Submitted:
07 April 2024
Posted:
08 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
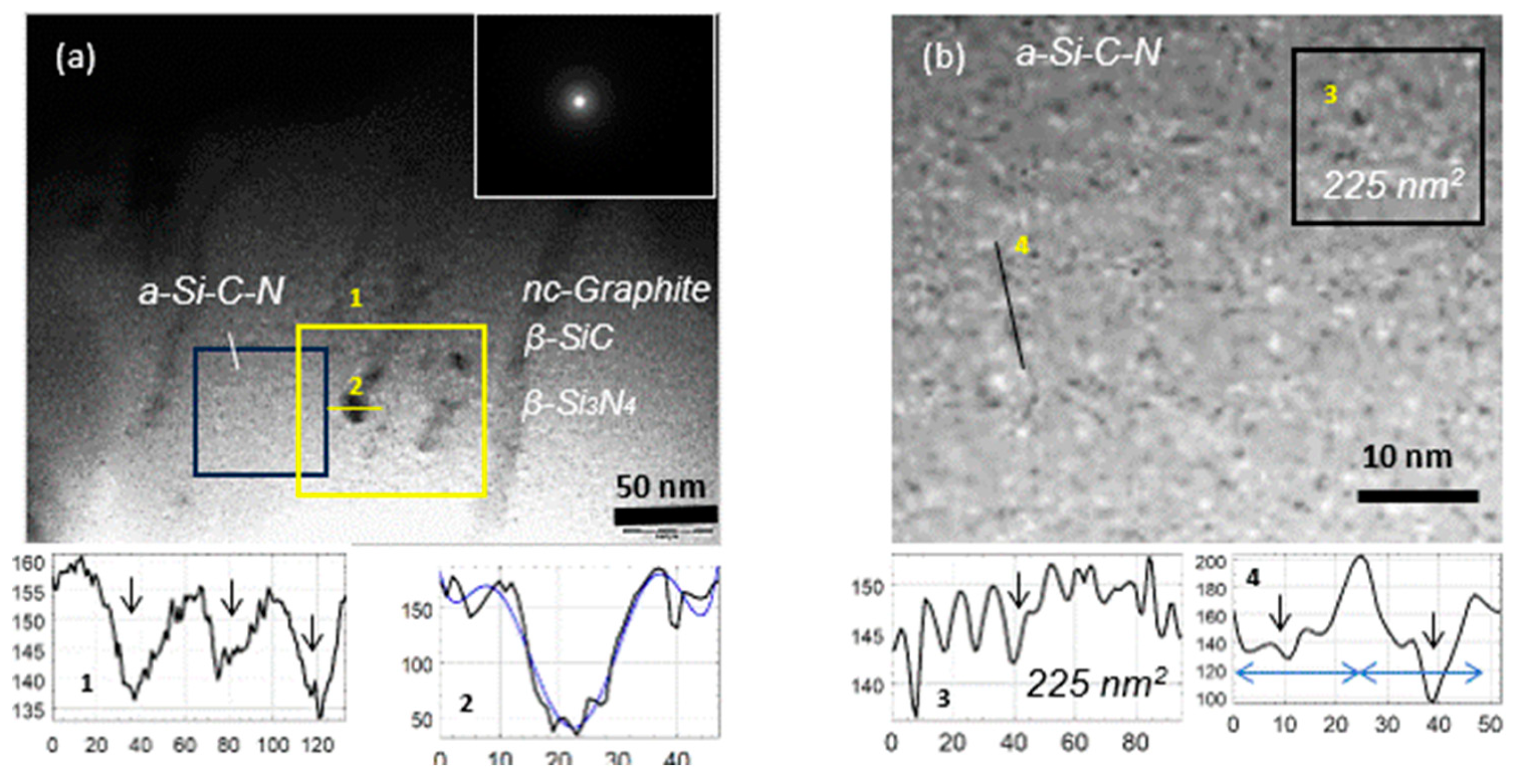
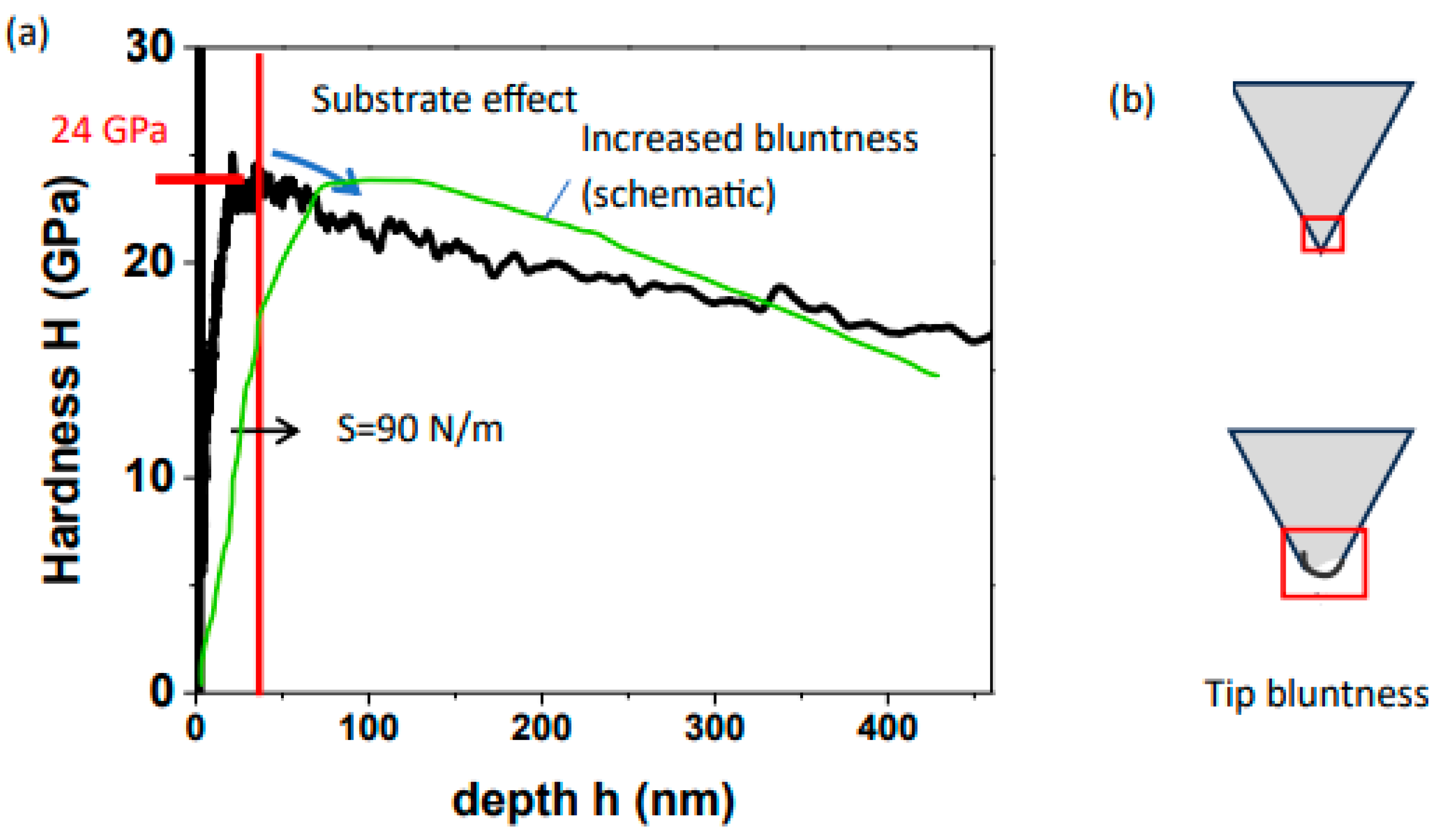
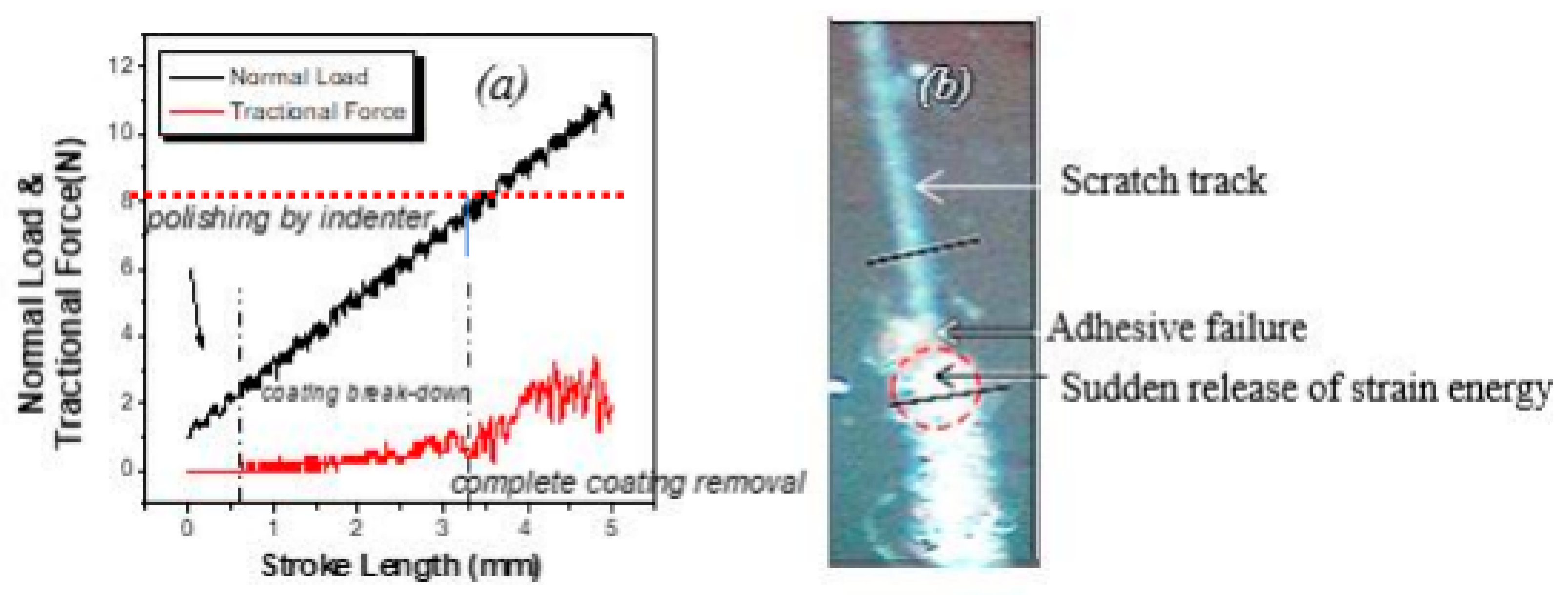
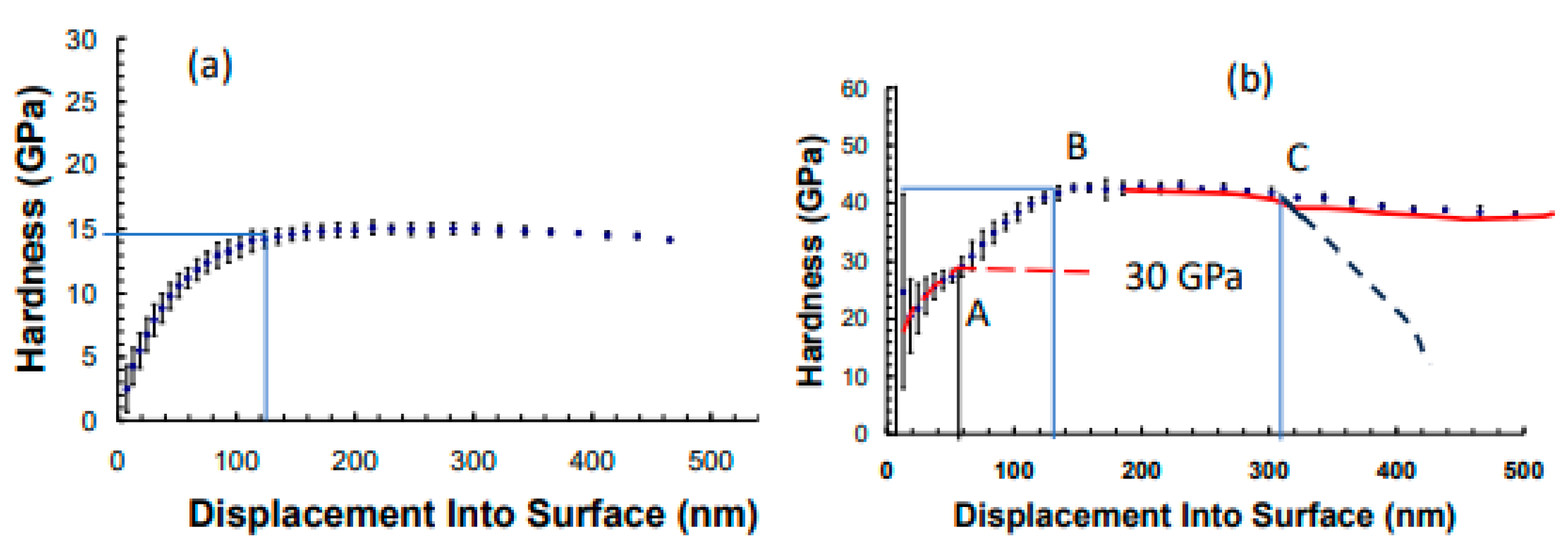
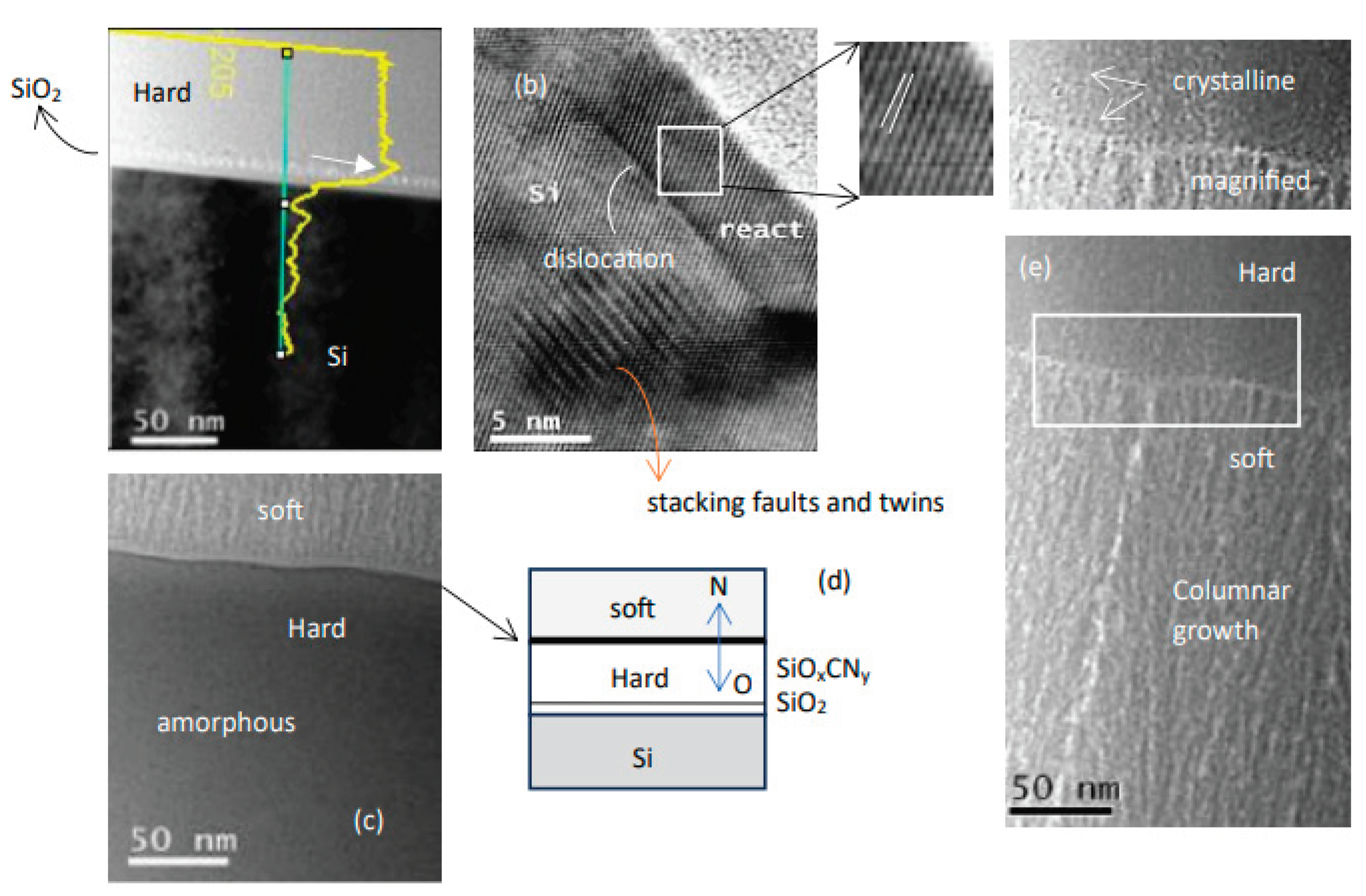
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
- The crystalline structure of the SiCN films regulated the formation of electrical conduction channels with ductile fracture and linear unloading.
