Submitted:
13 May 2024
Posted:
14 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemical Characterization
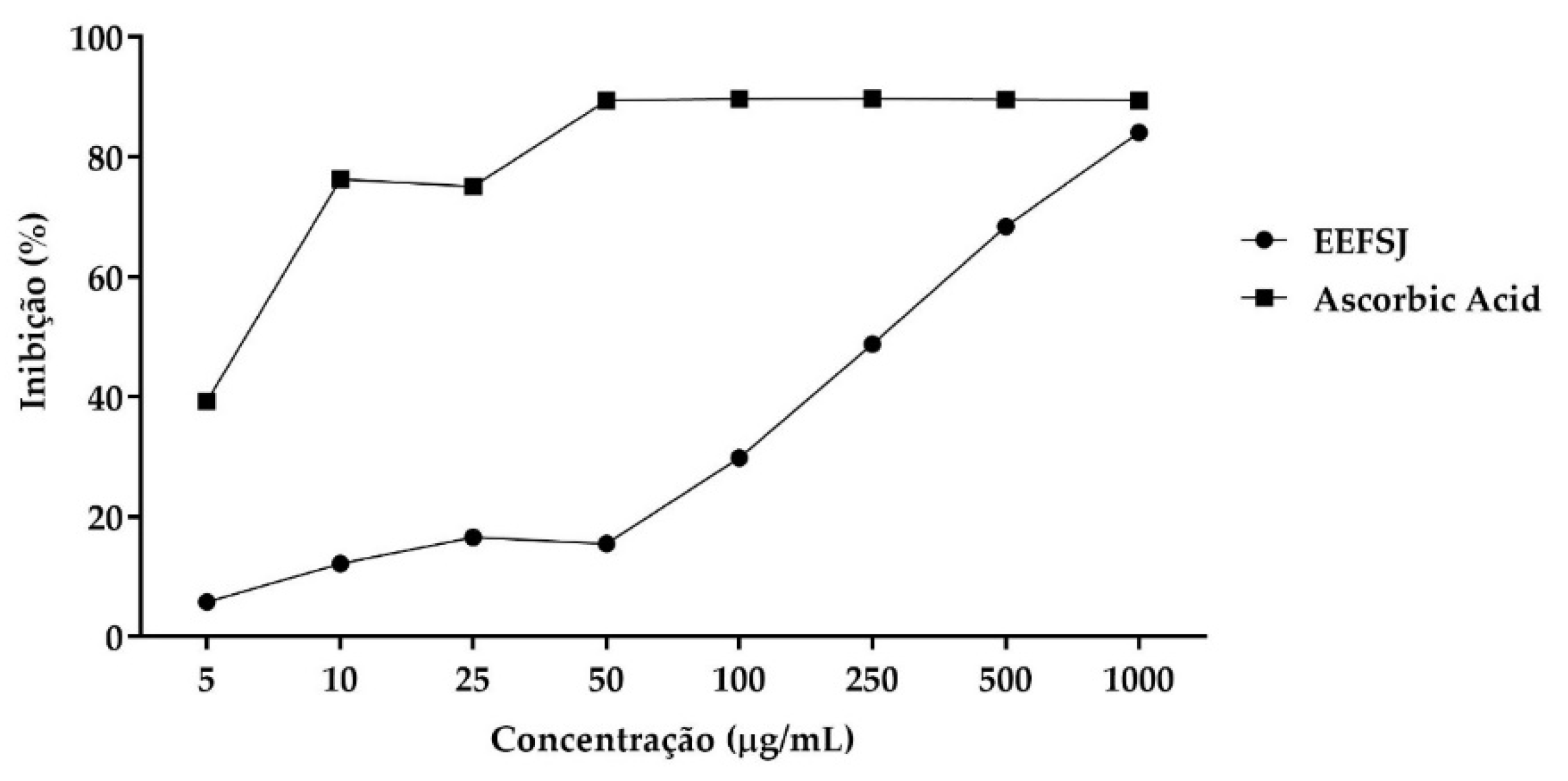
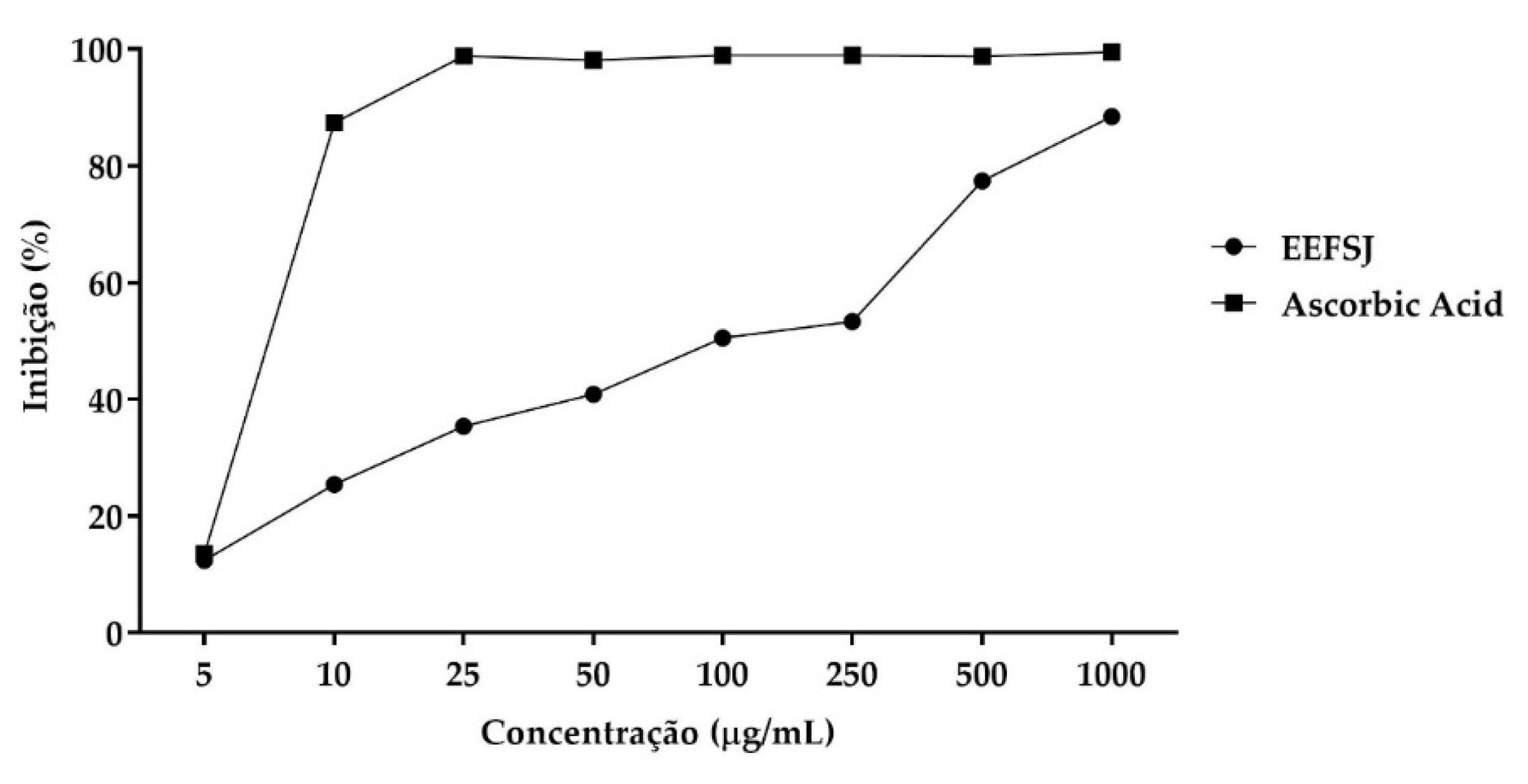
2.2. Antioxidant Activity
2.3. 96h Acute Toxicity
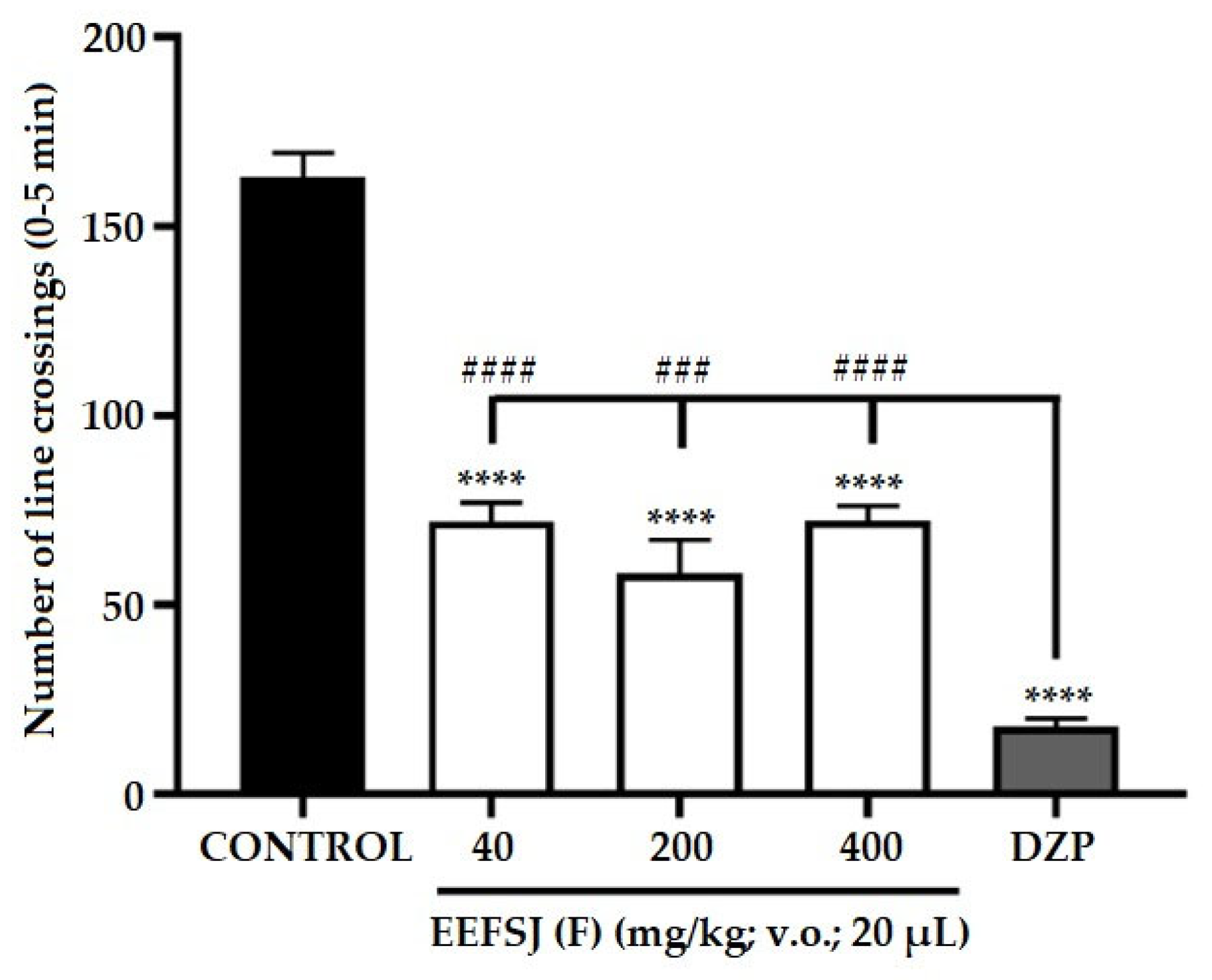
2.4. Locomotor Activity (Open Field Test)
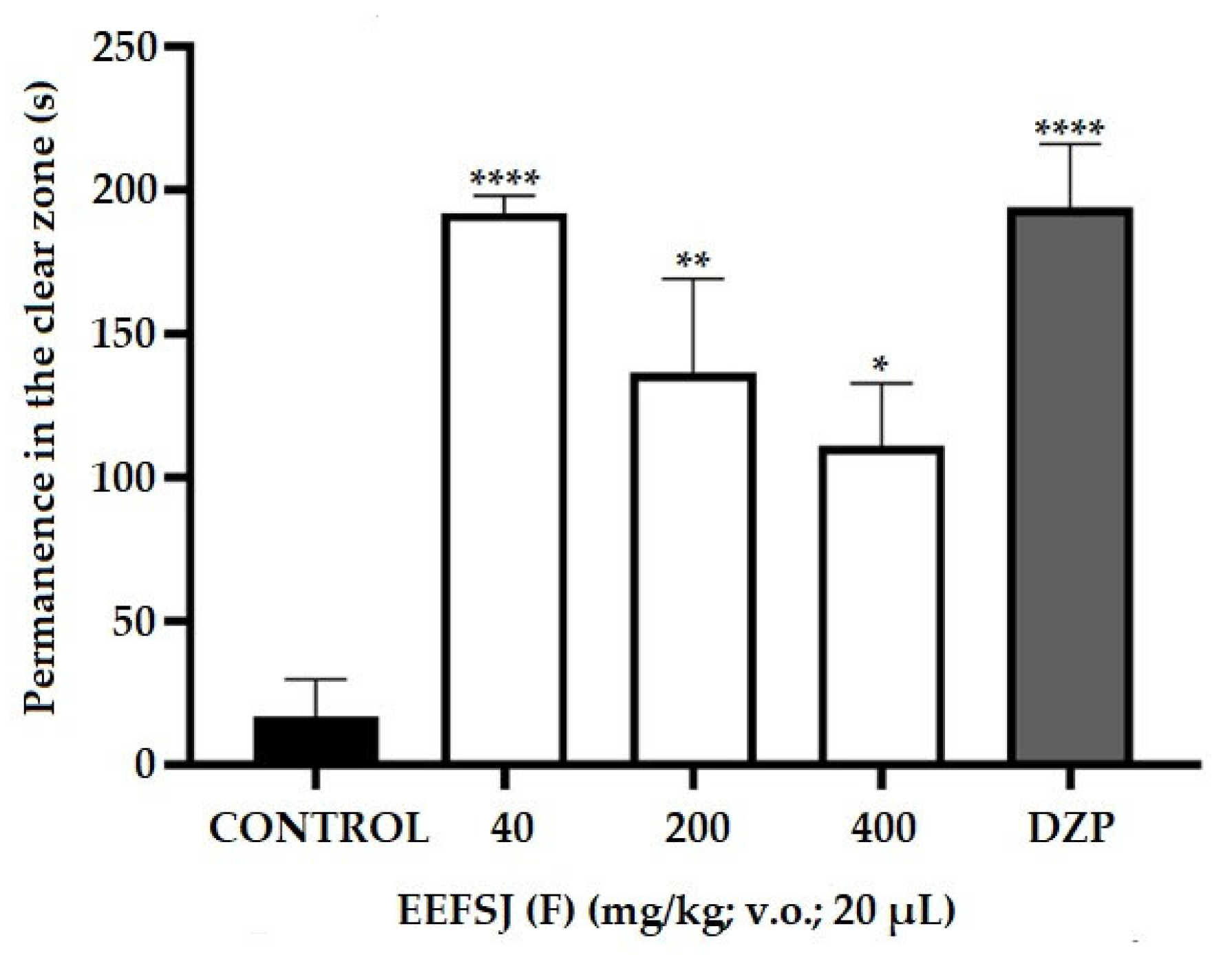
2.5. Anxiolytic Activity
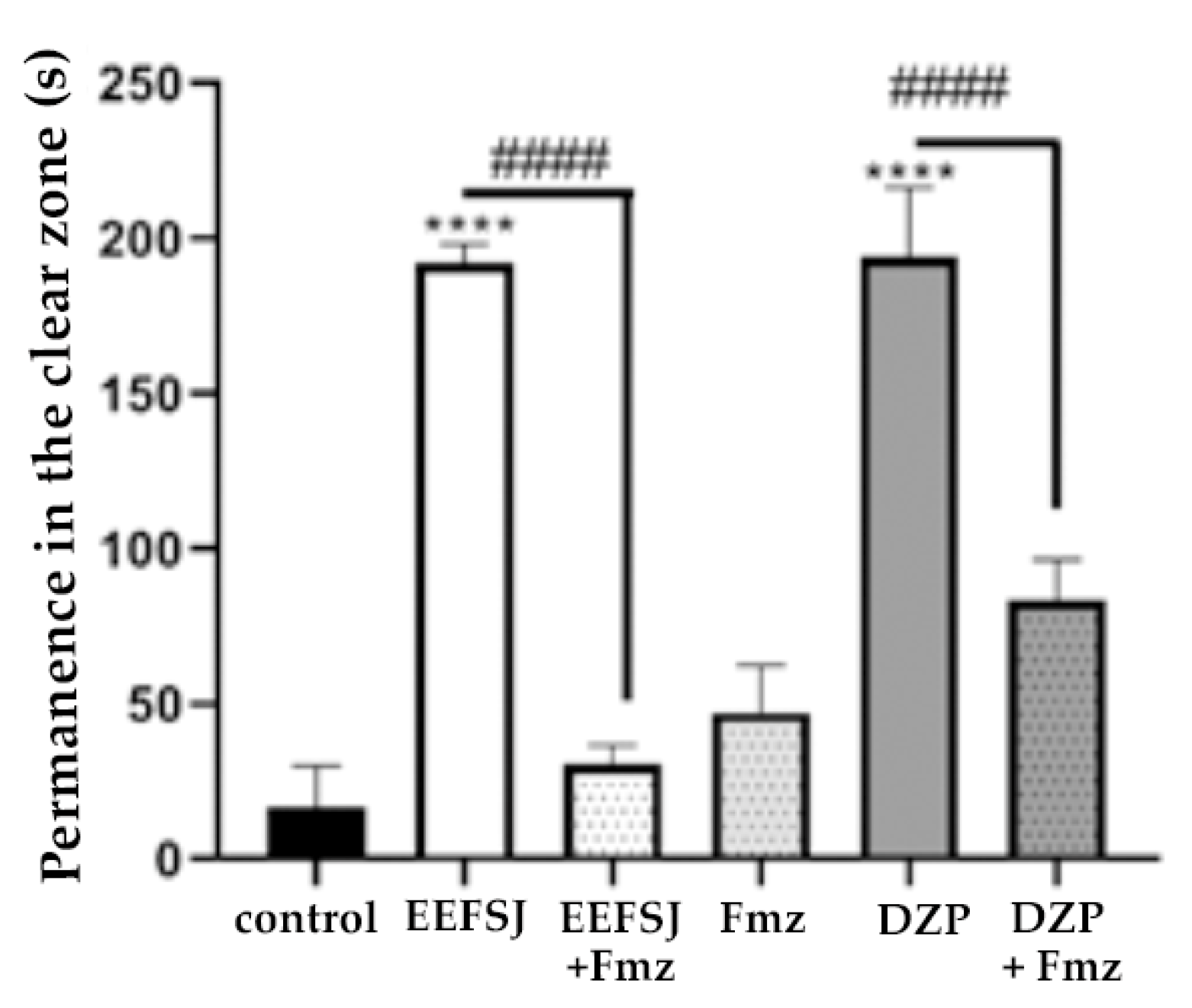
2.6. Involvement of the GABAergic System
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection and Preparation of Extract
4.2. Chemical Characterization
4.2.1. Extract Preparation
4.2.2. Analisys by UPLC-PDA-ESI-QDA
4.3. Antioxidant Assays
4.3.1. Determination of Antioxidant Activity by the DPPH● Method
4.3.2. ABTS●+ Free Radical Capture
4.4. Toxicity and Anxiolytic Assays
4.4.1. Zebrafish
4.4.2. General Protocol
4.4.3. Assessment of Locomotor Activity (Open Field Test)
4.4.4. 96. h Acute Toxicity
4.4.5. Anxiolytic Assessment
4.4.6. Assessment of GABAergic Neuromodulation
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of Interest
References
