Submitted:
10 May 2024
Posted:
13 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Integrated Approach: The study utilized an integrated approach by combining AHP, BWM, and GIS techniques to evaluate potential sites for solar energy plant development in Yemen. This comprehensive method involved the use of multiple decision-making tools and spatial analysis, resulting in a thorough and holistic assessment.
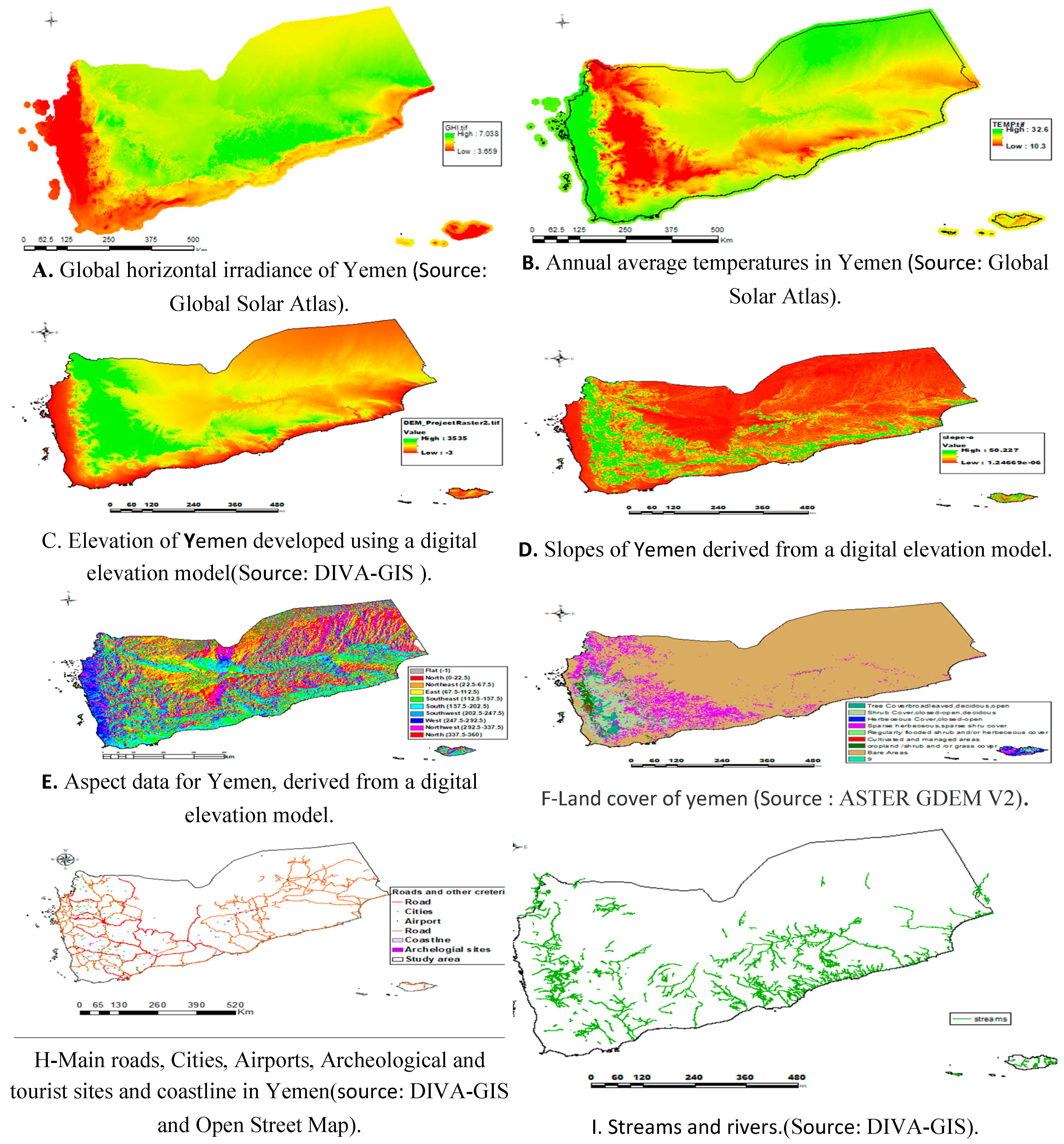
- Criteria Selection and Weighting: The researchers meticulously selected twelve criteria that impact the suitability of sites for solar energy plants, including factors like temperature and land coverage. Through the application of AHP and BWM methods to assign weights to these criteria, a comprehensive and comparative evaluation was achieved, capturing diverse perspectives on the importance of each criterion.
