Submitted:
25 March 2024
Posted:
26 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. Genetic Analysis and Immunohistochemistry Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
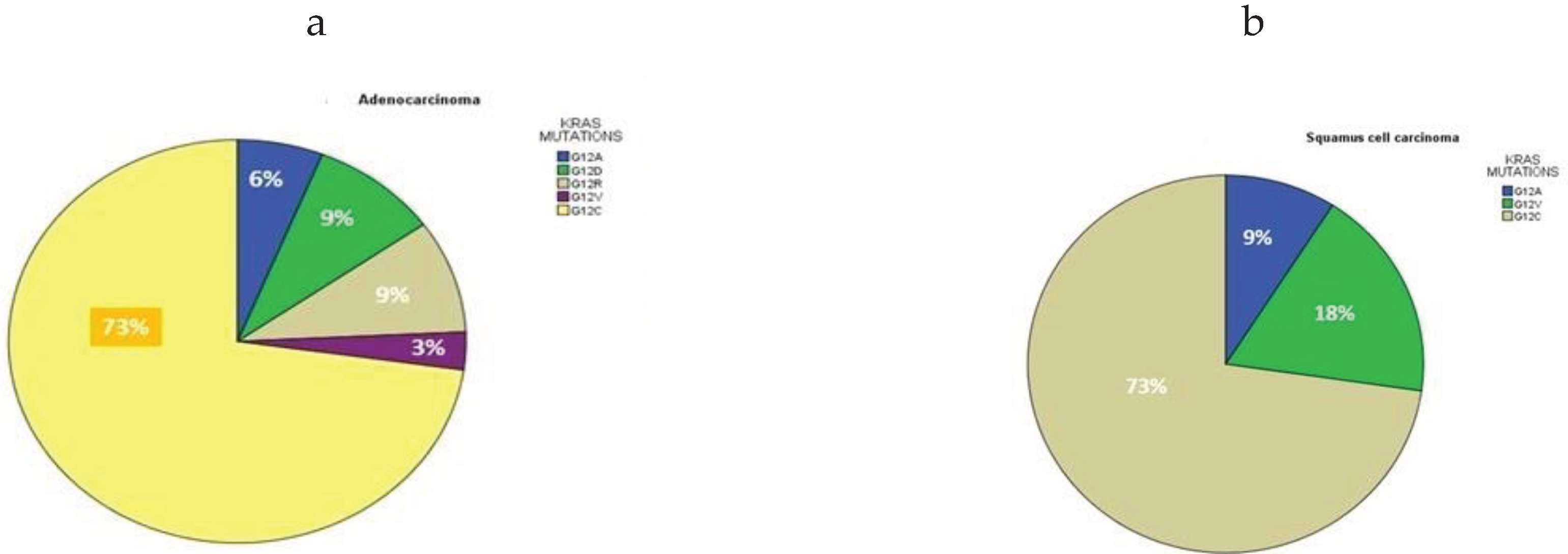
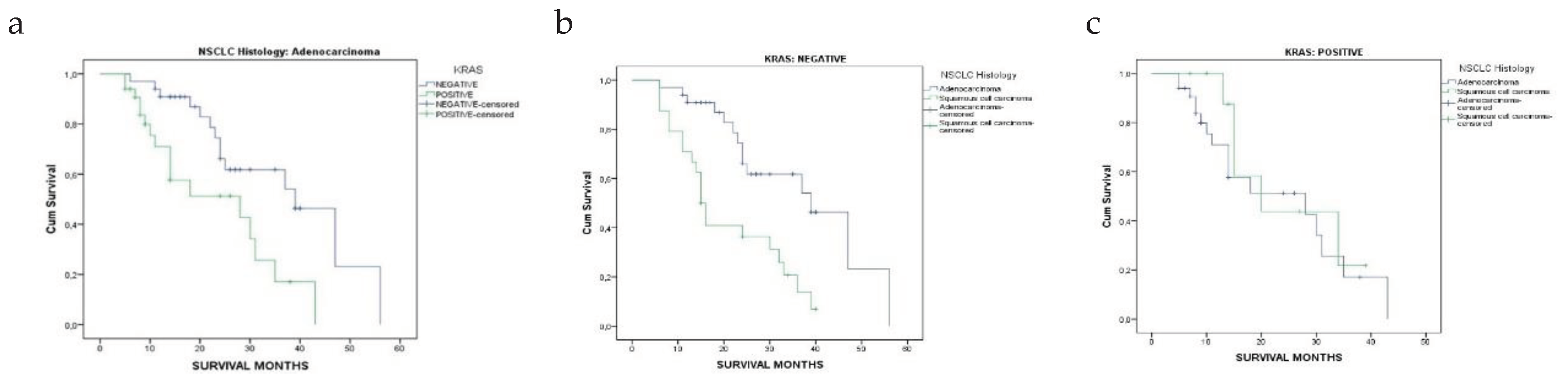
3.2. Patients’ Survival Regarding KRAS Mutational Status in Relation to NSCLC Histology
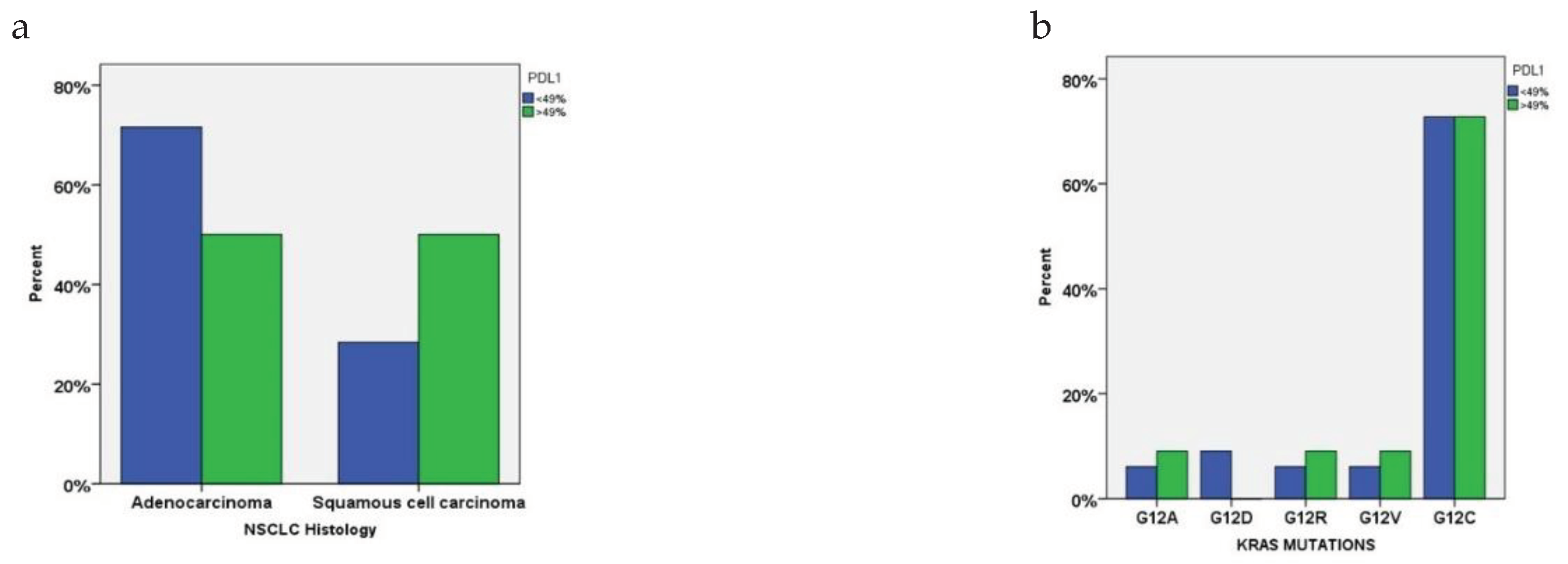
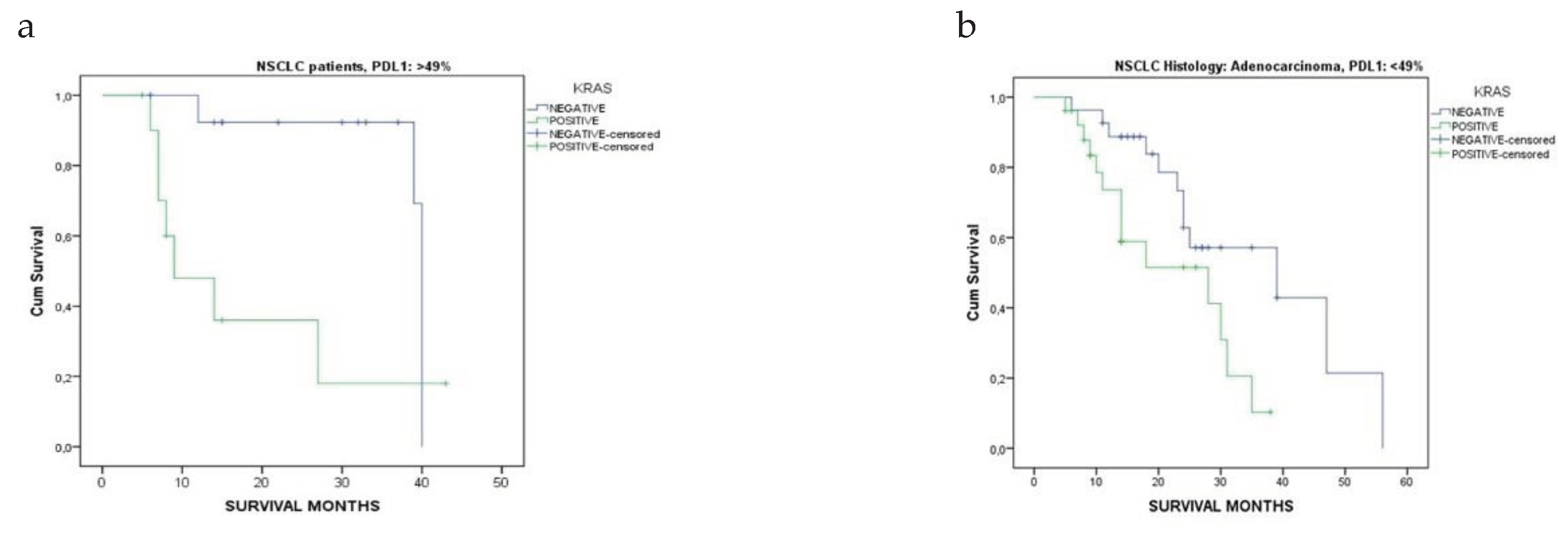
3.3. PDL1 Expression in Relation to KRAS Mutational Status and Clinical Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aisner, D.L.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.R.; Bharat, A.; et al. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2022, 20, 497–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Cordero, R.; Devine, W.P. Targeted Therapy and Checkpoint Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer. Surg Pathol Clin. 2020, 13, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Taube, J.M.; Anders, R.A.; Pardoll, D.M. Mechanism-driven biomarkers to guide immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016, 16, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Baas, P.; Kim, D.W.; Felip, E.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.Y.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016, 387, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Trapani, J.A.; Neeson, P.J. Challenges of PD-L1 testing in non-small cell lung cancer and beyond. J Thorac Dis. 2020, 12, 4541–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perol, M.; Felip, E.; Dafni, U.; Polito, L.; Pal, N.; Tsourti, Z.; et al. Effectiveness of PD-(L)1 inhibitors alone or in combination with platinum-doublet chemotherapy in first-line (1L) non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (Nsq-NSCLC) with PD-L1-high expression using real-world data. Ann Oncol. 