Submitted:
18 April 2024
Posted:
18 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
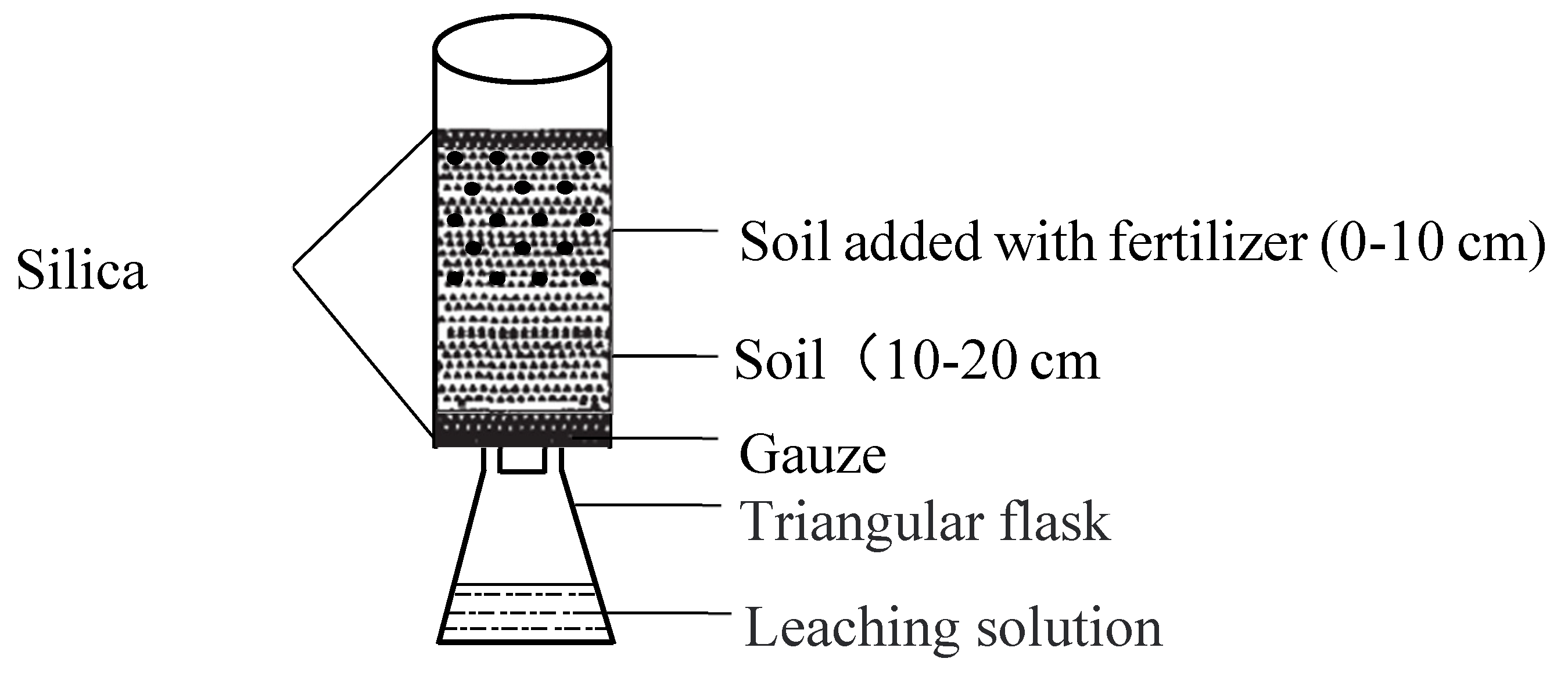
2.1. Simulation Experiment Design
2.2. Field Experiment
2.2.1. Experiment Design
2.2.2. Soil Sampling and Measurements
2.2.3. Maize Plant Sampling and Determination
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Simulation Experiment
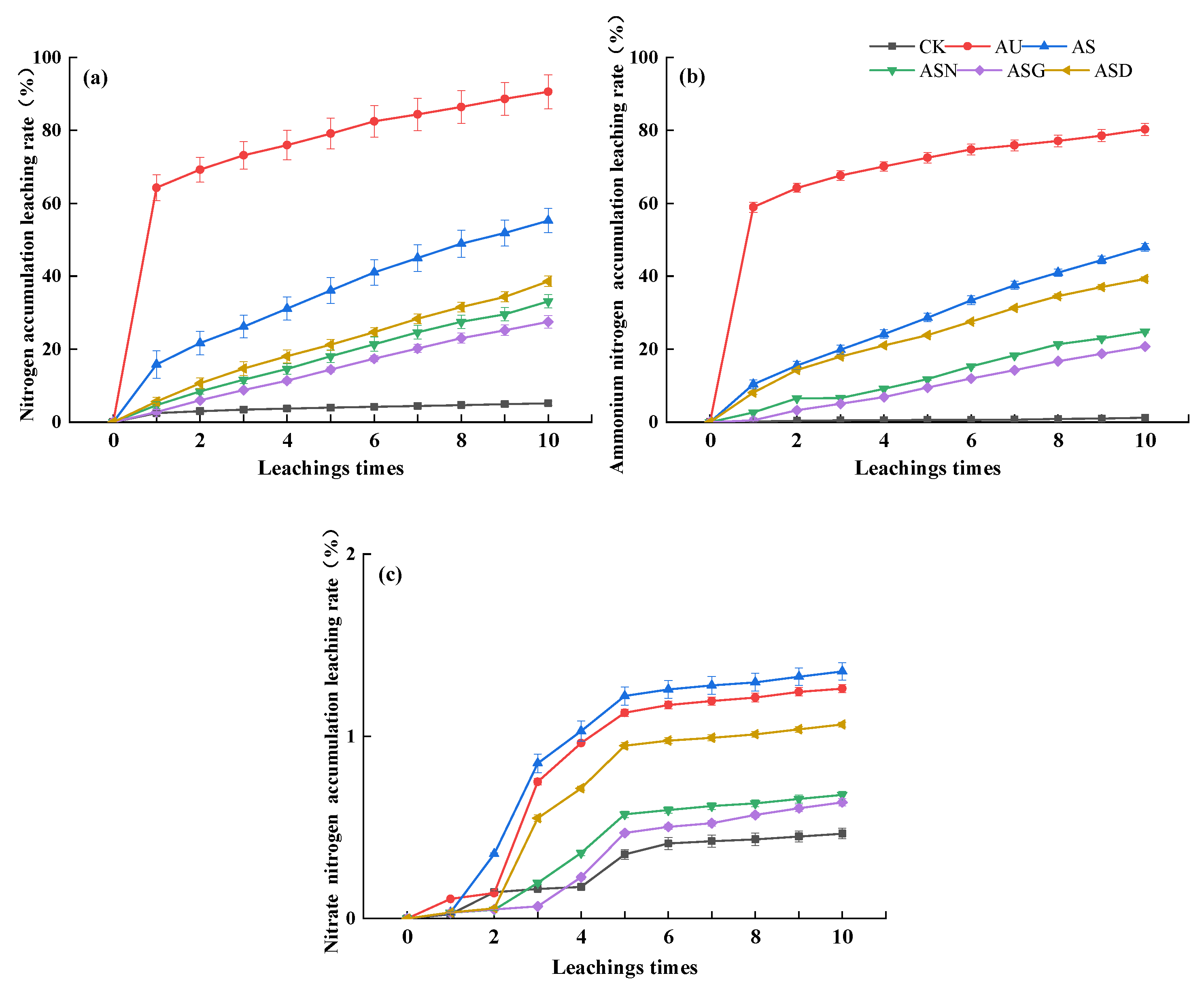
3.1.1. N Leaching Rate
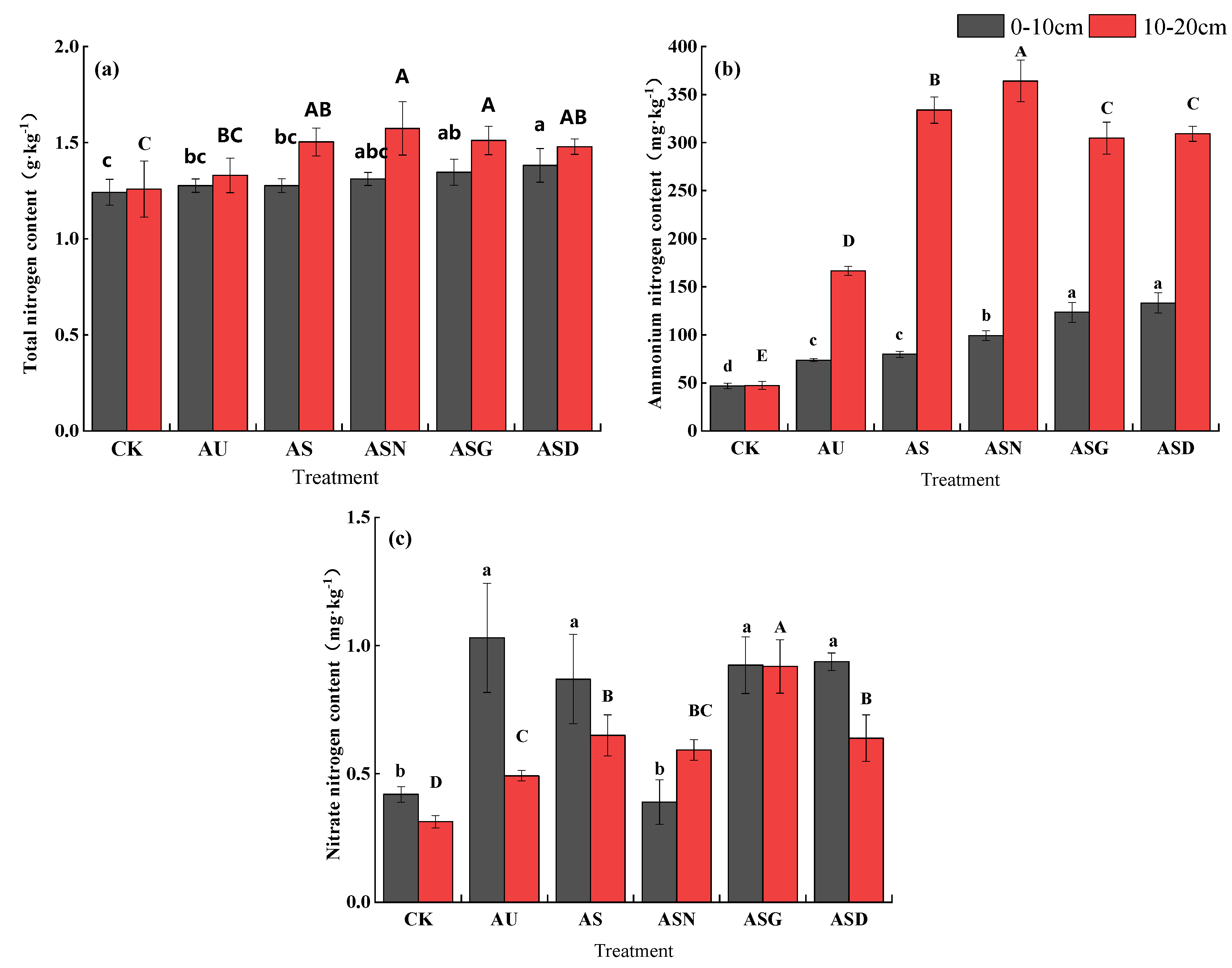
3.1.2. Soil N Residual
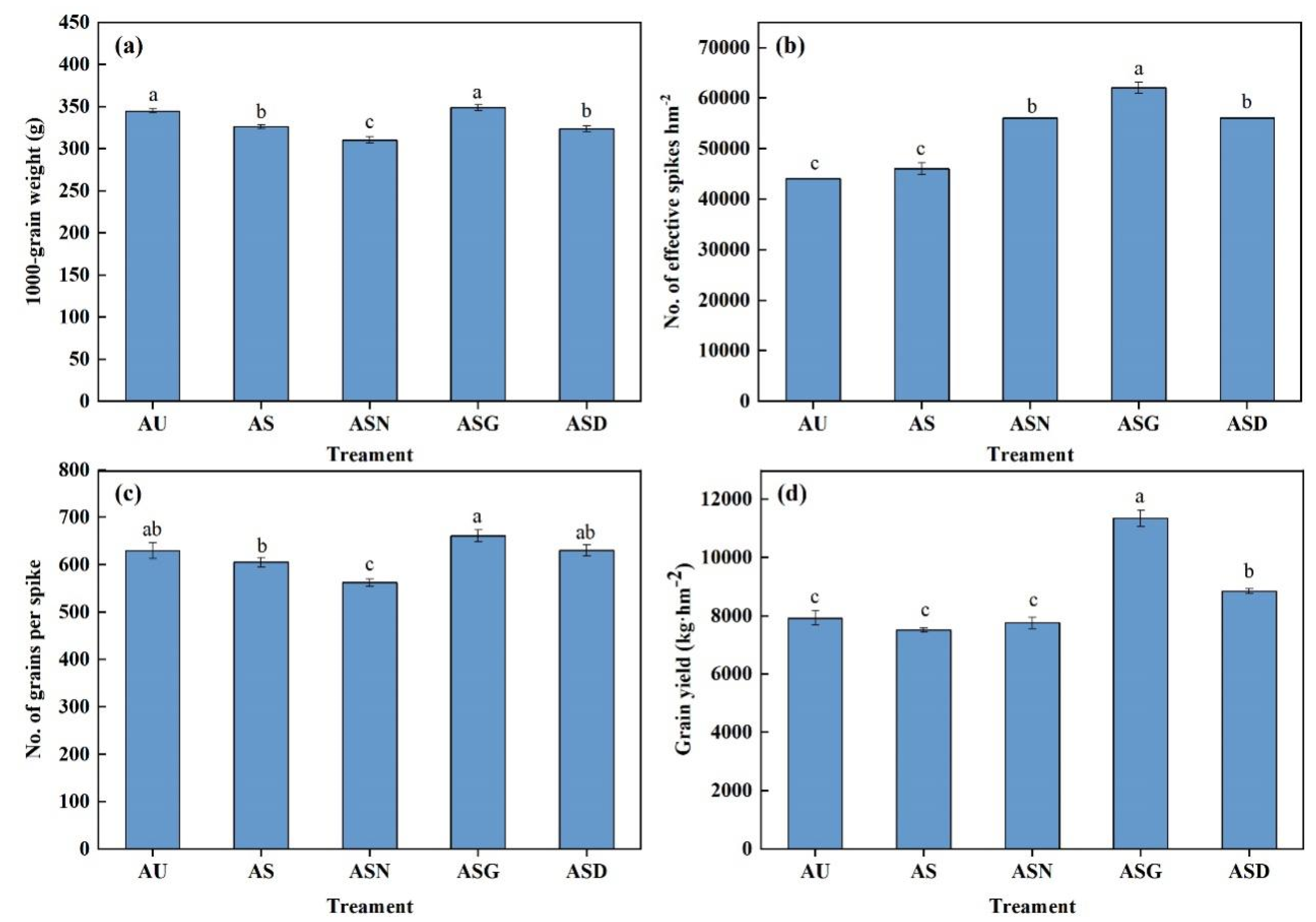
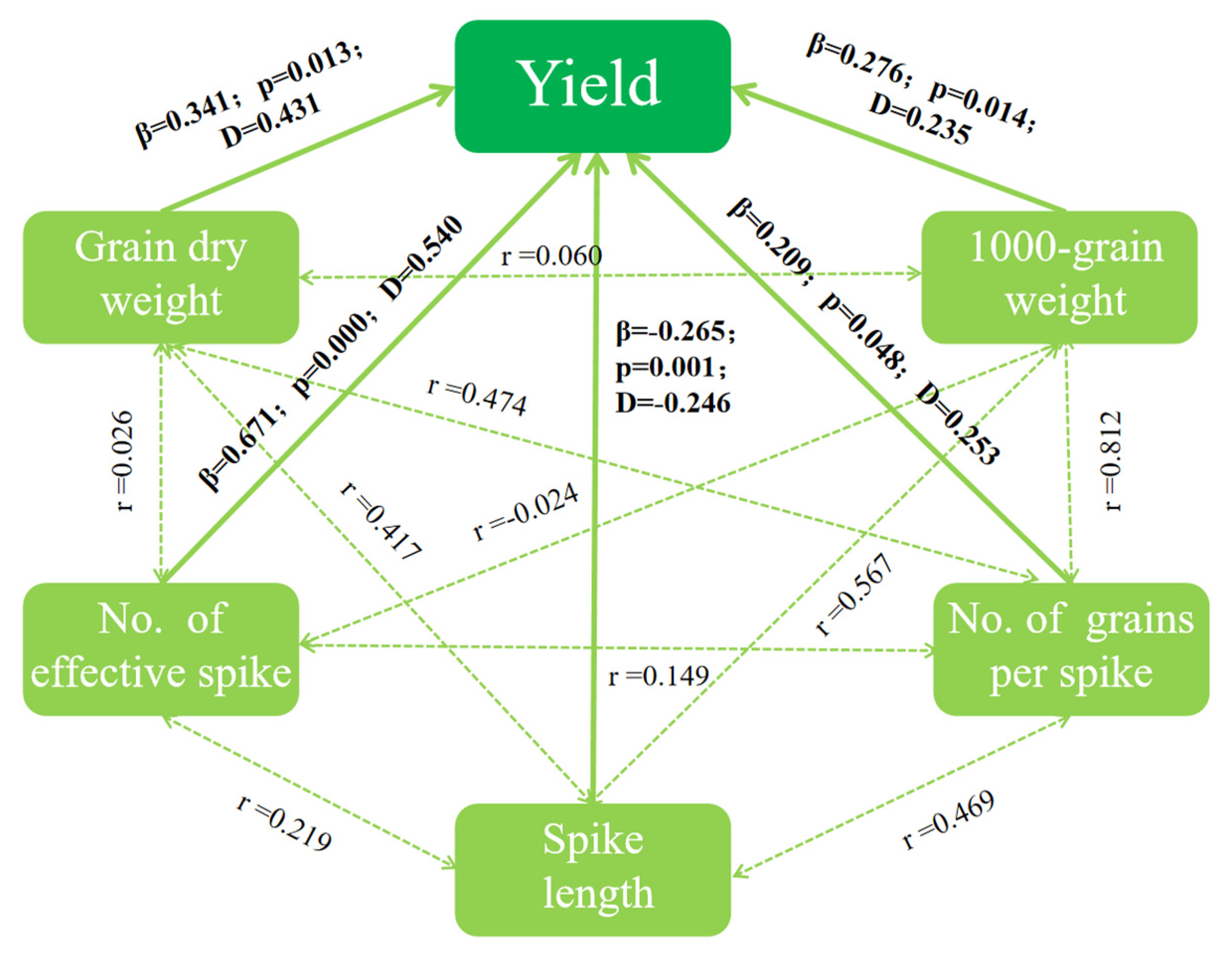
3.2. Maize Growth and Yield Components
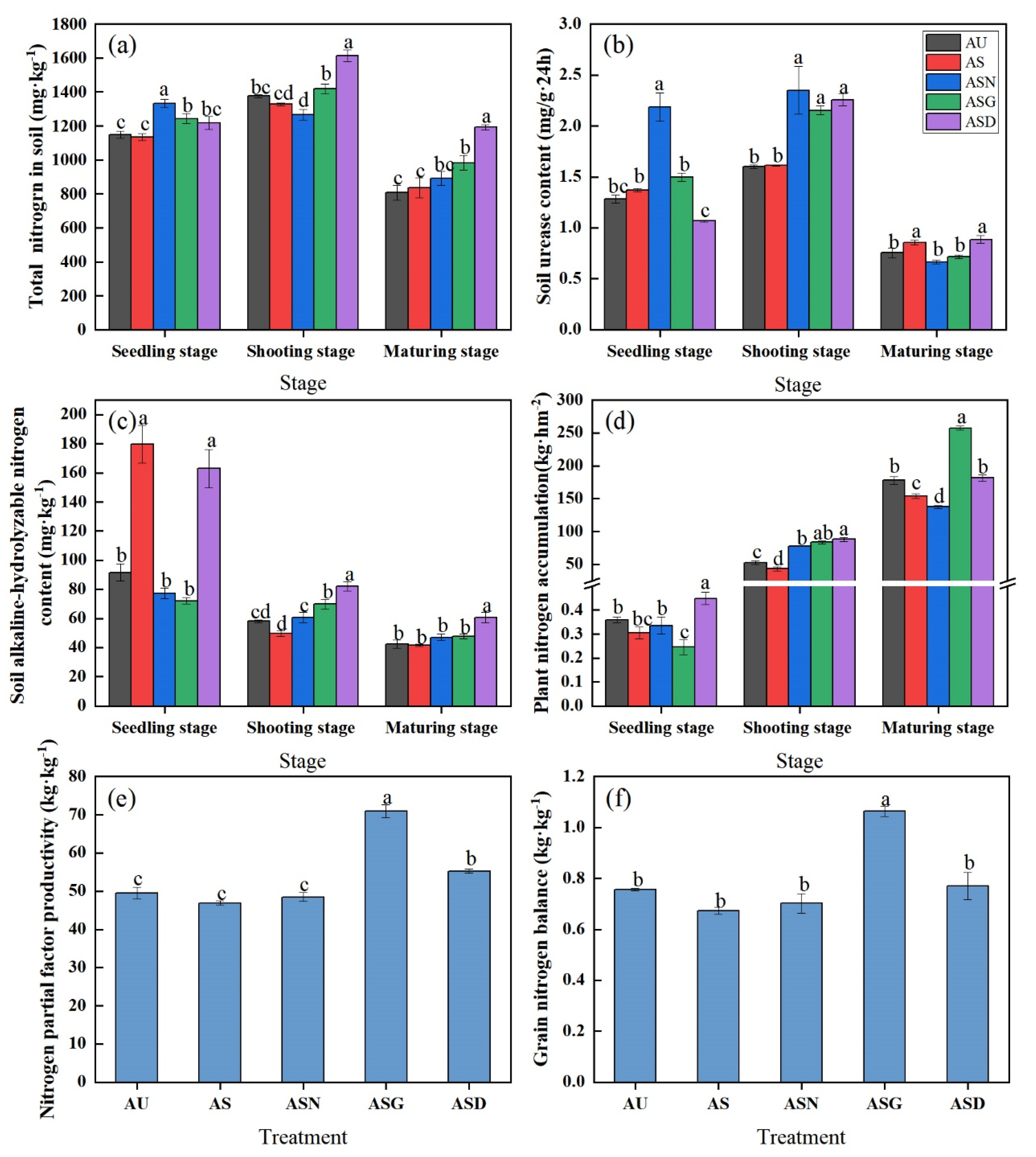
3.3. Soil Nitrogen, Plant Nitrogen Accumulation and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
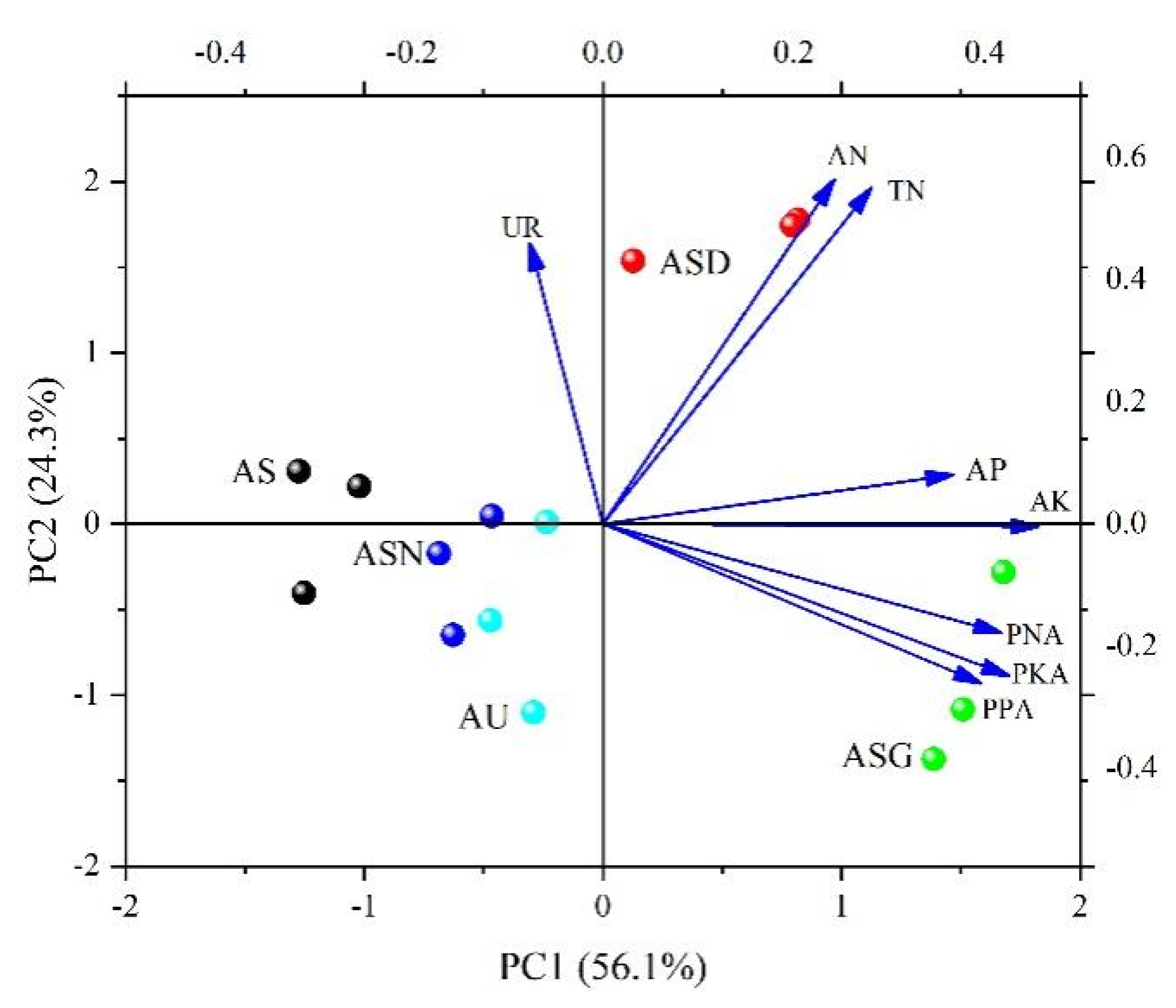
3.4. Available P(K) in Soil, P(K) in Plants and Effective Use of P(K)
