Submitted:
12 April 2024
Posted:
15 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Definition and Implications of the HS Trait
Internal and External Factors Affecting the HS Trait
QTL Mapping of HS Trait in Soybean
Genes Related to HS in Soybean
Lessons from Other Plants
Summary and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Medic, J.; Atkinson, C.; Hurburgh, C.R. Current knowledge in soybean composition. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, K. Soybean protein and oil variants identified through a forward genetic screen for seed composition. Plants. 2022, 11, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Guan, R.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Lin, F.; Luan, W.; Chen, P.; Yan, Z. Genetic structure and diversity of cultivated soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) landraces in China. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.Y.; Van, K.; Kang, Y.J.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.H. Tracing soybean domestication history: From nucleotide to genome. Breed Sci, 2012; 61, 445–452. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Fujita, T.; Yan, Z.H.; Sakamoto, S.; Xu, D.; Abe, J. QTL mapping of domestication-related traits in soybean (Glycine max). Ann. Bot. 2007, 100, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, T.; Gai, J. Genetic diversity and peculiarity of annual wild soybean (G. soja Sieb. et Zucc.) from various ecoregions in China. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 119, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Yuan, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qi, G.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y. Identification of genetic loci conferring seed coat color based on a high-density map in soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 968618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Sekizaki, H.; Yang, Z.; Sawa, S.; Pan, J. Phenolics in the seed coat of wild soybean (Glycine soja) and their significance for seed hardness and seed germination. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Han, W.; He, Q.; Yang, H.; Xiang, S.; Gai, J. Identifying wild versus cultivated gene-alleles conferring seed coat color and days to flowering in soybean. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyten, D.; Song, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Choi, I.; Nelson, R.L.; Costa, J.M.; Specht, J.E.; Shoemaker, R.C.; Cregan, P.B. Impacts of genetic bottlenecks on soybean genome diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2006, 103, 16666–16671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, C.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, L.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y. A single origin and moderate bottleneck during domestication of soybean (Glycine max): implications from microsatellites and nucleotide sequences. Ann. Bot. 2010, 106, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysmierski, P.T.; Vello, N.A. The genetic base of Brazilian soybean cultivars: evolution over time and breeding implications. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2013, 36, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H.; Bai, D.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, T.; Li, Y.H.; Qiu, L.J. The elite variations in germplasms for soybean breeding. Mol. Breed. 2023, 43, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, Z.; Gou, Z.; Lyu, J.; Li, W.; Yu, Y.; Shu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y. Resequencing 302 wild and cultivated accessions identifies genes related to domestication and improvement in soybean. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Ma, Q.B.; Li, X.P.; Dong, W.W.; Nian, H. Identification of wild soybean miRNAs and their target genes responsive to aluminum stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.F.; Ning, K.; Xu, H.L.; Yu, D.H.; Bi, Y.X. Research progress of wild soybean germplasms and utilization. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2017, 18, 812–817. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.S.; Lozano, R.; Kim, J.H.; Bae, D.N.; Kim, S.T.; Park, J.H.; Choi, M.S.; Kim, J.; Ok, H.C.; Park, S.K. The patterns of deleterious mutations during the domestication of soybean. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleem, M.; Aleem, S.; Sharif, I.; Aleem, M.; Shahzad, R.; Khan, M.I.; Batool, A.; Sarwar, G.; Farooq, J.; Iqbal, A. Whole-genome identification of APX and CAT gene families in cultivated and wild soybeans and their regulatory function in plant development and stress response. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022, 11, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Paul, P.J.; Sameer Kumar, C.V.; Nimje, C. Utilizing wild Cajanus platycarpus, a tertiary genepool species for enriching variability in the primary genepool for pigeonpea improvement. Front Plant Sci 2020, 11, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, E.E.; Potts, H.C. Development and evaluation of impermeable seed coats for preserving soybean seed quality. Crop Sci. 1987, 27, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, J.M. Effect of impermeable seed coat on germination of seed from early maturing of soybean. Seed Scio. Technol. 