1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most frequent cancer worldwide and the second leading cause of cancer-related death. It is considered one of the most dangerous and burdensome tumors in the world [
1]. In recent years, the global prevalence of colorectal cancer has increased at an alarming rate [
2]. Patients diagnosed with CRC accounted for 10% of global cancer incidence and 9.4% of cancer deaths in 2020 and projected to reach 3.2 million by 2040 [
2,
3]. Smoking, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, physical inactivity, and excess body weight account for more than half of all cases and deaths [
5]. Unfortunately, CRC often remains asymptomatic until later stages, at which point it becomes aggressive, malignant, and prone to spread [
2]. As a result, the majority of patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage when symptoms such as rectal bleeding, anemia, or stomach discomfort manifest. When the tumor is localized at the time of diagnosis, surgery or radiotherapy is the preferred treatment, along with the development of molecularly targeted therapy and immunotherapy (
i.e., immune checkpoint inhibitors). However, the systemic approach to chemotherapy remains essential for effective cancer management [
5]. The main chemotherapeutic drugs used in CRC patients are platinum-based agents (
i.e., oxaliplatin, cisplatin, carboplatin) and fluoropyrimidines (
i.e., 5-fluorouracil, capecitabine) [
6]. The main fundamental mechanisms of most chemotherapeutic drugs such as oxaliplatin (OXA), 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), and irinotecan (IRI) lead to DNA damage by forming DNA strand breaks, disrupt DNA/RNA synthesis and inhibit topoisomerase I activity, which subsequently inhibits neoplastic cell proliferation [
7,
8]. So far, the 5-year survival rate of patients with early-stage, locally advanced and metastatic CRC is estimated to reach 90%, 70%, and 15%, respectively (Wang et al, 2022). Thus, although chemotherapy represents a mainstay clinical intervention, its effectiveness is hampered by the emergence of drug resistance. For instance, IRI was initially licensed for use as a second-line monotherapy in patients with metastatic CRC who had previously failed 5-FU-based therapy [
5]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to search for novel therapeutic agents to circumvent resistance and improve the clinical outcomes of CRC patients.
N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) are nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds having one bivalent carbon atom and six valence electrons [
9]. Due to their inherent qualities, NHCs have recently attracted much attention because they are readily accessible and their physicochemical properties can be easily fine-tuned by changing the wingtip N-substituents, thereby enabling the production of very stable metal complexes [
10]. NHCs are commonly used as powerful and efficient nucleophilic catalysts [
11]. Organocatalysis with NHCs is a sophisticated approach to rapidly produce physiologically and medicinally relevant molecules from simple and affordable substrates [
12]. Recent studies have highlighted the potential of NHC ligands as carriers of anticancer drugs [
13]. The focus on using this class of ligands to construct physiologically relevant carbene complexes stems from the core moiety, benzimidazole, which is more biologically accessible as a component of multiple metalloenzymes and proteins [
14].
The purpose of the current study was to evaluate the potential anti-CRC effects of the NHC compound named IMBZC (i.e., 1-(Isobutyl)-3-(4-methylbenzimidazolium chloride). The study employed colorectal adenocarcinoma HT29 and metastatic CRC (mCRC) SW620 cell lines as CRC models for this in vitro investigation. To evaluate the effect of IMBZC on these cell lines, several assays were carried out, including single and combined cytotoxicity assays with conventional chemotherapeutic agents (i.e., OXA, 5-FU, IRI), cell migration analysis, colony formation assay, Western blot analysis, and reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). This investigation provides insight into the anti-CRC potential of IMBZC and the associated underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
All reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (USA) unless indicated otherwise.
2.2. Cell Culture
Human colorectal adenocarcinoma HT29 (#HTB-38), mCRC SW620 (#CCL-277) and normal embryonic kidney HEK293 (#CRL-1573) cell lines were obtained from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, United States) and grown in complete Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) medium (#1200252, Gibco
®, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, #10270106, Gibco
®), 1% antibiotic (penicillin/streptomycin) solution (#10378016, Gibco
®). The cells were cultured at 37°C in a 5% CO
2-incubator maintaining a humidified atmosphere [
15]. Every 2-3 days, the cells were passaged at confluence using 0.25% trypsin/EDTA (#25200056, Gibco
®) and were used between passage 2 and 3 throughout this study.
2.3. IMBZC Synthesis and Preparation
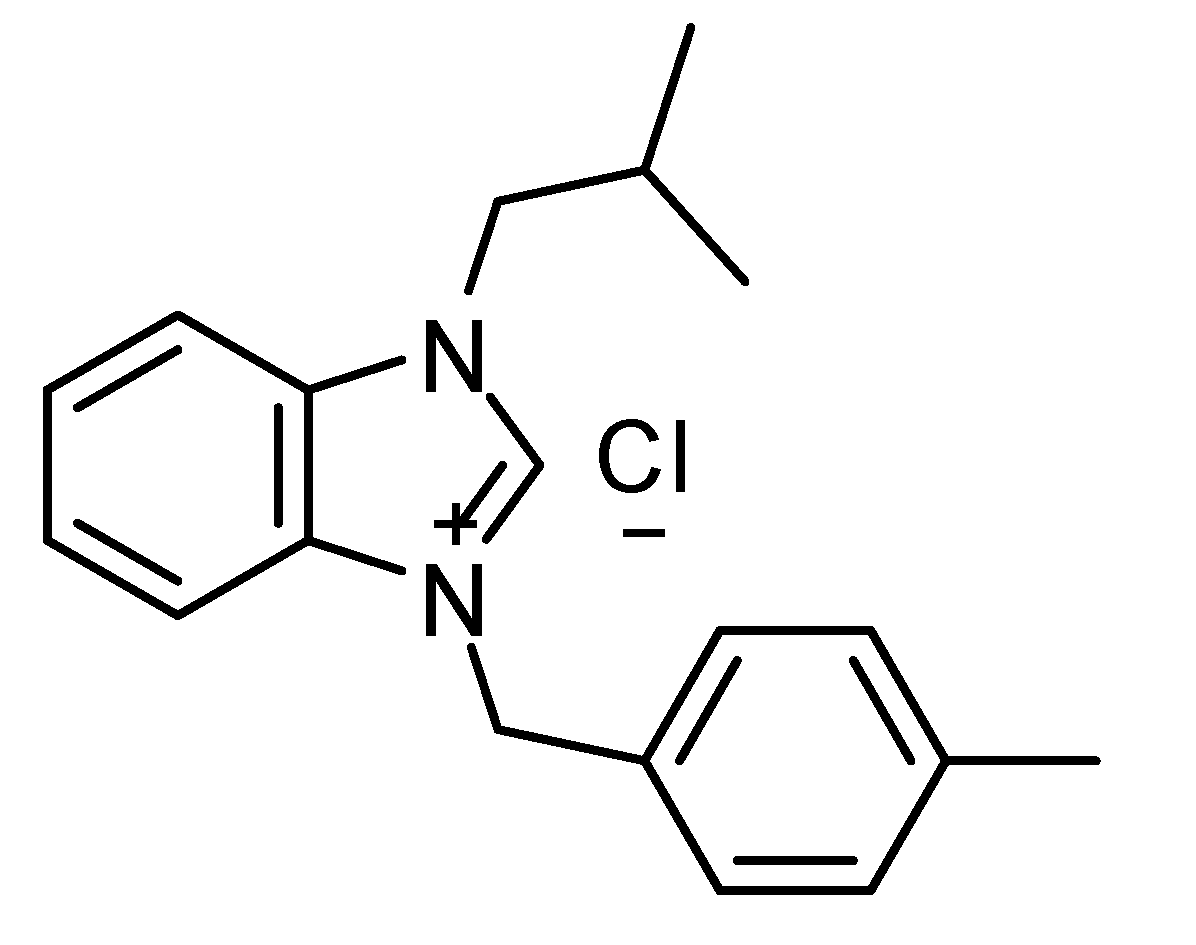
1-(Isobutyl)-3-(4-methylbenzyl) benzimidazolium chloride (IMBZC) compound was synthesized and prepared as previously described [
16]. Briefly, the synthesis of IMBZC was created by reacting 1 mmol N-(isobutyl)-benzimidazole with 1.1 mmol chloro toluene, an alkyl chloride, in 5 ml of dimethylformamide (DMF) at 80°C for 24 hours. Diethyl ether (15 ml) was added to produce a white crystalline solid, which was then filtered off. The solid was washed with diethyl ether (3 × 10 ml) and dried under vacuum, and the crude product was recrystallized from dichloromethane/diethyl ether (1:3 ratio). The IMBZC compound was dissolved in methanol to prepare 10 mg/ml stock solution and stored at room temperature until use. The structure of IMBZC was previously characterized by elemental analyses, including
1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR),
13C NMR, and infrared (IR) spectroscopy techniques [
17].
