Submitted:
08 May 2024
Posted:
09 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Spawning and Larval Rearing
2.1.1. Broodstock and Spawning
2.1.2. Larval Rearing
2.1.3. Post-Larvae and Juveniles’ Cultivation
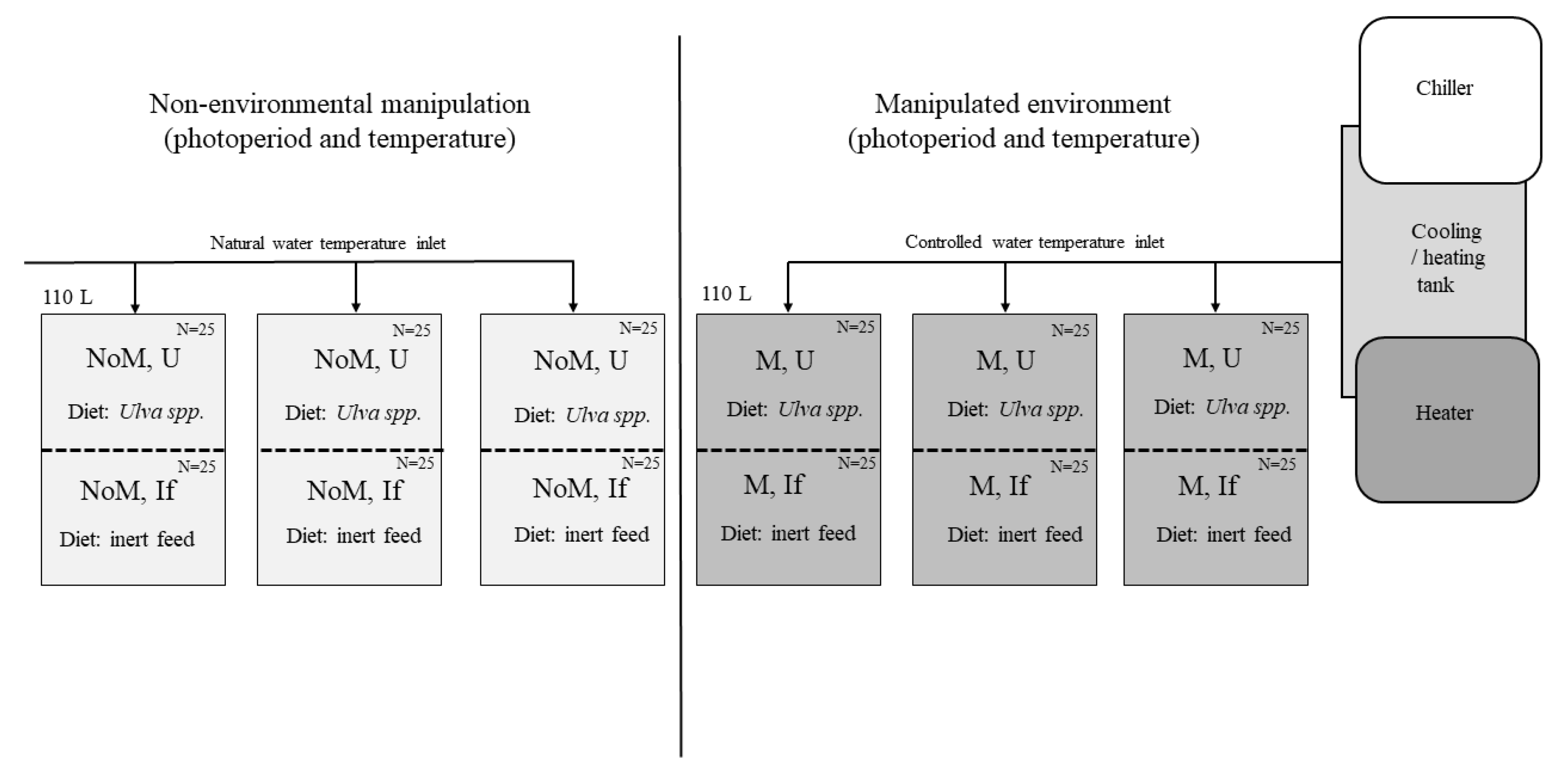
2.2. Experimental Design
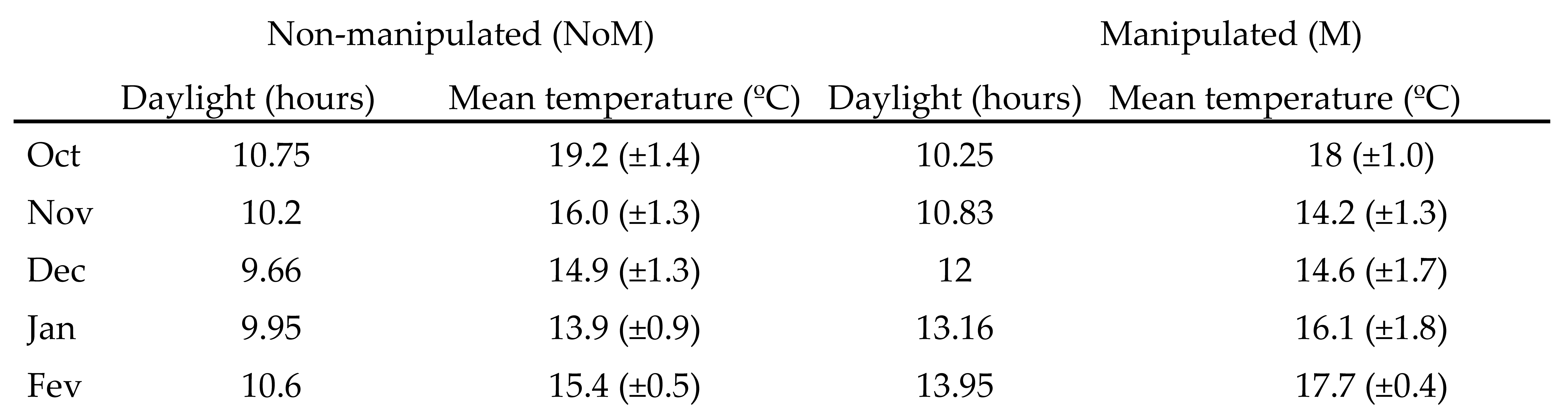
2.2.1. Environment Conditions
2.2.2. Feeding
2.3. Sampling
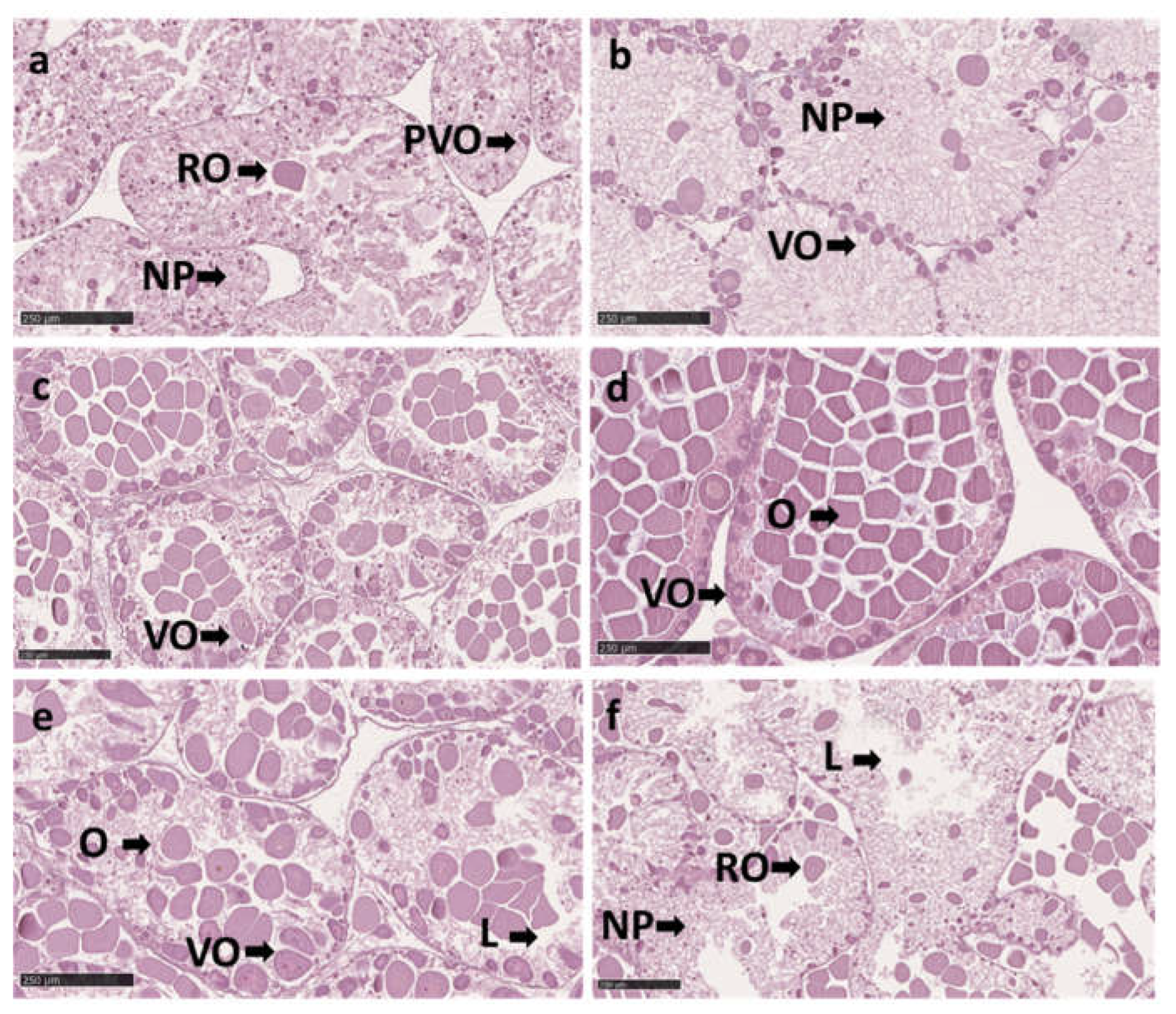
2.4. Histology
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gonadosomatic Index
3.1. Gonad Development
4. Discussion
4.1. Gonadossomatic Index
4.2. Gonadal Maturity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, J.; Chiang, F.S. Use and Exploitation of Sea Urchins. In Echinoderm Aquaculture eds Brown, N.P., Eddy, S.D. 2015; 22–45. [Google Scholar]
- Carboni, S.; Vignier, J.; Chinatore, M.; Tocher, D.; Migaud, H. Effects of dietary microalgae on growth, survival and fatty acidcomposition of sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus throughout larval development. Aquac. 2012, 324–325, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudouresque, C.F.; Verlaque, M. Ecology of Paracentrotus lividus, in: Lawrence, J.M. (Ed.) Edible sea urchins: biology and ecology. Developments in aquaculture and fisheries science. 2001 32: pp. 177–216.
- Régis, MB. Analyses des fluctuations des indices physiologiques chez deux khinoides (Paracentrotus lividus (Lmk) et Arbacia lixula L.) du Golfe de Marseille. Thkthys. 1979, 9, 167–181. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, M. Annual reproductive cycles of the commercial sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus from an exposed intertidal and a sheltered subtidal habitat on the west coast of Ireland. Mar. Biol. 1990, 104, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.; Crook, A. Quantifying behavioural determinants of the coastal European sea-urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Mar.Biol. 2001, 138, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Cyrus, M.D.; Bolton, J.J.; De Wet, L.; Macey, B.M. The development of a formulated feed containing Ulva (Chlorophyta) to promote rapid growth and enhanced production of high quality roe in the sea urchin Tripneustes gratilla (Linnaeus). Aquacult. Res. 2014, 45, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.; Araújo, J.; Soares, F.; Pousão Ferreira, P. Produção de larvas e juvenis de ouriços-do-mar (Paracentrotus lividus) na estação piloto de piscicultura de Olhão (EPPO). Relat. Cient. Téc. IPMA 2018, Série digital nº20. [Google Scholar]