- T. I. dos Santos Sampaio et al., “Leaves of Spondias mombin L. a traditional anxiolytic and antidepressant: Pharmacological evaluation on zebrafish (Danio rerio),” J. Ethnopharmacol., vol. 224, no. February, pp. 563–578, 2018. [CrossRef]
- H. P. S. Hozana Patrícia et al., “Anxiolytic-like effect of brominated compounds from the marine sponge Aplysina fulva on adult zebrafish (Danio rerio): Involvement of the GABAergic system,” Neurochem. Int., vol. 146, no. March, 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. C. de Melo et al., “Anxiolytic and antidepressant effects of the hydroethanolic extract from the leaves of Aloysia polystachya (Griseb.) moldenke: A study on zebrafish (Danio rerio),” Pharmaceuticals, vol. 12, no. 3, 2019. [CrossRef]
- E. Palazidou, “The neurobiology of depression,” Br. Med. Bull., vol. 101, no. 1, pp. 127–145, 2012. [CrossRef]
- M. Shafiee et al., “Depression and anxiety symptoms are associated with prooxidant-antioxidant balance: A population-based study,” J. Affect. Disord., vol. 238, pp. 491–498, 2018. [CrossRef]
- G. P. da S. M. Matos, A. F. Dos Santos, D. M. S. Acioli, E. F. Da Silva, and J. I. Guerra Junior, “Benzodiazepínicos: uma revisão de literatura sobre uso indiscriminado, dependência e efeitos colaterais,” Brazilian J. Heal. Rev., vol. 7, no. 2, p. e67735, 2024. [CrossRef]