2.4. MTT Cytotoxicity Assay
Cell lines (
i.e., HT29, SW620, and HEK293) were plated at 5 × 10
3 cells per well in complete medium in 96-well culture plates for 24 hours of incubation. Cells were then cultured in the absence (
i.e., untreated control cells) or presence of various doses of IMBZC (1.25, 2.5, 5, 7.5, and 10 µg/ml) for 24 hours of incubation. To assess the cytotoxic effect of conventional CRC chemotherapeutic drugs combined with IMBZC, cells were exposed to 5-FU, IRI, and OXA, tested at 2.5, 5 and 10 μM. Ten µl of MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide) solution were added to the cells 2 hours before the 24-hour completion, which resulted in violet formazan crystal formation in metabolically active cells. After that, 100 μl of isopropanol were added to each well to dissolve the crystals. Colorimetric absorbance was measured at 540 nm using a Synergy
™ 2 multi-mode microplate reader (BioTek Inc., Winooski, VT, United States). For each condition, experiments were carried out in triplicate as previously described [
18]. The value of half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC
50) leading to 50% decrease in cell viability was also determined.
2.5. Scratch Wound-Healing Assay
HT29 and SW620 cells were seeded at 1 × 10
6 cells per well in complete medium in 6-well plates and incubated until confluence. A sterile 200 µL pipette tip was used to scratch a wound in the center of each confluent cell monolayer. The old medium was replaced with fresh complete culture medium to remove dislodged cells. Wells containing cells exposed only to complete medium were used as controls (
i.e., untreated cells). IBMZC tested at 5 and 10 µg/ml was added to wells containing HT29 cells, while IBMZC tested at 2.5 and 5 µg/ml was added to wells with SW620 cells. The healing area was measured to assess the capacity and motility of the cells to close the wound. This was accomplished by photographing the scratch at 0 times (t0) using an inverted light microscope (MICROS, Sundew MCX 1600, Austria). The plates were then incubated at 37ºC for 24 hours (t final) in a CO
2-incubator (Sanyo, MCO175). The second photos were taken after the final incubation and the average gap widths at t0 and t final were qualitatively evaluated compared to untreated control cells [
13].
2.6. Clonogenic Assay
The colony formation experiment was performed as described previously by Al-Khayal [
19]. Briefly, HT29 and SW620 cells were cultured at 500 cells per well in 6-well plates with complete medium. After adding IMBZC (5 and 10 μg/ml) to the cells for 24 hours, each well was replaced with fresh medium then cultured for 10-12 days in a CO
2 incubator. Colonies were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with 0.05% crystal violet. The colonies consisting of more than 50 cells were quantified using a microscope.
2.7. Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
HT29 and SW620 cells (1 × 10
6) were grown in complete medium for 24 hours in a 100-mm dish up to 60% confluency. The following day, cells were treated with or without 2.5, 5 and 10 µg/ml of IMBZC for an additional 24-h incubation. The RNeasy
® Mini kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) was used to extract total RNA from untreated and treated cells. The FIREScript
® RT cDNA synthesis kit containing Mix with oligo (dT) and Random Primers kit (Solis BioDyne, Estonia) was used to synthesize the complementary (c)DNA. The ratio of absorbance readings 260/280 (1.8-2.0) was calculated to evaluate RNA quality using a NanoDrop
® ND-2000 UV-VIS spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). SYBR
™ Green PCR Master Mix (#4385612, Thermo Fisher Scientific) was used for qPCR analysis using the Applied Biosystems
™ ViiA
™ 7 real-time PCR system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.).
B-cell lymphoma (BCL)-2,
BCL-extra large (BCL-xL),
BCL-associated X protein (BAX), and
tumor suppressor TP53 mRNA expression levels were adjusted to
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (
GAPDH) used as an internal control for real-time RT-qPCR. The sequences of primer pairs are shown in
Table 1. A negative control lacking cDNA template was used for each gene analysis. All reactions were carried out in triplicate as described previously [
20].
2.8. Western Blot Technology
HT29 and SW620 cells were cultured in complete medium for 24 hours before being in the presence or absence of (2.5, 5 and 10 μg/ml) IMBZC. Cells were collected the next day and washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Radio-immunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) lysis buffer was used to generate total cell lysates from cell pellets for 15 minutes at 4°C. After that, the entire mixture was centrifuged at 15,000 g, then the supernatant containing the soluble proteins was collected and the protein concentration was determined using Bradford reagent on a SmartSpec
™ Plus spectrophotometer (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, United States). On sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), 10-20 μl of proteins were loaded (4-20% Mini-Protean TGX precast gels, Bio-Rad Laboratories). Using the rapid protein transfer system (Bio-Rad Laboratories), protein separated on precast gels were transferred to a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane. Following this, the membranes containing the transferred proteins were saturated with blocking buffer for 1 hour at room temperature. Membranes were then washed twice in PBS with 0.1% Tween-20 (PBST). Membranes were then incubated with primary antibodies directed against Bcl-2 (#A86278, Antibodies.com, Cambridge, UK), Bcl-xL (#A36576, Antibodies.com), Bax (#A249822, Antibodies.com), TP53 (#A250176, Antibodies.com), and β-Actin (#sc-69879, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, United States) with 1:1,000 dilution in blocking buffer. After overnight incubation with the primary antibodies on an orbital shaker at 4°C, the membranes were washed twice with PBST before being incubated for 1 hour at room temperature with rabbit anti-mouse IgG-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) secondary antibodies (#A301453, Antibodies.com) (1:10000 dilution). The chemiluminescence signal was detected by a high-sensitivity enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) substrate kit (Millipore, Thermo Fisher Scientific), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The C-DiGit
® blot scanner (LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln NE, United states) was used to detect the signals [
19].
2.9. Statistical Analysis
All experiments were done in triplicate and data were provided as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments. The student's t-test was used to assess differences between the control and treated groups. A p-value of less than 0.05 was used to determine statistical significance.