- Tip bluntness causing the substrate effect to be obtained at higher depths of penetration
- When nitrogen was added to Ti-B-Si-C, Si-C-N instead of TiC or TiB2 formed, which resulted in a decrease in hardness. due to formation of alternate harder and softer films
- The oxide at the interfacial region is responsible for the amorphization of the hard films developed on the silicon whose relative concentration with nitrogen decreases as one moves further away from the substrate
References
- A. Karimzadeh et al Sci Rep 9, 15763 (2019).
- M. Wang, Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica 36(2), 327 (2023).
- Z. Hu Micro Nano Tech 6 165 (2017).
- Y. Sato, Nat Commun 11, 4177 (2020).
- W. C. Olver, G.M. Pharr J. Mater Res 7(6), 1564 (1992).
- A. C. Fischer Cripps, Nanoindentation, Springer (2004).
- X. Li, B. Bhushan Materials Characterization, 48(1) 11(2002).
- V. Maier-Kiener et al JOM 74, 2177 (2022).
- L.M. Oyen ed. Handbook of nanoindentation: with biological applications. CRC Press (2019).
- G. Wu et al Sci Rep 10.1 18784 (2020).
- B.Cantor et al Mater Sci Eng: A, 375–377, 2004, 213(2004).
- B.Cantor, Ann. Chim. -Sci. Mater. 2007, 32, 245(2007).
- E.P. George et al Nat Rev Mater 4 (2019) 515–534.
- W. Li, et al Prog Mater. Sc. 118 (2021) 100777.
- S. Sinha et al Sci Rep 9, 6639 (2019).
- X. Jin et al Ceram Int. 48 (23A) 135445(2022).
- G. Laplanche et al, J. Alloys Compd. 647, 548 (2015).
- B. Gludovat et al. JOM 67, 2262 (2015).
- A. Gali et al George, Intermetallic 39, 74 (2013).
- M. Mirkhalaf et al Sci Rep 11, 6951(2021).
- Shah, S. Ret al. Acta Mater. 2002, 50(16), 4093–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, Ret al. Nature 1995, 374(6522), 526–528.
