Submitted:
08 March 2024
Posted:
11 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Collection and Sample Preparations
2.2. Application of Husking Procedure
2.3. Determination of the Crude Protein
2.4. Determination of Dry Matter
Weight of Original Sample
2.5. Determination of Mineral Elemental Contents
2.6. Evaluation of Hulled S.bicolor Grain Colour
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of the (HFTU) Process Attributed to Diverse Sorghum Races
3.1.1. Influence of the (HFTU) Process on the Dry Matter and Crude Protein
3.1.2. Influence of the (HFTU) Process on the Mineral Contents
Phosphorus
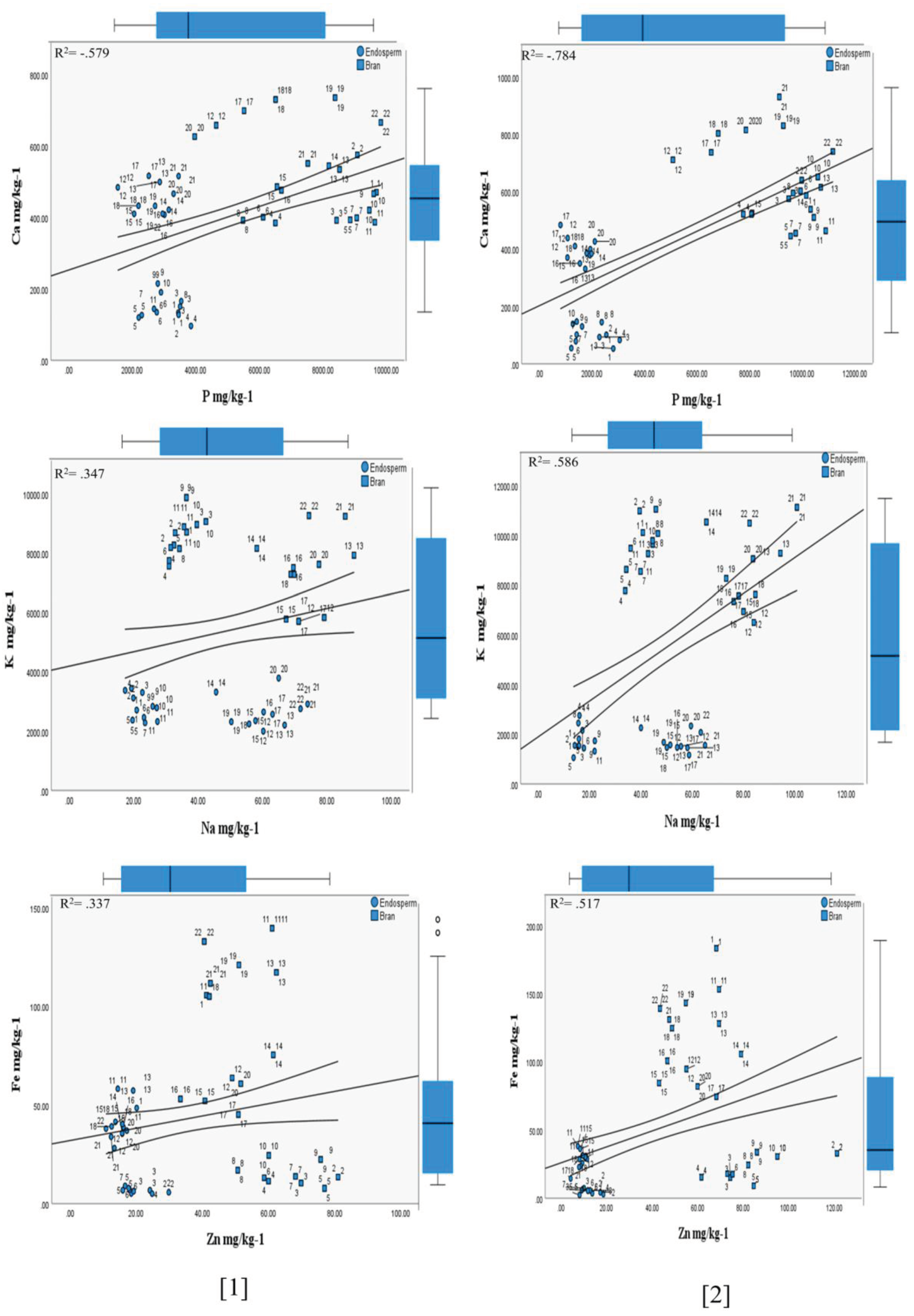
Potassium
Sulphur
Calcium
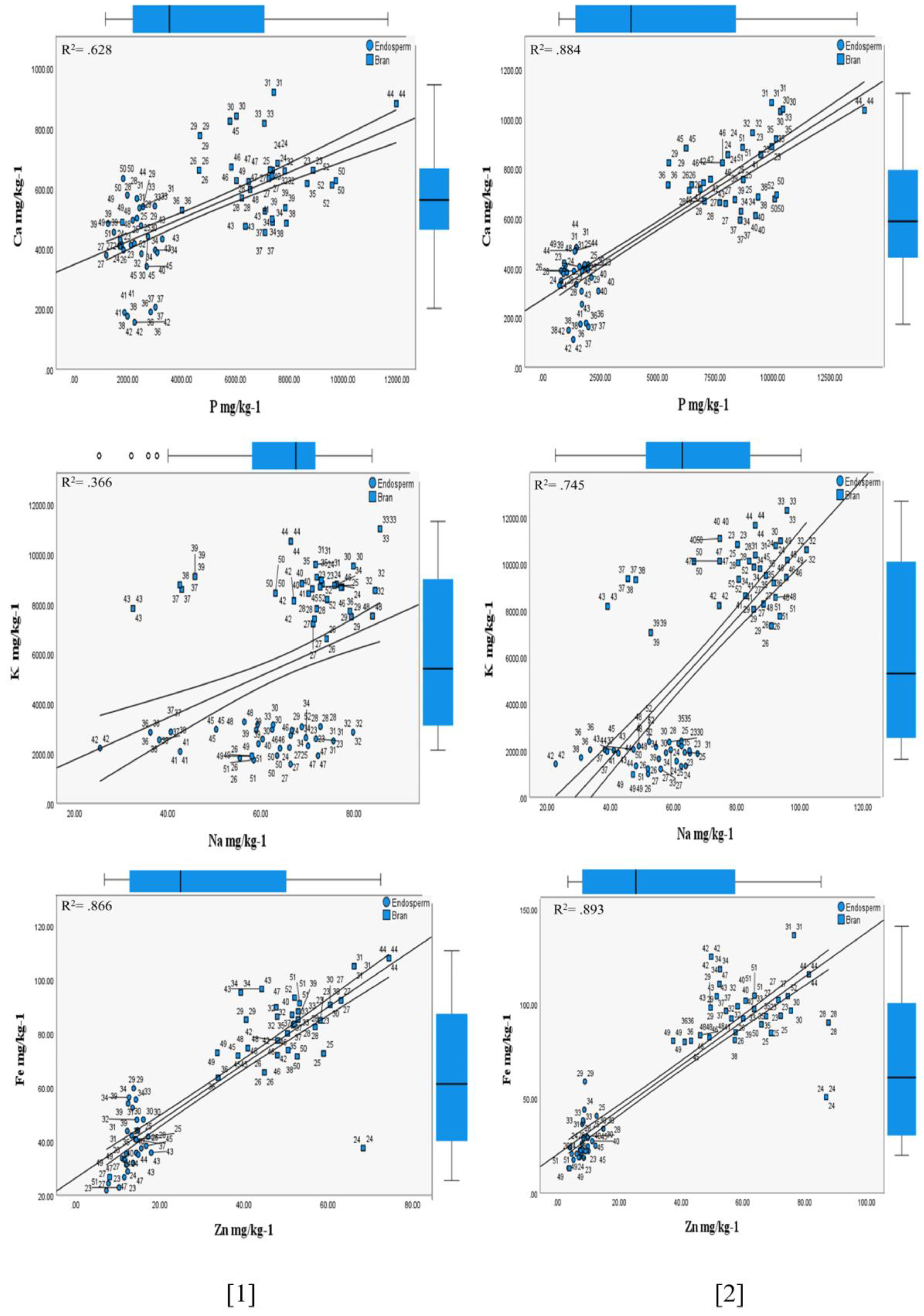
Magnesium
Sodium
Copper
Iron
Zinc
Manganese
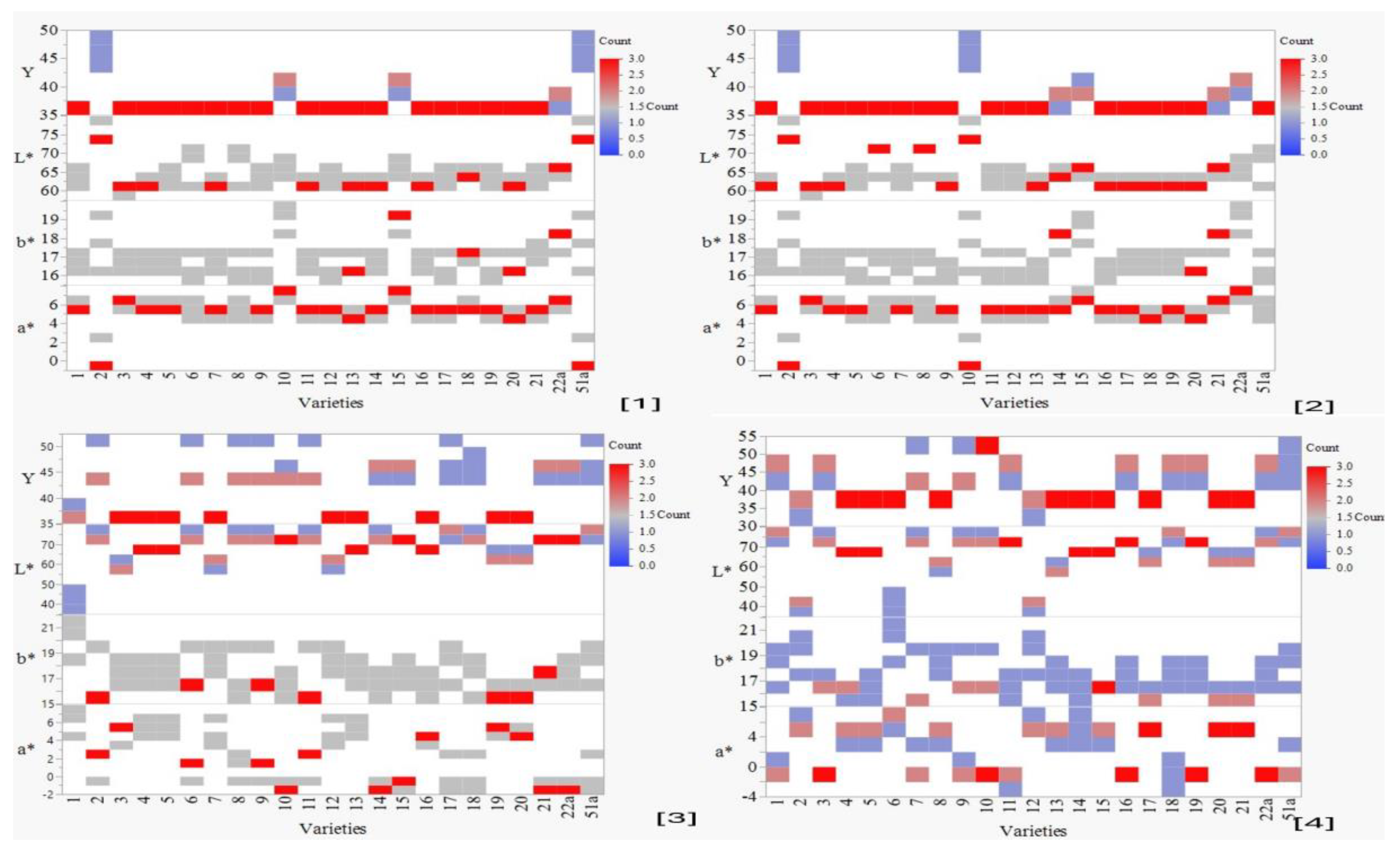
3.1.3. Evaluation of Colour Profile
Colour Characteristics Attributed to 30 (S) and 80 (S) Time Unites
4. Conclusion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- M. S. Hossain, M. N. Islam, M. M. Rahman, M. G. Mostofa, and M. A. R. Khan, “Sorghum: A prospective crop for climatic vulnerability, food and nutritional security,” J. Agric. Food Res., vol. 8, no. October 2021, p. 100300, 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. V. Aguiar, F. G. Santos, V. A. V. Queiroz, and V. D. Capriles, “A Decade of Evidence of Sorghum Potential in the Development of Novel Food Products: Insights from a Bibliometric Analysis,” Foods, vol. 12, no. 20, 2023. [CrossRef]
- T. T. George, A. O. Obilana, A. B. Oyenihi, A. B. Obilana, D. O. Akamo, and J. M. Awika, “Trends and progress in sorghum research over two decades, and implications to global food security,” South African J. Bot., vol. 151, pp. 960–969, 2022. [CrossRef]
- C Henley, “Sorghum : An Ancient , Healthy and Nutritious Old World Cereal Sorghum : An Ancient , Healthy and Nutritious Old World Cereal Table of Contents,” p. 33, 2010.
- R. C. N. Thilakarathna, G. D. M. P. Madhusankha, and S. B. Navaratne, “Potential food applications of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) and rapid screening methods of nutritional traits by spectroscopic platforms,” J. Food Sci., vol. 87, no. 1, pp. 36–51, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Jóvér, G. Kovács, L. Blaskó, C. Juhász, and E. Kovács, “Evaluation of Sweet Sorghum (Sorghum Bicolor) Hybrids As Bioenergy Feedstocks in Relation To Climatic Aspects,” Nat. Resour. Sustain. Dev., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 161–174, 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. Jóvér, E. Kovács, P. Riczu, J. Tamás, and L. Blaskó, “Spatial decision support for crop structure adjustment - A case study for selection of potential areas for sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) production,” Agrokem. es Talajt., vol. 67, no. 1, pp. 49–59, 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. G. Höhn and R. P. Rötter, “Impact of global warming on European cereal production,” CAB Rev. Perspect. Agric. Vet. Sci. Nutr. Nat. Resour., vol. 9, no. December 2017, 2014. [CrossRef]
- J. Berenji, J. Dahlberg, V. Sikora, and D. Latkovič, “Origin , History , Morphology , Production , Improvement , and Utilization of Broomcorn [ Sorghum bicolor ( L .) Moench ] in Serbia Author ( s ): Janoš Berenji , Jeff Dahlberg , Vladimir Sikora and Dragana Latković Published by : Springer on behalf of New,” vol. 65, no. 2, pp. 190–208, 2011.