3. Results
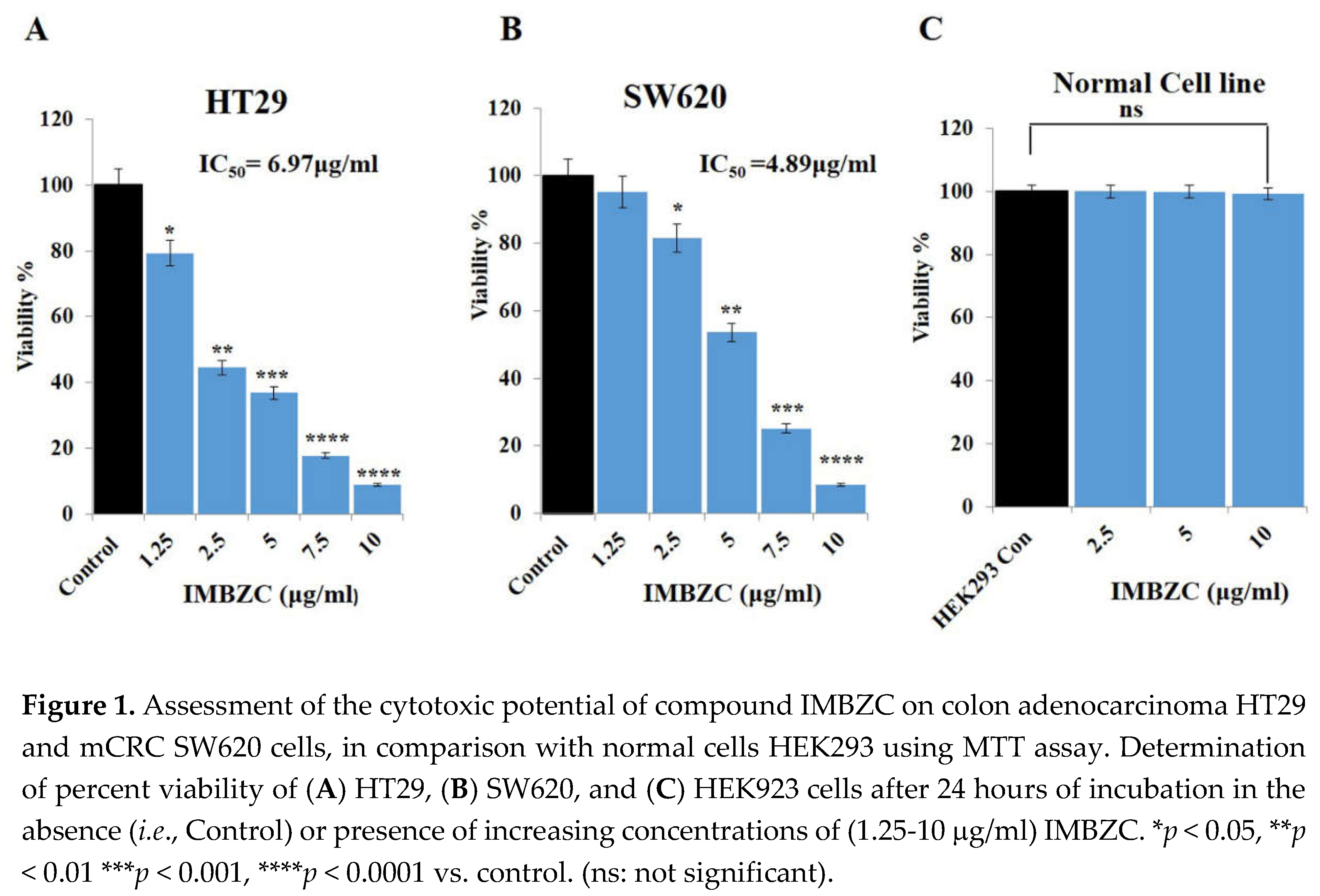
3.1. IMBZC Compound Inhibits CRC Cell Viability in a Dose-Dependent Manner
The MTT assay was used to determine the anticancer impact of the compound IMBZC on CRC cell viability, the main cellular event contributing to tumor development and cancer cell survival potential. Human colon adenocarcinoma HT29 and mCRC SW620 cells were exposed to increasing concentrations (from 1.25 μg/ml to 10 μg/ml) of IMBZC for 24 hours. Compared to high viability of untreated cells (
i.e., control) corresponding to 100%, IMBZC tested at the lowest concentration (
i.e., 1.25 μg/ml) decreased significantly the viability of HT29 cells by 20% (
p < 0.05), while a decrease of 60% and 90% (
p < 0.01 and
p < 0.001) was observed when HT29 cells were exposed to 2.5-5 μg/ml and 7.5-10 μg/ml of IMBZC, respectively (
Figure 1A). Regarding mCRC SW620 cells, IMBZC tested at 2.5 μg/ml significantly decreased cell viability by 20% (
p < 0.05) followed by 50%, 80% and 90% decrease when SW620 cells were exposed to 5 μg/ml, 7.5 μg/ml, and 10 μg/ml of IMBZC, respectively (
Figure 1B). The IMBZC IC
50 value for HT29 cells was calculated to be 6.97µg/ml, while the IMBZC IC
50 value for SW620 was 4.89 µg/ml. Thus, the compound exhibited significant cytotoxicity toward CRC cells in a dose-dependent manner, whereas the percentage viability of normal cells HEK293 was not affected at all IBMZC concentrations tested (
Figure 1).
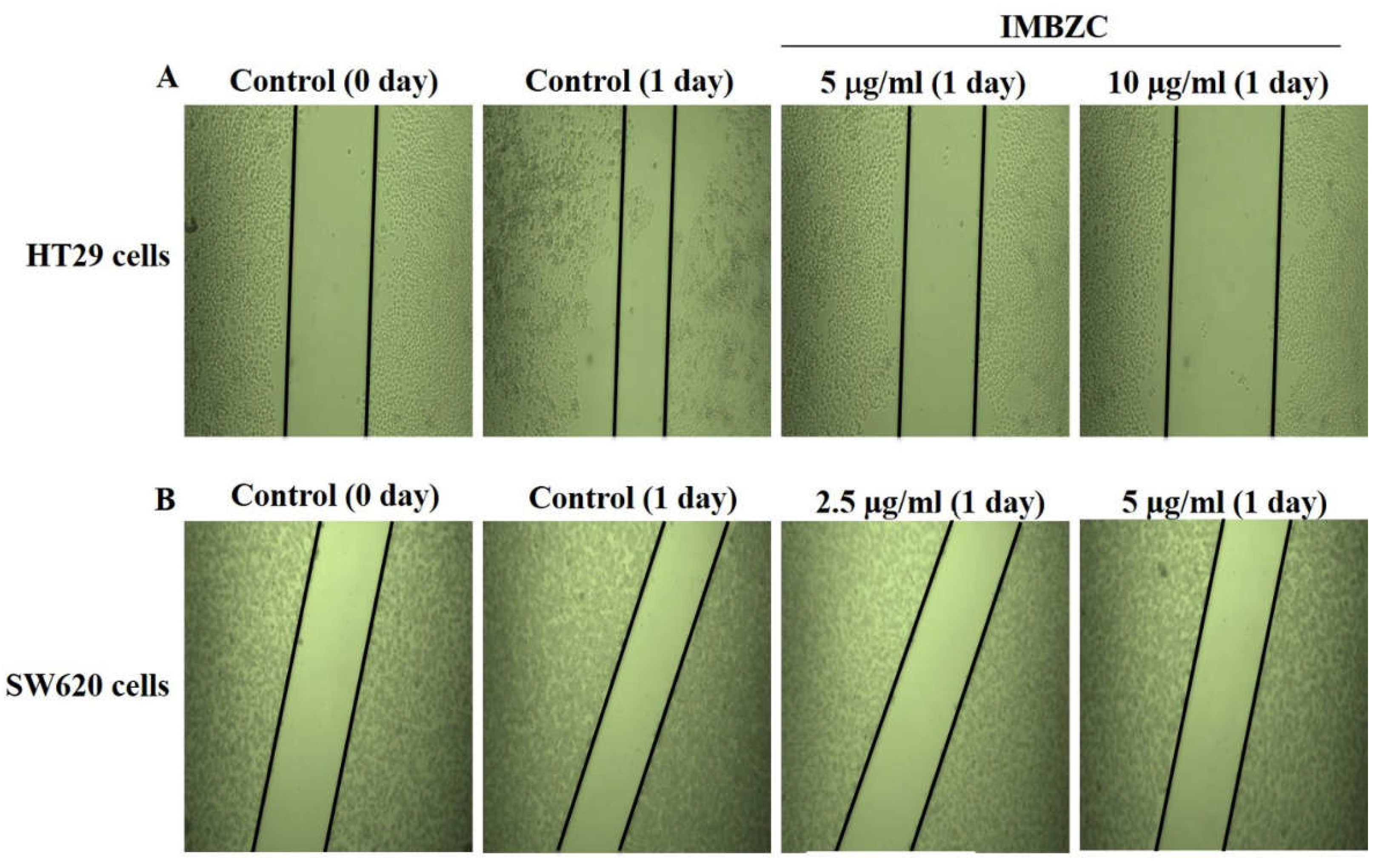
3.2. IMBZC Compound Decreases CRC Cell Migration and Inhibits Colony Formation
The wound healing assay was assessed by monitoring the shrinkage and closure of damaged wounded regions generated by scratches on a cell monolayer. The anticancer properties of IMBZC on cancer cell motility were assessed at concentrations close to its IC
50 values determined for each CRC cell line. As shown in the representative photomicrographs, after 24 hours of incubation, the gap size in wounded HT29 (
Figure 2A) and SW620 (
Figure 2B) cell monolayer treated with IMBZC was nearly one-fold larger than in untreated controls, demonstrating that the IMBZC compound considerably inhibited the migration of both CRC cell lines (
Figure 2). In addition, the gap distances in IMBZC-treated HT29 (
Figure 2A) cells were progressively larger with increasing concentrations (5 and 10 μg/ml) of IMBZC, indicating an inhibitory effect of the compound in a dose-dependent manner (
Figure 2).
