Submitted:
26 March 2024
Posted:
26 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
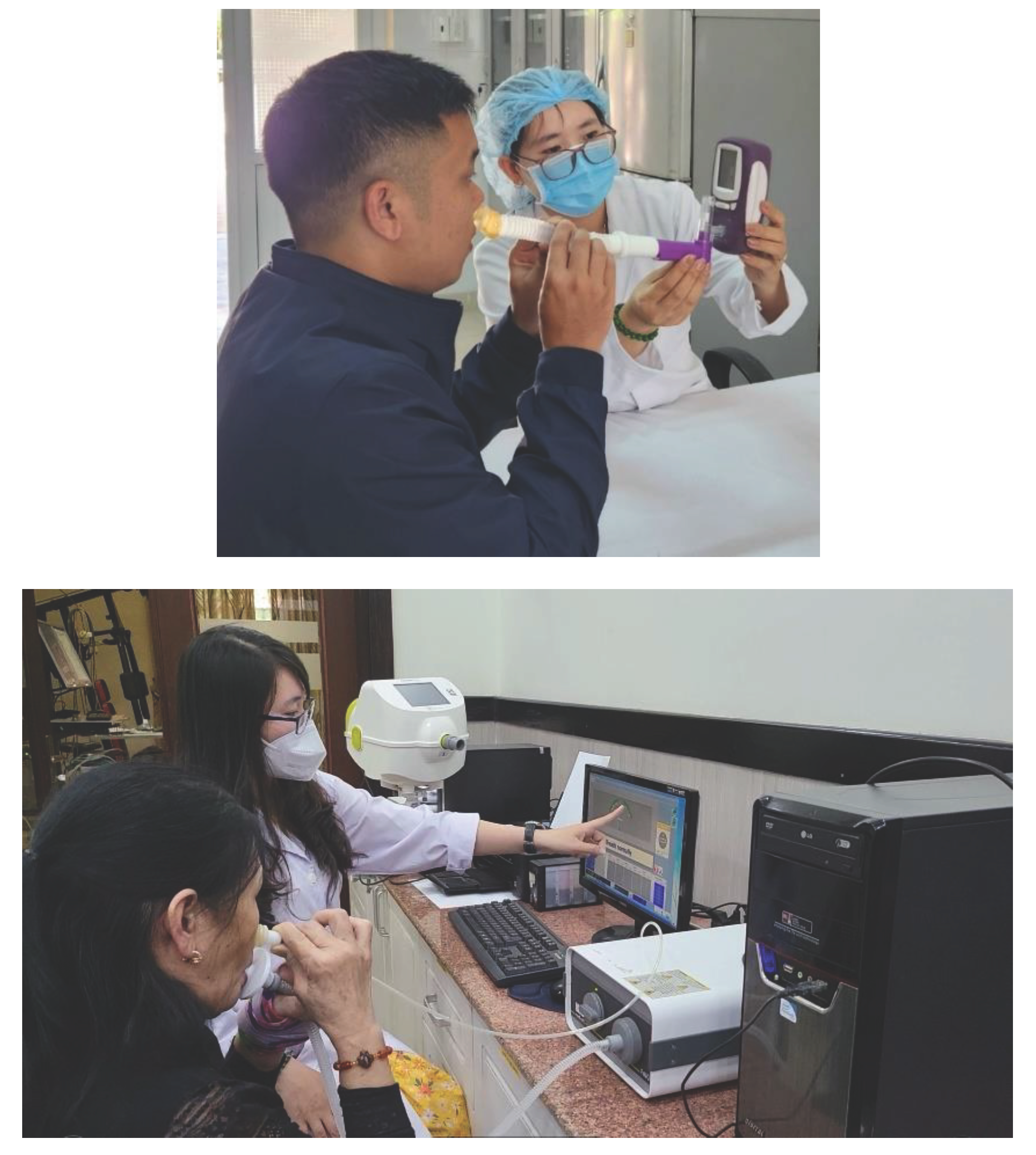
2.2. Measurement of Nasal FENO
2.3. Measurement of Bronchial FeNO
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anthropometric Characteristics
3.2. Results of Nasal and Bronchial FeNO Levels in Two Study Groups
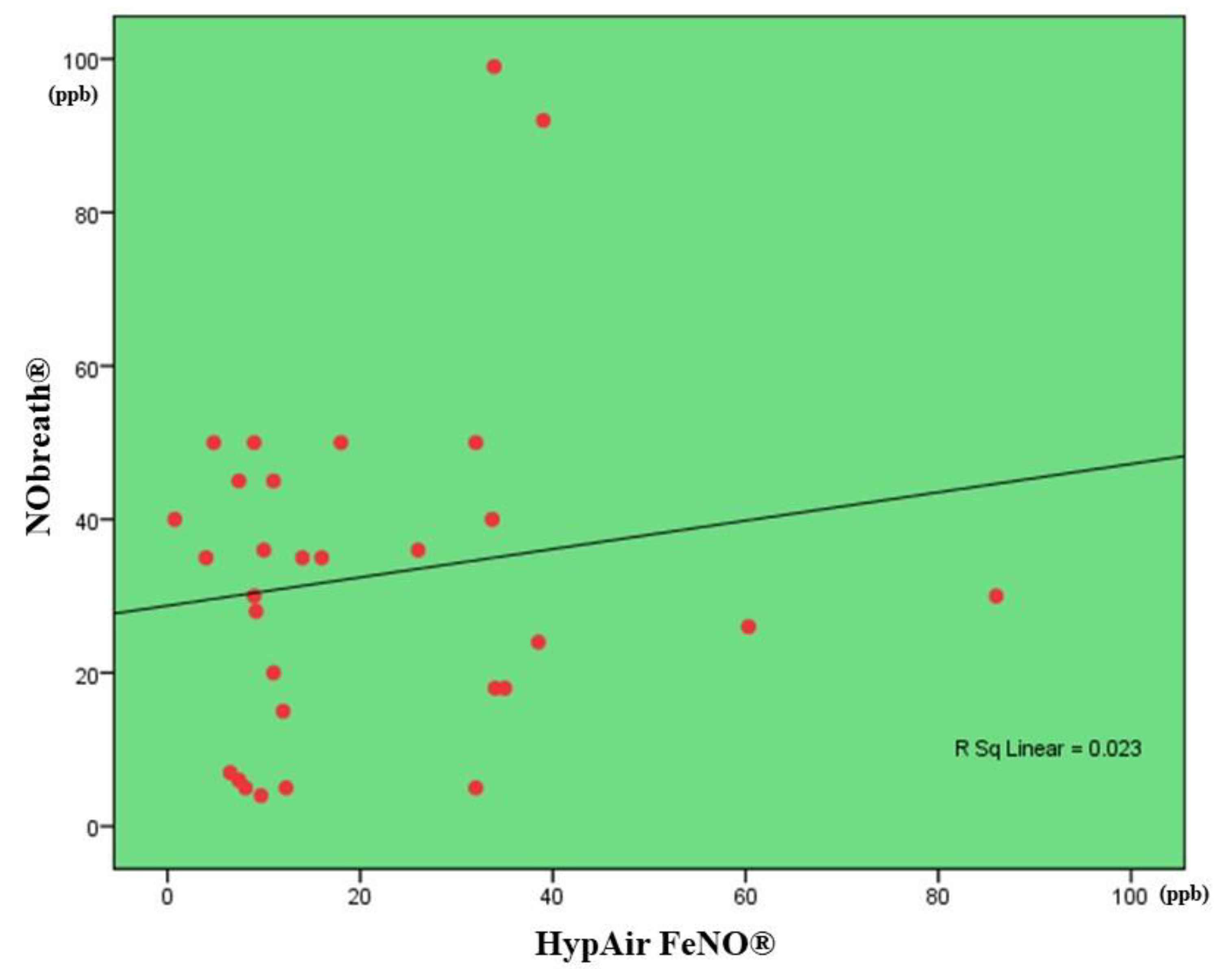
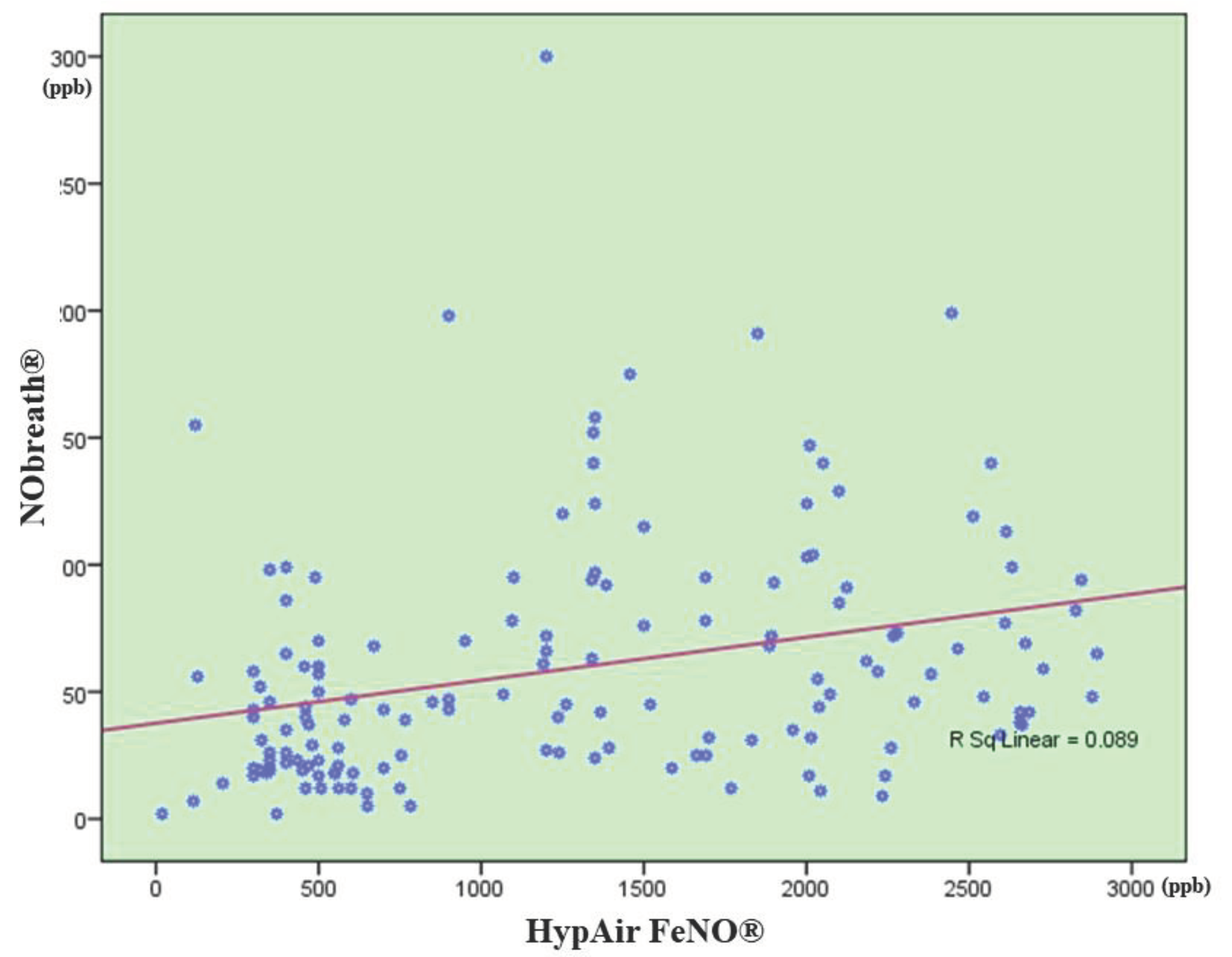
3.3. Correlation between FENO Levels Measured by NObreath® and That One Measured by Hypair FeNO®
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
References
- Gustafsson LE, Leone AM, Persson MG, Wiklund NP, Moncada S. Endogenous nitric oxide is present in the exhaled air of rabbits, guinea pigs and humans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 16;181(2):852-857. https://10.1016/0006-291x(91)91268-h. [CrossRef]