- Suitability Mapping: By integrating the weighted criteria using a GIS-based weighted overlay tool, the researchers created a detailed suitability map classifying regions in Yemen into optimal, highly suitable, and suitable categories. This spatial analysis provided decision-makers with a visual representation of the most promising areas for solar energy plant development.
- Comparative Analysis: The research also compared the results of the suitability assessment obtained through AHP and BWM methods. This comparative analysis shed light on the variations in decision-making outcomes when different multi-criteria decision-making techniques are utilized, helping in selecting the most suitable method for the specific context of Yemen.
- Practical Implications: The findings of this research are beneficial for decision-makers involved in renewable energy projects in Yemen. By facilitating informed decision-making processes, this study can play a significant role in promoting the sustainable growth of the renewable energy sector in the country.
- The first objective is to pinpoint the most ideal locations for the establishment of solar energy plants in Yemen. This will be achieved by utilizing a combination of AHP, BWM, and GIS techniques to assess various factors and determine the best sites.
- Another key goal is to carefully analyze and select a specific set of criteria that play a significant role in determining the suitability of locations for solar energy plant development in Yemen. By evaluating these criteria, the study aims to identify the most crucial factors that need to be considered.
- The third objective involves determining the relative importance of the selected criteria through the use of both AHP and BWM methods. By comparing the results obtained from these two decision-making techniques, the study aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the weightage assigned to each criterion.
- The next step is to combine the weighted criteria layers into a GIS-based suitability analysis. This will enable the creation of a detailed suitability map that categorizes the regions of Yemen into different zones based on their suitability for establishing solar energy plants.
- Furthermore, the study aims to offer insights into the spatial distribution of these suitability classes across Yemen. By highlighting regions with the most favorable conditions for solar energy plant development, the research aims to guide future planning and implementation of renewable energy projects in the country.
- Lastly, the research seeks to demonstrate the effectiveness of the integrated AHP, BWM, and GIS approach in assessing potential sites for solar energy plant deployment. By comparing the results obtained from the two multi-criteria decision-making methods, the study aims to showcase the strengths and differences in using these techniques.
2. Methodology
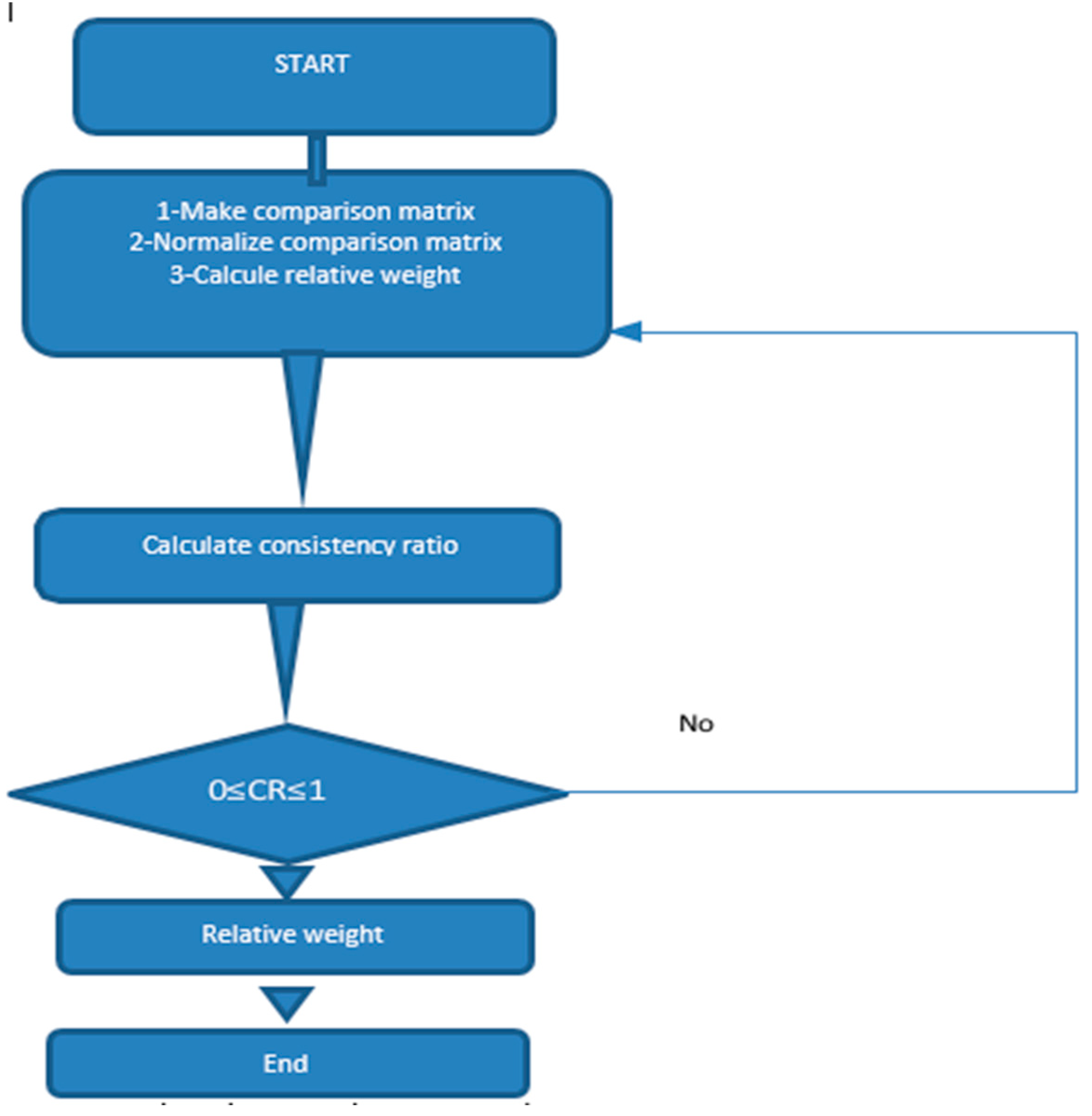
2.2. Criteria Weighting
