Submitted:
31 March 2024
Posted:
01 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Influential Parameters
2.1. Interplay of Composition, and Preparation
2.2. Bimodal Mesoporous Structure and Surface Oxygen Vacancies
2.3. Si/Al Ratio
2.4. Porosity, Thermal Stability, and Structural Integrity
2.5. Electrical and Plasma Interactions
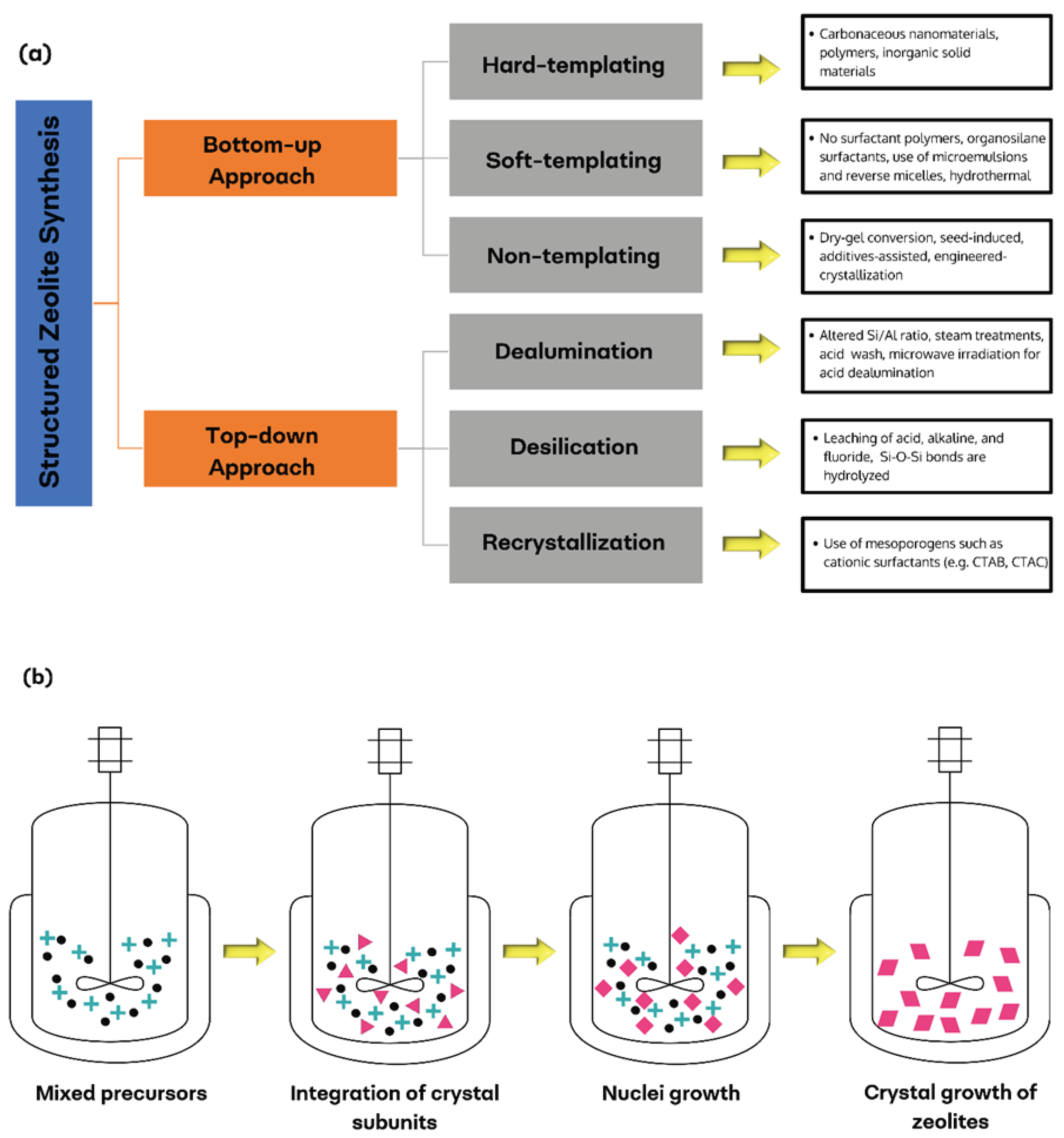
3. Synthesis Methods
3.1. Bottom-Up Approach
3.2. Top-Down Approach
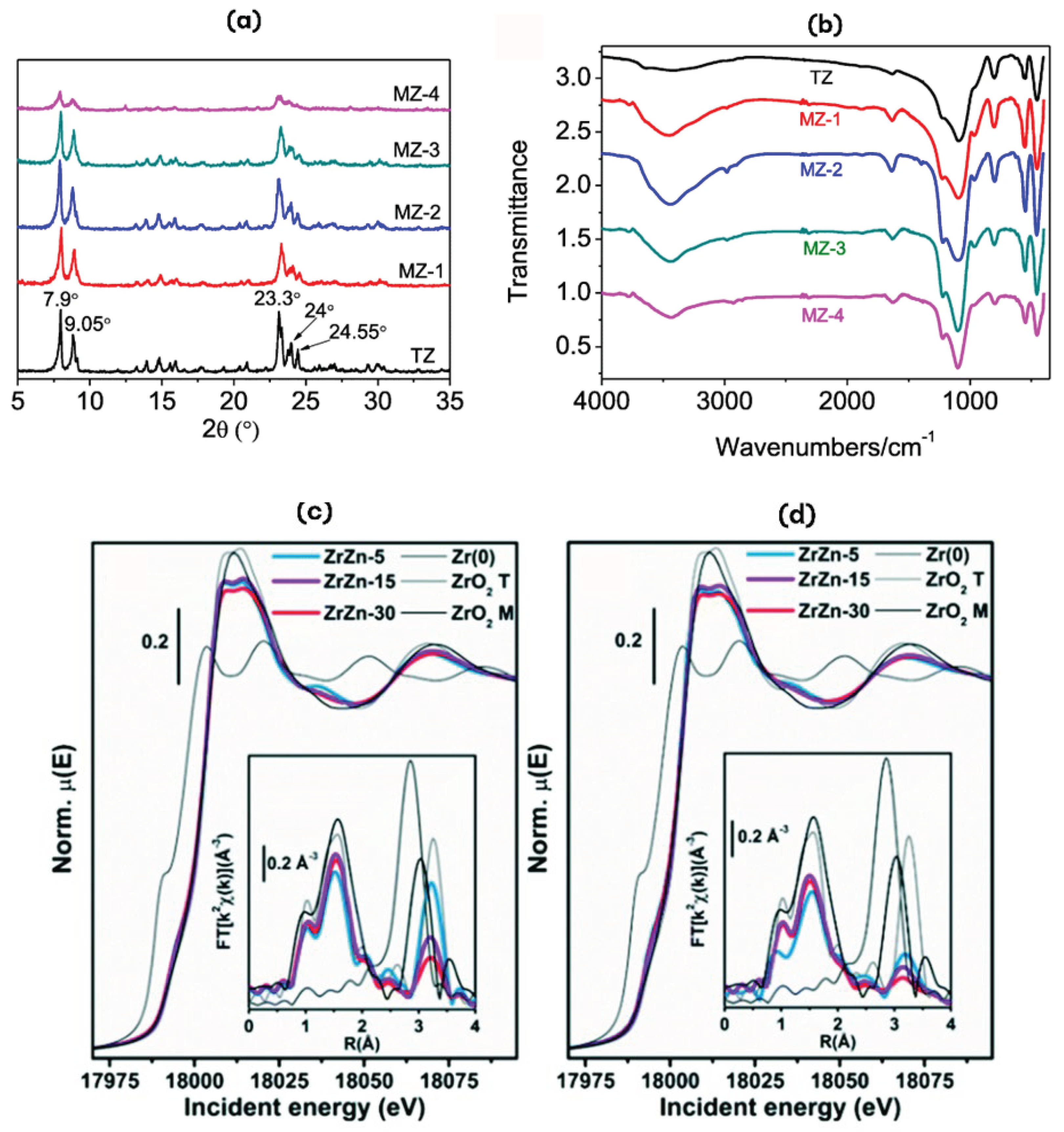
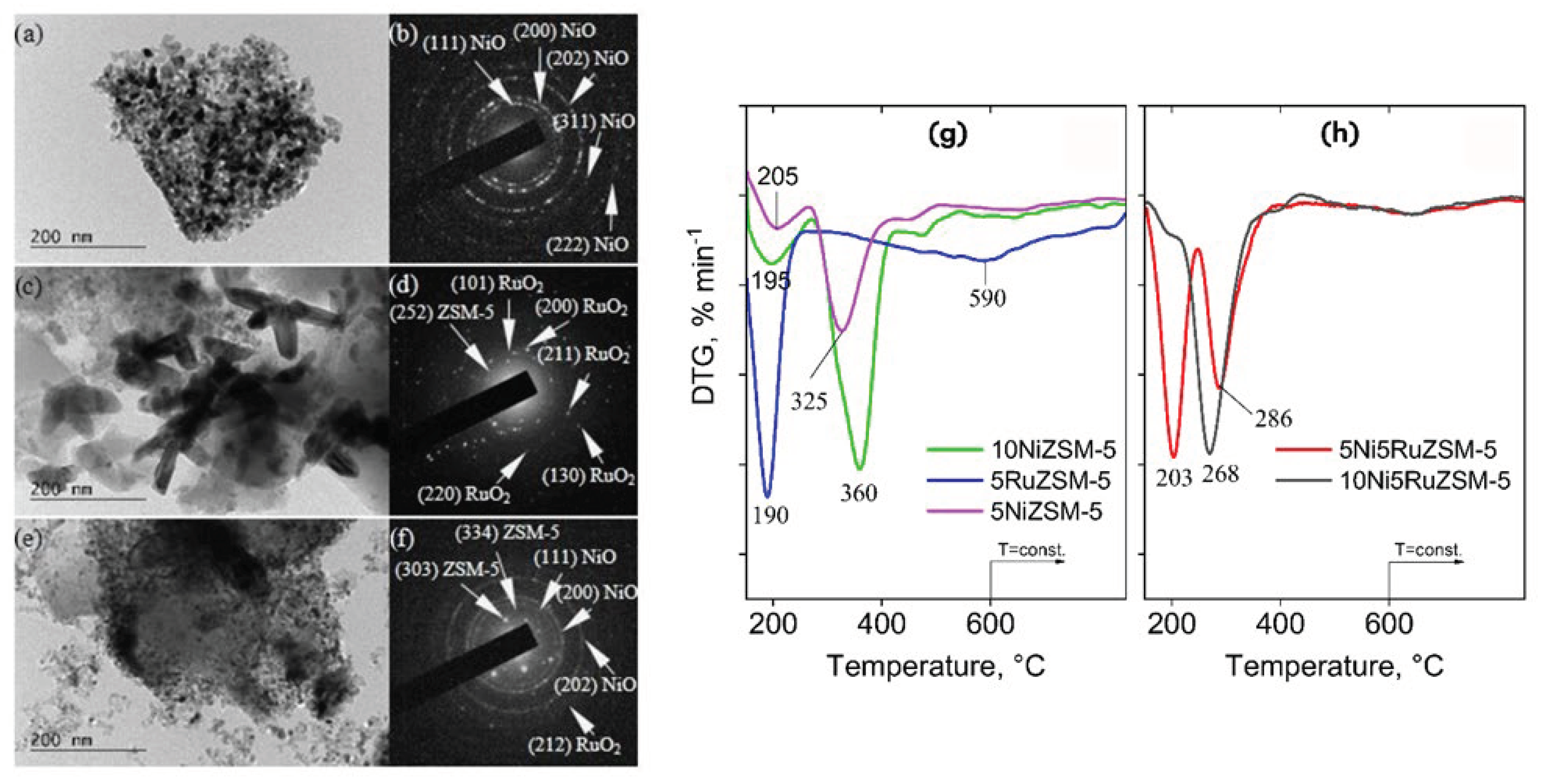
4. Characterization Techniques
5. Conclusion
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rafiee, A.; Rajab Khalilpour, K.; Milani, D.; Panahi, M. Trends in CO2 conversion and utilization: A review from process systems perspective. J Environ Chem Eng 2018, 6, 5771–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, M.; Styring, P. Perspectives