1997, 19, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kulik, M.M.; Yaklich, R.W. Soybean seed coat structures. Relationship to weathering and infection by the fungus Phomopsis phaseoli. Crop Sci. 1991, 31, 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, K.W.; Keith, B.C.; Andrews, C.H. Resistance of hardseeded soybean lines to seed infection by Phomopsis, other fungi and soybean mosaic virus. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1995, 16, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilen, T.C.; Hartwig, E.E. An inheritance study of impermeable seed in soybeans. Field Crop Res. 1978, 1, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Cholewa, E.; Mohamed, T.; Peterson, C.A.; Gijzen, M. Cracks in the palisade cuticle of soybean seed coats correlate with their permeability to water. Ann. Bot. 2004, 94, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.J.; Steudle, E.; Peterson, C.A. Patterns and kinetics of water uptake by soybean seeds. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 717–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskin, C.C.; Baskin, J.M. Seeds: ecology, biogeography, and evolution of dormancy and germination. Crop Sci. 2014, 40, 564. [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen, T.R.; Högstedt, G.; Thompson, K.; Vandvik, V.; Eliassen, S.; Leishman, M. Conditions favouring hard seededness as a dispersal and predator escape strategy. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, M.E. Seed dormancy: an update on terminology, physiological genetics, and quantitative trait loci regulating germinability. Weed Sci. 2001, 49, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch-Savage, W.E.; Leubner-Metzger, G. Seed dormancy and the control of germination. New Phytol. 2006, 171, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, T.R.; Colville, L.; Kranner, I.; Daws, M.I.; Högstedt, G.; Vandvik, V.; Thompson, K. Physical dormancy in seeds: a game of hide and seek? New Phytol. 2013, 198, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nik, W.Z.; Parbery, D.G. Studies of seed-borne fungi of tropical pasture legume species. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1997, 28, 821–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandis, P.; Herranz, J.M.; MartinezSanchez, J.J. Effect of fire on hard-coated Cistaceae seed banks and its influence on techniques for quantifying seed banks. Plant Ecol. 1999, 144, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed-Yasseen, Y.; Barringer, S.A.; Costanza, S.S. The role of seed coats in seed viability. TBR. 1994, 60, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koornneef, M.; Bentsink, L.; Hilhorst, H. Seed dormancy and germination. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Dalling, J.W.; Davis, A.S.; Schutte, B.J.; Arnold, A.E. Seed survival in soil: interacting effects of predation, dormancy and the soil microbial community. J. Ecol. 2011, 99, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolston, M.P. Water impermeable seed dormancy. Bot. Rev. 1978, 44, 365–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heatherly, L.G.; Kenty, M.M.; Kilen, T.C. Effects of storage environment and duration on impermeable seed coat in soybean. Field Crop Res. 1995, 40, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chachalis, D.; Smith, M.L. Imbibition behavior of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) accessions with different testa characteristics. Seed Sci. Technol. 2000, 28, 321–31. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, S.I.; Abe, J.; Kanazawa, A.; Shimamoto, Y. Marker-assisted analysis for soybean hard seededness with isozyme and simple sequence repeat loci. Breeding Sci. 2004, 54, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, H.; Smith, J.R.; Ray, J.D. Identification of a single gene for seed coat impermeability in soybean PI 594619. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1991–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullin, W.J.; Xu, W. Study of soybean seed coat components and their relationship to water absorption. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5331–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Meyer, C.J.; Ma, F.; Peterson, C.A.; Bernards, M.A. The outermost cuticle of soybean seeds: chemical composition and function during imbibition. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, H.C.; Duangpatra, J.; Hairston, W.G.; Delouche, J.C. Some influences of hardseededness on soybean seed quality. Crop Sci. 1978, 18, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, B.C.; Delouche, J.C. Seed quality, production and treatment. In: Heatherly lG, Hodges HF (eds) Soybean production in the midsouth. CrC Press, 1999, 197–239.
- Chris, J.M.; Ernst, S.; Carol, A.P. Patterns and kinetics of water uptake by soybean seeds. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 717–732. [Google Scholar]
- Abbo, S.; Zezak, I.; Schwartz, E.; Lev-Yadun, S.; Gopher, A. Experimental harvesting of wild peas in Israel: implications for the origins of near east farming. J Archaeol Sci. 2008, 35, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, P.; Chen,C. Y.; Wang,D.; Shi, A.; Hou, A.; Ishibashi, T. Quantitative trait loci mapping of seed hardness in soybean. Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smýkal, P.; Vernoud, V.; Blair, M.W.; Soukup, A.; Thompson, R.D. The role of the testa during development and in establishment of dormancy of the legume seed. Front Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Argel, P.J.; Paton, C.J.; Ferguson, J.E. Overcoming legume hard seededness. Forage seed, 1999, 247–276.