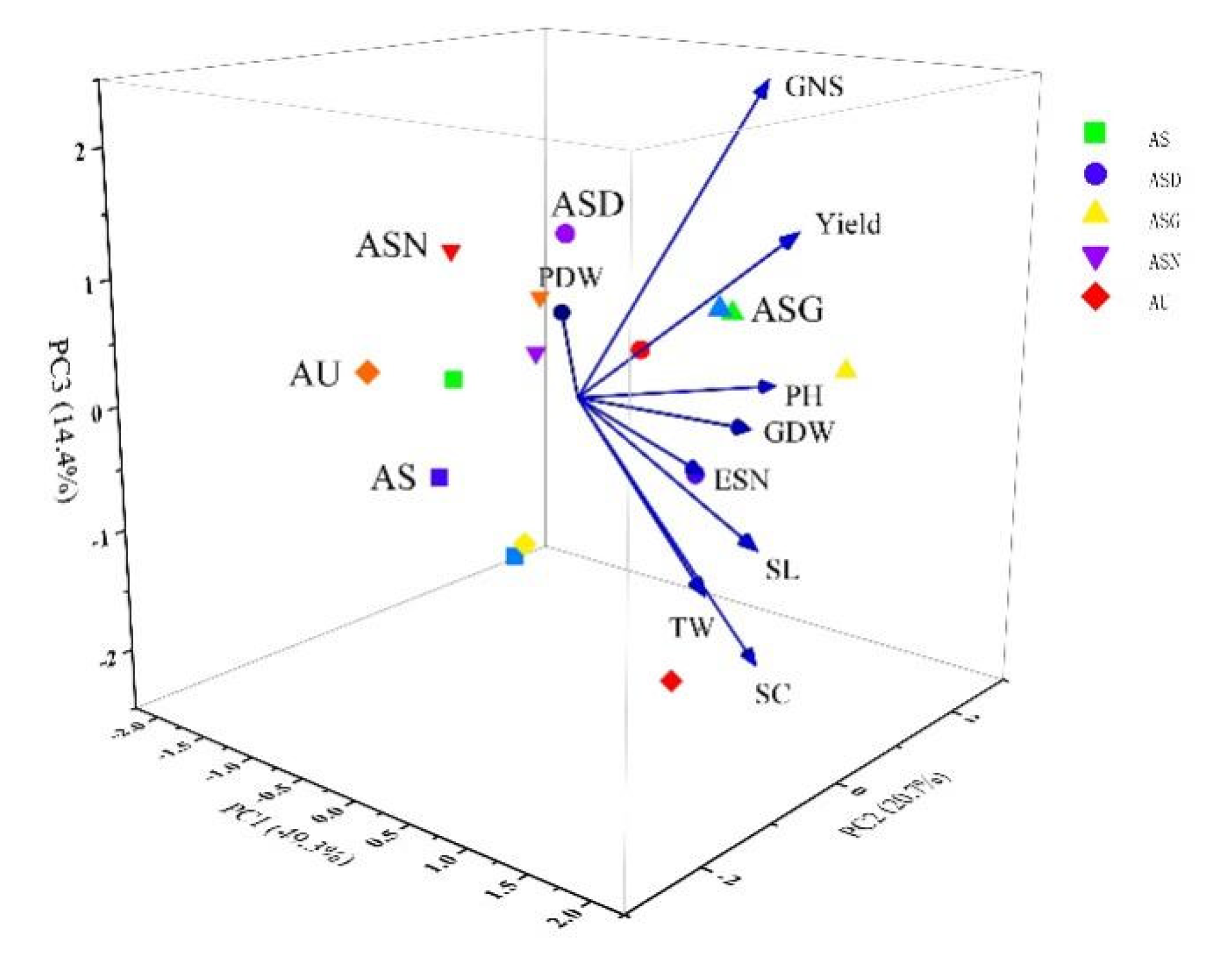
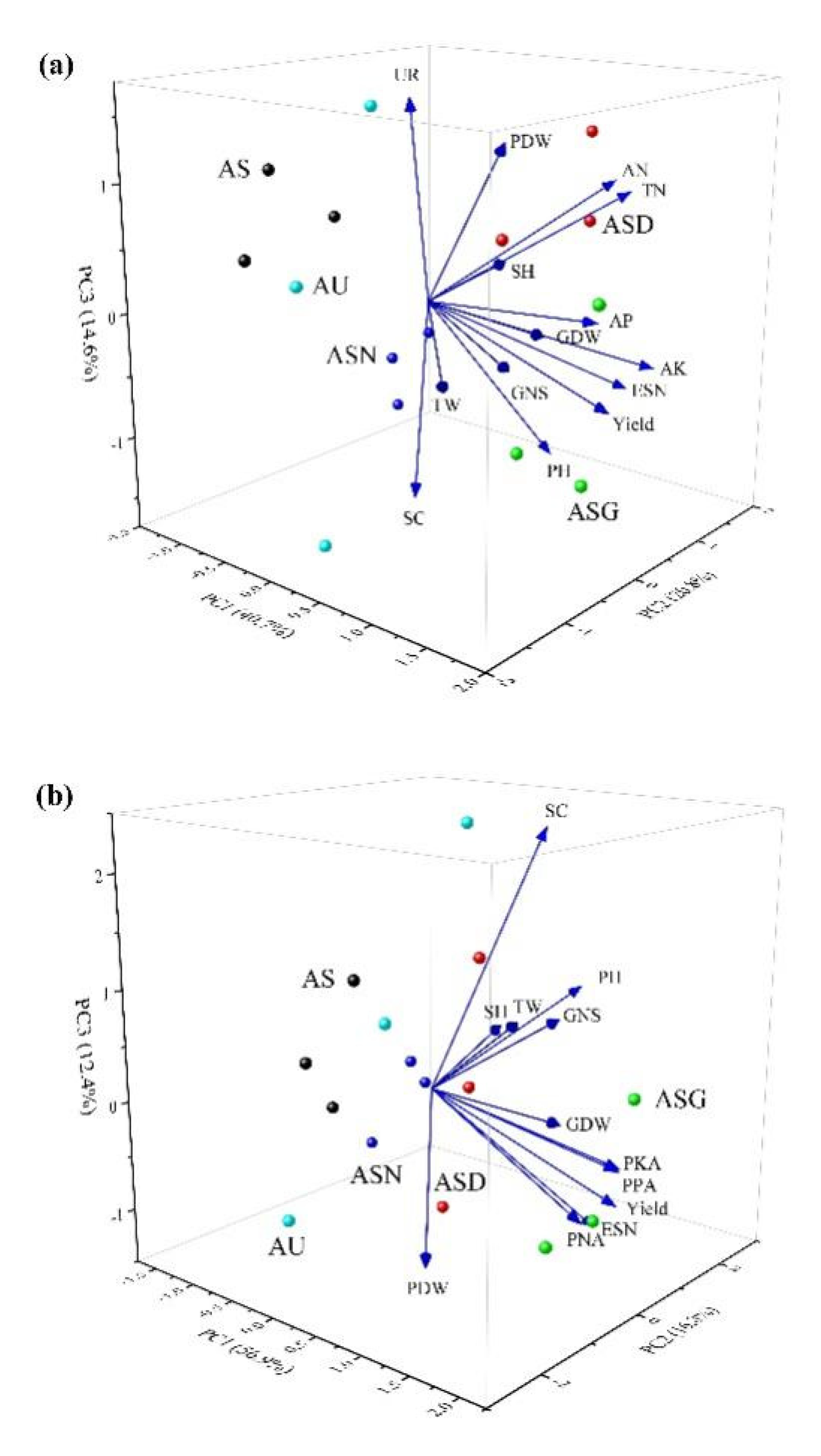
3.5. Principal Components Analysis (PCA)
4. Discussion
4.1. Ammonium Sulfate Coupled with Aids Could Inhibit Nitrogen Leaching to Deeper Soil Layer
4.2. Oil-Coated Ammonium Sulfate Improved Maize Yield Due to Higher Effective Spike Number
4.3. Oil-Coated Ammonium Sulfate Improved Fertilizer Utilization
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Declaration of competing interest
References
- Zhang W S, Liang Z Y, He X M, Wang X Z, Shi X J, Zou C Q, Chen X P. The effects of controlled release urea on maize productivity and reactive nitrogen losses: a meta-analysis. Environment Pollution 2019, 246, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo J J, Fan J L, Zhang F C, Yan S C, Zheng J, Wu Y, Li J, Wang Y l, Sun X, Liu X Q, Xiang Y Z, Li Z J. Blending urea and