- J. da C. Xavier et al., “Anxiolytic-like and anticonvulsant effect in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) through gabaergic system and molecular docking study of chalcone derived from natural products,” Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem., vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 14021–14031, 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. Aguirre-Hernández, M. E. González-Trujano, T. Terrazas, J. H. Santoyo, and P. Guevara-Fefer, “Anxiolytic and sedative-like effects of flavonoids from Tilia americana var. mexicana: GABAergic and serotonergic participation,” Salud Ment., vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 37–46, 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. U. Rehman et al., “Neuroprotective Strategies for Neurological Disorders by Natural Products: An update,” Curr. Neuropharmacol., vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 247–267, 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. J. S. Araújo et al., “Chemical characterization UPLC-ESI-QToF-MSE, antibacterial and antibiofilm potential of Sarcomphalus joazeiro (MART.) Hauenschild,” Food Biosci., vol. 50, no. August, 2022. [CrossRef]
- B. de Souza et al., “Antibacterial activity and anxiolytic-like effect of Ziziphus joazeiro Mart. leaves in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio),” Fish Shellfish Immunol. Reports, vol. 5, no. April, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. M. O. Brito et al., “Analysis of bioactivities and chemical composition of Ziziphus joazeiro Mart. using HPLC-DAD,” Food Chem., vol. 186, pp. 185–191, 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. R. Hanrahan, M. Chebib, and G. A. R. Johnston, “Flavonoid modulation of GABA A receptors,” Br. J. Pharmacol., vol. 163, no. 2, pp. 234–245, 2011. [CrossRef]
- D. V. de Azevedo et al., “Evaluation of antioxidant, toxicological and anxiolytic-like effect of ethanolic extracts of Ziziphus cotinifolia Reissek in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio),” Phytomedicine Plus, vol. 4, no. 1, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Y. Cao, H. Yan, G. Yu, and R. Su, “Flumazenil-insensitive benzodiazepine binding sites in GABAA receptors contribute to benzodiazepine-induced immobility in zebrafish larvae,” Life Sci., vol. 239, p. 117033, 2019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- J. Cosmo