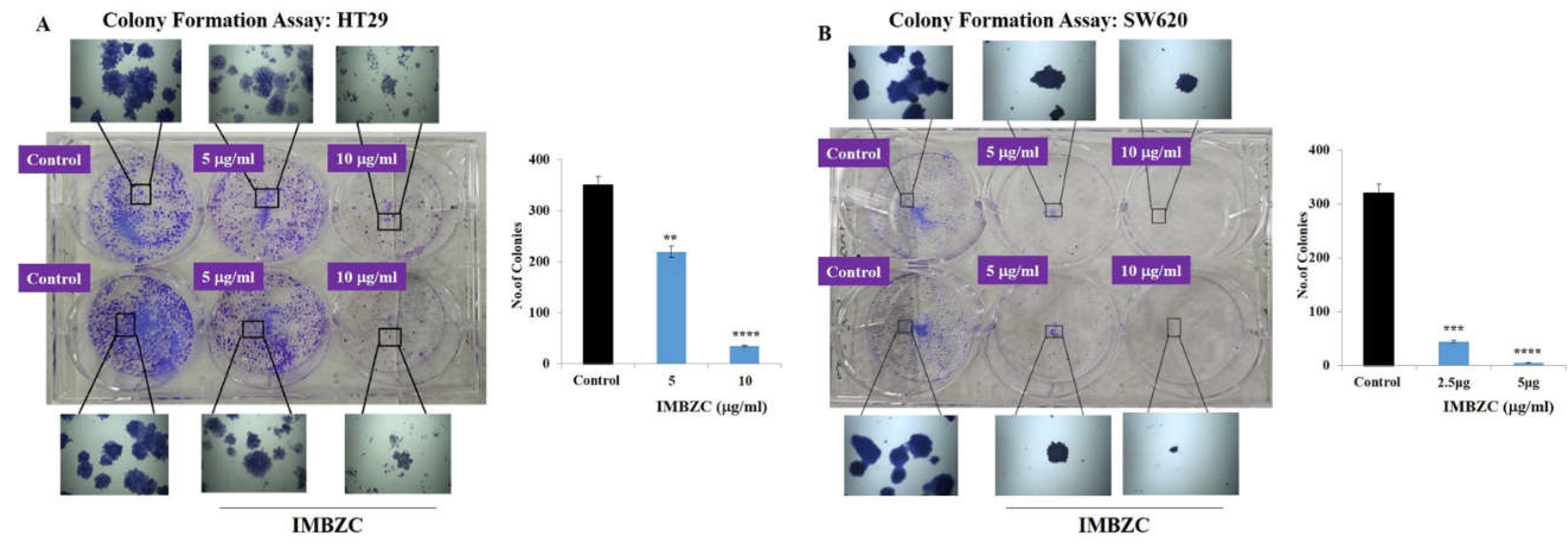
The antitumorigenic effect of compound IMBZC on HT29 and SW620 cells was investigated using a colony formation assay at a similar range of doses (5 and 10 µg/ml) on HT29 and (2.5 and 5µg/ml) on SW620 cells. Compared to untreated colony-generating cells based on CRC cells, IMBZC significantly inhibited colony formation using HT29 (
Figure 3A) and SW620 (
Figure 3B) cells. Compared to the number of colonies generated in the control, IMBZC significantly decreased by 40% (
p < 0.01) and 90% (
p < 0.0001) HT29 cell-based colony formation when tested at 5 μg/ml and 10 μg/ml, respectively (
Figure 3A). Regarding the SW620 cell line, IMBZC significantly decreased by 80% (
p < 0.001) and 98% (
p < 0.0001) colony formation when tested at 2.5 μg/ml and 5 μg/ml, respectively , compared to untreated control cells (
Figure 3B).
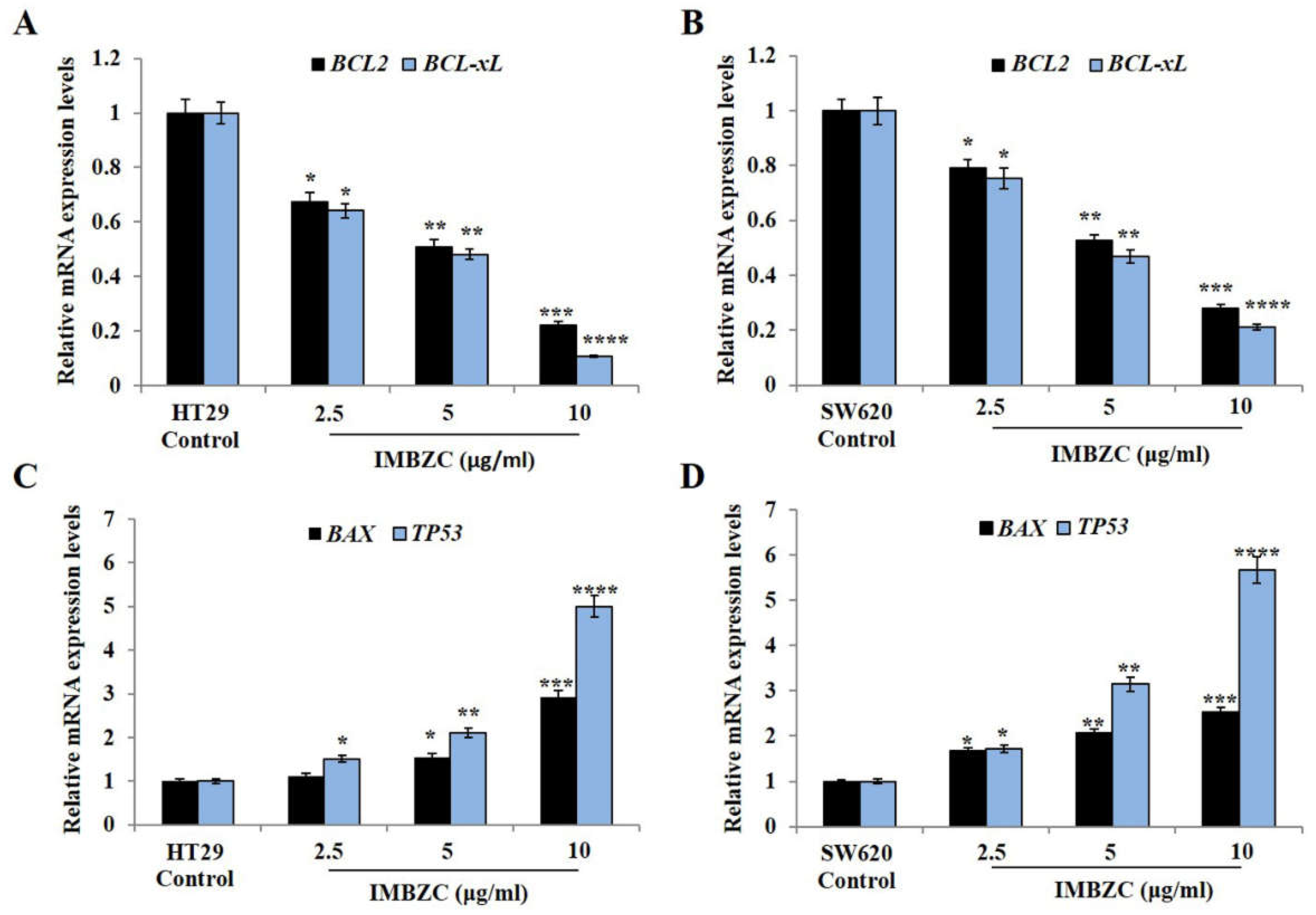
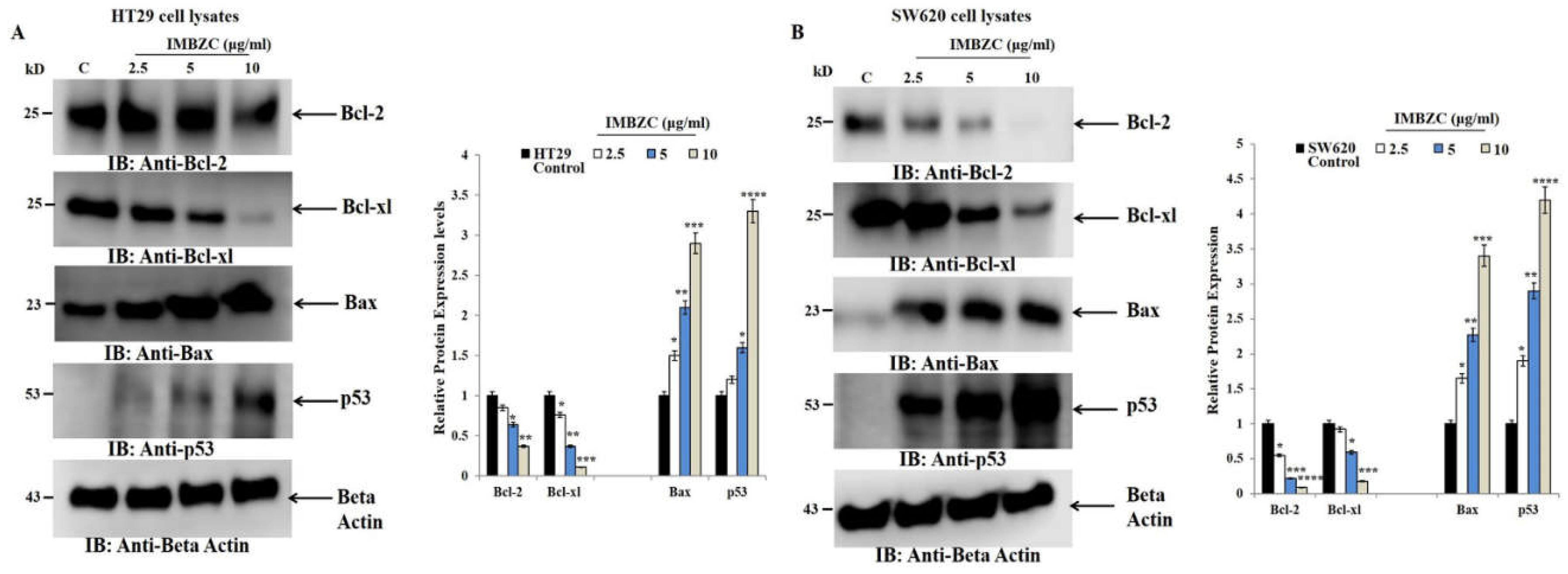
3.3. IMBZC Downregulates the Expression Levels of Anti-Apoptotic Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL while Upregulates Pro-Apoptotic Bax and p53 in a Dose-Dependent Manner
Figure 4 shows the expression levels of major anti-apoptotic (
i.e.,
BCL-2 and
BCL-xL) and pro-apoptotic (
i.e.,
TP53,
BAX) genes in the CRC cell lines HT29 and SW620 after treatment with various concentrations (2.5, 5 and 10 μg/ml) of IMBZC compound, compared to untreated cells (
i.e., control). IMBZC significantly decreased
BCL-2 and
BCL-xL gene expression levels by 30% (
p < 0.05,