- Lundberg JO, et al. High nitric oxide production in human paranasal sinuses. Nat Med. 1995 Apr;1(4):370-373. https://10.1038/nm0495-370. [CrossRef]
- Abba AA. Exhaled nitric oxide in diagnosis and management of respiratory diseases. Ann Thorac Med. 2009 Oct;4(4):173-181. https://10.4103/1817-1737.56009. [CrossRef]
- Vo-Thi-Kim A, Van-Quang T, Nguyen-Thanh B, Dao-Van D, Duong-Quy S. The effect of medical treatment on nasal exhaled nitric oxide (NO) in patients with persistent allergic rhinitis: A randomized control study. Adv Med Sci. 2020 Mar;65(1):182-188. https://10.1016/j.advms.2019.12.004. [CrossRef]
- Duong-Quy S, et al. Study of Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Subjects with Suspected Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Pilot Study in Vietnam. Pulm Med. 2016;2016:3050918. https://10.1155/2016/3050918. [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005 Apr 15;171(8):912-930. https://10.1164/rccm.200406-710ST. [CrossRef]
- Dweik RA, et al. An official ATS clinical practice guideline: interpretation of exhaled nitric oxide levels (FENO) for clinical applications. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Sep 1;184(5):602-615. https://10.1164/rccm.9120-11ST. [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco M, et al. Fractional exhaled nitric oxide-measuring devices: technology update. Med Devices (Auckl). 2016 Jun 23;9:151-160. https://10.2147/MDER.S91201. [CrossRef]
- Ragnoli B, et al. Fractional nitric oxide measurement in exhaled air (FeNO): perspectives in the management of respiratory diseases. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2023 Aug 1;14:20406223231190480. https://10.1177/20406223231190480. [CrossRef]
- Weschta M, Deutschle T, Riechelmann H. Nasal fractional exhaled nitric oxide analysis with a novel hand-held device. Rhinology. 2008 Mar;46(1):23-27.
