Submitted:
11 April 2024
Posted:
15 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell line and Cultures
2.2. EV Isolation
2.3. EV Characterization
2.3.1. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.3.2. Atomic Force Microscopy Analysis (AFM)
2.3.3. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) Purification and Counts
2.5. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.6. Treatment of PBMCs with Capan-2 or Control Heterologous EVs and Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting of CD3+ Lymphocytes
2.7. Label-Free Proteomic Analysis
2.8. Bioinformatics and Proteomics Data Processing
2.9. Elisa Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
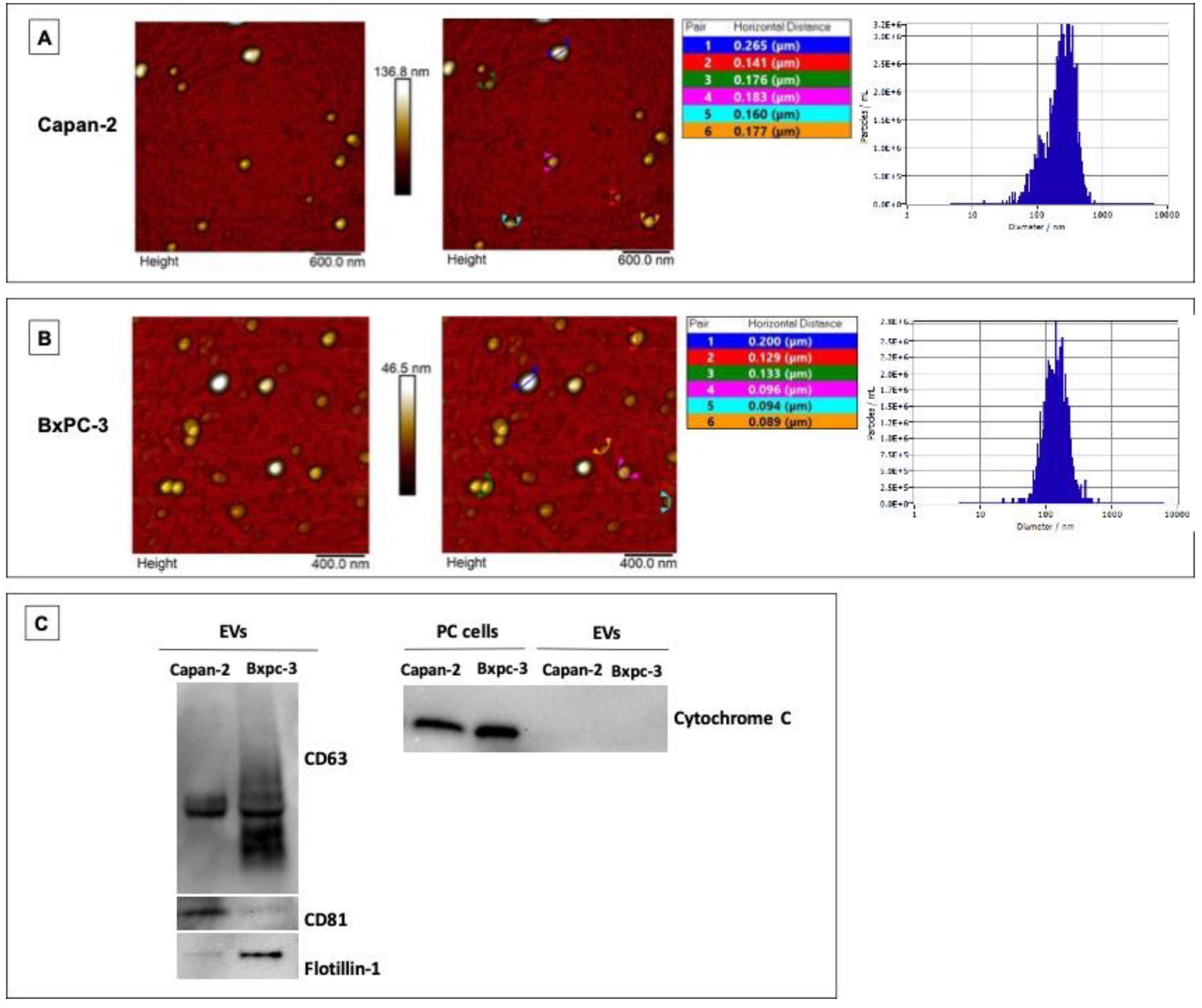
3.1. Characterization of EVs Derived from Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines
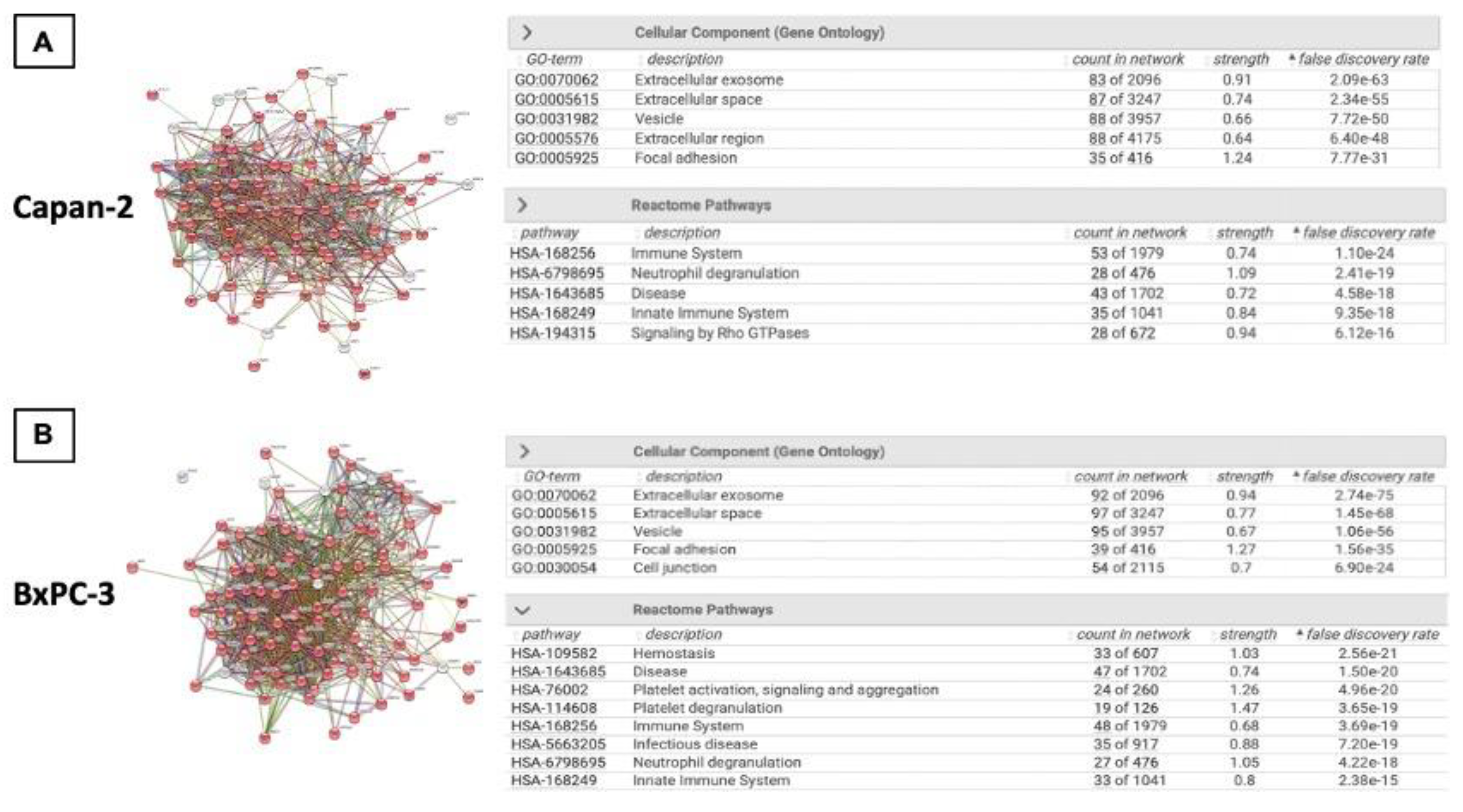
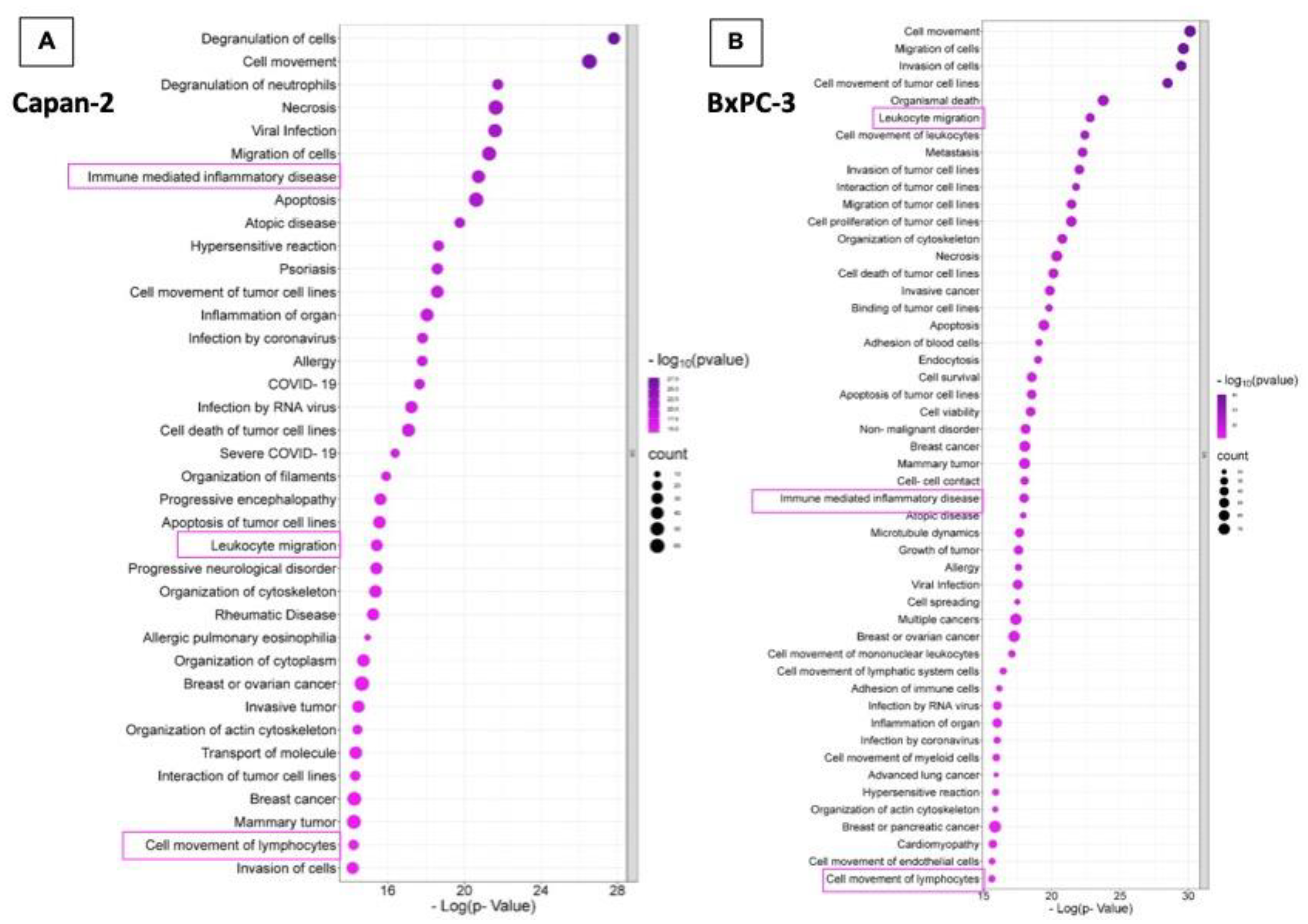
3.2. Proteomic Analysis of Capan-2 and BxPC-3 Derived EVs
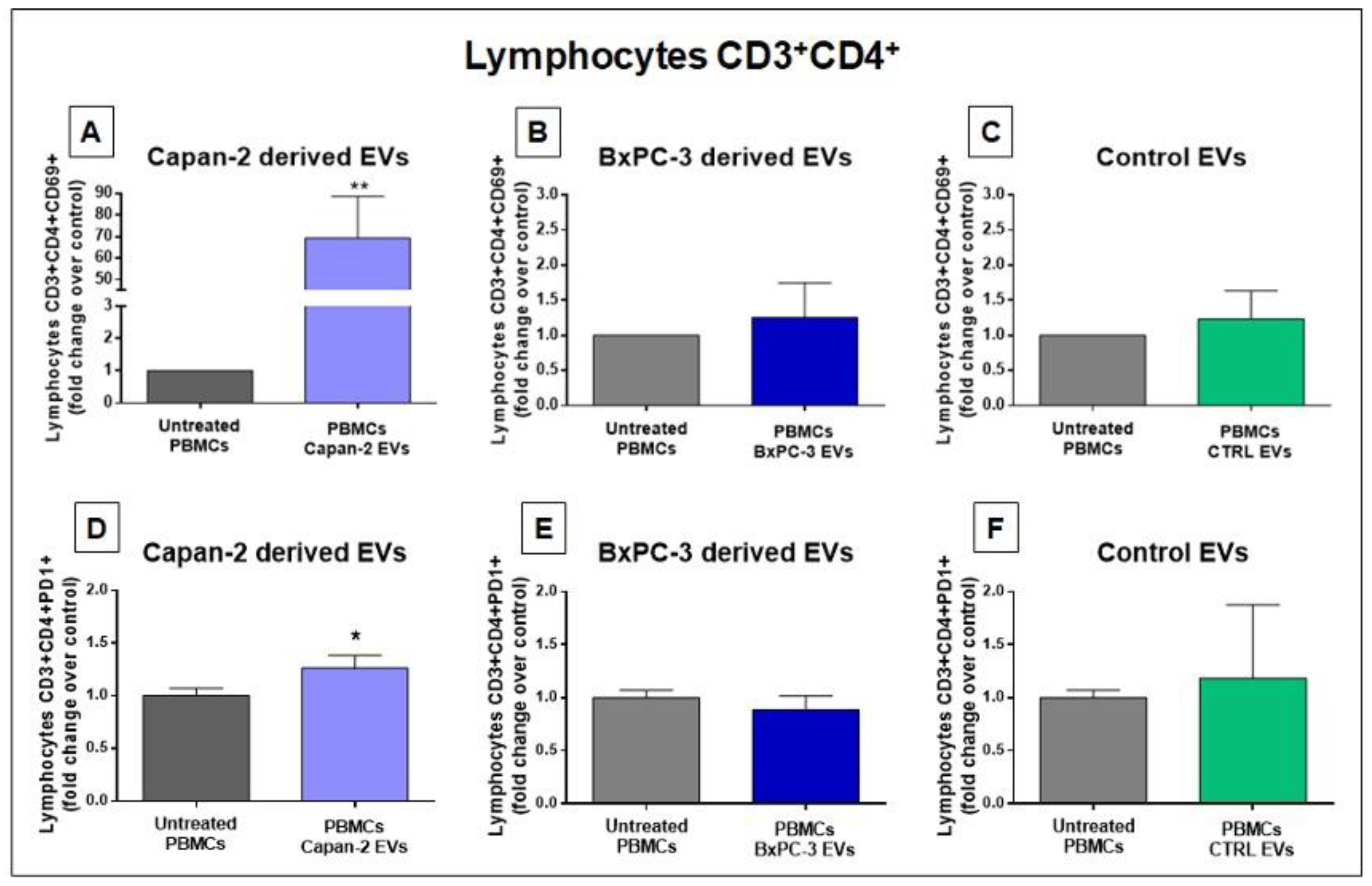
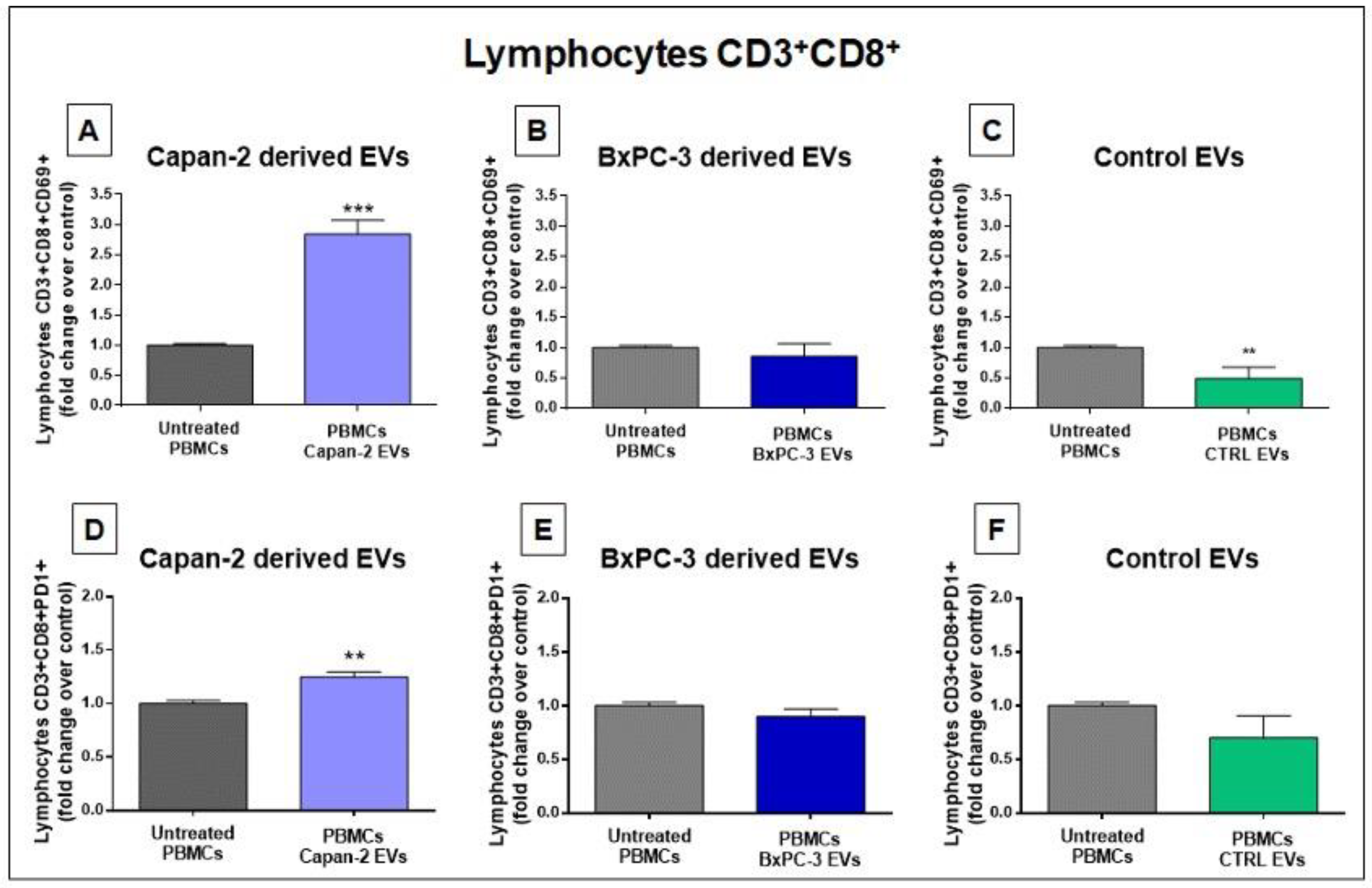
3.3. Capan-2 Derived EVs Increase the Expression of Early Activation Markers in CD4+ and CD8+ Lymphocytes
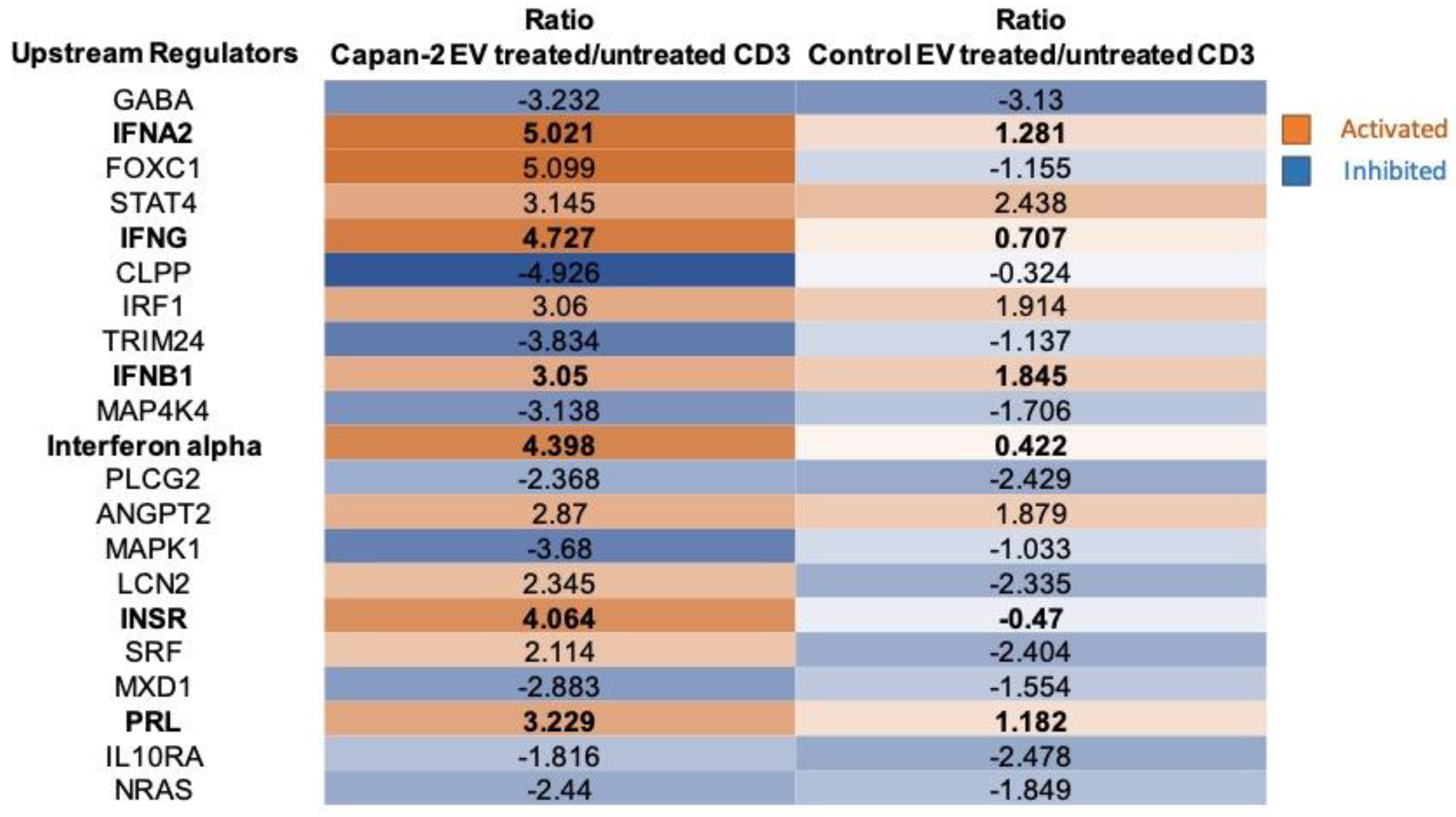
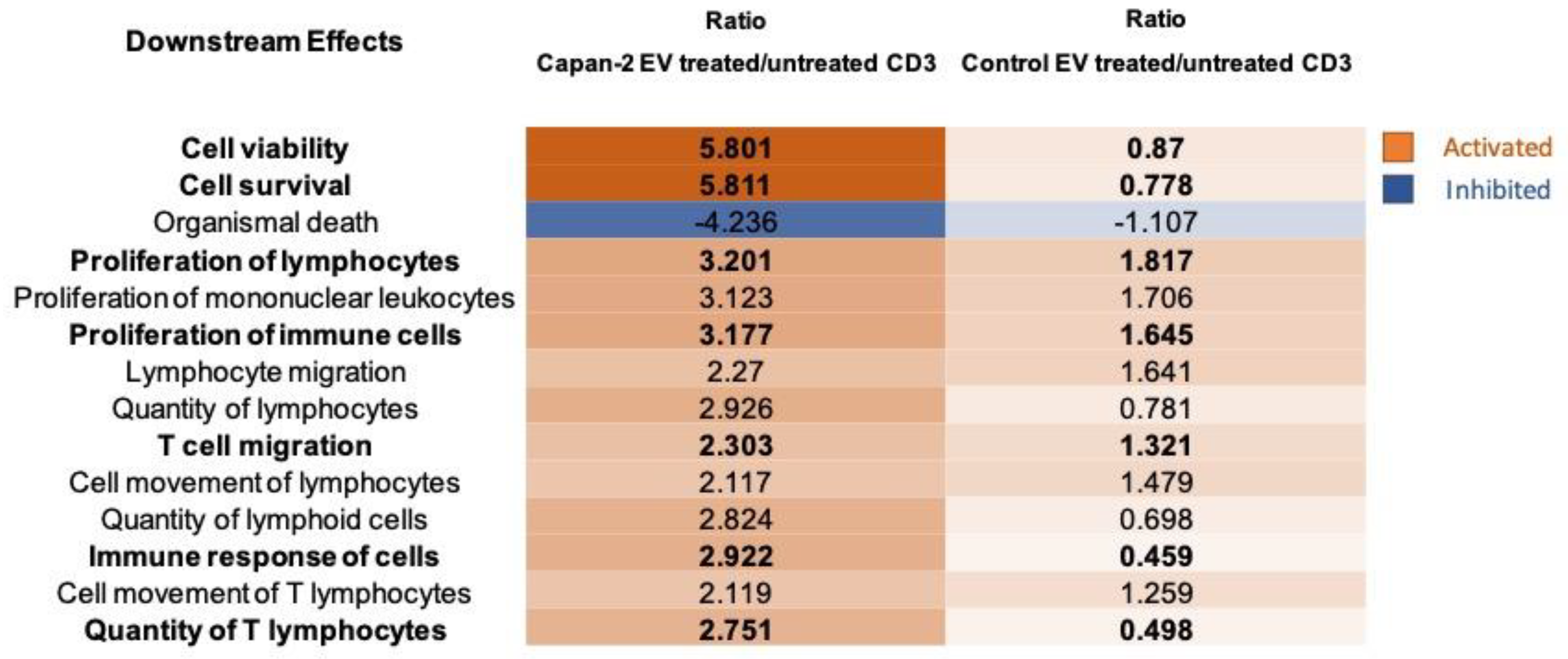
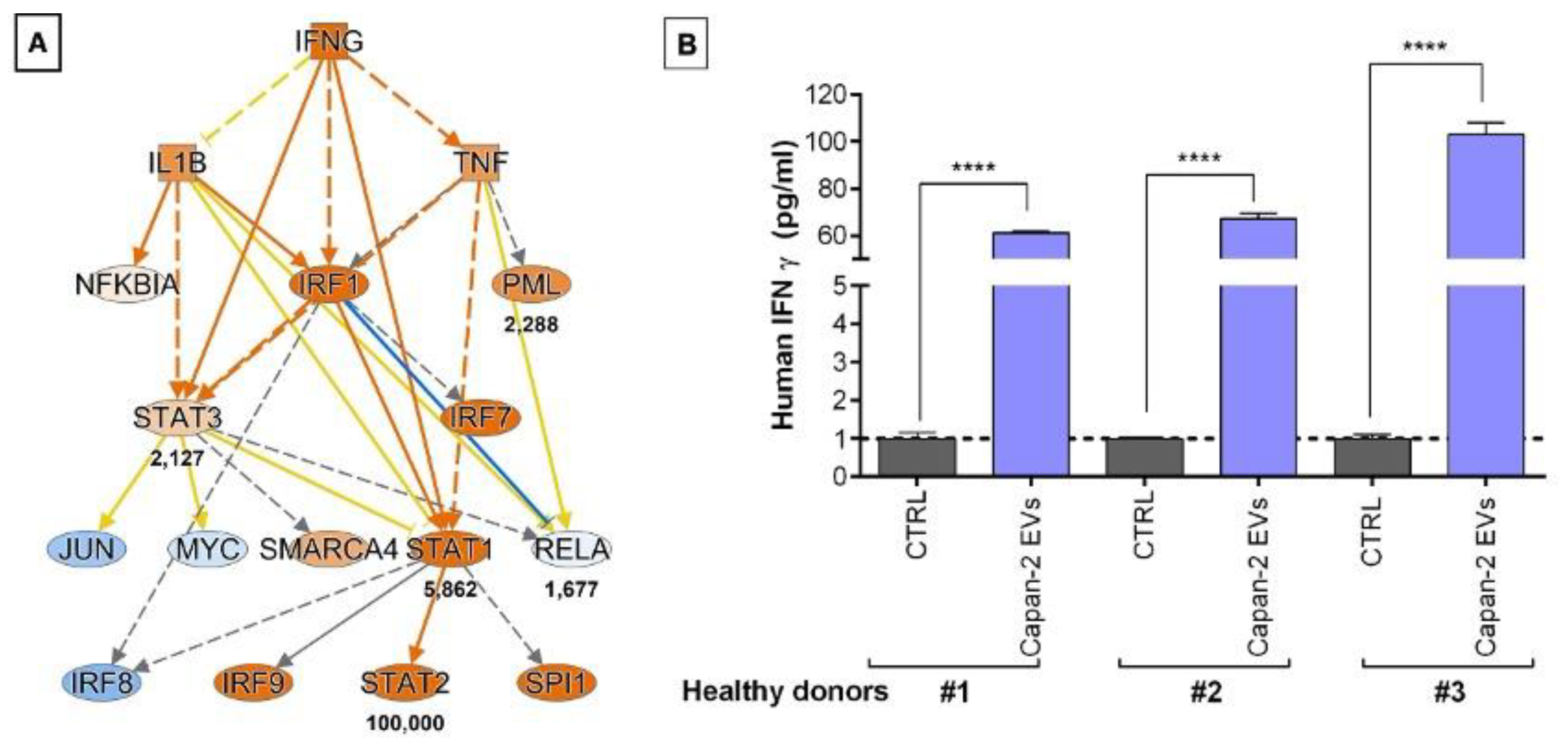
3.4. CD3+ Lymphocytes Proteomics in Response to Treatment with Capan-2 and Control EVs