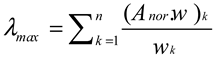
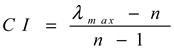
2.2.2. Criteria Weighting Using the Best-Worst Method (BWM)
2.3. Combining Criteria Using Geographic Information System
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
References
- Al Garni, H.; Awasthi, A. Solar energy utilization in Saudi Arabia: Status and future prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 1843–1862. [Google Scholar]
- Ajrina, A.S.; Sarno, R.; Ginardi, R.H. Comparison of AHP and BWM methods based on geographic information system for determining potential zone of Pasir Batu mining. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Seminar on Application for Technology of Information and Communication, Surabaya, Indonesia, 8–9 September 2018; pp. 453–457. [Google Scholar]
- Babatunde, O.M.; Munda, J.L.; Hamam, Y. A comprehensive state-of-the-art survey on hybrid renewable energy system operations and planning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 75313–75346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branker, K.; Pathak, M.J.M.; Pearce, J.M. A review of solar photovoltaic levelized cost of electricity. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 4470–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Y. Site selection for solar power plants using a hybrid model based on BWM and AHP in Taiwan. Renew. Energy 2019, 135, 769–779. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Systems Research Institute. ArcGIS Desktop: Release 10.8.1; Environmental Systems Research Institute: Redlands, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- DIVA-GIS. DIVA-GIS (Version 7.5.0) [Computer Software]. 2024. Available online: https://www.diva-gis.org/ (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Dong, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H. Wind and solar power integration: A review of designs, models, and optimization techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 123, 109760. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, S.; Mishra, S.; Chand, A.K. Modeling and simulation of photovoltaic array characteristics under partial shading conditions. Sol. Energy 2013, 93, 205–215. [Google Scholar]
- Ellabban, O.; Abu-Rub, H.; Blaabjerg, F. Renewable energy resources: Current status, future prospects and their enabling technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 748–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltawil, M.A.; Lin, Z. Grid-connected photovoltaic power systems: Technical and potential problems—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 21, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroozesh, F.; Monavari, S.M.; Salmanmahiny, A.; Robati, M.; Rahimi, R. Assessment of sustainable urban development based on a hybrid decision-making approach: Group fuzzy BWM, AHP, and TOPSIS–GIS. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Solar Atlas. Available online: https://globalsolaratlas.info/ (accessed on 3 May 2023).
