Submitted:
08 May 2024
Posted:
09 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
- inclusion criteria: age > 18 years, presence of obesity (body mass index BMI ≥ 30 kg/m^2), absence of T2D according to ADA criteria [10], and other metabolic comorbidities and treatments;
- exclusion criteria: previous anti-obesity treatment (GLP1-RAs or others) and/or bariatric surgery, pregnancy.
2.2. Data Collection and Definition
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
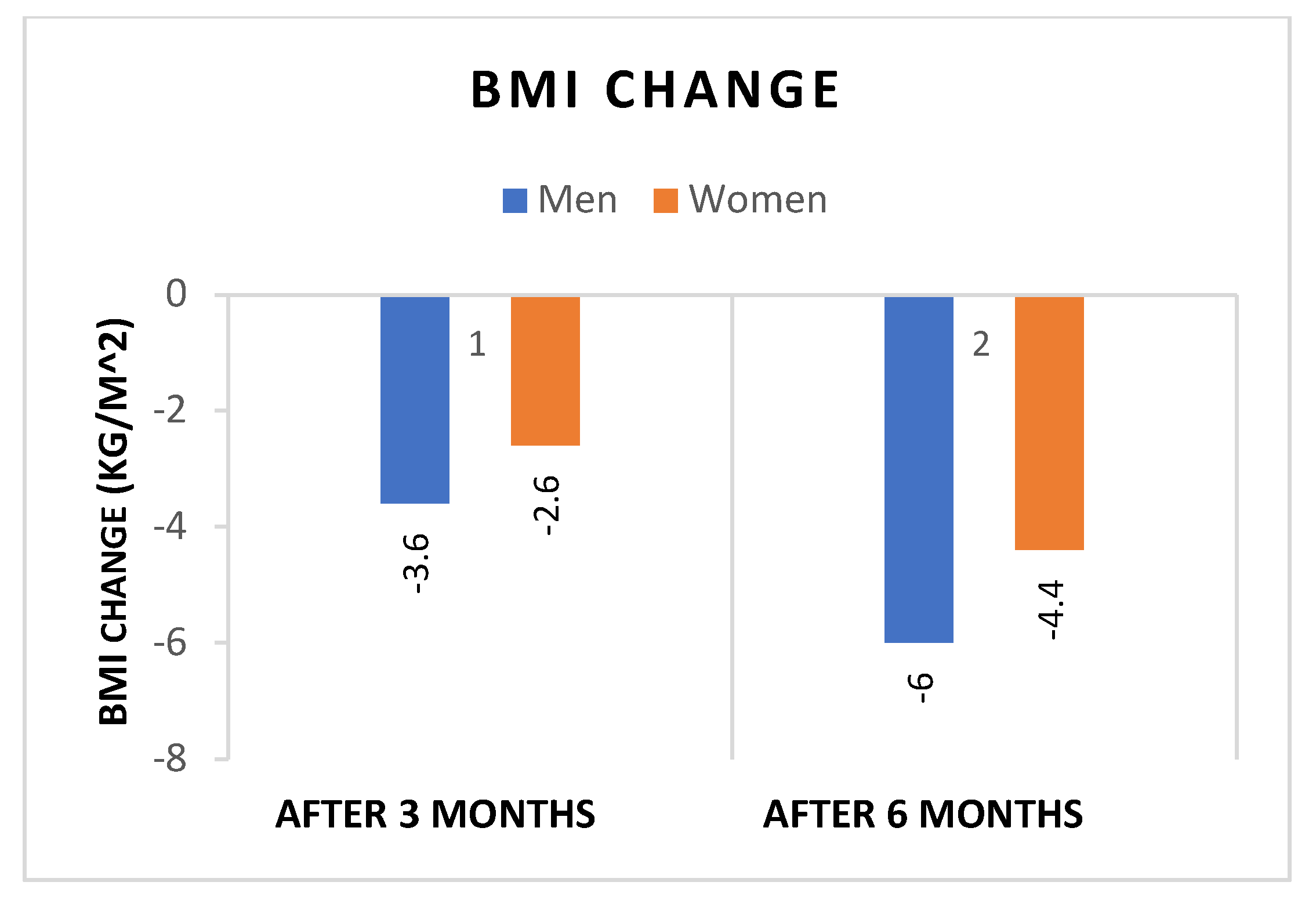
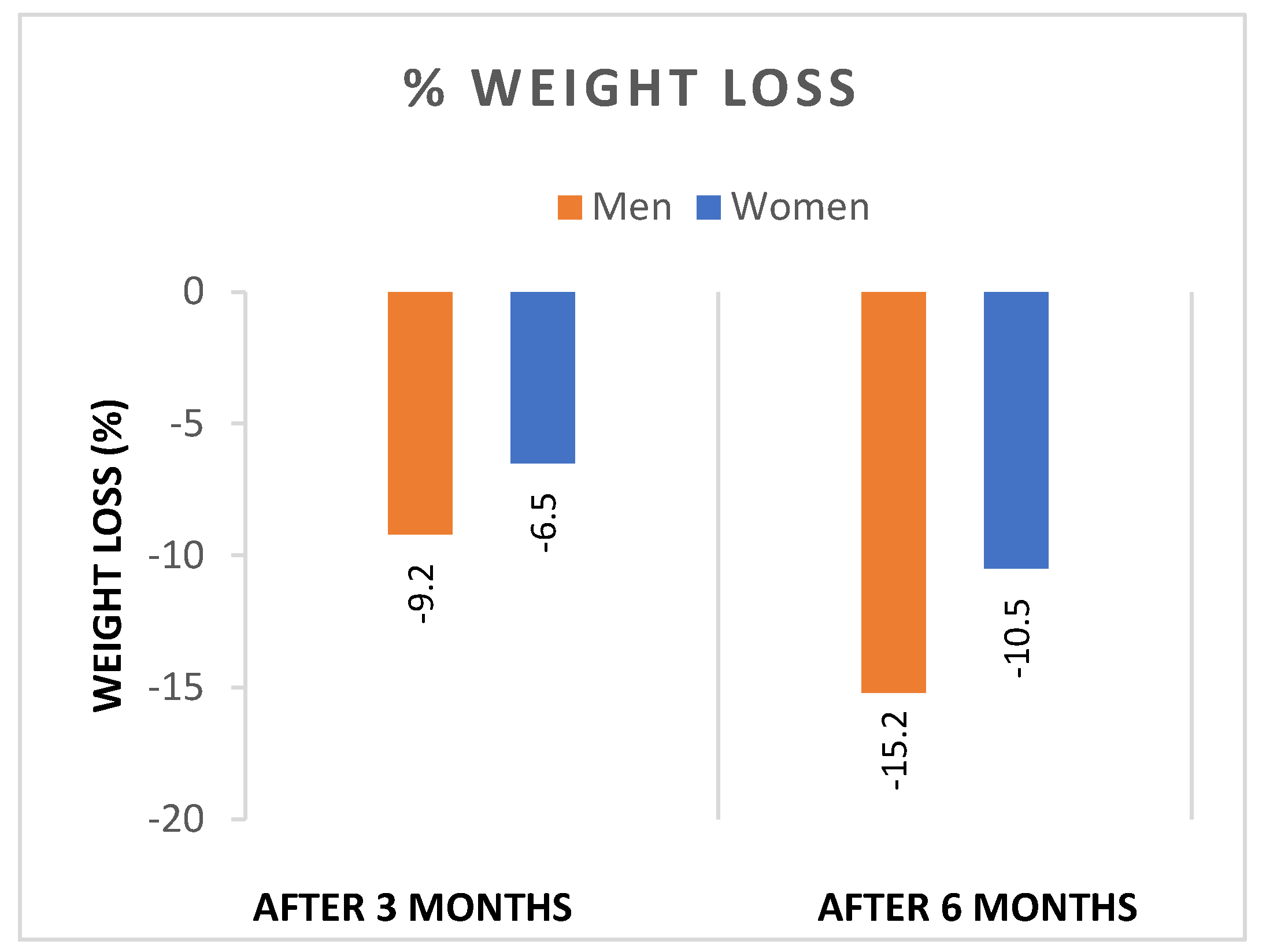
- Both sexes showed significant reductions in WL and BMI after 3 and 6 months of liraglutide treatment, with significantly greater reductions in both weight (Figure 1), and BMI (Figure 2) in men. In addition, the percentage of patients achieving WL > 5% at 3 months and WL > 10% at 6 months was significantly higher in men.
