Submitted:
19 April 2024
Posted:
19 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
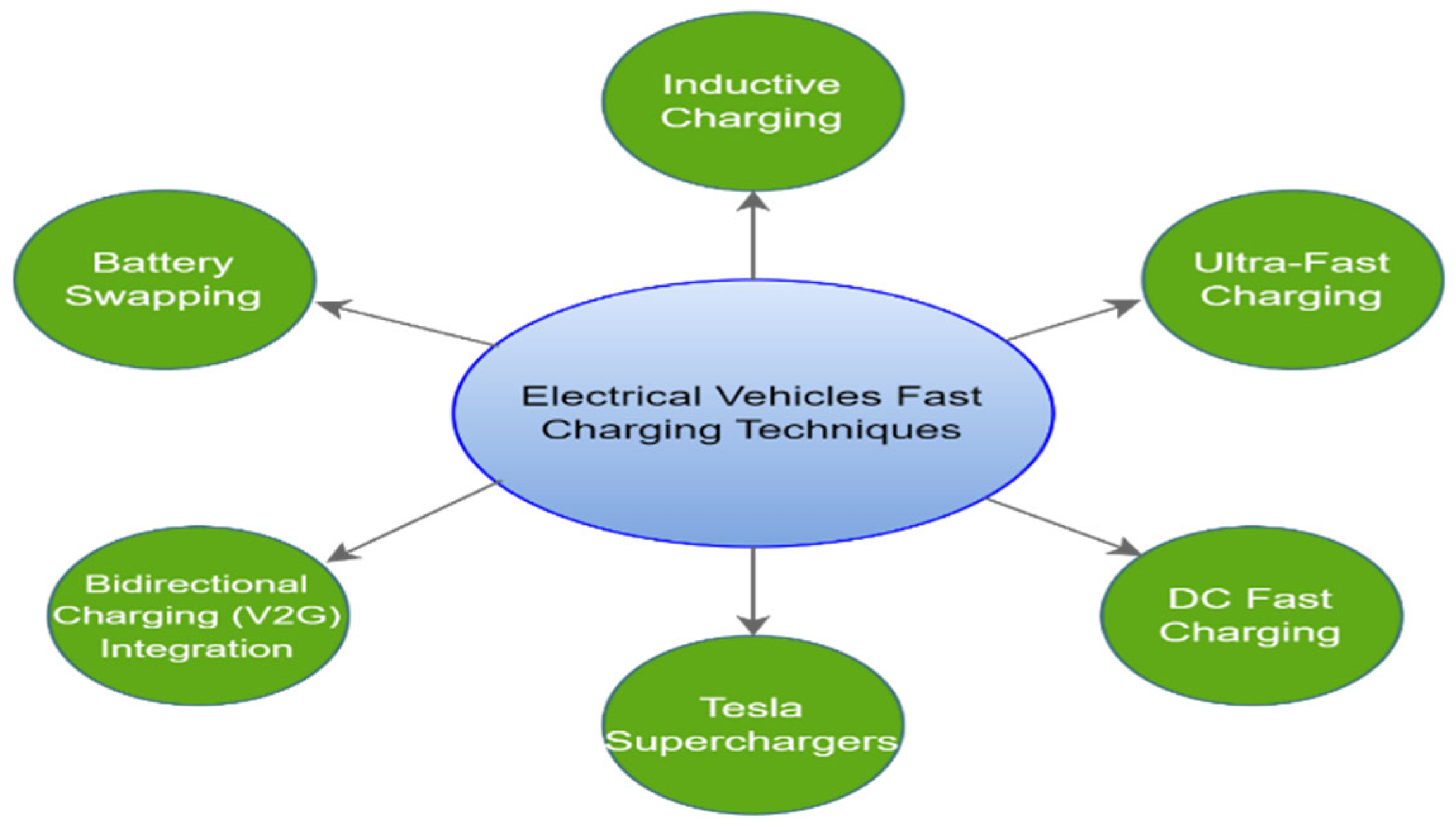
2. Electrical Vehicle’s Fast Charging Techniques
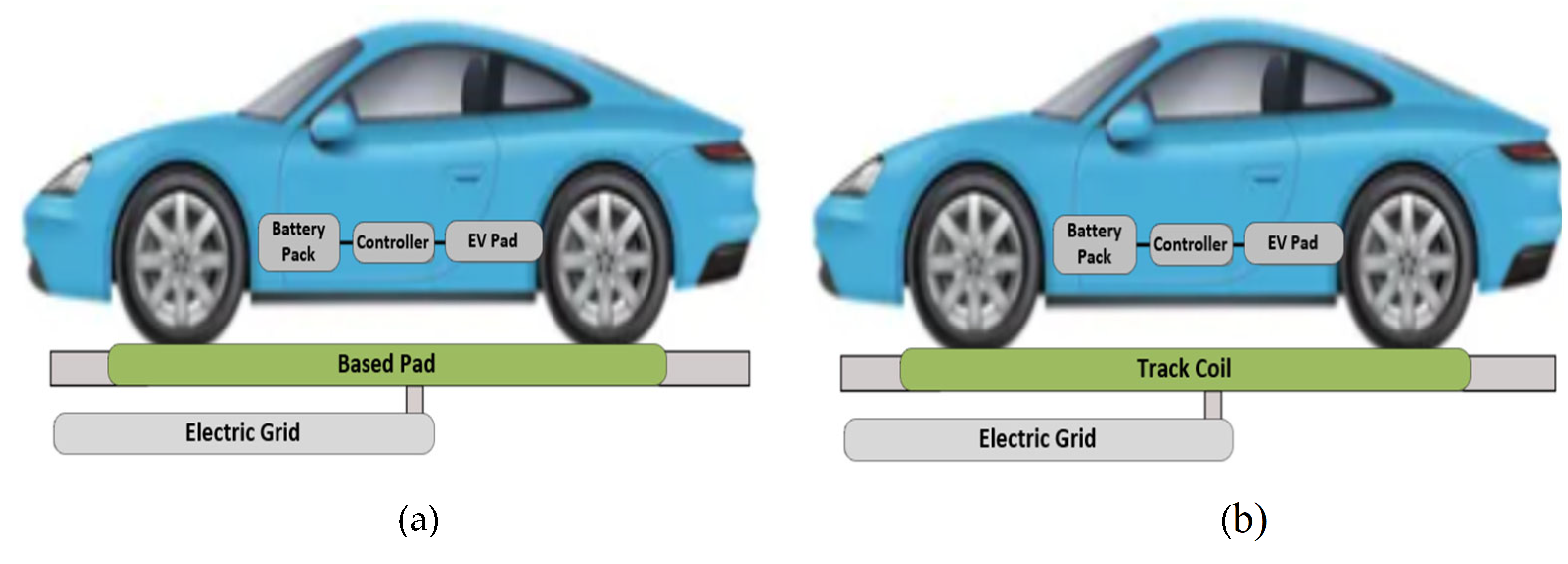
2.1. Inductive Charging
2.2. Ultra-Fast Charging (UFC)
2.3. DC Fast Charging (DCFC)
2.4. Tesla Superchargers
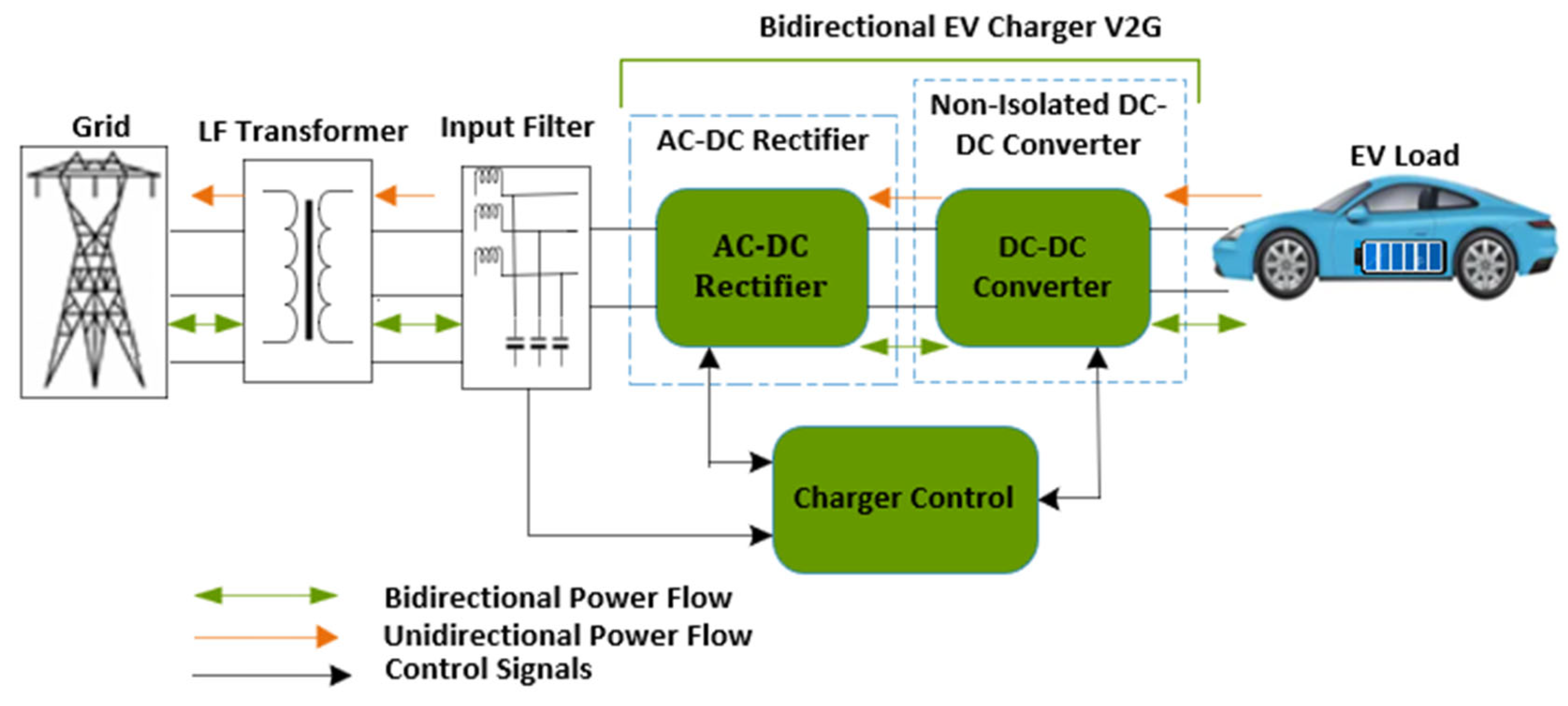
2.5. Bidirectional Charging Integration
2.6. Battery Swapping
3. Advanced Infrastructure DC Fast Charging for Electric Vehicles
3.1. Charging Standards
3.1.1. Organizations for Standardization
3.1.2. Charging Connector Types
3.1.3. Communication Protocols
3.1.4. Power Level and Charging Speeds
3.2. Charging Modes Control
3.2.1. Constant Current Charging