Figure 4A) in HT29 cells and by 20% (
p < 0.05,
Figure 4B) in SW620 cells when tested at 2.5 μg/ml, compared to basal levels measured in untreated cells. At high concentrations (5 μg/ml and 10 μg/ml), IMBZC significantly inhibited by 50% (
p < 0.01) and 80% (
p < 0.001)
BCL-2 and
BCL-xL gene expression levels in both cell lines, compared to the control (
Figure 4). Regarding the pro-apoptotic
BAX and
TP53 expression levels, IMBZC tested at 2.5 μg/ml significantly upregulated
TP53 expression by 1.5-fold (
p < 0.05,
Figure 4C) in HT29 cells and upregulated
BAX and
TP53 expression by approximately 1.5-fold (
p < 0.05,
Figure 4D) in SW620 cells, compared to the basal expression levels measured in the control (
Figure 4). When tested at 5 and 10 μg/ml, IMBZC significantly increased by 1.5-2.0-fold (
p < 0.05) and 3.0-5.0-fold (
p < 0.001) pro-apoptotic BAX and TP53 gene expression levels in HT29 cells (
Figure 4C) while a 2.0-3.0-fold (
p < 0.01) and 3.0-5.0-fold (
p < 0.001) increase in these pro-apoptotic gene expression levels was observed in SW620 cells (
Figure 4D), compared to the control (
Figure 4). Altogether, IBMZC described a stimulatory effect on the pro-apoptotic BAX and TP53 gene expression levels and an inhibitory effect on the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 and BCL-xL gene expression levels in both CRC cells, in a dose dependent manner (
Figure 4). This modulatory effect was confirmed at protein expression levels using Western blot analysis in both HT29 (
Figure 5A) and SW620 (
Figure 5B) cells.