2022, 33, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Carbone, D.P.; Garassino, M.; Barlesi, F. Targeting KRAS in non-small-cell lung cancer: recent progress and new approaches. Ann Oncol. 2021, 32, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landre, T.; Justeau, G.; Assie, J.B.; Chouahnia, K.; Davoine, C.; Taleb, C.; et al. Anti-PD-(L)1 for KRAS-mutant advanced non-small-cell lung cancers: a meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022, 71, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judd, J.; Abdel Karim, N.; Khan, H.; Naqash, A.R.; Baca, Y.; Xiu, J.; et al. Characterization of KRAS Mutation Subtypes in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 2577–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciuti, B.; Alessi, J.V.; Elkrief, A.; Wang, X.; Cortellini, A.; Li, Y.Y.; et al. Dissecting the clinicopathologic, genomic, and immunophenotypic correlates of KRAS(G12D)-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2022, 33, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.H.; Adib, E.; Kwiatkowski, D.J. Distribution of KRAS (G12C) Somatic Mutations across Race, Sex, and Cancer Type. N Engl J Med. 2021, 384, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reita, D.; Pabst, L.; Pencreach, E.; Guerin, E.; Dano, L.; Rimelen, V.; et al. Direct Targeting KRAS Mutation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Focus on Resistance. Cancers (Basel). 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, A.M.; Sun, K.Y.; Ruestow, P.; Cowan, D.M.; Madl, A.K. Lung cancer mutation profile of EGFR, ALK, and KRAS: Meta-analysis and comparison of never and ever smokers. Lung Cancer. 