Andrade et al., “Control of bacterial and fungal biofilms by natural products of Ziziphus joazeiro Mart. (Rhamnaceae),” Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis., vol. 65, no. March, pp. 226–233, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Y. Pu, T. Ding, N. Zhang, P. Jiang, and D. Liu, “Identification of bitter compounds from dried fruit of Ziziphus jujuba cv. Junzao,” Int. J. Food Prop., vol. 20, no. 1, pp. S26–S35, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Tools, “Integrated UPLC-HRMS, Chemometric Tools, and Metabolomic Analysis of Forage Palm (,” vol. 32, no. 8, pp. 1617–1627, 2021.
- M. Masullo, A. Cerulli, P. Montoro, C. Pizza, and S. Piacente, “In depth LC-ESIMS n -guided phytochemical analysis of Ziziphus jujuba Mill. leaves,” Phytochemistry, vol. 159, no. October 2018, pp. 148–158, 2019. [CrossRef]
- N. R. Sucupira, A. B. Da Silva, G. Pereira, and J. N. Da Costa, “Métodos Para Determinação da Atividade Antioxidante de Frutos,” UNOPAR Científica Ciências Biológicas e da Saúde, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 263–269, 2014, [Online]. Available: http://revistas.unopar.br/index.php/biologicas/article/view/442.