- R. Maurya and D. G. , Thirupataiah Boini , Lakshminarayana Misro , Thulasi Radhakrishnan , Aswani Pulikunnel Sreedharan, “Comprehensive review on millets : Nutritional values , effect of food processing and dietary aspects,” J. Drug Res. Ayurvedic Sci. |, 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. Baholet, K. Mrvova, P. Horky, and L. Pavlata, “Comparison of nutrient composition of sorghum varieties depending on different soil types,” Proc. 25Th Int. Phd Students Conf. (Mendelnet 2018), vol. 25, pp. 100–103, 2018, [Online]. Available: http://mendelnet.cz/artkey/mnt-201801-0019_Comparison-of-nutrient-composition-of-sorghum-varieties-depending-on-different-soil-types.php.
- Conference, T. H. E. Geneticss, S. Of, and B. O. F. Proceedings, “Annual conference the geneticss society of nigeria book of proceedings,” no. October, 2021.
- S. Widowati and P. Luna, “Nutritional and Functional Properties of Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench)-based Products and Potential Valorisation of Sorghum Bran,” IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci., vol. 1024, no. 1, 2022. [CrossRef]
- L. Girard and J. M. Awika, “Sorghum polyphenols and other bioactive components as functional and health promoting food ingredients,” J. Cereal Sci., vol. 84, no. October, pp. 112–124, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. N. S. Htet, B. Feng, H. Wang, L. Tian, and V. Yadav, “Comparative assessment of nutritional and functional properties of different sorghum genotypes for ensuring nutritional security in dryland agro-ecosystem,” Front. Nutr., vol. 9, no. November, pp. 1–13, 2022. [CrossRef]
- D. A. S. John Milton Poehlman, “Breeding Field Crops,” Iowa State Univ. Press /Ames, no. Fourth Edition, 1995, [Online]. Available: ISBN 0 8138 2427 3.
- J. Chen, Y. Jiao, H. Laza, P. Payton, D. Ware, and Z. Xin, “ Identification of the First Nuclear Male Sterility Gene ( Male-sterile 9 ) in Sorghum ,” Plant Genome, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 1–12, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Z. Xin et al., “Morphological characterization of a new and easily recognizable nuclear male sterile mutant of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor),” PLoS One, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 1–14, 2017. [CrossRef]
- C. K. Black and J. F. Panozzo, “Accurate technique for measuring color values of grain and grain products using a visible-NIR instrument,” Cereal Chem., vol. 81, no. 4, pp. 469–474, 2004. [CrossRef]
- M. Sedghi, A. Golian, P. Soleimani-Roodi, A. Ahmadi, and M. Aami-Azghadi, “Relationship between color and tannin content in sorghum grain: Application of image analysis and Artificial Neural Network,” Rev. Bras. Cienc. Avic., vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 57–62, 2012. [CrossRef]
- L. Li et al., “Grain color formation and analysis of correlated genes by metabolome and transcriptome in different wheat lines at maturity,” Front. Nutr., vol. 10, no. February, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Batariuc, I. Coțovanu, and S. Mironeasa, “Sorghum Flour Features Related to Dry Heat Treatment and Milling,” Foods, vol. 12, no. 11, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Muthamilarasan and M. Prasad, “Small Millets for Enduring Food Security Amidst Pandemics,” Trends Plant Sci., vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 33–40, 2021. [CrossRef]
- D. Saha, M. V. C. Gowda, L. Arya, M. Verma, and K. C. Bansal, “Genetic and Genomic Resources of Small Millets,” CRC. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci., vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 56–79, 2016. [CrossRef]
- G. A. Nayik, T. Tufail, F. Muhammad Anjum, and M. Javed Ansari, Cereal Grains: Composition, Nutritional Attributes, and Potential Applications, no. February. 2023.