3.2.2. Constant Voltage Charging
3.2.3. Constant Power Charging
3.2.4. Demand Response Charging
3.2.5. Bidirectional Flow Charging
3.2.6. Temperature Monitoring and Control
3.2.7. State of Charge (SoC) Estimation
4. Electric Vehicles Battery Chargers Category
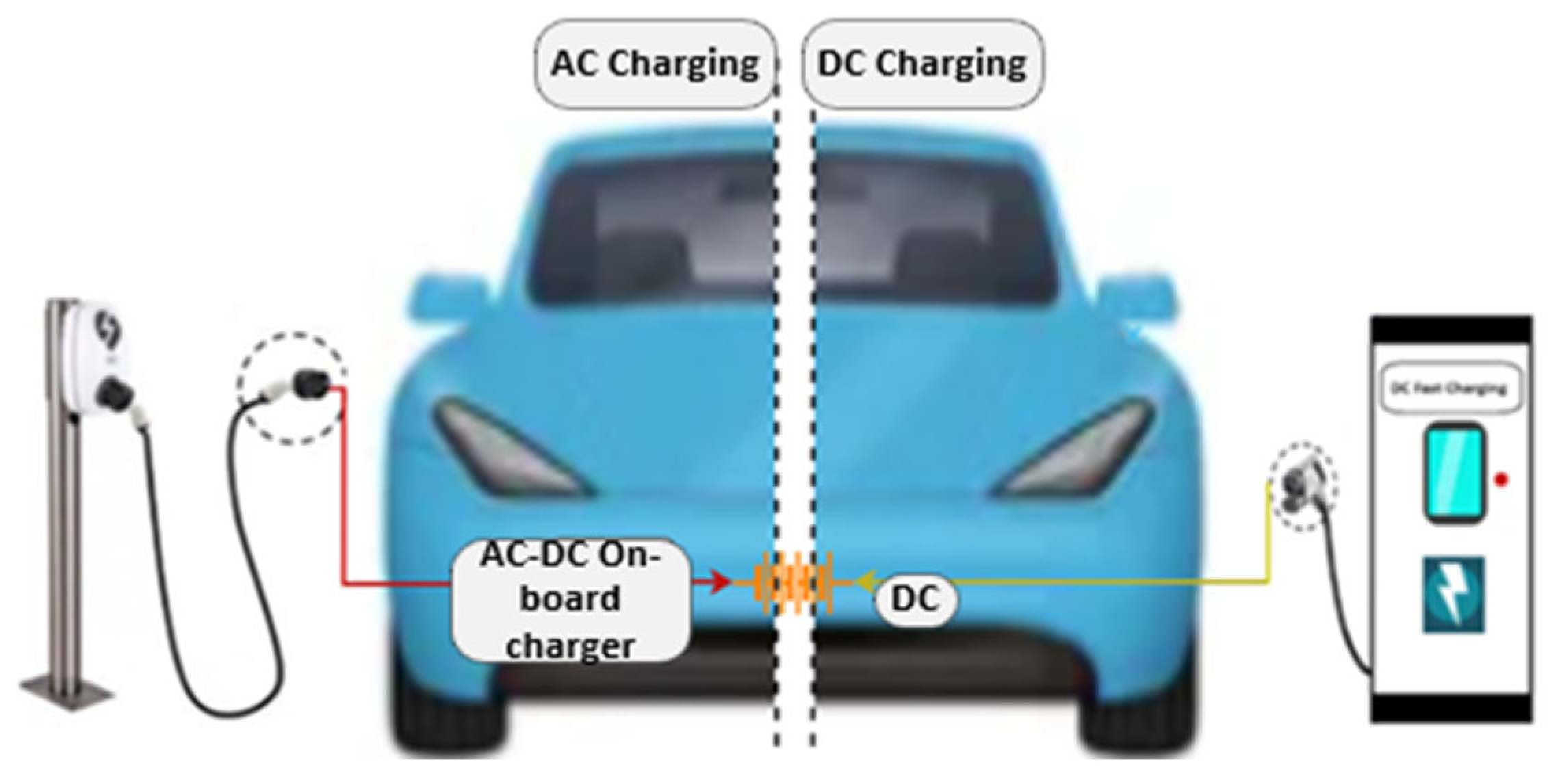
4.1. On-Board Charging
4.2. OFF-Board Charging
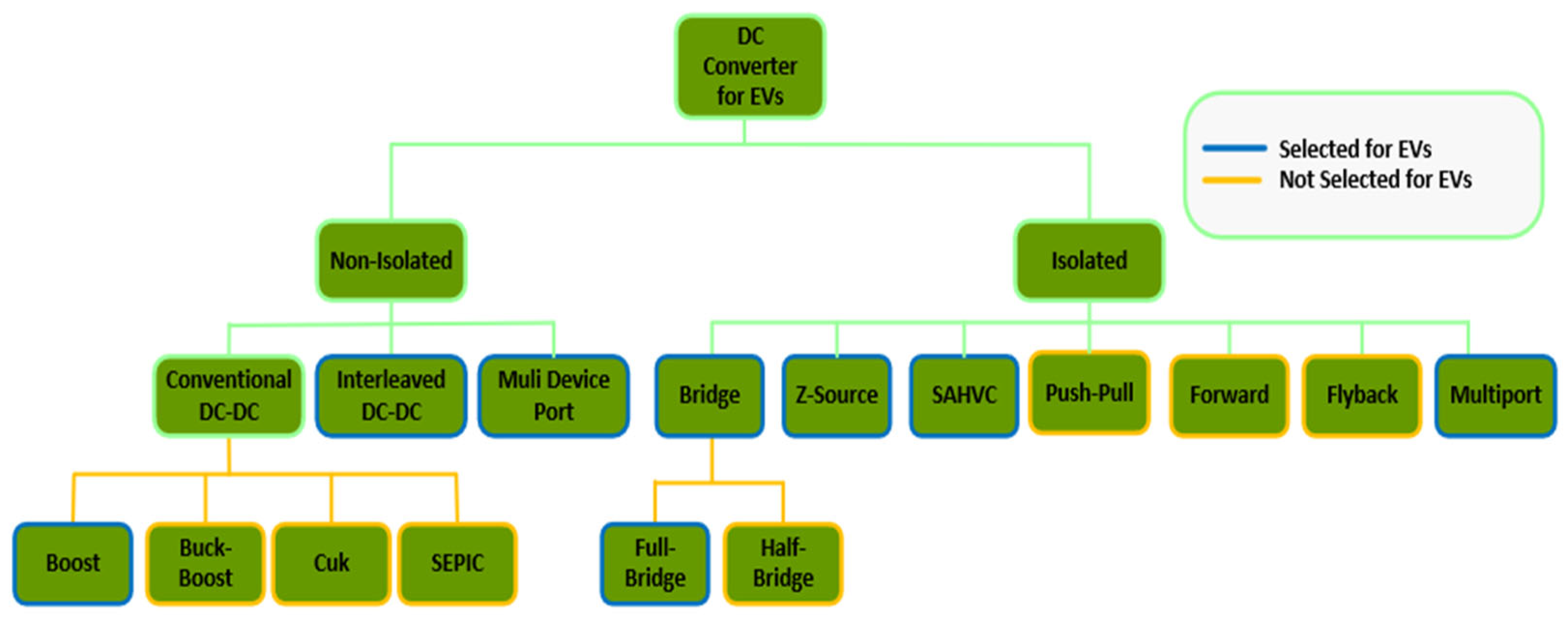
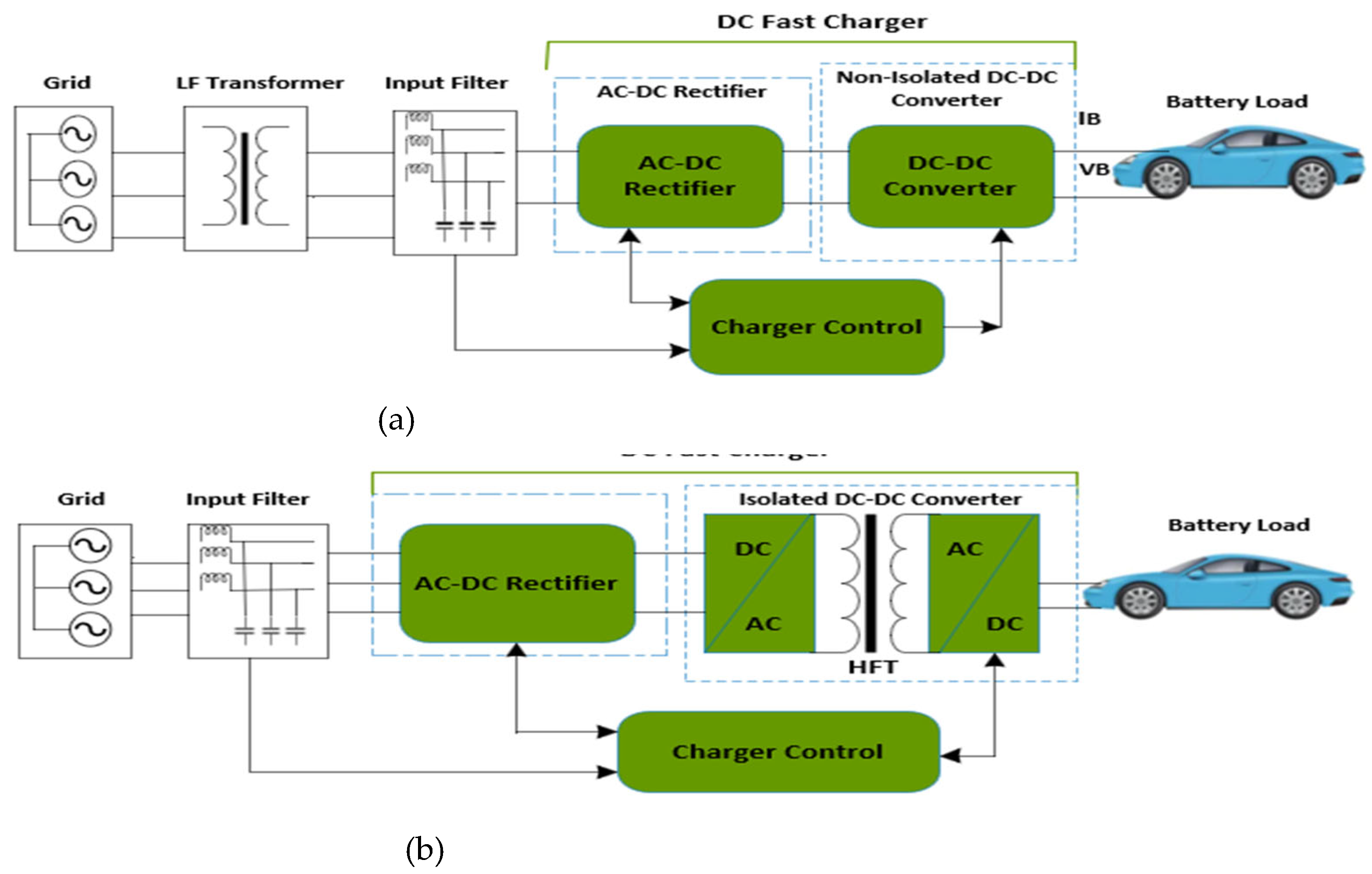
5. Status of DC Fast Charging Station DC-DC Converters Classification
6. Control Strategies for EV System
7. Challenges and Future Trends in EV Fast Charging
8. Research Contribution
- Comprehensive Landscape Analysis: It paints a complete picture, delving into diverse charging categories, methods, infrastructure specifics, and crucial elements like charging modes control, standards, converters, and control strategies. This holistic view informs future research and development efforts.
- Detailed Comparative Evaluation: By meticulously analysing various charging techniques, including their advantages and limitations, the paper empowers informed decision-making for future infrastructure advancements and technology choices.
- Challenges and Future Outlook: The article doesn't shy away from addressing current limitations and boldly proposes future research directions. This forward-thinking approach paves the way for overcoming obstacles and achieving faster, more efficient, and sustainable EV charging solutions.