- W. M. Arika, C. M. Kibiti, J. M. Njagi, and M. P. Ngugi, “Effects of DCM Leaf Extract of Gnidia glauca (Fresen) on Locomotor Activity, Anxiety, and Exploration-Like Behaviors in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Rats,” Behav. Neurol., vol. 2019, 2019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L. Gebauer, N. Pagnussat, Â. L. Piato, I. C. Schaefer, C. D. Bonan, and D. R. Lara, “Effects of anxiolytics in zebrafish: Similarities and differences between benzodiazepines, buspirone and ethanol,” Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., vol. 99, no. 3, pp. 480–486, 2011. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Andrade et al., “UPLC-MS-ESI-QTOF characterization and evaluation of the antibacterial and modulatory antibiotic activity of Ziziphus joazeiro Mart. aqueous extracts,” South African J. Bot., vol. 123, pp. 105–112, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Z. Liu et al., “Flavonoid compounds isolated from Tibetan herbs, binding to GABAA receptor with anxiolytic property,” J. Ethnopharmacol., vol. 267, p. 113630, 2021. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S. T. Sakna, Y. R. Maghraby, M. S. Abdelfattah, and M. A. Farag, “Phytochemical diversity and pharmacological effects of triterpenes from genus Ziziphus: a comprehensive review,” Phytochem. Rev., vol. 22, no. 6, pp. 1611–1636, 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. Yoshikawa, N. Shimono, and S. Arihara, “Antisweet substances, jujubasaponins I-III from zizyphus jujuba revised structure of ziziphin,” Tetrahedron Lett., vol. 32, no. 48, pp. 7059–7062, 1991. [CrossRef]
- S. Seri, T. A. Okpekon, P. A. Yao-Kouassi, A. A. Magid, C. Sayagh, and L. Voutquenne-Nazabadioko, “Saponins and flavonoid glycosides from the leaves of Ziziphus mauritiana Lam. native of a forest area of Ivory Coast,” Phytochem. Lett., vol. 37, no. March, pp. 5–9, 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Macedo, L. G. P. J. M. Macedo, L. G. P. Souza, V. del C. Troncozo Valenzuela, A. B. Oliveira, R. Oliveira Castilho, and R. L. Ribeiro Jácome, “Variação sazonal nos teores de flavonoides, taninos e atividade antioxidante de Davilla rugosa poir,” Rev. Ciencias Farm. Basica e Apl., vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 585–590, 2013.
- T. C. de L. E. Silva, “AVALIAÇÃO COMPARATIVA DE CASCAS E FOLHAS DE Ziziphus joazeiro Mart (RHAMNACEAE) EM RELAÇÃO AOS PERFIS FITOQUIMICO E TOXICOLÓGICO E AS ATIVIDADES ANTIOXIDANTE E ANTIMICROBIANA,” p. 73, 2009.
- C. M. F. E Silva, D. I. M. Pereira, and G. V. Mesquita, “Análise do uso indiscriminado de benzodiazepínicos em graduandos de medicina de um centro universitário no Piauí,” Brazilian J. Heal. Rev., vol. 6, no. 6, pp. 28005–28020, 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. B. Lydiard, “The role of GABA in anxiety disorders,” J. Clin. Psychiatry, vol. 64, no. SUPPL. 3, pp. 21–27, 2003.
- S. K. J. Njapdounke et al., “Anxiolytic - Like properties of Hallea ciliata in mice,” African J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med., vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 1–7, 2016. [CrossRef]
- N. Bao, J. Ou, W. Shi, N. Li, L. Chen, and J. Sun, “Highly Efficient Synthesis and Structure–Activity Relationships of a Small Library of Substituted 1,4-Naphthoquinones,” European J. Org. Chem., vol. 2018, no. 19, pp. 2254–2258, 2018. [CrossRef]
- C. I. Calero, A. N. B. González, J. Gasulla, S. Alvarez, P. Evelson, and D. J. Calvo, “Quercetin antagonism of GABAAρ1 receptors is prevented by ascorbic acid through a redox-independent mechanism,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., vol. 714, no. 1–3, pp. 274–280, 2013. [CrossRef]
- J. L. Ríos, G. R. Schinella, and I. Moragrega, “Phenolics as GABAA Receptor Ligands: An Updated Review,” Molecules, vol. 27, no. 6, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. do S. Rufino, R. E. Alves, E. S. De Brito, S. M. De Morais, C. D. G. Sampaio, and F. D. Saura-calixto, “ISSN 1679-6535 Julho, 2007 Fortaleza, CE,” pp. 0–3, 2007.
- M. do S. M. Rufino et al., “Determinação da atividade antioxidante total em frutas pela captura do radical livre DPPH.,” Comun. Técnico Online EMBRAPA, vol. 127, pp. 1–4, 2007, [Online]. Available: https://www.infoteca.cnptia.embrapa.br/bitstream/doc/426953/1/Cot127.pdf.