- C. P. Karumba, “Improvement of somatic embryogenesis and androgenesis systems for sorghum [ Sorghum bicolor ( L .) Moench,” Ph.D. Diss., 2021.
- Kumar et al., “Recent Advances in Sorghum Genetic Enhancement Research at ICRISAT,” Am. J. Plant Sci., vol. 02, no. 04, pp. 589–600, 2011. [CrossRef]
- K. B. Gaikwad et al., “Enhancing the Nutritional Quality of Major Food Crops Through Conventional and Genomics-Assisted Breeding,” Front. Nutr., vol. 7, no. November, 2020. [CrossRef]
- T. L. Souza, L. A. Souza, I. S. Barbosa, D. C. M. B. Santos, R. G. O. Araujo, and M. G. A. Korn, “Mineral and Trace Elements in Nutritious Flours: Total Contents, In Vitro Bioaccessibility and Contribution to Dietary Intake,” Biol. Trace Elem. Res., vol. 201, no. 9, pp. 4600–4611, 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. Ertl and W. Goessler, “Grains, whole flour, white flour, and some final goods: an elemental comparison,” Eur. Food Res. Technol., vol. 244, no. 11, pp. 2065–2075, 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. U. Sruthi, P. S. Rao, and B. D. Rao, “Decortication induced changes in the physico-chemical, anti-nutrient, and functional properties of sorghum,” J. Food Compos. Anal., vol. 102, no. June, p. 104031, 2021. [CrossRef]
- T. S. Steinberg, E. P. Meleshkina, O. G. Shvedova, O. V. Morozova, and N. S. Zhiltsova, “Changes of the Optical Properties of Top-Grade Flour (Semolina) From Durum Wheat During Its Ripening,” Pis. Sist. Syst., vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 24–28, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Konica Minolta, “Chroma Meter Konica Minolta Cr-400/410. Instruction Manual,” p. 160, 2002, [Online]. Available: http://sensing.konicaminolta.com.mx/products/cr-410-chroma-meter-difference-with-colorimeter/support/cr-400-410_instruction_eng.pdf.
- N. Wang, “Optimization of a laboratory dehulling process for lentil (Lens culinaris),” Cereal Chem., vol. 82, no. 6, pp. 671–676, 2005. [CrossRef]
- ISO 20483:2013, “INTERNATIONAL STANDARD of the nitrogen content and calculation of the crude protein content — Kjeldahl method iTeh STANDARD PREVIEW iTeh STANDARD PREVIEW,” vol. 2013, 2013.
- K. J. Hellevang, “Grain Moisture Content Effects and Management,” NDSU Extension Service. pp. 1–8, 1995, [Online]. Available: http://www.ag.ndsu.edu/extension-aben/documents/ae905.pdf.
- 37. J. T. John R.N. Taylor, “ICC Handbook of 21st Century Cereal Science and Technology.” pp. 161–171, 2023. [CrossRef]
- B. Kovács, Z. Gyôri, and J. Prokisch, “Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis A study of plant sample preparation and inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry parameters,” Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal., no. October 2014, pp. 37–41, 1996. [CrossRef]
- N. R. D. H. Smith, Applied Regression Analysis. 1998.
- R. Rumler1, D. Bender2*, A. Marti3, S. Biber1, and Regine Schönlechner, “Investigating the impact of sorghum variety and type of flour on chemical, functional, 4 rheological and baking properties.” 2024. [CrossRef]
- Osman et al., “Nutrient Composition and In Vitro Fermentation Characteristics of Sorghum Depending on Variety and Year of Cultivation in Northern Italy,” Foods, vol. 11, no. 20, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. E. Cuevas, K. H. S. Peiris, and S. R. Bean, “Assessment of Grain Protein in Tropical Sorghum Accessions from the NPGS Germplasm Collection,” Agronomy, vol. 13, no. 5, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Khan, N. A. Khan, S. R. Bean, J. Chen, and and Y. J. , Zhanguo Xin, “Variations in Total Protein and Amino Acids in the Sequenced Sorghum Mutant Library,” pp. 1–14, 2023. [CrossRef]
- N. M. Kamal, Y. S. A. Gorafi, H. Tomemori, J. S. Kim, G. M. I. Elhadi, and H. Tsujimoto, “Genetic variation for grain nutritional profile and yield potential in sorghum and the possibility of selection for drought tolerance under irrigated conditions,” BMC Genomics, vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 1–16, 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. S. Poutanen et al., “Grains - a major source of sustainable protein for health,” Nutr. Rev., vol. 80, no. 6, pp. 1648–1663, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Gutiérrez, “The connection between dietary phosphorus, cardiovascular disease, and mortality: Where we stand and what we need to know,” Adv. Nutr., vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 723–729, 2013. [CrossRef]
- N. Chhikara, B. Abdulahi, C. Munezero, R. Kaur, G. Singh, and A. Panghal, “Exploring the nutritional and phytochemical potential of sorghum in food processing for food security,” Nutr. Food Sci., vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 318–332, Jan. 2019. [CrossRef]
- W. Khalid et al., “Nutrients and bioactive compounds of Sorghum bicolor L. used to prepare functional foods: a review on the efficacy against different chronic disorders,” Int. J. Food Prop., vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 1045–1062, 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. Laskowski, H. Górska-Warsewicz, K. Rejman, M. Czeczotko, and J. Zwolińska, “How important are cereals and cereal products in the average polish diet?,” Nutrients, vol. 11, no. 3, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Z. S. Mohammed, A. H. Mabudi, Y. Murtala, S. Jibrin, S. Sulaiman, and J. Salihu, “Nutritional Analysis of Three Commonly Consumed Varieties of Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) in Bauchi State, Nigeria,” J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag., vol. 23, no. 7, p. 1329, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Torbica, M. Belović, L. Popović, J. Čakarević, M. Jovičić, and J. Pavličević, “Comparative study of nutritional and technological quality aspects of minor cereals Aleksandra,” J. Food Sci. Technol., vol. 58, no. 1, pp. 311–322, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. M. Tasie and B. G. Gebreyes, “Characterization of Nutritional, Antinutritional, and Mineral Contents of Thirty-Five Sorghum Varieties Grown in Ethiopia,” Int. J. Food Sci., vol. 2020, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. G. Galán, A. Weisstaub, A. Zuleta, and S. R. Drago, “Effects of extruded whole-grain sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) based diets on calcium absorption and bone health of growing Wistar rats.,” Food Funct., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 508–513, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Vötterl, J. Klinsoda, Q. Zebeli, I. Hennig-Pauka, W. Kandler, and B. U. Metzler-Zebeli, “Dietary phytase and lactic acid-treated cereal grains differently affected calcium and phosphorus homeostasis from intestinal uptake to systemic metabolism in a pig model,” Nutrients, vol. 12, no. 5, 2020. [CrossRef]
- F. Thielecke, J. M. Lecerf, and A. P. Nugent, “Processing in the food chain: Do cereals have to be processed to add value to the human diet?,” Nutr. Res. Rev., vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 159–173, 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. B. Costello, A. Rosanoff, Q. Dai, L. G. Saldanha, and N. A. Potischman, “Perspective: Characterization of Dietary Supplements Containing Calcium and Magnesium and Their Respective Ratio-Is a Rising Ratio a Cause for Concern?,” Adv. Nutr., vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 291–297, 2021. [CrossRef]
- and M. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, Dietary Reference Intakes for Sodium and Potassium. 2019.
- N. Khan et al., “Determination of Macronutrients in Spices by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry,” Anal. Lett., vol. 47, no. 14, pp. 2394–2405, 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. Qamar, M. Aslam, F. Huyop, and M. A. Javed, “Comparative study for the determination of nutritional composition in commercial and noncommercial maize flours,” Pakistan J. Bot., vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 519–523, 2017.