3.5. PC-Derived EVs Stimulate IFNG Secretion in PBMCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Purushothaman, A.; Oliva-Ramírez, J.; Treekitkarnmongkol, W.; Sankaran, D.; Hurd, M.W.; Putluri, N.; Maitra, A.; Haymaker, C.; Sen, S. Differential Effects of Pancreatic Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Driving a Suppressive Environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; He, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Fan, Z.; Wang, Y. Extracellular Vesicles in Pancreatic Cancer Immune Escape: Emerging Roles and Mechanisms. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 183, 106364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.-M.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological Properties of Extracellular Vesicles and Their Physiological Functions. J. Extracell. vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeone, P.; Bologna, G.; Lanuti, P.; Pierdomenico, L.; Guagnano, M.T.; Pieragostino, D.; Del Boccio, P.; Vergara, D.; Marchisio, M.; Miscia, S.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles as Signaling Mediators and Disease Biomarkers across Biological Barriers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lellis, L.; Florio, R.; Di Bella, M.C.; Brocco, D.; Guidotti, F.; Tinari, N.; Grassadonia, A.; Lattanzio, R.; Cama, A.; Veschi, S. Exosomes as Pleiotropic Players in Pancreatic Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Lam, E.W.-F.; Sun, Y. Extracellular Vesicles in the Tumor Microenvironment: Old Stories, but New Tales. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marar, C.; Starich, B.; Wirtz, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Immunomodulation and Tumor Progression. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggio, M.; Hu, T.; Pai, C.-C.; Chu, B.; Belair, C.D.; Chang, A.; Montabana, E.; Lang, U.E.; Fu, Q.; Fong, L.; et al. Suppression of Exosomal PD-L1 Induces Systemic Anti-Tumor Immunity and Memory. Cell 2019, 177, 414–427.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Vayalil, J.; Lee, G.; Wang, Y.; Peng, G. Emerging Role of Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in T Cell Suppression and Dysfunction in the Tumor Microenvironment. J. Immunother. cancer 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.S.; Roy, A.; Rajpoot, S.; Liu, D.; Savai, R.; Banerjee, S.; Kawada, M.; Faisal, S.M.; Saluja, R.; Saqib, U.; et al. Tumor-Derived Exosomes in the Regulation of Macrophage Polarization. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 69, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannan, L.; Oudart, J.-B.; Monboisse, J.C.; Ramont, L.; Brassart-Pasco, S.; Brassart, B. Extracellular Vesicle-Dependent Cross-Talk in Cancer-Focus on Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; Huang, Z.; Shi, C.; Pu, X.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Ding, G.; Cao, L. Pancreatic Cancer-Derived Exosomes Induce Apoptosis of T Lymphocytes through the P38 MAPK-Mediated Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 8442–8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, G.; Zhou, L.; Qian, Y.; Fu, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Xiang, J.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, G.; Cao, L. Pancreatic Cancer-Derived Exosomes Transfer MiRNAs to Dendritic Cells and Inhibit RFXAP Expression via MiR-212-3p. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29877–29888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, D.; Gnatta, E.; Padoan, A.; Fogar, P.; Furlanello, S.; Aita, A.; Bozzato, D.; Zambon, C.-F.; Arrigoni, G.; Frasson, C.; et al. PDAC-Derived Exosomes Enrich the Microenvironment in MDSCs in a SMAD4-Dependent Manner through a New Calcium Related Axis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 84928–84944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menay, F.; Herschlik, L.; De Toro, J.; Cocozza, F.; Tsacalian, R.; Gravisaco, M.J.; Di Sciullo, M.P.; Vendrell, A.; Waldner, C.I.; Mongini, C. Exosomes Isolated from Ascites of T-Cell Lymphoma-Bearing Mice Expressing Surface CD24 and HSP-90 Induce a Tumor-Specific Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daßler-Plenker, J.; Reiners, K.S.; van den Boorn, J.G.; Hansen, H.P.; Putschli, B.; Barnert, S.; Schuberth-Wagner, C.; Schubert, R.; Tüting, T.; Hallek, M.; et al. RIG-I Activation Induces the Release of Extracellular Vesicles with Antitumor Activity. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1219827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastpar, R.; Gehrmann, M.; Bausero, M.A.; Asea, A.; Gross, C.; Schroeder, J.A.; Multhoff, G. Heat Shock Protein 70 Surface-Positive Tumor Exosomes Stimulate Migratory and Cytolytic Activity of Natural Killer Cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 5238–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlert, C.; Kalluri, R. Exosomes in Tumor Microenvironment Influence Cancer Progression and Metastasis. J. Mol. Med. (Berl). 2013, 91, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfers, J.; Lozier, A.; Raposo, G.; Regnault, A.; Théry, C.; Masurier, C.; Flament, C.; Pouzieux, S.; Faure, F.; Tursz, T.; et al. Tumor-Derived Exosomes Are a Source of Shared Tumor Rejection Antigens for CTL Cross-Priming. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, R.-S.; Lin, C.; Ding, G.-P.; Wu, Z.-R.; Cao, L.-P. Increasing the Immune Activity of Exosomes: The Effect of MiRNA-Depleted Exosome Proteins on Activating Dendritic Cell/Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells against Pancreatic Cancer. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2016, 17, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklefs, F.L.; Alayo, Q.; Krenzlin, H.; Mahmoud, A.B.; Speranza, M.C.; Nakashima, H.; Hayes, J.L.; Lee, K.; Balaj, L.; Passaro, C.; et