- M. K. A. Ferreira et al., “Chalcones reverse the anxiety and convulsive behavior of adult zebrafish,” Epilepsy Behav, vol. 117, p. 107881, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Oecd, “Fish, acute toxicity test,” Guidel. Test. Chem., no. July, pp. 1–9, 1992.
- N. G. G. Gonçalves et al., “Protein fraction from Artocarpus altilis pulp exhibits antioxidant properties and reverses anxiety behavior in adult zebrafish via the serotoninergic system,” J. Funct. Foods, vol. 66, no. April 2019, p. 103772, 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. K. Benneh, R. P. Biney, P. K. Mante, A. Tandoh, D. W. Adongo, and E. Woode, “Maerua angolensis stem bark extract reverses anxiety and related behaviours in zebrafish—Involvement of GABAergic and 5-HT systems,” J. Ethnopharmacol., 2017. [CrossRef]
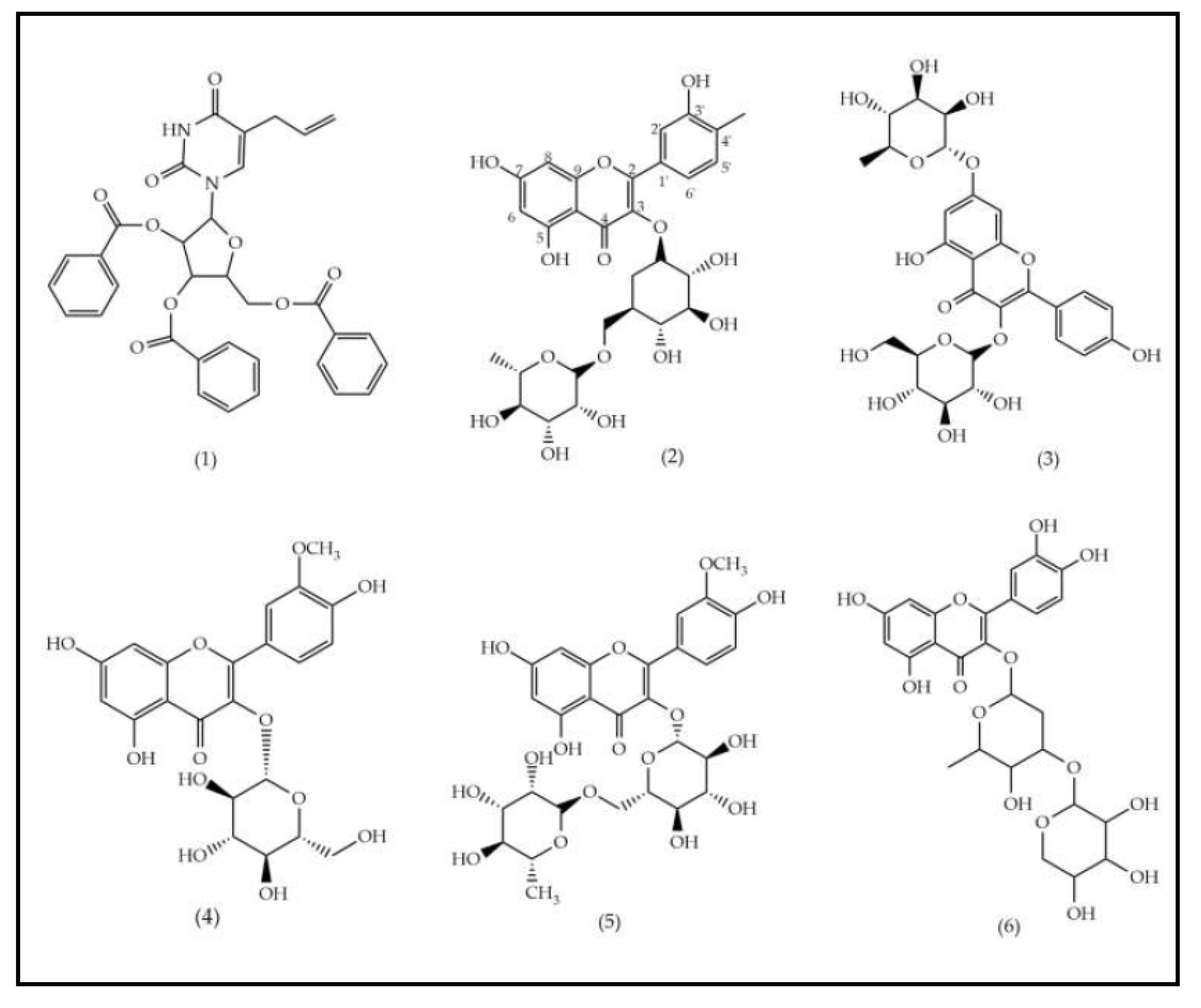
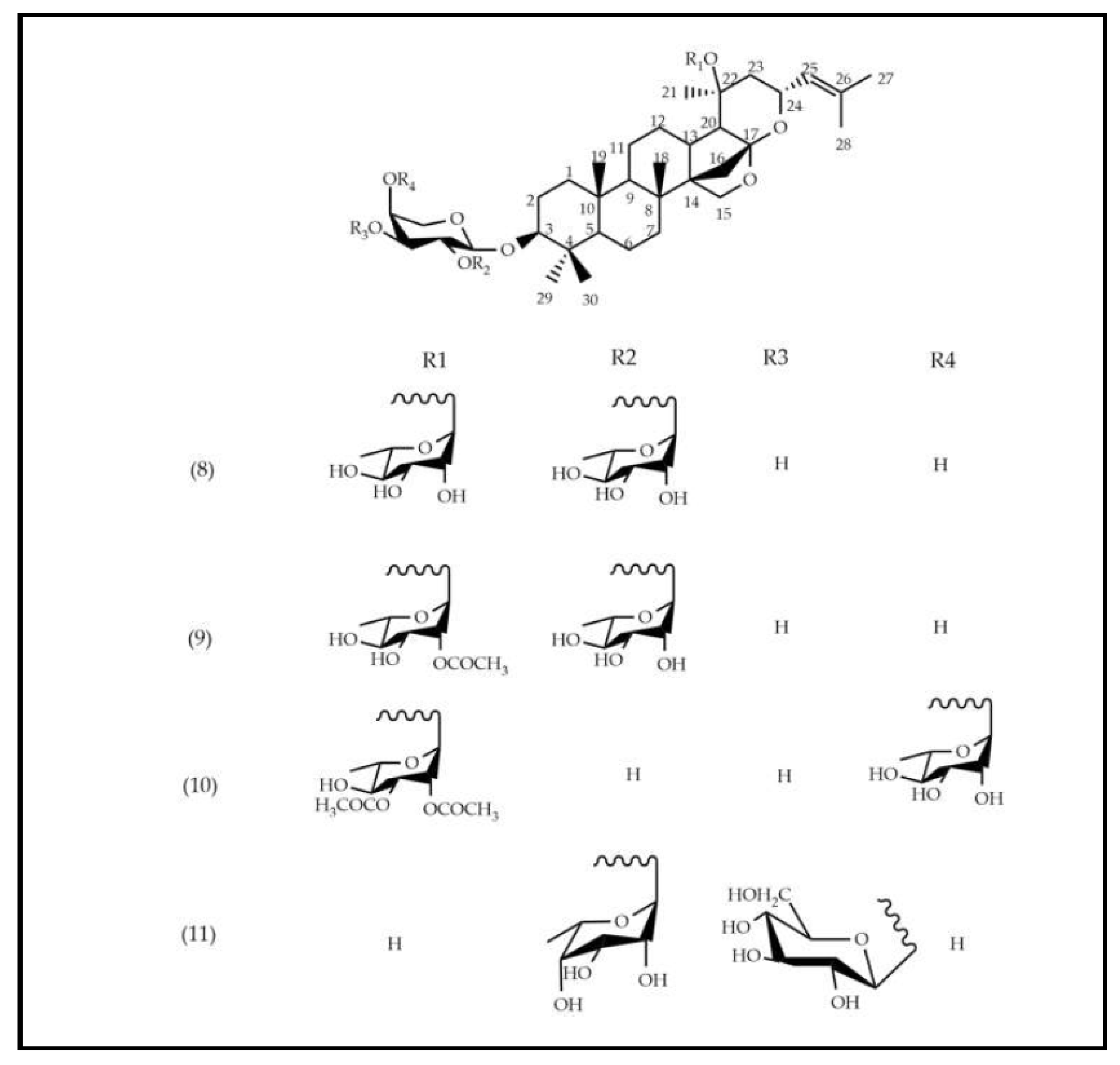