- Ren, Z. Materials 2021, 14, 614.
- Barrios, EMol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2020, 5(10), 1606–1641.
- Lin, X. , Ceram Int. 2023, 49 (14A), 23851–23863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T. B. Rare Metals, 2023, 42(5), 1635-1644.
- Xue, J. , J Al Com, 2023, 931, 167499.
- Han, D. et al J Mater Chem C, 2023, 11(18), 6130-6137.
- Wu, C. , et al Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 463, 142518.
- Chen, G. Surf Coat Technol, 2023,464, 129536.
- Li, L. Polymers, 2023 15(15), 3319.
- Cui, Z. , Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2023, 350, 114144.
- Ma, Ket al. IEEE 73rd (ECTC) conference 2023 1110-1114.
- Stiharu, I. , Micromachines, 14(5), 925.
- Xia, X et al Materials, 16(15), 5318.(2023).
- Choi, H. J et al. J. Mater Sci, 58(8), 3790-3801. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.et al Ceramics International, 49(2), 2296(2023.
- Sulyaeva, V. S. Materials, 16(4), 1467.(2023).
- Tomastik, J.; et al Sci. Rep. 2018, 8 (1).
- Bernauer, J Adv Eng Mater. 2024, 10.1002/adem.202301864.
- Bernauer, J Adv Eng Mater. 10.1002/adem.202301820 (2024).
- Thor, Nathalie et al. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2023 43 (4) 1417–1431.
- Zhu, Runqiu et al J Am Ceram Soc10.1111/jace.19715.
- Wang, Beibei et al J. Mat Sci: Mater in Elect. 35. 10.1007/s10854-024-11941-w.
- Ye, Xiao-et al. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 25. 10.1039/D3CP03236A. 2023.
- Chiang, Chao-Ching Materials. 16. 5751. 2023.
- Qiang Yan, et al J Eur Ceram Soc 2023, 43 (16) 2023, 7373-7380.
- Yan, Yuangao et al J Am Ceram Soc. 2023, 106(11), 6951-6961.
- Anand, J Am Ceram Soc.2023 107(3), 1657-1668.
- Chery, Emmanuel et al. IEEE Tran on Device and Mater Rel 2023 23, 615–622.
- Ramlow, Heloisa et al. Open Ceramics. 2023 14. 10 0351.
- H. Ramlow J Mater Sci: Mater in Electronics. 34.2023, (22) 1631.
- Ramlow, Heloisa et al J. Europ Ceram Soc. 2024 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2024.01.035.
- d'Eril, Marco et al Batteries & Supercaps. 2023 6 (3) e202200491.
- Li, Qiang et al. J Mater Res Technol. 2021 15, 460–467.
- Jiang, Minming et alCeram Int. 2021,48 (2) 2112-2117.
- Das, S et al. Silicon 2022, 14, 9643–9657.
- Haofan, Shi et al . J. Mater Sci: Mater Elect. 2023, 34. 1401.
- Matar, Samir et al. Silicon. 2022 15. 511–520.
- Bhattacharyya, AS, et al, Chem Phys Imp 2024, 8,100454(2024).
- Bhattacharyya, A. S et al Eur. Coat. J. 2009, 3, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, A. S et al . J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41(10), 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, AS et al J. Vac. Sci. Technol A 2010, 28, 505(2010).
- Wu, C. et al. Small, 2023, 19(5), 2206628.
- Lida Xu, Xiong Zhou, Fuxin Zhao, Yanzhang Fu, Lantian Tang, Yingjun Zeng, Guochun Chen, Chao Wu, Lingyun Wang, Qinnan Chen, Kai Yang, Daoheng Sun, Zhenyin Hai, Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,658,2024,913-922.
- S. Veprek Thin Solid Films, 317, 449(1998).
- M. Char et al Adv. Eng. Mater. 24, 2100679 (2022).
- A.S. Bhattacharyya, et al Next Materials 3, 2024, 100038.
- A.S. Bhattacharyya, Chem Phy Imp 8 100551(2024).