- C. Williams, C. Ronco, and P. Kotanko, “Whole grains in the renal diet-Is it time to reevaluate their role?,” Blood Purif., vol. 36, no. 3–4, pp. 210–214, 2014. [CrossRef]
- X. Zhou, T. Yue, Z. Wei, L. Yang, L. Zhang, and B. Wu, “Evaluation of nutritional value, bioactivity and mineral content of quinoa bran in China and its potential use in the food industry.,” Curr. Res. food Sci., vol. 7, p. 100562, 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. L. Bresson et al., “Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for copper,” EFSA J., vol. 13, no. 10, pp. 1–51, 2015. [CrossRef]
- E. H. Horst, S. López, M. Neumann, F. J. Giráldez, and V. H. B. Junior, “Effects of hybrid and grain maturity stage on the ruminal degradation and the nutritive value of maize forage for silage,” Agric., vol. 10, no. 7, pp. 1–17, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Ashok Kumar, K. Anuradha, and B. Ramaiah, “Increasing grain Fe and Zn concentration in sorghum: progress and way forward,” J. SAT Agric. Res., vol. 11, no. 12, pp. 1–5, 2013.
- S. Anitha et al., “Millets Can Have a Major Impact on Improving Iron Status, Hemoglobin Level, and in Reducing Iron Deficiency Anemia–A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis,” Front. Nutr., vol. 8, no. October, pp. 1–14, 2021. [CrossRef]
- F. Dasa and T. Abera, “Factors Affecting Iron Absorption and Mitigation Mechanisms : A review,” Int. J. Agric. Sci. Food Technol., vol. 4, pp. 24–30, 2018.
- Kotla et al., “Identification of QTLs and candidate genes for high grain Fe and Zn concentration in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.)Moench],” J. Cereal Sci., vol. 90, p. 102850, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Gaddameedi et al., “The location of iron and zinc in grain of conventional and biofortified lines of sorghum,” J. Cereal Sci., vol. 107, no. May, p. 103531, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. H. S. Omer and Jing Hong Xueling Zheng and Reham Khashaba, “Sorghum Flour and Sorghum Flour Enriched Bread :,” 2023.
- R. Rumler and R. Schönlechner, “Effect of Sorghum on Rheology and Final Quality of Western Style Breads: A Literature Review,” Foods, vol. 10, no. 6, p. 1392, 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. Habyarimana, P. De Franceschi, S. Ercisli, F. S. Baloch, and M. Dall’Agata, “Genome-Wide Association Study for Biomass Related Traits in a Panel of Sorghum bicolor and S. bicolor × S. halepense Populations,” Front. Plant Sci., vol. 11, no. November, pp. 1–19, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. A. Ayuba, Z. H. Bello, Z. Shehu, and T. Ibrahim, “Effect of Processing on White Sorghum Variety Consumed in Sokoto,” vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 45–50, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Abd El-Raouf, E.-M. El - Metwally, and A. Bahar Elddin, “PERFORMANCE OF SOME GRAIN SORGHUM (Sorghum bicolor l. Moench) GENOTYPES UNDER DIFFERENT SOWING DATES IN EGYPT,” J. Plant Prod., vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 763–772, 2013. [CrossRef]
| Codes | Processed Grains | Pericap Colour |
D.M g/kg-1 |
Protein g/kg-1 |
P mg/kg-1 |
K mg/kg-1 |
S mg/kg-1 |
Ca mg/kg-1 |
Mg mg/kg-1 |
Cu mg/kg-1 |
Fe mg/kg-1 |
Zn mg/kg-1 |
Na mg/kg-1 |
Mn mg/kg-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 986±0.03 | 22±0.13 | 4201±36.1 | 3932±2926.3 | 1727±12.4 | 174±6.1 | 2643±0.16 | 4±.23 | 83±0.07 | 29±0.003 | 23±00.31 | 16±1.1 | |
| 2 | Brown | 987±0.47 | 8±0.64 | 2630±201.7 | 2965±166.9 | 1372±54.3 | 114±14.3 | 1721±447.5 | 5±.70 | 25±0.73 | 24±6.8 | 18±2.1 | 11±2.8 | |
| 3 | 987±0.47 | 14±0.21 | 9993±347.8 | 9404±771.8 | 1889±130.2 | 505±37.7 | 4722±166.3 | 8±2.8 | 145±42.6 | 55±14.7 | 34±2.4 | 37±13.6 | ||
| 2 | 1 | 890±0.13 | 23±0.03 | 3877±81.2 | 3650±.41 | 1517±202.1 | 176±8.0 | 2313±0.13 | 6.4±.30 | 39±0.31 | 31±0.12 | 21±.37 | 15±2.2 | |
| 2 | White | 990±0.05 | 16±0.26 | 3005±496.7 | 2929±87.4 | 1591±32.6 | 93±43.7 | 1645±541.6 | 3±0.70 | 39±10.5 | 15±5.1 | 18±3.6 | 8±3.0 | |
| 3 | 990±0.05 | 13±0.10 | 9525±492.9 | 9830±1260.4 | 1705±95.3 | 607±36.3 | 4951±458.3 | 13±4.41 | 23±10.6 | 101±21.9 | 36±3.6 | 57±20.7 | ||
| 3 | 1 | 991±0.04 | 12±0.60 | 3712±14.2 | 2983±0.44 | 1760±67.2 | 261.3±12.1 | 2344±0.27 | 4±0.20 | 35±.01 | 28±0.10 | 21±1.0 | 15±2.2 | |
| 2 | Brown | 991±0.04 | 9±0.58 | 2396±119.2 | 3729±469.0 | 1579±142.6 | 122±31.2 | 1645±468.8 | 3±0.78 | 26±0.63 | 18±6.7 | 20±2.9 | 9±3.1 | |
| 3 | 991±0.04 | 18±0.55 | 9525±492.9 | 9830±1260.4 | 1705±95.3 | 607±36.3 | 4951±458.3 | 13±4.4 | 23±10.6 | 101±21.9 | 36±3.9 | 57±20.7 | ||
| 4 | 1 | 990±0.05 | 20±0.11 | 4185±128.0 | 4047±11.0 | 1555±20.3 | 243±11.2 | 2350±0.33 | 3±0.51 | 30±0.82 | 30±0.10 | 27±0.5 | 14±.23 | |
| 2 | Brown | 990±0.05 | 15±0.02 | 8452±1527.8 | 9565±208.01 | 1412±67.5 | 90±7.3 | 2906±507.6 | 10±0.20 | 94±1.1 | 22±11.3 | 17±0.6 | 33±2.4 | |
| 3 | 990±0.05 | 12±0.09 | 8953±579.6 | 9345±319.1 | 1703±214.2 | 484±100.8 | 4312±233.3 | 9±1.5 | 13±2.5 | 72±2.4 | 44±1.2 | 36±.15 | ||
| 5 | 1 | 98.4±0.28 | 17±0.41 | 2155±125.1 | 2289±192.2 | 1437±234.0 | 192±118.5 | 1399±248.8 | 3.2±0.20 | 39±15.2 | 24±7.0 | 23±.31 | 16±1.12 | |