9. Conclusion
References
- Szumska, E.M. Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure along Highways in the EU. Energies 2023, 16, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Saif, O.; Abo-Adma, M.; Fahmy, A.; Elazab, R. Strategies and sustainability in fast charging station deployment for electric vehicles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M. S. Mastoi et al., “An in-depth analysis of electric vehicle charging station infrastructure, policy implications, and future trends,” Energy Reports. 2022, 8, 11504–11529.
- Emmanuel Augustine Etukudoh, Ahmad Hamdan, Valentine Ikenna Ilojianya, Cosmas Dominic Daudu, and Adefunke Fabuyide, “Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure: a Comparative Review in Canada, USA, and Africa,” Eng. Sci. Technol. J. 2024, 5, 1–245.
- Ntombela, M.; Musasa, K.; Moloi, K. A Comprehensive Review of the Incorporation of Electric Vehicles and Renewable Energy Distributed Generation Regarding Smart Grids. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. Mod. POWER Syst. CLEAN ENERGY. 2023, XX, 1–19.
- Arya, H.; Das, M. Fast Charging Station for Electric Vehicles Based on DC Microgrid. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2023, 4, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, A.A.; Edpuganti, A.; Khadkikar, V.; Zeineldin, H. A Novel Simultaneous AC and DC Charging Scheme for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2024, PP, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Kumar, K. P. Panda, R. T. Naayagi, R. Thakur, and G. Panda, “Comprehensive Review of Electric Vehicle Technology and Its Impacts: Detailed Investigation of Charging Infrastructure, Power Management, and Control Techniques,” Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 15–1.
- Khalid, M.; Ahmad, F.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Al-Fagih, L. A comprehensive review on advanced charging topologies and methodologies for electric vehicle battery. J. Energy Storage 2022, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadou, K.; Rigogiannis, N.; Fountoukidis, S.; Kotarela, F.; Kyritsis, A.; Papanikolaou, N. Current Trends in Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure; Opportunities and Challenges in Wireless Charging Integration. Energies 2023, 16, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. Mehndiratta and R. Kumar, “Wireless Charging for Electric Vehicles: A Survey and Comprehensive Guide,” World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 1065, 485–493.
- Barman, P.; Dutta, L. Charging infrastructure planning for transportation electrification in India: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lin, Y.; Lim, M.K.; Zhou, F.; Liu, F. Electric vehicle charging station diffusion: An agent-based evolutionary game model in complex networks. Energy 2022, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. S. Mastoi et al., “An in-depth analysis of electric vehicle charging station infrastructure, policy implications, and future trends,” Energy Reports. 2022, 8, 11504–11529.
- Costantino, G.; De Vincenzi, M.; Martinelli, F.; Matteucci, I. Electric Vehicle Security and Privacy: A Comparative Analysis of Charging Methods. 2023 IEEE 97th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2023-Spring). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, ItalyDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 1–7.
- P, S. ; G.K, N. Review of Battery Charging Methods for Electric Vehicle. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Informatics, Communication and Energy Systems (SPICES). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, IndiaDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 395–400.
- Savari, G.F.; Sathik, M.J.; Raman, L.A.; El-Shahat, A.; Hasanien, H.M.; Almakhles, D.; Aleem, S.H.A.; Omar, A.I. Assessment of charging technologies, infrastructure and charging station recommendation schemes of electric vehicles: A review. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. Yu, S. Niu, Y. Shang, Z. Shao, Y. Jia, and L. Jian, “Electric vehicles integration and vehicle-to-grid operation in active distribution grids: A comprehensive review on power architectures, grid connection standards and typical applications,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 1–22.
- El Kattel, M.B.; Mayer, R.; Ely, F.; Filho, B.d.J.C. Comprehensive review of battery charger structures of EVs and HEVs for levels 1–3. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2023, 51, 3514–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegbohun, F.; von Jouanne, A.; Agamloh, E.; Yokochi, A. A Review of Bidirectional Charging Grid Support Applications and Battery Degradation Considerations. Energies 2024, 17, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoi, M.S.; Zhuang, S.; Munir, H.M.; Haris, M.; Hassan, M.; Alqarni, M.; Alamri, B. A study of charging-dispatch strategies and vehicle-to-grid technologies for electric vehicles in distribution networks. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 1777–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, G.; Bompard, E.; Mazza, A.; Pons, E.; Jaboeuf, R.; Tosco, P.; Zampolli, M. Impact of bidirectional EV charging stations on a distribution network: a Power Hardware-In-the-Loop implementation. Sustain. Energy, Grids Networks 2023, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. İnci, M. M. Savrun, and Ö. Çelik, “Integrating electric vehicles as virtual power plants: A comprehensive review on vehicle-to-grid (V2G) concepts, interface topologies, marketing and future prospects,” J. Energy Storage. 2022, 55, 1–20.
- S. Mateen, M. Amir, A. Haque, and F. I. Bakhsh, “Ultra-fast charging of electric vehicles: A review of power electronics converter, grid stability and optimal battery consideration in multi-energy systems,” Sustain. Energy, Grids Networks. 2023, 35, 1–34.
- M. A. H. Rafi and J. Bauman, “A Comprehensive Review of DC Fast-Charging Stations with Energy Storage: Architectures, Power Converters, and Analysis,” IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 345–368.
- Sharma, G.; Sood, V.K.; Alam, M.S.; Shariff, S.M. Comparison of common DC and AC bus architectures for EV fast charging stations and impact on power quality. eTransportation 2020, 5, 100066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmouatamid, A.; Ouladsine, R.; Bakhouya, M.; El Kamoun, N.; Khaidar, M.; Zine-Dine, K. Review of Control and Energy Management Approaches in Micro-Grid Systems. Energies 2020, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, E.L.V.; Gray, E.M.A. Optimization and integration of hybrid renewable energy hydrogen fuel cell energy systems–A critical review. Appl. Energy 2017, 202, 348–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. Dragičević, X. Lu, J. C. Vasquez, and J. M. Guerrero, “DC Microgrids - Part II: A Review of Power Architectures, Applications, and Standardization Issues,” IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 3528–3549.
- Waheed, A.; Rehman, S.U.; Alsaif, F.; Rauf, S.; Hossain, I.; Pushkarna, M.; Gebru, F.M. Hybrid multimodule DC–DC converters accelerated by wide bandgap devices for electric vehicle systems. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Gupta, J. A Bidirectional Charging System for Electric Two-Wheelers and Three Wheelers. 2022 IEEE Global Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GlobConPT). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, IndiaDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 1–6.
- Gupta, J.; Singh, B. A Bidirectional On-Board Charging System for LEVs. 2021 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Smart Technologies for Power, Energy and Control (STPEC). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, IndiaDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 1–6.
- Suresh, P.; Kalirajan, K.K.; Soundarapandian, K.A.; Nadar, E.R.S. Performance evaluation of improved Y source power factor correction converter with enhanced power quality in EV rapid charger application. Electr. Eng. 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Afshar, P. Macedo, F. Mohamed, and V. Disfani, “Mobile charging stations for electric vehicles — A review,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 152, 1–13.
- S. M. Shariff et al., “A state-of-the-art review on the impact of fast EV charging on the utility sector,” Energy Storage. 2022, 4, 1–21.
- Venegas, F.G.; Petit, M.; Perez, Y. Active integration of electric vehicles into distribution grids: Barriers and frameworks for flexibility services. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. Tavakoli, S. Saha, M. T. Arif, M. E. Haque, N. Mendis, and A. M. T. Oo, “Impacts of grid integration of solar PV and electric vehicle on grid stability, power quality and energy economics: A review,” IET Energy Syst. Integr. 2020, 2, 215–225.
- Arena, G.; Emiliani, P.; Chub, A.; Vinnikov, D.; De Carne, G. DC Fast Charging of Electric Vehicles: a Review on Architecture and Power Conversion Technology. 2023 IEEE 17th International Conference on Compatibility, Power Electronics and Power Engineering (CPE-POWERENG). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, EstoniaDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 1–6.