- Duong-Quy S. Clinical Utility Of The Exhaled Nitric Oxide (NO) Measurement With Portable Devices In The Management Of Allergic Airway Inflammation And Asthma. J Asthma Allergy. 2019 Oct 7;12:331-341. https://10.2147/JAA.S190489. [CrossRef]
- Takeno S, Okabayashi Y, Kohno T, Yumii K, Hirakawa K. The role of nasal fractional exhaled nitric oxide as an objective parameter independent of nasal airflow resistance in the diagnosis of allergic rhinitis. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017 Aug;44(4):435-441. https://10.1016/j.anl.2016.09.007. [CrossRef]
- Duong-Quy S, et al. Study of nasal exhaled nitric oxide levels in diagnosis of allergic rhinitis in subjects with and without asthma. J Asthma Allergy. 2017 Mar 22;10:75-82. https://10.2147/JAA.S129047. [CrossRef]
- Nur Husna SM, Tan HT, Md Shukri N, Mohd Ashari NS, Wong KK. Allergic Rhinitis: A Clinical and Pathophysiological Overview. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 7;9:874114. https://10.3389/fmed.2022.874114. [CrossRef]
- Wang IJ, Tung TH, Tang CS, Zhao ZH. Allergens, air pollutants, and childhood allergic diseases. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2016 Jan;219(1):66-71. https://10.1016/j.ijheh.2015.09.001. [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich M, et al. Is there a sex-shift in prevalence of allergic rhinitis and comorbid asthma from childhood to adulthood? A meta-analysis. Clin Transl Allergy. 2017 Dec 5;7:44. https://10.1186/s13601-017-0176-5. [CrossRef]
- Duong-Quy S, et al. Study of Nasal Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FENO) in Children with Allergic Rhinitis. Sinusitis. 2021 Oct 8; 5(2):123-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/sinusitis5020013. [CrossRef]
- Cho WS, et al. Increased expression of arginase I and II in allergic nasal mucosa. Laryngoscope. 2011 Feb;121(2):236-240. https://10.1002/lary.21288. [CrossRef]
- Hood CM, Schroter RC, Doorly DJ, Blenke EJ, Tolley NS. Computational modeling of flow and gas exchange in models of the human maxillary sinus. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009 Oct;107(4):1195-203. https://10.1152/japplphysiol.91615.2008. [CrossRef]
- Bautista AP, Eisenlohr CP, Lanz MJ. Nasal nitric oxide and nasal eosinophils decrease with levocetirizine in subjects with perennial allergic rhinitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2011 Nov-Dec;25(6):383-7. https://10.2500/ajra.2011.25.3668. [CrossRef]
- Nesic VS, et al. Measuring nasal nitric oxide in allergic rhinitis patients. J Laryngol Otol. 2016 Nov;130(11):1064-1071. https://10.1017/S0022215116009087. [CrossRef]
- Korn S, Telke I, Kornmann O, Buhl R. Measurement of exhaled nitric oxide: comparison of different analysers. Respirology. 2010 Nov;15(8):1203-1208. https://10.1111/j.1440-1843.2010.01847.x. [CrossRef]
- Pisi R, et al. Measurement of fractional exhaled nitric oxide by a new portable device: comparison with the standard technique. J Asthma. 2010 Sep;47(7):805-809. https://10.3109/02770903.2010.485667. [CrossRef]
- Heffler E, et al. Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FENO) in the management of asthma: a position paper of the Italian Respiratory Society (SIP/IRS) and Italian Society of Allergy, Asthma and Clinical Immunology (SIAAIC). Multidiscip Respir Med. 2020 Feb 19;15(1):36. https://10.4081/mrm.2020.36. [CrossRef]