- 2.
- The analysis of metabolic parameters showed a significant reduction in total and LDL cholesterol, and FIB-4 in men. However, there was no significant gender difference in glucose metabolism and renal function.
4.1. Study Limitations and Strenghts
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang J-Y, Wang Q-W, Yang X-Y, et al. (2023) GLP−1 receptor agonists for the treatment of obesity: Role as a promising approach. Front. Endocrinol14:1085799. [CrossRef]
- Malik, V.S., Willet, W.C. & Hu, F.B. (2020), Nearly a decade on — trends, risk factors and policy implications in global obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol 16, 615–616. [CrossRef]
- Boutari, Chrysoula et al. (2022) A 2022 update on the epidemiology of obesity and a call to action: as its twin COVID-19 pandemic appears to be receding, the obesity and dysmetabolism pandemic continues to rage on. Metabolism: clinical and experimental, Vol 133. [CrossRef]
- Italian Central Statistics Institute (Istituto Nazionale di Statistica). BES 2021: Equitable and sustainable well-beeing in Italy, Available at: https://www.istat.it/it/files/2021/10/BES-Report-2020.pdf.
- 5. Cooper, A.J., Gupta, S.R., Moustafa, A.F. et al. (2021) Sex/Gender Differences in Obesity Prevalence, Comorbidities, and Treatment. Curr Obes Rep 10, 458–466 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-021-00453-x.
- Muscogiuri, G., Verde, L., Vetrani, C., Barrea, L., Savastano, S., & Colao, A. (2024). Obesity: a gender-view. Journal of endocrinological investigation, 47(2), 299–306. [CrossRef]
- Cataldi, M., Muscogiuri, G., Savastano, S., et al. (2019). Gender-related issues in the pharmacology of new anti-obesity drugs. Obesity reviews: an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity, 20(3), 375–384. Gender-related issues in the pharmacology of new anti-obesity drugs. [CrossRef]
- Jensterle, M., Rizzo, M., Haluzík, M. et al. (2022) Efficacy of GLP-1 RA Approved for Weight Management in Patients With or Without Diabetes: A Narrative Review. Adv Ther 39, 2452–2467. 39. [CrossRef]
- Santini, S., Vionnet, N., Pasquier, J., et al. (2023). Marked weight loss on liraglutide 3.0 mg: Real-life experience of a Swiss cohort with obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.), 31(1), 74–82. [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N. A., Aleppo, G., Aroda, V. R, et al. (2023). 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes care, 46(Suppl 1), S19–S40. [CrossRef]
- European Association for Study of Liver, & Asociacion Latinoamericana para el Estudio del Higado (2015). EASL-ALEH Clinical Practice Guidelines: Non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis. Journal of hepatology, 63(1), 237–264. [CrossRef]
- Tempia Valenta, S., Stecchi, M., Perazza, F. et al. (2023) Liraglutide 3.0 mg and mental health: can psychiatric symptoms be associated to adherence to therapy? Insights from a clinical audit. Eat Weight Disord 28, 99. [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, N., Arora, S., & Kalra, S. (2021). Gender Disparities in People Living with Obesity - An Unchartered Territory. Journal of mid-life health, 12(2), 103–107. [CrossRef]
- World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas 2022. London: World Obesity Federation; (2002) 4:1–289. Available at: https://www.worldobesity.org/resources/resource-library/world-obesity-atlas-2022.
