Submitted:
08 April 2024
Posted:
11 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Experimental Infection of Ducks
Protein Extraction
Sample Preparation for LC-MS Analysis
Bioinformatics Analysis
Results and Discussion
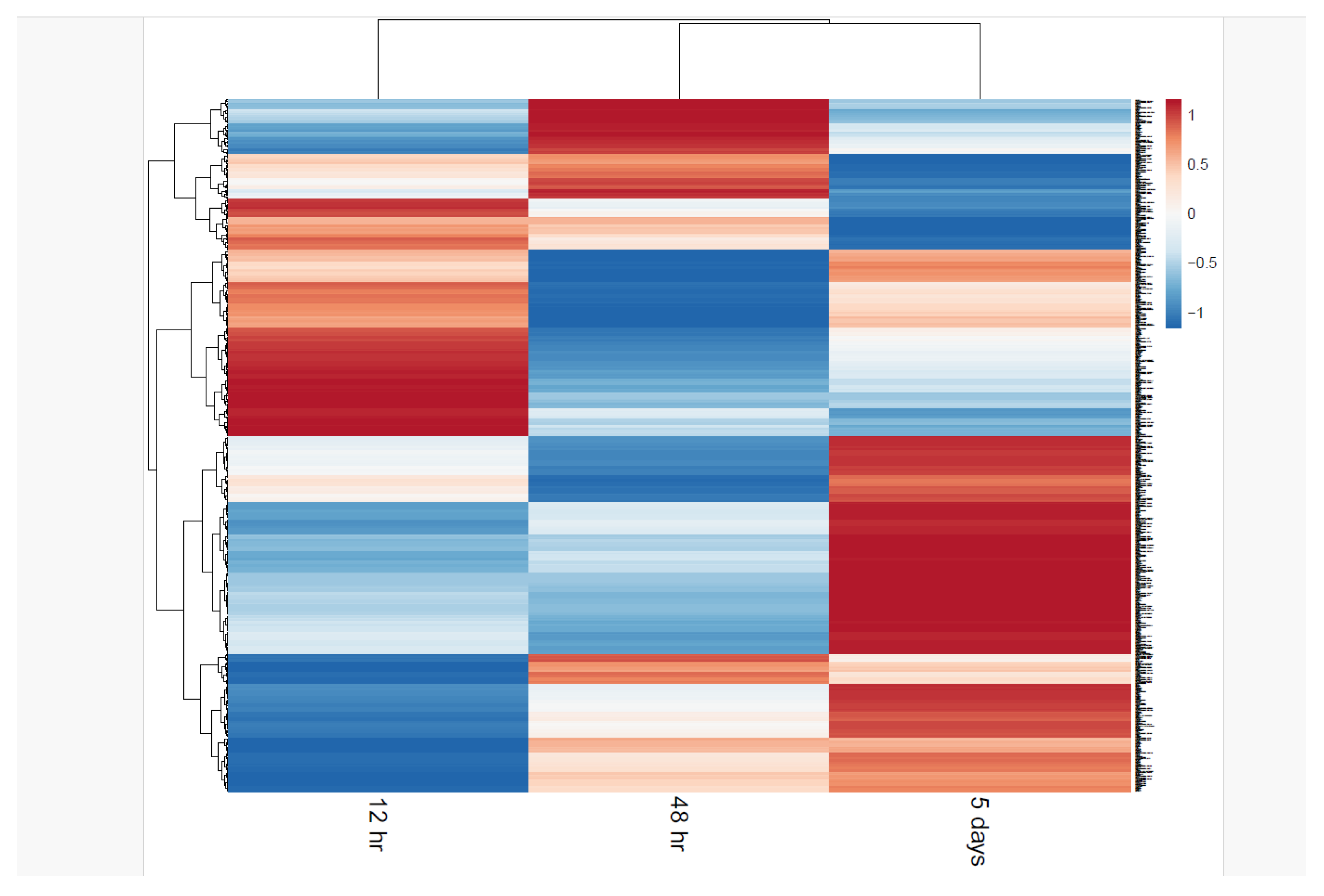
Differential Protein Expression Analysis
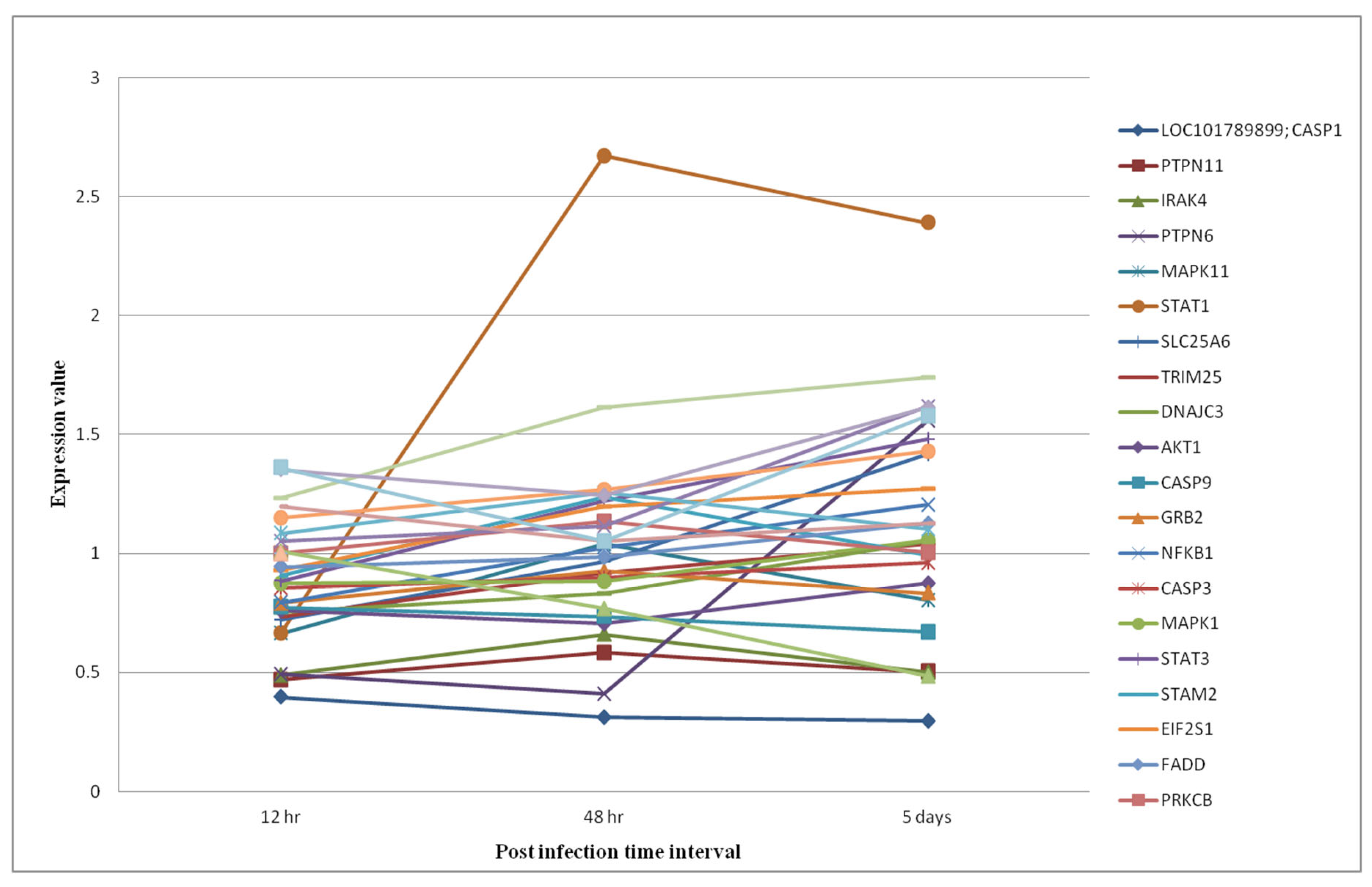
Differential Phosphoproteomic Expression Analysis
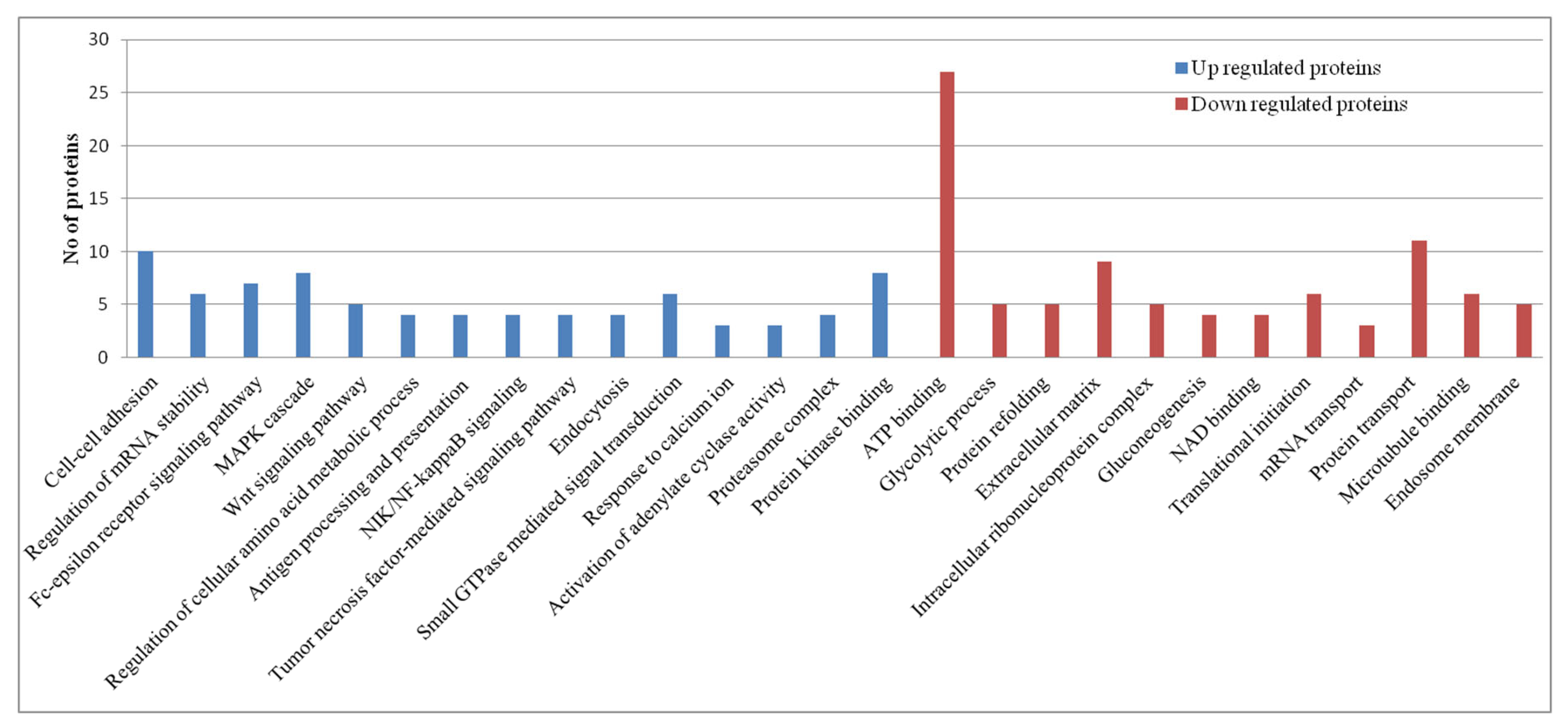
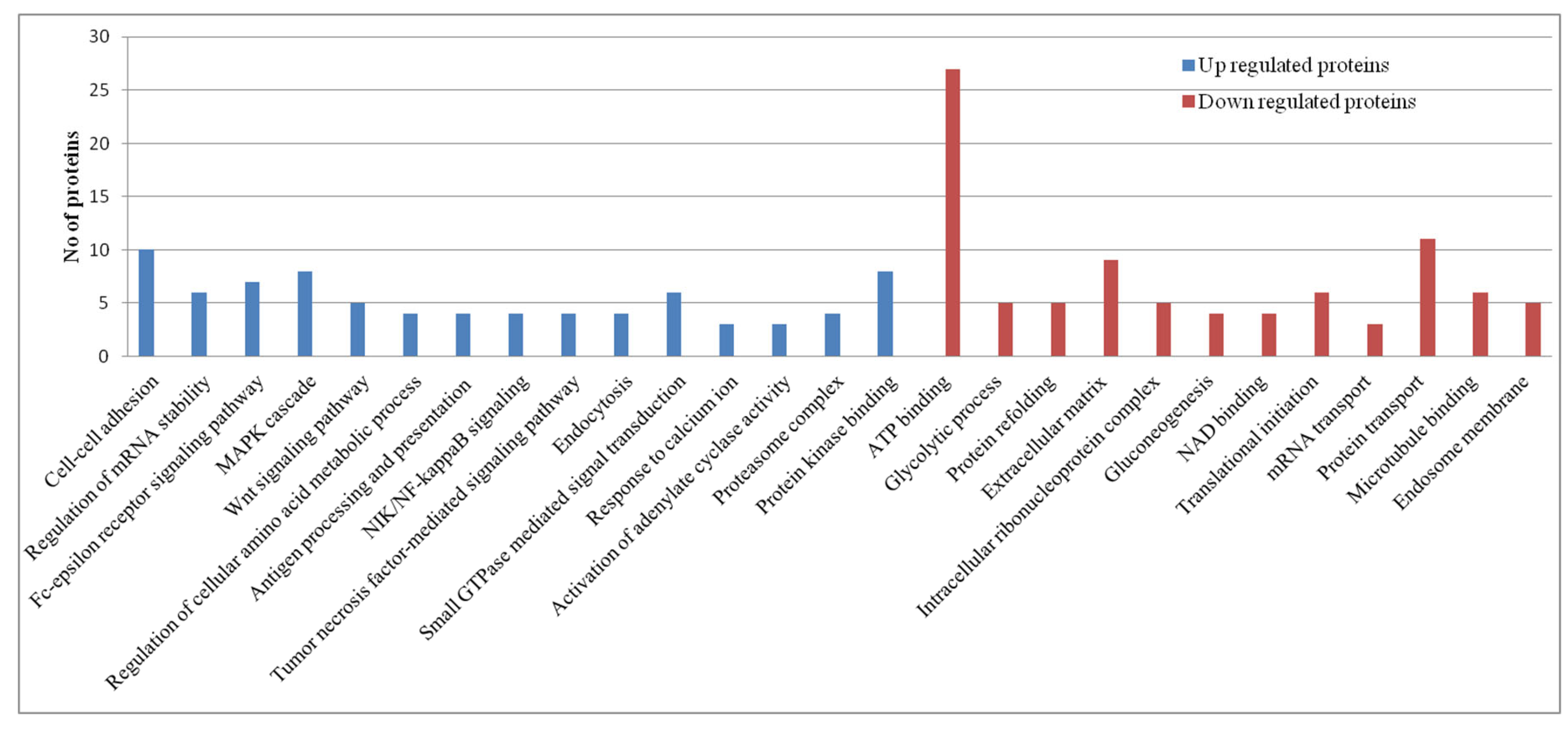
Pathway Analysis of Proteomics Datasets
RIG-I-Like Receptors Signaling Pathway
Interferon Signaling: The Jak-Stat Pathway
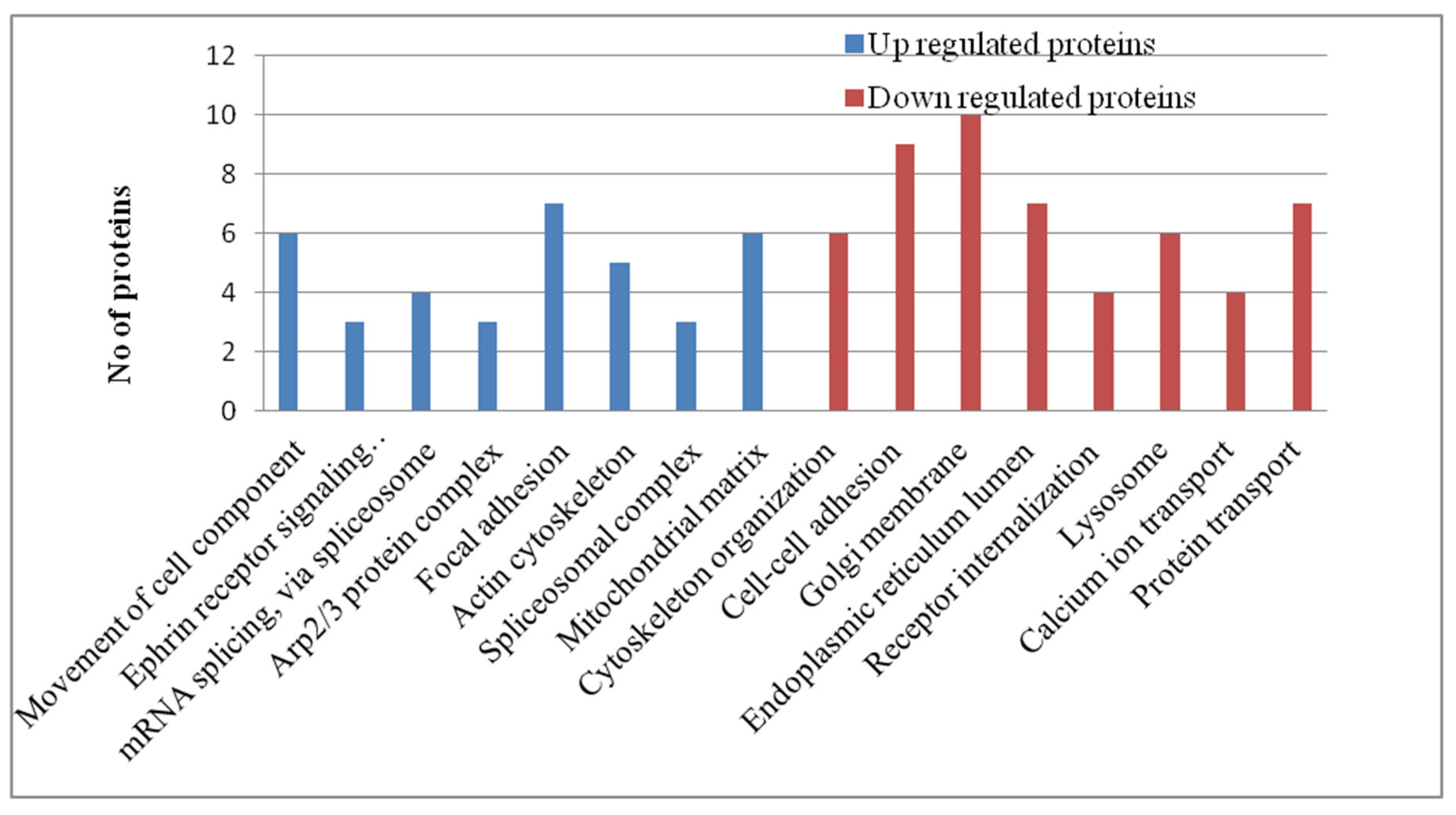
Pathway Analysis of Phosphoproteomics Datasets
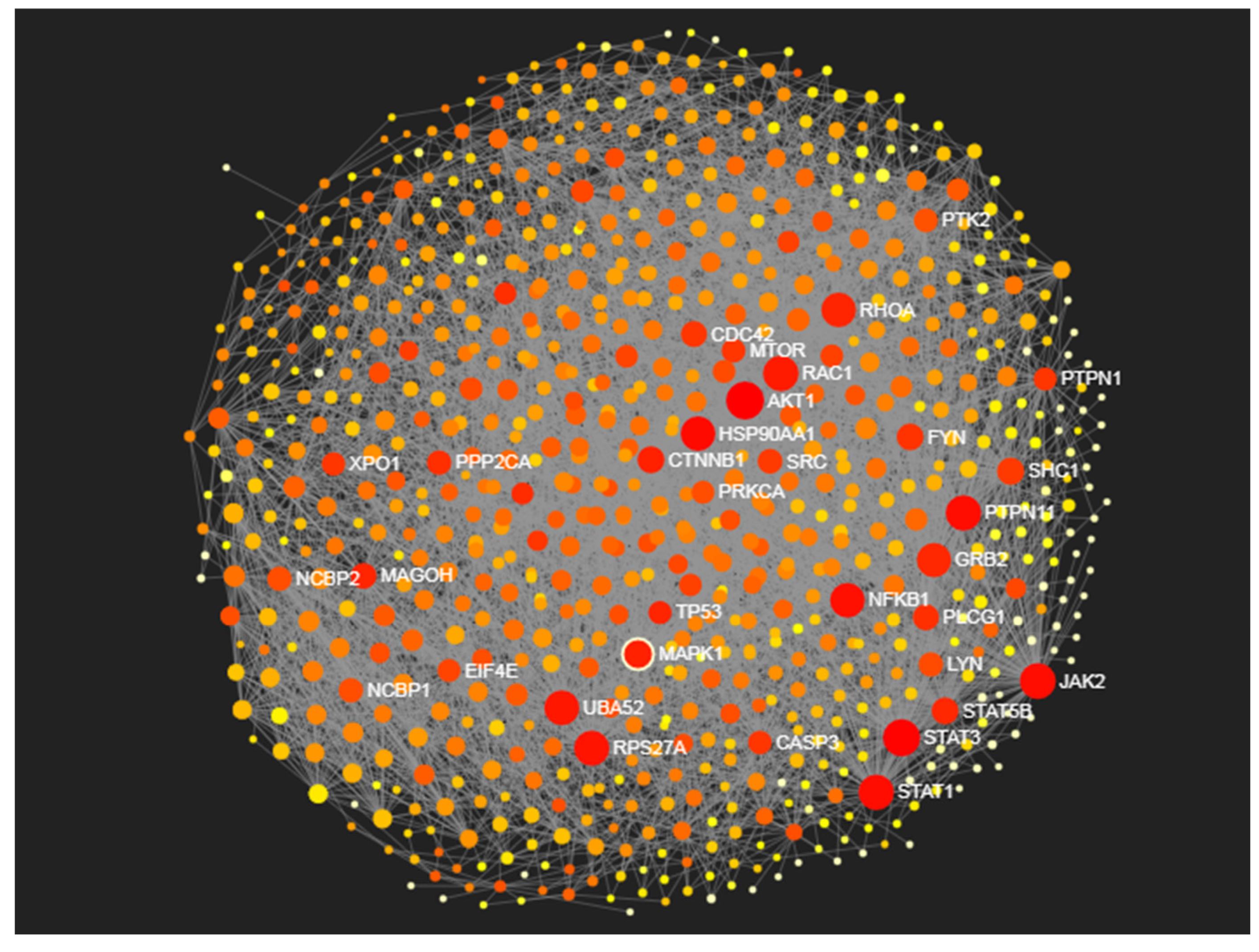
Identification of Proteomic Determinants
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethics statement
Acknowledgements
Competing Interests
References
- Herold, S.; Becker, C.; Ridge, K.M.; Budinger, G.R.S. Influenza Virus-Induced Lung Injury: Pathogenesis and Implications for Treatment. Eur Respir J 2015, 45, 1463–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Vijayakumar, P.; Raut, A.A. Emerging Avian Influenza Infections: Current Understanding of Innate Immune Response and Molecular Pathogenesis. Int Rev Immunol 2017, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Burt, D.W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, W.; Kim, H.; Gan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; et al. The Duck Genome and Transcriptome Provide Insight into an Avian Influenza Virus Reservoir Species. Nat Genet 2013, 45, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maughan, M.N.; Dougherty, L.S.; Preskenis, L.A.; Ladman, B.S.; Gelb, J.; Spackman, E. V.; Keeler, C.L. Transcriptional Analysis of the Innate Immune Response of Ducks to Different Species-of-Origin Low Pathogenic H7 Avian Influenza Viruses. Virol J 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.; Smith, N.; Yu, L.; Paton, I.R.; Gutowska, M.W.; Forrest, H.L.; Danner, A.F.; Seiler, J.P.; Digard, P.; Webster, R.G.; et al. A Comparative Analysis of Host Responses to Avian Influenza Infection in Ducks and Chickens Highlights a Role for the Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Proteins in Viral Resistance. BMC Genomics 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Vijayakumar, P.; Gandhale, P.N.; Ranaware, P.B.; Kumar, H.; Kulkarni, D.D.; Raut, A.A.; Mishra, A. Genome-Wide Gene Expression Pattern Underlying Differential Host Response to High or Low Pathogenic H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus in Ducks. Acta Virol 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klees, S.; Schlüter, J.S.; Schellhorn, J.; Bertram, H.; Kurzweg, A.C.; Ramzan, F.; Schmitt, A.O.; Gültas, M. Comparative Investigation of Gene Regulatory Processes Underlying Avian Influenza Viruses in Chicken and Duck. Biology (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, P.; Raut, A.A.; Chingtham, S.; Murugkar, H.V.; Kulkarni, D.D.; Sood, R.; Singh, V.P.; Mishra, A. Proteomic Analysis of Differential Expression of Lung Proteins in Response to Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus Infection in Chickens. Arch Virol 2022, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, M.R.W.; Aldridge, J.R.; Webster, R.G.; Magor, K.E. Association of RIG-I with Innate Immunity of Ducks to Influenza. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 5913–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, L.; Afonso, C.L.; Estevez, C.; Wasilenko, J.; Pantin-Jackwood, M. Differential Host Gene Expression in Cells Infected with Highly Pathogenic H5N1 Avian Influenza Viruses. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 2008, 125, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q. long; Luo, J.; Zhou, K.; Dong, J. xin; He, H. xuan Immune-Related Gene Expression in Response to H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus Infection in Chicken and Duck Embryonic Fibroblasts. Mol Immunol 2011, 48, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burggraaf, S.; Bingham, J.; Payne, J.; Kimpton, W.G.; Lowenthal, J.W.; Bean, A.G.D. Increased Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in Organs Is Associated with a Higher Severity of H5N1 Influenza Virus Infection. PLoS One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchipudi, S. V.; Tellabati, M.; Sebastian, S.; Londt, B.Z.; Jansen, C.; Vervelde, L.; Brookes, S.M.; Brown, I.H.; Dunham, S.P.; Chang, K.C. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus Infection in Chickens but Not Ducks Is Associated with Elevated Host Immune and Pro-Inflammatory Responses. Vet Res 2014, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, L.K.; Fleming-Canepa, X.; Webster, R.G.; Magor, K.E. Tissue Specific Transcriptome Changes Upon Influenza A Virus Replication in the Duck. Front Immunol 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Su, Q.; Luo, J.; Li, M.; Wu, Q.; Chang, H.; Du, J.; Huang, C.; Ma, J.; Han, S.; et al. Differences in Highly Pathogenic H5N6 Avian Influenza Viral Pathogenicity and Inflammatory Response in Chickens and Ducks. Front Microbiol 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josset, L.; Tisoncik-Go, J.; Katze, M.G. Moving H5N1 Studies into the Era of Systems Biology. Virus Res 2013, 178, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, D.E.; Tam, V.C.; Aderem, A. Systems-Level Analysis of Innate Immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 2014, 32, 547–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, F.; Mann, M. Quantitative Shotgun Proteomics: Considerations for a High-Quality Workflow in Immunology. Nat Immunol 2014, 15, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Ke, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, M.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, H.; Tu, J.; Chen, H.; Jin, M. Proteomics Analysis of Differential Expression of Chicken Brain Tissue Proteins in Response to the Neurovirulent H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus Infection. J Proteome Res 2010, 9, 3789–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ming, F.; Huang, H.; Guo, K.; Chen, H.; Jin, M.; Zhou, H. Proteome Response of Chicken Embryo Fibroblast Cells to Recombinant H5N1 Avian Influenza Viruses with Different Neuraminidase Stalk Lengths. Sci Rep 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Qian, W.; Zou, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhou, H.; Jin, M. Proteomic Analysis of Chicken Embryo Fibroblast Cells Infected with Recombinant H5N1 Avian Influenza Viruses with and without NS1 EIF4GI Binding Domain. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 8350–8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, B.G.; Jackson, D.; Chen, Y.H.; Lamb, R.A.; Randall, R.E. Influenza A Virus NS1 Protein Binds P85beta and Activates Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase Signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 14194–14199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and Integrative Analysis of Large Gene Lists Using DAVID Bioinformatics Resources. Nat Protoc 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Benner, M.J.; Hancock, R.E.W. NetworkAnalyst--Integrative Approaches for Protein-Protein Interaction Network Analysis and Visual Exploration. Nucleic Acids Res 2014, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New Perspectives on Genomes, Pathways, Diseases and Drugs. Nucleic Acids Res 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metsalu, T.; Vilo, J. ClustVis: A Web Tool for Visualizing Clustering of Multivariate Data Using Principal Component Analysis and Heatmap. Nucleic Acids Res 2015, 43, W566–W570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.; Gack, M.U. Post-Translational Control of Intracellular Pathogen Sensing Pathways. Trends Immunol 2017, 38, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderholm, S.; Kainov, D.E.; Ohman, T.; Denisova, O. V.; Schepens, B.; Kulesskiy, E.; Imanishi, S.Y.; Corthals, G.; Hintsanen, P.; Aittokallio, T.; et al. Phosphoproteomics to Characterize Host Response During Influenza A Virus Infection of Human Macrophages. Mol Cell Proteomics 2016, 15, 3203–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yángüez, E.; Hunziker, A.; Dobay, M.P.; Yildiz, S.; Schading, S.; Elshina, E.; Karakus, U.; Gehrig, P.; Grossmann, J.; Dijkman, R.; et al. Phosphoproteomic-Based Kinase Profiling Early in Influenza Virus Infection Identifies GRK2 as Antiviral Drug Target. Nat Commun 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cao, J.; Ma, Q.; Gao, X.; Wang, Q.; Jin, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wen, L.; Ren, J. GPS 2.1: Enhanced Prediction of Kinase-Specific Phosphorylation Sites with an Algorithm of Motif Length Selection. Protein Eng Des Sel 2011, 24, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.; Dam, S.; Saul, V. V.; Kuznetsova, I.; Müller, C.; Fritz-Wolf, K.; Becker, K.; Linne, U.; Gu, H.; Stokes, M.P.; et al. Phosphoproteome Analysis of Cells Infected with Adapted and Nonadapted Influenza A Virus Reveals Novel Pro- and Antiviral Signaling Networks. J Virol 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, D.J.; Parsons, G.; Manvell, R.J. Experimental Assessment of the Pathogenicity of Eight Avian Influenza A Viruses of H5 Subtype for Chickens, Turkeys, Ducks and Quail. Avian Pathol 1986, 15, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins LE; Swayne DE Pathogenicity of a Hong Kong-Origin H5N1 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus for Emus, Geese, Ducks, and Pigeons. Avian Dis. 2002, 46, 53–63. [CrossRef]
- Cagle, C.; Wasilenko, J.; Adams, S.C.; Cardona, C.J.; To, T.L.; Nguyen, T.; Spackman, E.; Suarez, D.L.; Smith, D.; Shepherd, E.; et al. Differences in Pathogenicity, Response to Vaccination, and Innate Immune Responses in Different Types of Ducks Infected with a Virulent H5N1 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus from Vietnam. Avian Dis 2012, 56, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, L.B.; Diaz-Satizabal, L.; Evseev, D.; Fleming-Canepa, X.; Mao, S.; Webster, R.G.; Magor, K.E. IFN and Cytokine Responses in Ducks to Genetically Similar H5N1 Influenza A Viruses of Varying Pathogenicity. J Gen Virol 2018, 99, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinchieri, G. Type I Interferon: Friend or Foe? J Exp Med 2010, 207, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Sato, S.; Yoneyama, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Matsui, K.; Uematsu, S.; Jung, A.; Kawai, T.; Ishii, K.J.; et al. Differential Roles of MDA5 and RIG-I Helicases in the Recognition of RNA Viruses. Nature 2006, 441, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumiya, T.; Stafforini, D.M. Function and Regulation of Retinoic Acid-Inducible Gene-I. Crit Rev Immunol 2010, 30, 489–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Cui, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, S.; Han, F.; Yuan, R.; Gong, L.; Jiao, P.; Liao, M. Duck MDA5 Functions in Innate Immunity against H5N1 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus Infections. Vet Res 2014, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.R.; Wei, L.M.; Song, Y.F.; Cui, J.; Zhang, S.; Han, F.; Yuan, R.Y.; Liao, M. Molecular Cloning and Immune Responsive Expression of LGP2 Gene, a Pivotal Member of the RLR Gene Family from Muscovy Duck Cairina Moschata. Poult Sci 2015, 94, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Kato, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Yoneyama, M.; Sato, S.; Matsushita, K.; Tsujimura, T.; Fujita, T.; Akira, S.; Takeuchi, O. LGP2 Is a Positive Regulator of RIG-I- and MDA5-Mediated Antiviral Responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Xue, Q.; Li, W.; Liao, M.; Jiao, P. Host Innate Immune Response of Geese Infected with Clade 2.3.4.4 H5N6 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses. Microorganisms 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Xue, Q.; Liu, J.; Huang, B.; He, Z.; Huang, J.; Zu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, B.; et al. Duck TRIM32 Functions in IFN-β Signaling Against the Infection of H5N6 Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus. Front Immunol 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Pal, A.; Baviskar, P. RIGI, TLR7, and TLR3 Genes Were Predicted to Have Immune Response Against Avian Influenza in Indigenous Ducks. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gack, M.U.; Shin, Y.C.; Joo, C.H.; Urano, T.; Liang, C.; Sun, L.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S.; Chen, Z.; Inoue, S.; et al. TRIM25 RING-Finger E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Is Essential for RIG-I-Mediated Antiviral Activity. Nature 2007, 446, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gack, M.U.; Albrecht, R.A.; Urano, T.; Inn, K.S.; Huang, I.C.; Carnero, E.; Farzan, M.; Inoue, S.; Jung, J.U.; García-Sastre, A. Influenza A Virus NS1 Targets the Ubiquitin Ligase TRIM25 to Evade Recognition by the Host Viral RNA Sensor RIG-I. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Kinch, L.N.; Brautigam, C.A.; Chen, X.; Du, F.; Grishin, N. V.; Chen, Z.J. Ubiquitin-Induced Oligomerization of the RNA Sensors RIG-I and MDA5 Activates Antiviral Innate Immune Response. Immunity 2012, 36, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranzo-Navarro, D.; Magor, K.E. Activation of Duck RIG-I by TRIM25 Is Independent of Anchored Ubiquitin. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauzzi, M.C.; Barbieri, G.; Richter, M.F.; Uzé, G.; Ling, L.; Fellous, M.; Pellegrini, S. The Amino-Terminal Region of Tyk2 Sustains the Level of Interferon Alpha Receptor 1, a Component of the Interferon Alpha/Beta Receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1997, 94, 11839–11844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragimbeau, J.; Dondi, E.; Alcover, A.; Eid, P.; Uzé, G.; Pellegrini, S. The Tyrosine Kinase Tyk2 Controls IFNAR1 Cell Surface Expression. EMBO J 2003, 22, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haan, C.; Kreis, S.; Margue, C.; Behrmann, I. Jaks and Cytokine Receptors--an Intimate Relationship. Biochem Pharmacol 2006, 72, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, K.; Schindler, C.; Prezioso, V.R.; Darnell, J.E. Activation of Transcription by IFN-Gamma: Tyrosine Phosphorylation of a 91-KD DNA Binding Protein. Science 1992, 258, 1808–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, T.; Kovarik, P.; Meinke, A. GAS Elements: A Few Nucleotides with a Major Impact on Cytokine-Induced Gene Expression. J Interferon Cytokine Res 1997, 17, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, J.E.; Kerr, lan M. ; Stark, G.R. Jak-STAT Pathways and Transcriptional Activation in Response to IFNs and Other Extracellular Signaling Proteins. Science 1994, 264, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Kasmi, K.C.; Holst, J.; Coffre, M.; Mielke, L.; de Pauw, A.; Lhocine, N.; Smith, A.M.; Rutschman, R.; Kaushal, D.; Shen, Y.; et al. General Nature of the STAT3-Activated Anti-Inflammatory Response. J Immunol 2006, 177, 7880–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.Y.; Kessler, D.S.; Veals, S.A.; Levy, D.E.; Darnell, J.E. ISGF3, the Transcriptional Activator Induced by Interferon Alpha, Consists of Multiple Interacting Polypeptide Chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1990, 87, 8555–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, C.; Fu, X.Y.; Improta, T.; Aebersold, R.; Darnell, J.E. Proteins of Transcription Factor ISGF-3: One Gene Encodes the 91-and 84-KDa ISGF-3 Proteins That Are Activated by Interferon Alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1992, 89, 7836–7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, E.K.; Schmolke, M.; Wolff, T.; Viemann, D.; Roth, J.; Bode, J.G.; Ludwig, S. Influenza