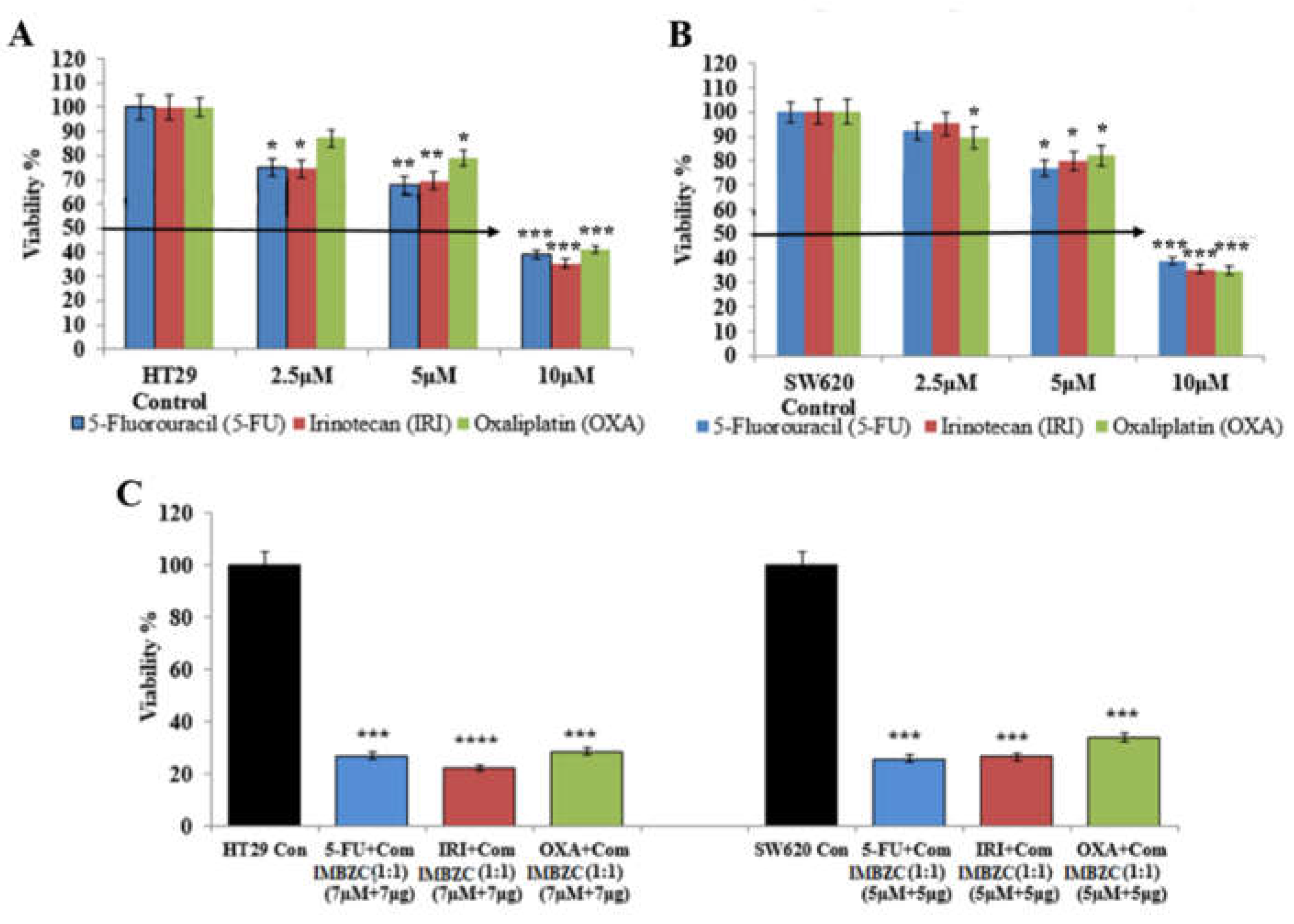
3.4. IMBZC Enhances the Cytotoxic Effects of Conventional CRC Drugs 5-FU, IRI and OXA
Determined by MTT assay, the cytotoxic effect of conventional CRC drugs (
i.e., 5-FU, IRI, OXA) on HT29 cell line is shown in
Figure 6A. 5-FU and IRI exhibited a significant cytotoxic effect at all concentrations tested (
i.e., 2.5, 5 and 10 μM), while OXA significantly inhibited HT29 cell viability when tested at 5 µM and 10 µM, compared to the control (
Figure 6A).
Figure 6B shows the cytotoxic effect of these conventional drugs on the SW620 cell line. A significant cytotoxic effect of 5-FU and IRI in SW620 cells was observed when tested at 5 µM and 10 µM, while OXA exhibited a cytotoxic effect at all concentrations tested, compared to the control (
Figure 6B). Overall, at the highest concentration (
i.e., 10 μM), each chemotherapeutic drug significantly inhibited by 65%-70% (
p < 0.001) CRC cell viability (Figure 6A-B). Combinations of each conventional drug with IMBZC compound significantly decreased CRC cell viability by 75%-80% (
Figure 6C), revealing an enhancement of the cytotoxic effect of all the drugs in both cell lines by the addition of IMBZC, compared to the single treatment (
Figure 6). For HT29 cells, the most significant effect was obtained with IRI+IMBZC at concentrations of 7 µM+7µg/ml, respectively, while for SW620 cells, the most significant cytotoxicity was obtained with 5-FU+IMBZC at the concentrations of 5µM+5µg/ml, compared to the control (
Figure 6C).
Discussion
According to GLOBOCAN 2020, colorectal cancer remains the top cause of cancer-related deaths among men and women, and its incidence and mortality rates are increasing each year. Chemotherapy is the most widely utilized therapeutic strategy against tumors; however, due to its toxicity to normal cells and the progressive increase in cancer cell resistance, there is an urgent need to identify novel drugs as alternative cancer treatments [
21,
22].
NHC ligands can be easily changed and are efficient σ-donors with a weak π-acceptor [
23]. NHC ligands might potentially stabilize metal complexes against demetallation under physiological conditions [
24]. Several biological studies have found that metal complexes containing NHCs are promising antineoplastic drugs [
23,
25].
In this study, we investigated cytotoxicity mechanism of compound IMBZC on CRC cell lines HT29 and SW620 and found that IMBZC decreased the cell viability of human CRC cell lines in a dose-dependent manner. IMBZC was found to exhibit a strong cytotoxic effect on colon adenocarcinoma CRC cells HT29 compared to mCRC cells SW620, with IC
50 values of 4.89 µg/ml and 6.97 µg/ml, respectively. However, no cytotoxic effect of IMBZC on the normal cell line (HEK293) was observed, indicating the compound IMBZC as a safe anticancer drug that kills high-proliferative cancer cells without damaging normal cells. A study conducted by Habib [
26] shows that the colon cell line HCT 116 is more sensitive to NHC salts and less sensitive to Ag(I)-NHC complexes.
The current study even investigated whether IMBZC compound treatment could reduce cancer cell migration in HT-29 and SW620 cells. Our findings revealed that IMBZC significantly inhibited cell migration of CRC cell lines in a dose-dependent manner. This shows that the IMBZC compound has potent anti-migration ability and therefore could inhibit cancer metastasis in CRC patients.
The final phase in the tumorigenicity cascade is the colonization of tumor cells in distant tissues [
27]. IMBZC treatment inhibited cancer cell colony formation, indicating that the compound has potential antimetastatic capabilities against human colorectal adenocarcinoma and mCRC. Interestingly, the colon metastatic cell line SW620 is more sensitive to the chemical IMBZC, resulting in a drastic reduction in the colony formation process than the adenocarcinoma cell line HT29. Further in vitro molecular investigations are needed to pinpoint the altered functions and expression of key proteins underlying IMBZC-inhibited SW620 cell-based colony formation, which would enhance our knowledge for better development of a targeted molecular strategy.
The cell fate toward cell death is determined by the balance of pro-apoptotic (
e.g., p53, Bax) and anti-apoptotic proteins (
e.g., Bcl-2, Bcl-xl). At the gene expression levels, upregulation of
BAX and tumor suppressor
TP53 is required for induction of apoptosis in colon cancer cells and, in contrast, overexpression of BCL-2 and BCL-xL is necessary for the suppression of apoptosis [
28,
29,
30]. In this study, we also confirmed at the protein level that IMBZC increases the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins p53 and Bax, while inhibiting the expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl in human colonic adenocarcinoma and mCRC cells.
The combination studies of standard chemotherapeutic drugs IRI, 5-FU, and OXA with IMBZC, increased chemotherapeutic drug efficacy in killing CRC cells, suggesting that IMBZC is a promising and safe anticancer chemotherapeutic agent for CRC patients. Due to the high degree of cancer clonal heterogeneity and intratumoral genetic variability, current treatments have limited anticancer efficacy. As a result, the use of medication combinations is becoming more widespread in the search for better treatments [
28]. According to an in vitro study conducted by Al-Obeed and colleagues, the combination of medicines increased the effect of doxorubicin on mCRC cell line SW620 [
28].
In conclusion, this study showed that the NHC compound IMBZC effectively inhibits viability through induction of apoptosis, movement, and colony forming ability of CRC cell lines. The process involves increasing the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins such as p53 and Bax, while decreasing the expression of anti-apoptotic factors such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl. IMBZC was demonstrated to enhance the effects of primary chemotherapeutic drugs against CRC. Further research is required, including in vivo studies, to evaluate the toxicity and efficacy of IMBZC in inhibiting development and metastasis of CRC tumors. If the results are validated, IMBZC could be developed as a novel therapeutic agent or chemosensitizer to improve CRC treatment outcomes.