and visions on CO2 capture and utilisation. Faraday Discuss 2015, 183, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Tan, C.-S. A Review: CO2 Utilization. Aerosol Air Qual Res 2014, 14, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezam, I.; Zhou, W.; Gusmão, G.S.; Realff, M.J.; Wang, Y.; Medford, A.J.; et al. Direct aromatization of CO2 via combined CO2 hydrogenation and zeolite-based acid catalysis. Journal of CO2 Utilization 2021, 45, 101405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, A.; Gong, X.; Caglayan, M.; Nastase, S.-A.F.; Abou-Hamad, E.; Gevers, L.; et al. Selectivity descriptors for the direct hydrogenation of CO2 to hydrocarbons during zeolite-mediated bifunctional catalysis. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murciano, R.; Serra, J.M.; Martínez, A. Direct hydrogenation of CO2 to aromatics via Fischer-Tropsch route over tandem K-Fe/Al2O3+H-ZSM-5 catalysts: Influence of zeolite properties. Catal Today 2023, 114404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Sun, X. Evaluation of zeolites synthesized from fly ash as potential adsorbents for wastewater containing heavy metals. Journal of Environmental Sciences 2009, 21, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaningtyas, G.S.A.; Krisnandi, Y.K.; Ekananda, R. Synthesis and characterization of NaY zeolite from Bayat natural zeolite: Effect of pH on synthesis. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 2019, 496, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitar, G.; Bogdanov, B.; Angelova, K.; Markovska, I.; Hristov, Y. SYNTHETHIC ZEOLITES-STRUCTURE, CLASIFICATION, CURRENT TRENDS IN ZEOLITE SYNTHESIS, n.d.