A Virus Inhibits Type I IFN Signaling via NF-KappaB-Dependent Induction of SOCS-3 Expression. PLoS Pathog 2008, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Rahbar, R.; Chan, R.W.Y.; Lee, S.M.Y.; Chan, M.C.W.; Wang, B.X.; Baker, D.P.; Sun, B.; Malik Peiris, J.S.; Nicholls, J.M.; et al. Influenza Virus Non-Structural Protein 1 (NS1) Disrupts Interferon Signaling. PLoS One 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Murti, A.; Pfeffer, L.M. STAT3 Complements Defects in an Interferon-Resistant Cell Line: Evidence for an Essential Role for STAT3 in Interferon Signaling and Biological Activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998, 95, 5568–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Stravopodis, D.; Teglund, S.; Kitazawa, J.; Ihle, J.N. Naturally Occurring Dominant Negative Variants of Stat5. Mol Cell Biol 1996, 16, 6141–6148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin JX; Mietz J; Modi WS; John S; Leonard WJ Cloning of Human Stat5B. Reconstitution of Interleukin-2-Induced Stat5A and Stat5B DNA Binding Activity in COS-7 Cells. J Biol Chem. 1996, 3, 10738–10744. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, Y.M.; Pichlmair, A.; Górna, M.W.; Superti-Furga, G.; Nagar, B. Structural Basis for Viral 59-PPP-RNA Recognition by Human IFIT Proteins. Nature 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderven, H.A.; Petkau, K.; Ryan-Jean, K.E.E.; Aldridge, J.R.; Webster, R.G.; Magor, K.E. Avian Influenza Rapidly Induces Antiviral Genes in Duck Lung and Intestine. Mol Immunol 2012, 51, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming-Canepa, X.; Aldridge, J.R.; Canniff, L.; Kobewka, M.; Jax, E.; Webster, R.G.; Magor, K.E. Duck Innate Immune Responses to High and Low Pathogenicity H5 Avian Influenza Viruses. Vet Microbiol 2019, 228, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ank, N.; West, H.; Bartholdy, C.; Eriksson, K.; Thomsen, A.R.; Paludan, S.R. Lambda Interferon (IFN-Lambda), a Type III IFN, Is Induced by Viruses and IFNs and Displays Potent Antiviral Activity against Select Virus Infections in Vivo. J Virol 2006, 80, 4501–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, M.J.; Elia, A. The Double-Stranded RNA-Dependent Protein Kinase PKR: Structure and Function. J Interferon Cytokine Res 1997, 17, 503–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, M.A.; Gil, J.; Ventoso, I.; Guerra, S.; Domingo, E.; Rivas, C.; Esteban, M. Impact of Protein Kinase PKR in Cell Biology: From Antiviral to Antiproliferative Action. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2006, 70, 1032–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakadamyali, M.; Rust, M.J.; Babcock, H.P.; Zhuang, X. Visualizing Infection of Individual Influenza Viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100, 9280–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Whittaker, G.R. Role of the Actin Cytoskeleton during Influenza Virus Internalization into Polarized Epithelial Cells. Cell Microbiol 2007, 9, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, C.; Wolff, T.; Pleschka, S.; Planz, O.; Beermann, W.; Bode, J.G.; Schmolke, M.; Ludwig, S. Influenza A Virus NS1 Protein Activates the PI3K/Akt Pathway to Mediate Antiapoptotic Signaling Responses. J Virol 2007, 81, 3058–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.K.; Liu, Q.; Tikoo, S.K.; Babiuk, L.A.; Zhou, Y. Effect of the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Pathway on Influenza A Virus Propagation. J Gen Virol 2007, 88, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhirnov, O.P.; Klenk, H.D. Control of Apoptosis in Influenza Virus-Infected Cells by up-Regulation of Akt and P53 Signaling. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, S. Disruption of Virus-Host Cell Interactions and Cell Signaling Pathways as an Anti-Viral Approach against Influenza Virus Infections. Biol Chem 2011, 392, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleschka, S.; Wolff, T.; Ehrhardt, C.; Hobom, G.; Planz, O.; Rapp, U.R.; Ludwig, S. Influenza Virus Propagation Is Impaired by Inhibition of the Raf/MEK/ERK Signalling Cascade. Nat Cell Biol 2001, 3, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Luo, J.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Su, W.; Zhao, N.; Liu, S.; Xie, L.; Jia, Y.; et al. HA Triggers the Switch from MEK1 SUMOylation to Phosphorylation of the ERK Pathway in Influenza A Virus-Infected Cells and Facilitates Its Infection. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, M.L.; Kracht, M.; Saul, V. V. The Intricate Interplay between RNA Viruses and NF-ΚB. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014, 1843, 2754–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, I.; Wurzer, W.J.; Ehrhardt, C.; Pleschka, S.; Puthavathana, P.; Silberzahn, T.; Wolff, T.; Planz, O.; Ludwig, S. Acetylsalicylic Acid (ASA) Blocks Influenza Virus Propagation via Its NF-KappaB-Inhibiting Activity. Cell Microbiol 2007, 9, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, C.; Rückle, A.; Hrincius, E.R.; Haasbach, E.; Anhlan, D.; Ahmann, K.; Banning, C.; Reiling, S.J.; Kühn, J.; Strobl, S.; et al. The NF-ΚB Inhibitor SC75741 Efficiently Blocks Influenza Virus Propagation and Confers a High Barrier for Development of Viral Resistance. Cell Microbiol 2013, 15, 1198–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Hu, H.; Li, H.S.; Yu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Brittain, G.C.; Zou, Q.; Cheng, X.; Mallette, F.A.; Watowich, S.S.; et al. Noncanonical NF-ΚB Pathway Controls the Production of Type I Interferons in Antiviral Innate Immunity. Immunity 2014, 40, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Luo, J.; Cantley, L.C. The Evolution of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinases as Regulators of Growth and Metabolism. Nat Rev Genet 2006, 7, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, N.; Suizu, F.; Matsuda-Lennikov, M.; Edamura, T.; Bala, J.; Noguchi, M. Inhibition of Akt Kinase Activity Suppresses Entry and Replication of Influenza Virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2014, 450, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, J.; Helenius, A. Vaccinia Virus Uses Macropinocytosis and Apoptotic Mimicry to Enter Host Cells. Science 2008, 320, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.F.; Kolokoltsov, A.A.; Freiberg, A.N.; Holbrook, M.R.; Davey, R.A. Phosphoinositide-3 Kinase-Akt Pathway Controls Cellular Entry of Ebola Virus. PLoS Pathog 2008, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhang, J.L.; Chen, W.; Xu, X.F.; Gao, N.; Fan, D.Y.; An, J. Roles of Small GTPase Rac1 in the Regulation of Actin Cytoskeleton during Dengue Virus Infection. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2010, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.C.; Bernstone, L.; Baskaran, D.; James, W. HIV-1 Infects Macrophages by Exploiting an Endocytic Route Dependent on Dynamin, Rac1 and Pak1. Virology 2011, 409, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, C.; Kardinal, C.; Wurzer, W.J.; Wolff, T.; Von Eichel-Streiber, C.; Pleschka, S.; Planz, O.; Ludwig, S. Rac1 and PAK1 Are Upstream of IKK-ε and TBK-1 in the Viral Activation of Interferon Regulatory Factor-3. FEBS Lett 2004, 567, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierkes, R.; Warnking, K.; Liedmann, S.; Seyer, R.; Ludwig, S.; Ehrhardt, C. The Rac1 Inhibitor NSC23766 Exerts Anti-Influenza Virus Properties by Affecting the Viral Polymerase Complex Activity. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Sheng, C.; Gu, X.; Liu, D.; Yao, C.; Gao, S.; Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Huang, W.; Fang, M. Suppression of Rac1 Signaling by Influenza A Virus NS1 Facilitates Viral Replication. Sci Rep 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitanio, J.S.; Wozniak, R.W. Host Cell Factors Necessary for Influenza A Infection: Meta-Analysis of Genome Wide Studies. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.B.; Dampier, W.; Tozeren, A.; Brown, J.R.; Magid-Slav, M. Identification of Common Biological Pathways and Drug Targets across Multiple Respiratory Viruses Based on Human Host Gene Expression Analysis. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard-Chapeau, E.A.; Li, S.; Ding, J.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhu, H.H.; Princen, F.; Fang, D.D.; Han, T.; Bailly-Maitre, B.; Poli, V.; et al. Ptpn11/Shp2 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Huang, X.; Tan, W.; Yu, D.; Du, Z.; Chang, J.; Wei, L.; Han, Y.; Wang, C.; Che, X.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer Risk Variant in LINC00673 Creates a MiR-1231 Binding Site and Interferes with PTPN11 Degradation. Nat Genet 2016, 48, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, L.; Bocchinfuso, G.; Flex, E.; Rossi, C.; Baldassarre, G.; Lissewski, C.; Pantaleoni, F.; Consoli, F.; Lepri, F.; Magliozzi, M.; et al. Structural, Functional, and Clinical Characterization of a Novel PTPN11 Mutation Cluster Underlying Noonan Syndrome. Hum Mutat 2017, 38, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiscott, J.; Alper, D.; Cohen, L.; Leblanc, J.F.; Sportza, L.; Wong, A.; Xanthoudakis, S. Induction of Human Interferon Gene Expression Is Associated with a Nuclear Factor That Interacts with the NF-Kappa B Site of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Enhancer. J Virol 1989, 63, 2557–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenardo, M.J.; Fan, C.M.; Maniatis, T.; Baltimore, D. The Involvement of NF-Kappa B in Beta-Interferon Gene Regulation Reveals Its Role as Widely Inducible Mediator of Signal Transduction. Cell 1989, 57, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, M.; Zheng, H.; Muster, T.; Palese, P.; Beg, A.A.; Garcı́a-Sastre, A. Influenza A Virus NS1 Protein Prevents Activation of NF-KappaB and Induction of Alpha/Beta Interferon. J Virol 2000, 74, 11566–11573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Laydon, J.T.; McDonnell, P.C.; Gallagher, T.F.; Kumar, S.; Green, D.; McNulty, D.; Blumenthal, M.J.; Keys, J.R.; Land Vatter, S.W.; et al. A Protein Kinase Involved in the Regulation of Inflammatory Cytokine Biosynthesis. Nature 1994, 372, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.C.W.; Cheung, C.-Y.; Law, A.H.Y.; Mok, C.K.P.; Peiris, M.; Lau, A.S.Y. P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Dependent Hyperinduction of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Expression in Response to Avian Influenza Virus H5N1. J Virol 2005, 79, 10147–10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Wong, C.K.; Chan, P.K.S.; Lun, S.W.M.; Lui, G.; Wong, B.; Hui, D.S.C.; Lam, C.W.K.; Cockram, C.S.; Choi, K.W.; et al. Hypercytokinemia and Hyperactivation of Phospho-P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Severe Human Influenza A Virus Infection. Clin Infect Dis 2007, 45, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, S.; Jibiki, I.; Asai, Y.; Gon, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Ichiwata, T.; Shimizu, K.; Hashimoto, S. Analysis of Gene Expression in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells upon Influenza Virus Infection and Regulation by P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase and c-Jun-N-Terminal Kinase. Respirology 2008, 13, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börgeling, Y.; Schmolke, M.; Viemann, D.; Nordhoff, C.; Roth, J.; Ludwig, S. Inhibition of P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Impairs Influenza Virus-Induced Primary and Secondary Host Gene Responses and Protects Mice from Lethal H5N1 Infection. J Biol Chem 2014, 289, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschner, L.S.; Stratakis, C.A. Structure of the Human Ubiquitin Fusion Gene Uba80 (RPS27a) and One of Its Pseudogenes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000, 270, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Tanaka, K. Regulatory Mechanisms Involved in the Control of Ubiquitin Homeostasis. J Biochem 2010, 147, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, T.; Chang, G.; Sun, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhou, H.; Liu, R.; Zheng, M.; et al. Host Interaction Analysis of PA-N155 and PA-N182 in Chicken Cells Reveals an Essential Role of UBA52 for Replication of H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus. Front Microbiol 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, S.; Gao, S.; Song, L.; Liu, P.; Huang, W. Influenza A Virus NS1 Induces G0/G1 Cell Cycle Arrest by Inhibiting the Expression and Activity of RhoA Protein. J Virol 2013, 87, 3039–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
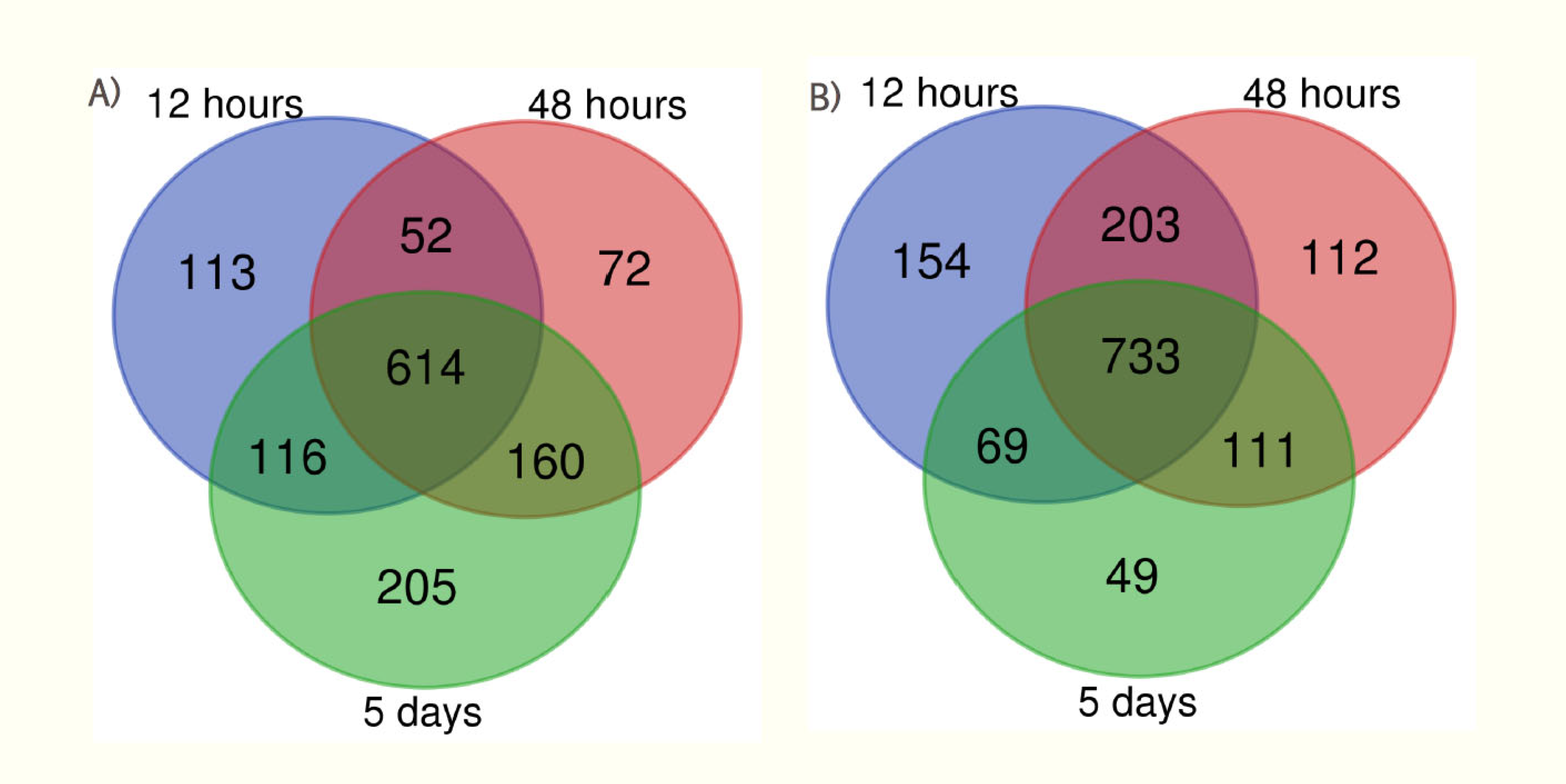
| Condition condition |
Upregulated proteins | Downregulated proteins | Upregulated proteins (>1.5 fold) | Downregulated Proteins (<1.5 fold) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 hr interval | 895 | 1159 | 128 | 225 |
| 48 hr interval | 898 | 1159 | 199 | 277 |
| 5 days interval | 1095 | 962 | 296 | 264 |
| Pathway | Hits | FDR |
|---|---|---|
| Focal adhesion | 179 | 3.20E-21 |
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 291 | 1.10E-20 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | 243 | 1.12E-17 |
| Cell cycle | 116 | 1.97E-17 |
| Endocytosis | 204 | 2.00E-16 |
| AMPK signaling pathway | 110 | 5.46E-15 |
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 179 | 1.36E-14 |
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | 130 | 3.91E-14 |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | 94 | 4.54E-14 |
| Chemokine signaling pathway | 159 | 3.77E-13 |
| Apoptosis | 119 | 8.99E-13 |
| Spliceosome | 117 | 1.91E-12 |
| Platelet activation | 109 | 4.49E-12 |
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | 117 | 4.00E-11 |
| mTOR signaling pathway | 128 | 8.53E-11 |
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | 64 | 1.68E-10 |
| Influenza A | 137 | 2.43E-10 |
| Jak-STAT signaling pathway | 132 | 1.20E-09 |
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | 134 | 1.32E-09 |
| Proteasome | 44 | 4.35E-09 |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 88 | 2.57E-08 |
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | 62 | 1.09E-07 |
| Metabolic pathways | 926 | 1.26E-07 |
| TNF signaling pathway | 91 | 1.26E-07 |
| Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 77 | 4.78E-07 |
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | 91 | 5.95E-07 |
| Pathway | Hits | P.Value |
|---|---|---|
| Jak-STAT signaling pathway | 5 | 0.0191 |
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | 5 | 0.0026 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | 14 | 5.84E-07 |
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 22 | 7.33E-13 |
| Focal adhesion | 34 | 2.84E-35 |
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 24 | 5.77E-20 |
| ErbB signaling pathway | 14 | 3.30E-14 |
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | 14 | 1.71E-12 |
| Ras signaling pathway | 16 | 3.65E-10 |
| Rap1 signaling pathway | 15 | 6.58E-10 |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | 10 | 3.29E-08 |
| Chemokine signaling pathway | 12 | 1.97E-07 |
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | 10 | 1.22E-06 |
| Tight junction | 9 | 3.13E-05 |
| Endocytosis | 8 | 0.00218 |
| Prolactin signaling pathway | 4 | 0.00439 |
| Proteins | Degree centrality | Betweenness centrality |
|---|---|---|
| AKT1 | 151 | 23549.86 |
| STAT3 | 138 | 20538.68 |
| JAK2 | 122 | 14684.79 |
| RAC1 | 117 | 9430.98 |
| STAT1 | 116 | 14916.66 |
| PTPN11 | 116 | 14221.68 |
| RPS27A | 113 | 11935.64 |
| UBA52 | 110 | 11175.27 |
| HSP90AA1 | 107 | 17096.24 |
| RHOA | 107 | 7556.94 |
| NFKB1 | 106 | 13320.84 |
| GRB2 | 103 | 6744.12 |
| MAPK1 | 100 | 8118.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