- Feng, J.; Khan, A.M. Accelerating urban road transportation electrification: planning, technology, economic and implementation factors in converting gas stations into fast charging stations. Energy Syst. 2024, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, T.; Tal, G.; Jenn, A.T. The costs and challenges of installing corridor DC Fast Chargers in California. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igbinovia, F.O.; Fandi, G.; Mahmoud, R.; Tlustý, J. A Review of Electric Vehicles Emissions and its Smart Charging Techniques Influence on Power Distribution Grid. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2016, 2016, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Liu, K.; Layeb, S.B.; Severino, A.; Jamal, A. Optimal Deployment of Electric Vehicles’ Fast-Charging Stations. J. Adv. Transp. 2023, 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Shaier, A.A.; Metwally, H.; Selem, S.I. A comprehensive overview of inductive pad in electric vehicles stationary charging. Appl. Energy 2020, 262, 114584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B. A. Rayan, U. Subramaniam, and S. Balamurugan, “Wireless Power Transfer in Electric Vehicles: A Review on Compensation Topologies, Coil Structures, and Safety Aspects,” Energies. 2023, 16, 1–46.
- N. Tesla, “Nikola Tesla U.S. Patent Apparatus for Transmitting Electrical Energy | Tesla Universe.” 1914. Available online: https://teslauniverse.com/nikola-tesla/patents/us-patent-1119732-apparatus-transmitting-electrical-energy (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- V. M. Macharia, V. K. Garg, and D. Kumar, “A review of electric vehicle technology: Architectures, battery technology and its management system, relevant standards, application of artificial intelligence, cyber security, and interoperability challenges,” IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2023, 13, 1–25.
- Williamson, S.S.; Madawala, U.; Kumar, D. Guest Editorial Advances in Wireless Power Transfer Technologies. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2022, 3, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamakani, B.E.; Mosallanejad, A.; Afjei, E.; Eshkevari, A.L. Investigation of triple quadrature pad for wireless power transfer system of electric vehicles. IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2021, 11, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Mao, X. Achieving misalignment tolerance with hybrid topologies in electric vehicle wireless charging systems. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, K.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Tong, X. Improving the Misalignment Tolerance of Wireless Power Transfer System for AUV with Solenoid-Dual Combined Planar Magnetic Coupler. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Amjad, M. Farooq-i-Azam, Q. Ni, M. Dong, and E. A. Ansari, “Wireless charging systems for electric vehicles,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 1–21.
- Ahmad, A.; Alam, M.S.; Rafat, Y.; Shariff, S. Designing and demonstration of misalignment reduction for wireless charging of autonomous electric vehicle. eTransportation 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palani, G.; Sengamalai, U.; Vishnuram, P.; Nastasi, B. Challenges and Barriers of Wireless Charging Technologies for Electric Vehicles. Energies 2023, 16, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, C.; Stegen, S.; Lu, J. Review of static and dynamic wireless electric vehicle charging system. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2018, 21, 922–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, R.; Kolar, J.W. Inductive power transfer for electric vehicle charging: Technical challenges and tradeoffs. IEEE Power Electron. Mag. 2016, 3, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Mateen, M. Amir, and A. Haque, “Ultra-Fast Charging of Electric Vehicles: An Integrated Review of Advancements in Power Electronics Converter Topologies, Route of Grid Stability and Optimal Battery Consideration,” Sustain. Energy, Grids Networks. 2023, 35, 1–34.
- Zhou, K.; Wu, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, Y.; Teng, D.; Liu, Y. Research and Development Review of Power Converter Topologies and Control Technology for Electric Vehicle Fast-Charging Systems. Electronics 2023, 12, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.; Wang, J. Integrating ultra-fast charging stations within the power grids of smart cities: a review. IET Smart Grid 2018, 1, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, C.; Longo, M.; Fernández-Ramírez, L.M. Optimal Size of a Smart Ultra-Fast Charging Station. Electronics 2021, 10, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. Franzese et al., “Fast DC Charging Infrastructures for Electric Vehicles: Overview of Technologies, Standards, and Challenges,” IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 3780–3800.
- Rajendran, G.; Vaithilingam, C.A.; Misron, N.; Naidu, K.; Ahmed, R. A comprehensive review on system architecture and international standards for electric vehicle charging stations. J. Energy Storage 2021, 42, 103099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashique, R.H.; Salam, Z.; Aziz, M.J.B.A.; Bhatti, A.R. Integrated photovoltaic-grid dc fast charging system for electric vehicle: A review of the architecture and control. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, F.M.; Malik, O.P. Vehicle-To-Grid Technology in a Micro-grid Using DC Fast Charging Architecture. 2019 IEEE Canadian Conference of Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, CanadaDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Saadaoui, A.; Ouassaid, M.; Maaroufi, M. Overview of Integration of Power Electronic Topologies and Advanced Control Techniques of Ultra-Fast EV Charging Stations in Standalone Microgrids. Energies 2023, 16, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.L.; Speidel, S.; Bräunl, T. A comparative study of AC and DC public electric vehicle charging station usage in Western Australia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Transit. 2022, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safayatullah; Elrais, M. T.; Ghosh, S.; Rezaii, R.; Batarseh, I. A Comprehensive Review of Power Converter Topologies and Control Methods for Electric Vehicle Fast Charging Applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 40753–40793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Qin, Z.; Wijekoon, T.; Bauer, P. An Overview on Medium Voltage Grid Integration of Ultra-Fast Charging Stations: Current Status and Future Trends. IEEE Open J. Ind. Electron. Soc. 2022, 3, 420–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, S.; Deb, S.; Singh, P.P.; Alam, M.S.; Shariff, S.M. A comprehensive review of standards and best practices for utility grid integration with electric vehicle charging stations. WIREs Energy Environ. 2021, 11, e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. Meintz et al., “Enabling fast charging – Vehicle considerations,” J. Power Sources. 2017, 367, 216–227.
- Burnham, A.; Dufek, E.J.; Stephens, T.; Francfort, J.; Michelbacher, C.; Carlson, R.B.; Zhang, J.; Vijayagopal, R.; Dias, F.; Mohanpurkar, M.; et al. Enabling fast charging – Infrastructure and economic considerations. J. Power Sources 2017, 367, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, A.; Hasanien, H.M.; Turky, R.A.; Aleem, S.H.A. Modeling and optimal operation of hybrid wave energy and PV system feeding supercharging stations based on golden jackal optimal control strategy. Energy 2023, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguesa, J.A.; Torres-Sanz, V.; Garrido, P.; Martinez, F.J.; Marquez-Barja, J.M. A Review on Electric Vehicles: Technologies and Challenges. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 372–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemavathi, S.; Shinisha, A. A study on trends and developments in electric vehicle charging technologies. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Tanim, T.R.; Dufek, E.J.; Scoffield, D.; Pennington, T.D.; Gering, K.L.; Colclasure, A.M.; Mai, W.; Meintz, A.; Bennett, J. Projecting Recent Advancements in Battery Technology to Next-Generation Electric Vehicles. Energy Technol. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Y. Yong, W. S. Tan, M. Khorasany, and R. Razzaghi, “Electric vehicles destination charging: An overview of charging tariffs, business models and coordination strategies,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 184, 1–25.
- O’neill, D.; Yildiz, B.; Bilbao, J.I. An assessment of electric vehicles and vehicle to grid operations for residential microgrids. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 4104–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. Seo-yeon and C. Sung-hoon, “Integrating Vehicle-to-Grid Technologies in Autonomous Electric Vehicle Systems,” Appl. Res. Artif. Intell. Cloud Comput. - ARAIC. 2022, 1, 105–120.
- K. Taghizad-Tavana, A. Alizadeh, M. Ghanbari-Ghalehjoughi, and S. Nojavan, “A Comprehensive Review of Electric Vehicles in Energy Systems: Integration with Renewable Energy Sources, Charging Levels, Different Types, and Standards,” Energies. 2023, 16, 1–23.