- Ruiz, A.Z.; Brühwiler, D.; Ban, T.; Calzaferri, G. Synthesis of Zeolite L. Tuning Size and Morphology. Monatshefte Für Chemie - Chemical Monthly 2005, 136, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, N.; Yu, J. Advances in Catalytic Applications of Zeolite-Supported Metal Catalysts. Advanced Materials 2021, 33, 2104442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, Y.T.; Lee, J.; Kumar, P.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, S.S. Natural zeolite and its application in concrete composite production. Compos B Eng 2019, 165, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, E.; Salvi, L.; Paoli, F.; Fucile, M.; Masciandaro, G.; Manzi, D.; et al. Application of Zeolites in Agriculture and Other Potential Uses: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacakova, L.; Vandrovcova, M.; Kopova, I.; Jirka, I. Applications of zeolites in biotechnology and medicine – a review. Biomater Sci 2018, 6, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallo, D. Applications of Natural Zeolites in Water and Wastewater Treatment. Rev Mineral Geochem 2001, 45, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruijtier-Pölloth, C. The safety of synthetic zeolites used in detergents. Arch Toxicol 2009, 83, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittcoff, H.A.; Reuben, B.G.; Plotkin, J.S. Industrial organic chemicals; John Wiley & Sons, 2012.
- Hölderich, W.; Hesse, M.; Näumann, F. Zeolites: Catalysts for Organic Syntheses. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English 1988, 27, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.; Müller, U. Catalytic Applications of Zeolites in Chemical Industry. Top Catal 2009, 52, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, M.; Oykova, M.; Dimitrov, M.; Karashanova, D.; Kovacheva, D.; Atanasova, G.; et al. CO2 Hydrogenation to Renewable Methane on Ni/Ru Modified ZSM-5 Zeolites: The Role of the Preparation Procedure. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, M.; Chang, X.; Hao, Z.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; et al. Hollow structured Cu@ZrO2 derived from Zr-MOF for selective hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol. Journal of Energy Chemistry 2022, 71, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveyeva, A.N.; Omarov, S.O.; Gavrilova, M.A.; Sladkovskiy, D.A.; Murzin, D.Y. CeFeO3–CeO2–Fe2O3 Systems: Synthesis by Solution Combustion Method and Catalytic Performance in CO2 Hydrogenation. Materials 2022, 15, 7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, M.K.; Wong, Y.J.; Mohamed, A.R. The effect of process parameters on catalytic direct CO 2 hydrogenation to methanol. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 2021, 1195, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paviotti, M.A.; Faroldi, B.M.; Cornaglia, L.M. Ni-based catalyst over rice husk-derived silica for the CO2 methanation reaction: Effect of Ru addition. J Environ Chem Eng 2021, 9, 105173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhao, S.; Xie, F.; Chen, S.; Xie, H. Construction of surface active centers on the mesoporous Co/CeO2-δ catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 28980–28997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Bian, B.; Fan, J.; Yang, J. Cobalt doped Ni based ordered mesoporous catalysts for CO2 methanation with enhanced catalytic performance. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 4893–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Liu, H.; Xing, Y.; Xu, S.; Xie, H.; Xiong, K. CO2 hydrogenation to methane over mesoporous Co/SiO2 catalysts: Effect of structure. Journal of CO2 Utilization 2018, 26, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Liang, J.; et al. Boosting Methanol-Mediated CO 2 Hydrogenation into Aromatics by Synergistically Tailoring Oxygen Vacancy and Acid Site Properties of Multifunctional Catalyst. Chemistry – A European Journal. [CrossRef]