- Sun, X.M.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.G.; Meng, F.F.; Wang, S.M.; Zhang, J.P. Progress on formation mechanism and breaking methods of hard seed in soybean. Soybean Sci. Tech. 2014, 23–27.
- Qutob, Q.D.; Ma, M.F.; Peterson, P.A.C.; Bernards, B.A.M.; Gijzen, G.M. Structural and permeability properties of the soybean seed coat. Botany. 2008, 86, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, P.; Diers, B.W.; Shoemaker, R.C. Genetic analysis of soybean hard seededness with molecular markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1990, 79, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L. Study on preservation of soybean germplasm using soybean hard seed. Soybean Sci. 1999, 18, 351–354. [Google Scholar]
- Saio, K.; Arai, K.; Watanabe, T. Fine structure of soybean seed coat and its changes on cooking. Cereal Sci. Today. 1973, 18, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Saio, K. Soybeans resistant to water absorption. Cereal Food World. 1976, 21, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Huhn, M.R.; Buss, G.R.; Gunduz, I.; Wilson, J.H. Interrelationship among seed quality traits of specialty soybeans for natto and tofu. ASA–CSSA–SSSA, Int. Annu. Meet, 2001, 21–25.
- Zhang, B.; Chen, P.; Shi, A.; Hou, A.; Ishibashi, T.; Wang, D. Putative quantitative trait loci associated with calcium content in soybean seed. J. Hered. 2009, 100, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Miao, Z.; Cai, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Swarm, S.A.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.J.; Nelson, R.L.; Ma, J. GmHs1-1, encoding a calcineurin-like protein, controls hard-seededness in soybean. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 939–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, M.R.; Vertucci, C.W.; Roos, E.E. Seed coat regulation of soybean seed imbibition. Crop Sci. 1988, 28, 987–992.
- Pietrzak, L.N.; Fregeau-Reid, J.; Chatson, B.; Blackwell, B. Observation on water distribution in soybean seed during hydration processes using nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2002, 82, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. ; Li,J. ; Yin, P.; Wang, G.; Yan, X.; Sun, B. Testa morphology structure and germination characteristic of Glycine soja. Soybean Sci. 2009, 28, 641–646. [Google Scholar]
- Boesewinkel, F.D.; Bouman, F. The seed: structure and function. Plenum Press. 1995, 1–24.
- Souza, F.H.; Marcos-Filho, J. The seed coat as a modulator of seed-environment relationships in Fabaceae. Braz. J. Bot. 2001, 24, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooker, N.L.; Lagalle, C.D.; Zlatanic, A.; Javni, I.; Petrovic, Z. Soy polyol formulations as novel seed treatments for the management of soil-borne diseases of soybean. Commun. Agric. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2007, 72, 35–43.
- Yaklich, R.W.; Vigil, E.L.; Erbe, E.F.; Wergin, W.P. The fine structure of aleurone cells in the soybean seed coat. Protoplasma. 1992, 167, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, A. Biophysical and biochemical characteristics of cutin a plant barrier biopolymer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2003, 1620, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranathunge, K.; Shao, S.; Qutob, D.; Gijzen, M.; Peterson, C.A.; Bernards, M.A. Properties of the soybean seed coat cuticle change during development. Planta. 2010, 231, 1171–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, S.S.; Nagarajappa, N.; Ranjitha, H.P. Seed coat composition in black and white soybean seeds with differential water permeability. Plant Biol. 2023, 25, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, W.H.J. Delayed permeability of soybean seeds: Characteristics and screening methodology. Seed Sci. Technol. 1989, 27, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, S.; Tajuddin, T.; Yamanaka, N.; Hayashi, M.; Harada, K. Analysis of QTLs for reproductive development and seed quality traits in soybean using recombinant inbred lines. Breeding Science. 2004, 54, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero, E.; West, S.H.; Hinson, K. Water absorption of soybean seeds and associated causal factors. Crop Sci. 1981, 21, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooden, L.D.; Blakley, K.A.; Grzybowski, J.M. Control of seed coat thickness and permeability in soybean: a possible adaptation to stress. Plant Physiol. 1985, 79, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, H.J.; West, S.H.; Hinson, K. Soybean seed size influences expression of the impermeable seed-coat trait 1. Crop Sci, 1986a, 26, 634–637.