| 2 | Brown | 991±0.06 | 8±0.02 | 1712±539.8 | 2213±170.5 | 1293±49.4 | 87±35.7 | 1525±97.7 | 3±0.50 | 30±3.0 | 12±4.2 | 17±3.1 | 8±0.9 | |
| 3 | 991±0.05 | 12±0.09 | 2128±407.8 | 3160±663.0 | 1716±85.5 | 453±75.3 | 2342±277.2 | 5±1.7 | 26±0.05 | 61±0.9 | 32±1.6 | 19±1.0 | ||
| 6 | 1 | 980±0.04 | 20±0.02 | 3505±97.1 | 5326±0.29 | 1612±164.0 | 264±21.8 | 2384±.21 | 4±0.1 | 46±0.11 | 26±0.20 | 22±9.7 | 25±6.5 | |
| 2 | White | 991±0.07 | 6±0.02 | 2081±756.2 | 2450±9.3 | 1482±99.3 | 107±30.3 | 143±521.4 | 3±0.5 | 24±0.8 | 16±2.5 | 21±2.8 | 9±3.2 | |
| 3 | 991±0.06 | 12±0.10 | 9199±383.6 | 8442±198.0 | 1688±16.9 | 419±29.1 | 4142±94.2 | 10±1.1 | 28±0.6 | 81±4.2 | 33±1.0 | 32±1.4 | ||
| 7 | 1 | Brown | 894±0.02 | 13±0.01 | 2521±357.1 | 2514±180.8 | 1522±246.2 | 323±153.1 | 1298±336.2 | 5±1.1 | 26±2.2 | 25±4.6 | 27±0.05 | 16±0.10 |
| 2 | 991±0.05 | 12±0.02 | 1861±481.1 | 1397±129.4 | 1251±23.2 | 114±13.6 | 1351±342.2 | 2±0.20 | 18±0.85 | 13±3.5 | 20±4.3 | 11±3.4 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.05 | 19±0.03 | 8130±2209.8 | 8606±947.0 | 1815±237.4 | 494±29.1 | 4542±617.7 | 10±0.50 | 15±2.4 | 67±9.0 | 34±2.7 | 40±6.3 | ||
| 8 | 1 | 984±0.07 | 20±0.02 | 3733±112.3 | 4041±0.24 | 1312±75.0 | 296±.15 | 2516±.08 | 6±0.41 | 28±.03 | 25±.23 | 29±12.5 | 21±7.4 | |
| 2 | White | 991±0.06 | 9±0.32 | 2958±638.7 | 2945±542.9 | 1141±62.8 | 155±10.9 | 1735±338.5 | 3±0.5 | 26±0.6 | 15±2.8 | 18±1.9 | 15±3.5 | |
| 3 | 991±0.06 | 11±0.11 | 9199±383.6 | 8442±198.0 | 1688±16.9 | 419±29.1 | 4142±94.2 | 10±1.1 | 28±0.6 | 81±4.2 | 33±1.0 | 32±1.4 | ||
| 9 | 1 | 985±0.08 | 12±0.001 | 2742±93.4 | 2547±447.0 | 1347±254.0 | 274±.38 | 1714±222.4 | 2±0.39 | 31±12.9 | 19±7.9 | 27±0.11 | 24±1.1 | |
| 2 | White | 991±0.06 | 19±0.33 | 2215±644.5 | 2782±55.9 | 1192±48.1 | 173±46.3 | 1316±429.0 | 3±0.30 | 26±0.42 | 16±4.0 | 24±2.0 | 10±2.6 | |
| 3 | 990±0.02 | 10±0.01 | 7564±2281.3 | 4105±1054.7 | 1689±213.7 | 427±31.1 | 4065±590.8 | 13±2.3 | 20±4.0 | 66±17.2 | 40±6.8 | 55±11.4 | ||
| 10 | 1 | White | 983±0.23 | 18±.003 | 2644±179.1 | 4617±311.0 | 1586±415.4 | 319±298.5 | 1578±254.7 | 4±1.0 | 35±12.0 | 23±7.8 | 28±57.1 | 19±7.9 |
| 2 | 990±0.02 | 14±0.35 | 2165±644.5 | 1659±138.1 | 1402±166.2 | 169±23.6 | 782±2.2 | 1±0.40 | 17±1.1 | 13±4.6 | 22±6.1 | 9±3.6 | ||
| 3 | 990±0.02 | 15.±0.39 | 10013±464.3 | 10455±646.6 | 1652±47.4 | 494±111.6 | 4744±363.6 | 14±2.2 | 28±5.5 | 81±5.5 | 41±5.2 | 53±6.6 | ||
| 11 | 1 | 983±0.23 | 8±0.001 | 2390±372.1 | 5261±197.0 | 1562±280 | 335±173.0 | 1712±155.6 | 4±0.51 | 36±8.4 | 23±3.6 | 30±14.7 | 13±2.9 | |
| 2 | Brown | 990±0.02 | 15.5±0.38 | 1981±771.7 | 2820±544.0 | 1331±103.0 | 142±2.4 | 1176±496.2 | 2±0.50 | 48±11.0 | 11±3.8 | 25±2.9 | 8±1.9 | |
| 3 | 990±0.02 | 10±0.26 | 10019±622.0 | 10868±94.9 | 1931±95.9 | 488±24.2 | 4045±191.8 | 11±0.23 | 27±3.3 | 78±19.1 | 42±2.7 | 61±4.6 | ||
| 12 | 1 | 986±0.01 | 19±0.50 | 2790±1824.1 | 5524±456.8 | 1044±237.0 | 534±119.5 | 1942±942.3 | 5±2.5 | 37±6.9 | 22±7.0 | 34±10.8 | 20±4.4 | |
| 2 | Brown | 991±0.06 | 12±0.34 | 1315±255.3 | 2753±266.4 | 901±35.5 | 461±24.8 | 929±163.5 | 4±0.20 | 33±2.4 | 13±2.6 | 58±2.5 | 8±1.9 | |
| 3 | 991±0.06 | 18±0.08 | 10259±690.5 | 9067±205.5 | 1688±82.1 | 536±126.9 | 4620±168.1 | 8±0.47 | 147±7.5 | 65±4.5 | 39±3.9 | 37±4.4 | ||
| 13 | 1 | Brown | 985±0.04 | 12±0.01 | 3589±114 | 2936±.38 | 1244±.24 | 509±2.12 | 2226±.16 | 6±0.30 | 44±.41 | 24±.20 | 66±12.8 | 15±.71 |
| 2 | 990±0.05 | 9±0.53 | 2307±611.3 | 1328±136.6 | 1086±47.6 | 415±91.8 | 1424±401.3 | 3±0.19 | 44±14.1 | 14±5.2 | 62±4.7 | 9±2.4 | ||
| 3 | 990±0.02 | 14±0.59 | 4860±240.1 | 6163±368.7 | 1335±44.8 | 425±42.4 | 2994±99.6 | 10±1.9 | 79±17.0 | 52±3.3 | 82±2.6 | 29±5.5 | ||
| 14 | 1 | 985±0.13 | 8±0.001 | 3740±520.9 | 4252±0.27 | 1150±77.2 | 274±4.6 | 1536±.17 | 4±0.40 | 41±.20 | 17±.43 | 73±.11 | 14±.10 | |
| 2 | White | 991±0.02 | .93±0.16 | 2546±662.8 | 3787±514.5 | 1057±66.3 | 411±11.7 | 1068±290.3 | 2±0.10 | 31±5.5 | 13±3.4 | 43±2.9 | 9±2.9 | |
| 3 | 990±0.02 | 14±0.12 | 9607±1194.0 | 11949±30.2 | 1622±117.4 | 684±29.3 | 4398±520.0 | 14±0.94 | 122±5.9 | 66±3.8 | 91±3.2 | 40±.20 | ||
| 15 | 1 | 981±0.11 | 15±0.02 | 3667±86.1 | 3443±126.8 | 1095±18.6 | 419±20.0 | 1883±.01 | 3±0.42 | 50±.05 | 22±.10 | 60±8.3 | 15±1.8 | |
| 2 | Brown | 990±0.01 | 8±0.42 | 2279±804.6 | 3056±451.6 | 885±56.9 | 379±31.5 | 1139±395.0 | 2±0.20 | 31±8.3 | 12±4.0 | 57±3.3 | 9±3.0 | |
| 3 | 990±0.02 | 19±0.12 | 7319±841.9 | 6363±636.1 | 1344±149.5 | 574±32.0 | 3079±261.6 | 8±1.7 | 68±17.7 | 42±1.2 | 74±6.9 | 24±3.4 | ||
| 16 | 1 | 985±0.36 | 7.8±0.003 | 3529±1038.1 | 3308±637.2 | 975±94.3 | 611±94.5 | 1747±547.3 | 3±0.9 | 34±5.3 | 18±4.1 | 63±.10 | 18±1.2 | |
| 2 | Brown | 990±0.06 | 13±0.15 | 1664±937.6 | 2365±221.9 | 1154±3.8 | 500±17.2 | 788±461.6 | 3±0.70 | 21±7.5 | 9±4.9 | 61±2.3 | 5±1.3 | |
| 3 | 991±0.02 | 15±0.09 | 7378±752.8 | 7421±89.3 | 1325±118.2 | 506±21.7 | 3404±81.7 | 4±0.94 | 77±26.1 | 40±7.3 | 73±3.6 | 26±5.7 | ||
| 17 | 1 | 983±0.15 | 13±0.1 | 4285±383.3 | 3308±637.2 | 1154±293.6 | 544±174.2 | 1747±547.3 | 3.5±.61 | 49±2.7 | 25±2.8 | 59±9.8 | 16±2.0 | |
| 2 | Brown | 991±0.01 | 15±0.39 | 1777±459.9 | 2354±123.3 | 1118±136.8 | 423±11.7 | 980±249.5 | 2±0.5 | 34±5.7 | 10±2.4 | 53±3.0 | 12±2.0 | |
| 3 | 990±0.07 | 15±0.25 | 6023±558.9 | 6628±1017.2 | 1131±81.5 | 499±24.9 | 2713±483.6 | 10±1.85 | 60±16.0 | 60±9.4 | 75±3.7 | 18±1.4 | ||