- Green, F.; Staffell, I.; Vasilakos, N. The costs and impacts of intermittent renewable energy systems. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 377–386. [Google Scholar]
- International Energy Agency. Renewable Energy. 2021. Available online: https://www.iea.org/topics/renewables (accessed on 3 May 2023).
- Kaya, T.; Kahraman, C. Multicriteria renewable energy planning using an integrated fuzzy VIKOR & AHP methodology: The case of Istanbul. Energy 2013, 49, 355–364. [Google Scholar]
- Kahraman, C.; Kaya, I. Multicriteria renewable energy planning using an integrated fuzzy VIKOR & fuzzy AHP methodology: The case of Istanbul. Energy 2015, 81, 649–658. [Google Scholar]
- Khatib, T.; Ibrahim, A.; Mohamed, A.; Sopian, K. A review of sizing methodologies of photovoltaic systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 20, 100785. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Yao, Y. Site selection for solar power plants in China: A GIS-based multi-criteria evaluation approach. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2017, 19, 173–183. [Google Scholar]
- Masud, M.H.; Nuruzzaman, M.; Ahamed, R.; Ananno, A.A.; Tomal, A.A. Renewable energy in Bangladesh: Current situation and future prospects. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2020, 39, 132–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Rezaei, J. Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method: An application to offshore wind energy sources. Energy 2020, 195, 116935. [Google Scholar]
- Moslem, S.; Farooq, D.; Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Blaschke, T. Application of the AHP-BWM model for evaluating driver behavior factors related to road safety: A case study for Budapest. Symmetry 2020, 12, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenStreetMap. OpenStreetMap. 2024. Available online: https://www.openstreetmap.org (accessed on 3 May 2023).