- Jaacks, L. M., Vandevijvere, S., Pan, A., et al. (2019). The obesity transition: stages of the global epidemic. The lancet. Diabetes & endocrinology, 7(3), 231–240. [CrossRef]
- Tchoukhine, E., Takala, P., Hakko, H., et al. (2011). Orlistat in clozapine- or olanzapine-treated patients with overweight or obesity: a 16-week open-label extension phase and both phases of a randomized controlled trial. The Journal of clinical psychiatry, 72(3), 326–330. [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C., Avenell, A., Boachie, C., et al. (2016). Should weight loss and maintenance programmes be designed differently for men? A systematic review of long-term randomised controlled trials presenting data for men and women: The ROMEO project. Obesity research & clinical practice, 10(1), 70–84. [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.J., Berkel, H.J., Parish, R.C. et al. (2001), Single-Dose Pharmacokinetics of Bupropion in Adolescents: Effects of Smoking Status and Gender. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 41: 770-778. [CrossRef]
- Findlay, J.W.A., Van Wyck Fleet, J., Smith, P.G. et al. (1981) Pharmacokinetics of bupropion, a novel antidepressant agent, following oral administration to healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 21, 127–135. [CrossRef]
- Laib, A. K., Brünen, S., Pfeifer, P., Vincent, P., & Hiemke, C. (2014). Serum concentrations of hydroxybupropion for dose optimization of depressed patients treated with bupropion. Therapeutic drug monitoring, 36(4), 473–479. [CrossRef]
- Rentzeperi, E., Pegiou, S., Koufakis, T., Grammatiki, M., & Kotsa, K. (2022). Sex Differences in Response to Treatment with Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists: Opportunities for a Tailored Approach to Diabetes and Obesity Care. Journal of personalized medicine, 12(3), 454. [CrossRef]
- Nuffer, W. A., & Trujillo, J. M. (2015). Liraglutide: A New Option for the Treatment of Obesity. Pharmacotherapy, 35(10), 926–934. [CrossRef]
- Wharton, S., Liu, A., Pakseresht, A., Nørtoft, E., et al. (2019). Real-World Clinical Effectiveness of Liraglutide 3.0 mg for Weight Management in Canada. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.), 27(6), 917–924. [CrossRef]
- Sbraccia, P., Busetto, L., Santini, F. et al. (2021) Misperceptions and barriers to obesity management: Italian data from the ACTION-IO study. Eat Weight Disord 26, 817–828 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Pagoto, S. L., Schneider, K. L., Oleski, J. L., Luciani, J. M., Bodenlos, J. S., & Whited, M. C. (2012). Male inclusion in randomized controlled trials of lifestyle weight loss interventions. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.), 20(6), 1234–1239. [CrossRef]
- Buysschaert, M., Preumont, V., Oriot, P. R., et al. (2010). One-year metabolic outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with exenatide in routine practice. Diabetes & metabolism, 36(5), 381–388. [CrossRef]
- Quan, H., Zhang, H., Wei, W., & Fang, T. (2016). Gender-related different effects of a combined therapy of Exenatide and Metformin on overweight or obesity patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of diabetes and its complications, 30(4), 686–692. [CrossRef]
- Mirabelli, M.; Chiefari, E.; Caroleo, P.; et al (2020) Long-Term Effectiveness of Liraglutide for Weight Management and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 17, 207. [CrossRef]
- Overgaard, R.V., Petri, K.C., Jacobsen, L.V. et al. Liraglutide 3.0 mg for Weight Management: A Population Pharmacokinetic Analysis. Clin Pharmacokinet 55, 1413–1422 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Kodoth, V., Scaccia, S., & Aggarwal, B. (2022). Adverse Changes in Body Composition During the Menopausal Transition and Relation to Cardiovascular Risk: A Contemporary Review. Women's health reports (New Rochelle, N.Y.), 3(1), 573–581. [CrossRef]