| 18 | 1 | 986±0.01 | 12±0.11 | 3723±249.1 | 3526±500.0 | 1236±64.5 | 478±3.1 | 1828±42.6 | 4±0.21 | 51±.65 | 22±2.3 | 61±6.9 | 15±2.4 | |
| 2 | White | 990±0.01 | 12±0.10 | 2323±433.9 | 1995±349.4 | 935±53.6 | 411±37.6 | 1149±196.8 | 3±0.20 | 35±6.2 | 14±2.3 | 50±.71 | 10±1.8 | |
| 3 | 990±0.05 | 14±0.41 | 6652±161.1 | 7449±185.4 | 1430±34.8 | 718±21.2 | 3249±215.9 | 6±0.28 | 115±10.8 | 45±3.6 | 77±18.6 | 36±11.8 | ||
| 19 | 1 | 990±0.60 | 10±0.1 | 3001±752.4 | 3521±1008.2 | 1308±177.1 | 265±29.4 | 1684±334.9 | 3±0.6 | 40..11 | 17±5.0 | 66±5.0 | 15±3.4 | |
| 2 | Brown | 990±0.07 | 15±0.30 | 2629±907.6 | 2234±744.3 | 757±84.5 | 433±64.4 | 1198±362.6 | 2±0.40 | 28±6.0 | 10±2.4 | 69±4.9 | 7±1.3 | |
| 3 | 99.12±0.01 | 17±0.40 | 8826±492.5 | 7765±542.1 | 1331±85.8 | 767±40.5 | 3434±146.2 | 8±0.47 | 132±12.2 | 53±2.0 | 71±1.8 | 35±4.9 | ||
| 20 | 1 | 984±0.01 | 12±0.1 | 3546±92.1 | 3760±1416.0 | 1022±49.6 | 534±22.2 | 2182±1103.3 | 3±2.2 | 34±.20 | 16±6.1 | 79±7.1 | 17±10.1 | |
| 2 | Brown | 990±0.05 | 15±0.47 | 2706±650.5 | 3061±795.8 | 757±84.5 | 433±64.4 | 1198±362.6 | 2±.40 | 28±6.0 | 10±2.4 | 69±4.9 | 7±1.3 | |
| 3 | 990±0.02 | 12±0.53 | 5909±133.4 | 8330±786.5 | 1308±32.4 | 783±52.6 | 3406±293.9 | 10±2.36 | 71±11.5 | 56±4.5 | 81±3.3 | 30±5.6 | ||
| 21 | 1 | 984±0.06 | 10±0.01 | 3792±123.2 | 4014±11.3 | 1179±19 | 426±4.0 | 1523±.01 | 4±0.10 | 48±.12 | 15±0.10 | 74±0.12 | 16±.10 | |
| 2 | White | 990±0.05 | 15±0.39 | 2471±530.7 | 2412±373.3 | 1119±136.8 | 398±14.5 | 1044±211.1 | 3±0.10 | 35±3.6 | 10±0.61 | 68±4.6 | 5±1.7 | |
| 3 | 990±0.02 | 12±0.53 | 83322±878.9 | 10177±1035.2 | 1206±160.0 | 721±130.8 | 3856±504.6 | 6±0.45 | 121±10.6 | 45±2.8 | 93±8.2 | 40±2.1 | ||
| Ground grains | - | - | 0.23 | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | 0.28 | <.001 | <.001 | 0.001 | 0.02 | <.001 |
| Husked grains | - | - | <.001 | <.001 | 0.49 | 0.91 | <.001 | <.001 | 0.28 | <.001 | <.001 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| Codes |
Processed grains |
Pericap color |
D.M g/kg-1 |
Protein g/kg-1 |
P mg/kg-1 |
K mg/kg-1 |
S mg/kg-1 |
Ca mg/kg-1 |
Mg mg/kg-1 |
Cu mg/kg-1 |
Fe mg/kg-1 |
Zn mg/kg-1 |
Na mg/kg-1 |
Mn mg/kg-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | 1 | Brown | 981±0.06 | 13±.001 | 2263±306.2 | 4642±375.2 | 1241±370.0 | 661±248.6 | 1159±890.0 | 7±0.10 | 26±3.5 | 21±9.7 | 74±7.9 | 19±6.0 |
| 2 | 991±0.05 | 9±0.07 | 1654±280.7 | 2239±386.0 | 757±84.5 | 409±4.5 | 885±154.2 | 2±0.4 | 23±.3 | 10±.10 | 68±4.6 | 10±.91 | ||
| 3 | 990±0.02 | 13±0.53 | 10486±737.6 | 9869±673.8 | 1462±144.0 | 741±208.1 | 3585±245.2 | 8±0.10 | 136±3.4 | 42±1.5 | 78±4.3 | 43±3.0 | ||
| 23 | 1 | White | 986±0.03 | 11±0.10 | 2762±184.2 | 3012±797.5 | 815±192 | 475±132 | 1450±416.4 | 4±1.0 | 28±5.3 | 24±7.9 | 64±8.9 | 23±6.2 |
| 2 | 991±0.49 | 14±0.22 | 1343±467.4 | 1891±381.2 | 715±53.9 | 412±34.4 | 711±248.8 | 3±0.50 | 41±.46 | 9±3.3 | 64±2.8 | 6±1.1 | ||
| 3 | 993±0.32 | 10±0.39 | 7802±266.5 | 9784±1094.4 | 1728±166.5 | 775±124.3 | 3718±549.5 | 16±1.6 | 44±7.2 | 78±10.2 | 84±8.7 | 21±3.9 | ||
| 24 | 1 | White | 987±0.98 | 19±0.12 | 3741±1127.1 | 4660±2206.3 | 1000±32.2 | 523±133.3 | 1395±176.4 | 5±0.01 | 30±9.9 | 22±4.1 | 70±5.6 | 17±9.9 |
| 2 | 990±3.45 | 9.3±0.12 | 2232±280.1 | 2113±215.9 | 989±34.5 | 431±36.1 | 1318±146.4 | 3±0.20 | 27±7.0 | 8±3.5 | 67±3.5 | 13±2.6 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.44 | 8±0.02 | 8046±737.1 | 9362±744.1 | 1226±135.3 | 770±93.8 | 3491±125.0 | 11±1.0 | 79±6.6 | 64±5.5 | 77±4.2 | 37±3.6 | ||
| 25 | 1 | White | 984±0.24 | 14±0.02 | 3105±66.0 | 3234±170.8 | 1046±16.0 | 554±.50 | 1611±0.01 | 3±0.9 | 51±.11 | 23±.10 | 64±.01 | 12±.07 |
| 2 | 991±0.01 | 14±0.01 | 1317±570.9 | 1406±449.9 | 804±54.1 | 389±6.1 | 703±315.5 | 3±0.50 | 24±.10 | 6±2.0 | 54±1.9 | 8±.93 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.07 | 16±1.3 | 5561±1002.1 | 6977±401.5 | 1091±111.8 | 708±51.6 | 2842±389.7 | 10±0.70 | 75±10.6 | 51±7.0 | 85±9.2 | 26±3.9 | ||
| 26 | 1 | White | 985±0.08 | 13±0.04 | 2453±313.1 | 3253±1483.5 | 996±202.0 | 4438±123.3 | 2718±949.4 | 4±0.10 | 54±.40 | 27±2.1 | 66±8.4 | 22±8.2 |
| 2 | 990±0.12 | 11±0.05 | 999±218.6 | 1390±201.2 | 877±75.2 | 370±90.1 | 517±122.6 | 3±0.84 | 35±6.0 | 6±2.0 | 61±5.7 | 13±.22 | ||
| 3 | 993±0.02 | 20±0.77 | 7467±249.9 | 7749±584.7 | 1182±190.3 | 698±40.3 | 3253±250.8 | 11±1.2 | 97±4.2 | 67±4.6 | 80±9.4 | 35±1.4 | ||
| 27 | 1 | White | 985±0.08 | 132±0.10 | 2069±11.0 | 3253±1483.5 | 1160±13.0 | 609±.90 | 1264±.01 | 4±1.3 | 29±.01 | 16±.10 | 79±10 | 17±.11 |
| 2 | 990±0.03 | 118±0.18 | 1670±338.6 | 2690±429.4 | 1048±56.9 | 476±98.7 | 1007±198.5 | 4±0.50 | 59±.30 | 12±2.5 | 67±6.1 | 9±.34 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.05 | 10.0±0.50 | 6635±441.6 | 8964±1260.2 | 1289±103.2 | 648±15.7 | 3383±360.7 | 10±1.5 | 92±16.8 | 72±16.8 | 82±3.2 | 35±4.0 | ||
| 28 | 1 | White | 983±0.01 | 13±0.10 | 2546±392.2 | 2589±291.0 | 1106±349.1 | 599±233.7 | 1434±389.2 | 2±0.30 | 40±10.2 | 35±24.2 | 70±9.5 | 28±.8 |
| 2 | 990±0.30 | 12±0.31 | 2230±358.5 | 2459±292.4 | 896±21.0 | 450±71.1 | 1070±210.0 | 3±0.42 | 41±7.7 | 11±2.7 | 64±2.0 | 7±.97 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.08 | 21±0.78 | 5079±440.9 | 7773±306.8 | 1724±70.4 | 619±54.7 | 2736±106.0 | 10±.030 | 93±17.2 | 45±4.9 | 86±7.9 | 42±3.8 | ||