- Candeias-Mendes, A.; Araújo, J.; Santos, M.; Namora, M.; Soares, F.; Gomes, R.; Cardoso, C.; Afonso, C.; Bandarra, N.M.; Pousão-Ferreira, P. Growth, survival and fatty acids profile of sea urchins, Paracentrotus lividus juveniles fed with Ulva spp. and maize in aquaculture production. First results using G1 generation in Portugal. J. Aquac. Mar. Biol. 2020, 9, 208–214. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, P.; M. , Albano; P., Raposo; A.; Ferreira, S.M.F.; Costa, J.L.; Pombo, A. The effect of temperature on somatic and gonadal development of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck, 1816). Aquac. 2020, 528, 735487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriminna, L.; Signa, G.; Vaccaro, A.M.; Messina, C.M.; Mazzola, A.; Vizzini, S. Formulation of a new sustainable feed from food industry discards for rearing the purple sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Aquacult. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, I.; Moura, P.; Pereira, F.; Vasconcelos, P.; Gaspar, M.B. Reproductive cycle of the commercially harvested sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) along the western coast of Portugal. Invertebr. Biol. 2019, 138, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, A.; Ferreira, S.; Ramos, R.; Anjos, C.; Baptista, T.; Tecelão, C.; M. , Santos; P.; Costa, J.; Pombo, A. Effect of three diets on the gametogenic development and fatty acid profile of Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck, 1816) gonads. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 10–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafidis, D.; Antoniadou, C.; Kyriakouli, K. Reproductive Cycle of the Edible Sea Urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata: Echinoidae) in the Aegean Sea. Water 2019, 11, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarron, E.; Burnell, G.; Kerry, J.; Mouzakitis, G. An experimental assessment on the effects of photoperiod treatments on the somatic and gonadal growth of the juvenile European purple sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Aqua. Res. 2010, 41, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellem, F.; Guillou, M. Reproductive biology of Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) in two contrasting habitats of northern Tunisia (south-east Mediterranean). J. Mar. Biol. Ass. 2007, UK 87, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyrus, M.; Bolton, J.; De