2016, 102, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.; Leighl, N.B.; Tsao, M.S.; Shepherd, F.A. KRAS mutations as prognostic and predictive markers in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013, 8, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoulidis, F.; Byers, L.A.; Diao, L.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Tong, P.; Izzo, J.; et al. Co-occurring genomic alterations define major subsets of KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma with distinct biology, immune profiles, and therapeutic vulnerabilities. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 860–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wankhede, D.; Bontoux, C.; Grover, S.; Hofman, P. Prognostic Role of KRAS G12C Mutation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J Thorac Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, N.H.; Robinson, A.G.; Temin, S.; Baker, S.; Jr Brahmer, J.R.; Ellis, P.M.; et al. Therapy for Stage IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer With Driver Alterations: ASCO and OH (CCO) Joint Guideline Update. J Clin Oncol. 2021, 39, 1040–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancer, V.S.; Buyukdogan, M.; Turkmen, I.; Bassullu, N.; Altug, T.; Diz-Kucukkaya, R.; et al. Comparison of KRAS mutation tests in colorectal cancer patients. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2011, 15, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelatto, M.C.; Midha, A.; Mistry, A.; Sabalos, C.; Schechter, N.; Li, X.; et al. Development of a programmed cell death ligand-1 immunohistochemical assay validated for analysis of non-small cell lung cancer and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 2016, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Goldberg, M.E.; Greenawalt, D.M.; Hellmann, M.D.; Awad, M.M.; Gainor, J.F.; et al. STK11/LKB1 Mutations and PD-1 Inhibitor Resistance in KRAS-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adderley, H.; Blackhall, F.H.; Lindsay, C.R. KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: Converging small molecules and immune checkpoint inhibition. EBioMedicine. 