Submitted:
10 May 2024
Posted:
13 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
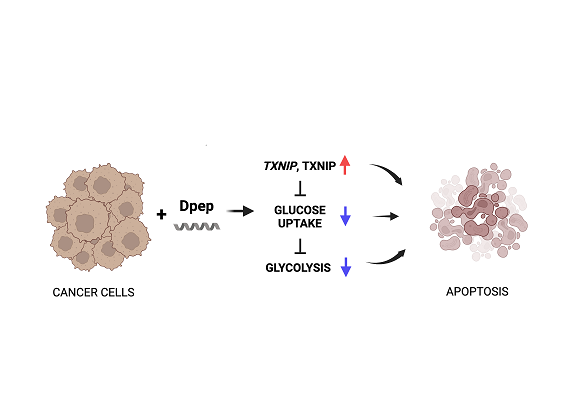
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Peptides and Reagents
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. Glycolytic Activity
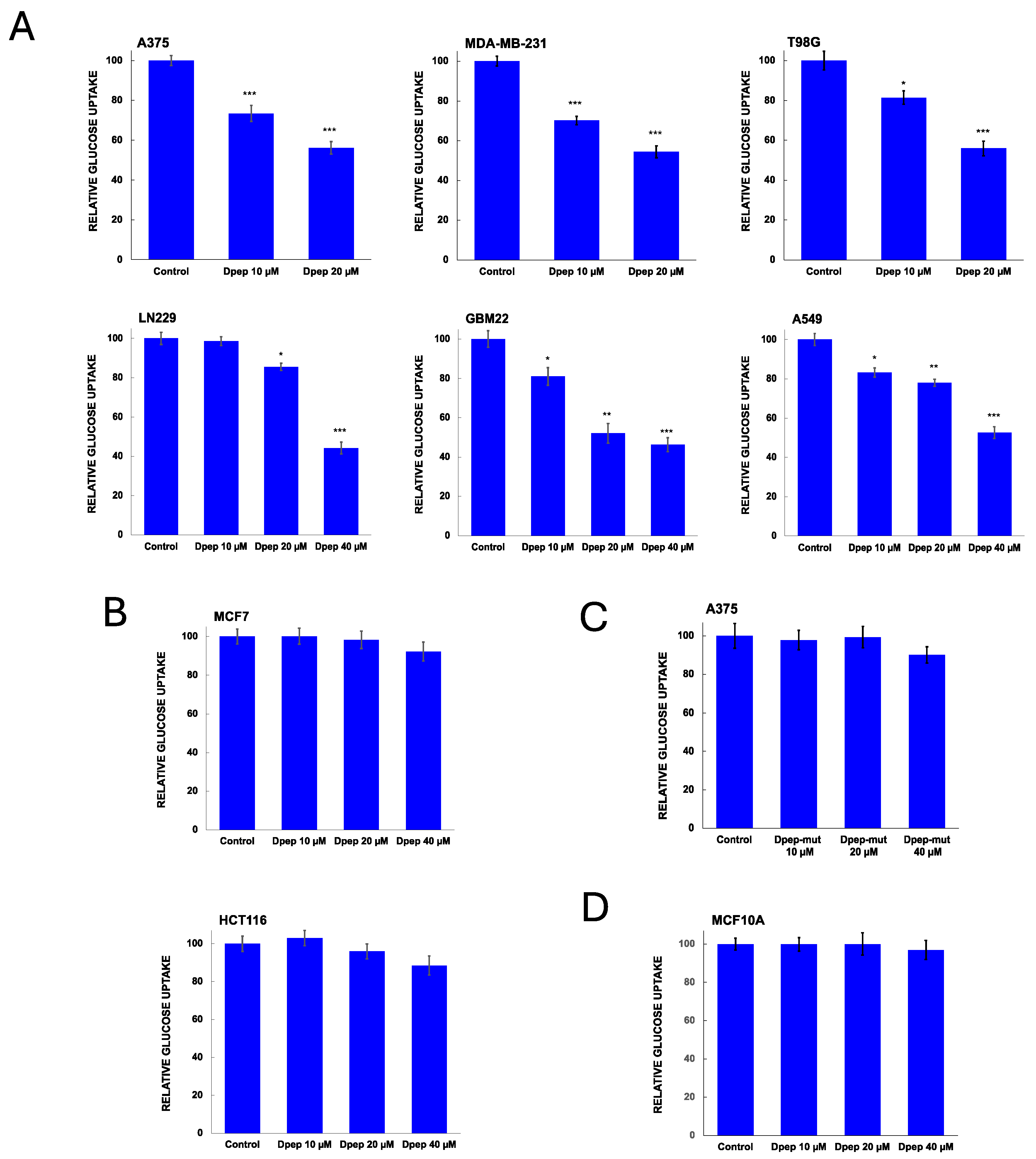
2.5. Glucose Uptake
2.6. siRNA Transfections
2.7. qPCR
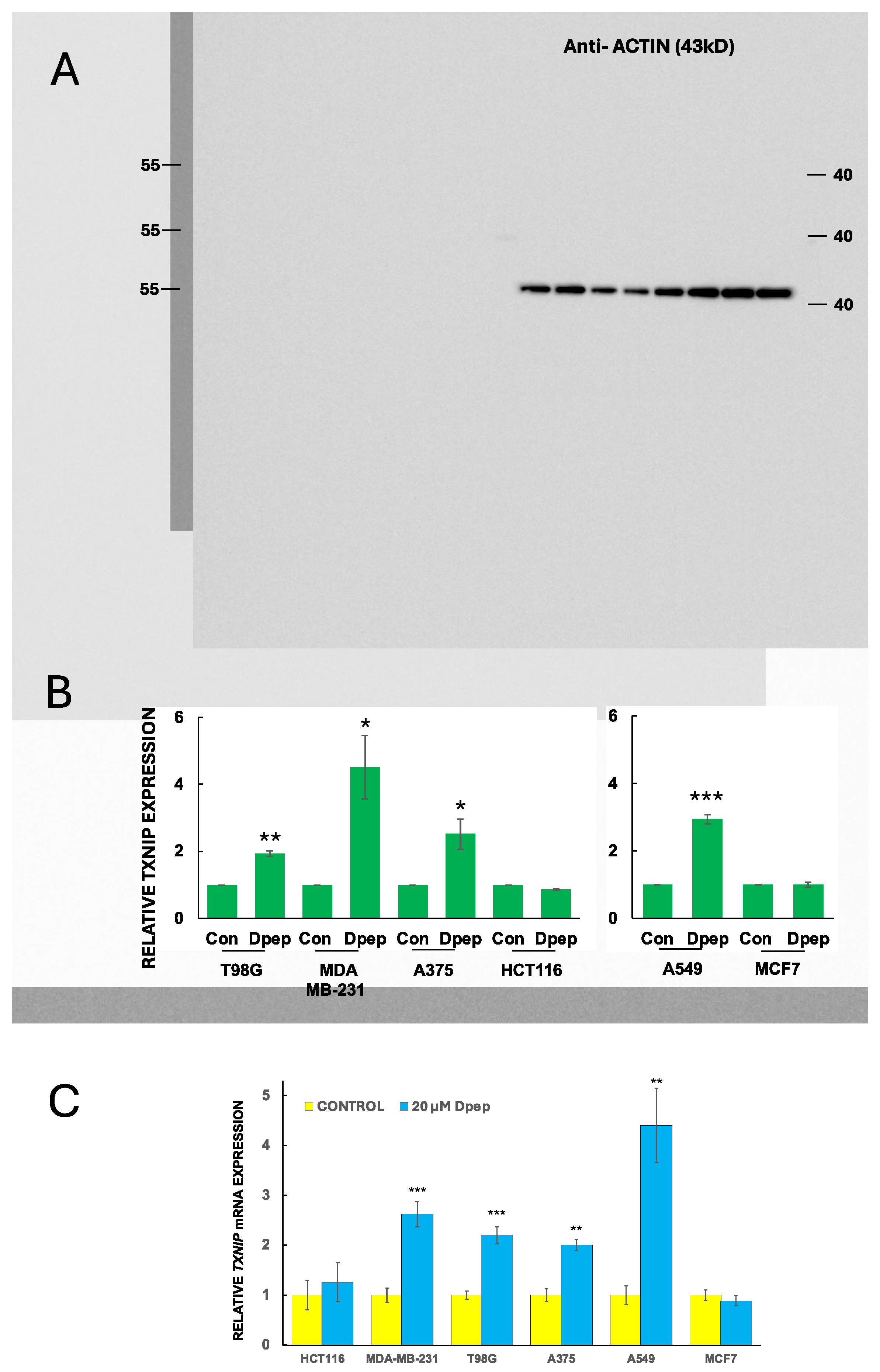
2.8. Western Immunoblotting
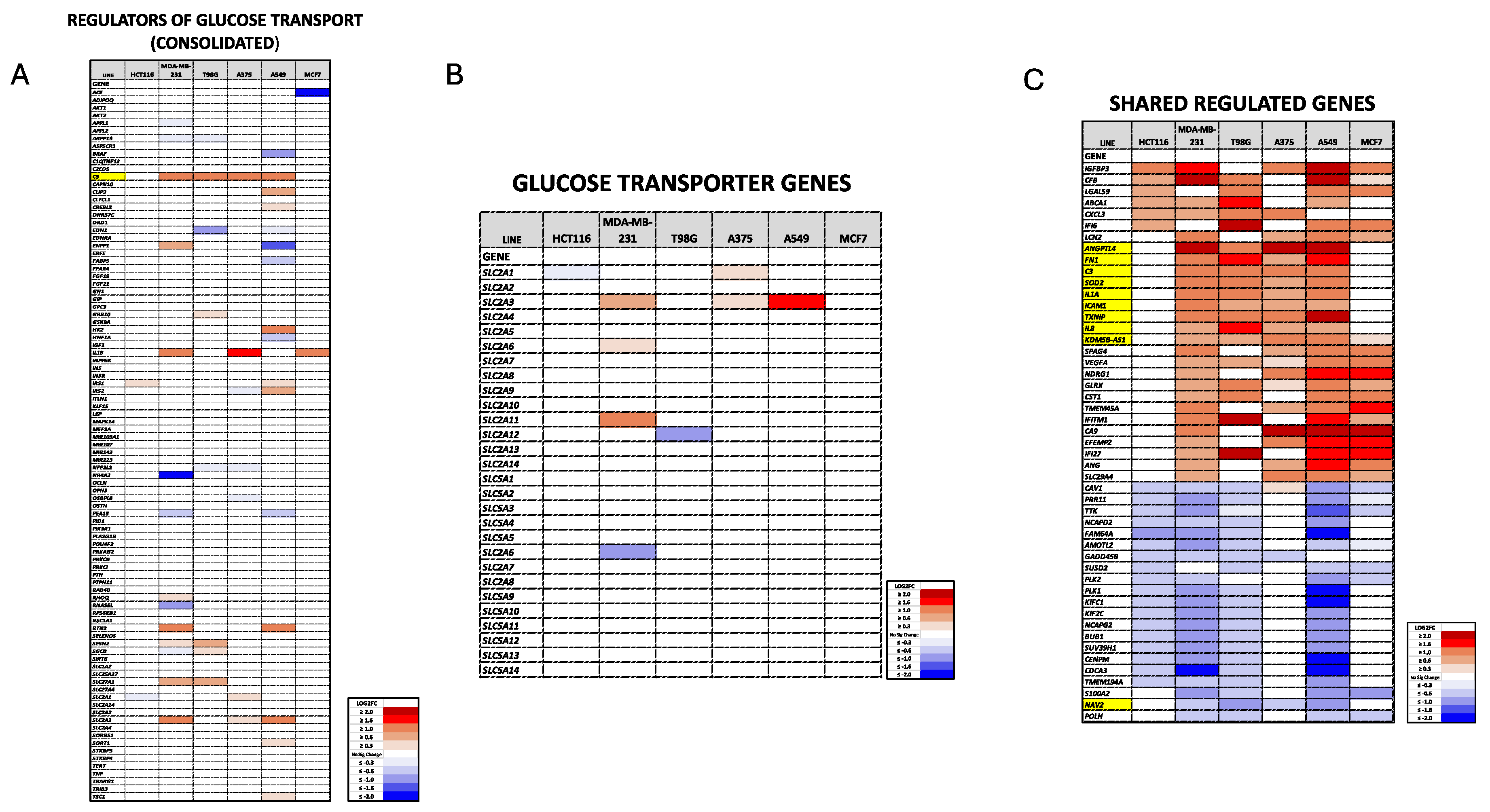
2.9. Plate-seq Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dpep Promotes Context-Dependent Suppression of Glycolysis in Diverse Cancer Cell Lines
3.2. Dpep Exhibits Context-Dependent Suppression of Glucose Uptake
3.3. Dpep Elevates TXNIP mRNA Levels in Lines with Reduced Glycolysis and Glucose Uptake, but Not in Lines without These Responses
3.4. Dpep Upregulates TXNIP Protein in Lines with Upregulated TXNIP Transcripts
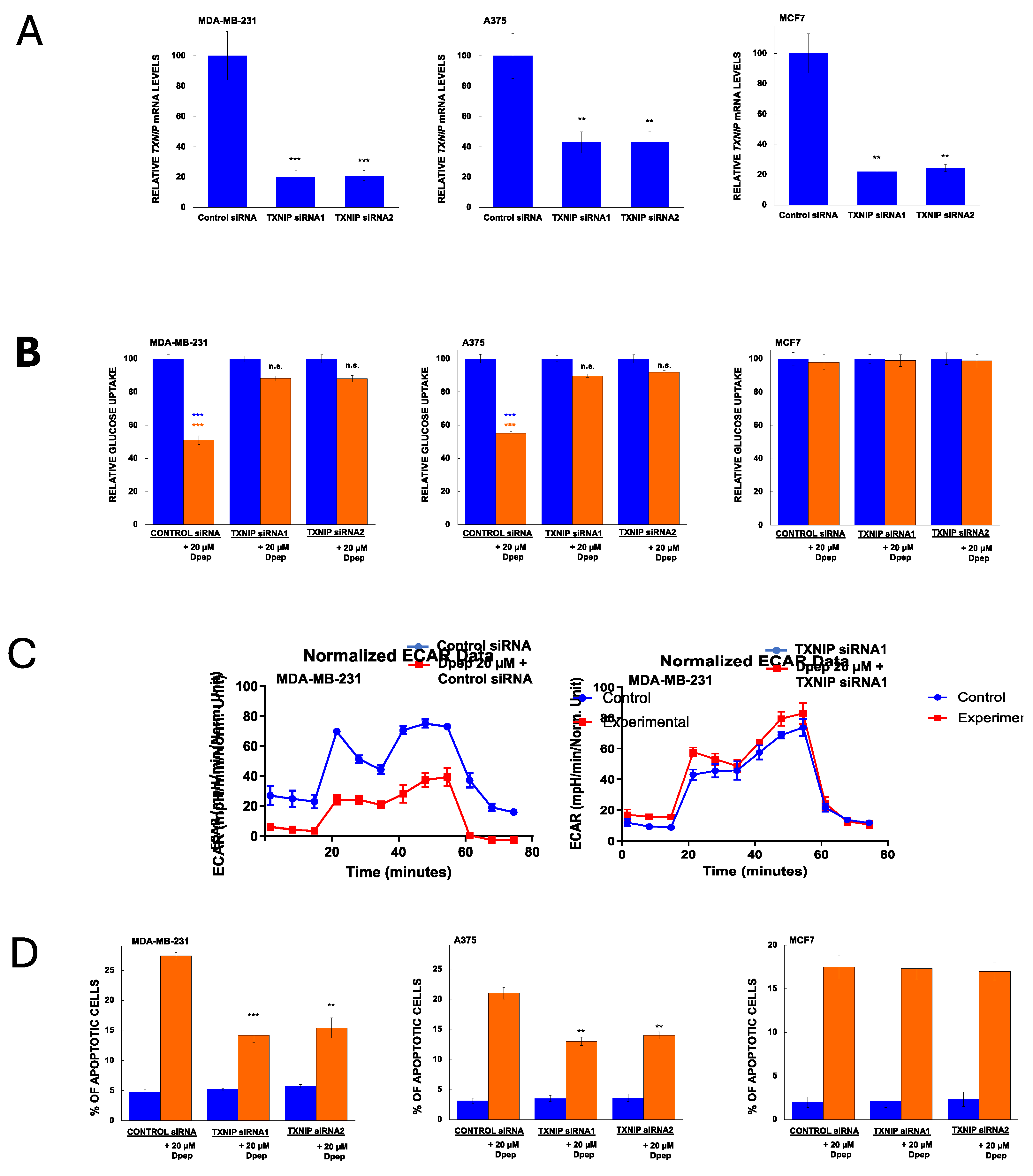
3.5. TXNIP Is Required for the Effects of Dpep on Glucose Uptake and Glycolysis and on Cell Survival
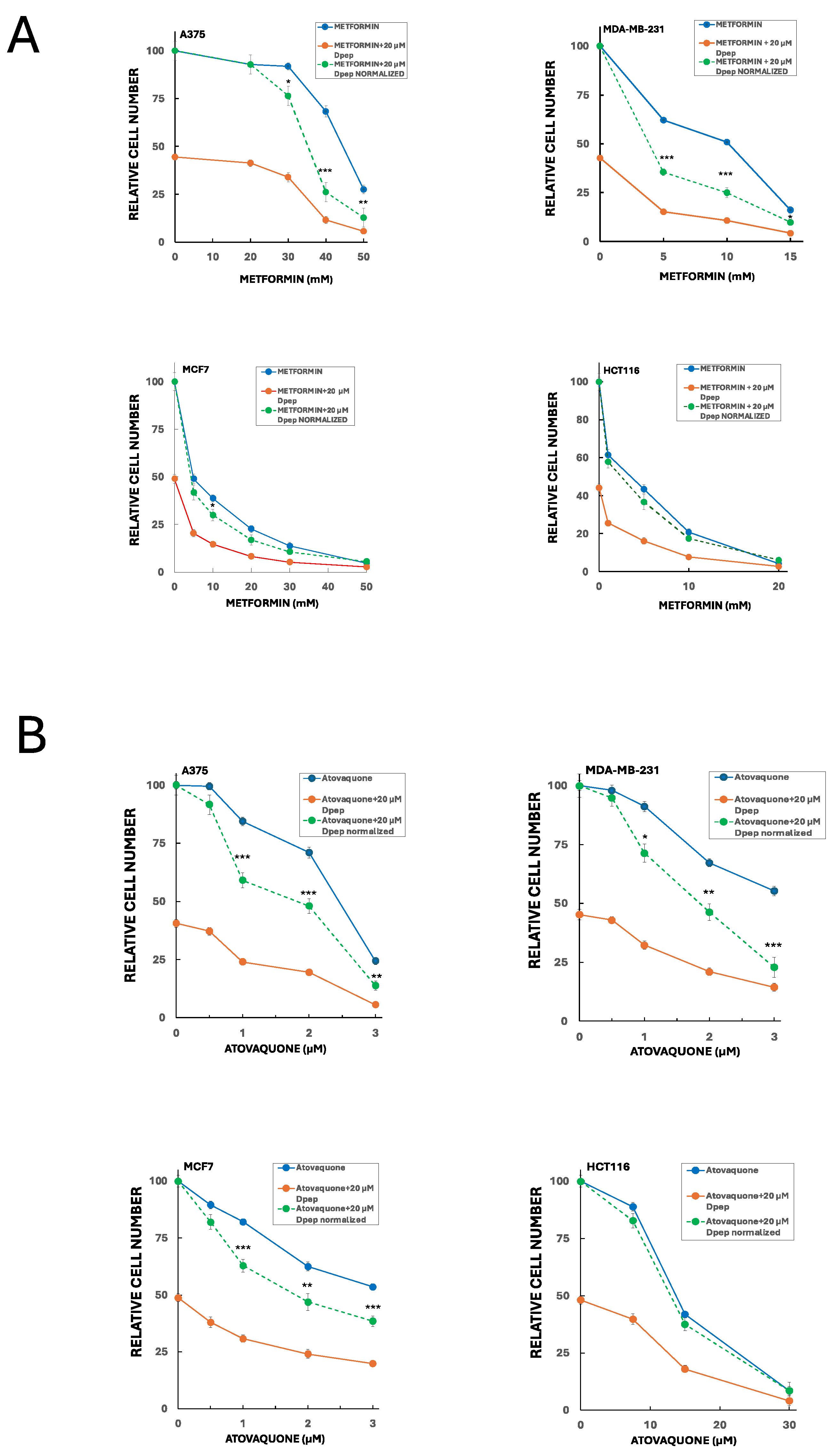
3.6. Dpep Shows Additive to Synergistic Activity with Inhibitors of Oxidative Phosphorylation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greene, L. A.; Zhou, Q.; Siegelin, M.D.; Angelastro, J.M., Targeting Transcription Factors ATF5, CEBPB and CEBPD with Cell-Penetrating Peptides to Treat Brain and Other Cancers. Cells 2023, 12(4).
- Paerhati, P.; Liu, J.; Jin, Z.; Jakos, T.; Zhu, S.; Qian, L.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, Y., Advancements in Activating Transcription Factor 5 Function in Regulating Cell Stress and Survival. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23(13).
- Angelastro, J. M.; Canoll, P. D.; Kuo, J.; Weicker, M.; Costa, A.; Bruce, J. N.; Greene, L. A. Selective destruction of glioblastoma cells by interference with the activity or expression of ATF5. Oncogene 2006, 25(6), 907-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sears, T. K.; Angelastro, J. M. The transcription factor ATF5: role in cellular differentiation, stress responses, and cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8(48), 84595–84609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, N.; Zhu, X.; Lu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Li, B.