- Kosinov, N.; Auffret, C.; Borghuis, G.J.; Sripathi, V.G.P.; Hensen, E.J.M. Influence of the Si/Al ratio on the separation properties of SSZ-13 zeolite membranes. J Memb Sci 2015, 484, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacariza, C.; Karam, L.; El Hassan, N.; Lopes, J.M.; Henriques, C. Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane over Nickel-Supported Zeolites: A Screening Study. Processes 2022, 10, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgschulte, A.; Callini, E.; Stadie, N.; Arroyo, Y.; Rossell, M.D.; Erni, R.; et al. Manipulating the reaction path of the CO 2 hydrogenation reaction in molecular sieves. Catal Sci Technol 2015, 5, 4613–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Highly Dispersed Ni Catalyst on Metal–Organic Framework-Derived Porous Hydrous Zirconia for CO 2 Methanation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020, 12, 17436–17442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Z.; Guo, J.; Wu, Z.; et al. Facile synthesis of hierarchical SAPO-56 zeolite as a highly efficient catalyst for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol. Fuel 2024, 361, 130663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T. Crystal phase effects on the structure and performance of ruthenium nanoparticles for CO 2 hydrogenation. Catal Sci Technol 2014, 4, 2058–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.-G.; Li, Y.-T.; Yu, L.; Zhang, H.; Hu, T.-L. Zeolite-Encapsulated Ultrasmall Cu/ZnOxNanoparticles for the Hydrogenation of CO 2 to Methanol. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021, 13, 18693–18703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliz, M.Q.; Polaert, I.; Ledoux, A.; Fernandez, C.; Azzolina-Jury, F. Influence of ionic conductivity and dielectric constant of the catalyst on DBD plasma-assisted CO 2 hydrogenation into methanol. J Phys D Appl Phys 2021, 54, 334003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henckel, D.; Saha, P.; Intia, F.; Taylor, A.K.; Baez-Cotto, C.; Hu, L.; et al. Elucidation of Critical Catalyst Layer Phenomena toward High Production Rates for the Electrochemical Conversion of CO to Ethylene. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2024, 16, 3243–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashford, B.; Poh, C.-K.; Ostrikov, K.; Chen, L.; Tu, X. Plasma-catalytic CO2 hydrogenation to ethane in a dielectric barrier discharge reactor. Journal of CO2 Utilization 2022, 57, 101882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Fernandez, S.; Converse, E.S.; Kobaslija, S. Exploring the impact of synthetic strategies on catalytic cracking in hierarchical beta zeolites via hydrothermal desilication and organosilane-templated synthesis. Catal Sci Technol 2020, 10, 4602–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Wu, Z.; Yip, A. Advances in the Green Synthesis of Microporous and Hierarchical Zeolites: A Short Review. Catalysts 2019, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Cho, H.J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Fan, W. Fluoride-free synthesis of a Sn-BEA catalyst by dry gel conversion. Green Chemistry 2015, 17, 2943–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Lu, J.; Dai, C.; Subhan, F.; et al. One-pot green synthesis of Fe-ZSM-5 zeolite containing framework heteroatoms via dry gel conversion for enhanced propylene selectivity of catalytic cracking catalyst. J Mater Sci 2021, 56, 18050–18060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Samrout, O.; Karam, L.; Jabbour, K.; Massiani, P.; Launay, F.; El Hassan, N. Investigation of new routes for the preparation of mesoporous calcium oxide supported nickel materials used as catalysts for the methane dry reforming reaction. Catal Sci Technol 2020, 10, 6910–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbe, T.; Temesgen, S.; Bitew, M. A Short Review on Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of Zeolites. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering 2021, 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurdin, S.; Yunus, R.M.; Azoddein, A.A.M.; Khairuddin, S.A.; Sukri, H.A.M.; Wooi, C.C. Green Palm Oil Mill Fuel Ash Zeolites (G-POMFAZ) Using Hydrothermal-Alkaline-Ultrasound Technique (HAUT). International Conference on Knowledge Transfer, Putrajaya: 2015.