- Nerpin E, et al. Determinants of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in healthy men and women from the European Community Respiratory Health Survey III. Clin Exp Allergy. 2019 Jul;49(7):969-979. https://10.1111/cea.13394. [CrossRef]
- Antus B, Horvath I, Barta I. Assessment of exhaled nitric oxide by a new hand-held device. Respir Med. 2010 Sep;104(9):1377-1380. https://10.1016/j.rmed.2010.06.005. [CrossRef]
- Rawy A.M. Measurement of exhaled nitric oxide in healthy Egyptian population: normal ranges and factors affecting. Egypt J Bronchol. 2015 Mar 20;9:48-54. https://doi.org/10.4103/1687-8426.153599. [CrossRef]
- Saito J, et al. Comparison of fractional exhaled nitric oxide levels measured by different analyzers produced by different manufacturers. J Asthma. 2020 Nov;57(11):1216-1226. https://10.1080/02770903.2019.1642351. [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto H, Takeno S, Yajin K. Increased expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in nasal epithelial cells in patients with allergic rhinitis. Laryngoscope. 1999 Dec;109(12):2015-2020. https://10.1097/00005537-199912000-00023. [CrossRef]
- Inoue Y, Sato S, Manabe T, Makita E, Chiyotanda M, Takahashi K, Yamamoto H, Yanagida N, Ebisawa M. Measurement of Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Children: A Comparison Between NObreath® and NIOX VERO® Analyzers. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018 Sep;10(5):478-489. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.5.478. PMID: 30088368; PMCID: PMC6082813. [CrossRef]
- Högman M, Bowerman C, Chavez L, Dressel H, Malinovschi A, Radtke T, Stanojevic S, Steenbruggen I, Turner S, Dinh-Xuan AT; Global Lung Function Initiative FENO Task Force. ERS technical standard: Global Lung Function Initiative reference values for exhaled nitric oxide fraction (FENO50 ). Eur Respir J. 2024 Jan 25;63(1):2300370. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00370-2023. PMID: 37973177. [CrossRef]
| Factors | All subjects (N = 153) |
Control group (N = 63) |
AR group (N = 90) |
P* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 38.7 ± 19.5 | 38.5 ± 19.7 | 37.1 ± 20.4 | NS |
| Sex Female, N (%) Male, N (%) |
62 (40.5) 91 (59.5) |
29 (46.0) 34 (54.0) |
28 (31.1) 62 (68.9) |
NS NS |
| Height, cm (mean ± SD) | 153.8 ± 13.5 | 155.6 ± 12.9 | 152.7 ± 12.2 | NS |
| Weight, kg (mean ± SD) | 50.9 ± 14.2 | 51.7 ± 14.4 | 50.5 ± 12.7 | NS |
| BMI, kg/m2 (mean ± SD) | 21.2 ± 3.6 | 21.7 ± 3.9 | 20.9 ± 3.3 | NS |
| Parameters | Control group | AR group | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| NObreath® | |||
| Nasal FeNO, ppb | 36.0 ± 28.1 (N = 63) |
76.0 ± 50.7 (N = 90) |
< 0.01 |
| Bronchial FeNO, ppb | 9.2 ± 5.6 (N = 63) |
32.3 ± 15.4 (N = 30) |
< 0.001 |
| Hypair FeNO® | |||
| Nasal FeNO, ppb | 400.2 ± 123.1 (N = 63) |
1796.9 ± 523.3 (N = 90) |
< 0.001 |
| Bronchial FeNO, ppb | 17.4 ± 18.3 (N = 63) |
37.3 ± 23.0 (N = 30) |
< 0.01 |
| Parameters | NObreath® (ppb) |
Hypair FeNO® (ppb) |
P |
| Control group (N = 63) | |||
| Nasal FeNO, ppb | 36.0 ± 28.1 (N = 63) |
400.2 ± 123.1 (N = 63) |
N/A |
| Bronchial FeNO, ppb | 9.2 ± 5.6 (N = 63) |
17.4 ± 18.3 (N = 63) |
N/A |
| AR group (N = 90) | |||
| Nasal FeNO, ppb | 76.0 ± 50.7 (N = 90) |
1796.9 ± 523.3 (N = 90) |
N/A |
| Bronchial FeNO, ppb | 32.3 ± 15.4 (N = 30) |
37.3 ± 23.0 (N = 30) |
N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