slow-release nitrogen fertilizer increases dry-land maize yield and nitrogen use efficiency while mitigating ammonia volatilization. Science of the Total Environment 2021, 790, 148058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant C A, Wu R. , Selles F, Harker K N, Clayton G W, Bittman S, Zebarth B J, Lupwayi N Z. Crop yield and nitrogen concentration with controlled release urea and split applications of nitrogen as compared to non-coated urea applied at seeding. Field Crop Research 2012, 127, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo P T, Nguyen H T, Trinh H T, Nguyen V M, Le A T, Huy T Q, Nguyen T T. The nitrogen slow-release fertilizer based on urea incorporating chitosan and poly (vinyl alcohol) blend. Environmental Technology & Innovation 2021, 22, 101528. [Google Scholar]
- Azeem B, KuShaari K, Man Z B, Basit A, Thanh T H. Review on materials & methods to produce controlled release coated urea fertilizer. Control Release 2014, 181, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Timilsena Y P, Adhikari R. , Casey P, Muster T, Adhikari B. Enhanced efficiency fertilisers: a review of formulation and nutrient release patterns. Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture 2015, 95, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y, Ni X, Zhou Z, Yu L, Liu B, Yang Y, Wu Y. Performance of matrix-based slow-release urea in reducing nitrogen loss and improving maize yields and profits. Field crops research 2017, 212, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan Y, Song C, Gan Y, Li F M. Increased maize yield using slow-release attapulgite-coated fertilizers. Agronomy for sustainable development 2014, 34, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma Q, Wang X, Li H, Li H, Cheng L, Cheng L, Zhang F, Shen J. Localized application of NH4+-N plus P enhances zinc and iron accumulation in maize via modifying root traits and rhizosphere processes. Field Crops Research 2014, 164, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien S H, Gearhart M M, Villagarcía S. Comparison of ammonium sulfate with other nitrogen and sulfur fertilizers in increasing crop production and minimizing environmental impact: A Review. Soil Science 2011, 176, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam T, Suryanto P, Kastono D, Putra E T S, Handayani S, Widyawan M H, Muttaqin A S, Kurniasih B. Interactions of biochar briquette with ammonium sulfate fertilizer for controlled nitrogen loss in soybean intercopping with Melaleuca cajuputi. Legume Research, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Casteel S N, Chien S H, Gearhart M M. Field evaluation of ammonium sulfate versus two fertilizer products containing ammonium sulfate and elemental sulfur on soybeans. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 2019, 50, 2941–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailegnaw N S, Mercl F, Kulhánek M, Száková J, Tlustoš P. Co-application of high temperature biochar with 3,4-dimethylpyrazole-phosphate treated ammonium sulphate improves nitrogen use efficiency in maize. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ai Y C, Zhang Y C, Ning Y W. Prospect of agricultural application of ammonium sulfate as by-product of ammonia desulfurization. Jiangsu Agricultural Science 2018, 46, 308–313 (In Chinese). (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu L H, Liu A H. China Statistical Yearbook. National Bureau of Statistics 2021, 385-414. (In Chinese).