- Yaklich, R.W.; Vigil, E.L.; Wergin, W.P. Pore development and seed coat permeability in soybean. Crop Sci. 1986, 26, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragus, L.N. Role of water absorbing capacity in soybean germination and seedling vigour. Seed Sci. Technol. 1987, 15, 285–296. [Google Scholar]
- Taira, H. Quality of soybeans for processed foods in Japan. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 1990, 24, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Lin, G.; Xu, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J. Water absorbing characteristics and its relation with germination in improved spring soybean varieties. Fujian J. Agric.Sci. 1999, 8–11.
- Hill, H.J.; West, S.H.; Hinson, K. Effect of water stress during seedfill on impermeable seed expression in soybean. Crop Sci. 1986b, 26, 807–812.
- Vieira, R.D.; Tekrony, D.; Egli, D.B. Effect of drought and defoliation stress in the field on soybean seed germination and vigor. Crop Sci. 1992, 32, 023110–023110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, D.B.; TeKrony, D.M.; Heitholt, J.J. Air temperature during seed filling and soybean seed germination and vigor. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Raipuria, P.K.; Bhatia, V.S.; Rani Pushpendra, A.; Husain, S.M.; Satyavathi, C.T.; Chauhan, G.S.; Mohapatra, T. Identification of SSR markers associated with seed coat permeability and electrolyte leaching in soybean. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Pla. 2008, 14, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, L.J.; Chen, Q.; Yang, C.Y.; Yan, L.; Wang, F.M.; Ge, R.C.; Zhang, M.C. Mapping main-effect and epistatic QTL for hard seededness in soybean. AAS. 2018, 44, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Yu, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Guan, R.; Qiu, L. QTL mapping of hard seededness in wild soybean using BSA method. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2019, 52, 2208–2219. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, S.; Taak, Y.; Rathod, D.Y.; Yadav, R.R.; Poonia, S.; Sreenivasa, V.; Talukdar, A. Genetics and mapping of seed coat impermeability in soybean using inter-specific populations. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants. 2020, 26, 2291–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.J.; Sato, M.; Sato, K.; Jisuyama, Y.; Fujino, K.; Mori, H.; Takahashi, R.; Beniez, E.R.; Liu, B.; Yamada, T.; et al. A single-nucleotide polymorphism in an endo-1,4-β-Glucanase gene controls seed coat permeability in soybean. Plos. One. 2015, 10, e0128527. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Sun, X.; Liu, B.; Kong, F.; Pan, X.; Zhang, H. A polygalacturonase gene PG031 regulates seed coat permeability with a pleiotropic effect on seed weight in soybean. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 1603–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishna, G.; Kaur, P.; Nigam, D.; Chaduvula, P.K.; Yadav, S.; Talukdar, A.; Singh, N.K.; Gaikwad, K. Genome-wide identification and characterization of InDels and SNPs in Glycine max and Glycine soja for contrasting seed permeability traits. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Feng, S.; Ma, X.; Chen, Q.; Liu, C.; Qi, Z. Meta-analysis and multiomics of a chromosome segment substitution line reveal candidate genes associated with seed hardness in soybean. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 16840–16854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, S.; Delsene, M.; Devic, M. BANYLUS, a novel negative regulator of flavonoid biosynthesis in the Arabidopsis seed coat. Plant J. 1997, 11, 289–299 [PubMed]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeaujon, I.; Léon-Kloosterziel, K.M.; Koornneef, M. Influence of the testa on seed dormancy, germination, and longevity in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Western, T.L.; Burn, J.; Tan, W.L.; Skinner, D.J.; Martin-McCaffrey, L.; Moffat, B.A.; Haughn, G.W. Isolation and characterization of mutants defective in seed coat mucilage secretory cell development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Davis, E.; Gardner, D.; Cai, X.; Wu, Y. Involvement of AtLAC15 in lignin synthesis in seeds and in root elongation of Arabidopsis. Planta. 2006, 224, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beisson, F.; Li, Y.; Bonaventure, G.; Pollard, M.; Ohlrogge, J.B. The acyltransferase GPAT5 is required for the synthesis of suberin in seed coat and root of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2007, 19, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, M.; Zhou, C.; Molina, I.; Fu, C.; Nakashima, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; Park, J.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; et al. A class II KNOX gene, KNOX4, controls seed physical dormancy. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2016, 113, 6997–7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, M.; Queralta Castillo, I.; Sonntag, A.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, W.; Du, J.; Xie, H.; Liao, F.; Yun, J.; et al. A seed coat-specific β-ketoacyl-CoA synthase, KCS12, is critical for preserving seed physical dormancy. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, A.; Walter, K.A.; Wiersma, A.T.; Santiago, J.P.; Quiqley, M.; Chitwood, D.; Porch, T.G.; Miklas, P.; McClean, P.E.; Osorno, J.M.; et al. The genetics and physiology of seed dormancy, a crucial trait in common bean domestication. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 58–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Sakai, H.; Ariga, H.; Teramoto, S.; Shimada, T.L.; Eun, H.; Muto, C.; Naito, K.; Tomooka, N. Domesticating Vigna stipulacea: chromosome-level genome assembly reveals VsPSAT1 as a candidate gene decreasing hard-seededness. Front Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1119625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Sakai, H.; Yoshitsu, Y.; Muto, C.; Anai, T.; Pandiyan, M.; Senthil, N.; Tomooka, N.; Naito, K. Domesticating Vigna Stipulacea: A potential legume crop with broad resistance to biotic stresses. Front Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
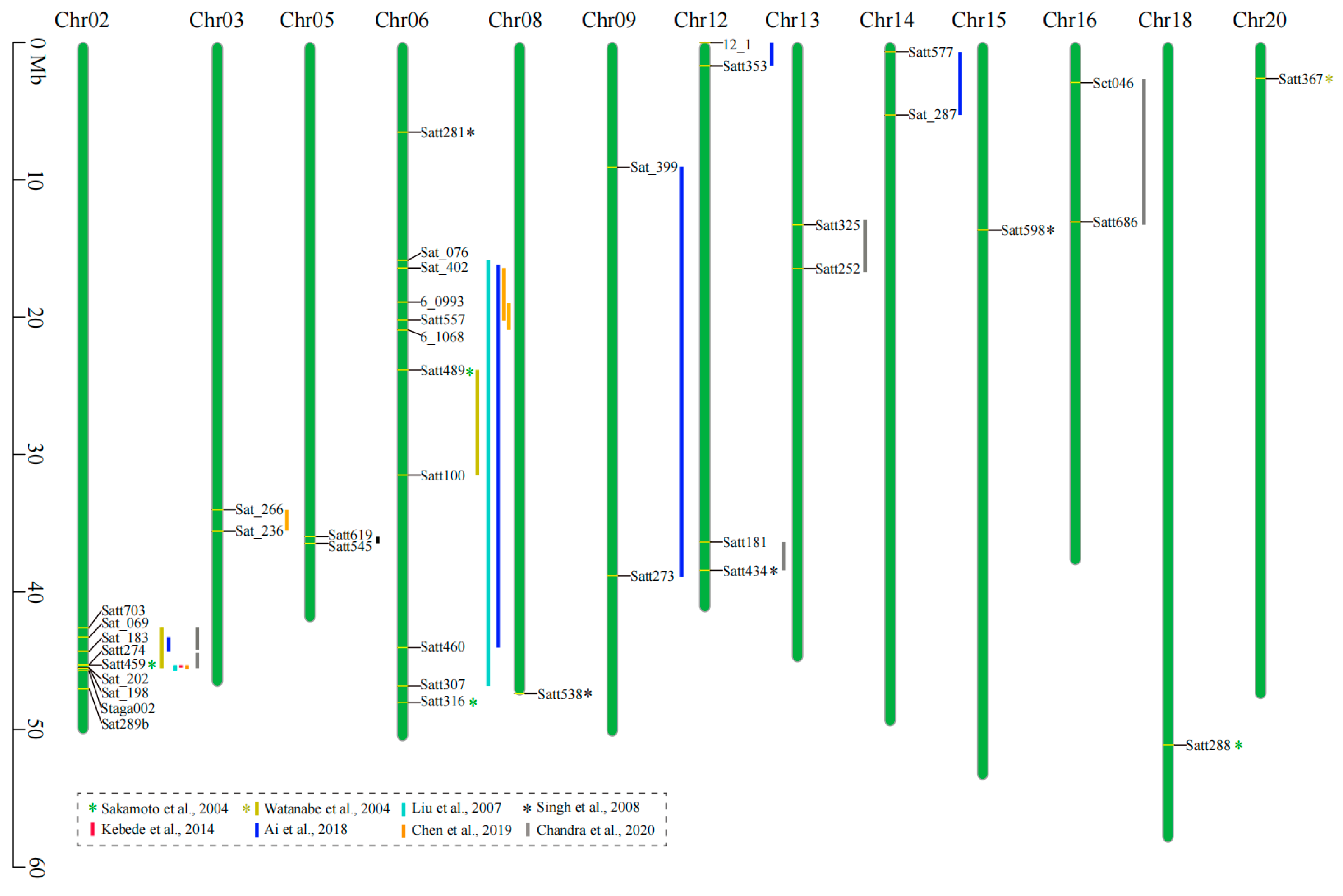
| Population | Chromosome | QTL | Marker(s) | Location | LOD | PVE(%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F2 (Tokei 780× B01167) | 6 | NG | Satt316 | 48016322 | NG | 24.8 | Sakamoto et al., 2004 |
| 6 | NG | Satt489 | 23848501 | NG | 8.6 | ||
| 2 | NG | Satt459 | 45311085 | NG | 23.8 | ||
| 18 | NG | Satt288 | 51127425 | NG | 9.1 | ||
| RIL (Misuzudaizu × Moshidou Gong 503) | 2 | RAS2 | Sat289b | 47042650 | 6.3 | 10.6 | Watanabe et al., 2004 |
| 6 | RAS1 | Satt489-Satt100 | 23848501-31490622 | 14 | 26 | ||
| 20 | RAS3 | Satt367 | 2615587 | 3.0 | 6.1 | ||
| RIL (Tokei 780 × Hidaka 4) | 6 | qHS-C2 | Sat_076-Satt307 | 16007694-46820673 | 5.9 | 18.5 | Liu et al., 2007 |
| 2 | qHS-D1b | Satt459-Staga002 | 45311085-46281147 | 12.5 | 42.5 | ||
| F2 (JS 71-05 × Brisa soya-1) | 12 | NG | Satt434 | 38428476 | NG | 3.9 | Singh et al., 2008 |
| 8 | NG | Satt538 | 47395378 | NG | 4.5 | ||
| 6 | NG | Satt281 | 6529270 | NG | 4.1 | ||
| 15 | NG | Satt598 | 13653981 | NG | 4.2 | ||
| F2 (PI 587982A × PI 594619) | 2 | Isc | Satt459-Sat_202 | 45311085-45497649 | 88.1 | 65.6 | Kebede et al., 2014 |
| RIL (Jidou 12 × ZDD03651) | 2 | qHS-2-1 | Sat_069-Sat_183 | 43278769-44317044 | 2.51 | 5.54 | Ai et al., 2018 |
| 6 | qHS-6-1 | Sat_402-Satt460 | 16418553-44049891 | 6.64 | 12.94 | ||
| 9 | qHS-9-1 | Sat_399-Satt273 | 9095532-38799271 | 7.24 | 3.36 | ||
| 12 | qHS-12-1 | 12_1-Satt353 | 18935-1687387 | 5.87 | 3.13 | ||
| 14 | qHS-14-1 | Satt577-Sat_287 | 675214-5287913 | 3.34 | 8.25 | ||
| F2 (ZH 39 × ZYD 2738) | 2 | NG | Satt274-Sat_198 | 45267040-45542863 | 13.3 | 17.2 | Chen et al., 2019 |
| 6 | NG | 6_0993-6_1068 | 18902966-20942203 | 13 | 17.8 | ||
| RIL (ZH 39 × ZYD 2738) | 3 | NG | Sat_266-Sat_236 | 34016929-35595364 | 2.7 | 4.9 | |
| 6 | NG | Sat_402-Satt557 | 16418553-20218893 | 11.5 | 20.4 | ||
| F2 (JS 335 × PI 424079)F2 (JS 335 × PI 136620)RIL (DS 9712 × DC 2008-1) | 2 | qScI-h 2-1 | Satt703-Satt274 | 42580676-45267040 | 6.32 | 16.49 | Chandra et al., 2020 |
| 2 | qScI-h 2-2 | Satt274-Sat_202 | 45267040-45497649 | 11.83 | 26.66 | ||
| 5 | qScI-h 5-1 | Satt619-Satt545 | 35971621-36463025 | 3.42 | 5.96 | ||
| 12 | qScI-h 12 | Satt181-Satt434 | 36365787-38428476 | 3.85 | 6.22 | ||
| 13 | qScI-h 13 | Satt325-Satt252 | 13272992-16454986 | 3.01 | 6.71 | ||
| 16 | qScI-h 16 | Sct046-Satt686 | 2919448-13053666 | 3.72 | 6.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