- Zheng, X.; Shen, G.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Dunphy, D.; Hasan, T.; et al. Bio-inspired Murray materials for mass transfer and activity. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 14921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Sodalite on Alkali-Activated Coal Fly Ash for Removal of Lead Ions. Procedia Environ Sci 2016, 31, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa-Serra, J.F.; Cerdá-Moreno, C.; Chica, A. Zeolite-Supported Ni Catalysts for CO2 Methanation: Effect of Zeolite Structure and Si/Al Ratio. Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourdon, A. On-Surface Covalent Coupling in Ultrahigh Vacuum. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2008, 47, 6950–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenten, I.G.; Dharmawijaya, P.T.; Aryanti, P.T.P.; Mukti, R.R.; Khoiruddin, K. LTA zeolite membranes: Current progress and challenges in pervaporation. RSC Adv 2017, 7, 29520–29539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debecker, D.P.; Le Bras, S.; Boissière, C.; Chaumonnot, A.; Sanchez, C. Aerosol processing: A wind of innovation in the field of advanced heterogeneous catalysts. Chem Soc Rev 2018, 47, 4112–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Martinez, J.; Xiao, C.; Cychosz, K.A.; Li, K.; Wan, W.; Zou, X.; et al. Evidence of Intracrystalline Mesostructured Porosity in Zeolites by Advanced Gas Sorption, Electron Tomography and Rotation Electron Diffraction. ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 3110–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramírez, J.; Christensen, C.H.; Egeblad, K.; Christensen, C.H.; Groen, J.C. Hierarchical zeolites: Enhanced utilisation of microporous crystals in catalysis by advances in materials design. Chem Soc Rev 2008, 37, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, N.; Guo, G.; Chen, X.; Yu, J. Synthesis of tri-level hierarchical SAPO-34 zeolite with intracrystalline micro–meso–macroporosity showing superior MTO performance. J Mater Chem A Mater 2015, 3, 19783–19789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yu, C.; Yu, L.; Miao, S.; Zou, M.; Jin, C.; et al. Bridging Dealumination and Desilication for the Synthesis of Hierarchical MFI Zeolites. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2017, 56, 12553–12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.S.; Lima, R.B.; Pergher, S.B.C.; Caldeira, V.P.S. Hierarchical Zeolite Synthesis by Alkaline Treatment: Advantages and Applications. Catalysts 2023, 13, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.G.H.; Nguyen, T.T.P.; Bui, T.L.; Dang, C.V.; Nguyen, L.Q.T.; Nguyen, T.G.H.; et al. Mesostructured Zeolites Prepared by One-Pot Top-Down Synthesis Route for Carbon Dioxide Adsorption. Chemical Engineering Transactions 2021, 83, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Um, W. Top-Down Synthesis of NaP Zeolite from Natural Zeolite for the Higher Removal Efficiency of Cs, Sr, and Ni. Minerals 2021, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konnov, S.V.; Dubray, F.; Clatworthy, E.B.; Kouvatas, C.; Gilson, J.; Dath, J.; et al. Novel Strategy for the Synthesis of Ultra-Stable Single-Site Mo-ZSM-5 Zeolite Nanocrystals. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2020, 59, 19553–19560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, P.S.; Dementiev, K.I.; Palankoev, T.A.; Kalmykova, D.S.; Malyavin, V.V.; Sagaradze, A.D.; et al. Synthesis of Highly Active Nanozeolites Using Methods of Mechanical Milling, Recrystallization, and Dealumination (A Review). Petroleum Chemistry 2021, 61, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airi, A.; Signorile, M.; Bonino, F.; Quagliotto, P.; Bordiga, S.; Martens, J.A.; et al. Insights on a Hierarchical MFI Zeolite: A Combined Spectroscopic and Catalytic Approach for Exploring the Multilevel Porous System Down to the Active Sites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021, 13, 49114–49127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapsens, P.Y.; Mondelli, C.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Design of Lewis-acid centres in zeolitic matrices for the conversion of renewables. Chem Soc Rev 2015, 44, 7025–7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magyarová, Z.; Králik, M.; Soták, T. Utilization of zeolite catalysts in biomass exploitation: A minireview. Monatshefte Für Chemie - Chemical Monthly 2023, 154, 815–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverett, J.; Daiyan, R.; Gong, L.; Iputera, K.; Tong, Z.; Qu, J.; et al. Designing Undercoordinated Ni–Nxand Fe–Nxon Holey Graphene for Electrochemical CO 2 Conversion to Syngas. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12006–12018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosari, M.; Anjum, U.; Xi, S.; Lim, A.M.H.; Seayad, A.M.; Raj, E.A.J.; et al. Revamping SiO 2 Spheres by Core–Shell Porosity Endowment to Construct a Mazelike Nanoreactor for Enhanced Catalysis in CO 2 Hydrogenation to Methanol. Adv Funct Mater 2021, 31, 2102896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Meng, Y.; Han, W.