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Tian, J.; Miao, X. Prioritization of risk genes in colorectal cancer by integrative analysis of multi-omics data and gene networks. Sci China Life Sci 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klempnauer, K. H. C/EBPbeta cooperates with MYB to maintain the oncogenic program of AML cells. Oncotarget 2023, 14, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jefferson, P.; Zhou, Q.; Angelastro, J. M.; Greene, L. A. Dominant-Negative ATF5 Compromises Cancer Cell Survival by Targeting CEBPB and CEBPD. Mol Cancer Res 2020, 18(2), 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, M.; Li, S. CEBPB upregulates P4HA2 to promote the malignant biological behavior in IDH1 wildtype glioma. FASEB J 2023, 37(4), e22848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, L.; Duitman, J.; Bijlsma, M. F.; Spek, C. A. The dual role of C/EBPdelta in cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2023, 185, 103983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cates, C. C.; Arias, A. D.; Nakayama Wong, L. S.; Lame, M. W.; Sidorov, M.; Cayanan, G.; Rowland, D. J.; Fung, J.; Karpel-Massler, G.; Siegelin, M. D.; Greene, L. A.; Angelastro, J. M. Regression/eradication of gliomas in mice by a systemically-deliverable ATF5 dominant-negative peptide. Oncotarget 2016, 7(11), 12718-30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpel-Massler, G.; Horst, B. A.; Shu, C.; Chau, L.; Tsujiuchi, T.; Bruce, J. N.; Canoll, P.; Greene, L. A.; Angelastro, J. M.; Siegelin, M. D. A Synthetic Cell-Penetrating Dominant-Negative ATF5 Peptide Exerts Anticancer Activity against a Broad Spectrum of Treatment-Resistant Cancers. Clin Cancer Res 2016, 22(18), 4698-711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Sun, X.; Pasquier, N.; Jefferson, P.; Nguyen, T. T. T.; Siegelin, M. D.; Angelastro, J. M.; Greene, L. A. Cell-Penetrating CEBPB and CEBPD Leucine Zipper Decoys as Broadly Acting Anti-Cancer Agents. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13(10). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, D.; Boboila, S.; Okochi, S.; Angelastro, J. M.; Kadenhe-Chiweshe, A. V.; Lopez, G.; Califano, A.; Connolly, E. P.; Greene, L. A.; Yamashiro, D. J. Activating Transcription Factor 5 Promotes Neuroblastoma Metastasis by Inducing Anoikis Resistance. Cancer Res Commun 2023, 3(12), 2518–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, S. E.; Angelastro, J. M.; Szabolcs, M.; Greene, L. A. The transcription factor ATF5 is widely expressed in carcinomas, and interference with its function selectively kills neoplastic, but not nontransformed, breast cell lines. Int J Cancer 2007, 120(9), 1883-90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Angelastro, J. M.; Merino, D.; Zhou, Q.; Siegelin, M. D.; Greene, L. A. Dominant-negative ATF5 rapidly depletes survivin in tumor cells. Cell Death Dis 2019, 10(10), 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Greene, L. A. Dpep Inhibits Cancer Cell Growth and Survival via Shared and Context-Dependent Transcriptome Perturbations. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15(22). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaupel, P.; Multhoff, G. Revisiting the Warburg effect: historical dogma versus current understanding. J Physiol 2021, 599(6), 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushi, A.; Kim, H. D.; Chang, Y. C.; Kim, C. H. Revisited Metabolic Control and Reprogramming Cancers by Means of the Warburg Effect in Tumor Cells. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23(17). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworska, M.; Szczudlo, J.; Pietrzyk, A.; Shah, J.; Trojan, S. E.; Ostrowska, B.; Kocemba-Pilarczyk, K. A. The Warburg effect: a score for many instruments in the concert of cancer and cancer niche cells. Pharmacol Rep 2023, 75(4), 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, T.; Hartleben, G.; Muller, C.; Mastrobuoni, G.; Groth, M.; Sterken, B. A.; Zaini, M. A.; Youssef, S. A.; Zuidhof, H. R.; Krauss, S. R.; Kortman, G.; de Haan, G.; de Bruin, A.; Wang, Z. Q.; Platzer, M.; Kempa, S.; Calkhoven, C. F. C/EBPbeta-LIP induces cancer-type metabolic reprogramming by regulating the let-7/LIN28B circuit in mice. Commun Biol 2019, 2, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Pang, J.; Wang, L.; Dong, Q.; Jin, D. CEBPB regulates the bile acid receptor FXR to accelerate colon cancer progression by modulating aerobic glycolysis. J Clin Lab Anal 2022, 36(11), e24703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Cai, X.; Ye, W.; Kong, L.; Qiu, X.; Ying, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Recombinant