| 29 | 1 | White | 981±0.01 | 11±0.10 | 2766±219.3 | 3043±681 | 1262±327 | 592±220.1 | 1218±217.3 | 4±0.80 | 40±7.6 | 37±29.7 | 65±7.1 | 24±4.7 |
| 2 | 990±0.04 | 14±0.14 | 2356±425.2 | 2668±330.5 | 1066±42.6 | 432±55.9 | 1306±142.3 | 3±0.50 | 40±3.9 | 16±.66 | 61±2.0 | 7±1.7 | ||
| 3 | 990±0.02 | 17±1.1 | 8184±2356.8 | 10249±799.8 | 1594±121.3 | 7100±26.2 | 3411±354.9 | 12±1.3 | 121±17.2 | 68±8.2 | 79±7.7 | 30±2.4 | ||
| 30 | 1 | White | 981±1.01 | 7.0±0.05 | 4299±317.9 | 2704±175.9 | 892±212.1 | 566±94.2 | 1464±311.8 | 3±0.70 | 56±27.5 | 16±12.0 | 77±8.9 | 23±7.4 |
| 2 | 990±0.20 | 14±0.15 | 1946±528.2 | 2188±352.5 | 765±48.5 | 483±55.5 | 1045±250.1 | 3±0.50 | 40±36.5 | 10±2.3 | 64±8.1 | 8±2.2 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.05 | 15±0.003 | 8682±1384.8 | 9980±435.5 | 1745±148.0 | 935±103.4 | 3995±49.0 | 14±2.0 | 92±6.8 | 71±5.6 | 93±9.5 | 30±1.9 | ||
| 31 | 1 | White | 980±0.46 | 10±0.001 | 2060±540.1 | 6371±452.4 | 1140±316.2 | 518±217.0 | 1674±335.0 | 4±0.85 | 59±27.4 | 22±6.9 | 78±10.9 | 17±8.1 |
| 2 | 991±0.03 | 13±0.30 | 1980±574.6 | 2430±467.7 | 954±78.5 | 385±80.9 | 1038±268.0 | 3±0.62 | 43±5.7 | 11±3.4 | 64±8.1 | 8±2.2 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.07 | 19±0.36 | 9473±711.0 | 9589±1128.2 | 1281±184.2 | 993±80.1 | 3412±204.3 | 10±0.80 | 93±5.0 | 53±5.6 | 91±5.6 | 28±4.1 | ||
| 32 | 1 | White | 987±0.16 | 16±0.03 | 2780±864 | 3709±1972.9 | 1016±153.0 | 485±.68 | 1483±395.9 | 4±1.50 | 45±6.1 | 28±126 | 67±9.1 | 23±7.0 |
| 2 | 991±0.03 | 12±0.08 | 2402±655.9 | 2596±614.7 | 933±89.0 | 450±71.1 | 1165±309.9 | 3±0.50 | 50±6.6 | 11±3.3 | 61±1.9 | 7±1.4 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.01 | 13±0.23 | 8755±1848.8 | 11658±696.1 | 1597±137.5 | 802±156.3 | 4074±233.3 | 12±1.7 | 107±12.6 | 58±5.8 | 81±5.2 | 38±4.6 | ||
| 33 | 1 | White | 980±0.21 | 12±1.0 | 2995±83.8 | 5270±349.1 | 1188±292.0 | 463±143.3 | 1477±333.5 | 4±1.5 | 46±4.7 | 26±2.9 | 67±8.0 | 17±1.8 |
| 2 | 990±0.11 | 12±0.19 | 2566±491.3 | 2269±399.1 | 1013±507.0 | 382±24.5 | 1311±215.5 | 3±0.21 | 33±9.5 | 11±2.2 | 64±6.6 | 9±1.4 | ||
| 3 | 980±0.10 | 16±0.35 | 7998±682.2 | 9301±604.5 | 1263±127.6 | 928±122.3 | 3132±90.6 | 7±1.1 | 87±7.3 | 46±4.3 | 81±9.4 | 26±1.9 | ||
| 34 | 1 | White | 982±0.19 | 10±0.01 | 3020±943.2 | 2894±840.2 | 998±159.0 | 450±76.4 | 1905±646.2 | 4±1.6 | 41±14.9 | 26±3.4 | 70±9.0 | 15±2.1 |
| 2 | 990±0.05 | 19±0.03 | 1974±291.2 | 2677±287.9 | 900±45.8 | 365±87.0 | 1084±154.7 | 2±.43 | 50±6.6 | 12±1.9 | 65±2.2 | 8±2.0 | ||
| 3 | 990±0.03 | 18±0.15 | 9399±810.6 | 9283±226.2 | 1499±4.1 | 558±76.5 | 3837±126.3 | 13±1.0 | 72±8.9 | 59±9.4 | 85±6.8 | 27±2.7 | ||
| 35 | 1 | White | 987±0.02 | 16±0.30 | 3337±523.2 | 2894±840.2 | 1051±237.1 | 278±159.4 | 1544±326.3 | 5±2.1 | 38±13.6 | 22±7.6 | 38±5.0 | 14±4.0 |
| 2 | 989±0.01 | 12±0.34 | 2368±526.1 | 2447±448.5 | 907±50.4 | 186±11.2 | 1144±257.1 | 2±0.04 | 39±14.4 | 11±.31 | 35±1.4 | 8±2.0 | ||
| 3 | 989±0.50 | 17±0.09 | 4729±790.3 | 8445±792.6 | 1279±135.4 | 768±165.6 | 2656±187.7 | 8±0.91 | 90±7.1 | 37±3.9 | 44±1.3 | 26±2.9 | ||
| 36 | 1 | White | 980±0.01 | 14±0.12 | 2692±598.4 | 3295±1472.3 | 1123±236.6 | 288±178 | 2135±869.4 | 3±00.50 | 36±11.6 | 22±7.6 | 41±2.4 | 17±1.5 |
| 2 | 990±0.06 | 8.5±0.70 | 2501±568.3 | 2457±450.9 | 987±63.1 | 179±21.4 | 1153±218.3 | 2±0.20 | 32±9.9 | 12±2.6 | 39±1.3 | 7±1.6 | ||
| 3 | 99.0±0.23 | 16±0.01 | 7839±812.7 | 8976±429.2 | 1385±97.1 | 631±113.1 | 3377±124.9 | 12±1.4 | 77±3.9 | 53±1.6 | 45±2.9 | 28±.90 | ||
| 37 | 1 | White | 983±0.01 | 11±0.001 | 2375±1462.0 | 4846±381.7 | 1062±180 | 291±220 | 1800±902.3 | 5±4.2 | 31±12.3 | 22.6.6 | 38±7.8 | 19±6.0 |
| 2 | 99. 1±0.03 | 13±0.07 | 1554±471.1 | 2122±470.0 | 958±80.6 | 214±33.0 | 730±264.5 | 2±1.0 | 32±12.7 | 11±3.8 | 34±4.0 | 7±2.1 | ||
| 3 | 990±0.54 | 12±0.25 | 8624±809.5 | 9042±296.9 | 1437±93.3 | 523±75.7 | 3198±190.0 | 10±0.60 | 89±3.9 | 54±1.6 | 49±3.8 | 27±.50 | ||
| 38 | 1 | White | 987±0.01 | 73±0.02 | 3254±361.1 | 2681±271.3 | 960±165.2 | 518±122.0 | 1705±237.8 | 5±1.3 | 28±1.8 | 21±7.4 | 62±7.2 | 18±8.7 |
| 2 | 990±0.06 | 12±0.88 | 1130±148.5 | 202±411.0 | 856±21.4 | 431±40.0 | 721±253 | 3±0.50 | 36±19.2 | 10±2.8 | 57±2.2 | 6±4.0 | ||
| 3 | 990±0.76 | 18±0.25 | 8105±277.5 | 8076±1118.7 | 1391±176.4 | 585±110.0 | 3107±387.9 | 10±0.82 | 94±7.3 | 56±3.9 | 72±3.6 | 34±1.0 | ||
| 39 | 1 | White | 982±0.21 | 13±0.005 | 4348±274.0 | 4448±3570.5 | 1113±169 | 403±9.9 | 1362±173.9 | 4±0.40 | 36±8.6 | 20±4.3 | 62±8.3 | 13±4.5 |
| 2 | 991±0.03 | 10±0.15 | 2753±367.9 | 2369±233.3 | 1007±23.3 | 312±78.8 | 1329±184.8 | 3±0.60 | 32±4.5 | 13±1.7 | 57±3.2 | 9±1.0 | ||
| 3 | 993±0.42 | 17±0.11 | 8304±1036.8 | 9951±1241.5 | 1242±120.6 | 605.2±76.0 | 3772±189.2 | 12±0.50 | 88±4.7 | 56±5.1 | 76±6.7 | 32±1.7 | ||
| 40 | 1 | White | 985±0.03 | 11±0.10 | 3097±607.2 | 3797±1549.2 | 1039±159.9 | 339±181.0 | 1478±331.8 | 3±1.3 | 45±29.0 | 27±4.6 | 54±14.6 | 23±4.7 |
| 2 | 991±0.44 | 16±0.50 | 1623±0.10 | 1935±.27 | 897±.01 | 169±6.5 | 836±.10 | 2±0.01 | 29±.11 | 8±.03 | 39±.10 | 8±.11 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.22 | 17±0.08 | 8420±1164.2 | 8523±118.2 | 1352±74.4 | 626±17.3 | 3534±205.8 | 13±1.2 | 101±26.0 | 54±2.3 | 71±4.0 | 31±1.8 | ||