2019, 41, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascaux, C.; Iannino, N.; Martin, B.; Paesmans, M.; Berghmans, T.; Dusart, M.; et al. The role of RAS oncogene in survival of patients with lung cancer: a systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 2005, 92, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartolo, A.; Feilotter, H.; Hopman, W.; Fung, A.S.; Robinson, A. A single institution study evaluating outcomes of PD-L1 high KRAS-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with first line immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2021, 27, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noordhof, A.L.; Damhuis, R.A.M.; Hendriks, L.E.L.; de Langen, A.J.; Timens, W.; Venmans, B.J.W.; et al. Prognostic impact of KRAS mutation status for patients with stage IV adenocarcinoma of the lung treated with first-line pembrolizumab monotherapy. Lung Cancer. 2021, 155, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin-Fenton, D.; Dalvi, T.; Movva, N.; Pedersen, L.; Hansen, H.; Fryzek, J.; et al. PD-L1 expression, EGFR and KRAS mutations and survival among stage III unresected non-small cell lung cancer patients: a Danish cohort study. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 16892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pao, W.; Girard, N. New driver mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 28. Wen Wang HL, Guoli Li. What’s the difference between lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma? Evidence from a retrospective analysis in a cohort of Chinese patients. Front Endocrinol, 2022; 13, 947443.