- Carlos S S, Rosa E, Kaseker J F, Sokal T F, Nohatto M A. Maize productivity as a result of application of controlled and slow release urea. Revista Brasileira de Milho e Sorgo 2020, 19, e1116. [Google Scholar]
- Khan A Z, Afzal M, Muhammad A, Akbar H, Amin N. Influence of slow release urea fertilizer on growth, yield and n uptake on maize under calcareous soil conditions. Pure & Applied Biology 2015, 4, 70–79. [Google Scholar]
- Campos O R, Mattiello E M, Cantarutti R B, Vergutz L. Nitrogen release from urea with different coatings or urease inhibitor. Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture 2018, 98, 775–780. [Google Scholar]
- Bao S, D. 2016. Methods of agricultural chemical analysis of soil. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press. (In Chinese).
- Guo Z, P. 1986. Quantitative characters genetic analysis. Beijing: Beijing Normal University Publishing House. (In Chinese).
- Tales T, Murilo V G M, Vítor G A, Magno B A, Cimélio B. Assessing linkage between soil phosphorus forms in contrasting tillage systems by path analysis. Soil & Tillage Research 2018, 175, 276–280. [Google Scholar]
- Luciano C G, Djalma E S, Tales T, Murilo G V, Danilo R S, João K, Gustavo B. Plant uptake of legacy phosphorus from soils without P fertilization. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 2021, 119, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao Y X, Xue S, Liu K X, et al. Mixture of controlled-release and conventional urea fertilizer application changed soil aggregate stability, soil humic acid molecular composition, and nitrogen uptake. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 789, 147778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng X T, Li Y Y, Yao H Y, Wang J, Dai F, Wu Y P, Chapman S. Nitrification and urease inhibitors improve rice nitrogen uptake and prevent denitrification in alkaline paddy soil. Applied Soil Ecology 2020, 154, 103665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 25. Said-Pullicino D, Cucu M A, Sodano M, Birk J J, Glaser B, Celi L. Nitrogen immobilization in paddy soils as affected by redox conditions and rice straw incorporation. Geoderma, 2014, 228-229, 44-53.
- Shaviv, A. Controlled release fertilizers. 2005. Germany: Frankfurt.
- Wu Z J, Chen L J. 2003. Slow release/controlled release fertilizers: Principles and applications. Beijing: Science Press. (In Chinese).
- Hou J, Dong Y, Fan Z. Effects of coated urea amended with biological inhibitors on physiological characteristics, yield, and quality of peanut. Communications in soil science and plant analysis 2014, 45, 896–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmaha B, S. Evaluating Animo model for predicting nitrogen leaching in rice and wheat. Arid Land Research and Management 2014, 28, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li X, Zhang G, Xu H, Cai Z, Yagi K. Effect of timing of joint application of hydroquinone and dicyandiamide on nitrous oxide emission from irrigated lowland rice paddy field. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu Z, Xie Y, Gao Y, Ren X, Cheng C, Wang S. Quantitative assessment of soil productivity and predicted impacts of water erosion in the black soil region of northeastern China. Science of the total environment 2018, 637, 706–716. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Q, Liu X, Hao T, Zeng M, Shen J, Zhang F, De V W. Modeling soil acidification in typical Chinese cropping systems. Science of the Total environment 2018, 613, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Fujinuma R, Balster N J, Norman J M. An Improved Model of Nitrogen Release for Surface-applied Controlled-release Fertilizer. Soil Science Society of America Journal 2009, 73, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incrocci L, Maggini R, Cei T, Carmassi G, Botrini L, Filippi F, Clemens R, Terrones C, Pardossi A. Innovative controlled-release polyurethane-coated urea could reduce N leaching in tomato crop in comparison to conventional and stabilized fertilizers. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran J K, Khanif Y M, Amminuddin H, Anuar A R. Effects of controlled release urea on the yield and nitrogen nutrition of flooded rice. Communications in soil science and plant analysis 2010, 41, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li G H, Fu P X, Cheng G G, Lu W P, Lu D L. Delaying application time of slow-release fertilizer increases soil rhizosphere nitrogen content, root activity, and grain yield of spring maize. The Crop Journal 2022, 6, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao B, Dong S, Zhang J, Liu P. Effects of controlled-release fertiliser on nitrogen use efficiency in summer maize. PloS one 2013, 8, e70569. [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y, Mi W, Su L, Shan Y, Wu L. Controlled-release fertilizer enhances rice grain yield and N recovery efficiency in continuous non-flooding plastic film mulching cultivation system. Field Crops Research 2019, 231, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun H, Zhou S, Zhang J, Zhang X, Wang C. Effects of controlled-release fertilizer on rice grain yield, nitrogen use efficiency, and greenhouse gas emissions in a paddy field with straw incorporation. Field Crops Research 2020, 253, 107814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivell P, Ahmed O H, Susilawati K, Ab Majid N M. Mitigating ammonia volatilization from urea in waterlogged condition using clinoptilolite zeolite. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology 2015, 17, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Cancellier E L, Silva D R G, Faquin V, Gonçalves B D A, Cancellier L L, Spehar C R. Ammonia volatilization from enhanced-efficiency urea on no-till maize in brazilian cerrado with improved soil fertility. Ciência e Agrotecnologia 2016, 40, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao C L, Liu T X, Gao Y X, Chen S G, Li Q Y, Li P P, Ding F J. Effects of Adding Humic Acid on Wheat Yield, Nutrient Uptake and the Soil Properties. Humic Acid 2022, (02), 5-11. (In Chinese).
