layers | 0→0 | 0→1 | 1→0 | 1→1 | MSE | NMSE | r | %error | AIC | MDL | |||
| GFF input-output GA | 1 | 98,90 | 1,085 | 11,465 | 88,52 | 0,072 | 0,1705 | 0,908 | 5776 | -1907,09 | -1796,44 | 55' 18'' | |
| GFF GA all | 3 | 97,14 | 2,845 | 17,885 | 82,10 | 0,128 | 0,304 | 0,834 | 8,3435 | 40259,12 | 284,345 | 2h 44' 43'' | |
| 1 | 97,56 | 2,425 | 18,805 | 81,18 | 0,133 | 0,3155 | 0,8275 | 8,2435 | -723,475 | -271,82 | 1h 38' 53'' | ||
| GFF GA all, | 7 | 96,64 | 3,35 | 19,26 | 80,73 | 0,136 | 0,323 | 0,825 | 9,119 | 1541,07 | 3429,31 | 7h 42' 32'' | |
| CV | 98,32 | 1,67 | 29,355 | 70,63 | 0,149 | 0,3535 | 0,8125 | 7,073 | 1608,295 | 3495,495 | |||
| GFF NN | 1 | 97,73 | 2,26 | 21,095 | 78,89 | 0,138 | 0,328 | 0,8215 | 9,6755 | -1225,82 | -1111,95 | 4'' | |
| GFF NN, CV | 8 | 98,23 | 1,755 | 26,14 | 73,85 | 0,143 | 0,3385 | 0,814 | 9,2845 | 709,44 | 2041,355 | 14,5'' | |
| CV | 98,23 | 1,755 | 26,14 | 73,85 | 0,143 | 0,3385 | 0,814 | 9,2845 | 709,44 | 2041,355 | |||
| GFF GA inputs | 10 | 97,98 | 2,005 | 26,6 | 73,16 | 0,144 | 0,341 | 0,8125 | 9,4695 | 1219,39 | 2873,695 | 1h 27' 44'' | |
| GFF GA all | 8 | 98,57 | 1,42 | 26,6 | 73,39 | 0,140 | 0,3295 | 0,8215 | 8,329 | 1262,655 | 2959,695 | 5h 59' 49'' | |
| GFF GA all, | 1 | 97,98 | 2,005 | 24,305 | 75,68 | 0,145 | 0,343 | 0,8105 | 8,646 | -1219,07 | -1126,3 | 1h 48' 31'' | |
| CV | 98,4 | 1,59 | 24,765 | 75,22 | 0,139 | 0,3305 | 0,8215 | 8,6865 | -1242,55 | -1149,79 | |||
| GFF NN | 10 | 98,65 | 1,34 | 31,185 | 68,80 | 0,147 | 0,348 | 0,8105 | 8,454 | 1557,505 | 3419,165 | 9,5'' | |
| Neural Network | Active Confusion Matrix | Performance | Time | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layers | 0→0 | 0→1 | 1→0 | 1→1 | MSE | NMSE | r | %error | AIC | MDL | ||
| SVM 500 epochs | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.035 | 0.072 | 0.999 | 5.43674 | 23073.68 | 39305.45 | 1’52’’ | |
| SVM 1000 epochs | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.035 | 0.066 | 0.999 | 4.85737 | 23016.76 | 39248.53 | 4’11’’ | |
| Hyb.SVM 500 ep.GAinput | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.045 | 0.086 | 0.999 | 6.55585 | 16159.80 | 27896.09 | 14h39’31’’ | |
| Hyb.SVM 500 epGAoutput | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.065 | 0.125 | 0.999 | 6.80503 | 23457.92 | 39689.69 | 1h 07’ 34’’ | |
| Hyb.SVM 1000 epGAoutput | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.049 | 0.095 | 0.999 | 6.23541 | 23253.32 | 39485.09 | 4h23’35’’ | |
| Hyb.SVM 500 ep GA in, Cro. Val. | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.023 | 0.045 | 0.999 | 4.01337 | 12044.20 | 21524.30 | 26h 56’ 14’’ | |
| 94.29 | 5.69 | 22.01 | 77.98 | 0.309 | 0.591 | 0.949 | 12.7284 | 13931.09 | 23409.93 | |||
| Hyb. SVM 1000 ep GA out., C.V. | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.098 | 0.505 | 0.999 | 6.13446 | 23292.73 | 39540.51 | 5h 38’ 12’ | |
| 94.63 | 5.36 | 24.31 | 75.68 | 0.522 | 0.679 | 0.971 | 1.71621 | 24663.75 | 40911.52 | |||
| Hyb. SVM 500 ep GA All, C.V. | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.091 | 0.175 | 0.999 | 9.06724 | 12375.85 | 21401.51 | 21h 16’ 32’’ | |
| 95.88 | 4.10 | 25.22 | 74.76 | 0.541 | 1.037 | 0.983 | 25.1262 | 13646.24 | 22672.40 | |||
| MLP N. N. 1 | 100 | 0 | 98.62 | 1.37 | 0.418 | 0.989 | 0.107 | 19.4320 | -468.25 | -374.8 | 15’’ | |