Acknowledgment
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University for funding through Vice Deanship of Scientific Research Chairs, Research Chair of colorectal cancer Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Abbreviations
ATCC, American type culture collection; Bax, B-cell lymphoma 2-associated X; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Bcl-xL, B-cell lymphoma-extra large; cDNA, complementary DNA; CRC, colorectal cancer; DMEM, Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium; DMF, dimethylformamide; FBS, fetal bovine serum; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; HEK, human embryonic kidney; HRP, horseradish peroxidase; IC50, half-maximal inhibitory concentration; IMBZC, 1-(Isobutyl)-3-(4-methylbenzimidazolium chloride); IR, infrared; IRI, irinotecan; mCRC, metastatic CRC; MTT, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide; NHC, N-heterocyclic carbene; NMR, nuclear magnetic resonance; OXA, oxaliplatin; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PVDF, polyvinylidene fluoride; RIPA, radio-immunoprecipitation assay; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; SD, standard deviation; SDS-PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; TP, tumor suppressor;
References
- Ahmad, Rehan, Jaikee Kumar Singh, Amoolya Wunnava, Omar Al-Obeed, Maha Abdulla, and Sandeep Kumar Srivastava. "Emerging trends in colorectal cancer: Dysregulated signaling pathways." International journal of molecular medicine 47, no. 3 (2021): 1-1. [CrossRef]
- Xi, Yue, and Pengfei Xu. "Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040." Translational oncology 14, no. 10 (2021): 101174. [CrossRef]
- Deo, S. V. S., Jyoti Sharma, and Sunil Kumar. "GLOBOCAN 2020 report on global cancer burden: challenges and opportunities for surgical oncologists." Annals of surgical oncology 29, no. 11 (2022): 6497-6500. [CrossRef]
- Islami, Farhad, Ann Goding Sauer, Kimberly D. Miller, Rebecca L. Siegel, Stacey A. Fedewa, Eric J. Jacobs, Marjorie L. McCullough et al. "Proportion and number of cancer cases and deaths attributable to potentially modifiable risk factors in the United States." CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 68, no. 1 (2018): 31-54. [CrossRef]
- Edward, C.; Sartorelli, A.C. Cancer chemotherapy. Lange’s Basic and Clinical Pharmacology 2018, 948–976. [Google Scholar]
- Aldahhan, Razan, Dana Almohazey, and Firdos Alam Khan. "Emerging trends in the application of gold nanoformulations in colon cancer diagnosis and treatment." In Seminars in Cancer Biology, vol. 86, pp. 1056-1065. Academic Press, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Branca, Jacopo Junio Valerio, Donatello Carrino, Massimo Gulisano, Carla Ghelardini, Lorenzo Di Cesare Mannelli, and Alessandra Pacini. "Oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy: Genetic and epigenetic profile to better understand how to ameliorate this side effect." Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 8 (2021): 643824. [CrossRef]
- Bukowski, Karol, Mateusz Kciuk, and Renata Kontek. "Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy." International journal of molecular sciences 21, no. 9 (2020): 3233. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Jing, Xiao-Ning Xing, Jin-Hai Huang, Liang-Qiu Lu, and Wen-Jing Xiao. "Light opens a new window for N-heterocyclic carbene catalysis." Chemical Science 11, no. 39 (2020): 10605-10613. [CrossRef]
- Lenis-Rojas, Oscar A., Sandra Cordeiro, Marta Horta-Meireles, Jhonathan Angel Araujo Fernández, Sabela Fernández Vila, Juan Andrés Rubiolo, Pablo Cabezas-Sainz, Laura Sanchez, Alexandra R. Fernandes, and Beatriz Royo. "N-heterocyclic carbene iron complexes as anticancer agents: In vitro and in vivo biological studies." Molecules 26, no. 18 (2021): 5535. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Jiean, and Yong Huang. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes as Brønsted Base Catalysts. Wiley-VCH, 2018.
- Barik, Shilpa, and Akkattu T. Biju. "N-Heterocyclic carbene (NHC) organocatalysis using aliphatic aldehydes." Chemical Communications 56, no. 99 (2020): 15484-15495. [CrossRef]
- Porchia, Marina, Maura Pellei, Marika Marinelli, Francesco Tisato, Fabio Del Bello, and Carlo Santini. "New insights in Au-NHCs complexes as anticancer agents." European journal of medicinal chemistry 146 (2018): 709-746. [CrossRef]
- Gürbüz, Nevin, Nazan Kaloğlu, Ümran Kızrak, İlknur Özdemir, Neşe Başak Türkmen, Osman Çiftçi, İsmail Özdemir, L. Mansour, and Hamdi Naceur. "Silver (I) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes: Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxic properties." Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 923 (2020): 121434. [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, Maha-Hamadien, Aminah Ahmad Alzailai, Mansoor-Ali Vaali-Mohammed, Sabiha Fatima, and Amer Mahmood. "The platinum coordination complex inhibits cell invasion-migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by altering the TGF-β-SMAD pathway in colorectal cancer." Frontiers in Pharmacology 14 (2023): 1178190. [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, Lamia, A. Chakchouk-Mtibaa, Abdullah S. Al-Ayed, L. Mansour, Nael Abutaha, Abdel Halim Harrath, L. Mellouli, I. Özdemir, S. Yasar, and Naceur Hamdi. "Ru (II)–N-heterocyclic carbene complexes: Synthesis, characterization, transfer hydrogenation reactions and biological determination." RSC advances 9, no. 59 (2019): 34406-34420. [CrossRef]
- Slimani, Ichraf, Lamjed Mansour, Nael Abutaha, Abdel Halim Harrath, Jameel Al-Tamimi, Nevin Gürbüz, I. Özdemir, and Naceur Hamdi. "Synthesis, structural characterization of silver (I)-NHC complexes and their antimicrobial, antioxidant and antitumor activities." Journal of King Saud University-Science 32, no. 2 (2020): 1544-1554. [CrossRef]
- Al-Obeed, Omar, Adila Salih El-Obeid, Sabine Matou-Nasri, Mansoor-Ali Vaali-Mohammed, Yazeid AlHaidan, Mohammed Elwatidy, Hamad Al Dosary et al. "Herbal melanin inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation by altering redox balance, inducing apoptosis, and modulating MAPK signaling." Cancer Cell International 20 (2020): 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Al-Khayal, Khayal, Mansoor-Ali Vaali-Mohammed, Mohammed Elwatidy, Thamer Bin Traiki, Omar Al-Obeed, Mohammad Azam, Zahid Khan, Maha Abdulla, and Rehan Ahmad. "A novel coordination complex of platinum (PT) induces cell death in colorectal cancer by altering redox balance and modulating MAPK pathway." Bmc Cancer 20 (2020): 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Vaali-Mohammed, Mansoor-Ali, Maha-Hamadien Abdulla, Sabine Matou-Nasri, Wagdy M. Eldehna, M. Meeramaideen, Eslam B. Elkaeed, Mohammed El-Watidy, Noura S. Alhassan, Khayal Alkhaya, and Omar Al Obeed. "The Anticancer Effects of the Pro-Apoptotic Benzofuran-Isatin Conjugate (5a) Are Associated With p53 Upregulation and Enhancement of Conventional Chemotherapeutic Drug Efficiency in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines." Frontiers in Pharmacology 13 (2022): 923398. [CrossRef]
- Fadholly, Amaq, Arif NM Ansori, Shara Jayanti, Annise Proboningrat, Muhammad KJ Kusala, Naimah Putri, Fedik A. Rantam, and Sri A. Sudjarwo. "Cytotoxic effect of Allium cepa L. extract on human colon cancer (WiDr) cells: in vitro study." Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology 12, no. 7 (2019): 3483-3486. [CrossRef]
- Siegel, Rebecca L., Kimberly D. Miller, Ann Goding Sauer, Stacey A. Fedewa, Lynn F. Butterly, Joseph C. Anderson, Andrea Cercek, Robert A. Smith, and Ahmedin Jemal. "Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020." CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 70, no. 3 (2020): 145-164. [CrossRef]