| 41 | 1 | White | 985±0.03 | 18±0.01 | 2826±573.1 | 3494±1644.0 | 1095±175.4 | 372±34.6 | 1419±199.1 | 3±1.0 | 36±8.8 | 16±4.1 | 44±27.3 | 14±3.3 |
| 2 | 990±0.05 | 10±0.12 | 1780±501.6 | 1822±434.0 | 1046±84.1 | 180±125.6 | 922±282.4 | 3±00.40 | 29±6.8 | 10±2.6 | 24±1.5 | 8±2.5 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.28 | 13±0.23 | 7162±106.8 | 8171±47.7 | 1233±40.7 | 678±195.6 | 3432±73.5 | 8±0.01 | 100±.01 | 49±.95 | 36±3.6 | 35±1.6 | ||
| 42 | 1 | White | 986±0.02 | 15±0.04 | 3324±1692.0 | 5285±2440.3 | 1269±256.2 | 605±254.2 | 1188±125.8 | 4±2.2 | 45±7.4 | 40±31.4 | 53±18.0 | 13±1.8 |
| 2 | 99.1±0.02 | 16±0.32 | 2492±861.3 | 2522±704.7 | 1037±73.4 | 365±132.1 | 968±308 | 2±0.70 | 29±6.8 | 14±48.2 | 51±9.1 | 8±2.7 | ||
| 3 | 990±0.82 | 20±0.68 | 7162±870.8 | 8003±195.9 | 1224±146.2 | 641±127.0 | 3379±191.8 | 6±0.30 | 112±4.2 | 48±4.0 | 76±10.3 | 35±2.9 | ||
| 43 | 1 | White | 985±0.01 | 10±0.01 | 3657±1946.0 | 5879±2889.8 | 1188±256.3 | 555±291.0 | 1948±808.9 | 6±2.6 | 34±10.5 | 24±8.1 | 58±14.7 | 23±8.5 |
| 2 | 991±0.01 | 10±0.44 | 1878±501.2 | 2501±496.8 | 1037±73.4 | 480±83.2 | 1035±275.4 | 3±0.62 | 29±6.5 | 12±3.7 | 53±6.3 | 7±1.9 | ||
| 3 | 990±0.06 | 15±0.23 | 10979±1088.0 | 11084±622.9 | 1643±115.1 | 567±101.0 | 4099±138.9 | 13±2.1 | 76±4.7 | 78±3.8 | 79±8.9 | 44±0.30 | ||
| 44 | 1 | White | 985±0.01 | 10±0.08 | 3699±1957.2 | 2632±497.4 | 1209±222.1 | 500±170.5 | 1987±779.3 | 4±1.8 | 39±15.1 | 25±6.6 | 59±17.0 | 16±4.6 |
| 2 | 990±0.01 | 8.8±0.48 | 2194±550.9 | 2491±529.5 | 1161±59.9 | 338±48.3 | 1062±273.4 | 3±0.60 | 32±7.2 | 15±2.4 | 46±5.0 | 9±1.5 | ||
| 3 | 990±0.01 | 24±0.85 | 6012±241.1 | 9196±645.7 | 1506±122.4 | 958±83.7 | 2936±144.9 | 9±0.53 | 77±5.6 | 41±2.5 | 87±9.9 | 25±2.3 | ||
| 45 | 1 | White | 984±0.01 | 10±0.06 | 2384±280.0 | 2968±815.4 | 1086±23.6 | 449±121.8 | 1458±313.6 | 3±0.70 | 34±7.8 | 17±3.6 | 58±14.1 | 19±1.0 |
| 2 | 991±0.03 | 9.2±0.36 | 1320±432.4 | 1767±487.3 | 933±99.2 | 405±21.6 | 729±289.0 | 2±0.50 | 25±7.3 | 11±2.8 | 63±.90 | 6±2.0 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.26 | 18±0.64 | 6829±1079.8 | 9047±403.7 | 1449±56.2 | 853±32.0 | 2904±116.6 | 9±.40 | 100±11.4 | 49±.67 | 74±.83 | 28±1.0 | ||
| 46 | 1 | White | 985±0.10 | 18±0.03 | 2532±271 | 4341±1161.4 | 1121±260.9 | 513±97.2 | 2117±918.6 | 4±2.2 | 40±14.5 | 20±1.7 | 75±9.7 | 17±2.6 |
| 2 | 990±0.04 | 7±0.35 | 1380±359.8 | 1620±317.6 | 849±33.7 | 410±43.7 | 772±214.0 | 3±.30 | 23±4.2 | 9±2.5 | 68±4.6 | 5±1.4 | ||
| 3 | 990±0.88 | 14±0.09 | 6737±272.6 | 9543±628.0 | 1567±31.6 | 747±83.2 | 3102±128.5 | 7±.60 | 79±4.8 | 50±2.6 | 88±4.5 | 26±.90 | ||
| 47 | 1 | White | 986±0.63 | 17±0.04 | 1801±641.1 | 3155±297.8 | 1056±325.2 | 508±126.7 | 1852±853.4 | 4±1.7 | 39±5.3 | 21±8.0 | 67±10.9 | 16±3.4 |
| 2 | 981±0.11 | 13±0.12 | 1787±433.6 | 2731±595.1 | 849±62.1 | 480±14.3 | 940±235.8 | 3±.10 | 28±5.7 | 10±2.3 | 53±4.0 | 11±2.6 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.02 | 15±0.30 | 6695±170.0 | 8038±561.7 | 1401±23.9 | 683±65.7 | 3147±109.1 | 9±.42 | 77±4.2 | 44±2.8 | 87±10.3 | 26±2.3 | ||
| 48 | 1 | White | 985±0.30 | 18±0.52 | 3090±593.8 | 3001±686.4 | 934±115.0 | 492±17.2 | 1553±154.5 | 4±1.0 | 49±1.4 | 21±5.8 | 58±7.0 | 14±4.0 |
| 2 | 991±0.05 | 12±0.28 | 1360±471.4 | 1434±508.1 | 858±22.4 | 478±83.3 | 523±303.4 | 2±.50 | 20±7.4 | 6±2.3 | 53±5.9 | 4±2.0 | ||
| 3 | 990±0.78 | 15±0.05 | 6198±183.4 | 9407±821.4 | 1417±14.1 | 657±65.7 | 2923±730.0 | 7±1.3 | 80±9.7 | 36±2.1 | 87±12.1 | 38±0.80 | ||
| 49 | 1 | White | 987±0.04 | 10±0.36 | 2898±420.0 | 2978±343.2 | 1043±327.0 | 549±134.3 | 2047±115.2 | 3±0.70 | 40±7.1 | 20±6.0 | 62±10.0 | 19±6.2 |
| 2 | 991±0.01 | 13±0.01 | 1364±507.3 | 1628±318.8 | 820±43.3 | 475±126.4 | 719±300.4 | 2±.50 | 24±7.5 | 9±3.7 | 56±8.4 | 4±1.5 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.10 | 13±0.10 | 9904±197.1 | 9266±915.8 | 1311±19.3 | 670±46.9 | 3395±194.4 | 10±2.0 | 98±7.2 | 59±7.3 | 77±3.5 | 29±1.5 | ||
| 50 | 1 | White | 988±0.34 | 16±0.05 | 2887±.15 | 3867±1131.4 | 954±66.1 | 635±.13 | 1326±.16 | 4±0.60 | 34±.05 | 15±.10 | 64±.50 | 10±0.21 |
| 2 | 990±0.02 | 12±0.28 | 1103±412.2 | 1482±287.8 | 734±26.7 | 400±78.9 | 531±230.4 | 2±0.50 | 17±4.7 | 5±2.0 | 55±3.6 | 5±0.30 | ||
| 3 | 991±0.24 | 15±0.16 | 7989±770.3 | 7582±187.9 | 1506±15.5 | 652±28.2 | 3733±220.5 | 11±3.1 | 99±5.9 | 6±.27 | 58±5.7 | 59±2.5 | ||
| 51 | 1 | White | 982±0.01 | 20±0.04 | 3307±1252 | 3058±638.0 | 1029±258.0 | 520±111.0 | 1907±654.4 | 3±0.80 | 40±11.1 | 24±7.0 | 68±14.5 | 15.3.8 |
| 2 | 991±0.02 | 9±0.14 | 1580±265.9 | 2726±379.1 | 875±48.7 | 448±48.7 | 929±5.5 | 3±0.10 | 33±4.5 | 12±3.9 | 61±9.0 | 8±00.84 | ||
| 3 | 90±90.30 | 14±0.63 | 12380±227.3 | 8760±631.8 | 1519±86.4 | 773±121.9 | 653±45.2 | 8±0.53 | 58±7.1 | 29±22.5 | 63±12.3 | 34±8.2 | ||
| Ground grains | - | - | <.001 | <.001 | 0.58 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.55 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.53 | <.001 | 0.28 |
| Husked grains | - | - | <.001 | <.001 | 0.76 | 0.08 | <.001 | <.001 | 0.93 | 0.54 | <.001 | 0.88 | <.001 | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