- Panwar, N.L.; Kaushik, S.C.; Kothari, S. Role of renewable energy sources in environmental protection: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, S.S.; Pant, S.; Kumar, A.; Ram, M.; Sharma, H.K.; Kumar, A. A state-of-the-art survey on analytical hierarchy process applications in sustainable development. Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Serv. 2022, 7, 883–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, B.; Sagl, G.; Törnros, T.; Bachmaier, A.; Eggers, J.B.; Herkel, S.; Narmsara, S.; Gündra, H. GIS-based planning and modeling for renewable energy: Challenges and future research avenues. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2014, 3, 662–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; El-Amin, I. Site selection for solar farms using GIS and multi-criteria decision analysis. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, J. Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method. Omega 2015, 53, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J. Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method: Some properties and a linear model. Omega 2016, 64, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process: Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Serv. Sci. 2008, 1, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Sohani, N.; Yadav, A. Comparative analysis of ranking the lean supply chain enablers: An AHP, BWM and fuzzy SWARA based approach. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2022, 39, 2252–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solargis. Solar Resource Data & Photovoltaic Simulation. 2024. Available online: https://www.solargis.com (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Tan, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, N.; Liang, J.; Xu, D.; Yang, Q. Comparison of AHP and BWM methods based on ArcGIS for ecological suitability assessment of Panax notoginseng in Yunnan Province, China. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 199, 116737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ren, X.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Yue, H.; Cui, S. Spatial-temporal variations and influencing factors of solar energy potential in the contiguous United States. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Guo, P.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C. Towards sustainable circular agriculture: An integrated optimization framework for crop-livestock-biogas-crop recycling system management under uncertainty. Agric. Syst. 2022, 196, 103347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
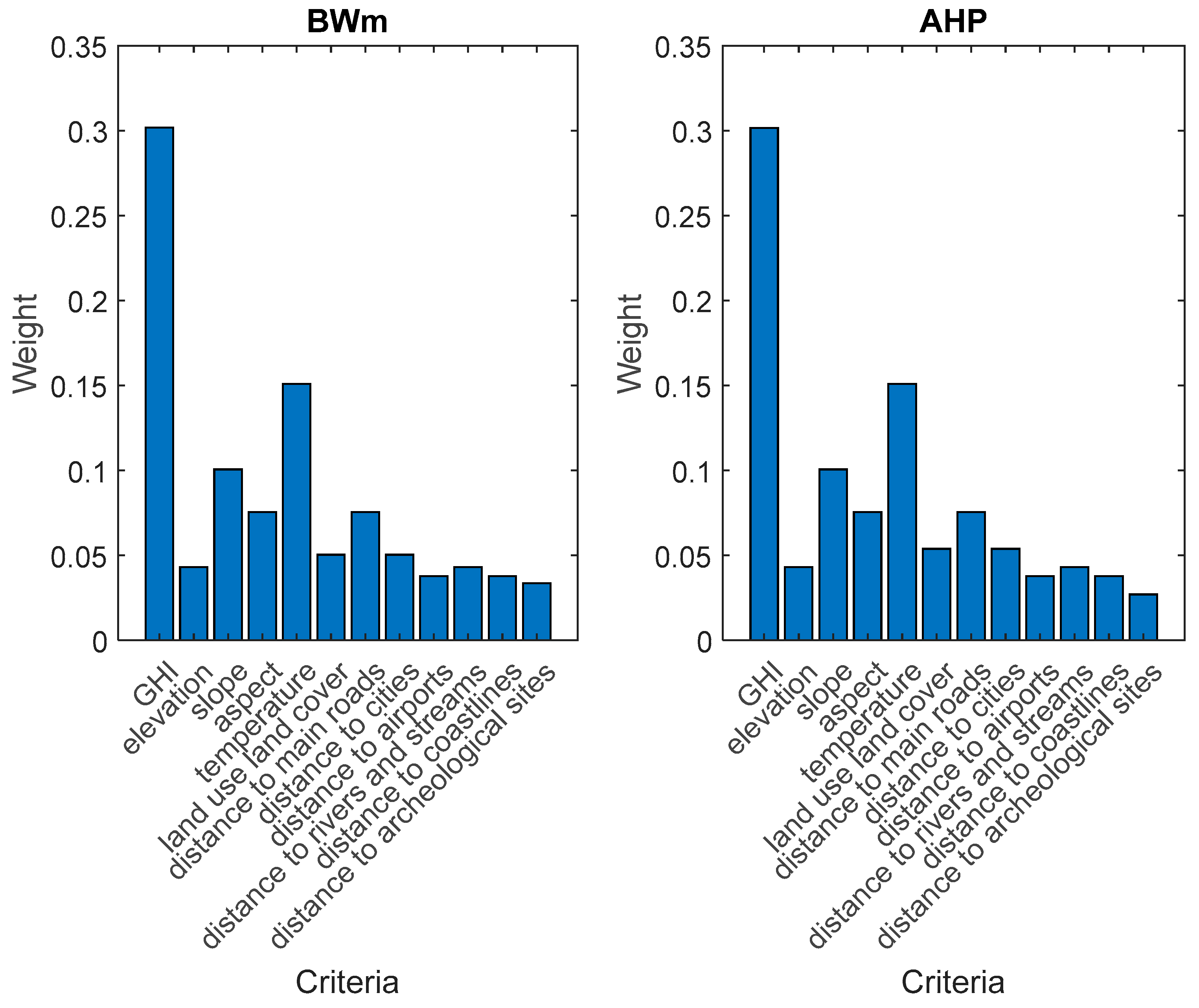
| Criterion | AHP weight | BWM weight |
| Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI) | 0.301638 | 0.301796 |
| Elevation | 0.043091 | 0.043114 |
| Slope | 0.100546 | 0.100599 |
| Aspect | 0.075409 | 0.075449 |
| Temperature | 0.150819 | 0.150898 |
| Land use land cover | 0.053788 | 0.050299 |
| Distance to main roads | 0.075409 | 0.075449 |
| Distance to cities | 0.053788 | 0.050299 |
| Distance to airports | 0.037705 | 0.037725 |
| Distance to rivers and streams | 0.043091 | 0.043114 |
| Distance to coastlines | 0.037705 | 0.037725 |
| Distance to archaeological sites | 0.027011 | 0.033533 |
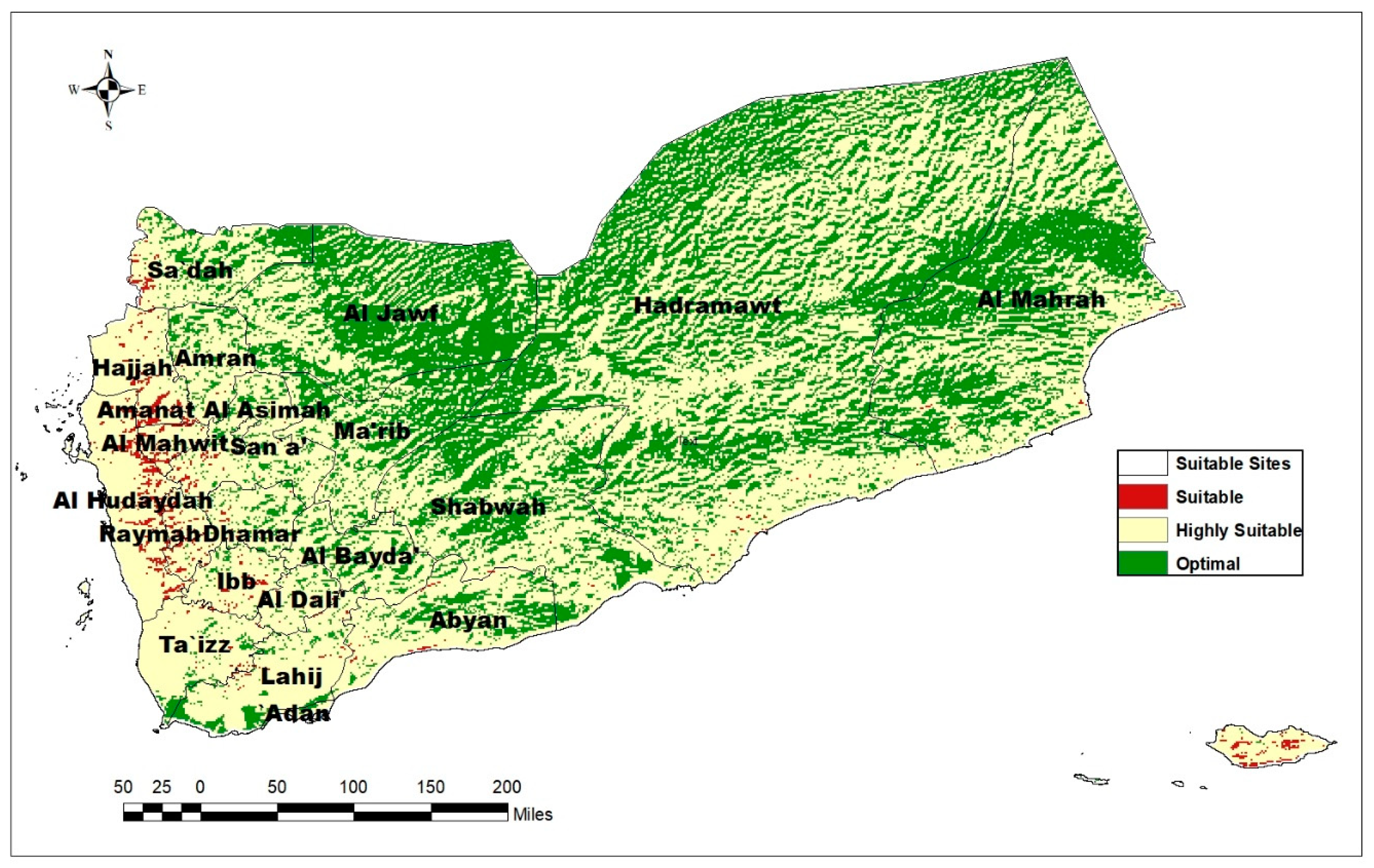
| No. | suitability level | Suitability Category | Percentage of Study Area(%) |
| 1 | 5 | optimal | 38 |
| 2 | 4 | highly | 61 |
| 3 | 3 | suitable | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