- Nan J, Chen X, Wang X, Lashari M S, Wang Y, Guo Z, Du Z. Effects of applying flue gas desulfurization gypsum and humic acid on soil physicochemical properties and rapeseed yield of a saline-sodic cropland in the eastern coastal area of China. Journal of soils and sediments 2016, 16, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke J, Xing X, Li G, Ding Y, Dou F, Wang S, Liu Z H, Tang S, Ding C Q, Chen, L. Effects of different controlled-release nitrogen fertilizers on ammonia volatilisation, nitrogen use efficiency and yield of blanket-seedling machine-transplanted rice. Field Crops Research 2017, 205, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Y F, Fang X L, Liu Y X, Liu P, Liu W J, Wang Y, Chen G H. Characteristics of nutrient accumulation distribution and its correlation with yield components in southern double-season early rice areas under triple maturity pattern. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops 2022, 1-10. (In Chinese).
- Li Q, Yang A, Wang Z, Roelcke M, Chen X, Zhang F, Liu X. Effect of a new urease inhibitor on ammonia volatilization and nitrogen utilization in wheat in north and northwest China. Field Crops Research 2015, 175, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Q, Cui X, Liu X, Roelcke M, Pasda G, Zerulla W, Wissemeier AH, Chen X, Goulding K, Zhang F. A new urease-inhibiting formulation decreases ammonia volatilization and improves maize nitrogen utilization in North China Plain. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 43853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang C, Lv J, Coulter J A, Xie J, Yu J, L J, Zhang J, Tang C N, Niu T H, Gan, Y. Slow-release fertilizer improves the growth, quality, and nutrient utilization of wintering Chinese chives (Allium tuberosum Rottler ex Spreng.). Agronomy 2020, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment | Fertilizer types | N fertilizer | Slow control material | P fertilizer | K fertilizer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AU | Urea | Urea+(NH4)2HPO4 | / | (NH4)2HPO4 | KCl |
| AS | Ammonium sulfate | Ammonium sulfate+(NH4)2HPO4 | / | (NH4)2HPO4 | KCl |
| ASN | Ammonium sulfate +Nitrification inhibitor | Ammonium sulfate+(NH4)2HPO4 | Nitrification inhibitor (1% of the pure N content) | (NH4)2HPO4 | KCl |
| ASG | Oil coated ammonium sulfate | Ammonium sulfate+(NH4)2HPO4 | Oil coated (9% of AS application) | (NH4)2HPO4 | KCl |
| ASD | Oil-humic acid coated ammonium sulfate | Ammonium sulfate+(NH4)2HPO4 | Oil-humic acid coated (0.9% of AS application) | (NH4)2HPO4 | KCl |
| Treatments | Nt=N0(1-e-kt) | R2 | Se |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | Nt=0.048(1-e-0.458t) | 0.949** | 0.071 |
| AU | Nt=0.830(1-e-1.188t) | 0.954** | 0.210 |
| AS | Nt=0.646(1-e-0.176t) | 0.984** | 0.024 |
| ASN | Nt=0.851(1-e-0.049t) | 0.999** | 0.006 |
| ASG | Nt=1.800(1-e-0.017t) | 0.999** | 0.004 |
| ASD | Nt=0.783(1-e-0.065t) | 0.997** | 0.010 |
| Treatment | Plant height (cm) |
Plant dry weight (g) |
Grain dry weight (g/spike) |
Spike coarse (cm) |
Spike length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AU | 260.67±12.77ab | 333.93±35.49a | 204.71±9.28b | 16.27±0.12b | 21.11±0.51b |
| AS | 245.00±7.64b | 327.24±13.10ab | 202.61±8.07b | 16.18±0.10ab | 21.08±0.32b |
| ASN | 268.33±8.33ab | 259.13±3.14b | 180.36±6.04c | 15.91±0.10c | 19.81±0.29c |
| ASG | 269.67±12.35ab | 363.50±25.14a | 231.28±4.71a | 16.75±0.10a | 22.27±0.16a |
| ASD | 279.67±2.91a | 330.59±18.23ab | 205.50±6.96b | 16.20±0.10ab | 21.45±0.27ab |
| Index | Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AU | AS | ASN | ASG | ASD | |
| Available P in Soil (mg·kg-1) | 5.55±0.28a | 2.41±0.22b | 3.43±0.76b | 5.76±0.49a | 5.62±0.51a |
| Available K in Soil (mg·kg-1) | 99.04±0.41cd | 90.03±1.53d | 107.04±2.08c | 140.05±2.00a | 120.04±3.61b |
| P accumulation in Plant (kg·hm-2) | 60.80±4.37bc | 49.65±3.72c | 58.43±3.20bc | 90.05±7.24a | 65.91±3.91b |
| K accumulation in Plant (kg·hm-2) | 19.80±1.25b | 14.82±0.91c | 16.84±1.10c | 34.24±0.57a | 21.21±0.61b |
| P partial factor productivity (kg·kg-1) | 88.06±2.70c | 83.46±0.87c | 86.22±3.77c | 126.11±3.06a | 98.29±1.00b |
| K partial factor productivity (kg·kg-1) | 0.27±0.02b | 0.21±0.02b | 0.28±0.02b | 0.41±0.05a | 0.29±0.02b |
| Grain P balance (kg·kg-1) | 132.08±4.05c | 125.19±1.30c | 129.33±3.26c | 189.16±4.59a | 147.4±1.49b |
| Grain K balance (kg·kg-1) | 0.046±0.005a | 0.027±0.003b | 0.012±0.000c | 0.053±0.001a | 0.023±0.000b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