- Durden, E., Lenhart, G., Lopez-Gonzalez, L., Hammer, M., & Langer, J. (2016). Predictors of glycemic control and diabetes-related costs among type 2 diabetes patients initiating therapy with liraglutide in the United States. Journal of medical economics, 19(4), 403–413. [CrossRef]
- Pencek, R., Blickensderfer, A., Li, Y., Brunell, S. C., & Anderson, P. W. (2012). Exenatide twice daily: analysis of effectiveness and safety data stratified by age, sex, race, duration of diabetes, and body mass index. Postgraduate medicine, 124(4), 21–32. [CrossRef]
- Ryczkowska, K., Adach, W., Janikowski, K., Banach, M., & Bielecka-Dabrowa, A. (2022). Menopause and women's cardiovascular health: is it really an obvious relationship?. Archives of medical science : AMS, 19(2), 458–466. [CrossRef]
- Li, K., Sun, J., Huang, N., Ma, Y., Han, F., Liu, Y., Hou, N., & Sun, X. (2020). Liraglutide improves obesity-induced renal injury by alleviating uncoupling of the glomerular VEGF-NO axis in obese mice. Clinical and experimental pharmacology & physiology, 47(12), 1978–1984. [CrossRef]
- Lv, X., Dong, Y., Hu, L., Lu, F., Zhou, C., & Qin, S. (2020). Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) for the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A systematic review. Endocrinology, diabetes & metabolism, 3(3), e00163. [CrossRef]
- Yen, FS., Hou, MC., Wei, J.CC. et al. (2024) Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on liver-related and cardiovascular mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. BMC Med 22, 8 (2024). [CrossRef]
- James W. P. (2008). WHO recognition of the global obesity epidemic. International journal of obesity (2005), 32 Suppl 7, S120–S126. [CrossRef]
- Crimmins, E. M., Shim, H., Zhang, Y. S., & Kim, J. K. (2019). Differences between Men and Women in Mortality and the Health Dimensions of the Morbidity Process. Clinical chemistry, 65(1), 135–145. [CrossRef]

| Men | Women | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (%) | 16/47 (34.0%) | 31/47 (65.9%) | |
| Age (years) | 52 ± 14.3 | 50 ± 11.5 | p=0.46 |
| Weight (kg) | 115.4 ± 18.1 | 108.3 ± 12.2 | p=0.12. |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 37.5 ± 5.6 | 40.1 ± 5.2 | p=0.10 |
| FBG (mg/dl) | 99.8 ± 20.9 | 92.3 ± 13.6 | p=0.16 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.7 ± 0.54 | 5.54 ± 0.3 | p=0.16 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dl) | 180.2±42.7 | 180.9 ± 26.6 | p=0.95 |
| LDL (mg/dl) | 106.0 ± 33.6 | 103.3± 25.3 | p=0.79 |
| HDL (mg/dl) | 50.2 ± 6.3 | 51.3 ± 9.8 | p=0.72 |
| TG (mg/dl) | 141.6 ± 73.5 | 115.6 ± 68.0 | p=0.31 |
| Creatinine /mg/dl) | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | <0.0001 |
| AST (U/L) | 23.45 ± 9.4 | 18.2 ± 4.2 | <0.0001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 33.2 ± 19.4 | 20.5 ± 6.7 | <0.0001 |
| FIB-4 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.3 | <0.0001 |
| Men | Women | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | |||
| T1-T0 | -10.7 ± 6.1 | -7.1 ± 3.1 | <0.0001 |
| T2-T1 | -17.9 ± 6.7 | -11.9 ± 5.3 | <0.0001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||
| T1-T0 | -3.6 ± 2.4 | -2.6 ± 1.1 | p=0.08 |
| T2-T0 | -6.0 ± 2.7 | -4.4 ± 1.9 | p=0.07 |
| %WL | |||
| T1-T0 | -9.2 ± 5.1 | -6.5 ± 2.9 | <0.0001 |
| T2-T1 | -15.2 ± 5.4 | -10.5 ± 4.4 | <0.0001 |
| WL > 5 % | N=15/16, 93.7% | N=18/31, 58.0% | <0.0001 |
| WL > 10 % | N=14/16, 87.5% | N=9/31, 29.0% | <0.0001 |
| Men | Women | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FBG (mg/dl) T2-T0 | -8.1 ± 16.4 | -5.4 ± 9.4 | p=0.61 |
| HbA1c (%) T2-T0 | -0.23 ± 0.9 | -0.16 ± 0.6 | p=0.83 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dl) T2-T0 | -14.0± 32.6 | 9.5 ± 22.1 | <0.0001 |
| LDL (mg/dl) T2-T0 | -19.0 ± 16.5 | 6.8 ± 21.2 | <0.0001 |
| HDL (mg/dl) T2-T0 | -2.0 ± 14.5 | 1.1 ± 7.1 | p=0.14 |
| TG (mg/dl) T2-T0 | -9.1 ± 59.9 | 2.8 ± 51.9 | p=0.56 |
| Creatinine (mg/dl) T2-T0 | -0.02 ± 0.14 | -0.02 ± 0.06 | p=0.99 |
| AST (U/L) T2-T0 | -3.5 ± 5.6 | -2.1 ± 4.8 | p=0.54 |
| ALT (U/L) T2-T0 | -5.0 ± 15.1 | -3.4 ± 7.7 | p=0.74 |
| FIB-4 T2-T0 | -0.25 ± 0.23 | -0.003 ± 0.12 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