Viral Capsid Protein L2 (rVL2) of HPV 16 Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Glucose Metabolism via ITGB7/C/EBPbeta Signaling Pathway in Cervical Cancer Cell Lines. Onco Targets Ther 2019, 12, 10415–10425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T. C.; Shiue, Y. L.; Li, C. F. The biological impacts of CEBPD on urothelial carcinoma development and progression. Front Oncol 2023, 13, 1123776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balamurugan, K.; Wang, J. M.; Tsai, H. H.; Sharan, S.; Anver, M.; Leighty, R.; Sterneck, E. The tumour suppressor C/EBPdelta inhibits FBXW7 expression and promotes mammary tumour metastasis. EMBO J 2010, 29(24), 4106-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Chu, F.; Wu, H.; Xiao, X.; Ye, J.; Li, K. Itraconazole inhibits tumor growth via CEBPB-mediated glycolysis in colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V. K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B. L.; Gillette, M. A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S. L.; Golub, T. R.; Lander, E. S.; Mesirov, J. P. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102(43), 15545-50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mootha, V. K.; Lindgren, C. M.; Eriksson, K. F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstrale, M.; Laurila, E.; Houstis, N.; Daly, M. J.; Patterson, N.; Mesirov, J. P.; Golub, T. R.; Tamayo, P.; Spiegelman, B.; Lander, E. S.; Hirschhorn, J. N.; Altshuler, D.; Groop, L. C. PGC-1alpha-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat Genet 2003, 34(3), 267-73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslowska, M.; Wang, H. W.; Cianflone, K. Novel roles for acylation stimulating protein/C3adesArg: a review of recent in vitro and in vivo evidence. Vitam Horm 2005, 70, 309-32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, S.; Seishima, R.; Yamasaki, J.; Hattori, K.; Ogiri, M.; Matsui, S.; Shigeta, K.; Okabayashi, K.; Nagano, O.; Li, L.; Kitagawa, Y. Angiopoietin-like 4 promotes glucose metabolism by regulating glucose transporter expression in colorectal cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2022, 148(6), 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwa, P.; Kordylewicz, K.; Bilecz, A.; Lastra, R. R.; Wroblewski, K.; Rinkevich, Y.; Lengyel, E.; Kenny, H. A. Cancer-associated mesothelial cell-derived ANGPTL4 and STC1 promote the early steps of ovarian cancer metastasis. JCI Insight 2023, 8(6). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Nai-Dong, W.; Jin-Xiang, Y.; Long, T.; Xiu-Rong, L.; Hong, G.; Jie-Cheng, Y.; Fei, Z. ANGPTL4 regulate glutamine metabolism and fatty acid oxidation in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med 2022, 26(7), 1876–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Lyu, L. H.; Miao, H. K.; Bahr, T.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Liang, T.; Zhou, H. B.; Chen, G. R.; Bai, Y. Redox regulation by SOD2 modulates colorectal cancer tumorigenesis through AMPK-mediated energy metabolism. Mol Carcinog 2020, 59(5), 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P. C.; Mao, M.; de Abreu, A. L.; Ansenberger-Fricano, K.; Ekoue, D. N.; Ganini, D.; Kajdacsy-Balla, A.; Diamond, A. M.; Minshall, R. D.; Consolaro, M. E.; Santos, J. H.; Bonini, M. G. MnSOD upregulation sustains the Warburg effect via mitochondrial ROS and AMPK-dependent signalling in cancer. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Tanaka, N. , IL-8-induced O-GlcNAc modification via GLUT3 and GFAT regulates cancer stem cell-like properties in colon and lung cancer cells. Oncogene 2019, 38(9), 1520–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagdeviren, S.; Lee, R. T.; Wu, N. Physiological and Pathophysiological Roles of Thioredoxin Interacting Protein: A Perspective on Redox Inflammation and Metabolism. Antioxid Redox Signal 2023, 38(4-6), 442–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, N.; Haseeb, M.; Kim, M. S.; Choi, S. Role of Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein in Diseases and Its Therapeutic Outlook. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22(5). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, E. TXNIP/TBP-2: A Master Regulator for Glucose Homeostasis. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9(8). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhawiti, N. M.; Al Mahri, S.; Aziz, M. A.; Malik, S. S.; Mohammad, S. TXNIP in Metabolic Regulation: Physiological Role and Therapeutic Outlook. Curr Drug Targets 2017, 18(9), 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S. Y.; Yu, F. X.; Luo, Y.; Hagen, T. Oncogenic activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway promotes cellular glucose uptake by downregulating the expression of thioredoxin-interacting protein. Cell Signal 2016, 28(5), 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; O’Shea, J. M.; Kaadige, M. R.; Cunha, S.; Wilde, B. R.; Cohen, A. L.; Welm, A. L.; Ayer, D. E. Metabolic reprogramming in triple-negative breast cancer through Myc suppression of TXNIP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015, 112(17), 5425-30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Ding, R.; Qu, X.; Li, Y.; Shen, T.; Wang, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Ru, Y.; Bu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Song, W.; Shen, L.; Zhang, P. BCR-ABL triggers a glucose-dependent survival program during leukemogenesis through the suppression of TXNIP. Cell Death Dis 2023, 14(4), 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Gong, L.; Xu, H.; Liu, B.; Fang, X.; Yu, D.; Li, L.; Wei, T.; Wang, Y.; Wong, C. N.; Lyu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Sham, P. C.; Guan, X. Y. C-terminal truncated HBx initiates hepatocarcinogenesis by downregulating TXNIP and reprogramming glucose metabolism. Oncogene 2021, 40(6), 1147–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, B.; Mao, Q.; Xia, W.; Zhang, T.; Song, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Dong, G.; Jiang, F. circDCUN1D4 suppresses tumor metastasis and glycolysis in lung adenocarcinoma by stabilizing TXNIP expression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ning, J.; Cao, W.; Wang, S.; Du, T.; Jiang, J.; Feng, X.; Zhang, B. Research Progress of TXNIP as a Tumor Suppressor Gene Participating in the Metabolic Reprogramming and Oxidative Stress of Cancer Cells in Various Cancers. Front Oncol 2020, 10, 568574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyanaraman, B.; Cheng, G.; Hardy, M.; You, M. OXPHOS-targeting drugs in oncology: new perspectives. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2023, 27(10), 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, T. M.; McKenna, W. G.; Kunz-Schughart, L. A.; Higgins, G. S. Oxidative Phosphorylation as an Emerging Target in Cancer Therapy. Clin Cancer Res 2018, 24(11), 2482–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Patnana, P. K.; Xie, X.; Frank, D.; Nimmagadda, S. C.; Rosemann, A.; Liebmann, M.; Klotz, L.; Opalka, B.; Khandanpour, C. High