- Varna, Despoina, Dini Iflakhah Zainuddin, Antonios G. Hatzidimitriou, George Psomas, Anastasia A. Pantazaki, Rigini Papi, Panagiotis Angaridis, and Paraskevas Aslanidis. "Homoleptic and heteroleptic silver (I) complexes bearing diphosphane and thioamide ligands: Synthesis, structures, DNA interactions and antibacterial activity studies." Materials Science and Engineering: C 99 (2019): 450-459. [CrossRef]
- Zou, Taotao, Chun-Nam Lok, Pui-Ki Wan, Zhi-Feng Zhang, Sin-Ki Fung, and Chi-Ming Che. "Anticancer metal-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes of gold, platinum and palladium." Current opinion in chemical biology 43 (2018): 30-36. [CrossRef]
- Kamal, Amna, Muhammad Adnan Iqbal, and Haq Nawaz Bhatti. "Therapeutic applications of selenium-derived compounds." Reviews in Inorganic Chemistry 38, no. 2 (2018): 49-76. [CrossRef]
- Habib, Aqsa, Mansoureh Nazari, Muhammad Adnan Iqbal, Haq Nawaz Bhatti, MB Khadeer Ahmed, and AMS Abdul Majid. "Unsymmetrically substituted benzimidazolium based Silver (I)-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes: Synthesis, characterization and in vitro anticancer study against human breast cancer and colon cancer." Journal of Saudi chemical society 23, no. 7 (2019): 795-808. [CrossRef]
- Asif, Muhammad, Muhammad Adnan Iqbal, Mouayed A. Hussein, Chern Ein Oon, Rosenani A. Haque, Mohamed B. Khadeer Ahamed, Aman Shah Abdul Majid, and Amin Malik Shah Abdul Majid. "Human colon cancer targeted pro-apoptotic, anti-metastatic and cytostatic effects of binuclear Silver (I)–N-Heterocyclic carbene (NHC) complexes." European journal of medicinal chemistry 108 (2016): 177-187. [CrossRef]
- Al-Obeed, Omar, Mansoor-Ali Vaali-Mohammed, Wagdy M. Eldehna, Khayal Al-Khayal, Amer Mahmood, Hatem A. Abdel-Aziz, Ahmed Zubaidi, Ahmed Alafeefy, Maha Abdulla, and Rehan Ahmad. "Novel quinazoline-based sulfonamide derivative (3D) induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer by inhibiting JAK2–STAT3 pathway." OncoTargets and therapy (2018): 3313-3322. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Shunqin, Tai Li, Juan Tan, Xiaomin Yan, Dunke Zhang, Chunqin Zheng, Yibiao Chen, Zhonghuai Xiang, and Hongjuan Cui. "Bax is essential for death receptor-mediated apoptosis in human colon cancer cells." Cancer Biotherapy and Radiopharmaceuticals 27, no. 9 (2012): 577-581. [CrossRef]
- Cherbonnel-Lasserre, C., and M. K. Dosanjh. "Suppression of apoptosis by overexpression of Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL promotes survival and mutagenesis after oxidative damage." Biochimie 79, no. 9-10 (1997): 613-617. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of 1-(Isobutyl)-3-(4- methylbenzyl) benzimidazolium chloride (IMBZC).
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of 1-(Isobutyl)-3-(4- methylbenzyl) benzimidazolium chloride (IMBZC).
Figure 2.
Evaluation of the anticancer potential of IMBZC on CRC cell migration using wound healing assay. (A) HT29 and (B) SW620 cells were seeded in 6-well plates and incubated with complete medium until confluence, then the cell monolayer was scratched with a sterile 200 μl tip and washed with PBS. The medium was replaced with or without IMBZC then incubated for 24 hours. Microscopy was used to examine the cells, and digital images were taken.
Figure 2.
Evaluation of the anticancer potential of IMBZC on CRC cell migration using wound healing assay. (A) HT29 and (B) SW620 cells were seeded in 6-well plates and incubated with complete medium until confluence, then the cell monolayer was scratched with a sterile 200 μl tip and washed with PBS. The medium was replaced with or without IMBZC then incubated for 24 hours. Microscopy was used to examine the cells, and digital images were taken.
Figure 3.
The compound IMBZC inhibits HT29 and SW620 cell-based colony formation. Both HT29 (A) and SW620 (B) cells were incubated for 10-12 days at 37°C for colony formation, along with untreated HT29 (A.A) and SW620 (B.A) cells (i.e., Control). The number of colonies is represented by a bar graph and the data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 vs. control.
Figure 3.
The compound IMBZC inhibits HT29 and SW620 cell-based colony formation. Both HT29 (A) and SW620 (B) cells were incubated for 10-12 days at 37°C for colony formation, along with untreated HT29 (A.A) and SW620 (B.A) cells (i.e., Control). The number of colonies is represented by a bar graph and the data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 vs. control.
Figure 4.
Expression levels of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 and BCL-xL and pro-apoptotic BAX and TP53 genes monitored in colorectal adenocarcinoma HT29 and mCRC SW620 cell lines using RT-qPCR. Bar graphs showing the relative gene expression levels calculated as a ratio to GAPDH, the internal control, and data presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 vs. control.
Figure 4.
Expression levels of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 and BCL-xL and pro-apoptotic BAX and TP53 genes monitored in colorectal adenocarcinoma HT29 and mCRC SW620 cell lines using RT-qPCR. Bar graphs showing the relative gene expression levels calculated as a ratio to GAPDH, the internal control, and data presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 vs. control.
Figure 5.
The effect of IMBZC on the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl and pro-apoptotic Bax and p53 protein expression levels. (A) HT29 and (B) SW620 cells were treated for 24 hours at different concentrations (2.5, 5 and 10 μg/ml) of IMBZC. Anti-Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, p53, and Bax antibodies were used to target these proteins in whole cell lysates. The strength of protein bands was semi-quantified relative to β-actin, used as a loading control, and was presented as relative to protein expression, compared to the untreated control. The bar graphs show the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 vs. control.
Figure 5.
The effect of IMBZC on the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl and pro-apoptotic Bax and p53 protein expression levels. (A) HT29 and (B) SW620 cells were treated for 24 hours at different concentrations (2.5, 5 and 10 μg/ml) of IMBZC. Anti-Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, p53, and Bax antibodies were used to target these proteins in whole cell lysates. The strength of protein bands was semi-quantified relative to β-actin, used as a loading control, and was presented as relative to protein expression, compared to the untreated control. The bar graphs show the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 vs. control.
Figure 6.
IMBZC potentiates the cytotoxicity of CRC conventional drugs (i.e., 5-FU, IRI and OXA) in (A) HT29 and (B) SW620 cells. 5-FU, IRI, and OXA drugs were tested at different concentrations (2.5, 5 and 10 μM) for 24 hours of incubation then cell viability percentage was determined using MTT assay. The bar graphs show the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 vs. control.
Figure 6.
IMBZC potentiates the cytotoxicity of CRC conventional drugs (i.e., 5-FU, IRI and OXA) in (A) HT29 and (B) SW620 cells. 5-FU, IRI, and OXA drugs were tested at different concentrations (2.5, 5 and 10 μM) for 24 hours of incubation then cell viability percentage was determined using MTT assay. The bar graphs show the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 vs. control.
Table 1.
Sequences of primer pairs monitoring target gene expression levels using RT-qPCR.
Table 1.
Sequences of primer pairs monitoring target gene expression levels using RT-qPCR.
| Target Gene |
Primer Sequence 5ʹ→3ʹ |
GAPDH
|
GTCTCCTCTGACTTCAACAGCG (forward)
ACCACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCAA (reverse) |
BAX
|
CCCGAGAGGTCTTTTTCCGAG (forward)
CCAGCCCATGATGGTTCTGAT (reverse) |
BCL2
|
TCCGCATCAGGAAGGCTAGA (forward)
AGGACCAGGCCTCCAAGCT (reverse) |
BCL-xL
|
AGTTCCCTTGGCCTCAGAAT (forward)
TCCTTTCTGGGGAAGAGGTT (reverse) |
TP53
|
CCTCAGCATCTTATCCGAGTGG (forward)
TGAGGCTCACGTCCATCTCGTC (reverse) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).