| Peak N° | Name | tR(min) | [M-H]-/ [M+HCOOH]- | Empirical formula | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5-allyl-1-(2,3,4,-tris-O-benzoylpentofuranosyl)-2, 4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione | 5.63 | 595 | C33H27N2O9 | [16], [17] |
| 2 | Rutin | 6.98 | 609 | C27H29O16 | [17] |
| 3 | Kaempferol O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→ 6)-β-D-hexoside | 7.37 | 593 | C27H29O15 | [17] |
| 4 | Isorhamnetin O-hexoside | 7.44 | 477 | C29H17O7 | [16] |
| 5 | Isorhamnetin O-rutinoside | 7.57 | 623 | C28H31O16 | [16] |
| 6 | Quercetin -O-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1 → 2)-α-L-rhamnopyranoside | 7.87 | 579 | C26H27O15 | [17] |
| 7 | Isorhamnetin O-hexoside | 7.94 | 477 | C29H17O7 | [18] |
| 8 | Jujubasaponin I | 8.30 | 941 | C48H77O18 | [19] |
| 9 | Jujubasaponin II | 9.28 | 983 | C50H79O19 | [19] |
| 10 | Ziziphin | 9.39 | 979 | C51H79O18 | [19] |
| 11 | Zizyphus saponin I | 9.88 | 911 | C47H75O17 | [19] |
| Sample | (mg/kg) | 96hLD50 (mg/kg) | ||
| 40 | 200 | 400 | >400 | |
| EEFSJ | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