Metabolic Dependence on Oxidative Phosphorylation Drives Sensitivity to Metformin Treatment in MLL/AF9 Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14(3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, Y. S.; Wang, L. C.; Huang, J. B. Advances in metformin-based metabolic therapy for non-small cell lung cancer (Review). Oncol Rep 2022, 47(3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, W.; Wei, L.; Zhu, S. Current status and frontier tracking of clinical trials on Metformin for cancer treatment. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2023, 149(18), 16931–16946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, A. M.; Schafer, E. S.; Li, M.; Terrell, M.; Rashid, R.; Paek, H.; Bernhardt, M. B.; Weisnicht, A.; Smith, W. T.; Keogh, N. J.; Alozie, M. C.; Oviedo, H. H.; Gonzalez, A. K.; Ilangovan, T.; Mangubat-Medina, A.; Wang, H.; Jo, E.; Rabik, C. A.; Bocchini, C.; Hilsenbeck, S.; Ball, Z. T.; Cooper, T. M.; Redell, M. S. Repurposing Atovaquone as a Therapeutic against Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): Combination with Conventional Chemotherapy Is Feasible and Well Tolerated. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15(4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, A.; Mehta, P.; Simmons, A. D.; Ericksen, S. S.; Mehta, G.; Palecek, S. P.; Felder, M.; Stenerson, Z.; Nayak, A.; Dominguez, J. M. A.; Patankar, M.; Barroilhet, L. M. Atovaquone: An Inhibitor of Oxidative Phosphorylation as Studied in Gynecologic Cancers. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14(9). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dykstra, H.; LaRose, C.; Fisk, C.; Waldhart, A.; Meng, X.; Zhao, G.; Wu, N. TXNIP interaction with GLUT1 depends on PI(4,5)P(2). Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 2021, 1863(12), 183757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldhart, A. N.; Dykstra, H.; Peck, A. S.; Boguslawski, E. A.; Madaj, Z. B.; Wen, J.; Veldkamp, K.; Hollowell, M.; Zheng, B.; Cantley, L. C.; McGraw, T. E.; Wu, N. Phosphorylation of TXNIP by AKT Mediates Acute Influx of Glucose in Response to Insulin. Cell Rep 2017, 19(10), 