- Huang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Ma, P.; Wang, M.; Long, Y.; Zhang, M. Economic-environmental scheduling of microgrid considering V2G-enabled electric vehicles integration. Sustain. Energy, Grids Networks 2022, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarar, M.O.; Hassan, N.U.; Naqvi, I.H.; Pecht, M. Techno-Economic Framework for Electric Vehicle Battery Swapping Stations. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrification 2023, 9, 4458–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayarshad, H.R.; Mahmoodian, V.; Gao, H.O. Non-myopic dynamic routing of electric taxis with battery swapping stations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 57, 102113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S. Use of battery swapping for improving environmental balance and price-performance ratio of electric vehicles. eTransportation 2021, 9, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. Patil, “Innovations in Electric Vehicle Technology: A Review of Emerging Trends and Their Potential Impacts on Transportation and Society,” Rev. Contemp. Bus. Anal. 2021, 2, 20–32.
- Sun, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, C. Technology Development of Electric Vehicles: A Review. Energies 2019, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, F. Electric Vehicles: Benefits, Challenges, and Potential Solutions for Widespread Adaptation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. A. Visaria, A. F. Jensen, M. Thorhauge, and S. E. Mabit, “User preferences for EV charging, pricing schemes, and charging infrastructure,” Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2022, 165, 120–143.
- Cedillo, M.H.; Sun, H.; Jiang, J.; Cao, Y. Dynamic pricing and control for EV charging stations with solar generation. Appl. Energy 2022, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanke, T.U.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Yong, J.Y.; Pasupuleti, J.; Kasinathan, P.; Rajagopalan, A. A review of strategic charging–discharging control of grid-connected electric vehicles. J. Energy Storage 2020, 28, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Alam, M.S.; Alsaidan, I.S.; Shariff, S.M. Battery swapping station for electric vehicles: opportunities and challenges. IET Smart Grid 2020, 3, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Cai, H.; Zou, G. Configuration and system operation for battery swapping stations in Beijing. Energy 2020, 214, 118883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naor, M.; Coman, A.; Wiznizer, A. Vertically Integrated Supply Chain of Batteries, Electric Vehicles, and Charging Infrastructure: A Review of Three Milestone Projects from Theory of Constraints Perspective. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Levy, I. J. Levy, I. Riu, and C. Zoi, “The Costs of EV Fast Charging Infrastructure and Economic Benefits to Rapid Scale-Up,” EVGO FAST Charg. STORYBLOK, 2020.
- Das, H.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Li, S.; Tan, C.W. Electric vehicles standards, charging infrastructure, and impact on grid integration: A technological review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 120, 109618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfeen, Z.A.; Khairuddin, A.B.; Azam, M.K.; Humayun, U.; Khidrani, A. V2G FACTS AND FACETS WITH MODELING OF ELECTRIC VEHICLE FAST-CHARGING STATION-STATUS AND TECHNOLOGICAL REVIEW. Pak. J. Sci. Res. 2021, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Gjelaj, S. Hashemi, C. Traeholt, and P. B. Andersen, “Grid integration of DC fast-charging stations for EVs by using modular li-ion batteries,” IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2018, 12, 4368–4376.
- Rubino, L.; Capasso, C.; Veneri, O. Review on plug-in electric vehicle charging architectures integrated with distributed energy sources for sustainable mobility. Appl. Energy 2017, 207, 438–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, N.; Singh, R.; Brooks, R.R.; Bai, K. A Review of Extremely Fast Charging Stations for Electric Vehicles. Energies 2021, 14, 7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Liu, C.; Li, S.; Lin, Z.; Huang, Y. Long-term strategic planning of inter-city fast charging infrastructure for battery electric vehicles. Transp. Res. Part E: Logist. Transp. Rev. 2018, 109, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roni, M.S.; Yi, Z.; Smart, J.G. Optimal charging management and infrastructure planning for free-floating shared electric vehicles. Transp. Res. Part D: Transp. Environ. 2019, 76, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Kaleybar, H.J.; Brenna, M.; Castelli-Dezza, F.; Carmeli, M.S. Integration of Distributed Energy Resources and EV Fast-Charging Infrastructure in High-Speed Railway Systems. Electronics 2021, 10, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, S.K.; Devassy, S.; Verma, B.K.; Mishra, S.; Akbar, S.A. Review on Renewable Energy Based EV Charging System with Grid Support Functionality. 2021 7th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, IndiaDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 482–487.
- Vosooghi, R.; Puchinger, J.; Bischoff, J.; Jankovic, M.; Vouillon, A. Shared autonomous electric vehicle service performance: Assessing the impact of charging infrastructure. Transp. Res. Part D: Transp. Environ. 2020, 81, 102283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Qiu, J.; Lai, S.; Sun, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, B.; Cheng, L. Data-driven on-demand energy supplement planning for electric vehicles considering multi-charging/swapping services. Appl. Energy 2022, 311, 118632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K, J.K.; Kumar, S.; V. S, N. Standards for electric vehicle charging stations in India: A review. Energy Storage 2021, 4, e261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Mateen, M. Amir, A. Haque, and F. I. Bakhsh, “Ultra-fast charging of electric vehicles: A review of power electronics converter, grid stability and optimal battery consideration in multi-energy systems,” Sustain. Energy, Grids Networks. 2023, 35, 1–34.
- Leone, C.; Longo, M. Modular Approach to Ultra-fast Charging Stations. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2021, 16, 1971–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L. Wang, Z. Qin, T. Slangen, P. Bauer, and T. Van Wijk, “Grid Impact of Electric Vehicle Fast Charging Stations: Trends, Standards, Issues and Mitigation Measures - An Overview,” IEEE Open J. Power Electron. 2020, 2, 56–74.
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; Hu, X. Charging optimization in lithium-ion batteries based on temperature rise and charge time. Appl. Energy 2017, 194, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, C.; Longo, M.; Fernandez-Ramirez, L.M.; Garcia-Trivino, P. Multi-Objective Optimization of PV and Energy Storage Systems for Ultra-Fast Charging Stations. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 14208–14224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoaki, Y.; Yi, W.; Salisbury, S. Empirical analysis of electric vehicle fast charging under cold temperatures. Energy Policy 2018, 122, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Liu, X.; He, R.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, X.; Peng, Z.; Feng, S.; Feng, X.; Yang, S. Challenges and opportunities toward fast-charging of lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2020, 32, 101837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; Hu, X. Charging optimization in lithium-ion batteries based on temperature rise and charge time. Appl. Energy 2017, 194, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wei, Z.; Knoll, A.C. Charging Optimization for Li-Ion Battery in Electric Vehicles: A Review. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrification 2021, 8, 3068–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.M.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Yong, J.Y. Integration of electric vehicles in smart grid: A review on vehicle to grid technologies and optimization techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Qu, G.; Sun, B.; Li, N.; Tsang, D.H.K. Optimal Scheduling of Battery Charging Station Serving Electric Vehicles Based on Battery Swapping. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 10, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, H.; Kang, H. Review of Electric Vehicle Ultra-Fast DC Charging Station. 2022 7th Asia Conference on Power and Electrical Engineering (ACPEE). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, ChinaDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 1–9.
- Mahfouz, M.M.; Iravani, M.R. Grid-Integration of Battery-Enabled DC Fast Charging Station for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 35, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanalian, S.; Sebaaly, F.; Zgheib, R.; Al-Haddad, K. Modular Multilevel Converters for Fast Charging Stations of Electric Vehicles: An Overview. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, United StatesDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 1–6.