- A. S. Bhattacharyya, Fatigue & Frac Eng Mater & Str (2024) https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.14198. [CrossRef]
- Ritambhara Dash, A. S. Bhattacharyya Fatigue & Fracture of Eng Mater & Struc. (2023) 46 (7) 2714-2719.
- R. Dash, K. Bhattacharyya, A. S. Bhattacharyya., Fatigue & Fracture of Eng Mater & Struct (2023) 46: 1641-1645.
- R. Dash, R. P. Kumar, K. Bhattacharyya, A. S. Bhattacharyya, IOP- Eng Res Exp, 2022 4 045012.
- R. Dash, K. Bhattacharyya, A S. Bhattacharyya., Nano. Prec. Eng. 6, Eng. 6, 042001 (2023).
- R. Dash, K. Bhattacharyya, A.S. Bhattacharyya. Eng Fail Anal (2023) 150, 107353.
- A S Bhattacharyya et al Res Surf Int, 2024, 100196.
- A. S. Bhattacharyya, R. Praveen Kumar, V. Ranjan, Gaurav Kumar, Current Smart Materials 2(1): 39 – 43, 2017.
- T. Sinani and G. Miskovic, 2022 IEEE 24th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference (EPTC), Singapore, Singapore, 2022, pp.452‐458.
- R. Dash, K. Bhattacharyya, A S. Bhattacharyya, Int J. Ref Met & Hard Mater, 116, 2023 106373.
- S. K. Mishra, D. Verma, S. Bysakh, L. C. Pathak J. Nanomat, 2013, 949416.
| S. No | Composites/Coatings | Properties | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiC/(Hf,Ta)C(N)/(B)C; SiHfTa(B)CN coatings; |
Exceptional high hardness and thermal cycle stability; crack-free; amorphous, good adhesion | [40,41] | |
| Si(HfxTa1-x)(C)N | residual carbon triggered decomposition reaction, resulting in the formation of Transition Metal Carbides, gaseous nitrogen and SiC, tetragonal hafnium oxide (t-HfO2) within the SiCN matrix-improved phase stability and oxidation resistance | [42,49] | |
| Ni–Fe–C/HfO2 /SiCN; SiCN/MWCNT |
metal-organic framework (Ni–Fe–MOF) and hafnium dioxide (HfO2) nanoparticles; improved brittleness and EM wave absorption; MWCNT-COOH increased the interfacial polarization loss and the conduction loss, improving microwave absorbing performance. | [43,44] | |
| Penta-SiCN monolayer; SiCN embedded carbon (SiCN–C); Porous SiCN(O) | low diffusion energy barrier and robust wettability useful in anode material for Li-ion batteries; stable cycling with a charge capacity, Reversible Na Plating/stripping Reaction for sodium metal batteries | [45,51,54] | |
| SiCN-coated implants | Hydrophobicity and Antibacterial Properties, replacing Ti implants to avoid Peri-implantitis | [46], | |
| PDC SiCN | Free carbon enriched interface, high conductivity, strain gauge | [64 | |
| polymer-derived SiBCN; PDCs-SiCN(BN) |
High-temperature sensing due to good thermomechanical properties, hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) with weakened polarization relaxation behavior, reduced porosity, and resistance to crack expansion causes low dielectric loss and high-temperature resistance | [47,48] | |
| SiCN–SiCN wafer-to-wafer hybrid-bonding | next generation of 3D Systems-on-Chip with interconnect densities above 10 mm-2 | [50] | |
| C/SiCN and SiCN(O) nanofiber, nonwoven | tunable electrical conductivity, EM reflection shielding in the 5G C-band, and thermo-oxidation resistance |
[52,53] | |
| Sputtered SiCN coatings | Photoelectric properties, SiCN-based MEMS pressure sensors. | [55,56] | |
| CVD-grown SiCN coatings | Increased intensity of Si-N-Si, decreased crystallite size with temperature along with increased hardness and modulus | [57] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