Wet, L.; Macey, B.M. The development of a Formulated Feed containing Ulva (Chlorophyta) to promote rapid growth and enhanced production of high-quality roe in the sea urchin Tripneustes gratilla (Linnaeus). Aquac. Res. 2012, 45, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.; Loureiro, P.; Candeias-Mendes, A.; Gamboa, A.; Bandarra, N.; Cardoso, C.; Soares, F.; Dias, J. ; Pousão-Ferreira. The effect of a formulated feed on the body growth and gonads quality of purple sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) aquaculture produced. J. Aquac. Mar. Biol. 2023; 12, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, P.M.; Ferreira, S.M.F.; Albano, P.; Raposo, A.; Costa, J.L.; Pombo, A. Can artificial diets be a feasible alternative for gonadal growth and maturation of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck, 1816)? J. World. Aquacult. Soc. 2020, 51, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosser, S.C. , Lupatsch, I. , Lawrence, J.M., Lawrence, A.L., & Shpigel, M. (2005). Protein and energy digestibility and gonad development of the European sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck) fed algal and prepared diets during spring and fall Aquac. Res. 2005, 36, 972–982. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, F.; Baião, L.F.; Moutinho, S.; Reis, B.; Oliveira, A.; Arenas, F.; Maia, M.R.G.; Fonseca, A.J.M.; Pintado, M.; Valente, L.M.P. The effect of sex, season and gametogenic cycle on gonad yield, biochemical composition and quality traits of Paracentrotus lividus along the North Atlantic coast of Portugal. Sci. Re.p 2019, 28, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, L.; Vasconcelos, P.; Machado, I.; Pereira, F.; Moura, P.; Carvalho, A.N.; Gaspar, M.B. Morphometric relationships, relative growth and roe yield of the sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) from the Portuguese coast, Reg. Stud. Ma.r Sci. 2022, 52, 102343. [Google Scholar]
- González-Irusta, J.; Cerio, F.; Canteras, J.C. Reproductive cycle of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus in the Cantabrian Sea (northern Spain): Environmental effects. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2010, 90, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchene, H.; Boutgayout, H.; Hermas, J.; Benbani, A.; Oualid, J.A.; Elouizgani, H. Reproductive Cycle of Sea Urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck, 1816) from the South Coast of Morocco: Histology, Gonads Index, and Size at First Sexual Maturity. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 5393–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Uz, S.; Carrasco, J.F.; Rodríguez, C. Temporal variability of spawning in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus from northern Spain Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2018, 23, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Allain, J.Y. Structure des populations de Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck) (Echinodermata, Echinoidea) soumises à la pêche sur les côtes Nord de Bretagne. Rev. Trav. Inst. Pêch. Marit 1975, 39, 171–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ouréns, R.; Fernández, L.; Freire, J. Geographic, population, and seasonal patterns in the reproductive parameters of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Mar. Biol. 2011, 158, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaili, A.; Haroufi, O.; Bouzaidi, H.; Maroua, H.; Bouzoubaa, A.; Rharrass, A.; Essalmani, H. Reproductive cycle of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck, 1816) from the Moroccan western Mediterranean Sea: histology, gonadal index and size at first sexual maturity. EJABF 2023, 27, 745–771. [Google Scholar]
- Guetaff, M.; San Martin, G.A. Étude de la variabilité de l’indice gonadique de l’oursin comestible Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) en Mediterranée nord-occidental. Vie Milieu, 1995; 45, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, C.; Boudouresque, C. Phenotypic plasticity of Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) in a lagoonal environment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 1997, 152, 145–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirlet, C.; Grosjean, P.; Jangoux, M. Reproductive cycle of the echinoid Paracentrotus lividus. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 1998, 34, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, S.; Cunha, B.; Raposo, A.; Neves, M.; Santos, P.M.; Gomes, A.S.; Tecelão, C.; Ferreira, S.M.F.; Baptista, T.; Silvia, C.G.; Pombo, A. Somatic growth and gonadal development of Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck, 1816) fed with diets of different ingredient sources. Aquac. 2021, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirino, P.; Ciaravolo, M.; Paglialonga, A.; Toscano, A. Long-term maintenance of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus in culture. Aquac. Res. 2017, 7, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