- Mohamed, A.A.S.; Meintz, A.; Zhu, L. System Design and Optimization of In-Route Wireless Charging Infrastructure for Shared Automated Electric Vehicles. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 79968–79979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.A.Q.; Jung, J.-W. A Comprehensive State-of-the-Art Review of Wired/Wireless Charging Technologies for Battery Electric Vehicles: Classification/Common Topologies/Future Research Issues. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 19572–19585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, S.; Dorrell, D.G.; Li, X.; Zhan, W. Operation optimization approaches of electric vehicle battery swapping and charging station: A literature review. Energy 2023, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Hou, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhai, H.; Wei, X. Joint charging scheduling of electric vehicles with battery to grid technology in battery swapping station. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Sun, F.; Wang, Z.; Lin, C.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, R.; Deng, J.; Zhu, X.; Xie, P.; Zhang, S.; et al. China's battery electric vehicles lead the world: achievements in technology system architecture and technological breakthroughs. Green Energy Intell. Transp. 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, G.; Vaithilingam, C.A.; Misron, N.; Naidu, K.; Ahmed, R. A comprehensive review on system architecture and international standards for electric vehicle charging stations. J. Energy Storage 2021, 42, 103099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronanki, D.; Kelkar, A.; Williamson, S.S. Extreme Fast Charging Technology—Prospects to Enhance Sustainable Electric Transportation. Energies 2019, 12, 3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, M.; Cigolotti, V.; Jannelli, E.; Fragiacomo, P. Current standards and configurations for the permitting and operation of hydrogen refueling stations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 19357–19371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. Draz, A. M. Othman, and A. A. El-fergany, “State-of-the-Art with numerical analysis on electric fast charging stations : infrastructures, standards, techniques, and challenges Electric vehicle Supply Equipment Point of Common Coupling,” Renew. Energy Focus J. 2023, 47, 1–23.
- Jaman, S.; Verbrugge, B.; Garcia, O.H.; Abdel-Monem, M.; Oliver, B.; Geury, T.; Hegazy, O. Development and Validation of V2G Technology for Electric Vehicle Chargers Using Combo CCS Type 2 Connector Standards. Energies 2022, 15, 7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neaimeh, M.; Andersen, P.B. Mind the gap- open communication protocols for vehicle grid integration. Energy Informatics 2020, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. Aretxabaleta, I. M. De Alegria, J. Andreu, I. Kortabarria, and E. Robles, “High-Voltage Stations for Electric Vehicle Fast-Charging: Trends, Standards, Charging Modes and Comparison of Unity Power-Factor Rectifiers,” IEEE Access. 2021, 9, 102177–102194.
- Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Cao, Y.; Huang, C.; Xu, Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, Y. Hybrid charging strategy with adaptive current control of lithium-ion battery for electric vehicles. Renew. Energy 2020, 160, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. F. Camacho and L. Mihet-Popa, “Fast Charging and Smart Charging Tests for Electric Vehicles Batteries Using Renewable Energy,” Oil Gas Sci. Technol. - Rev. IFP Energies Nouv. 2014, 71, 1–14.
- Elma, O. A dynamic charging strategy with hybrid fast charging station for electric vehicles. Energy 2020, 202, 117680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Sassi, H.; Alaoui, C.; Errahimi, F.; Es-Sbai, N. Vehicle-to-grid technology and its suitability for the Moroccan national grid. J. Energy Storage 2020, 33, 102023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, T.; Tal, G.; Jenn, A.T. The costs and challenges of installing corridor DC Fast Chargers in California. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, S. Review of power electronics in vehicle-to-grid systems. J. Energy Storage 2019, 21, 337–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subashini, M.; Vijayan, S. Smart Charging for Zero Emission Vehicles – A Comprehensive Review. Renew. Energy Focus 2023, 46, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharavat, N.; Golla, N.K.; Sudabattula, S.K.; Velamuri, S.; Kantipudi, M.V.V.P.; Kotb, H.; AboRas, K.M. Impact of plug-in electric vehicles on grid integration with distributed energy resources: A review. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassiliadis, N.; Schneider, J.; Frank, A.; Wildfeuer, L.; Lin, X.; Jossen, A.; Lienkamp, M. Review of fast charging strategies for lithium-ion battery systems and their applicability for battery electric vehicles. J. Energy Storage 2021, 44, 103306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. S. Hossain Lipu et al., “Intelligent algorithms and control strategies for battery management system in electric vehicles: Progress, challenges and future outlook,” J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 1–27.
- Wu, M.; Qin, L.; Wu, G. State of charge estimation of Power lithium-ion battery based on an Affine Iterative Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter. J. Energy Storage 2022, 51, 104472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucer, E.; Koyuncu, I.; Kisacikoglu, M.C.; Yavuz, M.; Meintz, A.; Rames, C. Modeling and Analysis of a Fast Charging Station and Evaluation of Service Quality for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrification 2019, 5, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, F.N.; Darwish, A.; Williams, B.W. Power Converter Topologies for Grid-Tied Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Powered Electric Vehicles (EVs)—A Comprehensive Review. Energies 2022, 15, 4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, L.; Huang, C. State-of-charge estimation of lithium-ion battery pack by using an adaptive extended Kalman filter for electric vehicles. J. Energy Storage 2021, 37, 102457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Y. Metwly, M. S. Abdel-Majeed, A. S. Abdel-Khalik, R. A. Hamdy, M. S. Hamad, and S. Ahmed, “A Review of Integrated On-Board EV Battery Chargers: Advanced Topologies, Recent Developments and Optimal Selection of FSCW Slot/Pole Combination,” IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 85216–85242.
- Khaligh, A.; D'Antonio, M. Global Trends in High-Power On-Board Chargers for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 3306–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommana, B.; Kumar, J.S.V.S.; Nuvvula, R.S.S.; Kumar, P.P.; Khan, B.; Muthusamy, S.; Inapakurthi, R. A Comprehensive Examination of the Protocols, Technologies, and Safety Requirements for Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure. J. Adv. Transp. 2023, 2023, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenna, M.; Foiadelli, F.; Leone, C.; Longo, M. Electric Vehicles Charging Technology Review and Optimal Size Estimation. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2020, 15, 2539–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.K.; Ghadi, M.J.; Li, L.; Hossain, J.; Zhang, J.; Ray, P.K.; Mohanty, A. A review on solid-state transformer: A breakthrough technology for future smart distribution grids. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 133, 107255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, A.F.; Bossche, A.V.D. Forward Converter Current Fed Equalizer for Lithium Based Batteries in Ultralight Electrical Vehicles. Electronics 2019, 8, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. L. Jou, J. J. Huang, J. C. Wu, and K. Der Wu, “Novel isolated multilevel DC-DC power converter,” IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 2690–2694.
- G. R. C. Mouli, P. Van Duijsen, F. Grazian, A. Jamodkar, P. Bauer, and O. Isabella, “Sustainable e-bike charging station that enables ac, dc andwireless charging from solar energy,” Energies. 2020, 13, 1–21.
- M. A. Hannan et al., “State of the art of solid-state transformers: Advanced topologies, implementation issues, recent progress and improvements,” IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 19113–19132.
- Atkar, D.D.; Chaturvedi, P.; Suryawanshi, H.M.; Nachankar, P.P.; Yadeo, D. Optimal Design of Solid State Transformer-Based Interlink Converter for Hybrid AC/DC Micro-Grid Applications. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 10, 3685–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Kang, B.; Kim, W.-S.; Yoon, S.-J. Reduction of input voltage/current ripples of boost half-bridge DC-DC converter for photovoltaic micro-inverter. Sol. Energy 2019, 188, 1084–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. Franzese et al., “Fast DC Charging Infrastructures for Electric Vehicles: Overview of Technologies, Standards, and Challenges,” IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 3780–3800.
- R. L. Da Silva, V. L. F. Borges, C. E. Possamai, and I. Barbi, “Solid-State Transformer for Power Distribution Grid Based on a Hybrid Switched-Capacitor LLC-SRC Converter: Analysis, Design, and Experimentation,” IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 141182–141207.