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Z. Morphology effects on surface chemical properties and lattice defects of Cu/CeO2 catalysts applied for low-temperature CO oxidation. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 12056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Mehta, S.K. Metallomicelle templated transition metal nanostructures: Synthesis, characterization, DFT study and catalytic activity. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2017, 19, 18372–18382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gómez, R.; Cusinato, L.; Bijani, C.; Coppel, Y.; Lecante, P.; Amiens, C.; et al. Carboxylic acid-capped ruthenium nanoparticles: Experimental and theoretical case study with ethanoic acid. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 9392–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, T.M.; Shaaban, S.M.; Ragab, E.M.; Mir, A. Photo-Catalytic Activity Improvement for Organic Pollutant Removal in Wastewater using Zinc Oxide Quantum Dots: An Experimental and Modeling Study. Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research 2023, 13, 12138–12144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountoupi, E.; Barrios, A.J.; Chen, Z.; Müller, C.R.; Ordomsky, V.V.; Comas-Vives, A.; et al. The Impact of Oxygen Surface Coverage and Carbidic Carbon on the Activity and Selectivity of Two-Dimensional Molybdenum Carbide (2D-Mo 2 C) in Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. ACS Catal 2024, 14, 1834–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, D.; Kizilkaya, A.C. Atomic-Scale Insights into Carbon Dioxide Hydrogenation over Bimetallic Iron–Cobalt Catalysts: A Density Functional Theory Study. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.-J.; Park, S.-J. H2O2/steam activation as an eco-friendly and efficient top-down approach to enhancing porosity on carbonaceous materials: The effect of inevitable oxygen functionalities on CO 2 capture. Green Chemistry 2018, 20, 5224–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticali, P.; Salusso, D.; Ahmad, R.; Ahoba-Sam, C.; Ramirez, A.; Shterk, G.; et al. CO 2 hydrogenation to methanol and hydrocarbons over bifunctional Zn-doped ZrO 2 /zeolite catalysts. Catal Sci Technol 2021, 11, 1249–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Gao, Z.; Ji, X.; Li, D.; Deng, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. Boosting CO2 hydrogenation to methane over Ni-based ETS-10 zeolite catalyst. Front Chem 2022, 10, 1041843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacariza, M.C.; Graça, I.; Lopes, J.M.; Henriques, C. Ni-Ce/Zeolites for CO 2 Hydrogenation to CH 4 : Effect of the Metal Incorporation Order. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 2773–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, S.; Li, D.; Okazaki, M.; Kinoshita, H.; Nishijima, M.; Yamauchi, N.; et al. Influence of Si/Al ratio of MOR type zeolites for bifunctional catalysts specific to the one-pass synthesis of lower olefins via CO2 hydrogenation. Catal Today, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iltsiou, D.; Mielby, J.; Kegnæs, S. Direct Conversion of CO 2 into Alcohols Using Cu-Based Zeolite Catalysts. Chempluschem 2024, 89, e202300313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, R.; Li, D.; Okazaki, M.; Kinoshita, H.; Ochiai, N.; Yamauchi, N.; et al. Precise tuning of the properties of MOR-type zeolite nanoparticles to improve lower olefins selectivity in composite catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation. Journal of CO2 Utilization 2023, 72, 102491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Goodarzi, F.; Mu, Y.; Chansai, S.; Mielby, J.J.; Mao, B.; et al. Effect of metal dispersion and support structure of Ni/silicalite-1 catalysts on non-thermal plasma (NTP) activated CO2 hydrogenation. Appl Catal B 2020, 272, 119013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yao, R.; Ge, Q.; Xu, D.; Fang, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Precisely regulating Brønsted acid sites to promote the synthesis of light aromatics via CO2 hydrogenation. Appl Catal B 2021, 283, 119648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Chen, W.; Dang, P.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Hierarchical ZSM-5 Zeolites with Outstanding Mesoporosity and Excellent Catalytic Properties. Nanoscale Res Lett 2018, 13, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzolina-Jury, F.; Thibault-Starzyk, F. Mechanism of Low Pressure Plasma-Assisted CO2 Hydrogenation Over Ni-USY by Microsecond Time-resolved FTIR Spectroscopy. Top Catal 2017, 60, 1709–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hurtado, E.; Rodríguez-Fernández, A.; Moliner, M.; Martínez, C. CO2 hydrogenation using bifunctional catalysts based on K-promoted iron oxide and zeolite: Influence of the zeolite structure and crystal size. Catal Sci Technol 2020, 10, 5648–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; He, R.