- Riely, G.J.; Kris, M.G.; Rosenbaum, D.; Marks, J.; Li, A.; Chitale, D.A.; et al. Frequency and distinctive spectrum of KRAS mutations in never smokers with lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5731–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toki, M.I.; Mani, N.; Smithy, J.W.; Liu, Y.; Altan, M.; Wasserman, B.; et al. Immune Marker Profiling and Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression Across NSCLC Mutations. J Thorac Oncol. 2018, 13, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, L.; Peng, X.; Xu, H.; Tang, B.; Xu, C. Resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022, 5, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, L.; Cheng, S.; Yu, J. The Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors vs. Chemotherapy for KRAS-Mutant or EGFR-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancers: A Meta-Analysis Based on Randomized Controlled Trials. Dis Markers. 2022, 2022, 2631852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.R.; Rosenberg, S.C.; McCormick, F.; Malek, S. Author Correction: RAS-targeted therapies: is the undruggable drugged? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, E.C.; Drezner, N.; Li, X.; Mishra-Kalyani, P.S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. FDAApproval Summary: Sotorasib for KRASG12C-Mutated Metastatic, N. S.C.L.C. Clin Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1482–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, A.; Milella, M.; Felicioni, L.; Cappuzzo, F.; Irtelli, L.; Del Grammastro, M.; et al. Clinical implications of KRAS mutations in lung cancer patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: an important role for mutations in minor clones. Neoplasia. 2009, 11, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linardou, H.; Kotoula, V.; Kouvatseas, G.; Mountzios, G.; Karavasilis, V.; Samantas, E.; et al. Genotyping KRAS and EGFR Mutations in Greek Patients With Non-small-cell Lung Cancer: Incidence, Significance and Implications for Treatment. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2019, 16, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Patients (n=100) |
|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD, years Age distribution 30-50 40-50 50-60 60-70 70-80 80-90 |
67 ± 8 1% (n=1) 3% (n=3) 13% (n=13) 41% (n=41) 38% (n=38) 4% (n=4) |
| Sex, (Male/Female) | 100%/0% |
| BMI (Mean ± SD) | 26 ± 4.8 |
| Smoking Status Never smokers Light smokers Current smokers |
4% 3% 93% |
| Pack/years | 77 |
| NSCLC Histology Adenocarcinoma/Squamous cell carcinoma |
66%/34% |
| PDL1 expression <49% ≥49% |
74% 26% |
| Overall survival, months, Mean ± SD (Median) | 15 ± 12 (22.5) |
| NEGATIVE KRAS | POSITIVE KRAS |
P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients n=100 | 57% | 43% | - |
| PDL1 | |||
| <49% | 74% (n=42) | 74% (n=32) | 0.934 |
| >49% | 26% (n=15) | 26% (n=11) | |
| NSCLC Histology | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 33% (n=33) | 33% (n=33) | 0.049* |
| Squamous Cell Carcinoma | 24% (n=24) | 10% (n=10) | |
| Smoking status | |||
| Never smokers | 7% (n=4) | 0 | 0.058 |
| Light smokers | 5% (n=3) | 0 | |
| Current smokers | 88% (n=50) | 100% (n=43) | |
| Overall survival, months, Mean ± SD, (Median) | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 25.3 ± 11.8 [24] | 15.1 ± 10.5 [11] | <0.001* |
| Squamous Cell Carcinoma | 19.4 ± 11.2 [15] | 19.4 ± 10.6 [15] | 1.000 |
| KRAS Positive n=43 |
Adenocarcinoma n=33 |
Squamous Cell Carcinoma n=10 |
p-values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD, years | 68.0 ± 5.6 | 63.7 ± 12.1 | 0.782 |
| Age distribution 40-50 50-60 60-70 70-80 |
0 9% (n=3) 36% (n=12) 55% (n=18) |
20% (n=2) 10% (n=1) 40% (n=4) 9% (n=3) |
0.056 |
| PDL1 <49% >49% |
79% (n=26) 21% (n=7) |
60% (n=6) 40% (n=4) |
0.233 |
| Response after 6 months PR CR SD PD |
18% (n=6) 9% (n=3) 12% (n=4) 61% (n=20) |
30% (n=3) 10% (n=1) 20% (n=2) 40% (n=4) |
0.695 |
| Overall survival, months, Mean ± SD, (Median) |
15 ± 10.5 [11] |
19 ± 10.6 [15] |
0.128 |
| KRAS mutations |
Number of patients n=44 |
Age Years, Mean ± SD |
Median Age | P-value | Overall Survival Months, mean ± SD | Median Survival Months |
P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G12A | 3 (7%) | 59 ± 4.5 | 59 | 0.232 | 17.0 ±13.1 | 15 | 0.215 |
| G12D | 3 (7%) | 71 ± 2.6 | 70 | 19.6 ± 13.4 | 14 | ||
| G12R | 3 (7%) | 65 ± 9.5 | 60 | 6.6 ± 1.5 | 7 | ||
| G12V | 3 (7%) | 68.3 ± 6 | 69 | 11 ± 4 | 11 | ||
| G12C | 32 (73%) | 67.6 ± 7.9 | 70 | 17 ± 10.6 | 14 | ||
| Total | 44 | 66 ± 8.9 | 65.5 | 23 ± 11.9 | 22.5 | ||
| PDL1 expression | Response after 6 months |
KRAS mutational status Negative Positive |
P-values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <49% | PR | 11% | 6% | 0.303 |
| CR | 5% | 2% | ||
| SD | 9% | 4% | ||
| PD | 17% | 20% | ||
| >49% | PR | 5% | 3% | 0.978 |
| CR | 3% | 2% | ||
| SD | 2% | 2% | ||
| PD | 5% | 4% | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