- Guo, W.; Chen, T.; Huang, A.Q. A Control Bandwidth Optimized Active Damping Scheme for LC and LCL Filter-Based Converters. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 34286–34296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Pang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wong, C.-K.; Lam, C.-S.; Wong, M.-C. Design, control and comparative analysis of an LCLC coupling hybrid active power filter. IET Power Electron. 2020, 13, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Al-Barashi, X. Meng, Z. Liu, M. S. R. Saeed, I. A. Tasiu, and S. Wu, “Enhancing power quality of high-speed railway traction converters by fully integrated T-LCL filter,” IET Power Electron. 2023, 16, 699–714.
- Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liang, W.; Peng, J.; Jiang, H. Active EMI Filter Design With a Modified LCL-LC Filter for Single-Phase Grid-Connected Inverter in Vehicle-to-Grid Application. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 10639–10650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| EV Specifications | Ref | Inductive Charging | Ultra-Fast Charging | DC Fast Charging | Tesla Superchargers | Bidirectional Charging | Battery Swapping |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convenience | [84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92] | Medium to Low | High | Medium to High | High | Medium to Low | Medium to High |
| Safety | [88,92,95,96,97,98] | Medium | Medium to High | Medium to High | High | Medium to High | Medium to High |
| Durability | [96,100] | Medium | Medium | Medium | High | Medium | Medium to High |
| Integration with Infrastructure | [25,61,99,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109] | Medium to Low | Medium to High | High | Medium to High | Medium to Low | Medium to Low |
| Compatibility | [91,94,106,111,112,113] | Low | Medium | Medium | Low | Medium to Low | Medium to High |
| Battery Degradation | [63,110,112,115,116,117,118,119,120,121] | Medium | High | High | Medium to High | Medium to High | Medium to High |
| Scalability and Upgradability | [15,25,100,122,123,124], | Medium | Medium to High | Medium | High | Medium to High | Medium to Low |
| Efficiency | [44,67,74,91,122,125,126,127,128], | Low | Medium to High | Medium | Medium to High | Medium to Low | Medium to High |
| Level of charging rating (A) | Supply system | Maximum power rating (kW) | Maximum current rating (A) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 (AC) (IEC) | 240 V | 4.7 | 16 |
| Level 2 (AC) (IEC) | 240 V | 11.5 | 32 |
| Level 3 (AC) (IEC) | 415 V | 90 | 250 |
| Fast DC Charging (DC) (IEC) | 600 V | 150 | 400 |
| Level 1 (AC) (SAE) | 120 V | 2 | 16 |
| Level 2 (AC) (SAE) | 208-240 V | 20 | 80 |
| Level 3 (AC)(SAE) | - V | ||
| Fast DC Charging (DC) (SAE) | -400 V |
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| IEC 60038 | Specifies the standard voltage levels used for electrical power systems. And charging applications |
| IEC 62196 | Standards conductive charging components for connectors, cables, outlets, plugs, inlets, and communication protocols used in AC charging of electric vehicles. |
| IEC 60664-1 | Insulation coordination for equipment within low-voltage systems |
| IEC 62752 | Provides guidelines for connecting of electric vehicles to information and communication technology ICT networks. |
| IEC 61851 | Covering various charging modes, communication protocols, and safety features. |
| SAE J1772 | Requirements for the electrical connectors and communication protocols for Level 1 and Level 2 charging used for AC charging of electric vehicles in North America. |
| SAE J2344 | Provides guidelines and test procedures for evaluating the crashworthiness and safety of electric vehicle battery systems. |
| SAE J2894/2 | Requirements for the power quality, conductive charge coupler used in DC fast charging electric vehicles. |
| SAE J2953 | Standards for interoperability to provide guidelines for conductive automated charging systems for electric vehicles |
| SAE J2847/1 | Communication between vehicles as a distributed energy source and grid |
| SAE J3068 | Wireless Power Transfer for Light-Duty Plug-In/Electric Vehicles and Alignment Methodology |
| SAE J2931/7 | Evaluating the electrical performance of components used in hybrid and electric vehicles |
| ISO 15118 | Standards for V2G communication protocols and interfaces between vehicle and charging infrastructure |
| ISO 17409 | Specifications and reliable measurement of energy consumption allow for accurate comparisons and evaluations of different EV models. |
| Category | Model | Type | Battery (KWh) | Range (Km) | Connector |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plug-in Hybrid (PHEV) | Chevrolet Volt | PHEV | 18.4 | 85 (battery) | Type 1 J1772 |
| Mitsubishi Outlander | PHEV | 20 | 84 (battery) | CCS, Type 2 | |
| Volvo XC40 | PHEV | 10.7 | 43 (battery) | CCS, Type | |
| Toyota Prius Prime | PHEV | 8.8 | 40 (battery) | SAE J1772 | |
| Nissan Leaf | PHEV | 64 | 480 | CHAdeMO, Type 2 | |
| Electric Vehicle (BEV) | Tesla Model S | BEV | 100 | 620 | Supercharger |
| Tesla Model X | BEV | 100 | 500 | Supercharger | |
| Tesla Model 3 | BEV | 82 | 580 | Supercharger | |
| Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) | Toyota Mirai | FCEV | 1.6 (hydrogen capacity) | 647 | N/A |
| Hyundai Nexo | FCEV | 40 (hydrogen capacity) | 570 | N/A | |
| Honda Clarity | FCEV | 25.5 (hydrogen capacity) | 550 | N/A | |
| Extended Range Electric Vehicle (E-REV) | BYD Atto3 | E-REV | 60.4 | 420 (battery) | CCS, Type 2 |
| Charging Methods | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| On-board charger |
|
|
| Off-board charger |
|
|
| Voltage Mode Control in Non-Isolated DC/DC Converters | Current Mode Control in Non-Isolated DC/DC Converters | Peak Current Control in Non-Isolated DC/DC Converters | Average Current Control in Non-Isolated DC/DC Converters | Voltage Mode Control in Isolated DC/DC Converters | Current Mode Control in Isolated DC/DC Converters | Peak Current Control in Isolated DC/DC Converters | Average Current Control in Isolated DC/DC Converters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improves charging efficiency. | - Enhancing charging efficiency. | Prevent overloading the converter and charging infrastructure. | Optimizes energy transfer and improves charging. | Maintaining a stable output voltage. | Provide efficient energy transfer, stable from the grid to the EV battery. | Regulates and limits the peak current to optimize the charging process. | Regulate and maintain a stable average output current. |
| Fast response | Regulation protects the EV battery from overcharging or undercharging. | Ensures the charging current remains within a predetermined threshold. | Reduce charging times, minimized energy losses, and improved efficiency. | Prevents overvoltage or under voltage conditions, improving the charging efficiency of EV batteries. | Ensures reliable, safe, and fast charging operations. | Prevents the current from exceeding the peak limit, ensuring efficient energy transfer and providing overcurrent protection. | Ensures optimal charging performance and improves power quality. |
| Compatibility with the charging infrastructure | Fast dynamic response to load variations. | Enhances charging efficiency by minimizing energy losses and heat generation. | Improves voltage regulation and stability while protecting the battery from voltage fluctuations. | Excellent adaptability to load variations conditions. | Demand for rapid and reliable EV charging increases. | Ensures compatibility with grid constraints. | |
| Maintain a stable output voltage | Safeguards the charging infrastructure. | Compatibility with grid constraints, maintaining safety, optimizing energy transfer, and increasing charging efficiency demand for EV fast charging. | It ensures compatibility with charging infrastructure and provides flexibility in adapting to changing load conditions. | Allowing the system to accommodate different charging scenarios, optimizing energy transfer, reducing charging times, reliable, and high-performance charging infrastructure. | Ensuring safety and improving charging efficiency. | Achieving reliable, safe, and high-performance charging operations. | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