| Hybrid Networks | Active Confusion Matrix | Performance | Time | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layers | 0→0 | 0→1 | 1→0 | 1→1 | MSE | NMSE | r | %error | AIC | MDL | ||
| RBF input-output GA | 3 | 97.24 | 2.76 | 27.52 | 72.48 | 0.166 | 0.393 | 0.925 | 9.039 | 672.93 | 1912.74 | 5h48’56’’ |
| RBF GA | 0 | 98.15 | 1.85 | 39.91 | 60.09 | 0.188 | 0.445 | 0.815 | 13.009 | 37.12 | 820.831 | 5h 02’28’’ |
| RBF inputs GA | 0 | 97.73 | 2.26 | 46.32 | 53.67 | 0.219 | 0.519 | 0.791 | 12.383 | 282.78 | 1154.02 | 4h 19’42’’ |
| Neural Network | Active Confusion Matrix | Performance | Time | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layers | 0→0 | 0→1 | 1→0 | 1→1 | MSE | NMSE | r | %error | AIC | MDL | ||||
| Hybrid SVM 500 ep GA in, C. V. | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.023 | 0.045 | 0.999 | 4.0133 | 12044.20 | 21524.3 | 26h 56’ 14’’ | |||
| 94.29 | 5.69 | 22.01 | 77.98 | 0.309 | 0.591 | 0.949 | 12.728 | 13931.09 | 23409.9 | |||||
| SVM 500 epochs | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.035 | 0.072 | 0.999 | 5.4367 | 23073.68 | 39305.4 | 1’52’’ | |||
| SVM 1000 epochs | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.035 | 0.066 | 0.999 | 4.8573 | 23016.76 | 39248.5 | 4’11’’ | |||
| HybridSVM 500 ep GA input | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.045 | 0.086 | 0.999 | 6.5558 | 16159.80 | 27896.0 | 14h39’31’’ | |||
| HybridSVM 1000 ep GA output | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.049 | 0.095 | 0.999 | 6.2354 | 23253.32 | 39485.0 | 4h23’35’’ | |||
| HybridSVM 500 ep GA output | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.065 | 0.125 | 0.999 | 6.8050 | 23457.92 | 39689.6 | 1h 07’ 34’’ | |||
| Hybrid SVM 1000 ep.GA outCV | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.098 | 0.505 | 0.999 | 6.1344 | 23292.73 | 39540.5 | 5h 38’ 12’ | |||
| 94.63 | 5.36 | 24.31 | 75.68 | 0.522 | 0.679 | 0.971 | 1.7162 | 24663.75 | 40911.5 | |||||
| Hybrid SVM 500 ep GA All,CV | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.091 | 0.175 | 0.999 | 9.0672 | 12375.85 | 21401.5 | 21h 16’ 32’’ | |||
| 95.88 | 4.10 | 25.22 | 74.76 | 0.541 | 1.037 | 0.983 | 25,126 | 13646.24 | 22672.4 | |||||
| RBF input-output GA 3 | 97.24 | 2.76 | 27.52 | 72.48 | 0.166 | 0.393 | 0.925 | 9.039 | 672.93 | 1912.74 | 5h48’56’’ | |||
| GFF input-output GA 1 | 98,90 | 1,08 | 11,46 | 88,52 | 0,072 | 0,170 | 0,908 | 5776 | -1907,09 | -1796,44 | 55' 18'' | |||
| GFF GA all 3 | 97,14 | 2,84 | 17,88 | 82,10 | 0,128 | 0,304 | 0,834 | 8,3435 | 40259,12 | 284,345 | 2h 44' 43'' | |||
| GFF GA all1 | 97,14 | 2,845 | 17,88 | 82,10 | 0,128 | 0,304 | 0,834 | 8,3435 | 40259,12 | 284,345 | 1h 38' 53'' | |||
| RBF GA All 0 | 98.15 | 1.85 | 39.91 | 60.09 | 0.188 | 0.445 | 0.815 | 13.00 | 37.12 | 820.831 | 5h02’28’’ | |||
| RBF inputs GA 0 | 97.73 | 2.26 | 46.32 | 53.67 | 0.219 | 0.519 | 0.791 | 12.383 | 282.78 | 1154.02 | 4h19’42’’ | |||
| MLP N. N. 1 | 100 | 0 | 98.62 | 1.37 | 0.418 | 0.989 | 0.107 | 19.432 | -468.25 | -374.8 | 15’’ | |||
VI. Results
VII. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ang, A. Hodrick R., Xing Y., and X., Zhang (2006), The Cross-Section of Volatility and Expected Returns, Journal of Finance, vol LXI, No1, February.
- Athayde, G. , and R. Flores, (2003), Incorporating skewness and Kurtosis in portfolio optimization: a multidimensional efficient set. In: Satchell, S., Scowcroft, A. (eds.) Advances in Portfolio Construction and Implementation, pp. 243–257.