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Q.; et al. Highly Selective Transformation of CO2 + H2 into Para-Xylene via a Bifunctional Catalyst Composed of Cr2O3 and Twin-Structured ZSM-5 Zeolite. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Shi, B.; et al. Operando Spectroscopic Study of Dynamic Structure of Iron Oxide Catalysts during CO2 Hydrogenation. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, S.; Cepollaro, E.M.; Lisi, L.; Fasolin, S.; Musiani, M.; Vázquez-Gómez, L. Ru/Ce/Ni Metal Foams as Structured Catalysts for the Methanation of CO2. Catalysts 2020, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, T.P.; Morales-Vidal, J.; Giannakakis, G.; Mondelli, C.; Eliasson, H.; Erni, R.; et al. Reaction-Induced Metal-Metal Oxide Interactions in Pd-In 2 O 3 /ZrO 2 Catalysts Drive Selective and Stable CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2023, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Han, H.; Hu, C.; Ye, C.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Fabrication of Transition Metal (Mn, Co, Ni, Cu)-Embedded Faveolate ZnFe2O4 Spinel Structure with Robust CO 2 Hydrogenation into Value-added C2 + Hydrocarbons. ChemCatChem 2023, 15, e202201403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Duan, H.; Wang, R.; Zhao, F.; Jin, F.; Jiang, W.; et al. Tailoring Zeolite L-Supported-Cu Catalysts for CO 2 Hydrogenation: Insights into the Mechanism of CH 3 OH and CO Formation. Inorg Chem 2023, 62, 13419–13427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sebastian, J.; Olsson, L.; Creaser, D. Experimental and kinetic modeling studies of methanol synthesis from CO2 hydrogenation using In2O3 catalyst. Chemical Engineering Journal 2021, 416, 129120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Jin, B.; He, X.; Li, S.; Liang, X. Ultra-thin ZrO2 overcoating on CuO-ZnO-Al2O3 catalyst by atomic layer deposition for improved catalytic performance of CO2 hydrogenation to dimethyl ether. Nanotechnology 2023, 34, 235401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Definition | Method | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular and Chemical Structure Analysis [73,74,75] |
Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy | Quantify absorption spectra in chemical bonds and functional groups in molecules |
| Raman spectroscopy | Postulate information about molecular vibrations, crystal structures, and phase transitions | |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy | Detect magnetic properties (physical/chemical) of atoms | |
| Small-angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) | Examine nanomaterial structures | |
| Crystallographic and Phase Analysis [20,76] |
X-ray diffraction (XRD) | Assess crystalline structures, crystal phases, and crystal defects |
| Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD) | Analyze powdered crystalline materials for crystal structure identification | |
| Selected Area Electron Diffraction (SAED) | Obtain crystallographic information from a sample area | |
| Surface and Elemental Analysis [73,74,77] |
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) | Examine the chemistry of the surface, including aspects such as elemental composition, chemical and empirical states, and the electronic state of elements |
| X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS) | Determine local geometric/electronic structural order | |
| Auger Electron Spectroscopy (AES) | Detect emitted energy of electrons from the catalyst surface | |
| Microscopy and Imaging [74] | Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) | Generate high-resolution images of the surface, internal structure, morphology, and crystallography of nanomaterials |
| Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) | ||
| Thermal Analysis [78,79,80,81] |
Temperature-Programmed Reduction-Thermogravimetric Analysis (TPR-TGA) | TPR: Measure the change in chemical state upon heating TGA: Measure changes in physical and chemical states upon heating |
| Temperature-Programmed Desorption (TPD) | Investigate adsorption and desorption behaviors on surface interactions and binding energies | |
| Temperature-Programmed Oxidation (TPO) | Evaluate oxidation behaviors, particularly in carbonaceous materials, catalyst deactivation investigations | |
| Temperature-Programmed Reaction (TPRe) | Study reaction kinetics, and catalytic stability under different thermal environments | |
| Temperature-Programmed Surface Reaction (TPSR) | Focus on surface reactions; mechanisms of surface-mediated reactions | |
| Temperature-Programmed Reduction/Oxidation (TPR-O) | Explore redox properties for redox reactions | |
| Temperature-Programmed Ammonia Desorption (TPAD) | Observe ammonia-desorption for acid catalysis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