al. Immune Evasion Mediated by PD-L1 on Glioblastoma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and Characterization of Exosomes from Cell Culture Supernatants and Biological Fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veschi, S.; De Lellis, L.; Florio, R.; Lanuti, P.; Massucci, A.; Tinari, N.; De Tursi, M.; di Sebastiano, P.; Marchisio, M.; Natoli, C.; et al. Effects of Repurposed Drug Candidates Nitroxoline and Nelfinavir as Single Agents or in Combination with Erlotinib in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marco, M.; Veschi, S.; Lanuti, P.; Ramassone, A.; Pacillo, S.; Pagotto, S.; Pepe, F.; George-William, J.N.; Curcio, C.; Marchisio, M.; et al. Enhanced Expression of MiR-181b in B Cells of CLL Improves the Anti-Tumor Cytotoxic T Cell Response. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossarizza, A.; Chang, H.-D.; Radbruch, A.; Acs, A.; Adam, D.; Adam-Klages, S.; Agace, W.W.; Aghaeepour, N.; Akdis, M.; Allez, M.; et al. Guidelines for the Use of Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting in Immunological Studies (Second Edition). Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 1457–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchisio, M.; Simeone, P.; Bologna, G.; Ercolino, E.; Pierdomenico, L.; Pieragostino, D.; Ventrella, A.; Antonini, F.; Del Zotto, G.; Vergara, D.; et al. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Circulating Extracellular Vesicle Subtypes from Fresh Peripheral Blood Samples. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brocco, D.; Lanuti, P.; Pieragostino, D.; Cufaro, M.C.; Simeone, P.; Bologna, G.; Di Marino, P.; De Tursi, M.; Grassadonia, A.; Irtelli, L.; et al. Phenotypic and Proteomic Analysis Identifies Hallmarks of Blood Circulating Extracellular Vesicles in NSCLC Responders to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falasca, K.; Lanuti, P.; Ucciferri, C.; Pieragostino, D.; Cufaro, M.C.; Bologna, G.; Federici, L.; Miscia, S.; Pontolillo, M.; Auricchio, A.; et al. Circulating Extracellular Vesicles as New Inflammation Marker in HIV Infection. AIDS 2021, 35, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madonna, R.; Pieragostino, D.; Cufaro, M.C.; Doria, V.; Del Boccio, P.; Deidda, M.; Pierdomenico, S.D.; Dessalvi, C.C.; De Caterina, R.; Mercuro, G. Ponatinib Induces Vascular Toxicity through the Notch-1 Signaling Pathway. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, A.; Green, J.; Pollard, J.; Tugendreich, S. Causal Analysis Approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A Position Statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and Update of the MISEV2014 Guidelines. J. Extracell. vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles (MISEV2023): From Basic to Advanced Approaches. J. Extracell. vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cibrián, D.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. CD69: From Activation Marker to Metabolic Gatekeeper. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzai, A.C.; Wagner, T.; Audsley, K.M.; Newnes, H. V.; Barrett, L.W.; Barnes, S.; Wylie, B.C.; Stone, S.; McDonnell, A.; Fear, V.S.; et al. Diverse Anti-Tumor Immune Potential Driven by Individual IFNα Subtypes. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukhaled, G.M.; Harding, S.; Brooks, D.G. Opposing Roles of Type I Interferons in Cancer Immunity. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2021, 16, 167–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgovanovic, D.; Song, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Roles of IFN-γ in Tumor Progression and Regression: A Review. Biomark. Res. 2020, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.; Clemente-Casares, X.; Zhou, A.C.; Lei, H.; Ahn, J.J.; Chan, Y.T.; Choi, O.; Luck, H.; Woo, M.; Dunn, S.E.; et al. Insulin Receptor-Mediated Stimulation Boosts T Cell Immunity during Inflammation and Infection. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 922–934.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legorreta-Haquet, M.V.; Santana-Sánchez, P.; Chávez-Sánchez, L.; Chávez-Rueda, A.K. The Effect of Prolactin on Immune Cell Subsets Involved in SLE Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1016427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