- Coeurdacier N., and H., Rey (2012), Home Bias in Open Economy Financial Macroeconomics, Journal of Economic Literature, 51(1), 63-11. [CrossRef]
- Cortes C. and Vapnik V. (1995), Support-vector network-. Machine Learning, 20:273–297, in Portfolio Selection, Journal of Global Optimization, Volume 43, Numbers 2-3, March.
- Courtis, J. K. , (1978), Modeling a Financial Ratios Categoric Framework, J. Bus.Fin. & Acc., 5(4): 371-386. [CrossRef]
- Fidora, M. Fratzscher M., and C., Thimann (2006), Home Bias in Global Bond and Equity Markets – The role of real Exchange Rate Volatility, European Central Bank, Working Paper Series 685 , October.
- Lai, K.K. Yu, L., and S. Wang, (2006), Mean-variance-skewness-kurtosis-based portfolio optimization. First International Multi-Symposiums on Computer and Computational Sciences (IMSCCS’06) Vol. 2 , 292–297.
- Loukeris, N. , Donelly D., Khuman A., Peng Y., (2009), A numerical evaluation of meta-heuristic techniques in Portfolio Optimisation, Operational Research, Volume 9(1), ed. Springer Verlang. [CrossRef]
- Loukeris, N. and I.Eleftheriadis, (2012a), Bankruptcy Prediction in Hybrids of Time Lag Recurrent Networks with Genetic optimisation, Multi Layer Perceptrons Neural Nets, and Bayesian Logistic Regression, Proceedings of the International Summer Conference of the International Academy of Business and Public Administration Disciplines (IABPAD), ISSN 547-4836 Library of Congress, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA (August 1- 5) - Research Paper Award.
- Loukeris, N. and I.Eleftheriadis, (2013), A novel Approach on Hybrid Support Vector Machines into Optimal Portfolio Selection, Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology, December 12-15, Athens, Greece. [CrossRef]
- Loukeris, N. Eleftheriadis I. and E. Livanis (2014a), Optimal Asset Allocation in Radial Basis Functions Networks, and hybrid neuro-genetic RBFΝs to TLRNs, MLPs and Bayesian Logistic Regression, World Finance Conference, Venice, Italy July 1-3.
- Loukeris, N. Eleftheriadis I. and E. Livanis (2014b), Portfolio Selection into Radial Basis Functions Networks and neuro-genetic RBFN Hybrids, IEEE 5th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems and Applications IISA , July 7-9, Chania Greece.
- Loukeris, N. Boutalis, Y.,; Livanis S., Arampatzis, A., and L. Maltoudoglou, (2015a), Hybrid Jordan Elman nets in portfolio selection, IEEE 6th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems and Applications IISA, Corfu, Greece, July 6-8, pp 1-6.
- Loukeris, N. Boutalis, Y.,; Livanis S., Arampatzis, A., and L. Maltoudoglou, (2015b), Computational intelligence in optimal portfolio selection - The PI model, IEEE 6th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems and Applications IISA, Corfu, Greece, July 6-8, pp 6-12.
- Loukeris N., Bekiros S., and Eleftheriadis I., (2016), The Portfolio Yield Reactive (PYR) model, IEEE 6th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems and Applications, IISA2016, 13-15 July, Porto Carras Grand Resort Hotel, Halkidiki, Greece.
- Loukeris, N. The Evolutional Returns Optimisation System – EROS, IEEE 2021 International Conference on Data Analytics for Business and Industry (ICDABI). 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukeris N., Eleftheriadis I., (2021), Selecting Optimal Portfolio in Generalised Feed Forward networks and Self Organized Features Maps hybrids, IEEE 2021 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence, CSCI 2021, Symposium on Artificial Intelligence (CSCI-ISAI) 15-17, December, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA.
- Loukeris N., (2022), Portfolio Selection in Efficient Hybrid Modular, and Self Organised Features Maps Networks, 18th HSSS International On-Line Conference of the Hellenic Society for Systemic Studies: The Value of Systemic Thinking in Our VUCA World Volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity (VUCA), 15-17 December, Athens, Greece.
- Loukeris, N. The Evolutional Returns Integrated System – ERIS, IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems, Communications, Circuits, CSCC 2023, 19-22, July, Rodos, Greece. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Maringer, D. and P. Parpas, (2009), Global Optimization of Higher Order Moments in Portfolio Selection, Journal of Global Optimization. Volume 43, Numbers 2-3, March. [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, H.M. (1952), Portfolio selection. J. Finance 7(1), 77–91.
- Merton, R.C. (2009), Continuous-time finance, revised edition, 1992 ed. Blackwell,.
- Min S., H. , Lee, J., and I. Han, (2006), Hybrid genetic algorithms and support vector machines for bankruptcy prediction, Expert Systems with Applications, 31(3), October, pp 652-660. [CrossRef]
- NeuroSolutions software- www.nd.com.
- Ranaldo, A. and L. Favre, (2003), How to price hedge funds: from two- to four-moment CAPM. Technical report, EDHEC Risk and Asset Management Research Centre.
- Subrahmanyam, A. (2007), Behavioral Finance: A Review and Synthesis, European Financial Management, Vol. 14, pp. 12–29.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