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Zheng, B.; Shaywitz, A.; Dagon, Y.; Tower, C.; Bellinger, G.; Shen, C. H.; Wen, J.; Asara, J.; McGraw, T. E.; Kahn, B. B.; Cantley, L. C. AMPK-dependent degradation of TXNIP upon energy stress leads to enhanced glucose uptake via GLUT1. Mol Cell 2013, 49(6), 1167–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls-Histed, S. J.; Nielsen, C. P.; MacGurn, J. A. Lysosomal trafficking of the glucose transporter GLUT1 requires sequential regulation by TXNIP and ubiquitin. iScience 2023, 26(3), 106150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ge, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, J. J.; Choi, Y. J.; Chen, W.; Bowman, J. W.; Foo, S. S.; Chang, L. C.; Liang, Q.; Hara, D.; Choi, I.; Kim, M. H.; Eoh, H.; Jung, J. U. TXNIP-mediated crosstalk between oxidative stress and glucose metabolism. PLoS One 2024, 19(2), e0292655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pliszka, M.; Szablewski, L. Glucose Transporters as a Target for Anticancer Therapy. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13(16). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancey, P. B.; Contat, C.; Meylan, E. Glucose transporters in cancer - from tumor cells to the tumor microenvironment. FEBS J 2018, 285(16), 2926–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y. C.; Chan, M. H.; Yang, Y. F.; Li, C. H.; Hsiao, M. Glucose transporter 4: Insulin response mastermind, glycolysis catalyst and treatment direction for cancer progression. Cancer Lett 2023, 563, 216179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwari, P.; Chutkow, W. A.; Cummings, K.; Verstraeten, V. L.; Lammerding, J.; Schreiter, E. R.; Lee, R. T. Thioredoxin-independent regulation of metabolism by the alpha-arrestin proteins. J Biol Chem 2009, 284(37), 24996–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Pan, T.; Liu, Z.; McCarthy, C.; Vicencio, J. M.; Cao, L.; Alfano, G.; Suwaidan, A. A.; Yin, M.; Beatson, R.; Ng, T. , The role of TXNIP in cancer: a fine balance between redox, metabolic, and immunological tumor control. Br J Cancer 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Zhang, P.; Hu, X.; Zhang, B. Integrated multiomic data analysis reveals the clinical significance of TXNIP and contributing to immune microenvironment in triple negative breast cancer. Transl Oncol 2023, 39, 101808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



